-
苯系物[1](苯、甲苯、乙苯和二甲苯,BTEX),作为单环芳烃类物质,主要存在于石油化工产品中,具有“致癌、致突变、致畸”等危害。在化工搬迁场地[2]、废加油站[3]以及钢铁焦化企业[4]的土壤中BTEX污染严重;另外,近年来国内发生多起BTEX泄露事故,泄露后污染物会扩散、渗透、残留在土壤的毛细孔道中,若处理不当会引发紧急公共安全事件[5-6]。因此,研究土壤环境中BTEX的原位修复技术具有重要的理论价值和应用前景。
工业上降解处理BTEX的传统技术有吸附法、吸收法、冷凝法等,近年来新发展的技术包括化学氧化法、低温等离子体法等[7]。其中,化学氧化法具有去除效率高、易操作、施工工期短等优点,常用氧化剂包括过硫酸钠、高锰酸钾、过氧化氢、Fenton试剂、类Fenton试剂等[8]。然而,采用化学氧化法降解处理土壤中有机物时,氧化剂费用在成本核算时所占比例过高,部分工程案例该项支出甚至在50%以上。这是由于在施工过程中,为保证污染物降解完全,防止因污染物不达标而返工,氧化剂用量往往过量很多,造成氧化剂浪费,且多余氧化剂可能会破坏土层结构及有机质含量等相关性质。前人曾研究用化学氧化法处理水中的苯系物[9-15],发现高锰酸钾、过氧化氢、Fenton试剂、类Fenton试剂及活化过硫酸盐氧化苯系物可以达到良好的处理效果。赵丹[16]等比较研究了Fenton试剂、类Fenton 试剂、高锰酸钾以及活化过硫酸钠4种常用的化学氧化剂对焦化工业污染场地中苯系物的去除效果,但考察的污染物浓度较低,最高BTEX含量仅有18.1 mg·kg−1,限制了该研究在焦化场地以外工况中的参考使用。
综合上述问题,本研究选择了5种常见的低成本氧化剂,在密闭顶空瓶中对人工污染的苯系物(浓度最高可达约1000 mg·kg−1)土壤进行处理,采用正交实验法探索最佳氧化条件和显著影响因素,分析对比氧化剂种类对各类苯系物的降解效果,确定氧化剂和苯系物间的最佳匹配关系。
-
土壤取自大连理工大学生物学院后山,采用2.36 mm孔尺寸过筛处理,去除树枝、草叶以及大石子等,筛下物晒干保存为待用土壤。经检测,此待用土壤不包含苯系物。
-
根据环境质量建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准的要求,定量配制苯系物溶液对待用土壤进行人工污染,密封老化24 h后测定各苯系物含量。由于不同污染物管制值范围差异较大,所以分成苯-乙苯,甲苯-二甲苯两组开展实验,具体见表1。在氧化反应中,当两种污染物同时存在,会产生竞争反应并对降解率存在影响,且污染物含量对氧化条件也存在影响。因此,正交实验考察了污染物相对含量的影响。
-
假定污染物经氧化处理后完全矿化为CO2和H2O,计算所需氧化剂的理论量,然后选取氧化剂理论量的0.25倍、0.5倍、1倍、2倍进行氧化反应。由于高锰酸钾溶解度较低,所以高锰酸钾氧化甲苯-二甲苯组选取了0.125倍、0.25倍、0.5倍和1倍。
-
采用硫酸亚铁作为Fenton试剂、类Fenton试剂以及过硫酸钠的活化剂,采用柠檬酸作为类Fenton试剂和过硫酸钠的络合剂,氧化剂与活化剂及络合物的比例见表2。
-
氧化反应时间分别选取6、12、24、48 h。
-
室温下,将污染物加入土壤进行老化,然后加入氧化药剂模拟原位反应,具体操作步骤如下:取2 g待用土壤放入顶空瓶内,用移液枪加入一定量的苯系物混合液,用封口器封口后老化24 h,然后加入氧化剂(1 mL)氧化设定时间后加入基体改性剂和氟苯,密封超声10 min,然后参照1.3.2节进行定性、定量分析。所有实验均按L16(45)正交表安排实验,无平行实验。
-
参照《固体废物挥发性有机物的测定顶空/气相色谱-质谱法(HJ 643—2013)》,采用顶空-气相色谱仪对土壤中苯系物进行定性、定量测定。污染物定量分析采用内标法,内标物为氟苯。顶空进样分析条件:加热平衡温度62 ℃,平衡时间30 min,取样针温度100 ℃,传输线温度110 ℃;气相色谱分析条件:进样器150 ℃,检测器250 ℃,程序升温40 ℃保持5 min后以10 ℃·min−1升温至180 ℃。
-
采用正交实验助手对数据进行直观分析、方差分析和显著性分析(置信区间为95%,α=0.05)
-
以过硫酸钠为氧化剂,氧化处理苯/乙苯以及甲苯/二甲苯混合污染物,通过正交实验助手分析,结果如图1所示。在设定范围内,5种因素对苯、甲苯、二甲苯的降解都无显著影响;除过硫酸钠和硫酸亚铁物质的量比外,其余4种因素对乙苯降解率均有显著影响,这可能是由于乙苯相比苯更容易被活化过硫酸钠氧化,更易受各种因素所影响;而甲苯/二甲苯组,甲苯氧化效果虽不如二甲苯,但是活化过硫酸钠氧化降解率都较高,所以在设定范围内无显著影响。当苯和乙苯质量比逐渐减小时,乙苯的降解率先减小后逐渐增大,m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:9时效果最好,这可能是由于乙苯浓度多于苯时,过硫酸钠与乙苯接触更多,且乙苯更易反应,所以降解率会升高。过硫酸钠质量及硫酸亚铁和柠檬酸物质的量之比与乙苯的降解率关系是先增大后减小,最佳条件在过硫酸钠40 mg(理论量的1倍),n(Na2S2O4):n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸)=10:1:3时,催化剂和络合剂的使用会大大增加氧化效果[18],但当过硫酸钠浓度较高时,若二价铁产生较少,则不能够完全活化过硫酸钠,所以降解率会下降。
16组正交实验结果中,乙苯降解率最高可达到94.3%,条件在m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:6,过硫酸钠40 mg,n(Na2S2O4):n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸)=40:1:3,时间48 h。通过正交实验可以得到活化过硫酸钠氧化苯的最佳氧化条件:过硫酸钠40 mg(理论量的1倍),n(Na2S2O4):n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸)=40:1:3,氧化48 h,苯的降解率可达91.5%;氧化甲苯、对二甲苯和邻二甲苯的最佳条件为:过硫酸钠480 mg(理论量的2倍),n(Na2S2O4):n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸)=20:4:3,氧化48 h,甲苯降解率最高为98.5%,对二甲苯和邻二甲苯降解率最高为97.0%和98.5%。
-
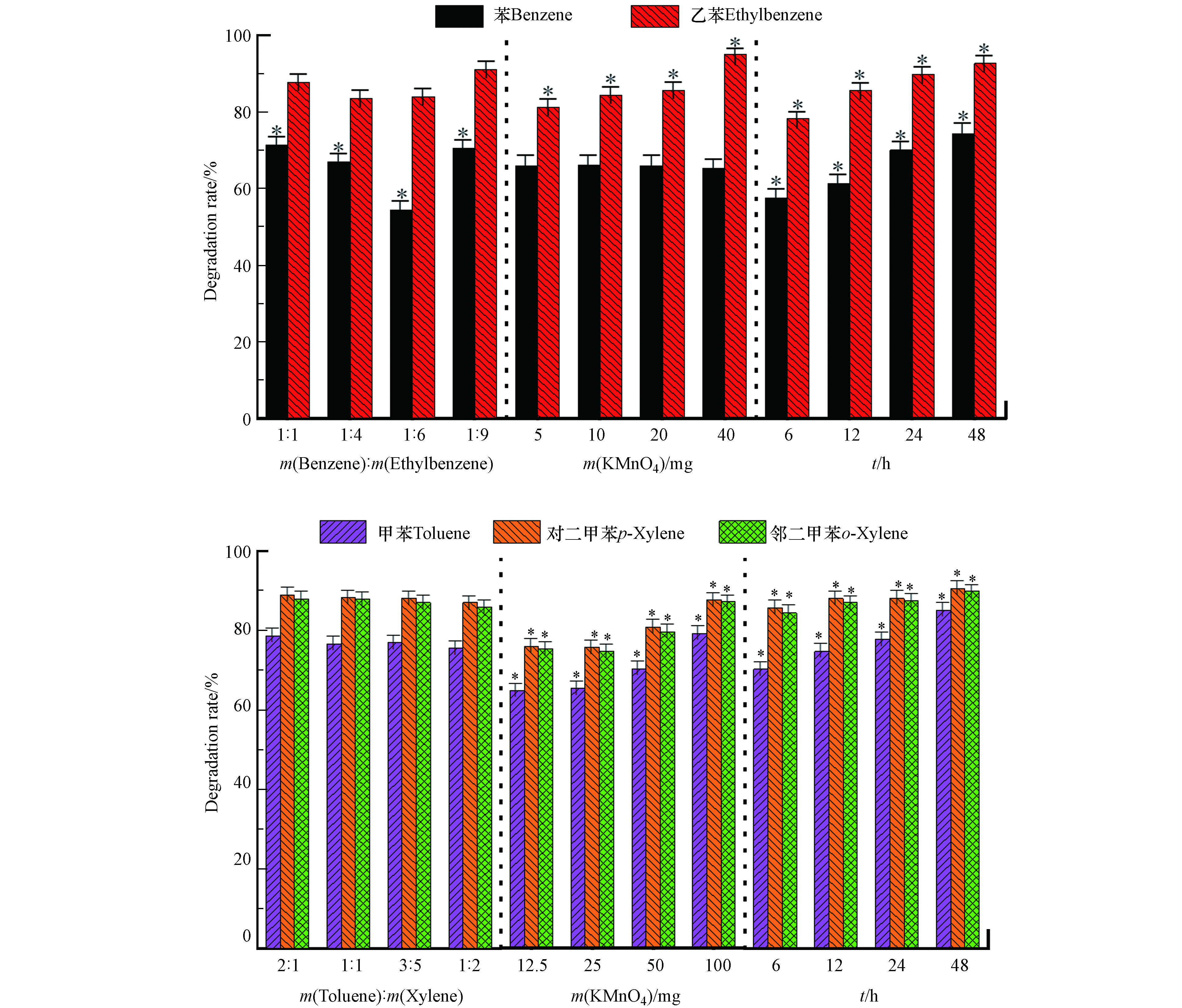
高锰酸钾氧化苯系物的降解结果如图2所示。通过显著性分析可知,在设定范围内,苯和乙苯的质量比及氧化时间对苯的降解率有显著性影响:在一定范围内,随着苯与乙苯质量比的减小,苯的降解率逐渐减小,m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:1时降解率最高。这可能是由于苯比较稳定,受竞争影响较大,当苯浓度较高时,竞争影响小,因此降解率较高。根据16组正交实验结果,当m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:4,0.02 g 高锰酸钾(理论量的1倍),氧化时间48 h时,苯降解率最高为83.5%。高锰酸钾用量以及氧化时间对乙苯、甲苯、对二甲苯和邻二甲苯的降解率有显著影响,随着高锰酸钾用量增多、氧化时间增加,乙苯、甲苯、对二甲苯和邻二甲苯的降解率呈上升趋势。这是因为高锰酸钾浓度越高,氧化剂与污染物反应速率越快;氧化时间越长越持久,则污染物降解率越完全。16组正交实验结果可知,当m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:1,0.04 g 高锰酸钾(理论量的2倍),氧化时间48 h时,乙苯降解率最高为96.0%。氧化降解甲苯、对二甲苯和邻二甲苯的最佳条件为:m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:1,高锰酸钾100 mg(理论量的1倍),氧化48 h,甲苯、对二甲苯及邻二甲苯降解率最高分别为93.5%、98.8%、98.8%。
-
图3是过氧化氢氧化苯系物的实验结果。显著性分析可知,在设定范围内,对苯和乙苯有显著影响的是氧化时间,时间越长,氧化越久,降解率越高。对甲苯、对二甲苯和邻二甲苯有显著影响的是过氧化氢用量以及氧化时间。16组正交实验数据结果中,当m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:4,4.8 mg过氧化氢(理论量的1倍),氧化时间为48 h时,苯降解率最高为78.8%;当m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:9,1.2 mg过氧化氢(理论量的0.25倍),氧化时间为48 h时,乙苯降解率最高为90.9%。
过氧化氢用量及氧化时间与甲苯、对二甲苯及邻二甲苯降解率的影响整体上呈正相关,与高锰酸钾氧化结果一致。因为高锰酸钾和过氧化氢都是单一氧化剂,氧化剂用量不受其他因素的影响,所以浓度越高,效果越好,但同时会造成成本增加,所以在应用上需要综合考虑。当过氧化氢量为72 mg(理论量的2倍),氧化时间48 h时,甲苯、对二甲苯及邻二甲苯降解率最高分别为92.1%、96.9%、96.8%。
-
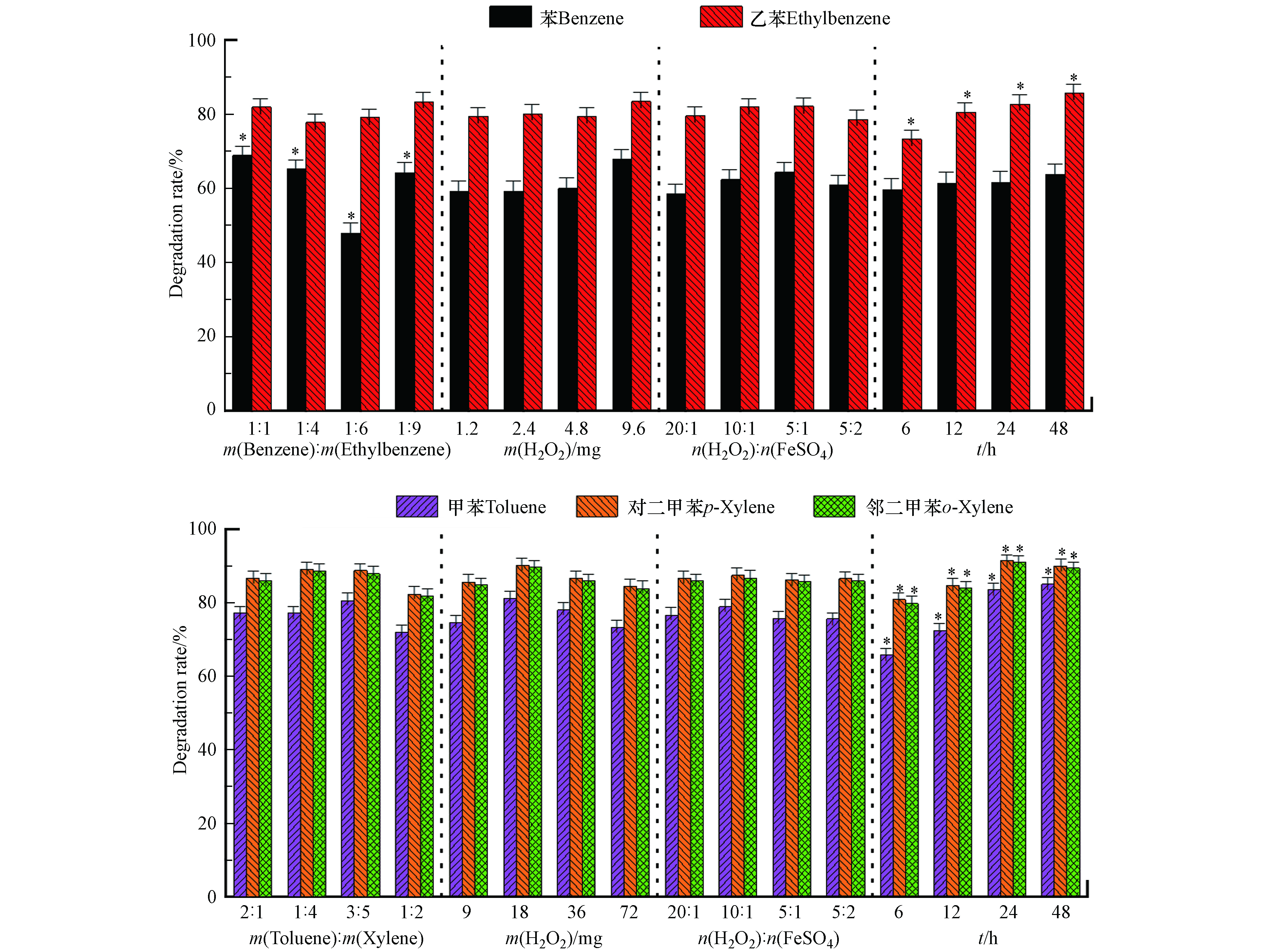
Fenton氧化苯/乙苯、甲苯/二甲苯混合物的直观分析和显著性分析如图4所示。由图4可知,在设定范围内,苯/乙苯质量比对苯的降解率有显著影响,规律和高锰酸钾氧化苯一致。受竞争关系影响,在一定范围内降解率随质量比减小而降低,当m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:1,过氧化氢9.6 mg(理论量的2倍),氧化时间48 h,苯的降解率最高为74.4%;氧化时间对甲苯、乙苯和二甲苯的降解率有显著影响,氧化时间越长,降解率越高;这可能是随着反应进行,体系pH降低,酸性环境更利于二价铁存活,利于反应进行。m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:9,过氧化氢4.8 mg(理论量的1倍),n(H2O2):n(FeSO4)=10:1,氧化时间48 h,乙苯的降解率最高为88.7%;m(甲苯):m(二甲苯)=1:1,过氧化氢18 mg(理论量的0.5倍),n(H2O2):n(FeSO4)=10:1,氧化时间48 h,甲苯、对二甲苯及邻二甲苯降解率最高分别为89.6%、96.4%、96.2%。过氧化氢用量与硫酸亚铁的比例没有显著影响,可能是硫酸亚铁活化能力较强,在实验比例范围内,加入的二价铁都能将过氧化氢活化。
-
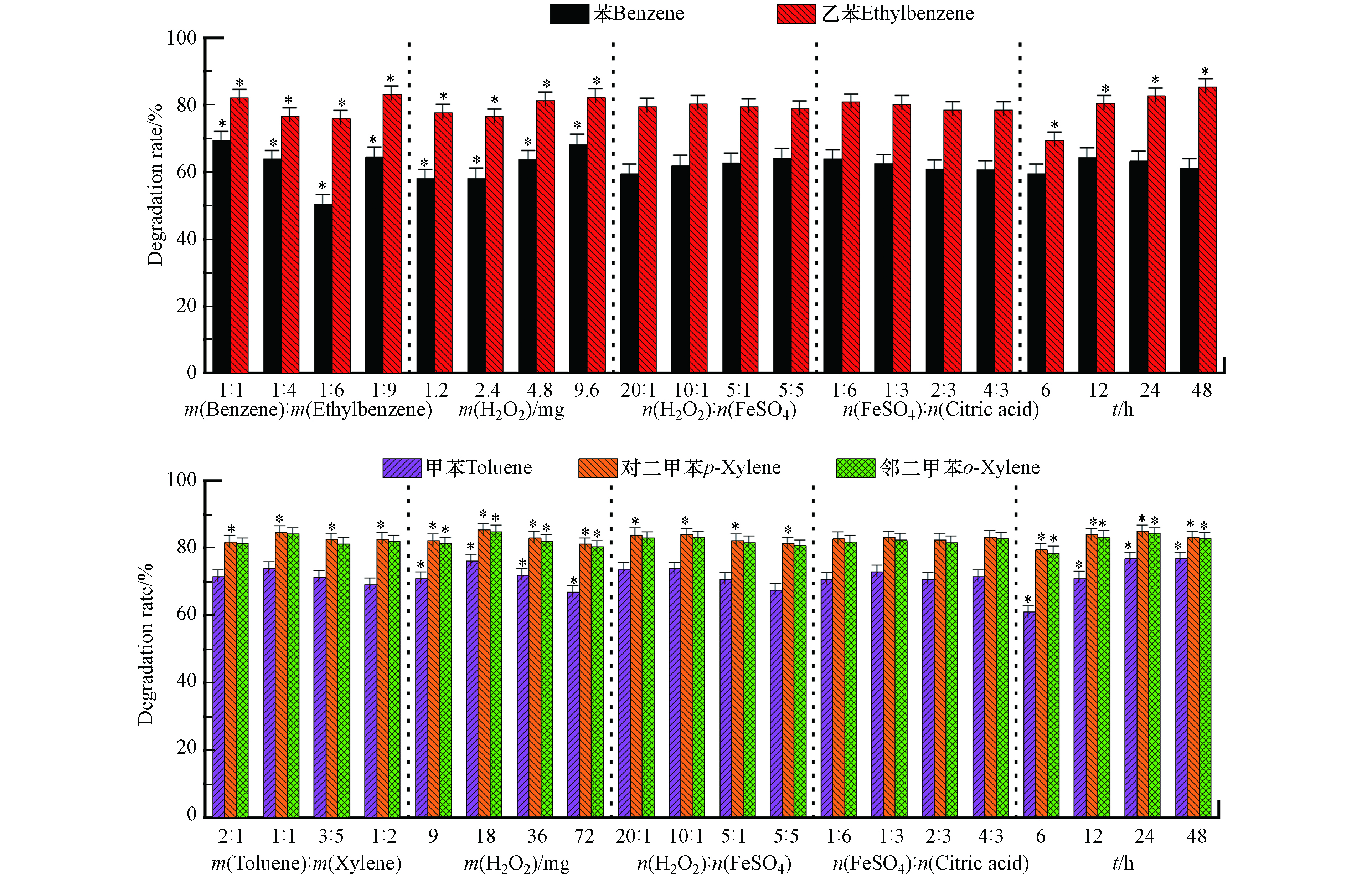
图5是类Fenton试剂对苯/乙苯混合氧化。在设定范围内,苯/乙苯质量比以及过氧化氢用量对苯和乙苯降解率均有显著影响,m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:1,过氧化氢9.6 mg(理论量的2倍)时,苯的降解率最高为75.3%。对乙苯降解率有显著影响的还包括反应时间;过氧化氢用量与苯和乙苯的降解率呈正相关,这是因为乙苯更容易氧化,时间长会降解的更多,效果也会更明显。m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:9,过氧化氢9.6 mg,氧化时间48 h时,乙苯氧化效果最好。16组正交实验结果中乙苯降解率最高为89.1%,条件为m(苯):m(乙苯)=1:1,9.6 mg过氧化氢,氧化时间48 h。
由图5的显著分析结果可得,在设定范围内,过氧化氢用量和氧化时间对甲苯和邻二甲苯降解率有显著影响,对于对二甲苯的降解,除络合物外,其他因素都有显著影响。在前述考察其他4种氧化剂时,对二甲苯和邻二甲苯的显著影响是一致的,而类Fenton却不一致,可能是由于类Fenton实际的氧化效果不如其他氧化剂,对于较容易氧化的对二甲苯和邻二甲苯,当条件变化时,对二甲苯和邻二甲苯的降解差异就会体现出来,因而显著影响因素也会不同。过氧化氢超过18 mg(理论量的0.5倍)时,甲苯及二甲苯降解率会降低,这是可能是因为过氧化氢量过多,而二价铁的含量不足以催化过氧化氢,产生足够的·OH降解污染物,所以降解率会降低;随着时间的增大,甲苯和二甲苯的降解率呈上升趋势。
16组正交实验结果表明,m(甲苯):m(二甲苯)=1:1,18 mg过氧化氢(理论量的0.5倍),n(H2O2):n(FeSO4) n(柠檬酸)=80:4:3,氧化24 h时,甲苯、对二甲苯、邻二甲苯降解率达到最高,分别为86.2%,90.6%,90.5%。
-
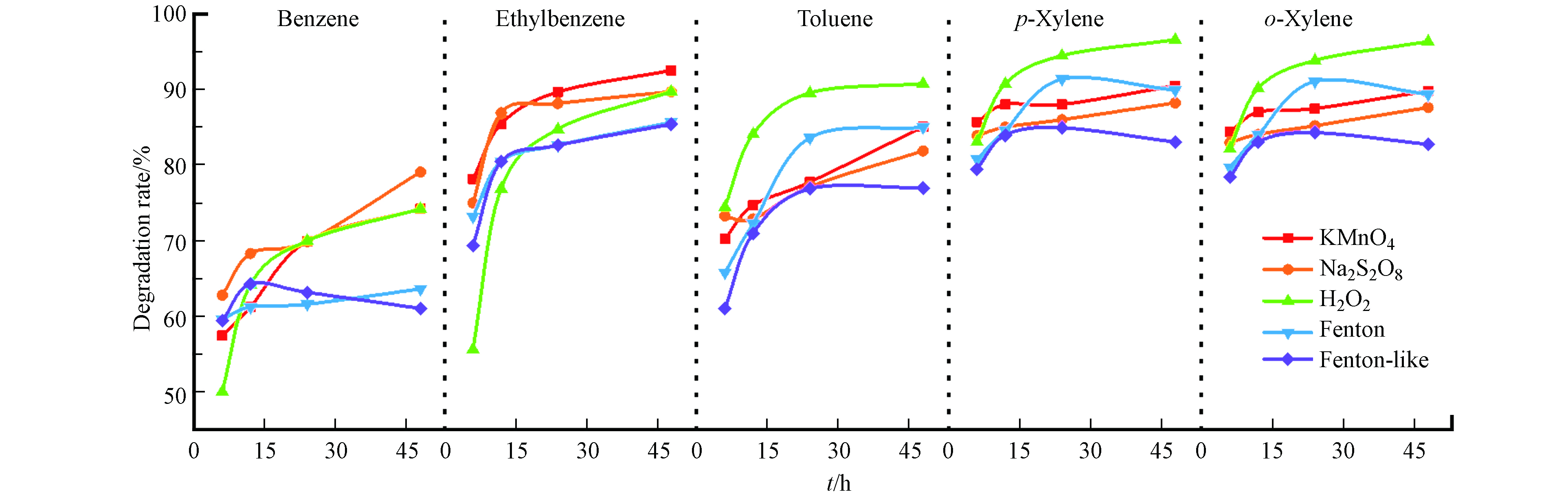
以时间为横坐标、降解率为纵坐标,对比考察不同氧化剂氧化苯系物的降解效果,结果如图6所示。通过横向分析可以发现:(1)在氧化降解处理苯/乙苯混合物时,乙苯更易被氧化,这是由于苯含有大π键,使苯的C—H键键能高于乙苯中甲基中的C—H键键能,键能越高越不易脱氢形成碳自由基;而Fenton、类Fenton和活化过硫酸盐氧化是自由基反应,所以苯受竞争影响更大[19]。在混合处理甲苯/二甲苯时,二甲苯降解率更高,对二甲苯和邻二甲苯的降解率差别不大,且都比甲苯高,这可能是由于二甲苯比甲苯多一个甲基,增大了C—H键的断裂几率,更容易生成碳自由基。高锰酸钾和过氧化氢是自身化合价的变化来氧化苯系物,从结构看,苯环更加稳定,甲基的存在更容易活化苯环,从而更易被氧化。研究发现,活化过硫酸盐在水中能快速降解有机物,浓度增加有利于苯系物的活化,乙苯、二甲苯去除率大于甲苯,苯的去除率最差[13,18,20-21],与本实验基本一致。Rinaldi等研究表明,高锰酸钾和过氧化氢氧化土壤中降解率二甲苯大于甲苯大于苯,高锰酸钾不与苯发生反应[22]。杨玲等研究认为,Fenton和类Fenton试剂在水中氧化苯系物均是二级反应,氧化速率常数乙苯>二甲苯>甲苯>苯[23],与图中开始的各氧化物降解的斜率基本一致。(2)在氧化初期各苯系物的降解都很快,这可能是因为氧化初始,苯系物含量较高,氧化剂与苯系物接触面积较大,所以氧化速率快,苯系物在土壤中的氧化不仅与污染物和氧化剂量有关,还与土壤的性质相关[24]。
通过纵向对比可知,(1)氧化降解苯时高锰酸钾、过硫酸钠和过氧化氢氧化效果较好,氧化降解甲苯时过氧化氢、高锰酸钾、过硫酸钠和Fenton试剂效果较好,氧化乙苯和二甲苯时,5种氧化剂差别不大。过氧化氢氧化效果较好是由于本研究采用密闭空间进行氧化,过氧化氢快速分解生成的氧气也在此空间中起到一定的氧化作用,若在实际工程中不是密闭环境,会造成大量浪费,所以,过氧化氢不适用于工程上对土壤的氧化。文献研究水中苯系物降解效果时发现,Fenton试剂氧化苯和甲苯时比活化过硫酸盐更加稳定,氧化速率也更高,过氧化氢的降解效果比高锰酸钾好,过硫酸钠体系比过氧化氢体系对苯系物的降解率更高,氧化也更持久[9,13,22];高锰酸钾作为氧化剂对二甲苯的降解率可达100%,Fenton 试剂和类 Fenton 试剂作为氧化剂分别可达到80%和71% [15-16]。但对于土壤污染物的原位氧化,高锰酸钾因为溶解度较低,所以其效果并不理想,且高锰酸钾氧化后会生成二氧化锰,固体二氧化锰存在在土壤里面会使得土壤的渗透性变差。(2)类Fenton试剂氧化降解甲苯和二甲苯效果不如Fenton试剂,这与杨玲等[23]处理苯系物污染地下水时结果一致,其原因是由于在氧化反应中起主要作用的是·OH,它是Fe2+与H2O2反应产生的,而类Fenton试剂产生·OH需要先将Fe3+转换成Fe2+,所以类Fenton试剂效果不好[25];而氧化降解苯和乙苯的效果与上述文献不一致,是由于氧化介质、氧化方式以及氧化苯系物难易程度不同造成的。本研究是在土壤环境下的原位氧化处理,土壤和苯系物之间存在一定的吸附作用,氧化剂需要扩散至苯系物分子附近方能体现效果,对于较难氧化的苯系物来说,生成·OH并不是限速步骤,所以对于本研究中类Fenton和Fenton试剂氧化降解苯和乙苯效果差别不大。
综上所述,从降解率及土壤保护角度考虑,处理土壤中苯系物,过硫酸钠、Fenton试剂以及类Fenton试剂是更佳选择,若土壤中存在更多苯、乙苯时,过硫酸钠更适合作为氧化剂;当土壤中存在更多甲苯时,Fenton更适合作为氧化剂;当土壤中存在更多二甲苯时,选择Fenton试剂和过硫酸钠作为氧化剂均可。
-
(1)各氧化剂去除土壤中苯系物时,除Fenton、类Fenton氧化苯和过硫酸钠氧化苯、甲苯、二甲苯,时间影响不显著外,其余反应氧化时间都是显著影响因素,且降解率与时间呈正相关。不同苯系物对应的显著影响因素有所差异:对苯来说,苯和乙苯在土壤中的质量比比较重要,对其他苯系物而言,氧化剂用量也是一重要影响因素。
(2)高锰酸钾氧化苯、甲苯、二甲苯最佳条件是理论量的0.5倍,氧化乙苯是理论量的2倍,氧化时间都是48 h;过氧化氢为理论量的2倍,氧化48 h;Fenton氧化苯、乙苯需要理论量的2倍,n(H2O2):n(FeSO4)=1:0.2,氧化48 h,氧化甲苯、二甲苯需要理论量的0.5倍,n(H2O2):n(FeSO4)=1:0.1,氧化48 h;类Fenton氧化苯系物需要2倍氧化剂量,n(H2O2):n(FeSO4)=1:0.1,n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸)=4:3,氧化48 h;过硫酸钠氧化苯系物需要2倍氧化剂量,n(Na2S2O8):n(FeSO4)=1:0.2,氧化苯和乙苯时n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸)=1:3,氧化甲苯二甲苯时n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸)=4:3,氧化48 h。
(3)从降解率和土壤保护角度考虑,氧化苯、乙苯污染物选用过硫酸钠,氧化甲苯污染物选用Fenton试剂,氧化二甲苯污染物选用Fenton试剂和过硫酸钠均可。
不同氧化剂氧化降解土壤中的苯系物
Study on degradation of volatile benzenes in soil by different oxidants
-
摘要: 化学氧化修复技术是处理土壤中有机污染物的一种有效方法,但在施工过程中,氧化剂添加往往过量很多,造成氧化剂浪费,且多余氧化剂还会破坏土层结构及有机质含量。目前采用化学氧化法处理苯系物大多针对于地下水环境,面对复杂工况时的土壤苯系物污染,氧化处理缺少相应的系统数据支持。据此,本研究采用正交实验的方法研究了活化过硫酸钠、高锰酸钾、过氧化氢、Fenton试剂和类Fenton试剂氧化不同苯系物的最佳条件和显著影响因素。结果表明,氧化时间是对降解率影响较大的因素,但是降解不同苯系物所采用的氧化剂、氧化条件及显著影响因素有所不同。整体来看,苯系物中乙苯和二甲苯比较容易被氧化;对于氧化剂来说,过氧化氢、高锰酸钾和过硫酸钠氧化效果更好。研究结果可为实际工程上处理不同种类、不同浓度及不同比例的苯系物时,在氧化剂的选择以及氧化剂、活化剂、络合剂的浓度和反应时间等参数设置上提供基础数据支持。Abstract: Chemical oxidation technology is regarded to be an effective method for the oxidative degradation of organic pollutants in soil remediation. However, excessive amounts of oxidants tend to be employed in the process of operation, which resulting in the waste of oxidant, also destroying the layer structure of soil and its content of organic compound due to the residual oxidant. At present, chemical oxidation technology is mainly used in the degradation treatment of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, o-xylene and p-xylene (BTEX) in groundwater environment, but less research is carried out in soil environment. Therefore, chemical oxidative degradation of BTEX in soil was systematacially studied in this thesis. The optimum conditions and significant influencing factors for BTEX degradation were investigated with sodium persulfate, potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, Fenton reagent and Fenton-like reagent as oxidants through orthogonal experiments method. The results showed that the oxidation time had a great influence on the degradation rate, but the effect seems to be different for the degradation of different BTEX compounds if it wholly taking into account of the oxidants, oxidation conditions and significant influencing factors. On the whole, ethylbenzene and xylene in BTEX are founded to be easier being oxidized. As for oxidizing agents, hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate and sodium persulfate are discovered to show better oxidation performance. In general, the research can provide basic data supporting for the selection of oxidants, activators and complexing agents and the reaction condition when it dealing with BTEX pollutants with different types, concentrations and proportions in soil remediation.
-
Key words:
- BTEX /
- sodium persulfate /
- potassium permanganate /
- hydrogen peroxide /
- Fenton reagent /
- Fenton-like reagent
-

-
表 1 苯-乙苯和甲苯-二甲苯土壤污染量的理论值及实际值
Table 1. The theoretical and actual values of benzene - ethylbenzene and toluene -xylene in soil
设定比
Setting ratio of benzene/ethylbenzene理论值/(mg·kg−1)
Theoretical value老化后实际值/(mg·kg−1)
Actual value after aging苯/乙苯 1/1 175/175 152.1/100.4 1/4 70/280 53.8/115.85 1/6 50/300 28.1/129.1 1/9 35/315 29.7/185.5 甲苯-二甲苯 2/0.5/0.5 1600/400/400 973.3/310.1/309.7 1/0.5/0.5 1200/600/600 773.7/510.9/501.5 3/2.5/2.5 900/750/750 588.0/608.8/580.0 1/1/1 800/800/800 457.9/587.6/571.0 表 2 氧化剂与活化剂、络合剂比例设定数值
Table 2. Setting values of oxidants, activators and complexant
因素
Factors水平1
Level 1水平2
Level 2水平3
Level 3水平4
Level 4n(H2O2):n(FeSO4) 1:0.05 1:0.1 1:0.2 1:0.4 n(Na2S2O8):n(FeSO4) 1:0.025 1:0.05 1:0.1 1:0.2 n(FeSO4):n(柠檬酸) 1:6 1:3 2:3 4:3 -
[1] 欧盛江. 环境空气中的苯系物检测及其治理研究 [J]. 科技资讯, 2009, 7(25): 241-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2009.25.198 OU S J. Study on detection and treatment of benzene series in ambient air [J]. Science & Technology Information, 2009, 7(25): 241-242(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2009.25.198
[2] 刘芬芬, 孙小华, 丁力, 等. 搬迁企业原址场地土壤挥发性有机物污染特征: 以北京某搬迁化工厂为例 [J]. 城市地质, 2021, 16(1): 18-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2021.01.003 LIU F F, SUN X H, DING L, et al. Characteristics of soil volatile organic compound pollution in the original site of relocated enterprises—A case study of a relocated chemical plant in Beijing [J]. Urban Geology, 2021, 16(1): 18-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2021.01.003
[3] 张宏凯, 左锐, 王金生, 等. 加油站泄漏污染物的迁移分布规律 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(4): 1532-1539. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.04.041 ZHANG H K, ZUO R, WANG J S, et al. The underground migration and distribution of petroleum contamination at a gas station [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(4): 1532-1539(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.04.041
[4] 王艳俊. 焦化工业区土壤中苯/甲苯污染状况及吸附行为研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2009. WANG Y J. The study of benzene/toluene pollution and adsorption in coked-area[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2009(in Chinese).
[5] 李克, 丁文娟, 王芳, 等. 石油开采行业土壤污染防治对策与建议 [J]. 化工环保, 2019, 39(6): 603-607. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.06.001 LI K, DING W J, WANG F, et al. Countermeasures and suggestions for soil contamination prevention and control of oil exploration industry [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(6): 603-607(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.06.001
[6] 董炎青, 陈英, 陈勇, 等. 土壤甲苯泄漏扩散及影响因素的三维数值模拟 [J]. 油气田地面工程, 2018, 37(7): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6896.2018.07.005 DONG Y Q, CHEN Y, CHEN Y, et al. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of toluene leakage and influencing factors in soil [J]. Oil-Gas Field Surface Engineering, 2018, 37(7): 14-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6896.2018.07.005
[7] 何黎, 白娟, 殷俊, 等. 苯系物污染治理的研究进展 [J]. 应用化工, 2017, 46(10): 2039-2042,2047. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.10.043 HE L, BAI J, YIN J, et al. Research progress of pollution control of benzene series [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(10): 2039-2042,2047(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.10.043
[8] 周欣, 张代荣, 李萍. 多环芳烃污染土壤化学氧化修复技术应用研究 [J]. 环境与发展, 2020, 32(2): 89-90. ZHOU X, ZHANG D R, LI P. Application of chemical oxidative remediation technology to PAHs contaminated soil [J]. Environment and Development, 2020, 32(2): 89-90(in Chinese).
[9] CRIMI M L, TAYLOR J. Experimental evaluation of catalyzed hydrogen peroxide and sodium persulfate for destruction of BTEX contaminants [J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:an International Journal, 2007, 16(1): 29-45. doi: 10.1080/15320380601077792 [10] 杨玲, 赵勇胜, 孙威, 等. Fenton试剂快速氧化处理地下水中BTEX可行性研究 [J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2010, 37(6): 107-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.06.021 YANG L, ZHAO Y S, SUN W, et al. Feasibility of rapid treatment of BTEX in groundwater by Fenton's reagent [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(6): 107-111(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.06.021
[11] LEMAIRE J, CROZE V, MAIER J, et al. Is it possible to remediate a BTEX contaminated chalky aquifer by in situ chemical oxidation? [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 84(9): 1181-1187. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.052 [12] ANDRADE L N, ARAUJO S F, MATOS A T, et al. Performance of different oxidants in the presence of oxisol: Remediation of groundwater contaminated by gasoline/ethanol blend [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 308: 428-437. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.069 [13] YANG Z H, VERPOORT F, DONG C D, et al. Remediation of petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater using optimized in situ chemical oxidation system: Batch and column studies [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 138: 18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.02.032 [14] 江晓铭, 蒋亚萍, 陈余道, 等. 过硫酸盐在岩溶管道地下水中的稳定性及其对苯系物的去除效果 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(4): 1395-1402. JIANG X M, JIANG Y P, CHEN Y D, et al. Stability of persulfate in Karst conduit groundwater and its removal effect of aromatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(4): 1395-1402(in Chinese).
[15] 盛益之, 张旭, 翟晓波, 等. 化学氧化技术异位处理地下水非水相有机污染物中试研究 [J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(2): 422-430. SHENG Y Z, ZHANG X, ZHAI X B, et al. Ex-situ chemical oxidation treatment for non-aqueous liquid contaminated groundwater: A pilot study [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(2): 422-430(in Chinese).
[16] 赵丹, 阎秀兰, 廖晓勇, 等. 不同化学氧化剂对焦化污染场地苯系物的修复效果 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(3): 849-856. ZHAO D, YAN X L, LIAO X Y, et al. Chemical oxidants for remediation of BTEX-contaminated soils at coking sites [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(3): 849-856(in Chinese).
[17] 杨永奇. 活化过硫酸盐降解BTEXs和PAHs研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018. YANG Y Q. Study on degradation of BTEXs and PAHs by activated persulfate[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2018(in Chinese).
[18] 孙威, 赵勇胜, 杨玲, 等. 过硫酸盐活化技术处理地下水中的BTEX及其动力学 [J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2012, 39(3): 446-450. SUN W, ZHAO Y S, YANG L, et al. Treatment of BTEX in groundwater by persulfate oxidation reaction and its kinetics [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2012, 39(3): 446-450(in Chinese).
[19] SUN P, SHEN G Q, TAN Q R, et al. Degradation of BTEXS with stable and pH-insensitive iron-manganese modified biochar from post pyrolysis [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 128092. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128092 [20] SRA K S, THOMSON N R, BARKER J F. Persulfate treatment of dissolved gasoline compounds [J]. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 2013, 17(1): 9-15. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000143 [21] LIANG C J, HUANG C F, CHEN Y J. Potential for activated persulfate degradation of BTEX contamination [J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(15): 4091-4100. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.06.022 [22] RINALDI A, SILVA M R. Degradation of BTX in contaminated soil by using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and potassium permanganate (KMnO4) [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2011, 217(1/2/3/4): 245-254. [23] 杨玲, 赵勇胜, 马百文, 等. Fenton和类Fenton氧化处理地下水中BTEX及其动力学 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(5): 992-996. YANG L, ZHAO Y S, MA B W, et al. Treatment of BTEX in groundwater by Fenton's and Fenton-like oxidation reaction and the kinetics [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 5(5): 992-996(in Chinese).
[24] WATTS R J, HALLER D R, JONES A P, et al. A foundation for the risk-based treatment of gasoline-contaminated soils using modified Fenton’s reactions [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2000, 76(1): 73-89. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3894(00)00173-4 [25] KANG N, HUA I. Enhanced chemical oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons in soil systems [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 61(7): 909-922. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.039 -




 下载:
下载: