-
大气气溶胶在广义上是指大气与悬浮在其中的固体和液体微粒共同组成的多相体系[1],但在通常情况下是指大气中悬浮的固态和液态颗粒物[2]. 气溶胶能够吸收和散射太阳辐射,从而影响整个地球的辐射收支[3],直接或间接地影响着全球环境和气候变化[4],也成为了人类健康的影响因子 [5]. 散射系数是气溶胶光学性质的重要参数之一,它反映了气溶胶对辐射传输过程的影响. 在国际上,20世纪90年代以来进行了多次气溶胶观测实验来了解其散射特性,如澳大利亚ACE-1、大西洋ACE-2、亚洲ACE-Asia和印度洋INDOEX等[6-9],获取了很多值得研究的气溶胶资料. 国内也有许多研究气溶胶散射系数的基本变化特征. 韩素芹等[10]根据GRIMM气溶胶粒谱分析仪得到的在线观测资料,计算分析天津地区春季的气溶胶消光特征. 袁亮等[11]结合Hysplit后向轨迹模式,探讨了黄山夏季在不同气团影响下气溶胶光学参数的变化特征. 于大江等[12]使用美国TSI公司生产的三波段积分浊度仪观测得到气溶胶散射系数,同时计算得到PM10气溶胶的散射Angstrom指数(SAE),反映了在观测期间气溶胶散射特征的季节变化和日变化. 任丹阳等[13]利用高时间分辨率大气气溶胶消光系数以及PM2.5化学组分的观测数据重建本地化消光系数与颗粒物化学组分浓度的经验关系式——IMPROVE公式,并发现观测期间硫酸盐对散射系数的贡献最高. 兰剑等[14]通过Hysplit后向轨迹分析表明,位于上海市西南中心城区的环境科学研究院的西向城市对上海市大气污染贡献大,潜在源分布较广.
然而针对前人的研究,在不同的气象要素下,关于较长时间序列的气溶胶散射特性的研究开展得不多. 本文主要结合天气要素,阐述杭州市主城区大气气溶胶散射系数的变化特征,并主要深入探讨2018年11月27日—12月3日一次典型的空气污染过程.
-
杭州国家基准气候站(120°10'E,30°14'N,海拔41.7 m)[15]位于杭州市上城区. 测站处于西湖景区和杭州市中心的结合部,其北方和东方是建筑群,而西方是山丘,南方紧邻钱塘江和城市建筑群[15]. 由于地形作用,该站监测到来自西面气团的污染物较少,而来自其它方向的气团的污染也相对较多.
-
杭州市气象局针对大气成分观测的气溶胶观测设备有:浊度仪、黑碳仪、颗粒物仪等仪器[15].
本文使用杭州国家基准气候站中的澳大利亚ECOTECH公司生产的Aurora-3000浊度仪进行连续观测365 d所得数据进行研究. 仪器可同时进行波长分别为3个波段进行测量,分别是:450、525、635 nm,其他关于Aurora-3000浊度仪的介绍详见文献[16]. 本次观测所用仪器安放于实验室内,进气管通过金属管延伸到离屋顶1.5 m上方,且进气口未安装切割头. 同时,在本次观测过程中,仪器每周会自动进行零检查(zero check)和人工跨检查(span check),高效颗粒过滤器用于零检查时,而R-134a标准气体用于跨检查时[15]. 若一旦存在零检查值或跨检查值超出允许范围的情况时,仪器将会进行全校准[15]. 另外,气溶胶的散射特性也受到相对湿度的影响[15]. 同时,根据Junge [17]研究得出,若环境中相对湿度高于60%时,由于气溶胶粒子的吸湿增长,使得其粒径和形状会显著不同,因此会影响对光的散射能力,并使散射能力增强. 为解决这一问题,安装加热进气管的装置,能够导致测量腔内的相对湿度保持在60%以下[15].
本文主要采用波长为525 nm所测量的散射系数进行研究 [18],同时本文采用杭州国家基准气候站测得的PM2.5、PM10质量浓度进行与散射系数相关的研究分析.
-
(1)散射系数季节变化特征
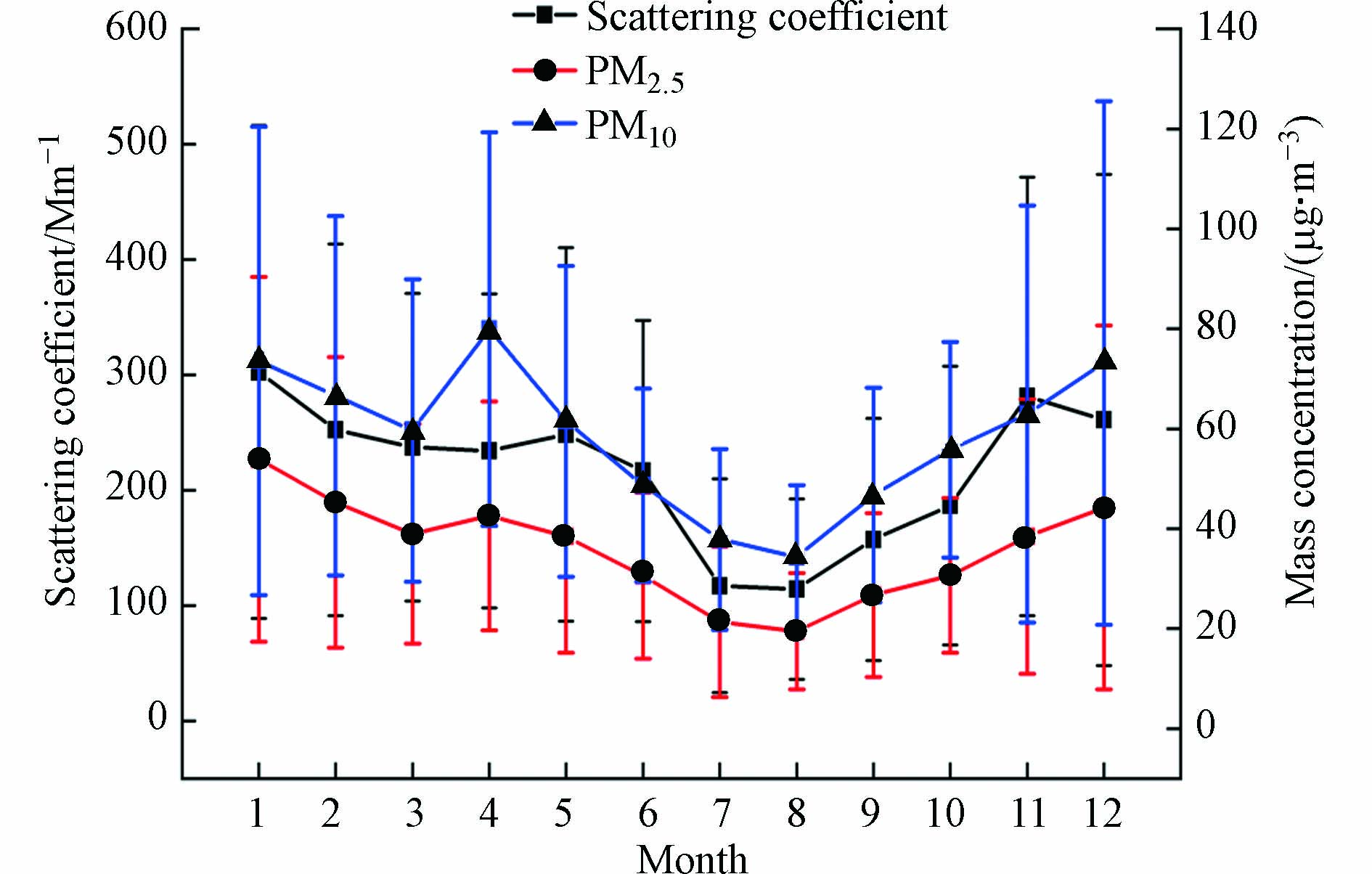
2018年杭州市主城区散射系数和PM2.5、PM10质量浓度季节变化如图1所示. 2018年杭州散射系数在春夏秋冬季的均值分别是:240.8、148.7、208.4、272.7 Mm−1;PM2.5质量浓度在春夏秋冬季的均值分别是:39.9、23.7、31.9、47.9 μg·m−3;PM10质量浓度在春夏秋冬季的均值分别是:66.9、40.2、55.2、71.3 μg·m−3. 其中,散射系数和PM2.5、PM10质量浓度的变化趋势基本相同,均呈现冬春两季明显大于夏秋两季.
PM2.5和PM10质量浓度的变化在夏秋两季几乎稳定,而在冬春两季变化较大. 且4个季节散射系数和PM2.5、PM10质量浓度的平均值均大于其50分位数,不同分位数的数据季节变化相似. 测站的散射系数和颗粒物质量浓度在整体上呈现:冬季>春季>秋季>夏季的特点. 且春、冬季散射系数的离散程度高,夏、秋季散射系数的离散程度低,这说明春、冬季散射系数变化幅度大,尤其是冬季的散射系数变化幅度最大.
春季,万物生长,大气对流活动旺盛,杭州市主城区偶尔也会受到生物气溶胶植物花粉[19]和沙尘气溶胶土壤尘[20]等自然源的影响,造成1—2 d的持续污染,导致大气散射系数的波动;夏季,由于西太平洋副热带高压向北方移动,高空风速增大,水汽通量增加,杭州进入梅雨季[20]. 由于较强的对流活动和较大的风速,杭州市主城区夏季的大气扩散条件较好,有利于气溶胶粒子的清除. 秋冬季,主要受到蒙古冷高压的稳定控制,杭州盛行西北-北气流,大气对流活动减弱,逐步转为较为稳定的大气层结,因此对污染物的扩散非常不利,会导致颗粒物在边界层内累积.
(2)散射系数和PM2.5质量浓度相关性的季节变化
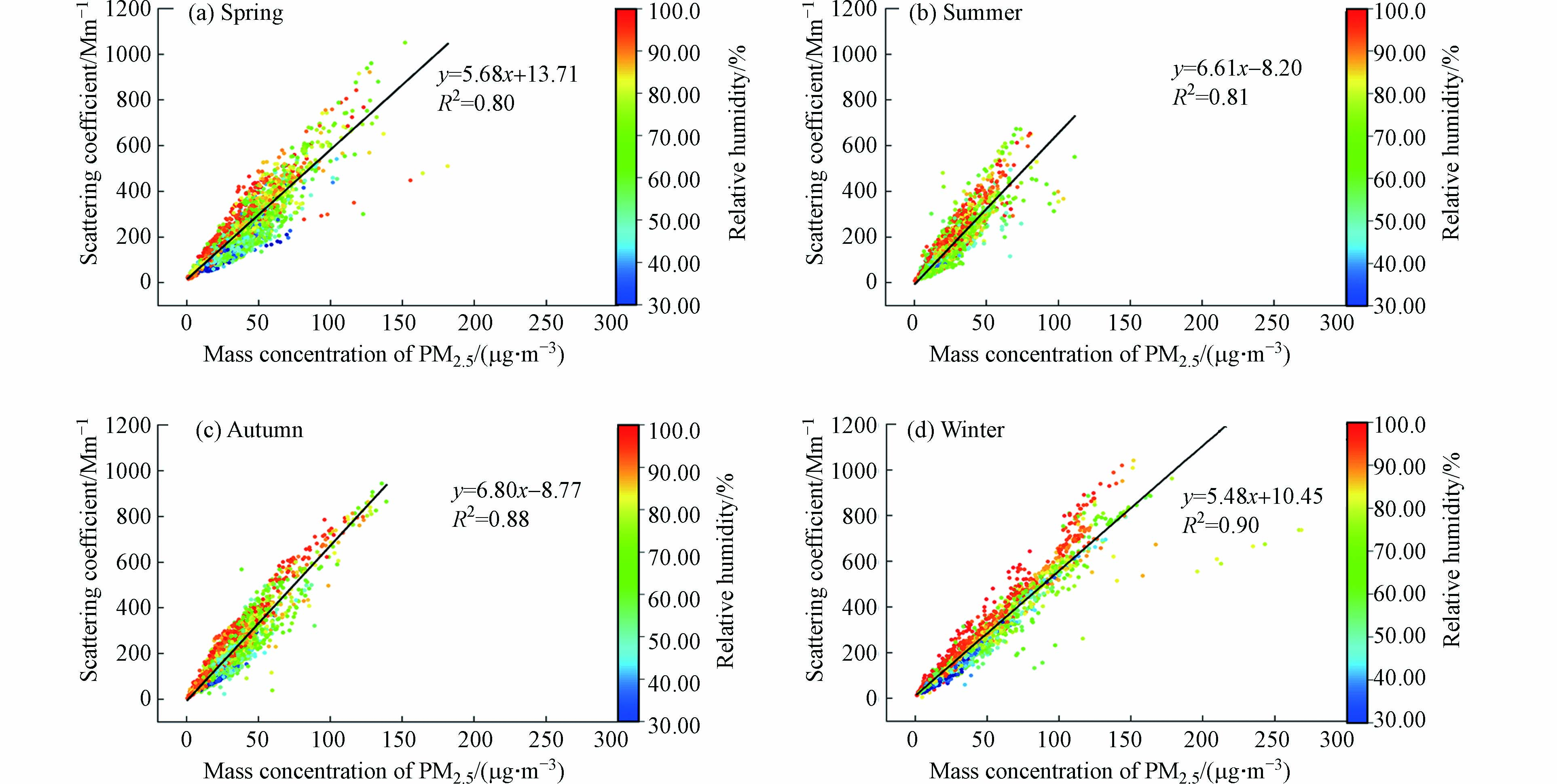
图2中给出了2018年杭州市主城区不同湿度条件下散射系数和PM2.5质量浓度在四季的分布情况,并分析了二者的相关性. 显然,在不同的相对湿度条件下,各季的散射系数和PM2.5质量浓度总体上均呈正相关关系. 根据散点的分布情况,春、冬季由于PM2.5光学散射特性所引起的散射系数明显较夏、秋季大. 这与上文中所提到的测站的散射系数和颗粒物质量浓度在整体上呈现:冬季>春季>秋季>夏季的特点一致.
通过计算各季散射系数(y)和PM2.5质量浓度(x)的线性相关程度,分别得到四季的拟合曲线和拟合度. 春季的散点拟合曲线为y=5.68x+13.71(拟合度R2=0.8036);夏季的散点拟合曲线为y=6.61x-8.20(拟合度R2=0.8083);秋季的散点拟合曲线为y=6.80x-8.77(拟合度R2=0.8821);冬季的散点拟合曲线为y=5.48x+10.45(拟合度R2=0.9018). 综上,秋、冬季的拟合效果好于春、夏季,即秋、冬季散射系数和PM2.5质量浓度相关性更强. 相比之下,散射系数和PM2.5质量浓度相关性在春季最弱. 当PM2.5质量浓度保持不变时,随着相对湿度的升高,散射系数和PM2.5质量浓度表现出越来越明显的正相关关系. 表明2018年杭州市主城区受到可入肺颗粒物PM2.5的污染特征明显. 根据图中暖色调的点明显位于拟合曲线上方,而冷色调的点多数位于拟合曲线的下方,同样也可以看出:湿度越大,PM2.5的散射能力越强,大气污染的态势愈加严重.
(3)散射系数季节变化的差异分析
2011年杭州市主城区散射系数最大的季节是秋冬季,且春夏两季的散射系数明显小于秋冬季[15]. 本文研究发现,2018年杭州市主城区散射系数最大的季节是春冬季,且春季不同分位数的散射系数均大于秋季. 因此,分析散射系数季节变化的差异,尤其是春季和秋季相对大小的差异显得更加重要.
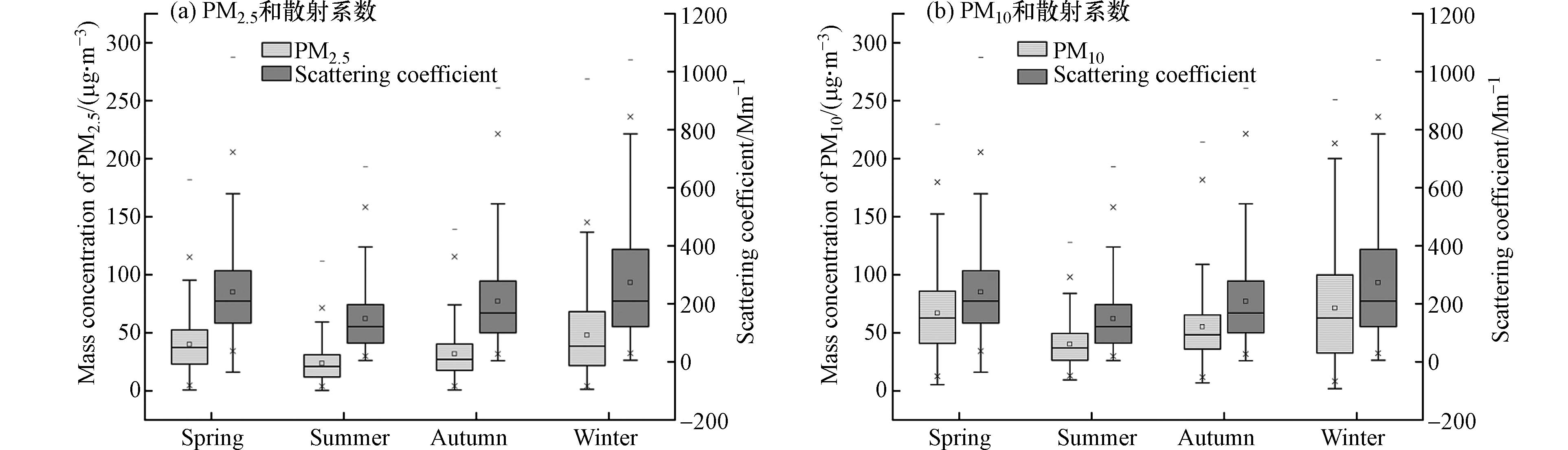
据上文和徐晓飞等[19]研究表明,散射系数与PM1、PM2.5、PM10质量浓度均存在显著正相关关系. 因此,利用2018年杭州国家基准气候观测站PM2.5和PM10的日质量浓度值来分析春季和秋季散射系数相对大小差异的原因.
据图3可知,2018年杭州市主城区春季PM2.5质量浓度的平均值为39.9 μg·m−3, PM10质量浓度的平均值为66.9 μg·m−3;秋季PM2.5质量浓度的平均值为31.9 μg·m−3、PM10质量浓度的平均值为55.2 μg·m−3;即:春季PM2.5、PM10浓度的均值均大于秋季PM2.5、PM10浓度的均值,且春季两种粒径的颗粒物浓度变化波动明显大于秋季两种粒径的颗粒物浓度变化. 该结果也与徐薇等[21]针对上海市2009年的大气散射系数的观测结果一致.
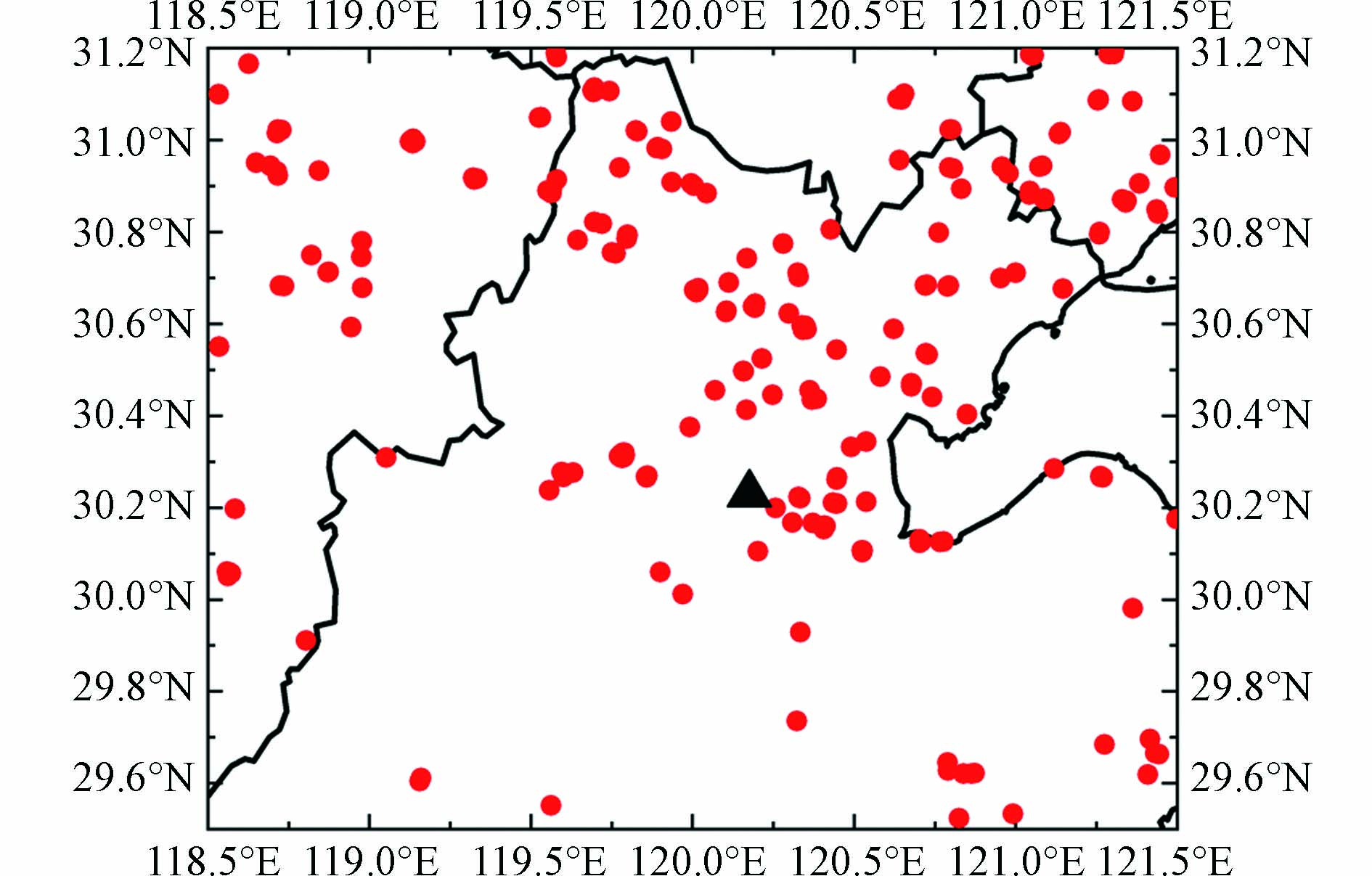
这主要是由两个原因导致,一是自然源土壤尘的影响. 据张芝娟等[22]针对2018年春季我国北方一次严重的沙尘天气过程分析可知:2018年3月27—30日我国北方的沙尘天气对杭州市的颗粒物浓度产生一定程度上的影响. 大量来自我国北方的沙尘粒子随气流到达杭州市,导致空气中的颗粒物浓度异常高于往年春季,进而影响到春季散射系数的大小,使得2018年杭州市春季的散射系数大于秋季. 二是人为源燃烧作用的影响. 采用美国国家航空航天局的MODIS火点数据(https://firms.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/)绘制图4可得:站点周边火点密集,特别是站点东北方向. 由于正值清明节,寺庙焚香和踏青扫墓等人为活动可能会导致更多的颗粒物进入大气,从而影响大气散射系数.
-
2018年杭州市主城区散射系数和PM2.5、PM10质量浓度的月变化趋势基本相同(见图5),总体上呈现1—8月递减,8—12月递增的趋势. 但在3—5月份,PM2.5和PM10的质量浓度均有一定程度增大,并在4月达到一个小峰值,这与春季的散射系数较往年更大也有关. 全年,月平均散射系数变化介于114.3—302.6 Mm−1之间. 同时,在1—8月,散射系数与颗粒物质量浓度的波动趋势呈现先降再升后降;在8—12月,标准差总体呈现上升趋势. 且三者中,PM10质量浓度的波动程度最大. 最大值出现在冬季(1月),与徐晓飞等[19]的研究结果(12月)相一致.
-
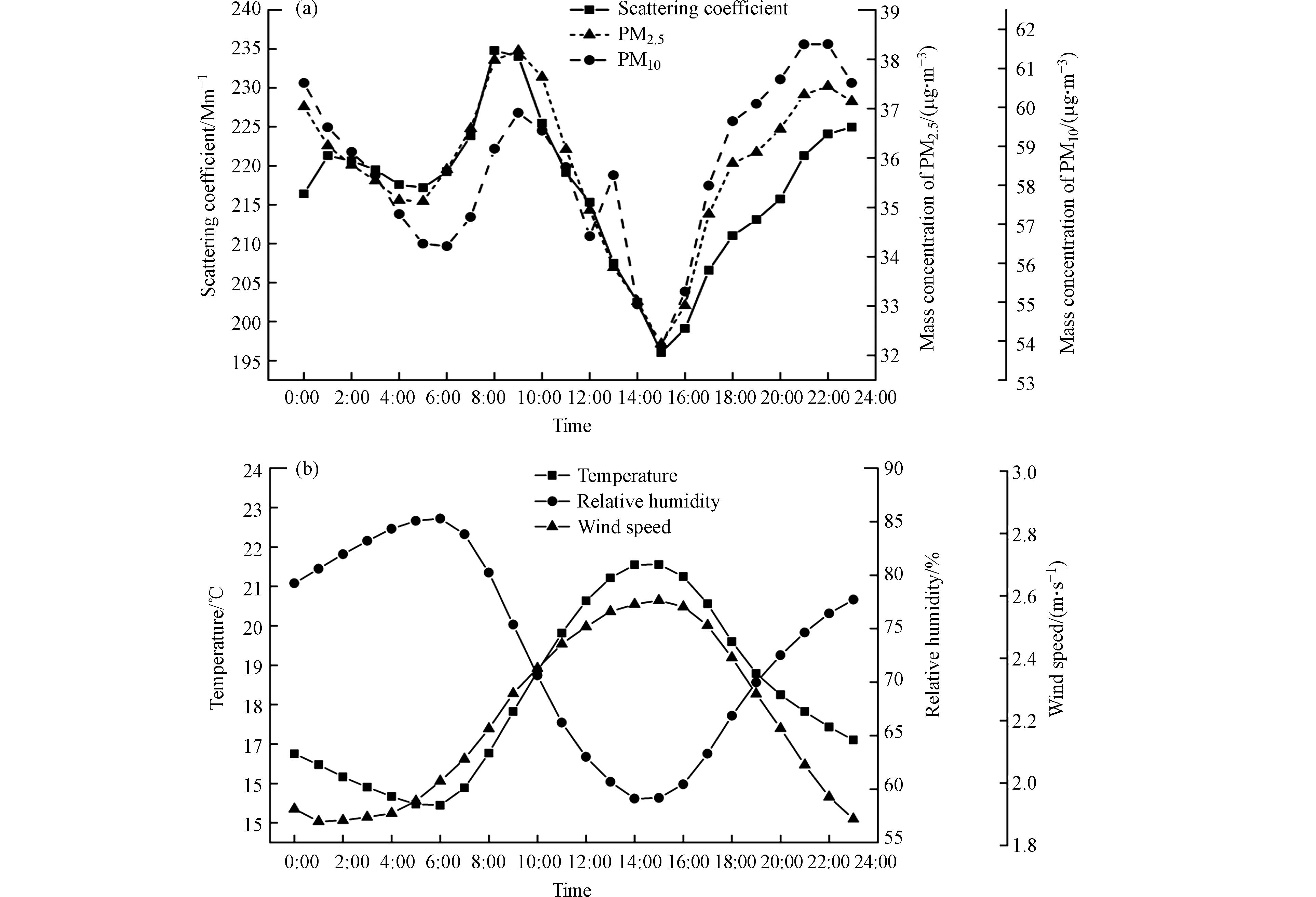
2018年杭州市主城区年平均散射系数为(217.4±161.9) Mm−1. 其中,日平均最高值出现在12月2日,为832.0 Mm−1;最低值出现在8月19日,为24.2 Mm−1. 小时最高值出现在5月30日15:00,为1050.0 Mm−1;最低值出现在9月17日3:00,为3.8 Mm−1. 据图6(a)可以看出,散射系数日变化特征表现为明显的“一峰一谷型”.
凌晨0:00—2:00时,地表对大气产生冷却作用,近地层形成“逆温”结构[23],不利于污染物的扩散,因此散射系数增大;早上6:00—7:00时,日出导致地面受到辐射作用而逐渐增温,相对湿度减小,近地面逆温层被打破;上午7:00—10:00时,由于受到上班上学“早高峰”的影响,人类活动增加,汽车尾气、工厂开工等导致气溶胶在混合层聚集,散射系数出现一天中的高峰;之后逐渐下降,据图6(b)显示,在15:00时,温度和风速均达到日最大值,利于污染物扩散,使得散射系数在15:00时达到一天中的谷值. 由于下班“晚高峰”和大气边界层稳定层结形成导致散射系数在15:00—20:00持续攀升,而夜间(20:00—23:00)散射系数则在小范围内波动.
其变化规律与2011年杭州市主城区散射系数的日变化特征值略有不同[15]. 一是散射系数谷值较2011年推迟1 h;二是2011年的散射系数存在明显“晚高峰”及回落现象,而本研究中散射系数在15:00之后一直呈现上升的趋势,且在23:00达到峰值后才有回落现象. 为探究不同现象的原因,将杜荣光[24]等研究的2011年杭州市气象要素的变化情况与本次研究比较得:由于2011年气温和风速在14:00达到一天中的峰值,相对湿度则为谷值,较好的扩散条件使散射系数在日间逐渐降低,直到14:00出现谷值[24];而与2018年气象要素的日变化趋势(图6(b))比较,大致趋势比较相似,只有气温和风速的峰值以及相对湿度的谷值大致出现在14:00—15:00,与2011年相比相差不大. 同时,由于观测站周围除了西方以外均不是利于污染物扩散的环境,因此个别的人为排放的局地输送可能会影响观测的效果 [24]. 根据崔晓雨等[25]研究表明,杭州市属于发展迅速的夜间经济综合提升型城市,近年来,其经济规模大、服务业比重高,“夜文化”盛行,因此“晚高峰”及回落现象可能是由于近年来杭州市夜间经济迅速发展、夜间排放增多而导致,同时日落之后逆温层开始形成,逐渐在边界层中积累污染物,也造成了差异.
-
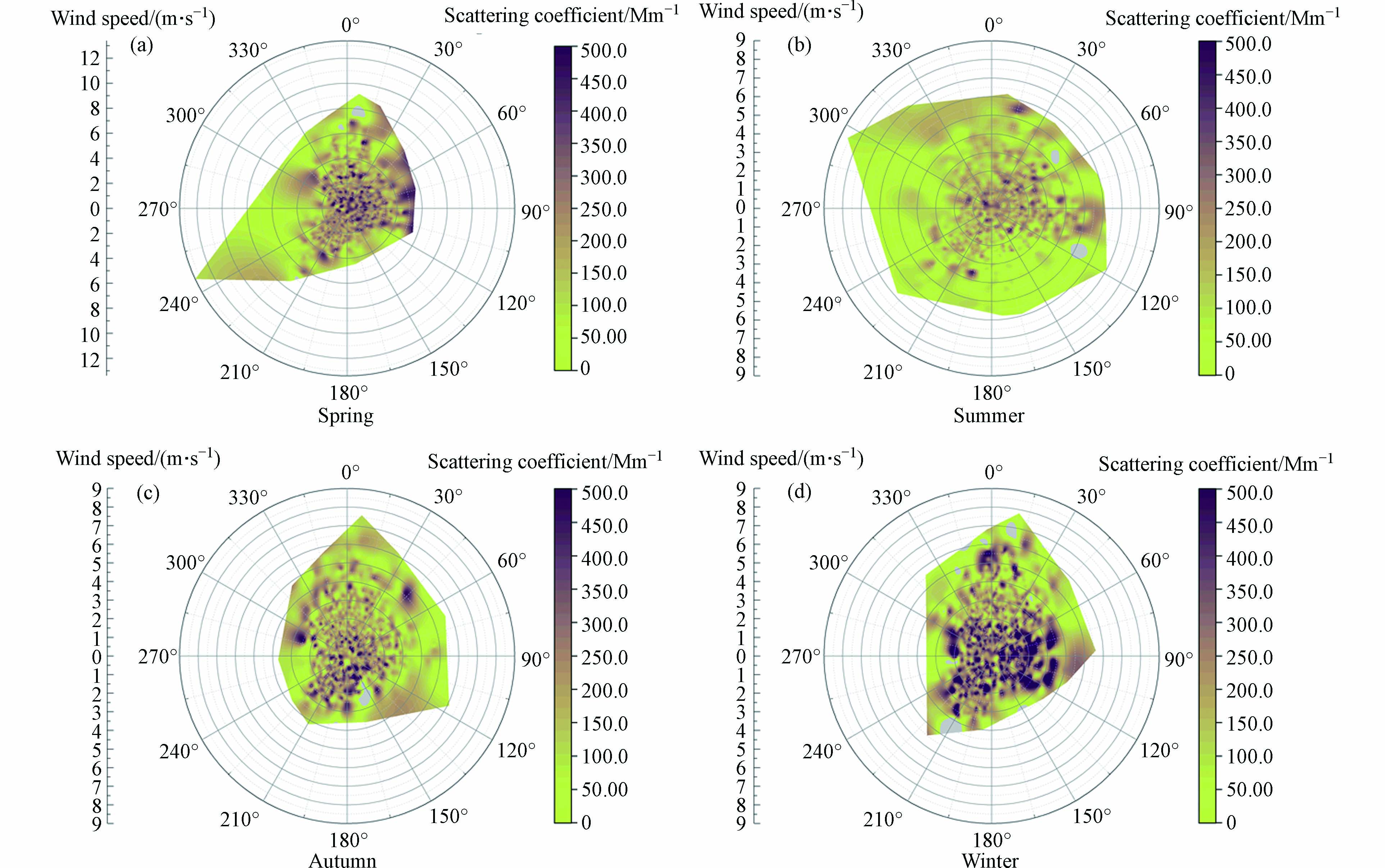
春季,大气对流旺盛,地面风速增大,杭州市主城区风速达到全年最大值,为西南风,达到极好的扩散条件,因此春季来自西面的气团都比较清洁,相比之下来自东侧的气团散射系数较高,分析是来自城市建筑群中的人为排放;夏季,由于地面风速较大,且水汽通量增加,降水增多,大气扩散条件较好,有利于气溶胶粒子的清除,因此来自各方向的气团都相对清洁;秋季,风速较夏季有明显的减弱,且副高逐渐退居西太平洋,大气层结相对稳定,因此逐渐在各方向上出现污染气团;冬季,受到蒙古冷高压的影响,杭州市主城区大气对流活动减弱,早晚“逆温层”的出现,对污染物的扩散非常不利. 研究表明杭州市冬季不仅更容易产生逆温层,而且平均逆温层厚度也更大[23],因此更有利于冬季污染物在边界层内积累. 图7为不同季节地面风对散射系数的影响.
由图7明显可见,散射系数随地面风的增大而减小. 地面风速大,有利于污染物扩散,导致散射系数偏小;地面静风,不利于污染物扩散,导致散射系数偏大. 根据杜荣光等[15]研究表明,当风速在6.0—8.0 m·s−1之间时,散射系数表现为随风速增大而迅速增加[15]. 而在本文研究中,总的来说,春夏两季的地面风速较大,常有6.0—8.0 m·s−1的情况,可能会导致散射系数增加;而秋冬两季地面风速常小于6.0 m·s−1,这时地面风对气溶胶有扩散作用,使得散射系数降低.
-
杭州地处长江三角洲,是环杭州湾大湾区核心城市,全年四季分明,雨量充沛,2018年平均散射系数为(217.4±161.9) Mm−1,属我国空气污染较轻的地区. 由于2018年11月27日—12月3日的平均散射系数为(603.0±235.5) Mm−1,是日平均散射系数的2.8倍. 同时,日平均最高值也出现在12月2日,为832.0 Mm−1,是日平均散射系数的3.8倍. 因此,研究该过程显得尤为重要.
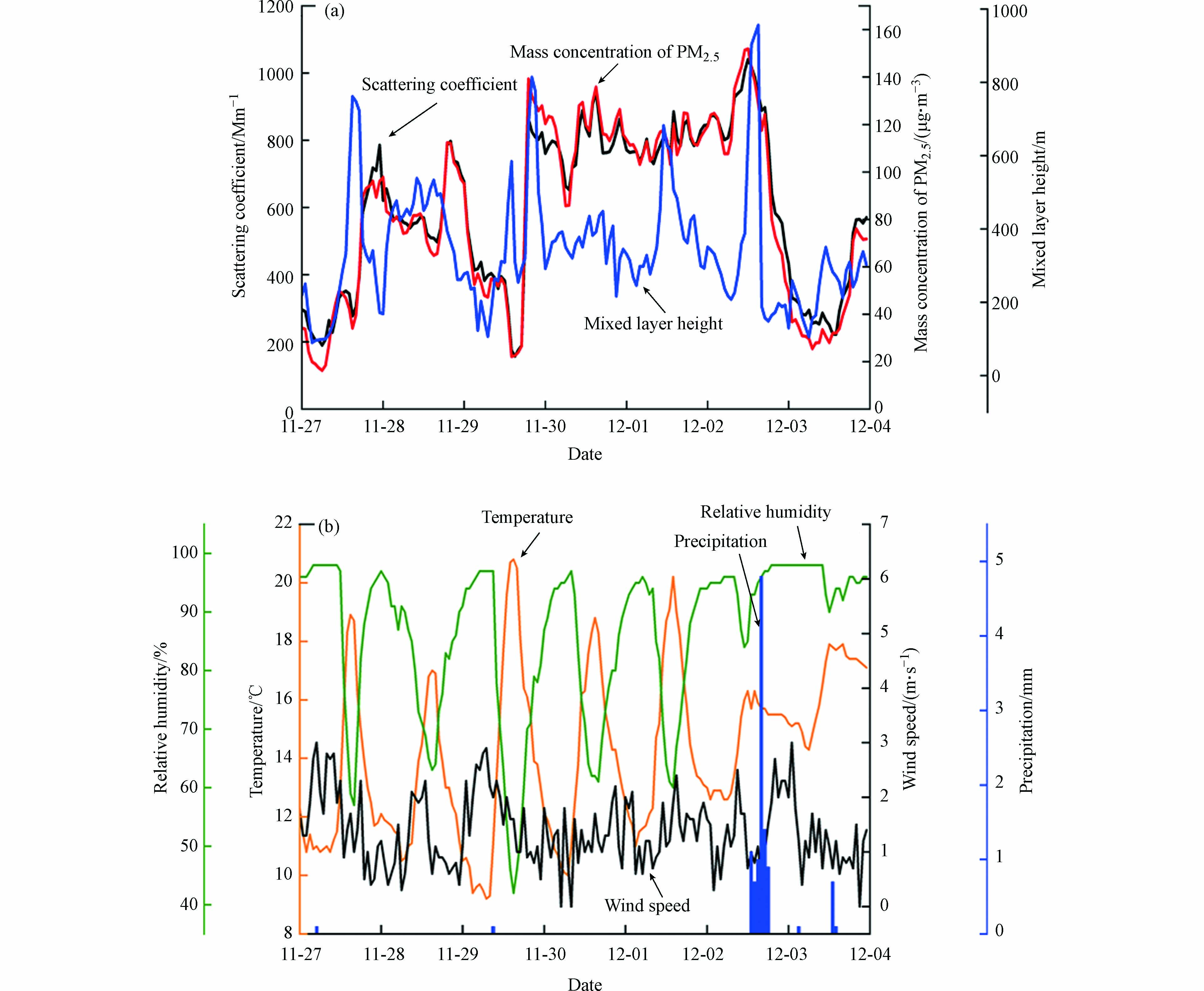
本文对杭州国家基准气候观测站2018年11月27日—12月3日的散射系数、PM2.5浓度值,以及通过激光云高仪反演出的混合层高度数据进行分析. 据图8(a)可得,2018年11月27日—12月3日的散射系数和PM2.5浓度呈现很好的正相关关系,这与徐晓飞等[19]对临安本底站的散射系数和PM2.5浓度之间的关系一致. 其中,混合层高度也与散射系数和PM2.5浓度呈现负相关关系. 即混合层高度越低,PM2.5浓度越大,大气散射系数越大;反之,混合层高度越高,大气散射系数越小.
结合图8(b)中典型过程时段的温度、相对湿度、风速和降水量,可以明显地看到在该次空气污染过程中温度和相对湿度始终呈现很好的负相关关系,即高湿低温的状态,这与常识相符. 这也与张勇[26]等发现石家庄春季散射系数的高值区一般都出现在大气条件为高湿低温时段的结论相一致. 这种大气中充裕水汽的条件也有利于气溶胶粒子的吸湿增长. 11月27日白天,散射系数和PM2.5浓度稳定在较低值,而在夜间由于稳定逆温层产生、风速小的高湿环境将PM2.5等颗粒物保存在边界层内,使得散射系数增大,之后一直保持增大的趋势. 11月29日,由于夜间逆温层消失、风速增大同时产生微弱的降水,使得大气中的部分颗粒物得以清除,散射系数有短暂的减小,散射系数降低至157.0 Mm−1. 从11月30日至12月2日夜间,散射系数不断增大并在12月2日中午达到峰值1040.9 Mm−1,在该过程中混合层高度一直保持较低水平. 12月2日晚上出现降水现象,使大气中的气溶胶被湿清除至地面,散射系数在该日内陡降至480.4 Mm−1,同时散射系数也受到由于相对湿度增大而导致的影响.
从天气形势上看,11月27日—12月3日杭州市主城区位于均压场内;而根据(https://earth.nullschool.net/#current/wind/isobaric/700hPa/anim=off/overlay=temp/orthographic=-247.43,4.31,404),在12月2日2:00时起,高空700 hPa上中心风带风速超过12 m·s−1,盛行西南低空急流. 这股来自西南方向的暖湿空气裹挟我国西南及周边地区的污染物向东南移动,导致长三角地区污染物浓度显著上升.
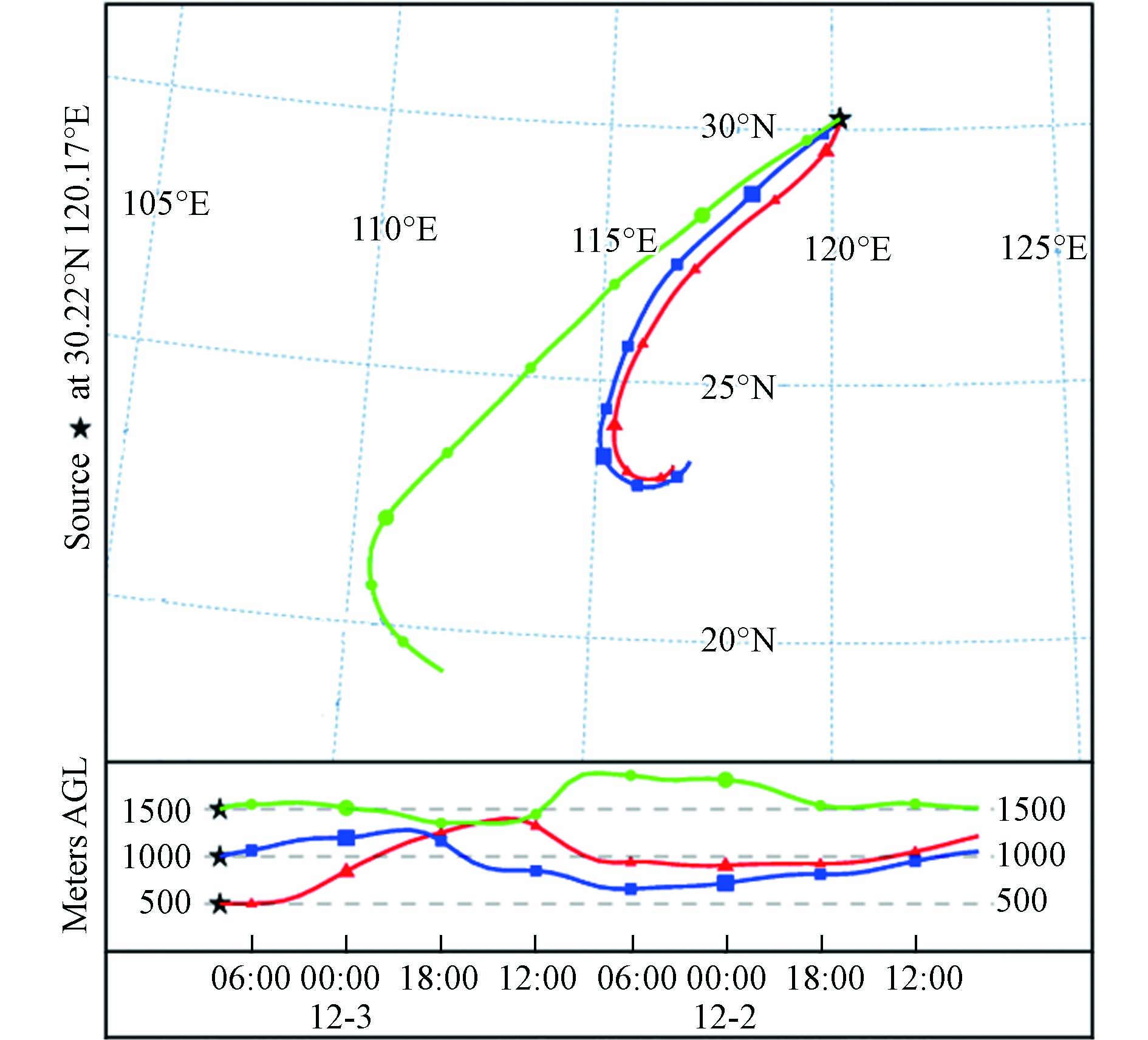
同时,采用美国国家海洋大气局NOAA网站(https://www.ready.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT_traj.php)的Hysplit后向轨迹模式对杭州国家基准气候观测站上空气流在12月3日的运动轨迹进行模拟分析(图9)可以得到:杭州2018年11月27日—12月3日的这一次典型空气污染过程细颗粒物来源于我国南方地区的空气团. 这也与天气形势上分析到的西南低空急流相对应. 且在后向轨迹中500 m高度的气团出现下沉运动,这使得近地层形成大气稳定层结,为颗粒物在边界层内累积提供了有利条件.
-
(1)2018年杭州市主城区年平均散射系数为(217.4±161.9) Mm−1,其季节差异明显,散射系数和PM2.5、PM10质量浓度的变化趋势基本相同. 冬、春季散射系数和颗粒物质量浓度较高,且冬季波动较大;夏、秋季数值较低. 该结论与一些研究者的结论稍有差异.
(2)散射系数出现“一峰一谷型”的日变化特征,峰值出现在8:00,谷值出现在15:00. 相较于2011年的散射系数存在明显“晚高峰”及回落现象,2018年散射系数在23:00之后才出现回落现象,这主要与夜间逆温层的形成、城市化发展、交通排放、人为活动和工厂持续生产有关.
(3)地面风与散射系数的大小紧密相关. 散射系数随地面风的增大而减小. 春季,地面风速达全年最大值,因此污染物主要来自东部城市建筑群中的人为排放;夏季水汽通量增加,有利于气溶胶粒子的湿清除,因此各方向的气团都相对清洁;秋冬季,由于人为排放的气溶胶局地性很强,因此不同风向的散射系数分布差异不大.
(4)对2018年11月27日—12月3日一次典型的空气污染过程进行分析,散射系数与PM2.5浓度呈现很好的正相关关系,混合层高度也与散射系数、PM2.5浓度呈现负相关关系. 且该次空气污染过程中温度和相对湿度始终呈现很好的负相关关系,即散射系数的高值区一般都保持高湿低温的状态. 结合天气形势和后向轨迹可以看出该时段由于受到西南低空急流的影响,污染气团主要是来自我国西南及周边地区.
2018年杭州市主城区气溶胶散射特性的观测
Observation of aerosol scattering characteristics in Hangzhou City in 2018
-
摘要: 本文利用2018年杭州国家基准气候站Aurora-3000浊度仪和相关气象要素观测资料,研究了杭州市主城区大气环境中气溶胶散射系数的变化特征. 结果表明,2018年杭州市主城区年平均散射系数为(217.4±161.9)Mm-1. 受大气环流形势,季节性气象条件变化以及人为源的影响,气溶胶散射系数表现为冬季和春季高于秋季和夏季. 在逆温层,交通排放,人为活动的共同作用下,散射系数呈“一峰一谷型”的日变化特征,峰值出现在8:00(北京时,下同),谷值出现在15:00. 随着PM2.5质量浓度的增加,散射系数和PM2.5质量浓度表现出越来越明显的正相关关系. 散射系数随地面风的增大而减小. 并且由于春季地面风速达全年最大值,具有较好的扩散条件,因此导致散射系数较冬季小;秋冬季,由于人为排放的气溶胶局地性很强,因此不同风向的散射系数分布差异不大. 对2018年11月27日—12月3日一次典型的空气污染过程分析表明,混合层高度与散射系数,PM2.5浓度呈现负相关关系. 该过程中散射系数的高值区一般都保持高湿低温的状态. 结合天气形势和后向轨迹模式分析可知,该时段由于受到西南低空急流的影响,污染气团主要是来自我国西南及周边地区.Abstract: In this paper, the variation characteristics of aerosol scattering coefficient in the atmospheric environment in the main urban area of Hangzhou were studied by using the Aurora-3000 turbidimeter of Hangzhou National Reference Climatological Station in 2018 and the observation data of related meteorological elements. The results show that the average annual scattering coefficient is (217.4±161.9) Mm-1 in the main urban area of Hangzhou in 2018. The aerosol scattering coefficient in winter and spring is higher than that in autumn and summer due to the influence of atmospheric circulation, seasonal meteorological conditions and anthropogenic sources. Under the combined effect of inversion layer, traffic emission and human activities, the scattering coefficient presents a diurnal variation characteristic of “one peak and one valley”, with the peak value appearing at 8:00 (Beijing time, the same below) and the valley value appearing at 15:00. With the increase of PM2.5 mass concentration, the scattering coefficient and PM2.5 mass concentration show more and more obvious positive correlation. The scattering coefficient decreases with the increase of the surface wind. Moreover, the surface wind speed in spring reaches the maximum of the whole year and has better diffusion conditions, so the scattering coefficient is smaller than that in winter.In autumn and winter, because of the strong local nature of anthropogenic aerosol emission, the scattering coefficient distribution of different wind direction has little difference. The analysis of a typical air pollution process from November 27 to December 3, 2018 shows that the mixing layer height is negatively correlated with the scattering coefficient and PM2.5 concentration. In this process, the high value region of scattering coefficient generally keeps the state of high humidity and low temperature. Combined with the analysis of the weather situation and the backward trajectory model, it can be seen that due to the influence of the southwest low-level jet during this period, the polluted air mass mainly came from southwest China and its surrounding areas.
-

-
-
[1] 唐孝炎, 张远航, 邵敏. 大气环境化学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 1-343. TANG X Y, ZHANG Y H, SHAO M. Atmospheric environmental chemistry [M] . Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006: 1-343(in Chinese).
[2] 孙俊英, 张璐, 沈小静, 等. 大气气溶胶散射吸湿增长特性研究进展 [J]. 气象学报, 2016, 74(5): 672-682. SUN J Y, ZHANG L, SHEN X J, et al. A review of the effects of relative humidity on aerosol scattering properties [J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2016, 74(5): 672-682(in Chinese).
[3] 章澄昌, 周文贤. 大气气溶胶教程 [J]. 北京:气象出版社, 1995: 323. ZHANG C C, ZHOU W X. Atmospheric aerosol tutorial [J]. Beijing:China Meteorological Press, 1995: 323(in Chinese).
[4] 徐梅, 韩素芹, 武国良, 等. 天津市区秋冬季大气气溶胶散射系数的变化特征 [J]. 气象, 2011, 37(12): 1566-1571. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.12.013 XU M, HAN S Q, WU G L, et al. The scattering properties of aerosols in urban site of Tianjin [J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2011, 37(12): 1566-1571(in Chinese). doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2011.12.013
[5] DOCKERY D W, POPE C A 3rd. Acute respiratory effects of particulate air pollution [J]. Annual Review of Public Health, 1994, 15: 107-132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pu.15.050194.000543 [6] 李放. 首次IGAC气溶胶表征实验(ACE-1) [J]. 地球科学进展, 1996, 11(4): 420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1996.04.018 LI F. First IGAC aerosol characterization experiment (ACE-1) [J]. Advence in Earth Sciences, 1996, 11(4): 420(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1996.04.018
[7] 李放. 国际全球大气化学计划第二次气溶胶表征实验(ACE—2) [J]. 地球科学进展, 1998, 13(2): 207-208. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1998.02.018 LI F. The Second Aerosol Characterization experiment of the international global atmospheric chemistry program (ACE-2) [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1998, 13(2): 207-208(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1998.02.018
[8] 张仁健, 王明星, 张文, 王秀玲. 北京和青岛的沙尘暴观测与ACE-ASIA及中日沙尘合作//第九届(2001)全国大气环境与污染学术会议论文集[C]. 中国空气动力学会风工程及工业空气动力学专业委员会: 中国空气动力学会, 2001: 1. ZHANG R J, WANG M X, ZHANG W, WANG X L. Sand-dust observation in Beijing and Qingdao and ACE-ASIA and Sino-Japanese cooperation on sand-dust //Proceedings of the 9th (2001) National Conference on Atmospheric Environment and Pollution [C]. Chinese Aerodynamic Association of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics Professional Committee: Chinese Aerodynamic Society, 2001: 1(in Chinese).
[9] DEVARA P C S, JAYA RAO Y, DANI K K, et al. Aerosol, ozone and water vapour distributions observed over land and sea regions during INDOEX field phases [J]. Marine Science, 2012, 2(5): 77-84. doi: 10.5923/j.ms.20120205.06 [10] 韩素芹, 张裕芬, 李英华, 等. 天津市春季气溶胶消光特征和辐射效应的数值模拟 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(1): 8-12. HAN S Q, ZHANG Y F, LI Y H, et al. Simulation of extinction and radiant effect of aerosol in spring of Tianjin City [J]. China Environmental Science, 2011, 31(1): 8-12(in Chinese).
[11] 袁亮, 银燕, 于兴娜, 等. 黄山夏季气溶胶光学特性观测分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(12): 2131-2139. YUAN L, YIN Y, YU X N, et al. Observational study of aerosol optical properties in summer in Mt. Huang [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(12): 2131-2139(in Chinese).
[12] 于大江, 宋庆利, 孙俊英, 等. 龙凤山大气气溶胶散射特性观测分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(3): 765-771. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101003 YU D J, SONG Q L, SUN J Y, et al. Characteristics of aerosol scattering coefficient at Longfengshan regional background station [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(3): 765-771(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101003
[13] 任丹阳, 周杨, 吴冠儒, 等. 香港郊区站点冬季污染背景下气溶胶消光特征及其与细颗粒物化学组成关系 [J]. 地球化学, 2021, 50(1): 12-21. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2021.01.002 REN D Y, ZHOU Y, WU G R, et al. Characteristics of atmospheric extinction and its relationship with fine particulate matter chemical composition in a polluted background at a suburban site in Hong Kong in winter [J]. Geochimica, 2021, 50(1): 12-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2021.01.002
[14] 兰剑, 乔利平, 郝继宗, 等. 上海市PM2.5及散射系数的监测 [J]. 广州化工, 2021, 49(1): 83-85,121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2021.01.027 LAN J, QIAO L P, HAO J Z, et al. Monitoring of PM2.5 and scattering coefficient in shangha [J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2021, 49(1): 83-85,121(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2021.01.027
[15] 齐冰, 杜荣光, 徐宏辉, 等. 杭州市区大气气溶胶散射特性观测分析 [J]. 高原气象, 2014, 33(1): 277-284. QI B, DU R G, XU H H, et al. An observational study on aerosol scattering properties in urban site of Hangzhou [J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2014, 33(1): 277-284(in Chinese).
[16] MÜLLER T, LABORDE M, KASSELL G, et al. Design and performance of a three-wavelength LED-based total scatter and backscatter integrating nephelometer [J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2011, 4(6): 1291-1303. doi: 10.5194/amt-4-1291-2011 [17] JUNGE C. The size distribution and aging of natural aerosols as determined from electrical and optical data on the atmosphere [J]. Journal of Meteorology, 1955, 12(1): 13-25. doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1955)012<0013:TSDAAO>2.0.CO;2 [18] 浊度计Aurora-3000中文操作手册[DB/OL]. 北京赛克玛环保仪器有限公司, 2019: 6-7. Aurora-3000 Chinese Operation Manual [DB/OL]. Beijing Secma Environmental Protection Instrument Co. , LTD. , 2019: 6-7. (in Chinese).
[19] 徐晓飞, 单萌. 临安大气本底站2017年气溶胶散射特性观测研究 [J]. 浙江气象, 2019, 40(3): 31-35. XU X F, SHAN M. Observation study on aerosol scattering characteristics of Lin'an atmospheric background station in 2017 [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Meteorology, 2019, 40(3): 31-35(in Chinese).
[20] 娄小芬, 罗玲, 孔照林. 2011年长江中下游梅雨特征及成因分析 [J]. 气象与环境学报, 2014, 30(2): 14-22. LOU X F, LUO L, KONG Z L. Characteristics of Meiyu and its forming reason in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in 2011 [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2014, 30(2): 14-22(in Chinese).
[21] 徐薇, 修光利, 陶俊, 等. 上海市大气气溶胶散射系数的季节变化特征 [J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2014, 31(3): 345-350,366. XU W, XIU G L, TAO J, et al. Seasonal variation characteristics of atmospheric aerosol scattering coefficients in Shanghai [J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014, 31(3): 345-350,366(in Chinese).
[22] 张芝娟, 衣育红, 陈斌, 等. 2018年春季中国北方大范围沙尘天气对城市空气质量的影响及其天气学分析 [J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 13-22. ZHANG Z J, YI Y H, CHEN B, et al. Effectof dust weather on urban air quality over Northern China in spring of 2018 and its weather analysis [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 13-22(in Chinese).
[23] 杜荣光, 齐冰, 郭惠惠, 等. 杭州市大气逆温特征及对空气污染物浓度的影响 [J]. 气象与环境学报, 2011, 27(4): 49-53. DU R G, QI B, GUO H H, et al. Characteristics of atmospheric inversion temperature and its influence on concentration of air pollutants in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2011, 27(4): 49-53(in Chinese).
[24] 杜荣光, 齐冰, 周斌, 等. 杭州市区大气气溶胶吸收系数观测研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(5): 769-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.05.001 DU R G, QI B, ZHOU B, et al. An observational study on aerosol absorption coefficient in urban site of Hangzhou [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(5): 769-774(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.05.001
[25] 崔晓雨, 付晓东. 夜间经济的现状与热点: 基于Citespace的政策文本分析 [J]. 开发研究, 2020(6): 97-104. CUI X Y, FU X D. Development status and hotspots of night-time economy: A policy textual analysis based on cite space [J]. Research on Development, 2020(6): 97-104(in Chinese).
[26] 张勇, 银燕, 肖辉, 等. 石家庄春季大气气溶胶的散射特征 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(5): 769-779. ZHANG Y, YIN Y, XIAO H, et al. An observation study of the scattering properties of aerosols over Shijiazhuang City in spring [J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(5): 769-779(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: