-
硅是湖泊硅质生物生长所必需的营养元素[1],也是水生生态系统中的关键限制元素[2],其生物地球化学循环对湖泊生态系统具有非常重要的作用。生物硅(biogenic silica,BSi)是一种无定型的二氧化硅[3],主要由硅藻、放射虫、硅鞭毛虫和少量的海绵骨针等组成[4],是硅的一种重要存在形式[5]。BSi是湖泊沉积物的重要组成部分,沉积物中的BSi主要来源于硅藻沉积[6],湖泊表层水体中的溶解硅被浮游植物和浮游动物吸收后进入硅质有机体内形成硅质介壳悬浮到水体中,沉降到湖底后也会形成BSi[1]。BSi的沉积和上层水体中的初级生产力的关系十分密切,与各营养盐的输入输出也密切相关,可以作为湖泊营养演化的指示指标[7]。当前对于BSi的研究主要集中于近海海域[8-10]、河口[6,11-12]和部分淡水湖泊[13-15],且湖泊多以深水湖泊为主,而关于浅水草型湖泊中BSi含量和分布的影响研究较少。
本文以典型浅水草型湖泊——南四湖为研究对象,在春季采集表层水和表层沉积物样品,分析沉积物中BSi的含量及空间分布特征,并结合水体理化性质探讨影响南四湖沉积物BSi分布的因素,以期为草型湖泊BSi的研究提供基础数据和资料。
-
南四湖(116°34'E —117°21'E,34°27'N —35°20′N)位于山东省济宁市微山县,呈西北东南方向展布,是微山湖、昭阳湖、独山湖、南阳湖四个相连湖泊的总称,是山东省第一大淡水湖。南四湖湖面面积为1266 km2,南四湖以二级坝闸为界分上、下级湖,上级湖水位为36.3 m时,湖面面积为606 km2,下级湖水位为35.8 m时,湖面面积为660 km2[16]。南四湖多年平均水深1.46 m,分布着大量的水生植物或湿生植物,优势种为菹草、蓖齿眼子菜和穗状狐尾藻[17],是我国华北地区典型的浅水草型湖泊。
-
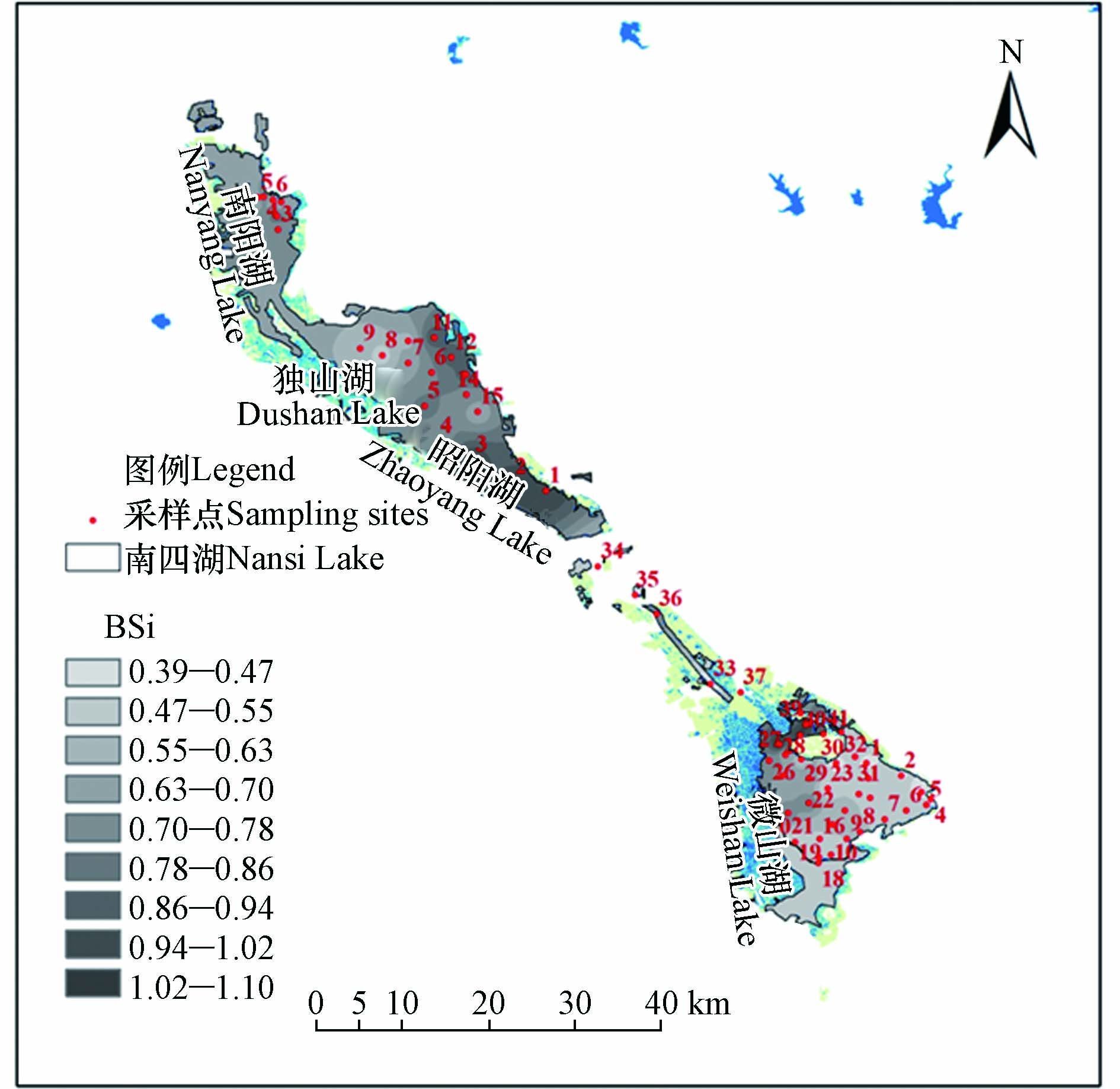
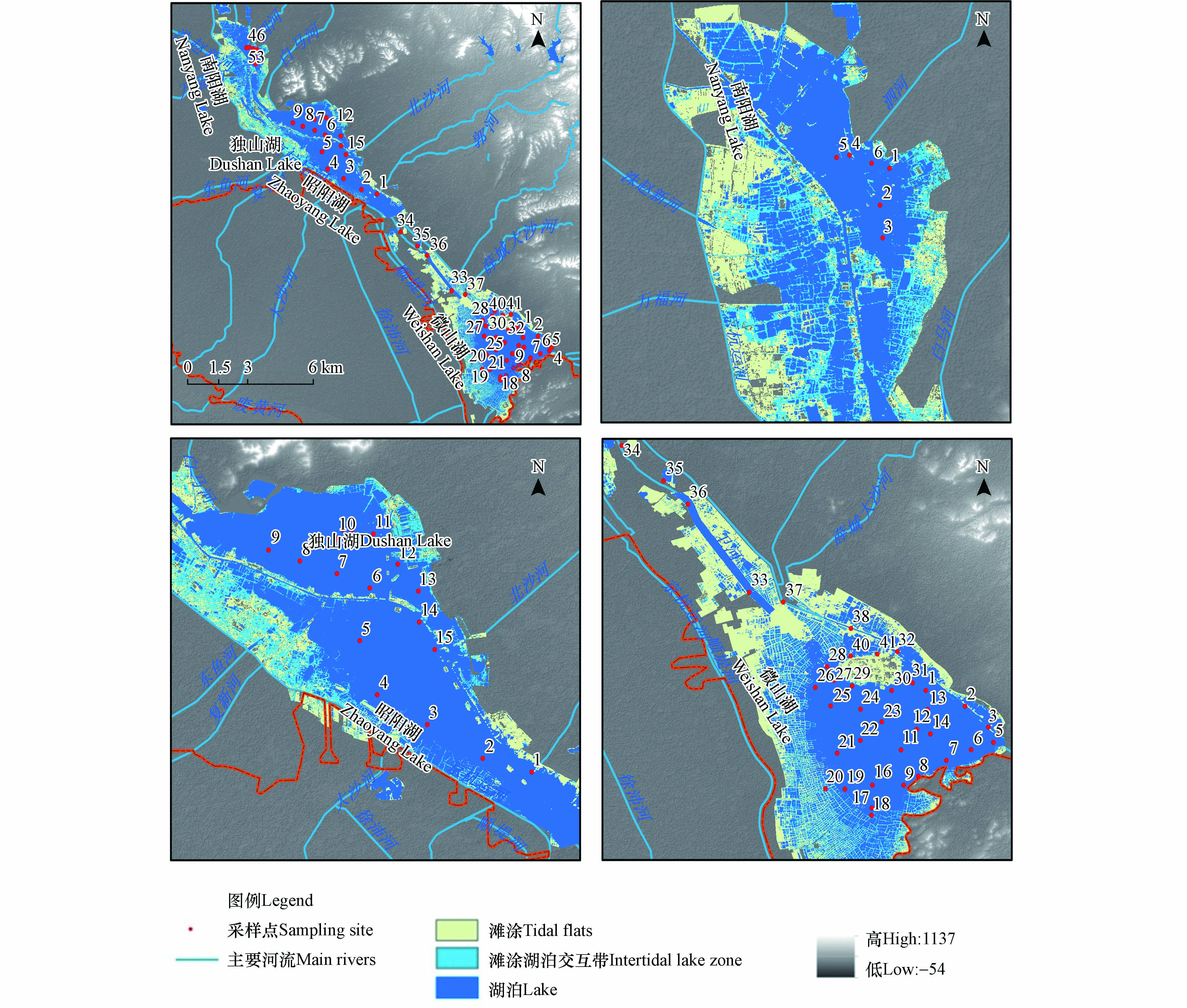
利用GPS定位系统在南四湖共设置了62个采样点(图1),其中微山湖、昭阳湖、独山湖和南阳湖各有41(WS 1-41)、7(DS 1-5、DS 14-15)、8(DS 6-13)和6(NY 1-6)个采样点,由于昭阳湖和独山湖无明显分界线,采样时样点按DS连续标注,采样点经纬度详见表1。于2019年4月用有机玻璃采水器采集水面下0.3 m处的水样置于聚乙烯瓶中,用Kajak柱状采泥器采集0—5 cm深的表层沉积物样品,现场分取0—1 cm深度置于聚乙烯自封袋中,置于便携式冷藏箱中4℃保存。现场采用HI9147便携式溶解氧仪(HANA,意大利)测定水温(WT)和溶解氧(DO),采用塞氏盘和自制水深测定装置测定水体透明度(SD)和水深(WD)。上岸后立即采用便携式土壤原位pH计(Spectrum,美国)测定表层水和沉积物pH,分别标注为pH(w)和pH(s)。取部分水样过0.45 μm滤膜后置于经泡酸洗净的聚乙烯塑料瓶中,另取未过滤水样冷冻保存待测,表层沉积物于阴凉通风处晾干,剔除贝壳等杂质,木棍碾碎后用玛瑙研钵研磨,过100目尼龙筛后备用。
-
取过滤后水样分别采用硅钼蓝光度法、纳氏试剂光度法、紫外分光光度法、N-(1-奈基)-乙二胺分光光度法和丙酮分光光度法测定水中可溶性二氧化硅(SiO2)、氨氮(NH3-N)、硝酸盐氮(NO3−-N)、亚硝酸盐氮(NO2−-N)和叶绿素a(Chl.a)的含量[18-19]。取未过滤水样分别采用过硫酸钾氧化—紫外分光光度法和钼锑抗分光光度法测定总氮(TN(w))和总磷(TP(w))[19]。
沉积物有机碳(OC)采用油浴加热重铬酸钾—容量法测定[20],总氮(TN(s))和总磷(TP(s))分别采用过硫酸盐消解法[21]和酸溶—钼锑抗比色法测定[22],有效磷(AP)采用碳酸氢钠提取—钼锑抗比色法测定[23],碱解氮(AN)采用碱解扩散法测定[22],BSi通过化学提取法提取后采用硅钼蓝光度法测定[24]。
另外,为保证分析的准确性,实验过程中采用三平行样分析、加标回收分析或标准物质对比分析法,测定结果的相对标准偏差均小于10%,加标回收率在93%—105%之间,所有实验均做空白对照。
-
采用Excel 2010对实验数据进行整理计算,采用SPSS 25.0中的Pearson 相关和多元线性回归对实验数据进行分析,运用ArcGIS 10.6和Origin 2018完成图形的绘制。
-
由表2可知,南四湖表层水中DO和NH3-N的平均浓度分别为9.93 mg·L−1和0.236 mg·L−1,均可达到《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838-2002)中的Ⅱ类水标准要求;但TN(w)和TP(w)平均浓度分别为1.41 mg·L−1和0.076 mg·L−1,仅达到Ⅳ类水标准。TN(w)和TP(w)含量略高于胡俊等[25]2018年5月的调查结果,与韦洁琳等[26]春季的结果相当;南四湖表层水中可溶性SiO2含量变化范围为0.298—4.97 mg·L−1,平均含量为(1.25±0.746) mg·L−1。TN(s)和TP(s)的含量水平与孙媛媛等[27]的调查结果较为接近,但表层沉积物中OC的含量较2012年研究结果有上升的趋势[27]。根据变异系数(CV)对空间变异性的划分[28],WT属于弱变异(CV < 10%),NO2−-N和TP(w)属于强变异(CV > 100%),表层水其他指标均属于中等变异(10% < CV < 100%);沉积物pH(s)属于弱变异,OC、TN(s)、TP(s)、AP、AN均属于中等变异,OC、AN、AP的空间变异性较TN(s)、TP(s)大。
-
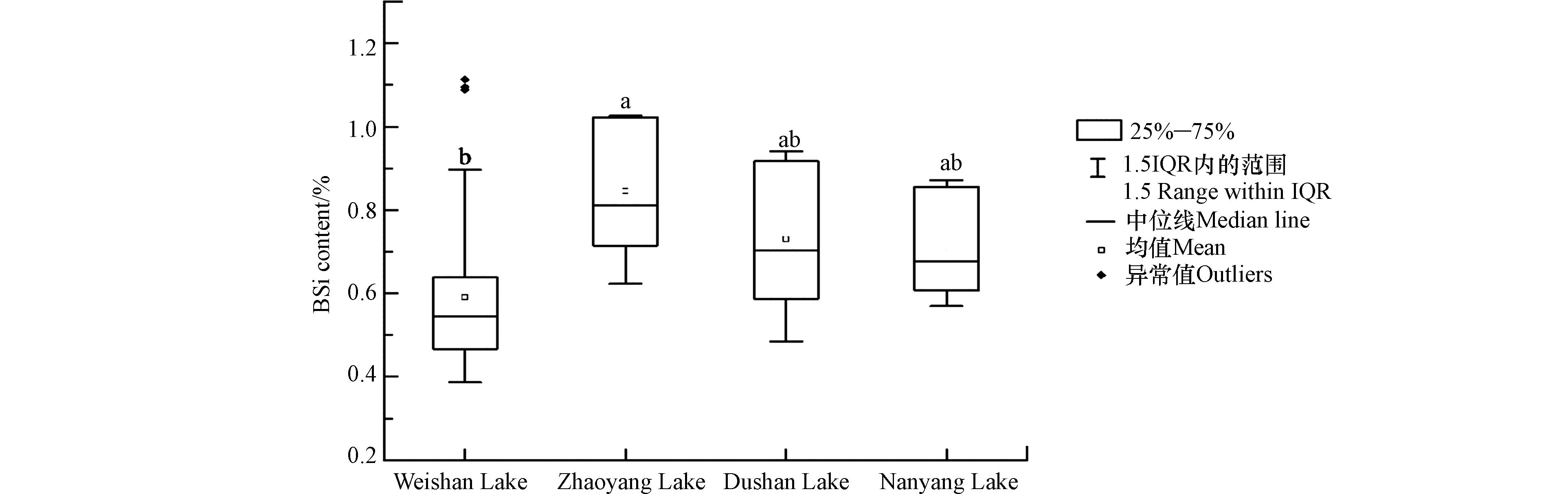
南四湖表层沉积物中BSi的含量变化范围为0.39%—1.11%,总平均值为0.65%±0.20%。由图2,昭阳湖BSi的含量最高,平均为0.82%±0.16%。其次为独山湖(0.72%±0.18%)、南阳湖(0.71%±0.13%),均高于总平均值。微山湖BSi的含量最低,平均为0.59%±0.19%。昭阳湖BSi的含量显著高于微山湖(P < 0.05),其他湖区间无显著性差异(P > 0.05)。南四湖各湖区BSi含量的空间平均变异系数为30.4%,其中各湖区BSi的空间变异系数为微山湖(31.7%)>独山湖(25.0%)>昭阳湖(19.8%)>南阳湖(18.6%),均属于中等变异。
由表3,南四湖表层沉积物中BSi含量明显低于我国东北镜泊湖和松花湖、西南泸沽湖和洱海[15],也低于较高纬度的呼伦湖[14]、以及贵州的红枫湖、平寨水库和普定水库[29],仅比杭州西湖的浴鹄湾高[13]。镜泊湖和松花湖富营养化水平高,充足的营养物质给藻类大量繁殖提供了营养条件[15],利于沉积物中BSi的积累;泸沽湖和洱海地处较低纬度,适宜的温度和降水条件使硅藻的生长相对旺盛[15],也有利于BSi的积累;而西湖浴鹄湾离钱塘江来水口较近,水体交换频繁且流速较快,同时还建有多处跌水营建景观[13],不适宜硅藻大量生长,BSi累积较少;南四湖属轻度富营养状态[26],营养化程度低于镜泊湖和松花湖,加上处于中纬度地区,其温度降水条件稍逊于泸沽湖和洱海,沉积物BSi含量较低。
由图3,南四湖表层沉积物BSi含量在空间分布上表现为微山湖从西北向东南递减的趋势,其他3个湖区则呈东南向西北递减的趋势,最大值出现在微山湖的28号点,最小值则出现在微山湖的30号点,空间分布差异较大。BSi与上层水体初级生产力有密切的关系,可有效指示环境变化[30]。沉积物BSi含量在微山湖西北部和北部、昭阳湖东南部形成高值区,微山湖的28、39、40号和昭阳湖的1、2、3号6个高值点均出现在该区域,高值区表层沉积物BSi含量高,表明该区域水体氮、磷营养元素丰富适宜硅藻生长[13]。
-
沉积物中BSi的积累受到多种理化指标的影响,为进一步分析理化因子对BSi含量的影响,采用Pearson相关分析和多元回归分析对其进行了分析。如表4所示,沉积物中BSi的含量与SD和NO2−-N分别呈显著正相关关系和负相关关系(P < 0.05),与表层水其他理化指标相关性不显著;与除pH(s)外的其他沉积物理化指标(OC、TP(s)、AP、TN(s)和AN)均呈极显著正相关关系(P < 0.01)。
由表4,南四湖表层沉积物中BSi含量与3个理化指标构建成立具有统计学意义的线性回归方程。南四湖表层沉积物BSi含量受AN、DO和NO2−-N的显著影响,且影响程度表现为AN > DO > NO2−-N,3个因子对BSi含量变异的解释率为47.5%。
水体中硅藻的种类和数量与水质营养水平密切相关,其中氮和磷是与硅藻生长密切相关的主要营养元素[31]。南四湖表层沉积物BSi含量与沉积物的TN(s)、TP(s)、AN、AP呈极显著正相关关系(P < 0.01),与TN(w)、TP(w)相关性不显著(P > 0.05)。硅藻是BSi的主要来源,BSi含量与浮游植物之间有着十分紧密的联系,硅藻又是南四湖浮游植物中仅次于绿藻的优势种[26, 32],BSi含量与Chl.a含量呈正相关性,但相关性不显著(表4),说明Chl.a对BSi含量有一定的影响,但不是主要的影响因素,因此推断采样期间南四湖硅藻以底栖硅藻为主。底栖硅藻生长的最适N/P为25:1,随着水体中氮浓度的升高,底栖硅藻的总生物量会逐渐增加[33]。南四湖沉积物AN/AP平均比值为4.32远低于25,表现为氮不足,氮成为底栖硅藻生长的限制因子。AN为TN中易被植物直接吸收利用的部分,对南四湖沉积物BSi的含量具有显著影响。微山湖28、39、40号点位于旅游景区内,快艇和观光游船活动扰动水体从而导致底泥中的N、P释放进入水体,28、39、40号点沉积物中AN含量相对较高,刺激硅藻的生长加速了BSi的沉积[13],从而使BSi含量较高。
南四湖表层沉积物中BSi含量与NO2−-N呈显著的负相关关系(表4),与浙江金华江支流白沙溪硅藻生物指数与NO2−-N呈显著负相关关系[34]的结论较为一致,代表了湖水营养盐变化对沉积物中BSi积累的间接影响[35]。但也有研究者发现东江干流底栖硅藻种类丰富度在2月和12月与NO2−-N呈显著负相关关系,在6月与NO2−-N呈极显著正相关关系[36],NO2−-N对硅藻的影响可能因季节不同而不同。因此水体中NO2−-N对沉积物BSi含量的影响还有待进一步的研究和探讨。表层沉积物中BSi的含量与SD呈显著正相关关系(表4),可能是由于SD越高,底栖硅藻的光合作用就越强,有利于硅藻的生长繁殖,这与水体的SD增加有利于硅藻发育和颗粒物中硅藻的含量比重增大的结论较为一致 [37-38]。菹草为南四湖的优势种,其在4月份开始大量生长繁殖,增加了水体中DO含量[39],菹草分布密集的区域由于光照受到影响,硅藻生长会受到抑制,因此,BSi的含量与DO的含量呈负相关关系,这也体现了草型湖泊BSi累积与其他湖泊的差异。
南四湖表层沉积物中BSi的含量与沉积物中OC呈极显著正相关关系(表4),说明南四湖沉积物中BSi的累积对OC有明显的依赖关系[24]。南四湖较浅,有利于水生植物生长,水生植物衰亡后未分解的死亡残体堆积于湖底淤泥中缓慢分解,导致底泥中OC含量增加。OC来源及比例的差异会影响OC/BSi的值,南四湖表层沉积物中OC/BSi的变化范围为0.84—13.76,平均值为7.26,高于Redfield比值(OC/BSi=6.63)[40],这与部分学者研究[6, 14, 24, 40]的沉积物中OC/BSi远低于Redfield比值相反,可能是南四湖本身有机碳含量高以及南四湖有机碳来自大量水生植物的植物残体,使OC/BSi相对增加[30],这也反映了草型湖泊中BSi累积的独特性。而在位于昭阳湖东南部围网养殖区的1、2、3号点,BSi含量较高,则可能是由于大量饵料的投放和生物的新陈代谢增加了OC含量,同时该区域湖区水面狭窄,水体流速缓慢,外来有机物易滞留于内[41],有利于增强硅藻生产力和BSi的累积。
-
(1)南四湖表层沉积物中BSi的含量变化范围在0.39%—1.11%之间,平均含量为0.65%,各湖区BSi的平均含量表现为昭阳湖>独山湖>南阳湖>微山湖,昭阳湖显著高于微山湖。
(2)南四湖表层沉积物中BSi含量在空间分布上各湖区略有不同,微山湖呈由西北向东南递减的趋势,其他三个湖区总体上呈由东南向西北递减的趋势,在微山湖西北部和北部、昭阳湖东南部形成BSi含量高值区。
(3)南四湖表层沉积物AN和表层水DO、NO2−-N是影响沉积物BSi含量的显著性因素。南四湖表层沉积物中OC/BSi值介于0.84—13.76之间,均值大于Redfield比值,体现了草型湖泊BSi累积的独特性。
春季南四湖表层沉积物中生物硅的分布及其影响因素
Study on the distribution and influencing factors of biogenic silica in surface sediments of Nansi Lake in spring
-
摘要: 为研究春季南四湖表层沉积物中生物硅(biogenic silica,BSi)的含量、分布特征及其影响因素,于2019年4月在全湖采集了62个点位的表层沉积物样品和表层水样品,通过对沉积物BSi以及沉积物和表层水理化指标的测定,探讨了南四湖BSi含量水平、分布特征及其影响因素。结果表明,南四湖表层沉积物中BSi含量在0.39%—1.11%之间,平均为0.65%±0.20%,表现为昭阳湖>独山湖>南阳湖>微山湖,昭阳湖(0.82%±0.16%)显著高于微山湖(0.59%±0.19%)(P < 0.05);空间分布上微山湖表现为从西北向东南递减的趋势,其他3个湖区则呈东南向西北逐渐递减的趋势。沉积物OC/BSi值介于0.84—13.76之间,平均为7.26,大于Redfield比值(6.63)。南四湖BSi与沉积物OC、TP(s)、AP、TN(s)、AN均呈极显著正相关关系(P < 0.01),与表层水SD和NO2−-N分别呈显著正相关和负相关关系(P < 0.05);AN、DO和NO2−-N能解释南四湖表层沉积物BSi含量变异程度的47.5%。Abstract: In order to study the content, distribution characteristics and influencing factors of biogenic silica (BSi) in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake in spring, surface sediment and surface water samples were collected at 62 sampling sites around the lake in April 2019. The content of BSi in sediment and the physicochemical properties of sediment and surface water were determined, and the BSi levels and spatial distribution characteristics as well as its influencing factors were discussed. The results showed that the BSi content in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake ranged from 0.39% to 1.11% with an average value of 0.65%±0.20%. The average BSi content in the four sub-lakes decreased in the order of Zhaoyang Lake > Dushan Lake > Nanyang Lake > Weishan Lake, and the average BSi content (0.82%±0.16%) in Zhaoyang Lake was significantly higher than that (0.59%±0.19%) in Weishan Lake (P < 0.05). In terms of spatial distribution, the BSi content in Weishan Lake showed a decreasing trend from northwest to southeast, while the change trend in the other three sub-lakes was on the contrary. The sediment OC/BSi values were between 0.84 and 13.76 with an average of 7.26, which was greater than the Redfield ratio (OC/BSi=6.63). The BSi content in Nansi Lake was significantly positively correlated with the OC, TP, AP, TN and AN content in sediment (P < 0.01), but only had a significant positive correlation with SD and negative correlation with NO2−-N in surface water (P < 0.05). The multivariate regression analysis indicated that AN, DO and NO2−-N could explain 47.5% of the variation of the BSi content in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake.
-
Key words:
- biogenic silica /
- surface sediments /
- spatial distribution /
- influencing factors /
- Nansi Lake
-

-
表 1 南四湖62个采样点的经纬度
Table 1. The latitude and longitude of 62 sampling points in Nansi Lake
采样点
Sampling site经度
Longitude纬度
Latitude采样点
Sampling site经度
Longitude纬度
LatitudeWS-1 117°17′0.06″ 34°38′19.05″ WS-32 117°15′25.66″ 34°40′16.12″ WS-2 117°19′9.95″ 34°37′31.36″ WS-33 117°7′13.87″ 34°43′14.41″ WS-3 117°20′27.10″ 34°36′28.91″ WS-34 117°0′11.46″ 34°50′36.04″ WS-4 117°21′2.25″ 34°36′4.24″ WS-35 117°2′30.10″ 34°48′49.63″ WS-5 117°20′44.03″ 34°35′42.88″ WS-36 117°3′51.21″ 34°47′39.57″ WS-6 117°19′30.16″ 34°35′21.16″ WS-37 117°9′6.56″ 34°42′44.71″ WS-7 117°18′8.55″ 34°34′48.54″ WS-38 117°12′51.73″ 34°41′25.31″ WS-8 117°16′35.04″ 34°34′1.03″ WS-39 117°13′11.68″ 34°40′42.50″ WS-9 117°15′46.55″ 34°33′34.08″ WS-40 117°12′50.60″ 34°40′3.07″ WS-10 117°14′47.11″ 34°32′35.02″ WS-41 117°14′18.89″ 34°40′8.47″ WS-11 117°15′37.75″ 34°35′20.42″ (ZY)DS-1 116°56′56.53″ 34°55′22.30″ WS-12 117°16′30.01″ 34°36′22.44″ (ZY)DS-2 116°54′46.59″ 34°55′55.53″ WS-13 117°17′6.29″ 34°37′21.65″ (ZY)DS-3 116°52′19.57″ 34°57′16.76″ WS-14 117°17′14.93″ 34°36′8.36″ (ZY)DS-4 116°50′6.52″ 34°58′28.65″ WS-15 117°14′50.83″ 34°34′28.78″ (ZY)DS-5 116°49′20.214″ 35°0′38.74″ WS-16 117°14′3.00″ 34°33′34.54″ DS-6 116°49′46.83″ 35°2′45.52″ WS-17 117°14′0.75″ 34°32′25.58″ DS-7 116°48′19.77″ 35°3′19.98″ WS-18 117°13′59.33″ 34°32′3.55″ DS-8 116°46′41.40″ 35°3′50.44″ WS-19 117°12′31.96″ 34°33′22.37″ DS-9 116°45′18.33″ 35°4′16.63″ WS-20 117°11′27.14″ 34°33′23.45″ DS-10 116°48′19.10″ 35°4′43.99″ WS-21 117°12′5.98″ 34°35′10.53″ DS-11 116°49′56.15″ 35°4′55.71″ WS-22 117°13′22.87″ 34°35′49.08″ DS-12 116°51′1.11″ 35°3′42.79″ WS-23 117°14′33.70″ 34°36′44.68″ DS-13 116°51′55.89″ 35°2′37.96″ WS-24 117°13′23.83″ 34°37′22.54″ (ZY)DS-14 116°51′57.72″ 35°1′23.26″ WS-25 117°11′44.18″ 34°37′32.44″ (ZY)DS-15 116°52′39.27″ 35°0′17.16″ WS-26 117°10′53.69″ 34°38′28.11″ NY-1 116°40′21.37″ 35°13′25.64″ WS-27 117°11′55.75″ 34°38′49.53″ NY-2 116°40′5.67″ 35°12′30.26″ WS-28 117°11′32.06″ 34°39′30.47″ NY-3 116°40′10.14″ 35°11′41.17″ WS-29 117°12′55.82″ 34°38′32.59″ NY-4 116°39′15.04″ 35°13′45.64″ WS-30 117°15′6.58″ 34°38′19.21″ NY-5 116°38′53.61″ 35°13′42.04″ WS-31 117°16′15.96″ 34°38′41.98″ NY-6 116°39′51.71″ 35°13′33.41″ 表 2 南四湖表层水和沉积物理化性质参数统计
Table 2. Statistics of physical and chemical parameters of surface water and sediment in Nansi Lake
理化指标
Physical and chemical indexes平均值
Average value标准偏差
Standard deviation变异系数/%
Coefficient of variation范围
Range表层水
Surface waterpH(w) 9.51 1.06 11.3 7.36—11.3 DO/(mg·L−1) 9.93 1.85 18.8 5.90—15.2 SD/m 1.13 0.427 38 0.3—2 SiO2/(mg·L−1) 1.25 0.746 60 0.298—4.97 TN(w)/(mg·L−1) 1.41 0.763 54.9 0.454—4.09 NH3-N/(mg·L−1) 0.236 0.096 41.2 0.063—0.478 NO3−-N/(mg·L−1) 0.822 0.552 67.7 0.005—2.451 NO2−-N/(mg·L−1) 0.018 0.019 107.4 0.002—0.096 TP(w)/(mg·L−1) 0.076 0.086 114 0.016—0.623 Chl.a/(mg·L−1) 0.054 0.040 76.4 0.009—0.214 WD/m 2.03 0.447 22.2 1—3.6 WT/℃ 18.3 1.67 9.21 13—21.5 沉积物
SedimentspH(s) 8.31 0.576 6.99 6.68—9.49 OC/(mg·g−1) 47.2 25.1 53.5 4.25—97.6 TN(s)/(mg·kg−1) 2581 967 37.8 285—3678 TP(s)/(mg·kg−1) 711 142 20.2 304—1094 AP/(mg·kg−1) 37.5 16.8 45.2 2.9—88.7 AN/(mg·kg−1) 162 81.7 50.7 1.7—347 表 3 我国不同区域表层沉积物中BSi含量比较(Si%)
Table 3. Comparison of BSi content in surface sediments of different regions in China (Si%)
区域
Region范围
Range平均值Average 参考文献
References西湖浴鹄湾West Lake Yuhu Bay 0.05%—0.41% 0.22% [13] 呼伦湖Hulun Lake 0.40%—1.83% 1.18% [14] 泸沽湖Lugu Lake 1.95%—4.11% 2.92% [15] 青海湖Qinghai Lake 1.19%—2.04% 1.55% [15] 松花湖Songhua Lake 1.49%—7.05% 2.91% [15] 洱海Erhai Lake 1.31%—5.31% 2.54% [15] 镜泊湖Jingbo Lake 3.36%—16.88% 6.92% [15] 红枫湖Hongfeng Lake 0.90%—1.90% 1.50% [29] 平寨水库Pingzhai Reservoir 0.40%—6.90% 1.60% [29] 普定水库Puding Reservoir 0.50%—1.80% 1.10% [29] 南四湖Nansi Lake 0.39%—1.11% 0.65% 本研究 表 4 沉积物中BSi与部分水体理化指标的Pearson相关系数及回归方程
Table 4. Pearson correlation coefficient and regression equation of BSi in sediments and some physical and chemical indexes of water bodies
WD DO SD pH(w) TN(w) NH3-N NO3−-N NO2−-N 0.101 −0.207 0.251* 0.065 −0.161 0.225 −0.240 −0.305* Chl.a TP(w) pH(s) OC TP(s) AP TN(s) AN 0.200 −0.138 0.190 0.524** 0.351** 0.396** 0.437** 0.591** 方程 BSi=0.588×AN-0.419×DO-0.220×NO2−-N P<0.001 R 2=0.475 注:*P<0.05,**P<0.01. -
[1] 李慧菊, 刘淑民, 简慧敏, 等. 长江口邻近海域沉积物和间隙水中硅的研究 [J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(4): 39-49. LI H J, LIU S M, JIAN H M, et al. The study of silica in sediment and pore water in the adjacent area of Changjiang Estuary [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(4): 39-49(in Chinese).
[2] MA N, SONG Z L, WANG B L, et al. Effects of river damming on biogenic silica turnover: Implications for biogeochemical carbon and nutrient cycles [J]. Acta Geochimica, 2017, 36(4): 626-637. doi: 10.1007/s11631-017-0153-7 [3] 周鹏, 李冬梅, 刘广山, 等. 南海东北部和南部海域表层沉积物生物硅研究 [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(4): 40-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.04.007 ZHOU P, LI D M, LIU G S, et al. Biogenic silica in surface sediments of the northeastern and southern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(4): 40-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2010.04.007
[4] 周鹏, 李冬梅, 李海涛, 等. 大亚湾西部海域沉积物中生物硅的含量及其分布特征 [J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2019, 38(1): 109-117. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2019.01.012 ZHOU P, LI D M, LI H T, et al. Biogenic silica contents and its distribution in the sediments of the west Daya Bay [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2019, 38(1): 109-117(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2019.01.012
[5] ZHANG L L, CHEN M H, XIANG R, et al. Distribution of biogenic silica content in surface sediments from the southern South China Sea and its environmental dignificance [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2009, 11(1): 43-52. [6] 闫慧敏, 刘敏, 侯立军, 等. 长江口沙洲表层沉积物中生物硅分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(1): 164-169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.01.028 YAN H M, LIU M, HOU L J, et al. Distribution of biogenic silica in surface sediments from the shoals in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(1): 164-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.01.028
[7] 吴峰炜, 汪福顺, 吴明红, 等. 滇池、红枫湖沉积物中总磷、分态磷及生物硅形态与分布特征 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(1): 88-94. WU F W, WANG F S, WU M H, et al. Distributions of total phosphorus, phosphorus fractions, and biogenic silica in Dianchi Lake and Hongfeng Lake sediments [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2009, 28(1): 88-94(in Chinese).
[8] 李欣, 邸宝平, 刘东艳, 等. 烟台四十里湾表层沉积物中生物硅的研究 [J]. 海洋科学, 2012, 36(12): 32-38. LI X, DI B P, LIU D Y, et al. Biogenic silica in the surface sediment of Sishili Bay, Yantai [J]. Marine Sciences, 2012, 36(12): 32-38(in Chinese).
[9] 李浩帅, 刘淑民, 陈洪涛, 等. 长江口及邻近海域表层沉积物中的生物硅 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(12): 72-79. LI H S, LIU S M, CHEN H T, et al. Biogenic silica in surface sediments of Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent waters [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(12): 72-79(in Chinese).
[10] 吴彬, 吕伟香, 鲁超, 等. 长江口邻近海域沉积物中生物硅溶解行为研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(3): 908-914. WU B, LÜ W X, LU C, et al. Study on the dissolution behavior of biogenic silica in the Changjiang Estuary adjacent sea [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(3): 908-914(in Chinese).
[11] 朱华刚. 河口海岸带硅的生物地球化学研究进展 [J]. 江苏水利, 2017(10): 32-36. ZHU H G. Advances in bio-geochemistry of silicon in estuary and coastal zones [J]. Jiangsu Water Resources, 2017(10): 32-36(in Chinese).
[12] 俞小勇, 徐杰, 龙爱民, 等. 夏季珠江口及近岸海域悬浮颗粒物生物硅分析 [J]. 海洋学研究, 2018, 36(3): 67-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.03.007 YU X Y, XU J, LONG A M, et al. Determination of suspended biogenic silica in the Pearl River Estuaryand its adjacent coastal waters in summer [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2018, 36(3): 67-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.03.007
[13] 胡胜华, 贺锋, 孔令为, 等. 杭州西湖湖湾生物硅沉积测定与营养演化的过程 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(12): 1892-1897. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.019 HU S H, HE F, KONG L W, et al. The determination of biogenic silica in the sediments and evaluative dynamics to eutrophication of Xihu Lake Bay, Hangzhou [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(12): 1892-1897(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.12.019
[14] 麻涛, 何江, 高际玫, 等. 呼伦湖沉积物生物硅的分布特征 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(4): 832-837. MA T, HE J, GAO J M, et al. Characteristics of biogenic silica distribution in the sediment of Hulun Lake [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(4): 832-837(in Chinese).
[15] 刘斌, 徐海, 盛恩国, 等. 我国湖泊表层沉积物生物硅的空间分布特征 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(12): 3480-3484. LIU B, XU H, SHENG E G, et al. Spatial distribution patterns of biogenic silica contents from lake sediments in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(12): 3480-3484(in Chinese).
[16] 高峰, 赵培青, 刘景华, 等. 南水北调南四湖水位分析 [J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2005(8): 36-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2005.08.013 GAO F, ZHAO P Q, LIU J H, et al. Analysis on the water level of Nansi Lake in the South-to-North Water Transfer Project [J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2005(8): 36-37(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2005.08.013
[17] 朱天顺, 王丽虹, 何亮, 等. 调蓄河湖群菹草(Potamogeton crispus L. )功能性状特征及其与环境因子的关系 [J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(6): 1990-1998. ZHU T S, WANG L H, HE L, et al. Characteristics of functional traits of Potamogeton crispus L. and their relationships with environmental factors in the channel river and impounded lakes [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(6): 1990-1998(in Chinese).
[18] HZ-HJ-SZ-0148, 水质 二氧化硅的测定 硅钼蓝光度法[S]. HZ-HJ-SZ-0148, Water quality Determination of silicon dioxide Silicon molybdenum blue photometric method[S] (in Chinese).
[19] 国家环境保护总局《水和废水监测分析方法》编委会. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. (第四版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 246-281. Editorial board of monitoring and analysis methods for water and wastewater of State Environmental Protection Administration. Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater[M]. (Fourth Edition). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002: 246-281(in Chinese).
[20] 靳彩霞. 油浴加热重铬酸钾容量法测定土壤有机质影响因素分析 [J]. 农业科技与信息, 2012(4): 33-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6997.2012.04.018 JIN C X. Analysis of influencing factors on Determination of soil organic matter by potassium dichromate volumetric method heated in oil bath [J]. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information, 2012(4): 33-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6997.2012.04.018
[21] 范成新. 湖泊沉积物调查规范[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 281-282. FAN C X. Specification for lake sediment survey[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018: 281-282(in Chinese).
[22] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000: 150-181. LU R K. Soil agricultural chemical analysis method [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Scientech Press, 2000: 150-181(in Chinese).
[23] OLSEN S R. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate [J]. Miscellaneous Paper Institute for Agricultural Research Samaru, 1954: 18-19. [24] 侯立军, 刘敏, 闫惠敏, 等. 长江口潮滩沉积物生物硅的分布及其影响因素 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2007, 27(5): 665-669. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2007.05.020 HOU L J, LIU M, YAN H M, et al. Distribution of biogenic silica in tidal flat sediments of Yangtze Estuary and its influence factors [J]. China Environmental Science, 2007, 27(5): 665-669(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2007.05.020
[25] 胡俊, 池仕运, 胡菊香. 南四湖浮游植群落与环境因子关系的pCCA分析 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(9): 33-39. HU J, CHI S Y, HU J X. Partial canonical correspondence analysis of phytoplankton community and environmental factors in Nansihu Lake [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(9): 33-39(in Chinese).
[26] 韦洁琳, 曹鹏飞, 胡文容, 等. 南四湖浮游硅藻季节性演替及其与环境因子的相关性 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(8): 1209-1218. WEI J L, CAO P F, HU W R, et al. Seasonal succession of planktonic diatom community and its relationship with environmental factors in nansi lake [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(8): 1209-1218(in Chinese).
[27] 孙媛媛, 张祖陆, 李爽. 南四湖表层沉积物营养元素分布分析 [J]. 水电能源科学, 2012, 30(8): 37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2012.08.011 SUN Y Y, ZHANG Z L, LI S. Analysis of nutrient distribution in surface sediment of Nansihu Lake [J]. Water Resources and Power, 2012, 30(8): 37-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2012.08.011
[28] 于玲红, 王铭浩, 李卫平, 等. 包头南海湖沉积物有机碳空间分布特征 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(3): 538-545. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1057 YU L H, WANG M H, LI W P, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of the organic carbon insediments of Nanhai Lake in Baotou City [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(3): 538-545(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1057
[29] 魏榆, 杨昌平, 晏浩, 等. 喀斯特水库碳、硅耦合循环: 红枫湖、普定水库和平寨水库为例 [J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(1): 1-9. WEI Y, YANG C P, YAN H, et al. Coupled cycling of carbon and silica in Karst reservoirs: Insights from Hongfeng Lake, Puding reservoir and pingzhai reservoir [J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(1): 1-9(in Chinese).
[30] SCHELSKE C L, STOERMER E F, KENNEY W F. Historic low-level phosphorus enrichment in the Great Lakes inferred from biogenic silica accumulation in sediments [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2006, 51(1part2): 728-748. doi: 10.4319/lo.2006.51.1_part_2.0728 [31] 张伟. 杉木河硅藻与氮磷及重金属关系的研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2015. ZHANG W. Study on correlation between diatom and nitrogen, phosphorous and heavy metals inshanmu river[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2015(in Chinese).
[32] 刘倩辉, 裴海燕, 胡文容, 等. 南四湖浮游植物种群构成特征及季节变化 [J]. 山东大学学报(理学版), 2010, 45(5): 12-18. LIU Q H, PEI H Y, HU W R, et al. Population characteristics and seasonal variations of phytoplankton in Nansi Lake [J]. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 2010, 45(5): 12-18(in Chinese).
[33] 宋玉芝, 秦伯强, 高光. 氮及氮磷比对附着藻类及浮游藻类的影响 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(2): 125-130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.02.003 SONG Y Z, QIN B, GAO G. Effect of nutrient on periphytic Aglae and phytoplankton [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2007, 19(2): 125-130(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.02.003
[34] 李钟群, 袁刚, 郝晓伟, 等. 浙江金华江支流白沙溪水质硅藻生物监测方法 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2012, 24(3): 436-442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.03.016 LI Z Q, YUAN G, HAO X W, et al. Diatom-based biomonitoring method of water quality in Baisha River, a tributary of Jinhua River, Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2012, 24(3): 436-442(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5427.2012.03.016
[35] 叶曦雯, 刘素美, 赵颖翡, 等. 东、黄海沉积物中生物硅的分布及其环境意义 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(3): 265-269. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.03.003 YE X W, LIU S M, ZHAO Y F, et al. The distribution of biogenic silica in the sediments of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea and its environmental signification [J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(3): 265-269(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.03.003
[36] 林罗敏. 东江干流底栖硅藻分布特征及生态系统健康评价研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2017. LIN L M. Distribution of benthic diatoms and water ecosystem health evaluation in the main stream of Dongjiang River[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2017(in Chinese).
[37] 王翠红, 张金屯. 汾河水库水源河着生硅藻群落的DCCA研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(1): 28-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.01.007 WANG C H, ZHANG J. Studies on DCCA of the attached diatom community in headwater rivers of Fenhe Reservoir [J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(1): 28-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2004.01.007
[38] 张欣泉. 长江干流及河口硅的生物地球化学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2006. ZHANG X Q. Research on the biogeochemical mechanism of silicon at the main stream and estuarine of Yangtze River[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2006(in Chinese).
[39] 侯春燕, 郭贵良, 孙晓丽. 菹草的作用、危害及预防措施 [J]. 吉林农业, 2011(7): 229. HOU C Y, GUO G L, SUN X L. Potamogeton crispus function, harm and preventive measures [J]. Jilin Agriculture, 2011(7): 229(in Chinese).
[40] 李学刚, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等. 胶州湾沉积物中高生源硅含量的发现: 胶州湾浮游植物生长硅限制的证据 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(6): 572-579. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.06.012 LI X G, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. High contents of biogenic silicate in Jiaozhou Bay sediments—evidence of si-limitation to phytoplankton primary production [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2005, 36(6): 572-579(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.06.012
[41] DENG H G, ZHANG J, ZHANG Z B, et al. Lab-scale study of the removal efficiencies for nitrogen and phosphorus from urban rainfall runoff using constructed riparian infiltration system [J]. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 32(3): 89-98. DENG H G, ZHANG J, ZHANG Z B, et al. Lab-scale study of the removal efficiencies for nitrogen and phosphorus from urban rainfall runoff using constructed riparian infiltration system [J]. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 32(3): 89-98(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: