-
汽车工业是我国经济的重要支柱产业,其在推动社会经济发展的同时,也带来了不容忽视的污染问题. 机动车在行驶过程中会产生包括一氧化碳(CO)、氮氧化物(NOx)、碳氢化合物(HCs)和颗粒物(PM)等多种化合物,已经成为大气污染的主要来源之一. 据《中国移动源环境管理年报(2021)》,2020年我国由机动车所排放的CO、HCs、NOx和PM总和达到1593万吨,这给我国大气环境治理带来了极大压力和挑战. 为了降低汽车尾气对大气环境的负面影响,全球多个国家和地区相继出台一系列政策和法规来对机动车尾气排放进行管控. 为满足日益严苛的尾气排放标准,机动车厂商需要采用更为高效的尾气催化净化系统来控制污染物的排放,其核心是提升催化剂的催化净化性能,这对催化材料提出了更高的要求.
稀土铈元素(Ce)的核外电子排布为4f15d16s2,受镧系收缩的影响和4f电子的作用,铈的氧化物非常容易发生Ce3+/Ce4+价态变化,使得CeO2拥有优异的储释氧能力和丰富可调的表面氧缺陷. 在机动车尾气后处理催化剂中引入铈元素可以:①增强氧化物体系的高温稳定性,尤其是水热稳定性;②提高活性金属的分散度,减少贵金属用量;③提高催化剂抗中毒的能力,延长催化剂寿命;④改善催化剂抗积碳的能力;⑤提高材料的储/放氧能力,从而增强氧化/还原气氛快速交替变换条件下催化剂的适应性等诸多特性. 这使得铈基材料作为机动车尾气净化催化剂的重要组分发挥着不可替代的作用. 随着纳米技术、材料科学及现代表征方法的发展,人们可以从分子或原子水平上研究铈基催化材料的结构、表面吸附与反应的动态过程和环境条件对稀土催化材料表面和体相结构等的影响,从而加深对稀土铈基材料催化作用的认识,为设计、制备高性能的稀土铈基催化材料提供了新的机遇,为发现和发展新结构、新功能的稀土铈基催化材料,并开拓其在环境治理领域中的应用提供理论支撑与技术基础.
本文对用于机动车尾气后处理铈基材料的性质以及性能进行了系统地梳理和总结,按照机动车后处理系统所涉及的反应过程,对铈基材料在不同的机动车尾气催化系统中所起到的催化作用进行了归纳,对目前铈基材料在尾气催化消除的最新研究进展进行了介绍. 最后,对铈基催化材料在机动车尾气后处理领域可能的发展方向进行了展望.
-
针对不同的燃料来源,机动车可被分为汽油车、柴油车以及燃气车等几大类. 由于燃料差异以及发动机工作原理不同,其所排放的尾气组分也具有明显差异. 《中国移动源环境管理年报(2020)》核算结果显示,移动源排放的NOx和PM主要来自柴油车,而汽油车贡献了大部分的CO和HCs,不同类型的机动车的尾气差异催生了针对特定发动机设计的尾气催化净化器.
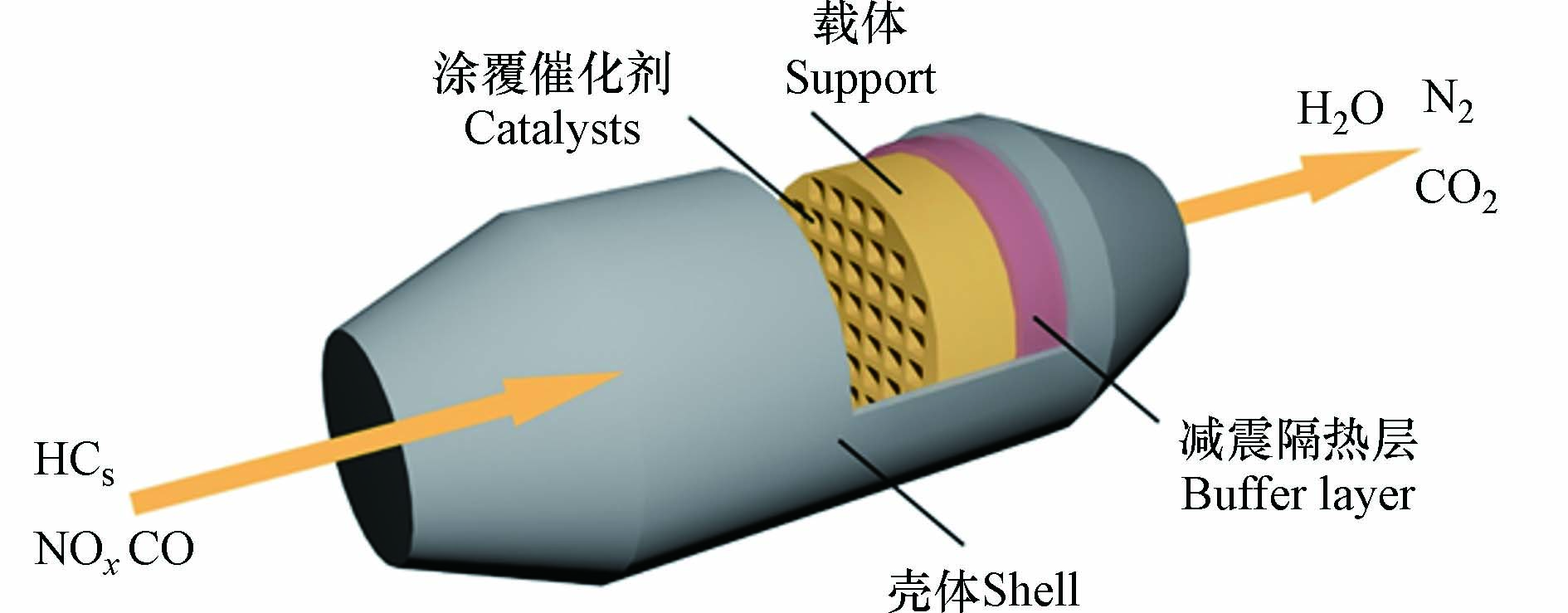
目前主要采用三效催化剂(three-way catalyst,TWC)来催化消除汽油车和燃气车尾气污染物,其基本结构如图1所示,其中催化剂是整个催化转化器的核心部分,决定着主要的性能指标. 随着排放法规的日益严苛、贵金属资源的枯竭和价格的增长,目前TWC催化技术的发展趋势是尽可能在降低贵金属用量的同时,提高催化活性、降低起燃温度以减少发动机的总排放量,这就要求在高性能稀土储氧材料、耐高温高比表面材料、贵金属及助剂的负载和耐久性涂层的制备等技术上取得突破性进展.
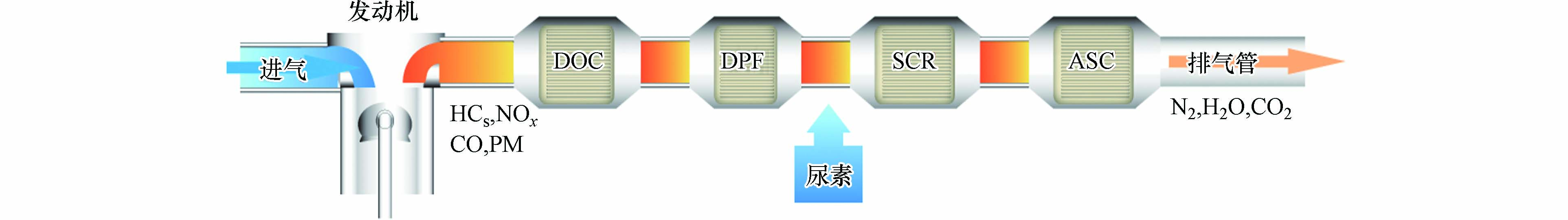
相比于汽油车和燃气车,柴油车尾气处理比较复杂,其包含多个后处理单元(图2). 柴油车催化氧化剂(diesel oxidation catalyst, DOC)能够氧化尾气中的还原性污染气体(如CO、NOx、HCs)和部分可溶性有机组分(soluble organic fraction, SOF);颗粒物捕集器(diesel particulate filter, DPF)能够捕集消除尾气中的颗粒物;尾气中含有的氮氧化物在SCR系统(selective catalytic reduction, SCR)中通过NH3-SCR反应被转化成为N2和H2O后,未反应的还原剂NH3还需要通氨逃逸催化剂(ammonia slip catalyst, ASC)进行消除. 随着国家对柴油车尾气专项整治行动的不断推进,不断严苛的排放标准也对柴油车后处理系统中的催化剂提出了更高的要求.
-
对于不同的后处理系统,其尾气特性和消除目标都有所差异. 表1给出了中国法规体系不同排放控制阶段对应的控制技术路线. 以国Ⅵ为分水岭,任何单一技术路线均难以满足国Ⅵ排放法规的要求,排放控制系统更复杂,而不同车型排放控制对象及技术路线则趋同.
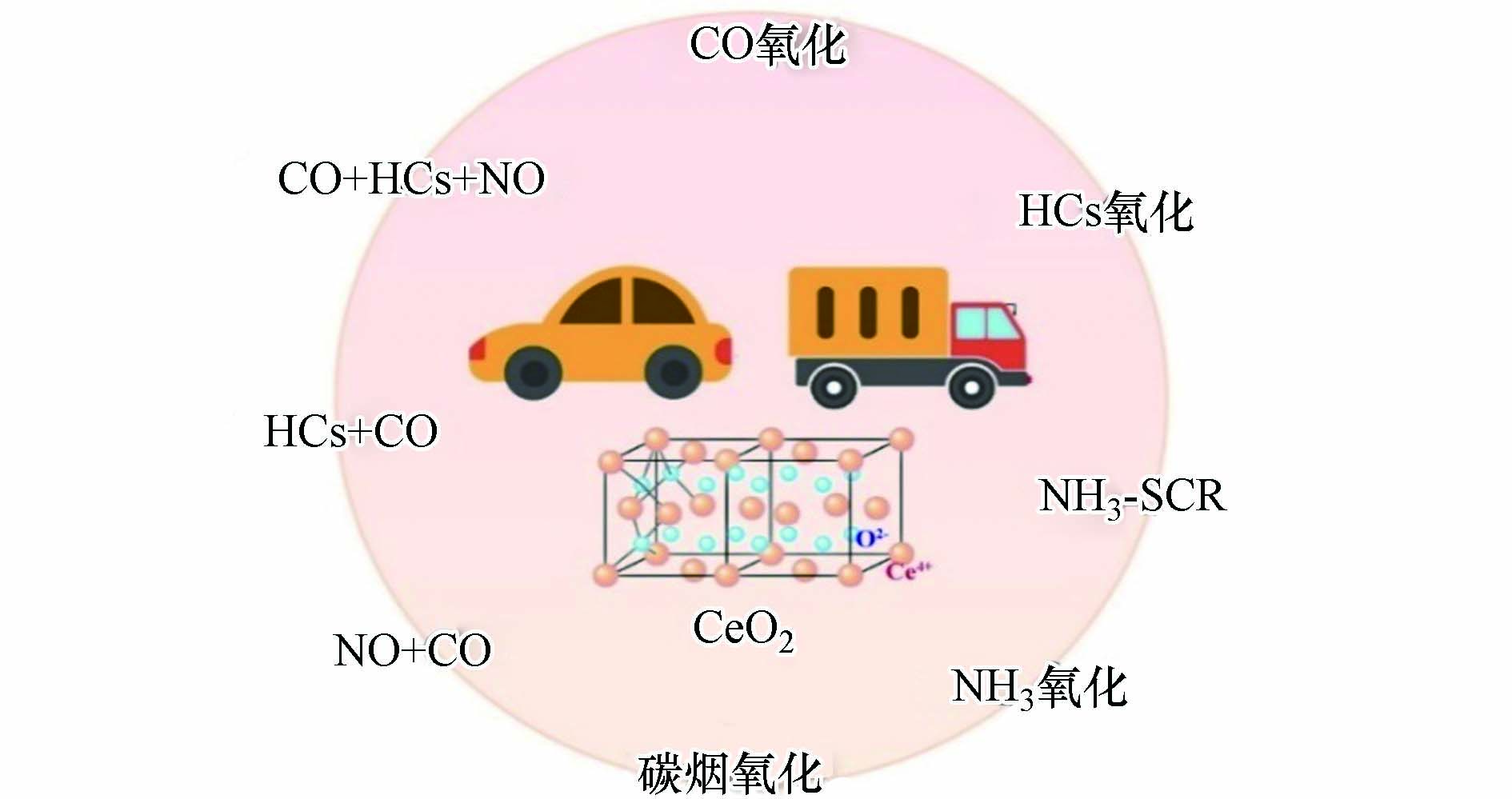
机动车排放控制所采用的技术路线及关键技术与车型、排放法规体系及其所处阶段密切相关. 但究其共性,各催化剂都要求具备更高的储释氧能力(OSC)、更好的氧化还原性能、更佳的低温起燃特性和更高的活性. 在大量材料中,氧化铈(CeO2)具有优异的性能表现,其良好的电子传递能力和氧化还原活性都能满足催化剂的发展要求. 通过对铈基材料的大量探索后发现,其独特的物理化学性质在不同的机动车尾气催化技术路线中都扮演了重要角色(图3). 不过对于不同类型的反应,催化剂也有着不同的性能要求,通过对铈基材料在不同尾气催化消除反应中的组成结构、反应过程进行探究,能够对催化剂的设计和制备起到有效的指导作用.
-
汽油车尾气中O2含量较低,为了将尾气中的CO、HCs等污染物去除,需要以NOx作为氧化剂来对污染物进行催化消除,TWC中主要通过以下反应实现几种污染物同时催化消除:
只有在尾气中的CO、HC和NOx达到反应计量比时,TWC才能具有较好的催化消除性能. 当空燃比(A/F)条件发生变化,尾气中主要污染物的消除效果会产生巨大差异. 贫氧条件下氧气浓度较低,CO难以得到充分氧化;而富氧条件下NOx的转化率会下降. 此外,TWC表面各种副反应的发生使得NOx转换为其他的含氮化合物. 通过下列途径发生的蒸汽重整和水煤气反应所产生的少量H2在催化剂的作用下也会与NO反应:
反应产生的其他含氮化合物又会发生进一步的相互反应,从而使得尾气成分变得更加复杂. 因此为了获得最佳净化效果,必须提高发动机标定精度,控制空燃比窗口在A/F≈14.6(λ = 1)为中心的狭窄范围内,或者通过优化催化剂,提高催化剂空燃比窗口适应性.
-
铈基材料良好的储释氧性能对环境气氛起到非常良好的缓冲作用. 在贫氧气氛下(λ < 1),CeO2可提供CO和HCs氧化所需的氧;在富氧气氛下(λ > 1),Ce2O3可与气氛中的氧结合,避免尾气中氧气浓度的过大波动. 同时,CeO2的Ce3+能够促进NOx在表面吸附活化形成活性硝酸盐物种[1]. 对于HCs的消除,CeO2的弱酸性也可削弱C—H强度,促进HCs中的C—H键断裂,而表面活性氧能将其氧化形成甲酸盐和乙酸盐等中间物种后进一步消除[2]. 但纯CeO2的储释氧能力难以满足越来越苛刻的尾气排放标准. 此外,纯CeO2在超过1000 oC的尾气中易发生烧结,导致储释氧能力下降. 因此,提高铈基材料的储释氧能力和热稳定性是三效催化剂关注的重点.
掺杂已被证明是材料改性的有效手段,对CeO2进行掺杂改性能够降低其氧空位形成能,促进缺陷位的形成[3-6]. 通过对比多种掺杂铈基材料,人们发现掺杂氧化锆(ZrO2)后所制得的铈锆固溶体(CeZrOx)具有以下特点:(1)ZrO2的引入造成了CeO2晶胞的扭曲和收缩,促进结构缺陷形成,提高了氧空穴浓度,有利于氧物种的迁移和扩散;(2)铈锆固溶体中体相氧也可以参与储释氧循环,对比表面的依赖程度减小,因此高温烧结对铈锆固溶体储氧能力的影响也相对减小;(3)在CeO2晶格中引入离子半径较小的Zr4+(0.084 nm),可以减弱体积膨胀的影响,促进晶格内的电子迁移;(4)铈锆固溶体具有更高的热稳定性. 目前受汽车厂商青睐的TWC主要是以铈锆固溶体为基本载体,多种金属改性的多元复合催化剂(图4).
为了寻求制备更高性能的CeZrOx,研究者对铈锆固溶体的制备条件进行了大量的探索[7-11]. 目前,CeZrOx已经成为发展最为成熟、应用最为广泛的TWC储释氧载体. 当前TWC的设计和生产也多基于CeZrOx,通过向其中掺入其他金属,如Al[12]、Nd[13]、Pr[14]、Fe[15]等;抑或是以CeZrOx作为基底,负载活性金属组分,如Pt[16]、Pd[16]、Rh[17]、Cu[18]等来制备多元尾气催化剂. 此外,铈基材料能够通过与表面活性金属组分产生稳定的相互作用来调控催化剂的表面性质和结构形态,从而提高催化剂的催化活性和稳定性.
TWC的核心目标是将汽油车尾气中的HCs和CO完全氧化成CO2和H2O,这和柴油车DOC催化剂的目标类似,因此此类完全氧化反应在柴油车DOC催化剂部分一并总结. 其另外一个重要目标就是利用尾气中的CO、HCs作为还原剂,选择性地还原NOx为氮气(N2).
(1)铈基材料与NO+CO(+O2)反应
Rh-CeO2是一种常用的NOx催化消除材料,它可以高效地将NOx选择性地还原成氮气. 但是Rh的价格昂贵,而Pd催化剂在一定条件下表现出良好的催化性能. 需要指出的是,Pd/CeO2目前并没有得到应用,这是由于在低温时(< 200 oC)对于N2O副产物的控制仍然无法满足排放要求. 近期研究表明[19],在Pd/CeO2中掺杂Fe能够大大提升催化剂表面的缺陷位,进而促进N2O在缺陷位的解离. 也就是说,稀土铈基材料表面的缺陷位能够抑制副产物N2O的形成,这为提升稀土铈基TWC催化剂的低温反应性能提供了新思路.
相比于贵金属,Cu等过渡金属价格较低,且CuO-CeO2间存在Cu2++Ce3+ ↔ Cu++Ce4+协同作用,两者的协同能够高效促进电子的迁移. 然而并不是所有在Cu/CeO2催化剂表面的铜物种都能够表现出高反应活性,因此需要对Cu/CeO2表面的Cu物种加以区分. 低载量的Cu能够分散在CeO2表面或进入体相取代部分Ce4+,其中表面的Cu物种具有不稳定的五配位结构,更易被还原,而反应的进行主要依赖于表面Cu+对NO的解离作用,生成的活性硝酸盐与吸附的CO发生反应,而体相的铜物种参与反应难度较大,因此在NO+CO反应中活性较低[20]. Cao等[21]通过掺杂的手段对CeO2进行改性,能够进一步调变铜物种的分散状态,提高其催化性能.
在稀燃条件下(λ > 1.01),尾气中存在的过量O2会优先与CO发生反应,导致NOx无法被有效还原. 因此如何在含氧条件下推动NO+CO反应的进行具有重要的现实意义. Jeon等[22]制备了(Pd1-xPtx)-In/CeO2,Pt的加入促进了InOx的还原,在富氧尾气中具有较高的NO和CO去除率. Li等[23]利用Cu作氧化还原位点,W作为酸性位点制备了CuW/CeZr催化剂,在含氧9%的条件下表现出优异的NO、CO转化率和N2选择性. Liu等[24]制备了耐氧的CuCoCe催化剂, NO和CO能够通过在催化剂表面吸附活化形成 (NO)2和Cu+-CO物种后进一步反应生成N2和CO2. 不可否认,在含氧工况下的NO+CO反应依然较难进行,因此对NO+CO+O2反应的研究还有待深入.
(2)铈基材料与HCs+NO反应
HCs+NO反应过程与NO+CO类似,主要涉及到HCs、NO在表面的吸附、断键和活化以及中间物种的重组和CO2、H2O等产物的形成. Pd具有非常好的HCs吸附性能,同时能高效促进C—H键的活化,在Pd/CeO2催化剂上,CO和C3H8的消除主要依赖于表面高度分散的PdO物种[25],而与CeO2作用较强的CexPd1-xO2在NO消除中具有较高活性[26]. 对于铑基催化剂来说,CeO2载体晶格中的Rh3+和分散在其表面的Rhn0团簇表现出良好的低温反应性能,其在较低温度下(< 100 oC)就可以将NO转化为氮气[27]. 但与Pd相比,Rh过高的N2O选择性以及较低的HCs氧化能力使得单铑催化剂的应用受到了限制[28].
为克服负载单一贵金属铈基催化剂的不足,目前主要通过多金属负载的策略来达到更令人满意的催化效果. Wang等[29]在CeZrLa表面负载Pt-Pd合金颗粒,通过提高氧物种在表面的迁移提高了催化消除HCs和NO的效率. 而Pd-Rh-CeO2双贵金属催化剂在具有更好的CH4、NO消除性能的同时也提高了N2的选择性,表现出更高的应用价值[28].
(3)铈基材料与CO+HCs+NO反应
无可置疑,TWC反应属于复杂的多相催化反应,目前针对CO、HCs和NO的同时去除还是需要活性贵金属元素Pt、Pd、Rh以及载体元素Ce、Zr、Al的共同作用. 多年的“构效关系”研究表明,催化剂中CeO2起着重要的桥梁作用:一方面提高氧化铝载体的热稳定性,另一方面提高贵金属的分散度. 近期有研究人员[30]将CeO2负载到预还原的γ-Al2O3表面,制备了尺度均一且具有大量缺陷的负载型纳米CeO2. 最后将金属前驱体沉积在CeO2上,制备了分散度达100%的金属态(Pt、Pd和Rh)集合式催化剂(ensemble catalysts, ESCs). 其在TWC催化反应中,特别是低温段,表现出优良的催化性能活性. 上述研究表明,通过制备手段的进步,实现对催化剂结构的精确调控,进而提升其TWC催化性能是可行路径,这为新一代TWC催化剂的研发提供了有价值的借鉴.
-
DOC结构和TWC类似,但尾气含氧量的差异及排气温度的不同使得两者在催化过程的作用有所差别. 对于稀燃发动机和柴油机来说,消除这类富氧尾气中的污染物主要依赖于O2的氧化作用. 作为需要氧气参与的氧化反应,催化剂的储释氧性能以及表面氧物种活化水平是推动反应进行的关键. 氧化铈作为一种良好的储释氧载体,是DOC的重要组分. 而柴油机相对较低的排气温度对其后处理系统的低温活性提出更严格的要求. 对氧化铈及表面活性物种状态的调控来增强催化剂对污染物的吸附活化,也被认为是设计具有高活性的DOC催化剂的关键步骤.
(1)铈基材料与CO(HCs)+O2反应
Pt/CeO2表面的Pt能够吸附活化CO,界面处的缺陷位会诱导O2的活化形成活性氧物种,从而表现出良好的催化氧化性能. 有研究表明,Ptδ+和Pt0在反应中的协同作用对Pt的催化性能有重要影响[31]. 当Pt粒径大小不同,Pt0/Ptδ+比例发生变化,两者间形成的协同作用也不同. 利用锆掺杂或改变铈氧化物前驱体的方式可以在催化剂表面引入更多缺陷位,进而改善了Pt的分散性,得到合适粒径的Pt纳米粒子,从而可以提升材料低温段的催化CO和HCs氧化的活性[32-33]. 此外,研究人员为了实现Pt物种的高原子利用率,对单原子Pt1-CeO2体系开展了大量研究,但其低温性能较差,通常需要采用比较苛刻的后处理方式(气氛、瞬时高温等)来提升Pt1的催化性能[34-36],目前并不适合在工业应用中推广. Pd也是一种在DOC中广泛使用的贵金属,Wang等[37]制备了Pd/Ce0.67Zr0.33O2用于氧化尾气中的CO、HC和NOx. 当载体表面的Pd主要是PdOx时,其具有较好的C3H6和C3H8氧化活性,而CO氧化主要和Pd0物种相关[38],单一的PdOx或Pd0并不能对尾气中所有的HCs、CO等污染物同时消除. 不难发现,不同反应物的氧化所对应的贵金属氧化态和表面状态存在差异,因此在提升贵金属的分散性的同时,还需要考虑不同贵金属物种在反应中的相互协同作用.
在非贵金属领域,铜铈材料是一种性能优良的氧化催化剂. 一般认为,铜铈物种间的协同作用对催化性能起到关键作用,如Qi等[39]认为CO氧化在Cu-CeO2上发生过程如下:CO吸附并还原在表面Cu-O-Ce物种形成表面协同氧空位(SSOV),即Cu-□-Ce物种. 由此产生的Cu+和Ce3+为CO和O2提供了吸附和活化位点并经由SSOV机理形成CO2. 倘若Cu-CeO2材料中Ce3+浓度升高,Cu2++Ce3+ ↔ Cu++Ce4+平衡更易右移,在两者的电子迁移下材料的活性得到了增强.
需要指出的是,在实际反应过程中,HCs的氧化会受到尾气中CO竞争性吸附的影响,其低温段的消除因此受到抑制[40],这在铈基DOC催化剂的设计中需要加以关注. 无论如何,提高催化剂在低温段的氧化活性是设计具有高活性DOC的必经之路.
(2)铈基材料与NO+O2反应
通常DOC上发生的NO氧化经由L-H机理(NO和O2在表面位点上吸附后再进一步发生氧化)或Eley-Rideal(E-R)机理(NO在酸性位点表面吸附形成中间体并与气相氧进一步氧化成为NO2)发生. NO氧化过程与O2在表面的活化效率关系密切,负载Pt、Pd等贵金属的铈基氧化物上形成的金属载体强相互作用(SMSI)能诱导产生氧空位,同时催化剂表面的活性氧物种能促进NO在表面活化形成硝酸盐物种,并促进NO氧化. 但是贵金属价格昂贵,在当今追求低廉、高效催化剂的研究大背景下,过渡金属氧化物催化剂引起人们广泛的关注. 为进一步增强CeO2的催化氧化性能,过渡金属常被用来改性CeO2形成复合氧化物. Co是一种酸性掺杂剂,能够增加材料的酸性位点. 相比于Fe、Cr、Ni等对CeO2的改性效果,Co-CeO2表面酸性位点浓度最高,同时Co2+/Co3+间电荷的转移能促进电荷转移和Ce3+形成,具有最佳的NO氧化性能提升效果[41]. Mn也具有多变价态,Li等[42]利用Ce改性MnOx,Ce的掺入提高了MnOx的比表面积,优化了其在低温段催化NO氧化的表现. 虽然过渡金属氧化物催化剂的研究取得不错的进展,但相比于贵金属催化剂,其抗H2O和SO2中毒能力较差[43-44],还无法满足实际应用的需求.
-
(1)铈基材料上的PM氧化过程
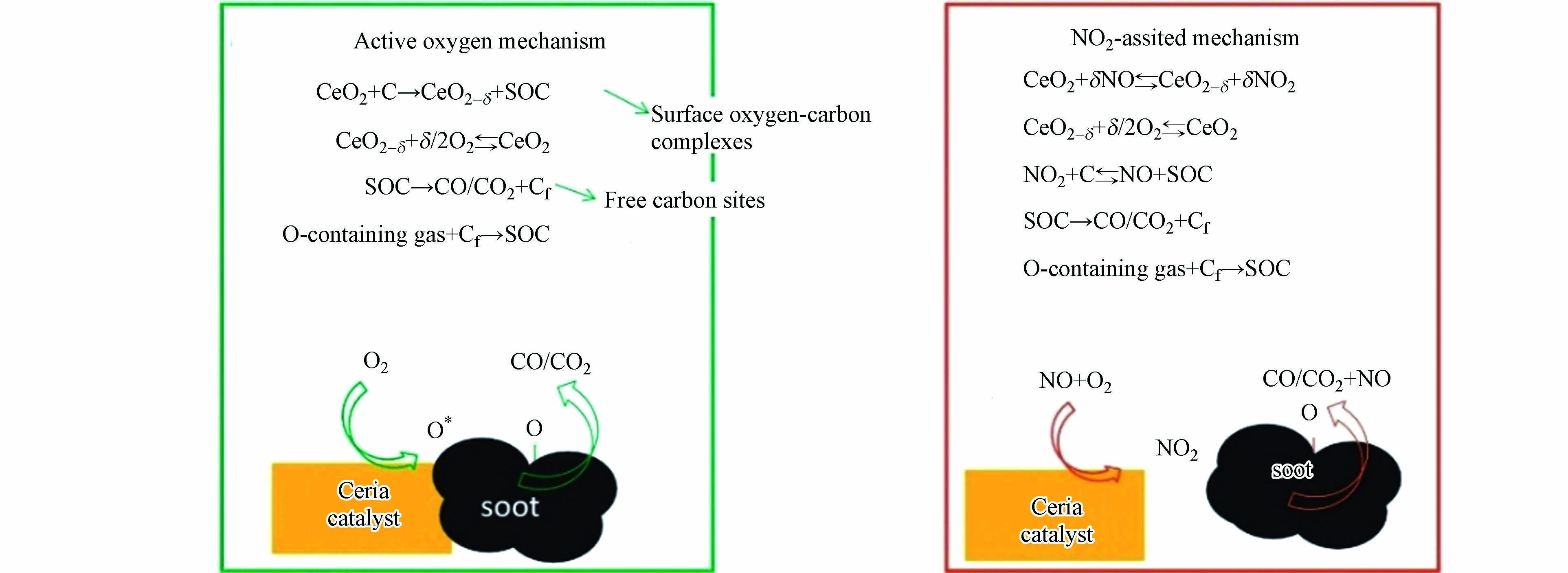
通常PM在CeO2上的氧化过程通过活性氧参与的MvK机理进行. 倘若尾气中存在一定的NOx时,CeO2能够与NOx反应形成表面碳氧物种(SOC),即通过NOx参与的增强MvK机理发生PM氧化反应[45],从而降低催化剂的起燃温度并且提升催化活性(图5).
不同结构CeO2的表面缺陷位存在差异,会显著影响其碳烟氧化性能. CeO2的不同暴露晶面具有不同的表面能和氧空位形成能,因此具有特定形貌的CeO2在氧活化能力上有较大差异(表2). 此外,具有高比表面积的多孔铈基材料能够暴露更丰富的表面活性位点,使得PM能够更充分与活性位点接触参与反应,同时O2的活化效率也得到提高,进而扩大催化剂的工作窗口[47-48].
(2)稀土金属改性的铈基催化剂
由于镧系收缩现象的存在,稀土元素的改性能够诱导CeO2晶格中形成畸变和缺陷,并促进气相氧在表面的吸附和活化. Harada等[51]通过Pr和La的改性极大地增强了CeO2体相氧的流动性,相比于纯CeO2的PM氧化活化能(Ea=311 kJ·mol−1),掺杂Pr、La后催化剂的表观活化能下降至135 kJ·mol−1. 研究发现,Sm[52]、Y[53]、Eu[54]、Yb[55]等稀土金属的掺杂都有类似的效果,这进一步佐证了促进O2活化对提高PM去除效率的重要性.
(3)贵金属改性的铈基催化剂
贵金属所具有的良好氧化性能使其除了在CO、HCs氧化中表现优异外,在PM消除中同样出色,如Rh/CeO2极低的表面缺陷位形成能可以促进O2在表面的活化,这使得Rh-Ce催化剂具有非常优异的催化性能. Pt也是催化碳烟燃烧的常用催化剂组分,其能够促进O2在表面的吸附解离并形成活性氧物种,这直接提升了催化剂碳烟燃烧活性. 同时Pt也能够将部分NO氧化成为NO2,从而使得PM氧化以NOx参与的增强MvK机理进行.
Ag具有良好的电子交换能力,其与CeO2能够形成较强的界面相互作用,这不仅能够促进表面氧空位的形成,还会影响表面Ag物种的价态[56]. 虽然Ag+被认为是高活性物种,Ag0在催化过程中依然扮演了非常重要的角色. Ag+与O更为紧密的结合抑制了其与PM的接触,而Ag0物种则恰好弥补了这个缺陷. Ag0/Ag+氧化还原对在催化过程中分别起到了“PM捕集者”和“活性氧物种生产者”的功能. 总之,只有对催化剂表面金属与载体间结构进行合理地调控,才能使催化剂在反应中达到理想的催化效率.
(4)碱金属改性的铈基催化剂
碱金属物种的熔沸点低,能够在CeO2表面发生迁移,将其用于铈基材料的改性中能使催化剂与PM接触更为充分,同时还能够提升催化剂氧化还原性能,是一种良好的助剂[57]. 如K能够提升催化剂表面氧物种流动性,同时可与PM氧化产生的CO2形成K2CO3,其在高温下与尾气中的NO2能形成KNO3物种,通过K2CO3 - KNO3物种间的循环,PM的氧化过程得到了有效增强[58]. 此外,除K外,Li、Na、Cs等碱金属同样表现出对碳烟燃烧氧化的促进作用[59].
(5)过渡金属改性的铈基催化剂
利用过渡金属对CeO2进行改性所制得的铈基材料在催化碳烟反应中表现出更为复杂的反应特性. 铈锆固溶体具有较强的氧化还原性能,如Zhang等[60]合成的具有三维孔道结构的Ce0.7Zr0.3O2表现出优异的PM燃烧活性. Mn很容易通过Mn-Ce间电子交换作用使铈基材料表现出更强的氧化还原能力. Ce3+-Ce4+及Mnδ+-Cen+间的电子迁移能促进氧在表面的活化,同时尾气中的NOx容易被Mn活化形成硝酸盐物种,从而促进PM氧化反应进行[61]. 除此之外,Cu、Co、Fe等过渡金属在碳烟燃烧中也具有非常好的表现[62-65]. 不难发现,过渡金属改性的CeO2可以促进O、NO等物种的吸附活化,结合对材料结构的合理调控,通过多机理协同作用,提升了PM的催化燃烧效率.
-
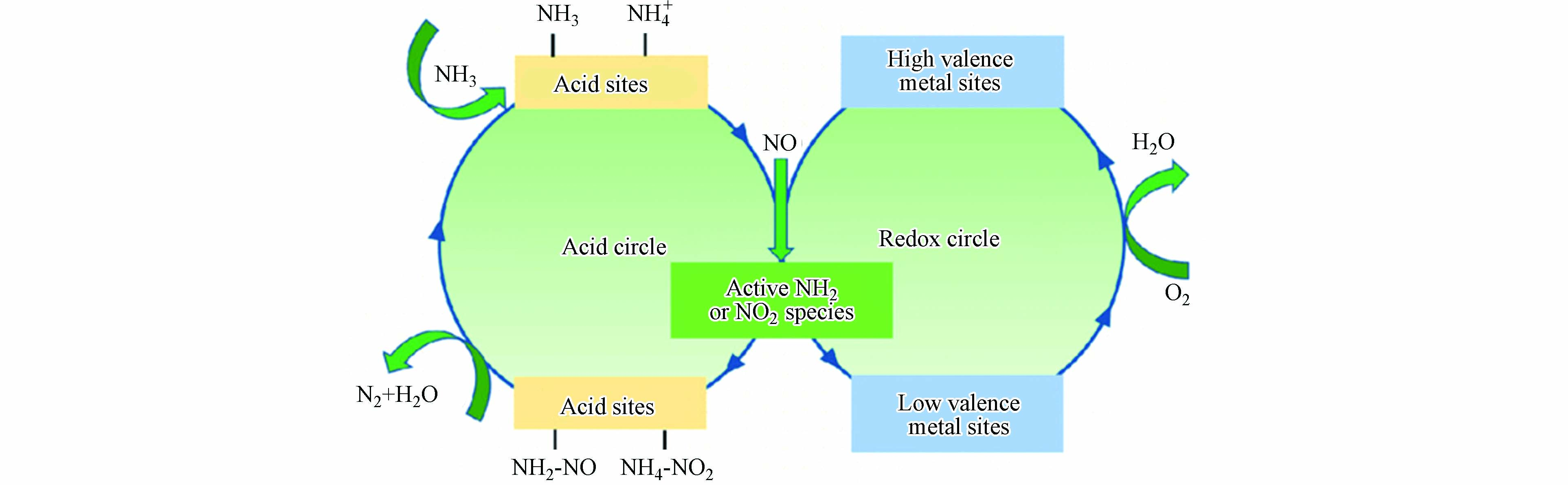
为减少柴油车NOx排放,目前采用的技术手段主要包括废气再循环(EGR)、稀燃NOx捕集(LNT)、NOx储存还原(NSR)、选择性催化还原(SCR)等. 其中SCR技术成熟度高、消除效果好,成为目前机动车厂商广泛选用的尾气后处理手段. NH3-SCR催化剂上发生的反应主要为:
NH3-SCR反应过程主要包括酸性循环和氧化还原循环(图6),其中酸性循环对NH3进行吸附和活化,氧化还原循环使NH3和NOx物种发生反应[66],要达到较好的NOx去除效果就必须要求催化剂表面具有适当的酸性位点和氧化还原位点. 就目前工业应用来说,钒钨钛(VWTi)催化剂热稳定性好,抗硫性能佳,是一种应用极为广泛的NH3-SCR催化剂,但其工作温度窗口窄、具有生物毒性,且热稳定性差. 对于Cu-SSZ-13、ZSM-5等分子筛类催化剂来说,其能够提供较宽的工作窗口和低温活性,因此在机动车SCR领域广受欢迎. 而氧化铈能够提供一定酸性位,同时具有良好的电子传递特性,可以作为一种良好的助剂来进一步提升分子筛的NH3-SCR性能.
(1)铈改性分子筛催化剂
目前广泛用于柴油车尾气中NOx催化消除的是各类Cu基和Fe基分子筛催化剂[67-68]. 分子筛催化剂具有较大的比表面积、较强的表面酸性和较高的热稳定性等特点. 同时,分子筛催化剂在中高温下(> 200 oC)具有优越的NH3-SCR活性和N2选择性. 人们发现, CeO2改性的分子筛具有更优异的性能,其低温活性和水热稳定性得到进一步增强,且拓宽了工作温度窗口.
Chen等[69]通过用CeO2改性Fe-ZSM-5催化剂,获得了一种低温活性更好、抗H2O能力更强、温度窗口更宽的Fe-ZSM-5@CeO2催化剂. CeO2与Fe-ZSM-5之间的相互作用有利于Ce3+/Ce4+氧化还原循环的进行和活性氧物种的产生,增强了NO向NO2的转化. 这能推动催化剂上的NH3-SCR反应更多地遵循快速SCR反应路线. Liu等合成一种CeO2包裹层厚度可控的Fe-Beta@CeO2催化剂. 适当厚度的CeO2包裹层可以改善Fe-Beta催化剂的酸性和氧化还原能力,在较宽的温度范围内(225—565 oC)表现出良好的催化活性和抗水抗硫性能[70]. Wang等[71]发现向Cu-SSZ-13内添加Ce能够大幅提升其催化活性和水热稳定性,同时创造了更丰富的酸性位点和活性物种,在提高NOx去除效率的同时具有较高的N2选择性,Usui等[72]也得到类似的结果. Guan等[73]发现CeO2修饰有利于增强分散态Cu2+物种的稳定性,同时可以抑制分子筛骨架脱铝,对Cu/SAPO-34催化剂的催化活性和水热稳定性同样具有促进作用. 此外,通过CeO2修饰还可以提升分子筛催化剂的抗积碳和抗碱金属中毒性能. Martinovic等[74]发现通过球磨法制备了CeO2-SnO2修饰的Cu-SSZ-13催化剂,其表现出更强的抗积碳作用,而Guo等[75]研究还发现CeO2修饰的Cu-SSZ-13催化剂还可以表现出优良的抗K中毒性能.
(2)过渡金属氧化物改性铈基催化剂
纯CeO2的SCR性能较差,当以负载或掺杂的方式向CeO2基材料中引入酸性位点,如:WO3、MoO3、Nb2O5等酸性金属氧化物或SO42-、PO43-等酸性基团,可以大大改善其NH3-SCR反应性能[76-78],目前研究比较广泛的是Ce-Zr、Ce-Mn、Ce-Ti等复合金属氧化物催化剂.
Zr掺杂制备的铈锆固溶体能够提高材料的热稳定性和氧化还原性能,通过Mo和W的掺杂能够增加其表面酸性位点的数量,促进NH3在表面的吸附,W还能够将部分NO氧化成为NO2,促使反应以快反应机理进行[79]. Ali等[80]制备了Cu0.2Ce0.3Zr0.5用于NH3-SCR反应,Cuδ+和Cen+之间的电子迁移极大促进了氧化还原反应的进行,单齿碳酸盐和桥式碳酸盐是SCR反应中的高活性物种. 同样,具有更多可变价态的Mn也能够与Ce通过有效的协同作用促进活性中间物种的形成,Mnδ+能够吸附NO形成NO+中间体,与Cen+表面所产生的活性氧物种相互作用生成NO2及吸附态硝酸盐物种,两者的协同共同促进尾气中NOx物种的消除. 相比于CeO2,Mn的掺杂降低了N-H断裂能垒,使得SCR过程能够在更低的温度下进行[81].
近年来,人们发现铈钛材料在NH3-SCR反应中表现出优异的反应活性和NOx去除效率,铈钛固溶体中的Ce-O-Ti结构不仅能诱导形成氧缺陷,还能够活化吸附的NO形成硝酸盐物种[82]. 相比于传统的钒钨钛和Fe-ZSM-5催化剂较高的工作温度区间,Shan等[83]合成的Ce-Ti在250 oC下即表现出较高的NOx转化率和N2选择性. 因此,CeTi作为一种高效的NH3-SCR催化剂和环境友好的材料,是未来移动源SCR中极具潜力的催化剂之一.
(3)高抗硫活性的铈基氧化物催化剂
需要指出的是,尾气中含有的微量SO2对于NH3-SCR催化剂是一种毒性物种,会引起催化剂的中毒失活. Zhang等[84-85]研究发现,CeO2的适度硫酸化能够形成表面硫酸盐,并促进反应的进行,但体相硫酸盐的形成则会导致催化剂中毒失活,而通过TiO2表面修饰可以抑制CeO2在反应过程中被SO2深度硫酸化,增强了铈基催化剂的抗硫性能. Tan等[86]还将常作为TWC催化剂中重要助剂的铈锆固溶体(CeZrOx)用于NH3-SCR中,得益于Zr体相掺杂固溶体材料硫酸化后可以生成较强的酸性位,材料也表现出优异的抗硫性能.
NH3-SCR催化剂的抗硫性能在很大程度上取决于SO2的吸附特性和反应机理,如果可以有效阻碍SO2吸附,则铈基NH3-SCR催化剂在SO2存在下将表现出更好的催化活性. 此外,考虑到活性硝酸盐种类难以吸附在催化剂的硫酸化表面上,E-R机理将是一条更有效的途径,因为在E-R反应路径中,气态的NOx可直接参与NH3-SCR反应. 基于对NH3-SCR催化剂的反应机理和硫中毒机理的理解,Tan等[87]设计制备了一种具有独特的Ce-O-Si结构和丰富的表面羟基的CeO2-SiO2复合氧化物催化剂. 这种特殊的表面结构不仅可以通过阻止惰性硝酸盐的吸附并改善表面酸性来提高NH3-SCR性能(<300 oC),而且还可以通过抑制SO2吸附来显著提高催化剂抗硫能力.
-
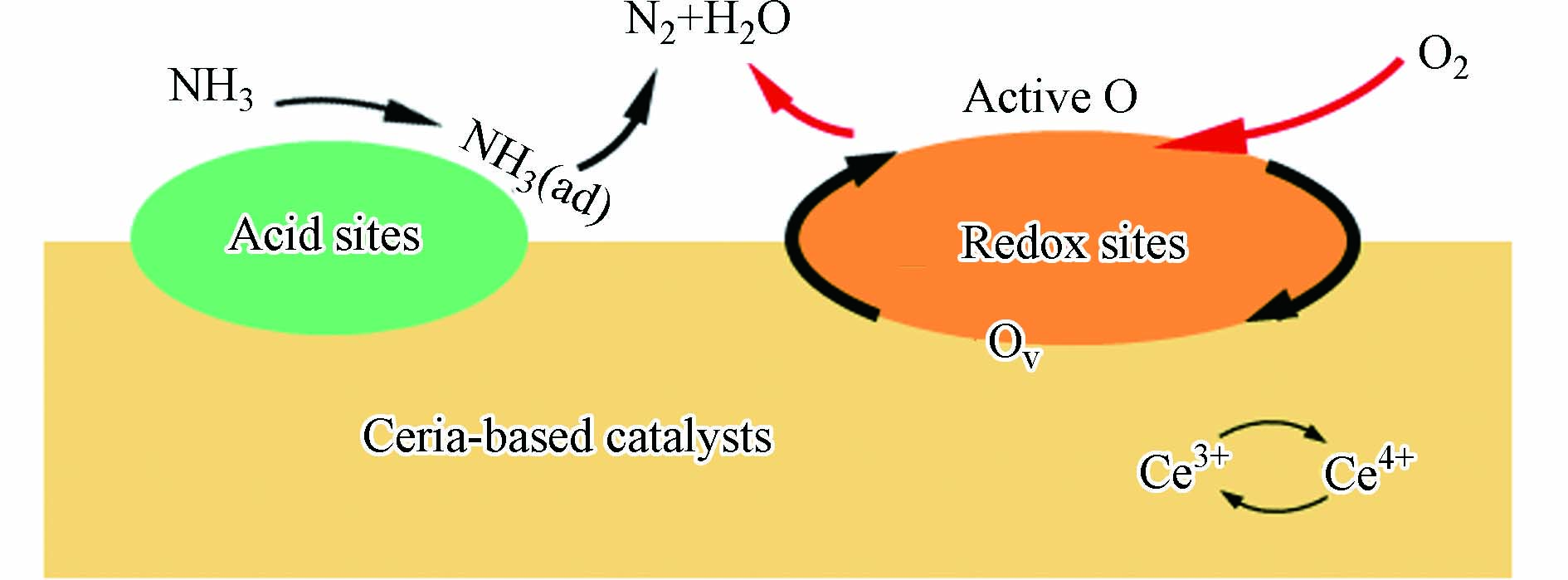
研究表明机动车排放的NH3是城市环境中氨的重要来源. 发动机处于高负荷运行或是贫氧工作状态下尾气中的NOx能够与H2反应形成NH3,三效催化剂在催化过程中发生副反应也会生成NH3[88],柴油车SCR系统中的NH3泄露也是重要的NH3源. 通过在机动车后安装ASC对尾气中的NH3进行催化处理是主要的净化手段,目前已经进行系统研究的氨氧化催化剂载体以Al2O3、ZSM-5、HY分子筛为主. 相较之下,铈基氧化物催化剂在氨氧化领域仍旧表现出非常大的发展潜力. Cu[89]、Ni[90]、Ti[91]改性的铈基氧化物催化剂能够与铈产生电子与几何结构上的作用,在NH3选择性氧化反应上表现出优良的催化活性.
作为一种碱性物质,NH3在催化剂表面的吸附活化涉及到两大活性位点:酸性位点和氧化还原位点. NH3能够有效结合在酸性位点上,同时在氧化还原位点的作用下发生活化,参与后续的氧化反应(图7). 早期的催化剂主要以Pt和Pd为催化活性物种,传统的Pt/Al2O3催化剂在较低温度(< 200 oC)下,催化活性较低,NH3无法得到有效去除. 随着温度升高,催化剂反应选择性也会发生下降,NH3会被氧化形成N2O,NOx等其他污染物[92]. 随着近年来对铈基材料的研究不断深入,人们发现当铈基材料用于改性载体时这些问题能够得到缓解,通过CeO2对储释氧过程的调节能够使得NH3在不同工况下都能够得到较好的消除,并因此体现出更大的工业应用价值. Chang等[93]将CeO2-SiO2作为载体替代Al2O3 负载Pt用于NH3氧化. CeO2以小团簇形态分散在SiO2上,这样的结构能够提供更多的酸性位点,促进NH3在表面的吸附. 在Pt-O-Ce结构的相互作用下,载体表面可形成丰富的氧缺陷,在促进N—H键的活化同时提供丰富的活性位以促进氧化反应进行,同时表面的氧化态Ptδ+物种能够诱导N2物种的形成,表现出良好的N2选择性.
在Cu-CeO2材料中[89],表面的CuO能够捕集活化NH3形成Cu-NH3配合物,而CeO2能够向表面提供活性氧物种. 在表面吸附的NH3会被活化形成NHx和HNO中间体并在进一步升温下氧化形成硝酸盐. 此时,硝酸盐中间物种能够通过iSCR机理与NH3反应生成N2和H2O. 除了NH3在铈基材料表面的吸附活化,活性氧物种在表面的氧化也是NH3-SCO反应的重要步骤. 在Cu-CeO2中,Cu进入CeO2的晶格中形成Cu2+-O-Ce4+结构. 环境条件的变化能够促使电荷和氧在其中迁移,形成Ce3+-□-Cu+等晶格缺陷. 这些缺陷位点能够诱导尾气中的氧气遵循下列路径从而在催化剂表面形成活性氧物种[94-95]:
若尾气中的O2浓度不足以在表面活化并支撑尾气中的NH3发生进一步氧化,Cu-CeO2晶相中的Cu2+-O-Ce4+甚至能够通过自身的氧化还原来贡献O2并在表面形成活性氧物种:
在尾气中O2浓度波动时,铈基材料能够利用自身良好的储释氧特性通过不同途径在表面构建活性氧物种,以推动氨氧化进行,铜铈间的协同作用是其表现出高NH3氧化活性的核心与关键.
-
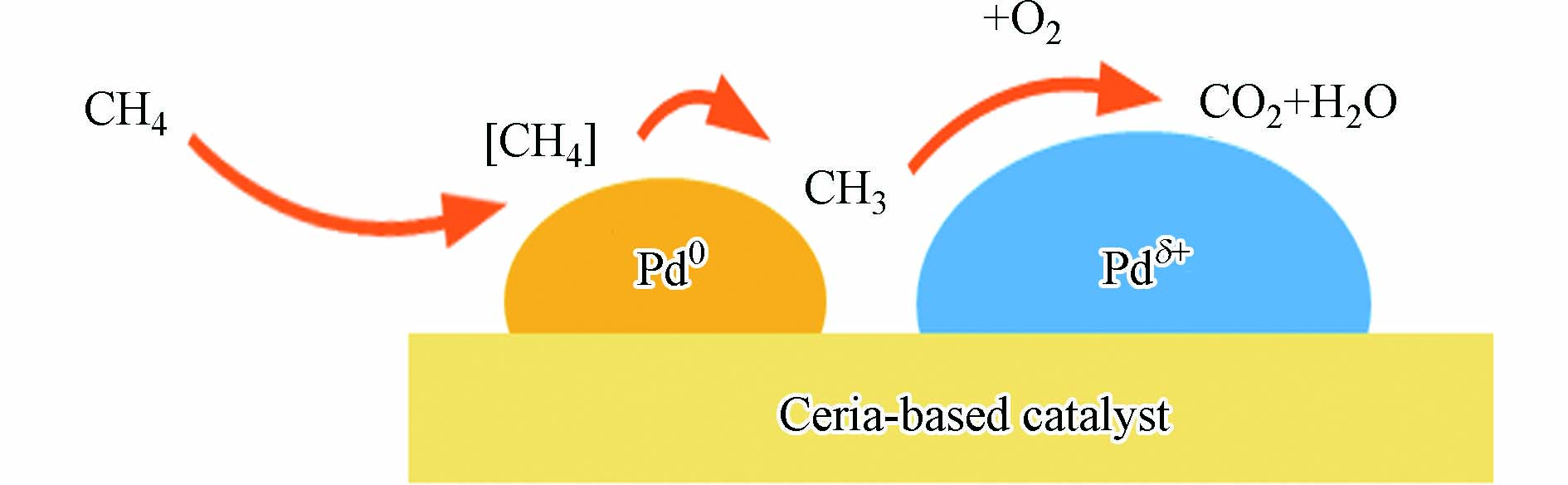
相比于汽柴油车,天然气车尾气中的碳氢化合物主要为CH4. CH4的C—H键非常稳定,需要更高的反应温度才能充分氧化. 天然气车的尾气催化涉及到如下CH4氧化过程:
目前人们对于提高天然气尾气催化剂的低温氧化活性以及稳定性做了大量的研究,以期在提高天然气汽车尾气的处理效果的同时降低生产成本. 天然气车尾气催化剂通常以氧化铈为载体,向其中掺杂Zr等过渡金属及La、Y等稀土金属作为改性剂,同时在表面负载以Pd、Rh为主的贵金属作为活性组分. 这些贵金属能够诱导C—H键断裂并形成CH3和H物种[96]. 图8给出了Pd/CeO2表面CH4氧化的机理:CH4首先在Pd0颗粒表面吸附解离,活化形成的CH3物种会在Pdδ+上与活性氧反应,完成CH4的氧化循环. 但相比于PdO,PdxCe1-xO2上的Pdδ+物种具有更低的甲烷氧化能垒[97]. 这意味着对于同样的Pdδ+物种,当其与CeO2间形成更强的作用,即Pd更多地形成PdxCe1-xO2固溶体(如制备具有丰富缺陷位的CeO2载体[98]、调节煅烧温度[99]、利用掺杂改性载体[100]等)会更有利于反应的进行. 固溶体所诱导产生的丰富结构畸变和电子迁移变化会促进Ce3+-Ce4+的转变,这也能够促进活性氧的迁移,实现CH4的高效氧化.
除贵金属外,过渡金属修饰的铈基催化剂也得到了深入的研究. Qiao等[101]制备了一系列Ce1-xFexO2催化剂,当Fe掺杂量低于10%时,Fe与CeO2能够形成固溶体,而更高载量的Fe则会堆积在CeO2表面形成α-Fe2O3,表面覆盖的α-Fe2O3会抑制CH4氧化的进行,还降低了材料的比表面积,阻碍氧的流动. 对Sn来说,Sn/Ce=7:3的Sn-Ce催化剂具有最佳的CH4消除性能[102].
-
机动车尾气的催化消除技术一直伴随着汽车行业的发展和环保法规的施行不断进步. 随着国VI标准的实施,尾气中污染物的排放限值愈发严格,CeO2作为最早在机动车后处理系统中得到应用的材料之一将会在其中发挥越来越大的作用. 我国有丰富的稀土资源,而其中铈的储量最为丰富. 文章对铈基材料在机动车后处理系统中的应用进行了整理归纳和总结,在这些催化剂中,铈作为一种良好的电子助剂、结构改性剂在催化过程中起到了重要的作用. 尽管铈在机动车尾气处理中发挥了不可或缺的作用,但着眼于未来的发展趋势,依然有不少问题亟待解决.
在机动车实际运行工况条件下,尾气温度可达上千摄氏度,同时燃油燃烧会产生大量水汽,这意味着设计具有高水热稳定性的稀土铈基催化材料具有非常重要的现实意义. 此外,机动车冷启动等工况下所产生的污染物由于催化剂低温活性的限制难以被有效处置. 针对中国目前的道路交通情况来看,大量机动车在冷启动阶段排放的过量污染物给城市大气环境造成了显著影响,美国也提出机动车尾气净化的“150 oC挑战”[103],但目前催化剂在低温段的活性仍然不尽人意. 虽说已有研究通过预活化处理的手段提升催化剂具有的低温反应活性,但其在机动车运行条件下多次高温循环后的催化稳定性依旧值得商榷. 这不仅要求催化剂具有较宽工作温度窗口,对其循环寿命也提出了考验.
贵金属材料被认为是机动车尾气催化中必不可少的组分之一,相比于其他金属,由于铂、钯、铑等几种贵金属在在目前机动车后处理催化剂领域几乎是不可替代的存在,全球每年所生产的这几种贵金属绝大多数都用于尾气后处理工业. 而贵金属的价格也随着机动车工业的发展水涨船高,近年来更是成倍增长,因此贵金属的价格将直接影响催化剂的成本. 与贵金属相比,Cu、Mn等过渡金属的工业使用具有非常高的性价比,利用过渡金属来替代尾气处理系统中的贵金属始终是目前的发展愿景之一. 如果能够设计制备活性媲美贵金属催化剂的过渡金属铈基材料,抑或是能够替代一部分贵金属的用量,将会极大降低尾气催化剂的生产成本,对过渡金属掺杂的铈基材料改性研究在未来将会是极具潜力的发展方向.
除此之外,利用生物柴油、醇类燃油等新型燃料来替代传统化石能源也是行业的发展大趋势,这些新型燃料的应用能够减少NOx及碳烟等污染物的排放. 需要注意的是,生物柴油的组成相较于化石燃料要复杂得多,尾气中会产生更为复杂的芳香烃、羰基化合物等物质. 如何设计更有效的铈基催化剂来对这些复杂挥发性有机污染物(VOCs)进行催化消除也是值得关注的研究方向.
当然也要认识到,在当前“碳中和碳达峰”战略的大背景下,交通领域的绿色转型是必然的结果. 新能源车替代燃油车是个趋势,但这并不意味着燃油车会完全消失,未来对于机动车尾气的治理依然任重而道远.
稀土铈基材料在机动车尾气催化消除中的研究进展
Research progress of rare earth ceria-based materials in the catalytic elimination of vehicle exhaust gas
-
摘要: 机动车尾气污染物造成了严重的生态环境问题,而催化净化是控制尾气排放、减少污染最有效的手段. 铈基材料具有优良的储释氧性能和氧化还原能力,是机动车尾气催化消除领域必不可少的组分之一. 自上世纪七十年代被用于催化消除机动车尾气以来,铈基催化材料得到了广泛关注和研究. 对铈基材料在尾气催化消除领域所起到的作用进行梳理,有助于对现有催化剂进行结构优化,同时能够将铈基材料的应用范围扩大到相关领域. 本文对铈基材料在机动车催化后处理不同环节中的研究和应用进行了归纳,并对其在机动车尾气后处理过程中的反应过程进行了总结. 最后,基于尾气处理行业的发展前景,本文对铈基催化材料未来的发展方向提出了展望.Abstract: Vehicle exhaust pollutants cause serious ecological problems, and catalytic purification is one of the most effective means to control exhaust emissions and reduce pollution. Ceria-based materials have excellent oxygen storage capacity and good redox ability, and are one of the essential components in the field of catalytic elimination pollutants of vehicle exhausts. Since they have been widely used for the catalytic elimination pollutants of vehicle exhausts in the 1970s, ceria-based catalytic materials have received extensive attention and research. The role of ceria-based materials in the field of exhaust gas catalytic abatement can be reviewed to help optimize the structure of existing catalysts and to expand the application of ceria-based materials to related fields. Herein, we summarize the research and application of ceria-based materials in different aspects of the vehicle exhaust aftertreatment, and the reaction process in the aftertreatment system of vehicle exhaust. Finally, based on the development prospect of the exhaust gas treatment industry, we present a perspective on the future development direction of cerium-based catalytic materials.
-
Key words:
- vehicle exhaust gas /
- catalytic elimination /
- rare earth /
- ceria-based materials
-

-
表 1 我国法规体系不同排放控制阶段对应的控制技术路线
Table 1. Vehicle emission control technology in different regulation stages in China
汽油车
Gasoline vehicles轻型柴油车
Light-duty diesel vehicles重型柴油车
Heavy-duty diesel vehicles国IV 控制对象 CO/HCs/NOx CO/HCs/PM NOx 技术路线 TWC DOC 或DOC+POC VWTi-SCR 国V 控制对象 CO/HCs/NOx CO/HCs/PM NOx 技术路线 TWC DOC+DPF VWTi-SCR 国VI 控制对象 CO/HCs/NOx/PM CO/HCs/NOx/PM 技术路线 传统:TWC
直喷:TWC+GPF(CGPF)LNT+DPF+SCR 或DOC+SCRF+SCR DOC+DPF+SCR+ASC 表 2 具有特定形貌及暴露晶面的CeO2的性质及碳烟氧化性能对比
Table 2. Comparison on property and soot oxidation performance of CeO2 with specific morphologies and exposed facets
-
[1] ŁAMACZ A, KRZTOŃ A, DJÉGA-MARIADASSOU G. Study on the selective catalytic reduction of NO with toluene over CuO/CeZrO2. A confirmation for the three-function model of HC-SCR using the temperature programmed methods and in situ DRIFTS [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 142-143: 268-277. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.030 [2] SU Y X, WEN N N, CHENG J H, et al. Experimental study on SCR-C3H6 over Cu–Fe/Al-PILC catalysts: Catalytic performance, characterization, and mechanism [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(33): 14776-14788. [3] DING W C, LI W X. First-principles study of NO reduction by CO on transition metal atoms-doped CeO2(111) [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(12): 1937-1943. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60169-8 [4] POLYCHRONOPOULOU K, ALKHOORI A A, EFSTATHIOU A M, et al. Design aspects of doped CeO2 for low-temperature catalytic CO oxidation: Transient kinetics and DFT approach [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(19): 22391-22415. [5] ZHAO S Z, KANG D J, LIU Y P, et al. Spontaneous formation of asymmetric oxygen vacancies in transition-metal-doped CeO2 nanorods with improved activity for carbonyl sulfide hydrolysis [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(20): 11739-11750. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c02832 [6] LEE J H, JO D Y, CHOUNG J W, et al. Roles of noble metals (M = Ag, Au, Pd, Pt and Rh) on CeO2 in enhancing activity toward soot oxidation: Active oxygen species and DFT calculations [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 124085. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124085 [7] KIM J R, LEE K Y, SUH M J, et al. Ceria–zirconia mixed oxide prepared by continuous hydrothermal synthesis in supercritical water as catalyst support [J]. Catalysis Today, 2012, 185(1): 25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.08.018 [8] CUIF J P, BLANCHARD G, TOURET O, et al. (Ce, Zr)O2 solid solutions for three-way catalysts[C]. SAE Technical Paper Series. 400 Commonwealth Drive, Warrendale, PA, United States: SAE International, 1997. [9] LIU C X, ZHOU J Y, MA H F, et al. Antisintering and high-activity Ni catalyst supported on mesoporous silica incorporated by Ce/Zr for CO methanation [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(43): 14406-14416. [10] LIU Y, ZHAI Y Q, LI Y D. Preparation of Ce-Zr-O solid solution [J]. Reaction Kinetics and Catalysis Letters, 2004, 82(2): 295-302. doi: 10.1023/B:REAC.0000034840.35124.1a [11] YUAN Q, LIU Q, SONG W G, et al. Ordered Mesoporous Ce1-xZrxO2 solid solutions with crystalline walls [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(21): 6698-6699. doi: 10.1021/ja070908q [12] YU Q, WU X X, YAO X J, et al. Mesoporous ceria-zirconia-alumina nanocomposite-supported copper as a superior catalyst for simultaneous catalytic elimination of NO-CO [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2011, 12(14): 1311-1317. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2011.05.002 [13] dos SANTOS XAVIER L P, RICO-PÉREZ V, HERNÁNDEZ-GIMÉNEZ A M, et al. Simultaneous catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons and soot with Ce-Zr-Nd mixed oxides in simulated diesel exhaust conditions [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 162: 412-419. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.07.013 [14] FRIZON V, BASSAT J M, POLLET M, et al. Tuning the Pr valence state to design high oxygen mobility, redox and transport properties in the CeO2–ZrO2–PrOx phase diagram [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(11): 6351-6362. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b11469 [15] CHENG Y, SONG W Y, LIU J, et al. Simultaneous NOx and particulate matter removal from diesel exhaust by hierarchical Fe-doped Ce-Zr oxide [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(6): 3883-3892. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b03387 [16] FORNASIERO P, KASPAR J, SERGO V, et al. Redox behavior of high-surface-area Rh-, Pt-, and Pd-loaded Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 mixed oxide [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1999, 182(1): 56-69. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1998.2321 [17] WU J, O’NEILL A E, LI C H, et al. Superior TWC activity of Rh supported on pyrochlore-phase ceria zirconia [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021, 280: 119450. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119450 [18] CUI B, YAN S, XIA Y K, et al. CuxCe1-xO2 nanoflakes with improved catalytic activity and thermal stability for diesel soot combustion [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2019, 578: 20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2019.03.025 [19] ZHANG L, SPEZZATI G, MURAVEV V, et al. Improved Pd/CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature NO reduction: Activation of CeO2 lattice oxygen by Fe doping [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(9): 5614-5627. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.1c00564 [20] DENG Y Q, SHI X B, WEI L Q, et al. Effect of intergrowth and coexistence CuO-CeO2 catalyst by grinding method application in the catalytic reduction of NOx by CO [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 869: 159231. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159231 [21] CAO Y, LIU L J, GAO F, et al. Understanding the effect of CuO dispersion state on the activity of CuO modified Ce0.7Zr0.3O2 for NO removal [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 403: 347-355. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.212 [22] JEON J, HAM H, XING F L, et al. PdIn-based pseudo-binary alloy as a catalyst for NOx removal under lean conditions [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(19): 11380-11384. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c03427 [23] LI Z L, CHENG H, ZHANG X B, et al. CuW/CeZr catalysts: A dual-function catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO and CO oxidation under oxygen-rich conditions [J]. Catalysis Letters, 2021, 151(11): 3361-3371. doi: 10.1007/s10562-021-03562-3 [24] LIU Z S, YU F, PAN K K, et al. Two-dimensional vermiculite carried CuCoCe catalysts for CO-SCR in the presence of O2 and H2O: Experimental and DFT calculation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 422: 130099. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130099 [25] LAN L, CHEN S H, ZHAO M, et al. The effect of synthesis method on the properties and catalytic performance of Pd/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2-Al2O3 three-way catalyst [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2014, 394: 10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.06.032 [26] LIU Y N, YANG J, YANG J, et al. Understanding the three-way catalytic reaction on Pd/CeO2 by tuning the chemical state of Pd [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 556: 149766. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149766 [27] KIBIS L S, SVINTSITSKIY D A, DEREVYANNIKOVA E A, et al. From highly dispersed Rh3+ to nanoclusters and nanoparticles: Probing the low-temperature NO+CO activity of Rh-doped CeO2 catalysts [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 493: 1055-1066. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.07.043 [28] ZHENG T T, LU B, HARLE G, et al. A comparative study of Rh-only, Pd-only and Pd/Rh catalysts [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2020, 602: 117649. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117649 [29] WANG T, CHEN K, ZHOU R X. Pt–Pd bimetallic effect in PtxPd1–x/(Ce, Zr, La)O2 catalysts for NOx, HC and CO elimination [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, 11(8): 2782-2791. [30] JEONG H, KWON O, KIM B S, et al. Highly durable metal ensemble catalysts with full dispersion for automotive applications beyond single-atom catalysts [J]. Nature Catalysis, 2020, 3(4): 368-375. doi: 10.1038/s41929-020-0427-z [31] MEUNIER F C, CARDENAS L, KAPER H, et al. Synergy between metallic and oxidized Pt sites unravelled during room temperature CO oxidation on Pt/ceria [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2021, 60(7): 3799-3805. doi: 10.1002/anie.202013223 [32] TAN W, XIE S H, CAI Y D, et al. Transformation of highly stable Pt single sites on defect engineered ceria into robust Pt clusters for vehicle emission control [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(18): 12607-12618. [33] TAN W, ALSENANI H, XIE S H, et al. Tuning single-atom Pt1–CeO2 catalyst for efficient CO and C3H6 oxidation: Size effect of ceria on Pt structural evolution [J]. ChemNanoMat, 2020, 6(12): 1797-1805. doi: 10.1002/cnma.202000431 [34] NIE L, MEI D, XIONG H, et al. Activation of surface lattice oxygen in single-atom Pt/CeO2 for low-temperature CO oxidation [J]. Science, 2017, 358(6369): 1419-1423. doi: 10.1126/science.aao2109 [35] JIANG D, YAO Y, LI T, et al. Tailoring the local environment of platinum in single-atom Pt1/CeO2 catalysts for robust low-temperature CO oxidation [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2021, 60(50): 26054-26062. doi: 10.1002/anie.202108585 [36] JEONG H, SHIN D, KIM B-S, et al. Controlling the oxidation state of Pt single atoms for maximizing catalytic activity [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2020, 59(46): 20691-20696. doi: 10.1002/anie.202009776 [37] WANG T, GUO X L, LIN S Y, et al. Effect of PdOx structure properties on catalytic performance of Pd/Ce0.67Zr0.33O2 catalyst for CO, HC and NOx elimination [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2019, 37(7): 706-713. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2018.10.017 [38] MAILLET T, SOLLEAU C, BARBIER J Jr, et al. Oxidation of carbon monoxide, propene, propane and methane over a Pd/Al2O3 catalyst. Effect of the chemical state of Pd [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 1997, 14(1): 85-95. [39] QI L, YU Q, DAI Y, et al. Influence of cerium precursors on the structure and reducibility of mesoporous CuO-CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 119-120: 308-320. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.029 [40] LEFORT I, HERREROS J M, TSOLAKIS A. Reduction of low temperature engine pollutants by understanding the exhaust species interactions in a diesel oxidation catalyst [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(4): 2361-2367. [41] SHANG D H, ZHONG Q, CAI W. High performance of NO oxidation over Ce-Co-Ti catalyst: The interaction between Ce and Co [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 325: 211-216. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.056 [42] LI H, TANG X L, YI H H, et al. Low-temperature catalytic oxidation of NO over Mn-Ce-Ox catalyst [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28(1): 64-68. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(09)60052-1 [43] 夏斌, 童志权, 黄妍, 等. CuSO4-CeO2/TS催化氧化NO及其抗H2O和SO2毒化性能 [J]. 过程工程学报, 2010, 10(1): 142-148. XIA B, TONG Z Q, HUANG Y, et al. Catalytic oxidation of NO over CuSO4-CeO2/TiO2 catalyst and its property against the effcts of H2O and SO2 [J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2010, 10(1): 142-148(in Chinese).
[44] WANG Z, SUN X Y, LIU J, et al. The NO oxidation performance over Cu/Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 catalyst [J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2017, 6: 103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2016.12.003 [45] 彭超, 于迪, 王斓懿, 等. 铈基氧化物催化燃烧柴油机炭烟颗粒的性能及机理研究进展 [J]. 中国科学:化学, 2021, 51(8): 1029-1059. doi: 10.1360/SSC-2021-0093 PENG C, YU D, WANG L Y, et al. Recent advances in performances and mechanisms of cerium-based oxide catalysts for catalytic combustion of soot particles released from diesel engines [J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2021, 51(8): 1029-1059(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SSC-2021-0093
[46] BUENO-LÓPEZ A. Diesel soot combustion ceria catalysts [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 146: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.02.033 [47] DAI Y Q, TIAN J L, FU W L. Shape manipulation of porous CeO2 nanofibers: Facile fabrication, growth mechanism and catalytic elimination of soot particulates [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(14): 10141-10152. doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-03648-9 [48] WEI Y C, JIAO J Q, ZHANG X D, et al. Catalysts of self-assembled Pt@CeO2–δ rich core–shell nanoparticles on 3D ordered macroporous Ce1–xZrxO2 for soot oxidation: Nanostructure-dependent catalytic activity [J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(13): 4558-4571. doi: 10.1039/C7NR00326A [49] FOO G S, HOOD Z D, WU Z L. Shape effect undermined by surface reconstruction: Ethanol dehydrogenation over shape-controlled SrTiO3 nanocrystals [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(1): 555-565. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b03341 [50] JIAN S Q, YANG Y X, REN W, et al. Kinetic analysis of morphologies and crystal Planes of nanostructured CeO2 catalysts on soot oxidation [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 226: 115891. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2020.115891 [51] HARADA K, OISHI T, HAMAMOTO S, et al. Lattice oxygen activity in Pr- and La-doped CeO2 for low-temperature soot oxidation [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(1): 559-568. doi: 10.1021/jp410996k [52] RANGASWAMY A, SUDARSANAM P, REDDY B M. Rare earth metal doped CeO2-based catalytic materials for diesel soot oxidation at lower temperatures [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2015, 33(11): 1162-1169. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60541-X [53] ATRIBAK I, BUENO-LÓPEZ A, GARCÍA-GARCÍA A. Role of yttrium loading in the physico-chemical properties and soot combustion activity of ceria and ceria-zirconia catalysts [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2009, 300(1): 103-110. [54] VINODKUMAR T, KUMAR J K P, REDDY B M. Supported nano-sized Ce0. 8Eu0.2O2-δ solid solution catalysts for diesel soot and benzylamine oxidations [J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2021, 133(3): 1-10. [55] MAŁECKA M A, KRASZKIEWICZ P, BEZKROVNYI O. Catalysis by shapely nanocrystals of the Ce1−xYbxO2−x/2 mixed oxides—Synthesis and phase stability [J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 155: 109796. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2019.109796 [56] GRABCHENKO M V, MAMONTOV G V, ZAIKOVSKII V I, et al. The role of metal-support interaction in Ag/CeO2 catalysts for CO and soot oxidation [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 260: 118148. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118148 [57] SHUKLA P C. Non-Noble Metal-Based Catalysts for the Application of Soot Oxidation Advanced Engine Diagnostics[M], 2019. [58] SHAN W, YANG L, MA N, et al. Catalytic activity and stability of K/CeO2 catalysts for diesel soot oxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis. 2012, 33(4), 970-976. [59] LIANG H, WU S T, HONG Y X, et al. Influence of alkali metals with different ionic radius doping into Ce0. 7Zr0. 3O2 on the active oxygen [J]. Catalysis Letters, 2014, 144(4): 685-690. doi: 10.1007/s10562-014-1195-7 [60] ZHANG G Z, ZHAO Z, LIU J, et al. Three dimensionally ordered macroporous Ce1-xZrxO2 solid solutions for diesel soot combustion [J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(3): 457-459. doi: 10.1039/B915027G [61] IL’ICHEV A N, SHIBANOVA M D, UKHARSKII A A, et al. Mechanism of the formation of O2- radical anions on CeO2 and (0.5–10)% CeO2/ZrO2 during the adsorption of an NO-O2 mixture [J]. Kinetics and Catalysis, 2005, 46(3): 387-395. doi: 10.1007/s10975-005-0090-z [62] ZHANG G L, CHENG X, YANG D, et al. Loofa sponage derived multi-tubular CuO/CeO2-ZrO2 with hierarchical porous structure for effective soot catalytic oxidation [J]. Fuel, 2019, 258: 116202. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116202 [63] WANG X, JIN B F, FENG R X, et al. A robust core-shell silver soot oxidation catalyst driven by Co3O4: Effect of tandem oxygen delivery and Co3O4-CeO2 synergy [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 250: 132-142. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.03.019 [64] CUI B, ZHOU L J, LI K, et al. Holey Co-Ce oxide nanosheets as a highly efficient catalyst for diesel soot combustion [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 267: 118670. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118670 [65] LI H C, LI K Z, WANG H, et al. Soot combustion over Ce1-xFexO2-δ and CeO2/Fe2O3 catalysts: Roles of solid solution and interfacial interactions in the mixed oxides [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 390: 513-525. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.08.122 [66] HAN L P, CAI S X, GAO M, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 by using novel catalysts: State of the art and future prospects [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(19): 10916-10976. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00202 [67] SHAN Y L, DU J P, ZHANG Y, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: Opportunities and challenges of Cu-based small-pore zeolites [J]. National Science Review, 2021, 8(10): nwab010. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab010 [68] LIU Q, BIAN C, MING S J, et al. The opportunities and challenges of iron-zeolite as NH3-SCR catalyst in purification of vehicle exhaust [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2020, 607: 117865. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117865 [69] CHEN L, WANG X X, CONG Q L, et al. Design of a hierarchical Fe-ZSM-5@CeO2 catalyst and the enhanced performances for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 957-967. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.055 [70] LIU J X, LIU J, ZHAO Z, et al. Fe-Beta@CeO2 core-shell catalyst with tunable shell thickness for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. AIChE Journal, 2017, 63(10): 4430-4441. doi: 10.1002/aic.15743 [71] WANG J C, PENG Z L, QIAO H, et al. Cerium-stabilized Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for the catalytic removal of NOx by NH3 [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(5): 1174-1182. [72] USUI T, LIU Z D, IBE S, et al. Improve the hydrothermal stability of Cu-SSZ-13 zeolite catalyst by loading a small amount of Ce [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(10): 9165-9173. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b01949 [73] GUAN B, JIANG H, PENG X S, et al. Promotional effect and mechanism of the modification of Ce on the enhanced NH3-SCR efficiency and the low temperature hydrothermal stability over Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2021, 617: 118110. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118110 [74] MARTINOVIC F, DEORSOLA F A, ARMANDI M, et al. Composite Cu-SSZ-13 and CeO2-SnO2 for enhanced NH3-SCR resistance towards hydrocarbon deactivation [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2021, 282: 119536. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119536 [75] GUO D Y, GUO R T, DUAN C P, et al. The enhanced K resistance of Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction by the modification with Ce [J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2021, 502: 111392. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111392 [76] TAN W, WANG J, CAI Y D, et al. Molybdenum oxide as an efficient promoter to enhance the NH3-SCR performance of CeO2-SiO2 catalyst for NOx removal[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021. [77] TAN W, WANG C Y, YU S H, et al. Revealing the effect of paired redox-acid sites on metal oxide catalysts for efficient NOx removal by NH3-SCR [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 125826. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125826 [78] YAO X J, WANG Z, YU S H, et al. Acid pretreatment effect on the physicochemical property and catalytic performance of CeO2 for NH3-SCR [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2017, 542: 282-288. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.06.003 [79] DING S P, LIU F D, SHI X Y, et al. Significant promotion effect of Mo additive on a novel Ce-Zr mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(18): 9497-9506. [80] ALI S, CHEN L Q, YUAN F L, et al. Synergistic effect between copper and cerium on the performance of Cux-Ce0.5-x-Zr0.5 (x = 0.1-0.5) oxides catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 210: 223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.065 [81] HE G Z, GAO M, PENG Y, et al. Superior oxidative dehydrogenation performance toward NH3 determines the excellent low-temperature NH3-SCR activity of Mn-based catalysts [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(10): 6995-7003. [82] XU W Q, YU Y B, ZHANG C B, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over a Ce/TiO2 catalyst [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2008, 9(6): 1453-1457. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2007.12.012 [83] SHAN W P, LIU F D, HE H, et al. An environmentally-benign CeO2-TiO2 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 in simulated diesel exhaust [J]. Catalysis Today, 2012, 184(1): 160-165. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.11.013 [84] ZHANG L, ZOU W X, MA K L, et al. Sulfated temperature effects on the catalytic activity of CeO2 in NH3-selective catalytic reduction conditions [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(2): 1155-1163. doi: 10.1021/jp511282c [85] ZHANG L, LI L L, CAO Y, et al. Getting insight into the influence of SO2 on TiO2/CeO2 for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2015, 165: 589-598. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.10.029 [86] TAN W, WANG J M, LI L L, et al. Gas phase sulfation of ceria-zirconia solid solutions for generating highly efficient and SO2 resistant NH3-SCR catalysts for NO removal [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 388: 121729. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121729 [87] TAN W, LIU A N, XIE S H, et al. Ce-Si mixed oxide: A high sulfur resistant catalyst in the NH3-SCR reaction through the mechanism-enhanced process [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(6): 4017-4026. [88] FRASER M P, CASS G R. Detection of excess ammonia emissions from in-use vehicles and the implications for fine particle control [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1998, 32(8): 1053-1057. [89] ZHANG X Y, WANG H, WANG Z, et al. Adsorption and surface reaction pathway of NH3 selective catalytic oxidation over different Cu-Ce-Zr catalysts [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 447: 40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.220 [90] NASSOS S, SVENSSON E E, BOUTONNET M, et al. The influence of Ni load and support material on catalysts for the selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia in gasified biomass [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2007, 74(1-2): 92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.01.015 [91] LEE S M, LEE H H, HONG S C. Influence of calcination temperature on Ce/TiO2 catalysis of selective catalytic oxidation of NH3 to N2 [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2014, 470: 189-198. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.10.057 [92] GHOSH R S, LE T T, TERLIER T, et al. Enhanced selective oxidation of ammonia in a Pt/Al2O3@Cu/ZSM-5 core–shell catalyst [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(6): 3604-3617. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b04288 [93] CHANG S Y, HARLE G, MA J L, et al. The effect of textural properties of CeO2-SiO2 mixed oxides on NH3-SCO activity of Pt/CeO2-SiO2 catalyst [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2020, 604: 117775. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117775 [94] WANG Z, QU Z, QUAN X, et al. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over CuO-CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by surfactant-templated method [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2013, 134-135: 153-166. [95] QU Z, WANG Z, ZHANG X, et al. Role of different coordinated Cu and reactive oxygen species on the highly active Cu–Ce–Zr mixed oxides in NH3-SCO: a combined in situ EPR and O2-TPD approach [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology. 2016, 6(12): 4491-4502. [96] CHEN H L, LIU S H, HO J J. Theoretical calculation of the dehydrogenation of ethanol on a Rh/CeO2(111) surface [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(30): 14816-14823. doi: 10.1021/jp0610259 [97] MAYERNICK A D, JANIK M J. Methane oxidation on Pd-Ceria: A DFT study of the mechanism over PdxCe1−xO2, Pd, and PdO [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2011, 278(1): 16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.11.006 [98] DUAN D, HAO C X, WANG L Q, et al. Rod-like nanoporous CeO2 modified by PdO nanoparticles for CO oxidation and methane combustion with high catalytic activity and water resistance [J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2019, 14(1): 199. doi: 10.1186/s11671-019-3029-4 [99] WU M W, LI W Z, ZHANG X, et al. Elucidation of the active phase in Pd-based catalysts supporting on octahedral CeO2 for low-temperature methane oxidation [J]. ChemistrySelect, 2021, 6(17): 4149-4159. doi: 10.1002/slct.202100511 [100] CHEN J J, HU W, HUANG F J, et al. Catalytic performance of a Pt-Rh/CeO2-ZrO2-La2O3-Nd2O3 three-way compress nature gas catalyst prepared by a modified double-solvent method [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2017, 35(9): 857-866. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(17)60987-6 [101] QIAO D S, LU G Z, LIU X H, et al. Preparation of Ce1−xFexO2 solid solution and its catalytic performance for oxidation of CH4 and CO [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2011, 46(10): 3500-3506. doi: 10.1007/s10853-011-5256-7 [102] ZENG X R, ZHANG R B, XU X L, et al. Study on ceria-modified SnO2 for CO and CH4 oxidation [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2012, 30(10): 1013-1019. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60171-9 [103] ZAMMIT M, DIMAGGIO C L, KIM C H, et al. Future Automotive Aftertreatment Solutions: The 150 oC Challenge Workshop Report[R]. Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), 2013. -



 下载:
下载: