-
随着社会的发展和人口老龄化趋势的加快,药物的生产和消费总量与日俱增,家庭中的废弃药品也随之增加[1]。由于缺少相应的处置管理意识[2],大量药物随生活垃圾的卫生填埋进入垃圾填埋场中。未经处理的药物经垃圾内源分解产水或外源降雨及径流淋滤[3]进一步迁移至垃圾填埋场深处,进入周边土壤和地下水环境[4-5],造成严重的生态和健康风险[6-7]。
根据目前国内的垃圾填埋场设计运行规范来看,部分垃圾填埋场设计运行时间可达20年以上[8-10],早期填埋的垃圾逐渐矿化[11],而新的垃圾会持续堆叠在已矿化的垃圾上。大量研究表明,矿化垃圾具有比表面积大、多孔结构稳定、有机质含量高、阳离子交换容量大等特点[12],可有效吸附并固定氨氮[13]、有机毒物[14-15]和磷酸盐[16]等,并进一步通过物理化学及生物作用,减轻垃圾渗滤液对周围环境的污染。但是,目前针对矿化垃圾吸附药物的相关报道尚不多见,对于药物随垃圾渗滤液在垃圾填埋场中的迁移过程尚未有明确的认识,矿化垃圾能否有效吸附并固定药物值得进一步探究。
作为一类广谱性抗生素,四环素因其成本低廉、毒副作用小等优点而广泛应用于人类疾病治疗和牲畜生产中。但是,由于四环素生物可利用性较低,导致其中的大量活性组分随代谢物排出体外,在环境中长时间停留且难以生物降解,已造成严重的土壤和地下水污染[17-18]。因此,本研究以四环素为典型模式药物,研究其在矿化垃圾上的吸附热力学及动力学,结合矿化垃圾的结构及组成等性质分析了吸附机理,并探究四环素初始浓度、pH及不同阳离子类型对吸附过程的影响,以明确垃圾渗滤液中的药物在矿化垃圾上的吸附特性。同时,通过土柱实验验证矿化垃圾对四环素的动态吸附能力。本研究通过研究四环素在矿化垃圾上的吸附特性,以期为控制垃圾填埋场中药物污染及环境风险提供数据支撑和理论参考。
-
矿化垃圾取自云南昆明某垃圾填埋场,呈棕褐色。将采集的矿化垃圾置于通风橱自然风干,去除石块、塑料、玻璃等杂质,过10目筛,采用干式灭菌法[19]170 ℃下真空干燥2 h,对材料进行干燥、灭菌。所得材料自然冷却后装瓶密封备用。对矿化垃圾的基本理化性质分析(表1)。采用电位法测定pH,重量法测定含水率,重铬酸钾稀释热法测定有机质含量,采用Zeta电位仪(NanoBrook90型,美国)测定矿化垃圾零点电荷。
四环素(tetracycline,TC),纯度≥98%,购自北京百灵威科技有限公司;氢氧化钠、浓盐酸、氯化钙、氯化钾、重铬酸钾均为分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
-
(1)静态吸附实验
通过一系列实验探究了矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附性能。在溶液初始浓度、pH和不同种类背景阳离子影响实验中,将100 mg矿化垃圾添加到20 mL浓度为30 mg·L−1四环素溶液中;在吸附等温线实验中,四环素溶液的初始浓度为20—60 mg·L−1、pH 6.1,封盖避光后在25 ℃、150 r·min−1下震荡48 h后,取上清液测定四环素浓度;对于动力学研究,将100 mg矿化垃圾添加到20 mL浓度为30 mg·L−1、初始pH6.1的四环素溶液中,在特定时间点取样并测定浓度。
(2)动态吸附实验
采用内径8 cm,高50 cm的PVC柱作为固定床,在上下两端设置进出水口。固定床底部放置孔径为1 mm筛板,筛板下层填充厚度2 cm石英砂,石英砂上层填入预处理的矿化垃圾30 cm,最后在固定床顶部填充3 cm石英砂。为避免实验过程中四环素发生光降解,对柱体进行锡箔纸包裹,全程避光。设置实验组和空白组,配制50 mg·L−1的四环素溶液于棕色容量瓶中,调节pH为6.1,用恒速供水的方式自上而下淋洗实验组矿化垃圾,保证流量在3—5 mL·min−1,待固定床出水速度与进水速度一致时,动态吸附达到稳定。同样条件下,用去离子水淋洗空白组,对照淋溶过程中矿化垃圾成分变化。出水稳定后,间隔取样,测定出水溶液的四环素浓度、pH、电导率以及UV254。
-
样品经0.45 μm水系膜过滤,使用紫外分光光度计(HACH,DR 5000)分别在359 nm处和254 nm处测定四环素和UV254的吸光度。pH采用玻璃电极法测量。采用电导率测量仪(DDS-307A)测量电导率。
采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(美国Nicolet 5DX)在4000—500 cm−1范围内表征矿化垃圾的红外光谱。采用X射线衍射仪(X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy,XPS)表征矿化垃圾表面的元素组成。使用多功能气体分析仪(美国TRISTAR Ⅱ 3020 M)在77 K下进行了N2吸附脱附测试,采用BET(Brunauer-Emmett-Teller)测定孔径分布。
-
采用Langmuir、Freundlich两种等温吸附模型对矿化垃圾吸附模型进行拟合。表达式如式(1)、(2)所示。
Langmuir:
Freundlich:
式中,qe为矿化垃圾平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;KF为吸附平衡参数;n为与吸附有关常数;Ce为平衡浓度,mg·L−1;qm为Langmuir饱和吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为吸附-解吸常数,L·mg−1。
采用拟一级动力学模型和拟二级动力学模型对矿化垃圾吸附四环素过程进行拟合,其表达式分别为:
拟一级动力学方程:
拟二级动力学方程:
式中,qt为矿化垃圾的吸附容量,mg·g−1;k1为拟一级速率常数,g·(mg·s)−1;t为时间,s;k2为拟二级速率常数,g·(mg·s)−1。
-
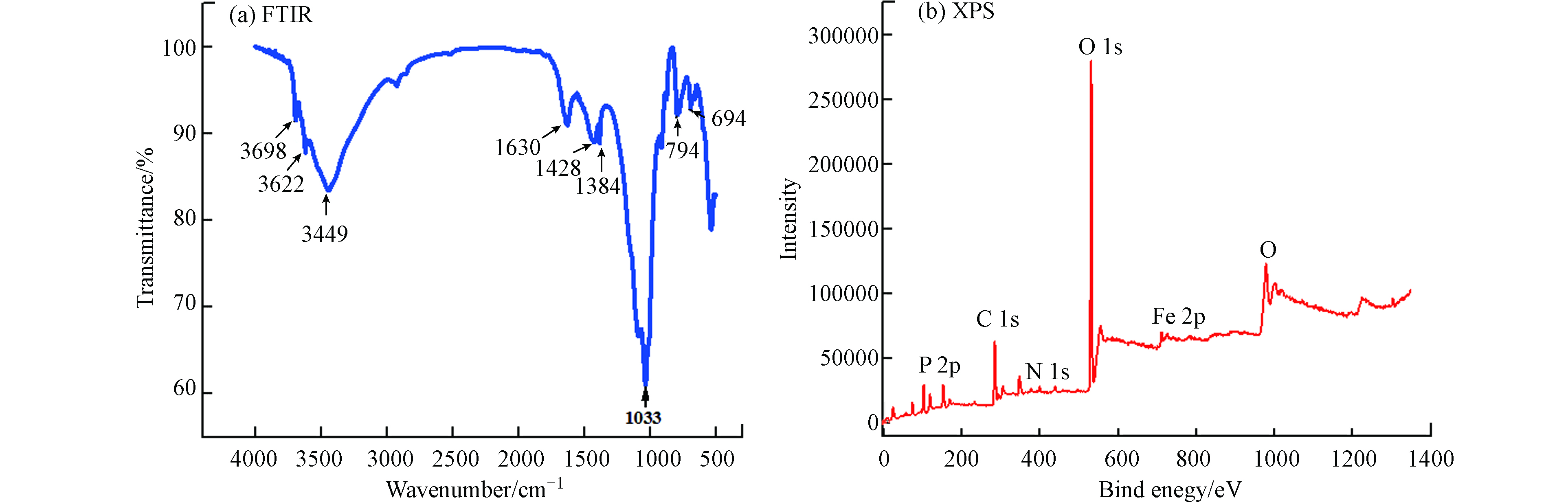
分别采用FTIR和XPS分析矿化垃圾的表面基团和主要元素组成。图1(a)为矿化垃圾的FTIR光谱。可以看出,矿化垃圾表面拥有丰富的官能团,这可能归因于矿化垃圾表面存在的腐殖质[16,20],主要特征吸收峰为3449 cm−1、3622 cm−1、3698 cm−1处的含氢键羟基(—OH)的伸缩振动,1633 cm−1处可能是烯烃的C=C骨架伸缩振动和酰胺的C=O伸缩振动峰,1428 cm−1处的峰归因于—O—CH3的变形振动,1033 cm−1处主要为多糖或糖类的C—O伸缩振动峰,794 cm−1附近的醇、酚类O—H和694 cm−1处=C—H芳环面外弯曲振动。图1(b)为矿化垃圾的XPS全谱图,可以看出矿化垃圾表面主要元素分别为C、O、Fe、N、P。
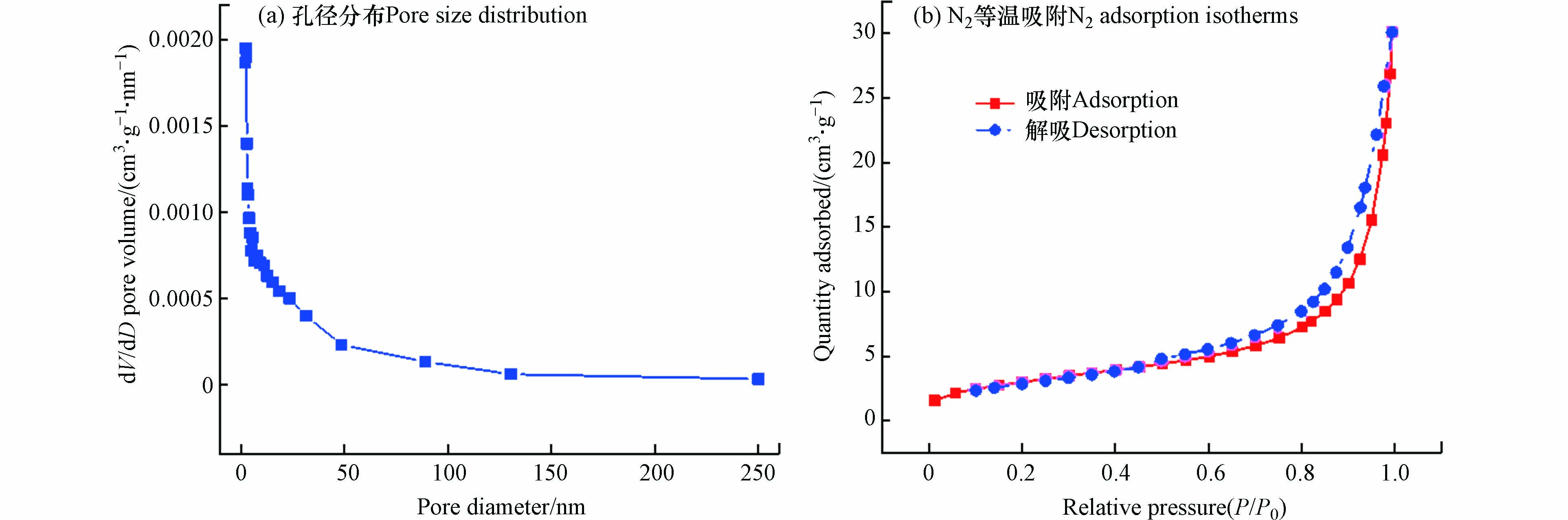
图2(a)为矿化垃圾的孔径分布。如图2所示,矿化垃圾孔径分布在2—250 nm,多数孔径小于50 nm,为介孔材料。图2(b)为矿化垃圾的吸附-解吸等温线。由图可知,矿化垃圾的物理吸附测试属于Ⅱ型吸附-解吸等温线,在高相对压力(P/P0)处未达到吸附极值,表现出无限制的单层-多层吸附特征[21],且吸附与解吸线不能完全重合,存在H3型滞后环,表明矿化垃圾的孔隙结构为片状颗粒堆积,具有层状结构,为介孔材料[22],与孔径分布表征结果一致。
-
本研究采用Langmuir和Freundlich两种等温吸附模型考察矿化垃圾吸附四环素机理,拟合模型参数如表2所示,矿化垃圾吸附四环素的Langmuir、Freundlich等温吸附拟合曲线如图3所示。由表2可知,Langmuir和Freundlich等温吸附模型的相关系数分别为0.968和0.979,拟合效果较好。其中,Langmuir吸附模型最大拟合吸附量为15.684 mg·g−1,与矿化垃圾的实际吸附容量相差较大,证明矿化垃圾吸附四环素并不是表面单分子吸附。Freundlich模型更高的拟合程度表明矿化垃圾吸附四环素的吸附过程更可能为非均质吸附,且Freundlich模型中1/n为0.615(<1),说明矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附性能良好,反应较容易进行。
-
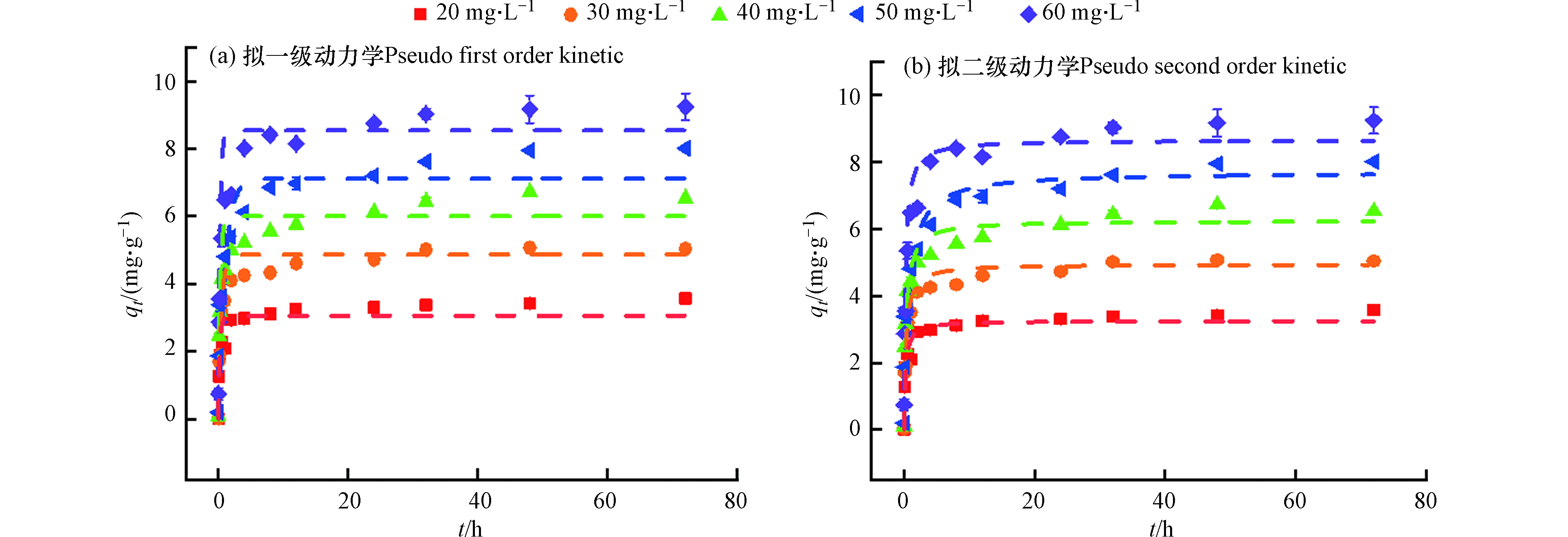
采用拟一级和拟二级动力学模型对矿化垃圾吸附四环素的吸附过程进行拟合分析,结果见图4和表3。由表3可知,矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附速率用拟一级、拟二级动力学均能较好的拟合,其中拟二级动力学拟合下的矿化垃圾吸附量均高于拟一级,表明阳离子交换、络合和沉淀等化学吸附过程可能是其主要的吸附机制。
-
(1)初始浓度
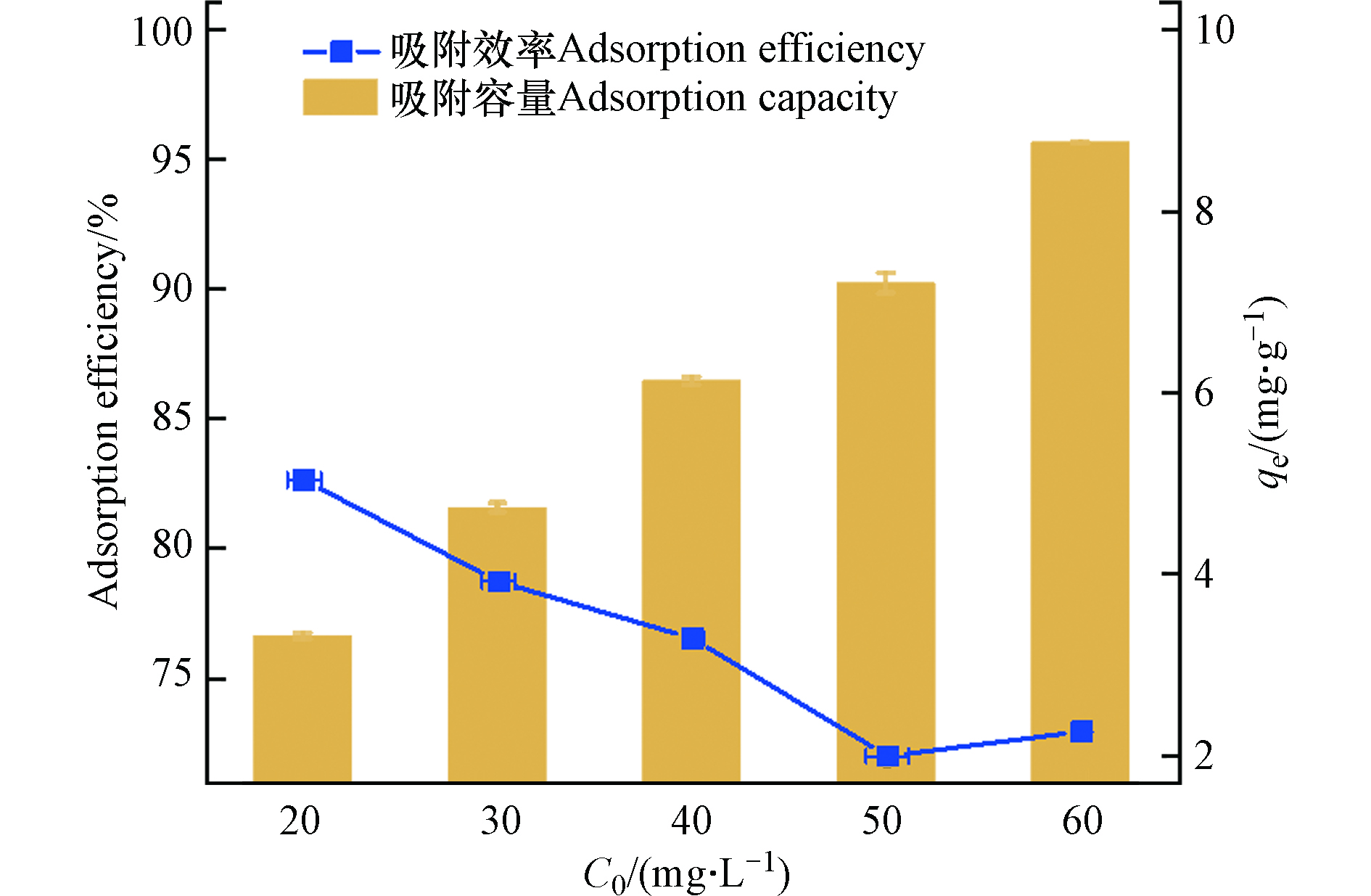
初始矿化垃圾浓度是评价矿化垃圾应对负荷冲击能力的重要指标。为了解溶液初始浓度对矿化垃圾吸附四环素的影响,分别设置了浓度为20、30、40、50、60 mg·L−1的梯度实验。由图5可知,随着初始浓度的增加,矿化垃圾的吸附容量呈线性增大(斜率为0.149,R2为0.998),这是因为初始浓度较大时,矿化垃圾与反应溶液固液微界面处四环素浓度也会随之升高,促进矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附。相对的,随着初始浓度的增加,矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附效率逐渐降低,这是因为随着四环素浓度的增加,矿化垃圾吸附量的提升较小(如初始浓度20 mg·L−1提升到50 mg·L−1,提升倍数为2.5,而相对应的吸附量从3.33 mg·g−1提升至7.14 mg·g−1,提升倍数为2.14),因此去除效率降低。由此可见,四环素初始浓度的增加对矿化垃圾的吸附能力影响较大。
(2)pH
不同溶液pH可改变吸附剂表面特性及污染物的存在形态,是直接影响吸附效果的重要参数。通过设置不同梯度pH,考察其对矿化垃圾吸附四环素的影响。如图6所示,矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附效率和吸附容量在整体趋势上是随pH升高而降低,溶液的初始pH对矿化垃圾吸附四环素的影响十分明显。其中,在初始pH为3时,矿化垃圾对四环素吸附效果最优,其吸附效率和吸附容量分别为82.15%和4.93 mg·g−1;在初始pH为11时,矿化垃圾对四环素吸附效果最差,其吸附效率和吸附容量分别为56.01%和3.36 mg·g−1。这是因为四环素是具有多个可电离的官能团的两性分子,其pKa分别为3.3、7.68、9.68[23-24],它在溶液中的存在形态取决于pH和质子化-去质子化反应,从而影响矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附去除。当pH<3.3时,四环素带正电荷,为单阳离子TCH3+,此时矿化垃圾(pHPZC=7.89)表面正电荷随pH提高而减少,因而当溶液pH从1.2上升至3.3时,吸附效率及吸附容量相应升高;随着pH的增加(3.3—11),四环素持续发生去质子化作用,相继转变为TCH2±(3.3<pH<7.68)、TCH−(7.68<pH<9.68)及TC2-(pH>9.68),与此同时,矿化垃圾表面负电荷也随pH提高持续积累,二者间的静电斥力进一步增强,导致吸附效率和吸附容量降低。
(3)不同阳离子种类
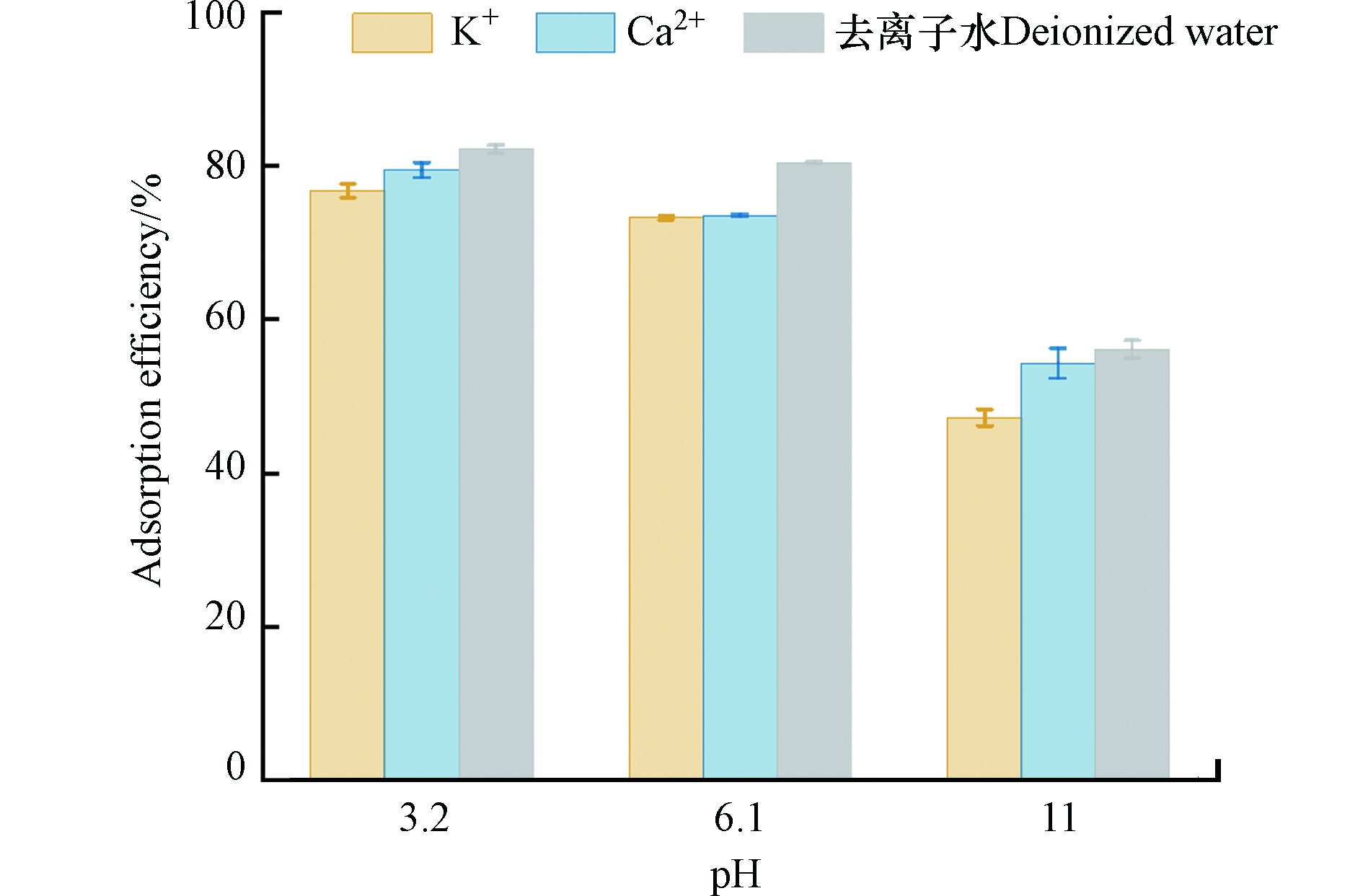
除pH外,不同阳离子类型是影响矿化垃圾吸附四环素的又一重要因素,然而关于金属阳离子对于四环素吸附过程影响的研究结果各异。Plis等[25]在研究K+和Ca2+对土壤系统吸附四环素的影响时发现,K+和Ca2+均可抑制吸附过程,其中K+的抑制作用更加明显,而Zhao等[26]在研究高岭土对四环素的吸附时发现Ca2+对吸附过程的抑制作用强于K+。因此,为明确K+、Ca2+对矿化垃圾吸附四环素的影响,本研究以0.1 mol·L−1 KCl和CaCl2为背景溶液并设置不同梯度pH进行探究。如图7所示,不同pH下K+和Ca2+存在均会抑制矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附效率,且含K+的背景溶液对矿化垃圾吸附四环素的抑制作用强于含Ca2+的背景溶液,这可能是由于K原子半径小于Ca,其反应所需活化能较低,使得易于占据矿化垃圾的吸附位点。同时,FTIR分析结果表明,矿化垃圾表面可能存在大量的腐殖质,而四环素可与金属阳离子及腐殖质形成配合物,附着在吸附剂上,因此更高价态的Ca2+与四环素和腐殖质之间的结合能力更强,减轻了对矿化垃圾吸附四环素的抑制作用。
-
上述研究结果初步明确了四环素在矿化垃圾表面静态吸附的过程,但静态吸附仅可有限地判断矿化垃圾对四环素的饱和吸附量,而实际过程中,垃圾渗滤液通常以淋洗的方式通过垃圾床层,矿化垃圾能否有效吸附并固定四环素还需要进一步探究。土柱实验可模拟目标溶质在土壤和地下水中的迁移过程,进而应用于研究相同水文地质条件下的土壤及地下水污染问题,是研究污染物在土壤和地下水中迁移规律的重要手段[27]。随时间推移,土柱实验已广泛应用于各种污染物在不同介质中的迁移特性及可能造成的污染风险[28-29]。因此,本研究期望借鉴土柱实验方法,以矿化垃圾为填充介质构建矿化垃圾固定床,模拟渗滤液中四环素在矿化垃圾床体上的动态吸附过程,探究矿化垃圾对四环素的载荷量及四环素在固定床内部的输移规律。
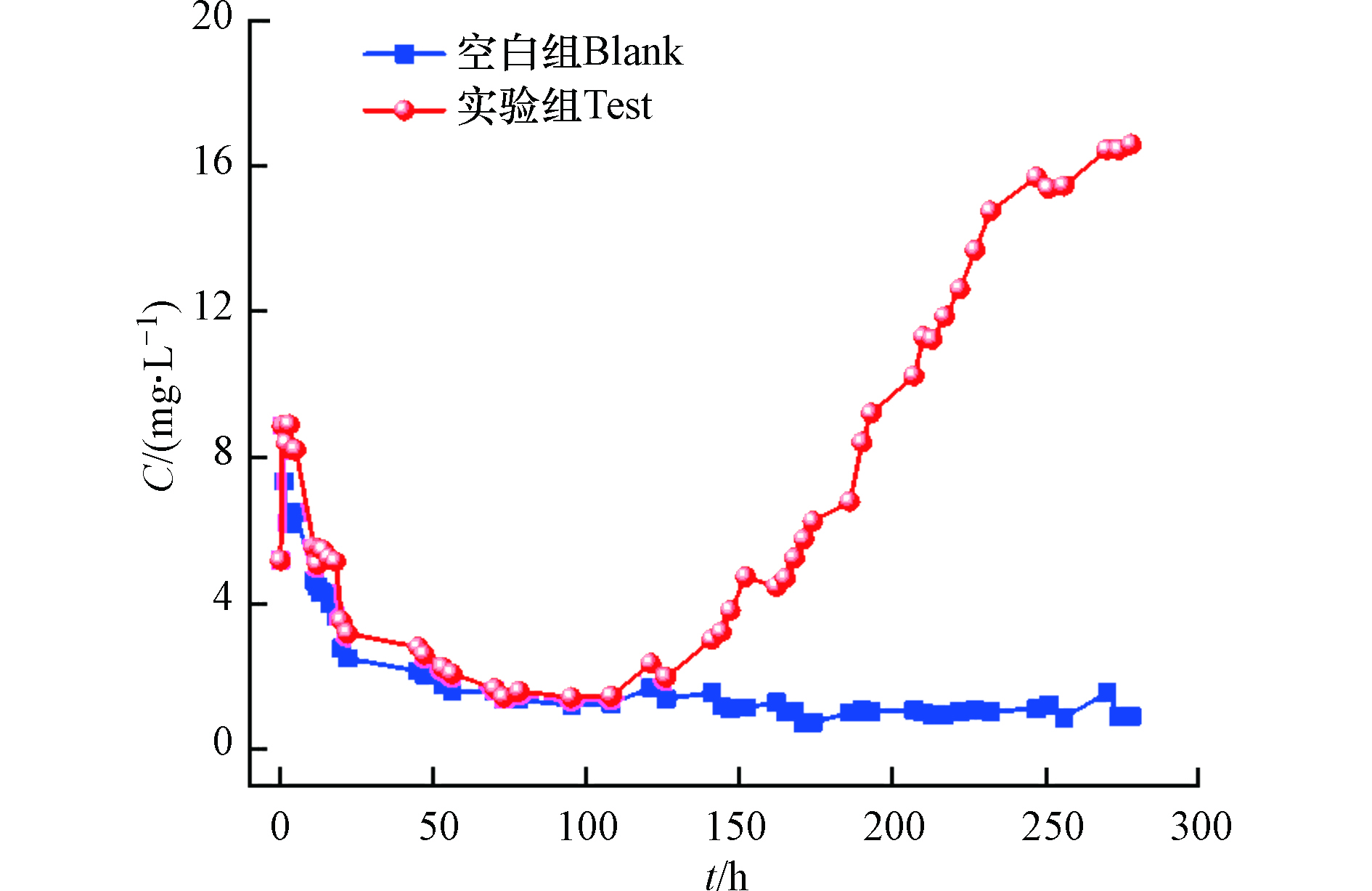
分别设置了以去离子水和四环素溶液作为淋洗液,通过其出水差异明确矿化垃圾对四环素的动态吸附性能。由图8可知,空白组和实验组在淋洗50 h内,出水溶液四环素浓度范围为2—10 mg·L−1,这表明矿化垃圾上存在部分四环素的沉积,随着去离子水的冲洗而逐渐被洗脱。在前100 h,样品柱中实际出水溶液中的四环素含量几乎可以忽略不计。以进料浓度的5%取为穿透点时,得出矿化垃圾固定床的穿透时间为147 h,此时固定床中四环素总量为2.21 g,相当于每克矿化垃圾吸附3.9 mg的四环素,且吸附未达到饱和。同时,随着出水四环素的浓度达到穿透点,固定床的穿透曲线开始呈现近似斜率为0.12的线性增长,出水溶液中的四环素浓度快速上升。这说明矿化垃圾柱对四环素的吸附主要是吸附在前期淋洗过程发生,随着淋洗时间的推移吸附能力下降或解吸,导致其吸附能力远低于前期。
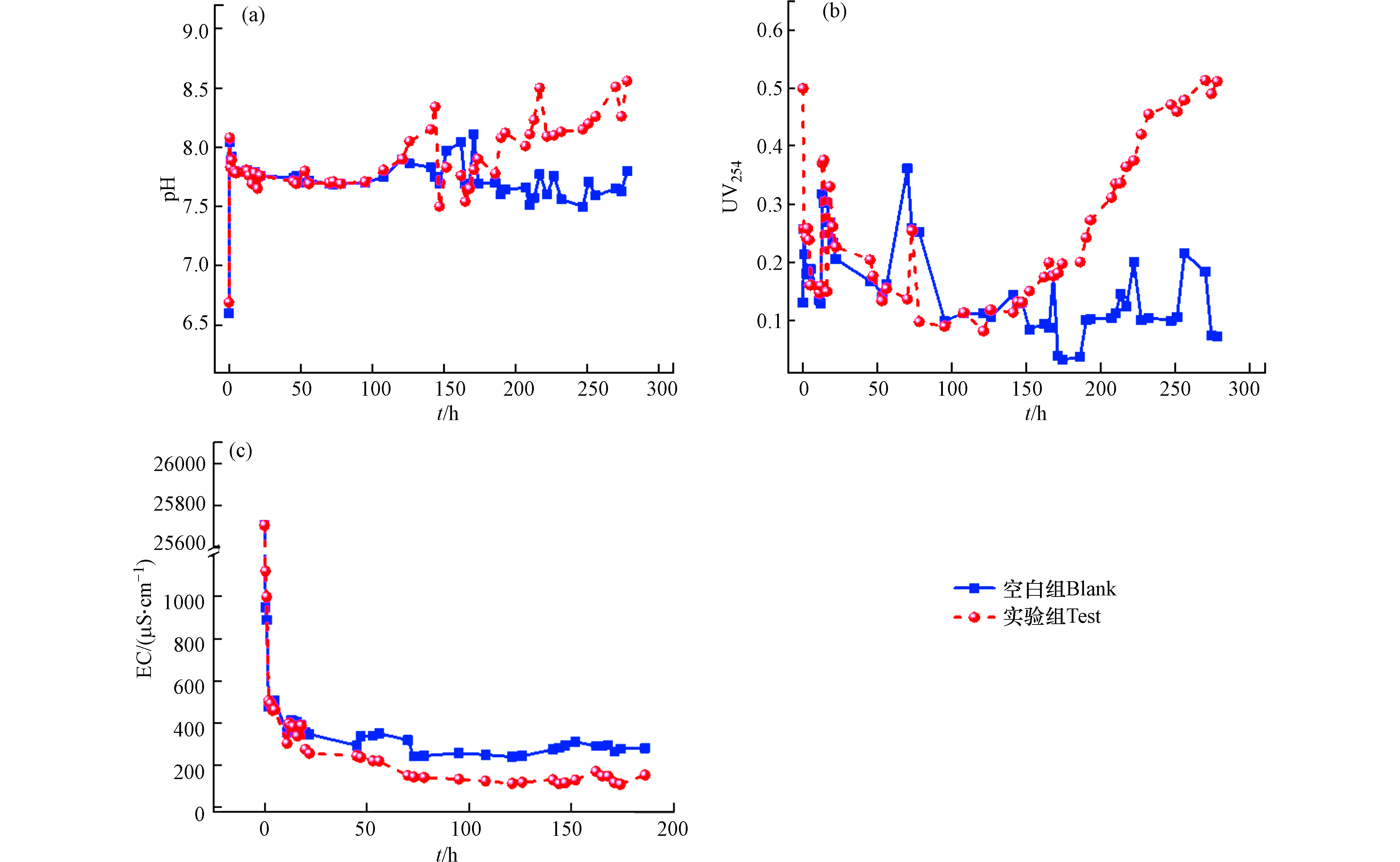
为进一步探究四环素溶液淋洗固定床时,其传质过程所导致的矿化垃圾物理化学变化,监测了出水溶液的电导率、UV254和pH值。如图9所示,空白组在淋溶过程中出水溶液pH迅速由弱酸性变为中性及弱碱性,与矿化垃圾本底pH相一致,实验组出水溶液pH波动上升至碱性,在穿透点后出水pH继续上升,高于空白组。同时,空白组和实验组穿透点后出水UV254浓度变化趋势与pH相一致,均随着出水四环素的浓度升高而升高。一般来说,四环素可与腐殖酸通过H键及离子桥接进行络合[30-32],因而当矿化垃圾吸附位点减少时,大量四环素与游离的腐殖酸络合,导致出水四环素浓度及UV254同时升高,而弱酸态的腐殖酸与强碱阳离子结合会表现出碱性,致使出水pH升高。此外,空白组和实验组出水电导率在淋洗初始阶段迅速降低,随后趋于平稳,且实验组出水电导率低于空白组。这说明淋洗开始时,矿化垃圾表面大量的金属阳离子溶解并随水流出,而实验组较低的出水电导率可能归结于阳离子架桥作用的影响,使得矿化垃圾固体颗粒上未被洗脱的阳离子与四环素结合并固定。
-
本研究考察了矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附行为,主要的出以下结论:
(1)矿化垃圾表面存在O—H、C=C、C—H、C=O、—O—CH3、=C—H等丰富的官能团;粒径分析表明,矿化垃圾表面孔径主要为50 nm介孔;N2吸附-解吸实验表明,矿化垃圾的物理吸附测试属于Ⅱ型吸附-解吸等温线,存在H3型滞后环。
(2)吸附等温和动力学拟合分析结果得出,矿化垃圾对四环素的吸附过程符合Freundlich等温模型和拟二级动力学模型,吸附类型为多层吸附,吸附速率受化学吸附控制。
(3)不同影响因素实验表明,初始浓度、pH以及阳离子类型均会显著影响矿化垃圾吸附四环素的过程,浓度越高,吸附量越高,吸附效率越低;pH越高,吸附效率越低;与Ca2+相比,K+对吸附过程的抑制更加明显。
(4)动态吸附实验表明,矿化垃圾对四环素的承载量较高,以2.5 mg·L−1作为穿透点时,矿化垃圾吸附四环素的容量为3.9 mg·g−1,动态吸附性能良好。
四环素在矿化垃圾上的吸附特性及动态过程
Research on the adsorption characteristics and dynamic process of tetracycline on aged refuse
-
摘要: 为明确垃圾渗滤液中四环素在矿化垃圾上的吸附规律,通过傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)、孔径测试及N2吸附解吸测试表征了矿化垃圾的结构特点和化学性质,探讨了矿化垃圾对四环素的静态吸附规律及初始浓度、pH和不同阳离子类型等环境因素对其吸附效率的影响,并进一步通过动态吸附实验模拟了实际动态条件下的吸附过程。结果表明,矿化垃圾表面含有大量的官能团及良好的孔隙结构;矿化垃圾对四环素具有良好的吸附效果,吸附过程符合Freundlich等温吸附模型和拟二级动力学模型;初始浓度和pH升高会降低吸附效率,K+对吸附性能的抑制高于Ca2+离子;动态吸附实验表明矿化垃圾对四环素的承载量为3.9 mg·g-1,动态吸附性能良好。Abstract: The present study aimed to clarify the adsorption pattern of tetracycline in leachate on aged refuse. The structural characteristics and chemical properties of aged refuse were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), pore size test and N2 adsorption/desorption test. The static adsorption pattern of tetracycline on aged refuse was explored. Moreover, the effects of environmental factors such as initial concentration, pH and different types of cations on its adsorption efficiency were reported. The adsorption process under actual dynamic conditions was further studied by a column adsorption experiment. The results showed that the aged refuse contained numerous functional groups and well-developed pore structures on the surface. A good adsorption efficiency was observed for the adsorption of tetracycline by aged refuse, and the adsorption process conformed to Freundlich’s isothermal adsorption model and pseudo second-order kinetic model. A decrease of the adsorption efficiency was observed when the initial concentration and pH increased, while the inhibition of K+ on the adsorption was higher than that of Ca2+. Finally, it was found from the dynamic adsorption test that the dynamic adsorption performance of aged refuse was good with a bearing capacity of 3.9 mg·g−1.
-
Key words:
- aged refuse /
- tetracycline /
- static adsorption /
- dynamic adsorption
-

-
表 1 矿化垃圾理化性质
Table 1. Physicochemical properties of aged refuse
材料
Material粒径/目
Particle sizepH 有机质/%
Organic matter含水率/%
Water contentpHPZC 矿化垃圾 <10 7.72 3.076 0.2 7.89 表 2 四环素的吸附等温线相关参数
Table 2. Fitting parameters for Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms of tetracycline adsorbed by aged refuse
吸附剂Sorbent Langmuir Freundlich qm/(mg·g−1) KL R2 1/n KF R2 矿化垃圾 15.684 0.069 0.968 0.615 1.517 0.979 表 3 矿化垃圾吸附不同浓度四环素的拟动力学参数
Table 3. The fitting parameters for pseudo kinetics of tetracycline adsorbed by aged refuse under different concentrations
初始浓度/(mg·L−1)
Initial concentration拟一级 Pseudo-first-order 拟二级 Pseudo-second-order k1 qe/(mg·L−1) R2 k2 qe/(mg·L−1) R2 20 4.162 3.052 0.981 1.387 3.253 0.992 30 2.159 4.872 0.952 0.711 4.948 0.977 40 3.478 6.003 0.805 0.510 6.248 0.900 50 0.945 7.123 0.872 0.187 7.701 0.965 60 3.891 8.544 0.958 0.553 8.658 0.993 -
[1] SREEDHAR A, APTE M, MALLYA R. Pharmaceutical waste management [J]. International Journal of Pharmaceuticals, 2018, 52(1): 82-86. [2] LAN J, HOU H Y, MENG K, et al. The recovery of expired ferrous gluconate and spent Li foils into high performance straw-bundle-like α-LiFeO2/C cathode [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 390: 138827. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138827 [3] YU X, SUI Q, LYU S G, et al. Rainfall influences occurrence of pharmaceutical and personal care products in landfill leachates: Evidence from seasonal variations and extreme rainfall episodes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(8): 4822-4830. [4] YU X, SUI Q, LYU S G, et al. Do high levels of PPCPs in landfill leachates influence the water environment in the vicinity of landfills?A case study of the largest landfill in China [J]. Environment International, 2020, 135: 105404. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105404 [5] WU D Q, SUI Q, YU X, et al. Identification of indicator PPCPs in landfill leachates and livestock wastewaters using multi-residue analysis of 70 PPCPs: Analytical method development and application in Yangtze River Delta, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 753: 141653. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141653 [6] LI L, ZHAO X L, LIU D, et al. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of PPCPs in typical inflow rivers of Taihu Lake, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 285: 112176. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112176 [7] LIU N, JIN X W, FENG C L, et al. Ecological risk assessment of fifty pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Chinese surface waters: A proposed multiple-level system [J]. Environment International, 2020, 136: 105454. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105454 [8] 穷达卓玛, 汪晶, 周文武, 等. 拉萨垃圾填埋场渗滤液处理站周边土壤重金属含量分析及评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(5): 1404-1409. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019081401 QIONG D, WANG J, ZHOU W W, et al. Analysis and evaluation of heavy metal content in soil around leachate treatment station of Lhasa landfill site [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(5): 1404-1409(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019081401
[9] 周文武, 陈冠益, 穷达卓玛, 等. 拉萨市垃圾填埋场地下水水质的居民健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(6): 1513-1522. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019041101 ZHOU W W, CHEN G Y, QIONG D, et al. Health risk assessment of groundwater quality in Lhasa landfill [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(6): 1513-1522(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019041101
[10] 刘洪华, 朱水, 董杰, 等. 某生活垃圾处理园区周边土壤重金属分布特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2388-2398. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020041802 LIU H H, ZHU S, DONG J, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around an integrated waste management facility [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2388-2398(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020041802
[11] 赵海涛, 刘平, 王小治, 等. 矿化垃圾基本理化性状剖面变化特征研究 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2010, 4(7): 1624-1628. ZHAO H T, LIU P, WANG X Z, et al. Profile characteristics in physical and chemical properties of aged-refuse [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2010, 4(7): 1624-1628(in Chinese).
[12] 谢明德, 唐一鸣, 冯梅, 等. 利用矿化垃圾层预防和控制渗滤液导排系统堵塞 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(2): 614-623. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020080302 XIE M D, TANG Y M, FENG M, et al. Prevent and control the clogging of leachate drainage system by using the aged refuse layer [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(2): 614-623(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020080302
[13] 聂发辉, 刘荣荣, 李文婷, 等. 改性矿化垃圾对渗滤液生化出水中COD和氨氮的吸附 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(6): 2786-2792. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501115 NIE F H, LIU R R, LI W T, et al. Adsorption of COD and ammonia nitrogen in leachate from biochemical process on modified aged refuse adsorbent [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(6): 2786-2792(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501115
[14] 陈炜鸣, 辜哲培, 何晨, 等. 老龄垃圾渗滤液中溶解性有机物在SAARB和MBR处理过程的转化特征 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(11): 4637-4647. CHEN W M, GU Z P, HE C, et al. Molecular insights into the removal characteristics of dissolved organic matters from mature landfill leachate by SAARB and MBR processes [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(11): 4637-4647(in Chinese).
[15] 柴晓利, 郭强, 李玉亮, 等. 酚类化合物在矿化垃圾中吸附性能的研究 [J]. 环境化学, 2007, 26(2): 164-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.02.010 CHAI X L, GUO Q, LI Y L, et al. Adsorption characteristics of phenolic compound by aged-refuse [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2007, 26(2): 164-167(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.02.010
[16] CHEN K N, ZHAO K Q, ZHANG H H, et al. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solutions using a synthesized adsorbent prepared from mineralized refuse and sewage sludge [J]. Environmental Technology, 2013, 34(9/10/11/12): 1489-1496. [17] 郭志伟, 赵宝龙, 郑志宏, 等. 碳化改性硅藻土对四环素的吸附研究[J/OL]. [2021-12-24]. 环境工程. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2097.X.20211022.1820.002.html. GUO Z W, ZHAO B L, ZHENG Z H, et al. Preparation of the modified diatomite via carbonization and its adsorption performance for tetracycline[J/OL]. [2021-12-24]. Environmental Engineering. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2097.X.20211022.1820.002.html(in Chinese).
[18] 陈瑞萍, 张丽, 于洁, 等. 活性污泥对四环素的吸附性能研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(1): 156-162. CHEN R P, ZHANG L, YU J, et al. Study on the sorption behavior of tetracycline onto activated sludge [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(1): 156-162(in Chinese).
[19] 刘萍, 夏江宝. 滨海盐碱地根际溶磷细菌磷素转化特征 [J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11): 4531-4540. LIU P, XIA J B. Properties of rhizosphere phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in coastal saline and alkaline land [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 4531-4540(in Chinese).
[20] 王芳芳. 矿化垃圾吸附—还原铬(Ⅵ)的机理研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2012, 85. WANG F F. Adsorption coupled reduction mechanism research on Cr(Ⅵ) by using aged refuse[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao Tehcnology University, 2012, 85(in Chinese).
[21] 朱丹琛, 李名洁, 陈彰旭, 等. 水热法合成二氧化锰及其对染料的脱色性能研究 [J]. 无机盐工业, 2021, 53(11): 60-65. ZHU D C, LI M J, CHEN Z X, et al. Study on hydrothermal synthesis of MnO2 and its decolorization performance on dyes [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2021, 53(11): 60-65(in Chinese).
[22] 方俊华, 张啸, 荆慧娟. 磁化改性污泥基生物炭对水中磷的吸附 [J]. 水处理技术, 2021(12): 37-41. FANG J H, ZHANG X, JING H J. Adsorption of phosphorus in water by magnetized modified sludge-based biochar [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2021(12): 37-41(in Chinese).
[23] 唐钰, 段艳平, 涂耀仁, 等. 重金属对药物和个人护理品在土壤/沉积物中吸附的影响机制: 现状与展望 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(1): 164-173. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019091902 TANG Y, DUAN Y P, TU Y R, et al. The effects mechanism of heavy metals on the adsorption of PPCPs in soils/sediments: Status and prospects [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(1): 164-173(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019091902
[24] 范世锁, 刘文浦, 王锦涛, 等. 茶渣生物炭制备及其对溶液中四环素的去除特性 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1308-1318. FAN S S, LIU W P, WANG J T, et al. Preparation of tea waste biochar and its application in tetracycline removal from aqueous solution [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1308-1318(in Chinese).
[25] PILS J R V, LAIRD D A. Sorption of tetracycline and chlortetracycline on K- and Ca-saturated soil clays, humic substances, and clay-humic complexes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(6): 1928-1933. [26] ZHAO Y P, GENG J J, WANG X R, et al. Tetracycline adsorption on kaolinite: pH, metal cations and humic acid effects [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2011, 20(5): 1141-1147. doi: 10.1007/s10646-011-0665-6 [27] 聂静, 曾强, 光布加甫·珊珠, 等. 土柱淋滤实验应用进展与展望[C]. 中国环境科学学会学术年会, 2014: 471-475. NIE J, ZENG Q, GUANGBUJIAFU S Z, et al. Environment science and resources utilization[A]. Annual meeting of Chinese society of Environmental Sciences, 2014: 471-475(in Chinese).
[28] SORWAT J, MELLAGE A, MAISCH M, et al. Chromium (VI) removal kinetics by magnetite-coated sand: Small-scale flow-through column experiments [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 415: 125648. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125648 [29] SUI Q, ZHAO W T, CAO X Q, et al. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the leachates from a typical landfill reservoir of municipal solid waste in Shanghai, China: Occurrence and removal by a full-scale membrane bioreactor [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 323: 99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.047 [30] CHRISTL I, RUIZ M, SCHMIDT J R, et al. Clarithromycin and tetracycline binding to soil humic acid in the absence and presence of calcium [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(18): 9933-9942. [31] GU C, KARTHIKEYAN K G, SIBLEY S D, et al. Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(8): 1494-1501. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.028 [32] ZHAO Y P, GENG J J, WANG X R, et al. Adsorption of tetracycline onto goethite in the presence of metal cations and humic substances [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 361(1): 247-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.05.051 -



 下载:
下载: