-
四氯乙烯(PCE)被广泛用作为干洗剂、杀虫剂、冰箱制冷剂等,泄露后逐渐下渗至含水层,其用量大、污染范围广,因此成为常见的地下水污染物[1-2]。此外,四氯乙烯水溶性低,疏水性强,往往以不连续的残余饱和相形式存在于介质孔隙中,不易随水流动,同时不断向地下水释放污染[3-4]。传统的抽取-处理方法很难将其去除,且费用较高[5]。表面活性剂强化含水层修复(SEAR)技术是对传统抽取-处理方法的改进[6-7],表面活性剂能够显著提升重质非水相污染物(DNAPLs)在水中的溶解度并增强其在多孔介质中的迁移能力[8-9],该方法的处理效率较传统抽取-处理的技术手段有大幅度提升。常用的表面活性剂存在增溶能力有限[10-11]、不耐受低温及电解质[7]、吸附损失大[12]及生产成本高等不足。另外,部分表面活性剂不易生物降解[13-14],可能对含水层产生二次污染。
近年来,烷基糖苷(APG)作为新一代环境友好绿色表面活性剂受到广泛关注[15],它具有表面活性优良、复配性能佳、耐强酸强碱及抗盐性强等诸多优点, 适合地下水低温、含盐的环境;其具有良好的生物降解性[16],且最终降解产物为二氧化碳、水和无机物等[17],不会给地下水引入新的污染。目前已经工业化生产并且价格低廉。相关研究[18-19]利用其对苯系物进行增溶,充分证明了其较强的增溶能力,优于Tween80、LAS等传统表面活性剂。单一表面活性剂对污染物的增溶能力有限,将表面活性剂与其他增溶材料或短链醇复配,能够显著提高污染物的增溶效果[20-22]。常见的增溶材料(如β-环糊精)[23-26]及短链醇[27-28]等都具有良好的协同增溶作用。
本研究选择四氯乙烯作为污染物,选用月桂基烷基糖苷(APG1214)表面活性剂作为增溶体系的主体,并用β-环糊精和短链醇与烷基糖苷进行复配以增强对PCE的增溶能力。测定了APG1214的临界胶束浓度及初级生物降解度,主要研究了单一APG1214溶液及其与β-环糊精、异丙醇的复配体系对PCE的增溶性能;溶液浓度、环境温度及无机盐离子浓度对PCE增溶效果的影响,考察复配体系相比于单一体系的优势及对于地下环境的适应能力,并确定最佳复配组合。研究作为SEAR技术中表面活性剂增溶试剂的实验室筛选阶段,可为后续污染场地的修复提供一定的参考依据。
-
实验用材料为月桂基烷基糖苷(APG1214,50%水溶液,山东优索化工科技有限公司),β-环糊精、异丙醇(国药集团化学试剂有限公司),吐温80(天津市光复精细化工研究所),四氯乙烯(麦克林),乙腈(赛默飞世尔科技),无机盐包括无水氯化钙、氯化钠、氯化镁、氯化钾、无水碳酸氢钠、碳酸钠和无水硫酸钠(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)。
实验中测定表面张力用QBZY-1型表面张力仪(上海方瑞仪器有限公司),增溶四氯乙烯时用SHZ-B型恒温振荡培养箱(上海博讯医疗生物仪器公司),离心所用仪器为SF-TGL-16M型高速离心机(上海菲恰尔分析仪器有限公司),测定四氯乙烯浓度用Agilent1260型高效液相色谱仪(安捷伦科技有限公司)。
-
配制浓度由1 mg·L−1至1000 mg·L−1 不同浓度的APG1214和Tween80溶液,使用全自动表面张力仪在室温下测定不同浓度 APG1214溶液和Tween80溶液的表面张力,每个浓度平行测定3次,并作出表面张力与浓度对数关系曲线图。
-
根据标准GB∕T 15818—2018 《表面活性剂生物降解度试验方法》[29],以烷基糖苷试样经培养驯化的活性污泥做降解生物源,加入试验份中进行振荡培养,测定培养周期中烷基糖苷的减少量,得到试样规定时间的生物降解度。烷基糖苷浓度的测定方法参照上述标准的附录部分。根据要求,最终降解结果为第7天(144—168 h)的降解度(%)。
-
配制10 mL APG1214浓度为10000 mg·L−1、β-环糊精浓度分别为250、625、1250、1875、2500、3750、5000 mg·L−1的溶液置于20 mL玻璃瓶中,分别加入0.25 mL PCE,密封。放于恒温振荡培养箱中。在25 ℃、150 r·min−1条件下振荡48 h,取出后将液体置于离心机中以5000 r·min−1的转速离心20 min,取上清液测定PCE浓度。根据测定结果选择PCE浓度最高的溶液中β-环糊精的浓度作为Aβ复配体系的β-环糊精浓度。在Aβ复配体系基础上,加入异丙醇共同配制10 mL溶液,使异丙醇体积分数分别为2.5%、5.0%、7.5%、10.0%和12.5%,加入0.25 mL PCE,密封。在相同条件下增溶及离心,取上清液测定PCE浓度。根据测定结果选择PCE浓度最高的溶液中异丙醇的浓度作为AβI复配体系的异丙醇浓度。测定PCE的方法为:用Agilent1260型高效液相色谱仪,选择乙腈及超纯水作为流动相,调整流动相比例为9∶1(乙腈∶水),设定流速为1 mL·min−1,进样量为10 μL,在紫外光波长为214 nm的条件下进行测量,PCE的出峰时间约为2.6 min。
-
分别配制10 mL浓度为2000、4000、6000、8000、10000 mg·L−1的APG1214水溶液及同浓度的Aβ复配溶液、AβI复配溶液置于20 mL玻璃瓶中,加入0.25 mL PCE,密封。放于恒温振荡培养箱中。在相同条件下增溶及离心,取上清液测定PCE浓度。
-
分别配制10000 mg·L−1APG1214、Aβ复配及AβI复配体系,分别加入0.25 mL PCE后置于恒温振荡培养箱中,调节培养箱温度分别为10、15、20、25 ℃后进行增溶实验,实验方法同1.2.4节,并测定增溶完成后的上清液PCE浓度。
-
配制10 mL浓度为10000 mg·L−1的APG1214水溶液置于20 mL玻璃瓶中,分别加入NaCl、CaCl2、KCl、MgCl2、NaCO3、NaHCO3和NaSO4固体,使每种无机盐浓度分别为10、20、30、40、50 mmol·L−1。然后再分别配制相同浓度无机盐和同浓度的Aβ复配溶液及AβI复配溶液置于20 mL玻璃瓶中,加入0.25 mL PCE,密封。在相同条件下增溶及离心,取上清液测定PCE浓度。
-
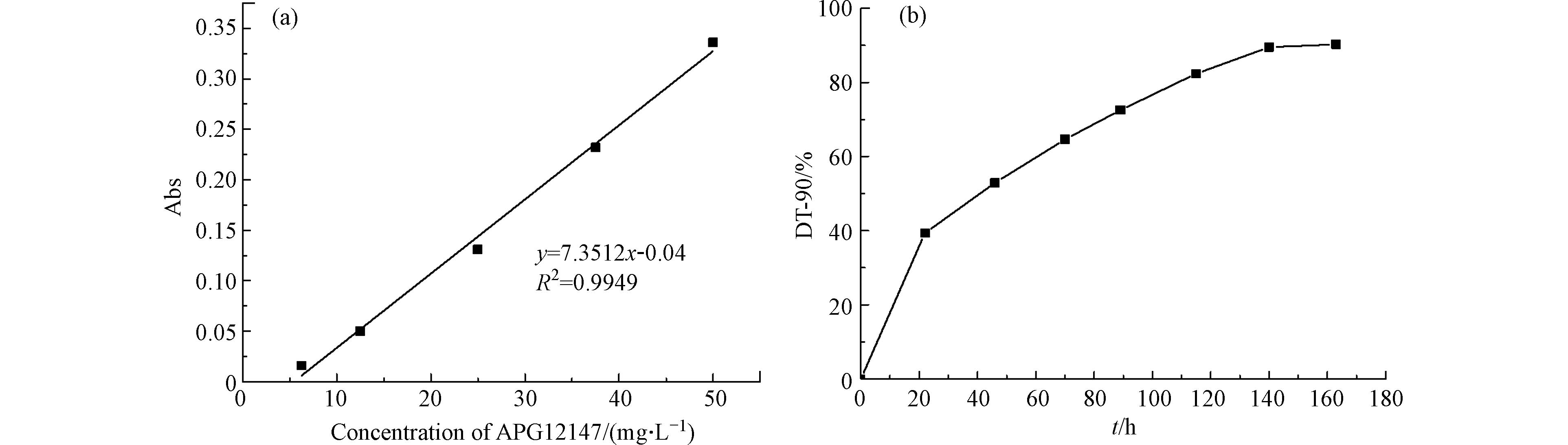
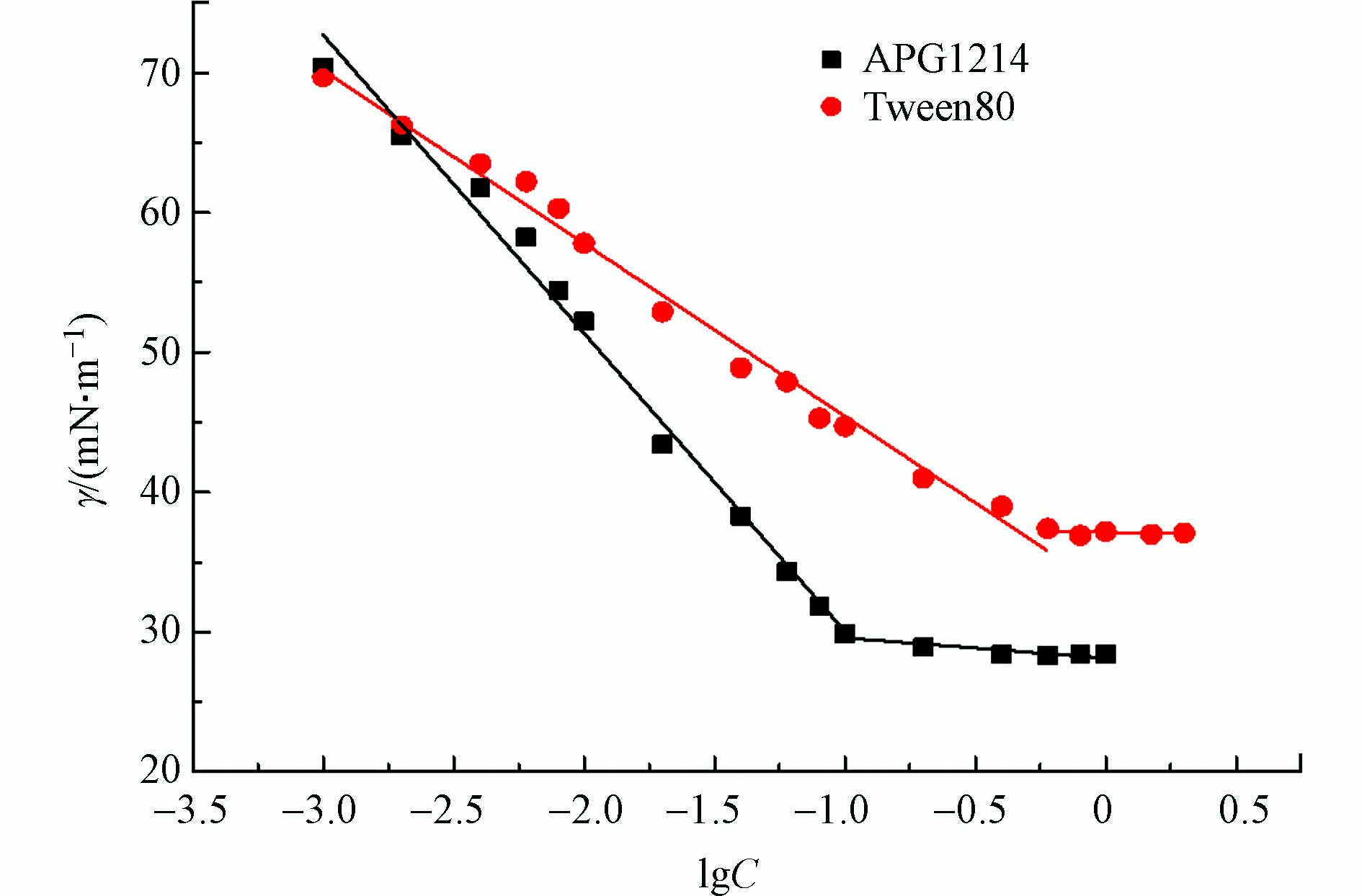
临界胶束浓度(CMC值)是指表面活性剂分子形成胶束的最小浓度,δ(CMC)为该浓度下的表面张力值,对应于lgC-γ曲线中的折点[30]。表面活性剂的CMC值越低,表面活性越高[31]。由图1可知,随着浓度的增加,APG1214溶液表面张力逐渐下降. 当APG1214浓度达到100 mg·L−1时,表面张力逐渐趋于稳定,APG1214在水溶液表面达到吸附饱和,开始形成胶束。由曲线可知,APG1214溶液的CMC值约为100 mg·L−1,δ(CMC)28.4 mN·m−1;而Tween80溶液的CMC值约为600 mg·L−1,δ(CMC)37.2 mN·m−1。表明APG1214具有良好的表面活性且优于非离子表面活性剂Tween80。
-
根据国家标准及相关法规[29,32],表面活性剂初级生物降解度达到90%以上时易于生物降解,且降解度达到90%的时间越短,生物降解性越好;由图2可以看出,APG1214在第163小时生物降解度为91%,证明其易于生物降解,不会给地下水引入新的污染。
-
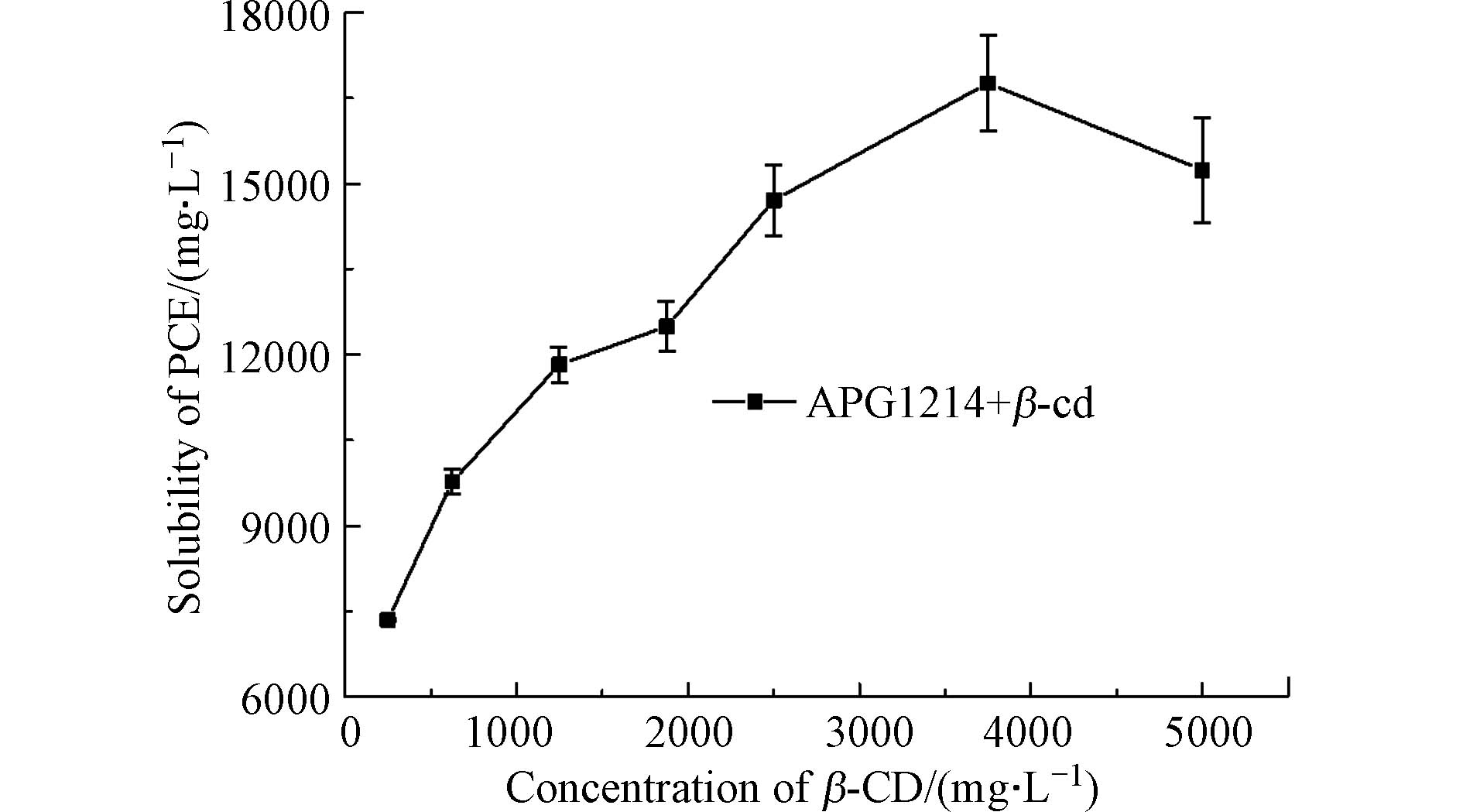
由图3可知,在APG1214溶液中加入β-环糊精后,体系对于PCE的溶解能力大幅度提升,PCE溶解度随β-环糊精浓度增大而先升高后降低,在β-环糊精浓度为3750 mg·L−1时达到最大。这是由于β-环糊精分子的加入改变了原本APG1214分子形成的胶束结构,两种分子相互作用形成混合胶束[33],共同增溶PCE分子,起到协同增溶的作用,并且β-环糊精分子越多,形成的混合胶束越大,从而增溶更多的PCE分子。而β-环糊精浓度由3750 mg·L−1增大到5000 mg·L−1时PCE溶解度降低,这是由于混合胶束的体积进一步增大时,胶束竞争水溶液内部的空间,影响PCE分子进入胶束内部,导致PCE的溶解度降低。同时也可以说明β-环糊精分子全部用于形成混合胶束,不存在单独增溶PCE的β-环糊精分子。由此确定了Aβ复配体系中β-环糊精的浓度为3750 mg·L−1。
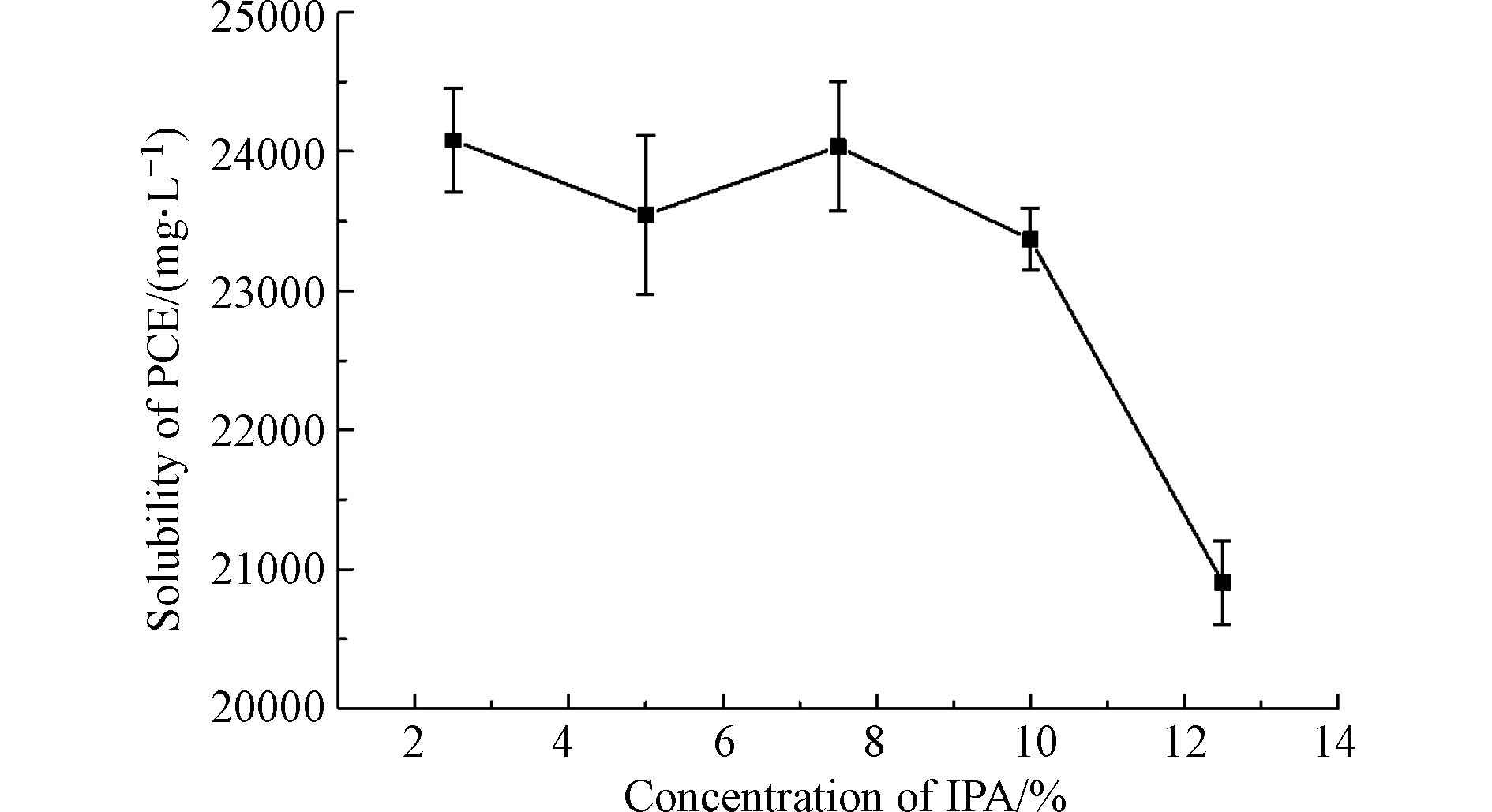
由图4可知,在Aβ复配体系中加入异丙醇之后,PCE溶解度随异丙醇浓度增大而呈降低趋势,并且整体对于PCE的溶解能力进一步提升。当异丙醇浓度为2.5%时,PCE溶解度最大。这是由于异丙醇分子的加入填补了胶束内部的“空隙”,增加了胶束分子的亲油能力,方便了PCE分子进入胶束并稳定在胶束内部。而当异丙醇浓度大于10.0%后PCE溶解度明显降低,这是因为异丙醇既亲水又亲油,异丙醇的浓度过高后更容易与PCE相溶,使原本可以被增溶在胶束中的PCE分子不易进入水相,而与异丙醇分子结合在油相中,造成PCE的水相溶解度明显降低。由此确定了AβI复配体系中异丙醇的体积浓度为2.5%。
-
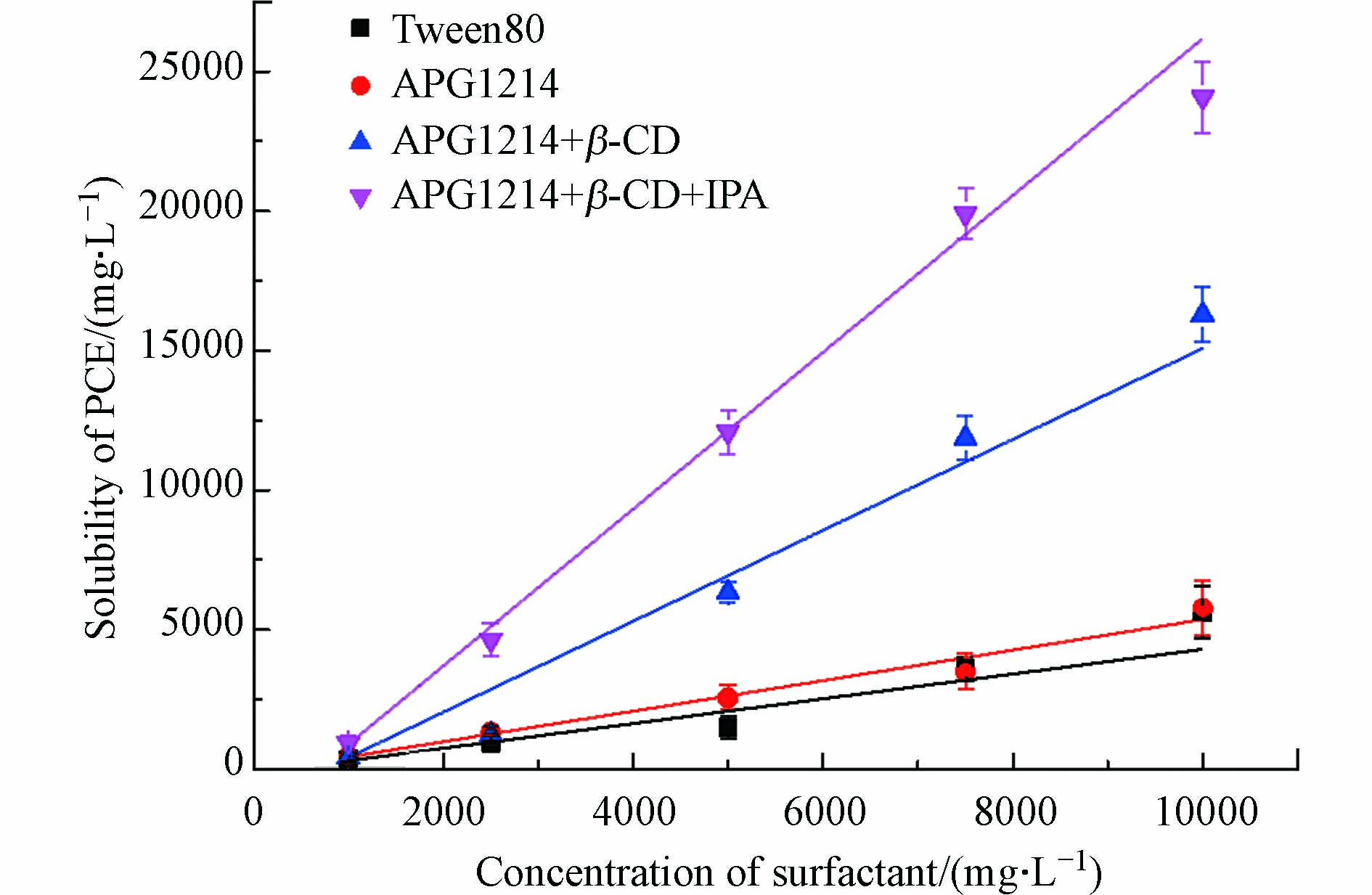
由图5可知,随着APG1214浓度增大,PCE在水溶液中的溶解度也逐渐增大,呈线性关系,这是由于其超过临界胶束浓度后,APG1214分子在水溶液中聚集形成胶束,从而使非水相污染物包裹在胶束中;而胶束含量随浓度增大而增多,对污染物的增溶量也随之提高[34]。由图5可知,单一APG1214体系对PCE的增溶效果与Tween80相似,在10000 mg·L−1时对PCE的溶解度为5758.6 mg·L−1。在与β-环糊精复配之后,对PCE的溶解度大幅度增加,并且浓度越高时增溶效果越明显,两者产生明显的协同增效作用,对PCE的溶解度增大至16281.9 mg·L−1。而进一步加入异丙醇复配之后,增溶效果的提升更加明显,可以使PCE的溶解度增大至24080.6 mg·L−1,较清水中PCE溶解度提高了346倍。根据质量增溶比(WSR,单位质量增溶材料增溶污染物的含量),单位质量APG1214体系可以增溶的PCE质量为体系的0.576倍,而单位AβI体系可以增溶PCE质量增加至体系质量的1.751倍,与未复配时相比提高了3倍,增溶相同质量的PCE所需要的增溶材料减少至1/3,说明复配不仅可以提升整个体系的增溶能力,更降低了增溶污染物所需增溶材料的质量,从而节省了增溶材料用量(表1)。
-
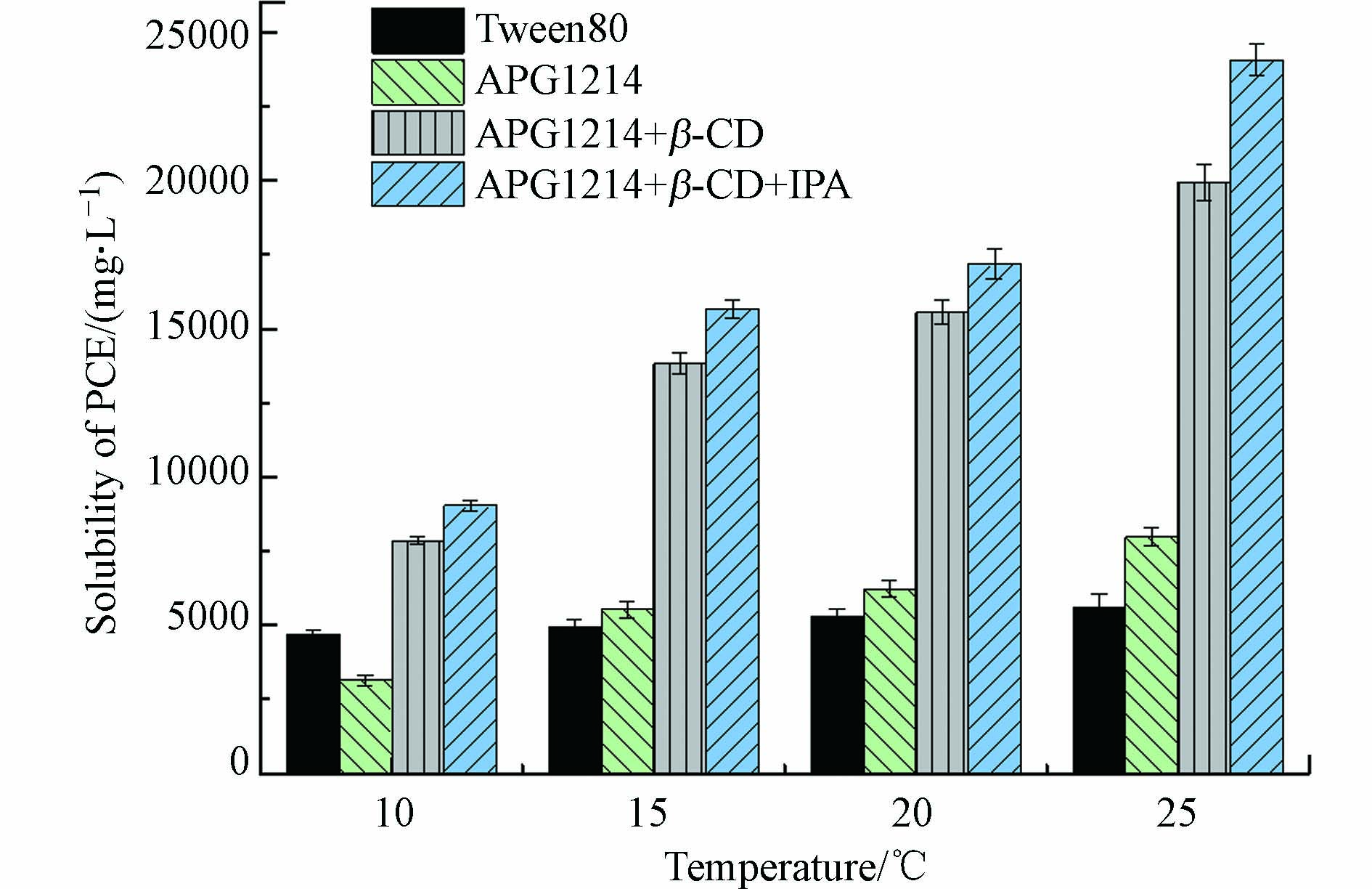
由图6可知,随温度升高,各个体系对于PCE的增溶能力均逐渐升高,这是由于随着温度升高,分子运动速率增大,胶束分子与溶液中游离的PCE分子“相遇”的几率增大;同时,温度升高使胶束体积膨胀,导致PCE分子更容易进入胶束的疏水内核[35]。Tween80对PCE的溶解度随温度变化较小,APG1214在10 ℃时对PCE的溶解度低于Tween80,15 ℃及以上时增溶效果优于Tween80。而在复配之后,整个体系在各个温度下对PCE的增溶能力均明显优于Tween80,说明复配不仅大幅提升了增溶能力,还明显增强了体系的抗低温能力,更能适应地下水的低温环境,且AβI复配体系的增溶效果优于Aβ复配体系。
-
地下水成分复杂,含有许多化学成分,如无机盐、有机质等,这些化学成分可能对材料的增溶能力产生影响。因此,在静态实验中设置了7种无机盐,涵盖了地下水常见离子(Na+、Ca2+、K+、Mg2+、Cl−、CO32-、HCO3−、SO42-),并设置接近于地下水的浓度梯度探究无机盐对3种体系增溶能力的影响。
由图7(a)可知,APG1214体系中加入无机盐后,体系对PCE的增溶能力整体增大,并且随不同无机盐浓度变化趋势不同:随NaCl、CaCl2、NA2CO3浓度增加,增溶能力整体呈上升趋势;随NaHCO3、Na2SO4浓度增加,增溶能力呈先升高后降低趋势;随MgCl2浓度增加,增溶能力整体呈先降低后升高趋势;而KCl浓度改变对体系增溶能力几乎无影响。由图7(b)看出,Aβ复配体系加入无机盐后对PCE的增溶能力降低,但仍在10000 mg·L−1以上。体系增溶能力随不同无机盐浓度变化趋势不同:随Na2CO3浓度增加,增溶能力整体呈上升趋势;随CaCl2、KCl、NaHCO3浓度增加,增溶能力呈先升高后降低趋势;随Na2SO4浓度增加,增溶能力整体呈下降趋势;随NaCl、MgCl2浓度增加,增溶能力呈先上升后下降趋势。图7(c)显示,AβI复配体系中加入无机盐后,增溶能力大部分降低,但仍在9000 mg·L−1以上。体系增溶能力随不同无机盐浓度变化趋势不同:随KCl、MgCl2、Na2CO3、NaHCO3、Na2SO4浓度增加,增溶能力呈先升高后降低趋势;随NaCl、CaCl2浓度增加而降低。
综上所述,在各个表面活性剂体系中,同种无机盐随浓度增加,PCE溶解度在一定范围内呈现先增大后减小趋势,这是因为APG 形成的胶团表面带有负电荷,使APG同时具有阴离子表面活性剂的性质,加入适量的无机盐会通过压缩双电层使分子间的斥力减弱,使胶束更容易形成[36],而加入过量的无机盐时可能会破坏APG头基上羟基与水形成的氢键,从而破坏胶束的稳定性,甚至造成胶束解体[37],导致无机盐浓度继续增加时,PCE溶解度呈降低趋势。另外,在不同种类无机盐条件下,烷基糖苷及复配体系对PCE仍有较高的溶解能力,APG1214增溶能力均在6000 mg·L−1以上,高于原体系增溶能力;而复配体系在无机盐的影响下对PCE的增溶能力均在9000 mg·L−1以上,表明这3种体系均具有较强的抗盐能力,有利于在含盐的地下环境中应用。
-
(1)烷基糖苷作为绿色表面活性剂,具有优良的表面活性,临界胶束浓度(CMC)约为100 mg·L−1,δ(CMC)28.4 mN·m−1。
(2)烷基糖苷的初级生物降解度超过90%,易于生物降解,不会给地下水带来二次污染。
(3)烷基糖苷对PCE的增溶能力较强,且复配性能好,在10000 mg·L−1时与3750 mg·L−1的β-环糊精形成Aβ复配体系,对PCE的增溶能力可提高至16281.9 mg·L−1;再与2.5 %的异丙醇形成AβI复配体系后增溶能力可大幅度提升,使PCE的溶解度增大至24080.6 mg·L−1,较清水中PCE溶解度提高了346倍。
(4)烷基糖苷本身具备一定的抗低温性能,与β-环糊精、异丙醇复配之后可提升抗低温能力,体系对于PCE的增溶能力随温度升高而增强。
(5)烷基糖苷及其复配体系具有较好的抗盐能力,在一定浓度范围内表现为PCE溶解度随离子浓度增大而先增大后减小的趋势。
(6)通过实验确定烷基糖苷最佳复配组合为AβI复配体系:烷基糖苷浓度10000 mg·L−1,β-环糊精浓度3750 mg·L−1,异丙醇体积浓度2.5%,该复配组合对四氯乙烯的增溶能力及抗低温、抗盐性能均优于其他体系,适合应用于地下水环境。
烷基糖苷复配体系对地下水中四氯乙烯的增溶作用
Solubilization of tetrachloroethylene in groundwater by alkyl glycoside compounded system
-
摘要: 为选出适用于地下水环境的四氯乙烯增溶试剂,选用高效绿色表面活性剂烷基糖苷及其与β-环糊精、异丙醇的复配体系对四氯乙烯进行增溶,分别考察了溶液浓度、环境温度和无机盐浓度变化对四氯乙烯增溶效果的影响,并筛选出最佳的复配组合。结果表明,烷基糖苷的临界胶束浓度约为100 mg·L−1,初级生物降解度为91%;烷基糖苷复配体系对四氯乙烯的增溶效果明显优于单一体系,且增溶能力随体系浓度增大而增强;复配体系的增溶能力随环境温度降低而略有降低,在一定范围内随无机盐浓度升高而先升高后降低。烷基糖苷增溶四氯乙烯的最佳复配组合为:烷基糖苷浓度10000 mg·L−1,β-环糊精浓度3750 mg·L−1,异丙醇体积浓度2.5%,该复配组合具备良好的增溶能力及抗低温、抗盐性能。该体系的筛选可为后续场地修复中提供一定的实验依据。Abstract: In order to screen out suitable tetrachloroethylene solubilizing reagent which can be used in groundwater environment, the high efficient, green surfactant alkyl glycoside and its compounded system with β-cyclodextrin and isopropanol were used to solubilize PCE. The critical micelle concentration and primary biodegradability of alkyl glycosides were determined. The influence of solution concentration, ambient temperature and electrolyte concentration on solubilization effect of PCE were investigated, and the optimal combination of compounded system was finally determined. The results show that the critical micelle concentration of alkyl glycosides is about 100 mg·L−1, and the primary biodegradability is 91%. The solubilization effect of the APG compounded system is better than that of the single system. The solubilization ability of the compound system decreases slightly with the decrease of ambient temperature, and increases first and then decreases with the increase of electrolyte concentration in a certain range. The optimal combination of APG compounded system is as follows: the concentration of APG is 10000 mg·L−1, the concentration of β-cyclodextrin is 3750 mg·L−1 and the volume concentration of isopropanol is 2.5%. The combination has good solubilization ability, low-temperature resistance and salt resistance. The screening of this system can provide some experimental basis for subsequent site restoration.
-
Key words:
- alkyl glycoside /
- perchloroethylene /
- solubilization /
- groundwater.
-

-
表 1 不同体系的增溶回归方程
Table 1. The static solubilization regression equation of different surfactants
体系
System回归方程
Regression equationR2 WSR Tween80
APG1214
APG1214+β-cd
APG1214+β-cd+IPAy = 0.5833x − 647.64
y = 0.5581x − 187.87
y = 1.8593x − 2444.4
y = 2.6744x − 1580.80.9493
0.9759
0.9870
0.99080.561
0.576
1.184
1.751 -
[1] 刘懿丹. 干洗服装中四氯乙烯残留量检测及环境释放行为的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2018. LIU Y D. Study on the determination and environmental release behavior of tetrachloroethylene residues in dry-cleaned apparels[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2018(in Chinese).
[2] 张凤君, 王斯佳, 马慧, 等. 三氯乙烯和四氯乙烯在土壤和地下水中的污染及修复技术 [J]. 科技导报, 2012, 30(18): 65-72. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2012.18.010 ZHANG F J, WANG S J, MA H, et al. Contaminations and remediation technologies of trichloroethylene and perchloroethylene in the soil and groundwater: A review [J]. Science & Technology Review, 2012, 30(18): 65-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2012.18.010
[3] ENGELMANN C, HÄNDEL F, BINDER M, et al. The fate of DNAPL contaminants in non-consolidated subsurface systems - Discussion on the relevance of effective source zone geometries for plume propagation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 375: 233-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.083 [4] CÁPIRO N L, STAFFORD B P, RIXEY W G, et al. Fuel-grade ethanol transport and impacts to groundwater in a pilot-scale aquifer tank [J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(3): 656-664. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.09.024 [5] SHENG Y Z, ZHANG X, ZHAI X B, et al. A mobile, modular and rapidly-acting treatment system for optimizing and improving the removal of non-aqueous phase liquids (NAPLs) in groundwater [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 360: 639-650. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.044 [6] QIN X S, HUANG G H, CHAKMA A, et al. Simulation-based process optimization for surfactant-enhanced aquifer remediation at heterogeneous DNAPL-contaminated sites [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 381(1/2/3): 17-37. [7] 王永剑, 单广波, 徐佰青, 等. 表面活性剂在石油烃污染土壤修复中的应用研究进展 [J]. 当代化工, 2021, 50(6): 1425-1430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2021.06.036 WANG Y J, SHAN G B, XU B Q, et al. Research progress in application of surfactants in petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil remediation [J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(6): 1425-1430(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2021.06.036
[8] 李隋. 表面活性剂强化抽取处理修复DNAPL污染含水层的实验研究: 以硝基苯为例[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008. LI S. Research on surfactant enhanced pump and treat remediation of a DNAPL contaminated aquifer—case study on nitrobenzene[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008(in Chinese).
[9] 侯泽宇, 王宇, 卢文喜. 地下水DNAPLs污染修复多相流模拟的替代模型 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(7): 2913-2920. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.07.027 HOU Z Y, WANG Y, LU W X. Surrogate models of multi-phase flow simulation model for DNAPL-contaminated aquifer remediation [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(7): 2913-2920(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.07.027
[10] PEI G P, ZHU Y E, CAI X T, et al. Surfactant Flushing remediation of o-dichlorobenzene and p-dichlorobenzene contaminated soil [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 185: 1112-1121. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.098 [11] LV C, CHEN J, WANG X. Evaluation of surfactant performance in in situ foam Flushing for remediation of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane-contaminated soil [J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 14(3): 631-638. doi: 10.1007/s13762-016-1175-0 [12] 王勇. 表面活性剂在砂岩上吸附规律研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2017. WANG Y. Study on adsorption law of surfactant on sandstone. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2017(in Chinese).
[13] UPADHYE S, SONDE R. Degradation of sodium dodecyl sulfate by the bacterial isolates obtained from polluted aquatic bodies [J]. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 2012, 6(1): 303-308. [14] 白利松, 赵勇. 表面活性剂的绿色化及研究进展 [J]. 中国洗涤用品工业, 2017(8): 48-54. BAI L S, ZHAO Y. Research progress of green surfactants [J]. China Cleaning Industry, 2017(8): 48-54(in Chinese).
[15] 雷自刚. 烷基糖苷APG1214的绿色合成及应用性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2020. LEI Z G. Study on the green synthesis and application performance of alkyl polyglycoside APG1214[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2020(in Chinese).
[16] 史晓宇, 唐天龙. 烷基糖苷的合成应用与知识产权状况 [J]. 大众科技, 2013, 15(7): 94-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2013.07.033 SHI X Y, TANG T L. Application and intellectual property rights of Alkyl polyglycoside [J]. Popular Science & Technology, 2013, 15(7): 94-96(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1151.2013.07.033
[17] 秦勇, 张高勇, 康保安, 等. 烷基多苷(APG)生物降解性的研究 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2003, 16(4): 28-31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2003.04.008 QIN Y, ZHANG G Y, KANG B A, et al. Research on primary biodegradation of APG [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2003, 16(4): 28-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.2003.04.008
[18] 赵少丹. 表面活性剂淋洗修复苯胺污染土壤的实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018. ZHAO S D. Experimental study on remediation of aniline contaminated soil by surfactant leaching[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2018(in Chinese).
[19] 孙崇凤. 可降解表面活性剂增效洗脱污染土壤中二氯苯的研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2015. SUN C F. Enhanced soil washing of dichlorobenzene by biodegradable surfactants[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2015(in Chinese).
[20] ZHOU W J, ZHU L Z. Enhanced desorption of phenanthrene from contaminated soil using anionic/nonionic mixed surfactant [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147(2): 350-357. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.025 [21] ZHOU W J, ZHU L Z. Enhanced soil Flushing of phenanthrene by anionic-nonionic mixed surfactant [J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(1/2): 101-108. [22] 李凯丽, 裴宗平, 张鑫. 复配表面活性剂APG/SDBS对菲、芘的增溶特性 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(8): 3260-3265. LI K L, PEI Z P, ZHANG X. Dissolution characteristics of phenanthrene and Pyrene in complex surfactant system [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(8): 3260-3265(in Chinese).
[23] 王博豪. β-环糊精在饮料工业上的研究应用 [J]. 广东化工, 2021, 48(16): 141-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2021.16.058 WANG B H. Research and application of β-cyclodextrin in beverage industry [J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2021, 48(16): 141-142(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2021.16.058
[24] 肖姗姗, 吉时蕾, 蒋欣欣, 等. 环糊精及其衍生物在药物制剂中的应用 [J]. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 34(6): 77-83,91. XIAO S S, JI S L, JIANG X X, et al. Application of cyclodextrin and its derivatives in pharmaceutical preparations [J]. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 34(6): 77-83,91(in Chinese).
[25] 邓军. 表面活性剂和环糊精对土壤有机污染物的增溶作用及机理[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2007. DENG J. Study on solubilization effects and mechanisms of soil organic contaminants in surfactant and cyclodextrin solutions[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2007(in Chinese).
[26] 刘宏, 刘迅. 环糊精和表面活性剂对多氯联苯污染土壤的洗脱增效修复对比研究 [J]. 四川环境, 2018, 37(2): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2018.02.001 LIU H, LIU X. Comparison study of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin(HPCD) and sodium dodecyl sulfate(SDS) on Aroclor1242 elution from contaminated soil [J]. Sichuan Environment, 2018, 37(2): 1-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2018.02.001
[27] SABATINI D A, KNOX R C, HARWELL J H, et al. Integrated design of surfactant enhanced DNAPL remediation: Efficient supersolubilization and gradient systems [J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2000, 45(1/2): 99-121. [28] TAYLOR T P, RATHFELDER K M, PENNELL K D, et al. Effects of ethanol addition on micellar solubilization and plume migration during surfactant enhanced recovery of tetrachloroethene [J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2004, 69(1/2): 73-99. [29] 中国日用化学研究院有限公司, 赞宇科技集团股份有限公司, 西安开米股份有限公司, 等. 表面活性剂生物降解度试验方法[S], 国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2018: 24. China Daily Chemical Research Institute Co. , Ltd. , Zanyu Technology Group Co. , Ltd. , Xi 'an Kaimi Co. , Ltd. Test method for biodegradability of surfactants[S]. State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of China, 2018: 24.
[30] 赵喆, 王齐放. 表面活性剂临界胶束浓度测定方法的研究进展 [J]. 实用药物与临床, 2010, 13(2): 140-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0070.2010.02.025 ZHAO Z, WANG Q F. Progress on methods of measuring surface active agent's critical micelle concentration [J]. Practical Pharmacy and Clinical Remedies, 2010, 13(2): 140-144(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0070.2010.02.025
[31] 刘霞, 王建涛, 张萌, 等. 螯合剂和生物表面活性剂对Cu、Pb污染塿土的淋洗修复 [J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(4): 1590-1597. LIU X, WANG J T, ZHANG M, et al. Remediation of Cu-Pb-contaminated loess soil by leaching with chelating agent and biosurfactant [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(4): 1590-1597(in Chinese).
[32] 冯瑜, 张广良, 宋鹏, 等. 表面活性剂生物降解性及其法规 [J]. 日用化学品科学, 2014, 37(6): 33-39. FENG Y, ZHANG G L, SONG P, et al. Standards and regulations of surfactant biodegradation [J]. Detergent & Cosmetics, 2014, 37(6): 33-39(in Chinese).
[33] VALENTE A J M, NILSSON M, SÖDERMAN O. Interactions between n-octyl and n-nonyl beta-D-glucosides and alpha- and beta-cyclodextrins as seen by self-diffusion NMR [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2005, 281(1): 218-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.018 [34] FATMA N, PANDA M, KABIR-UD-DIN. A study on the solubilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in gemini-conventional mixed surfactant systems by 1H NMR spectroscopy [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 254: 123223. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123223 [35] 吴振. 温度和pH影响OSβG胶束化及其增溶和控释β-胡萝卜素的机制研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2021. WU Z. Molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of temperature and pH on OSβG micellization, solubilization and controlled-release of β-carotene by the resultant micelles[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021(in Chinese).
[36] 籍海燕, 闵洁. 烷基糖苷水溶液的表面活性以及电解质的影响 [J]. 毛纺科技, 2010, 38(2): 12-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1456.2010.02.004 JI H Y, MIN J. Study of alkyl polyglucosides' surface activity and electrolyte effects on the surface tension and micellization of the solutions [J]. Wool Textile Journal, 2010, 38(2): 12-15(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1456.2010.02.004
[37] 贾少华, 宋存义, 栾海波, 等. 烷基糖苷对石油增溶作用及其影响因素研究 [J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(4): 697-702. JIA S H, SONG C Y, LUAN H B, et al. Enhanced solubilization of crude oil by using alkyl polyglucoside [J]. Soils, 2014, 46(4): 697-702(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: