-
为应对日益增长的污水处理需求,我国城镇污水处理厂的规模不断扩大,污泥产量与日俱增. 据统计,2019年我国污水处理量超过2亿m3·d−1,以污泥含水率为80%计算,同年污泥产量超过6000万t[1]. 污泥是污水处理过程中的副产物,既含有重金属、有机污染物、致病微生物、微塑料等对人体健康和生态环境有害的污染物,又有一定的资源化利用价值. 因此,如何科学、高效、安全地对污泥进行处理处置成为污染防治工作的重中之重.
常用的污泥处理技术包括污泥浓缩、污泥脱水、厌氧消化、好氧堆肥、污泥干化等,常见的污泥处置途径包括土地利用、建材利用、卫生填埋、焚烧等[2]. 据统计,目前我国重点流域的污泥处置方式仍以填埋为主,污泥资源化利用率与发达国家相比仍有较大差距[3],处理处置过程中存在一定的安全隐患和二次污染风险. 为实现污泥的减量化、稳定化、无害化和资源化,改变过去“重水轻泥”的治理现象,住建部和国家发改委相继发布了《“十四五”城镇污水处理及资源化利用发展规划》和《关于加快推进城镇环境基础设施建设指导意见》,明确提出:到2025年,我国城市污泥无害化处理率应达到90%以上;到2035年,全面实现污泥无害化处理和污泥资源化利用水平的显著提升.
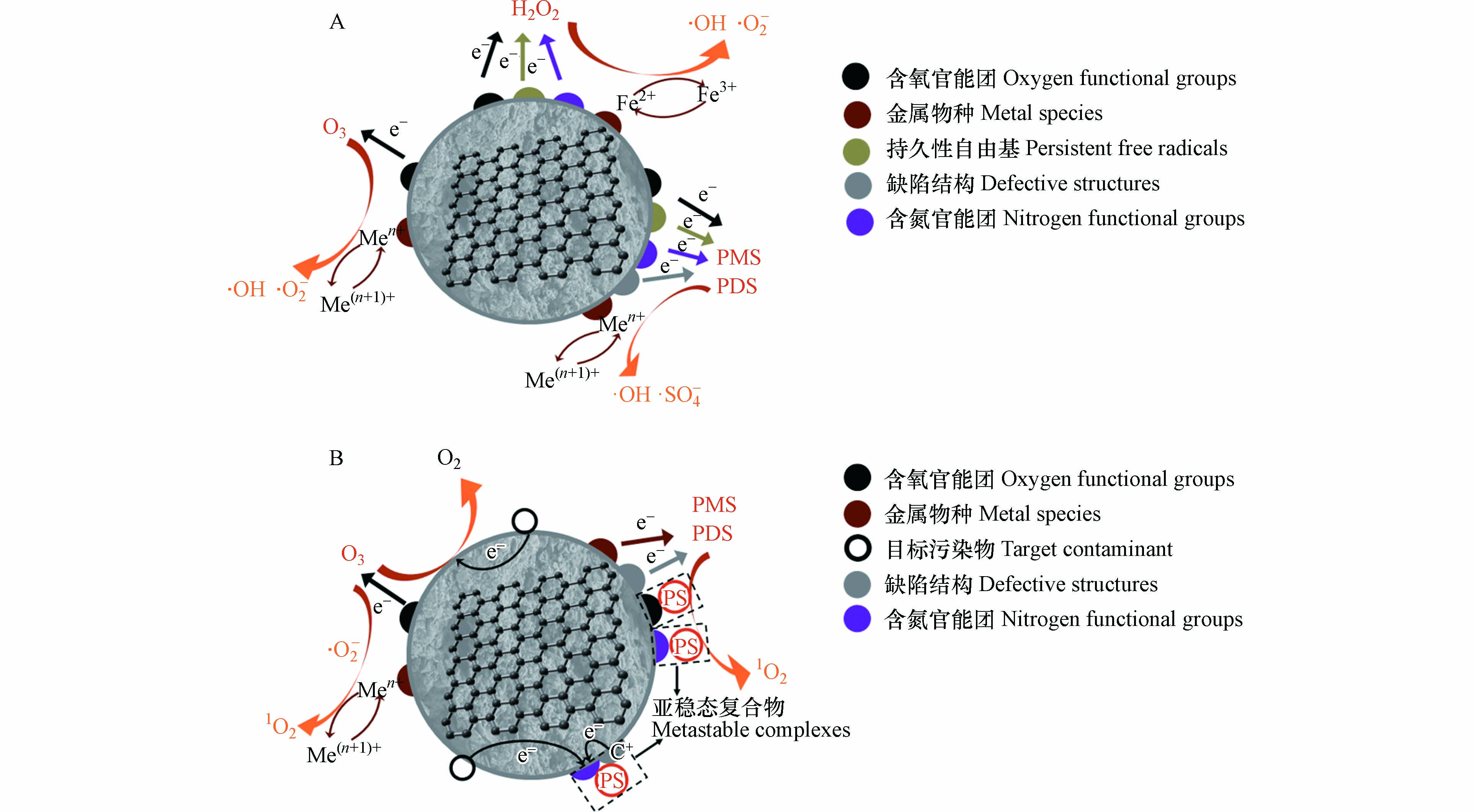
生物炭是指生物质原料在无氧或限氧条件下通过热解或水热炭化形成的多孔材料,在环境修复特别是水处理领域有着广泛的应用. 污泥中含有丰富的氮元素和金属元素,可制备污泥生物炭基催化材料,应用于过硫酸盐(PS)体系、芬顿/类芬顿体系以及臭氧氧化体系,可实现水体污染物的高效降解(如图1所示),达到 “以废治废”的目的.
-
按照来源的不同,污泥可分为市政污泥和工业污泥. 市政污泥主要来源于污水处理厂和自来水厂,可进一步细分为污水污泥和给水污泥;工业污泥主要来源于纺织、石油化工、皮革制造、造纸、制药等行业,其成分更加复杂,对处理技术有更高的要求[4].
-
给水污泥主要来源于自来水厂的沉淀池和滤池,由混凝剂残渣、无机矿物以及少量有机质组成[5]. 自来水源多为天然水体,净水过程中大量使用含Fe和Al的混凝剂,因此给水污泥的特点为污染物含量低且铁铝含量高. Choi等将脱水给水污泥分别在N2和CO2气氛中热解得到污泥生物炭并测定了元素含量,发现污泥生物炭中Al含量高达21.4% wt,占金属元素总量的86% [6]. Ryu等通过X射线衍射证实污泥中的聚合氯化铝在热解过程中倾向于与K、Si等元素形成稳定的硅酸盐矿物[7]. Zeng等使用含Fe的给水污泥制备了负载Fe3O4的污泥生物炭,发现污泥中的Fe有助于增大生物炭的比表面积和孔隙度,负载的Fe3O4可增强生物炭的磁性,使其能够从水溶液中快速分离回收[8].
-
污水污泥来源于城镇污水处理厂,其固体部分主要由有机物、无机盐、重金属、营养物质和微生物组成. 污水污泥中含有大量蛋白质和多肽等有机成分,因此含氮量显著高于其他类型污泥[9]. 此外,污水污泥含有重金属和多环芳烃等有毒物质[10],污染风险高于给水污泥. 虽然污水来源和处理工艺的差别使得污泥的组分和性质呈现差异,但其主要成分保持稳定. 不同絮凝剂的添加会影响污泥的元素组成以及生物炭的性质,聚合硫酸铁和聚丙烯酰胺能够分别增加污泥中Fe和N的含量,有利于催化位点的形成[11-12].
-
相比市政污泥,工业污泥成分更加复杂,污染性更强[13]. 不同来源的工业污泥在性质和组分上有所区别,特征污染物有所差异. 造纸污泥含有大量纤维素、木质素等有机物以及Ca、Si等无机矿物,重金属含量相对较低[14],可用于制备磷酸盐吸附剂,处理富营养化废水[15]. 印染污泥中含有各类染色剂、添加剂、多环芳烃、重金属(Cu、Cr、Ni)等污染物,具有很强的毒性和污染性[16-17]. 高温热解法作为最常用的生物炭制备技术,能够有效降低印染污泥中重金属的浸出浓度,提高使用安全性[18]. 石油污泥是由水、各类石油烃、重金属和固体颗粒组成的复杂乳液,通常含有苯系物和酚类物质[19]. Duan等指出,在水热炭化过程中,石油污泥中的酚类、醇类和有机酸等物质能促进生物炭表面羟基官能团的形成,改善生物炭的表面特性并降低重金属的可利用性[20]. 制药污泥中含有大量难降解有机物,经高温热解后有机物分解形成大量孔隙,能够对小分子的有机污染物进行富集,提高催化氧化的效率[21].
-
污泥可通过特定的热化学过程转化为污泥生物炭,其中高温热解法、微波热解法以及水热炭化法是最常用的制备方法. 不同的制备方法对污泥含水率的要求不同. 生污泥和脱水污泥的含水率能够达到85%和65%以上,可直接进行微波热解或水热炭化;若采用高温热解法,须在热解前进一步降低污泥的含水率以降低能量消耗[22], 或直接使用含水率低于10%的干化污泥进行热解.
-
高温热解法是指在无氧条件下将污泥进行高温热处理以获得生物炭、生物油和热解气体的方法,具有产量大、操作简便等优点,但反应时间较长且能耗较高,产生的热解气体具有二次污染风险[23]. 在热解过程中,可通过调节热解温度、升温速率、停留时间、载气种类等工艺参数来控制产物的性质,其中热解温度和载气种类对生物炭性质影响最大. 热解温度(300—1000 ℃)决定了污泥各组分的分解程度,从而影响污泥生物炭的产率和理化性质,进而影响污泥生物炭的催化性能和环境风险. 在热解过程中,污泥中的水分于60—200 ℃时释放;温度达到200 ℃以上,脂肪酸和糖类物质分解释放H2O、CO2、CH4、乙酸等小分子物质,形成醇类和烃类物质;温度达到400 ℃以上,蛋白质开始分解;温度达到600 ℃以上,残留有机物进一步分解和芳香化[24-25]. 随着热解温度的升高,生物炭的产率逐渐下降[26],生物炭碱性不断增强[27],这归因于热解时酸性官能团的损失和碱金属/碱土金属化合物的释放. 为保持热解过程的稳定,通常使用N2作为保护性气体,而CO2和NH3常被用于改善生物炭的表面特性和元素组成. 研究表明,以CO2作为载气能够提升生物炭的比表面积和微孔数量,促进石墨化结构的形成,增强电子传导能力[28]. 污泥在NH3气氛中热解能够转化为具有丰富孔隙度的N掺杂生物炭,N含量尤其是石墨化N含量显著上升[29-30].
-
微波热解的原理是将微波能量转化为物体内部的热能,达到快速升温的目的,能够有效缩短加热时间,提升能量利用效率. 湿污泥中的水具有良好的微波吸收能力,因此含水率高的湿污泥可直接进行微波热解处理,但微波处理会导致热解气体和生物油的产量增大,生物炭中固定碳含量降低,官能团损失,因此微波热解多用于优化热解气体的组分,提升生物油、沼气的产量[31-32]. 与高温热解法相比,通过微波热解制备的生物炭表面孔隙发育较差,这可能会影响生物炭对污染物的富集潜力,但较少的孔隙会抑制重金属和有机污染物的浸出,提高使用安全性[31]. Lin等对比了高温热解与微波热解制备的污泥生物炭中重金属的浸出风险,发现微波热解污泥生物炭中Cu、Zn、Pb的浸出率低,重金属稳定性更强,使用风险低[33].
-
水热炭化法是将污泥置于一定温度(150—350 ℃)和压力(2—10 MPa)下,以水作为能量传递介质,制备污泥水热炭的方法. 相比高温热解法,水热法不需要对污泥进行干燥[34],具有反应过程温和、产率高、污染较少等优点,对表面官能团有一定保留能力[35]. Alipour等比较了热解污泥生物炭和污泥水热炭的性质差异,发现热解生物炭具有较大的比表面积、孔隙率和更高的芳香性,污泥水热炭中重金属含量更低[36].
-
污泥生物炭的比表面积和孔隙特征会影响污染物的吸附与扩散. 微孔(<2 nm)为污染物提供吸附位点,中孔(2—50 nm)和大孔(>50 nm)可作为污染物的扩散通道,有助于提高吸附速率[37]. 在催化氧化反应中,多孔结构不仅能够加速污染物的扩散过程,还能提高H2O2和PS的分解速率,加快活性氧物种的产生[38]. 与传统农林生物炭相比,污泥生物炭的比表面积较小,孔隙发育较差[39],但平均孔径(3—10 nm)相当,这表明污泥生物炭的孔隙以中孔、大孔为主,微孔数很少,这有助于污染物快速扩散至催化位点,缩短反应时间[40].
热解温度会影响生物炭的比表面积和孔隙特征. 较低的热解温度(<400 ℃)会导致挥发性有机物的不完全分解,大部分孔隙被挥发性物质堵塞[41],生物炭的比表面积较小,且孔隙主要由中孔和大孔组成[42];随着热解温度的升高,生物炭的比表面积和孔隙率急剧增加,微孔数量增加[27, 43];而过高的热解温度会导致微孔的塌陷,生物炭平均孔径增加且比表面积下降[42]. 研究表明,化学活化、金属负载、水热预处理等方法能够显著增加污泥生物炭的比表面积,形成发达的孔隙结构[44-46].
-
相比于传统生物炭,污泥生物炭具有更高的灰分含量(>40%),这主要归因于污泥生物炭中矿物质含量较高,包括K、Ca、Mg、Na和Al离子等,通常以碳酸盐、磷酸盐、硅酸盐或氧化物的形式存在,对生物炭的催化性能具有重要的影响. 研究表明,生物炭中的矿物质能促进污染物在生物炭的表面吸附[47],为后续催化氧化创造条件. Zhang等探究了生物炭中内源矿物对PS活化的影响,发现生物炭中的内源矿物不仅能促进多孔结构的形成,还能促进石墨化结构和边缘缺陷结构的形成,增强生物炭的催化性能[48]. Liang等分别制备了富含矿物质的污泥生物炭以及脱矿生物炭,活化PS降解苯酚,结果表明不同类型的矿物成分对催化氧化的影响不同;含Fe矿物能够促进苯酚的氧化,含Mg、Al矿物对反应影响可以忽略,而含Ca矿物会抑制自由基的形成,不利于苯酚的氧化[49].
污泥中含有大量多肽和蛋白质等含氮有机物,氮含量远高于其他生物质,在热解过程中更容易形成具有催化活性的含氮结构. 热解过程通常伴随有氮的损失. 随着热解温度的升高,各类含氮官能团转化为吡咯氮和吡啶氮,进一步转化为季铵盐,最终进入石墨化结构中,表现出优异的催化性能[50]. Yu等证实了N掺杂污泥生物炭能有效活化PS降解四环素,其催化性能高于石墨碳材料和木质生物炭[12]. 此外,污泥生物炭中的杂环N能够促进持久性自由基的形成,提高生物炭的催化性能[51].
富含Fe的污泥生物炭可作为芬顿/类芬顿固相催化剂,通过活化H2O2和PS实现污染物的高效降解[38]. Wang等在未经改性的污泥生物炭表面检测到6.34% wt的Fe含量,并成功实现了PS的非均相催化. 作者进一步发现与其他Fe基催化剂相比,污泥生物炭中起催化作用的Fe基团更加稳定[52].
-
人工合成的碳质材料中存在持久性自由基(PFRs),其具有较长的半衰期和强氧化活性,既能够参与H2O2或过硫酸盐的活化,也能够直接参与污染物的降解[53]. Fang等利用富含PFRs的生物炭活化H2O2产生·OH,实现了对2-氯联苯的降解,并证实生物炭中的PFRs与·OH的产生有关[54]. 此外,Yang等也研究发现PFRs直接参与了对硝基苯酚的降解[55].
PFRs的形成必须由前驱体和过渡金属氧化物(Fe、Cu、Al、Zn、Ni等)的共同参与,常见的前驱体有木质素、绿原酸、含氯芳烃、酚类化合物、多环芳烃类以及醌类化合物等[56]. 污泥中的酚类/醌类化合物可以将电子转移至过渡金属氧化物上形成PFRs[35],该过程需要外界能量的干预,而污泥热解过程可以提供大量能量,因此PFRs广泛存在于热解污泥生物炭中. Zhang等发现,低温热解生物炭通过PFRs活化PS产生·OH、·SO4−,而高温热解生物炭表面的PFRs几乎完全损失,此时主要催化位点是缺陷结构[57]. 过渡金属的种类、含量以及颗粒粒径等因素都会影响PFRs的形成[58].
-
污泥中含有大量重金属、有机物以及微塑料等难降解污染物,热解处理不当会产生环境污染,因此污泥生物炭在使用前应进行安全性评价.
-
Jin等探究了不同热解温度下污泥生物炭的重金属总量、形态以及环境风险,其中Zn的浓度远高于其他重金属,达到了2579.8 mg·kg−1,这与我国大部分地区使用镀锌市政管道有关,检出的重金属总量排顺为Zn>Cu>Mn>Cr>Ni>Pb. 随着热解温度升高,生物炭中非金属物质不断分解挥发导致重金属总量增加,但BCR分步浸提结果显示高温热解能够降低重金属的可利用性,重金属由酸溶态和可还原态逐渐转化为较稳定的可氧化态和残渣态. 作者还通过计算重金属的生态风险指数证实热解温度的升高能够极大地降低生物炭中重金属的潜在环境风险[59]. Phoungthong等模拟了酸雨和垃圾渗滤液对污泥生物炭中重金属浸出的影响,明确了污泥生物炭的使用安全性[60]. 综上所述,污泥生物炭中重金属的生物可利用性较差、生态风险较低,具有较高的使用安全性,但部分研究中重金属的总量超过了标准限值,在后续研究中应当持续关注.
污泥生物炭中重金属的稳定性还与污泥种类和制备方式有关. Cui等发现有机物含量更高的市政污泥生物炭主要通过酰胺官能团(−CO−NH−)对重金属的表面络合作用、芳香结构π电子与金属阳离子的结合以及金属与卤素离子的静电吸引作用稳定重金属;无机物含量更高的制药污泥生物炭稳定重金属的主要途径是金属矿物盐和多金属氧化物的形成,而生物炭表面无定形碳对重金属的包覆形成了“碳屏蔽”作用,也能够抑制重金属的可利用性[61]. Wang等发现水热处理温度较低,重金属的稳定效果较差,而水热-热解联合处理能够有效降低重金属的析出风险[46]. 此外,在污泥热解过程中加入一定比例的农林生物质(稻草、竹屑等)能够起到对重金属的“稀释”作用,降解生物炭中重金属的总量和潜在析出风险[62-63].
-
自由溶解态浓度是指污染物自由溶解在水相中的浓度,能够准确评估污染物的生物有效性,因此自由溶解态多环芳烃(free-PAHs)含量是影响污泥生物炭使用安全性的重要因素[64]. 与原污泥相比,热解污泥生物炭中PAHs总量降低了1.8—9.7倍,free-PAHs含量降低了2.3—3.4倍[64-65],由于提高热解温度能够有效降低污泥生物炭中的PAHs和free-PAHs含量,因此高温热解能够去除大部分的PAHs,提高污泥生物炭的使用安全性.
水热炭化技术对污泥中的有机污染物具有很好的去除作用. Tasca等研究发现,水热炭化处理能够将污泥中多种农药、多氯联苯和PAHs的含量降至很低的水平[66]. Wang等通过水热炭化处理还有效去除了污泥中的医药和个人护理产品(PPCPs),为处置含有大量PPCPs成分的制药污泥安全处置提供了新思路[67].
-
环境中的微塑料(MPs)被认为对人体具有潜在的危害. 在污水处理过程中,超过90%的MPs吸附在污泥颗粒上,需要评估污泥生物炭中微塑料的环境风险[68]. Ni等研究了污泥热解过程中MPs的转化,发现过低的热解温度(<400 ℃)会导致污泥中原有MPs与有机物反应产生新的MPs聚合物并形成PAHs,当热解温度达到450 ℃时,99.7%的MPs被分解,污泥生物炭的使用风险大大降低[69]. 相比高温热解法,水热炭化处理对污泥中MPs的去除能力有所下降,水热处理温度达到260 ℃时,MPs的去除率为79.7%,除聚丙烯和聚乙烯塑料外的其他MPs被完全分解,其中聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯塑料等缩聚塑料在高温高压下通过水解反应解聚形成聚合物单体,而聚丙烯等加聚塑料在高温下发生了随机链断裂[70].
-
污泥生物炭不仅具有一定的比表面积和孔隙结构,而且富含催化位点,能够在富集污染物的同时催化各类高级氧化反应的进行(表1),实现水体中污染物的高效降解. 研究表明,污泥生物炭表面的催化位点主要包括石墨和醌类结构、PFRs、碳/氧缺陷结构、含氧官能团、金属及其氧化物以及N、S等杂原子基团[71]. 在催化氧化过程中,有机污染物的降解途径分为自由基途径和非自由基途径. 自由基途径包括羟基自由基(·OH)、硫酸根自由基(·SO4−) 以及超氧自由基(·O2−)等强氧化性的活性氧物种对污染物的氧化(图2);非自由基途径包括单线态氧(1O2)的生成以及污染物向氧化剂的直接电子转移过程[9](图2).
-
污泥生物炭能够活化H2O2和PS产生具有强氧化性的·OH. 在PS活化中,生物炭表面的缺陷结构、含氧官能团等能够将电子传递至HSO5−,使其分解产生·OH[式(1)][71],而·SO4−也能够分解产生·OH[式(2)].
H2O2分解是产生·OH的主要途径,如式(3)—(8)所示[72]. 污泥生物炭中的含Fe基团在催化H2O2分解中起到重要作用,在酸性条件下,生物炭表面的的Fe以Fe2+的形式浸出到溶液中,浸出的Fe2+可引发传统芬顿反应[式(3)—(5)],催化引发H2O2分解产生游离的·OH. 而含铁基团中的≡Fe2+物质也可以催化H2O2分解产生表面结合的·OH[式(6)],且形成的≡Fe3+可以依次与H2O2[式(7)]和HO2·[式(8)]反应生成更多的≡Fe2+,形成非均相的芬顿反应.
此外,污泥生物炭中PFRs以及含氮结构也能够通过电子转移活化H2O2分解产生·OH. 研究表明,HNO3改性的污泥生物炭中的C=C、C=O以及吡啶N结构能够将单电子转移至H2O2,从而破坏H2O2的O—O,催化H2O2的分解[73].
-
·SO4−是基于PS活化产生的具有强氧化性的自由基,相比于·OH,·SO4−在水溶液中具有更长的寿命(30—40 μs),对含有芳香结构和给电子基团的污染物有更高的选择氧化能力[27]. 如图2所示,污泥生物炭表面的PFRs、含氧官能团、缺陷结构、含N基团以及过渡金属及其氧化物能够为PS的活化提供丰富的催化位点. 研究表明,C=O等含氧官能团具有孤对电子并能够与过一硫酸盐(PMS)形成C=O—H—O—OSO3复合结构,破坏PMS的O—O,促使电子转移至PMS,形成·SO4−[式(9)][74]. 缺陷结构和含N基团的存在会打破C—C结构的电荷平衡,导致C原子周围电子分布不均匀,使得PS能够接受电子分解产生·SO4−[式(9)、式(10)][9]. 此外,当生物炭表面存在PFR时, PFR能够直接介导电子由生物炭转移至PS[式(11)][75],也能够通过促进·O2−的形成,间接催化PS产生·SO4−[式(12)][76].
污泥生物炭中含有大量含Fe基团,可作为PS的催化活性位点,其中Fe(Ⅱ)能够直接催化PS产生·SO4−[式(13)、式(14)],而Fe(Ⅲ)需要先在溶液中还原为Fe(Ⅱ) [式(15)、式(16)],所以提高生物炭中Fe(Ⅱ)的比例能够有效提升生物炭的催化性能[9].
-
·O2−是臭氧氧化体系中的主要氧化剂之一,在H2O2的催化氧化反应中也会产生. 在污泥生物炭/O3体系中,O3能够直接或间接攻击生物炭的C=O、C=C以及—OH等基团,产生·O2−和·OH[式(17)—(20)],其中C原子的离域π电子能够与H2O互相作用产生OH−[式(17)],促进反应的发生[77]. 此外污泥生物炭表面可变价的过渡金属元素也能够催化H2O2分解产生·O2−[式(21)、式(22)][71].
-
1O2是一种具有高度选择性的强氧化剂,在污泥生物炭/PS体系中可作为主要氧化剂对污染物进行降解. 研究表明,污泥生物炭表面的C=O能够催化PS产生1O2,其过程较为复杂,涉及HSO5−或S2O82−对羰基官能团的攻击、二恶烷中间产物的形成以及与HSO5−或S2O82−进一步反应生成1O2的过程,总反应如式(23)、式(24)所示[78-79]. 生物炭的含N结构也能够催化1O2的生成,相比吡啶N和吡咯N,高温热解产生的石墨化N结构具有更优异的催化能力,能够与PS分子形成亚稳态复合物从而促进其自分解产生1O2[式(25)、式(26)][80]. 此外,当水溶液中存在溶解氧时,原位生成的·O2−能够重组形成1O2[式(27)][79].
-
电子转移途径不依赖活性氧物种的形成,而是通过污泥生物炭对PS的吸附形成具有高氧化还原电位的复合物,如图2所示,当污染物的氧化还原电位低于复合物电位时,会发生电子从污染物向PS的直接转移,在整个过程中,污泥生物炭可作为电子传导的媒介. 在非自由基途径中,电子转移效率与污泥生物炭的性质和污染物的种类密切相关. 催化剂与氧化剂之间存在强烈的结合趋势[78],因此污泥生物炭的表面基团与含C结构会直接影响其与氧化剂的结合能力,从而影响电子转移途径. 研究表明,石墨化C结构、吡啶N以及石墨N都能够有效促进电子由污染物到氧化剂的直接转移. 其中,含N基团具有较高的电负性,能够改变电荷分布,从而提高催化性能[12]. Mian等研究发现,吡啶N能够将PMS分子吸附在相邻带正电荷的C原子上,而sp2杂化的C结构为电子由污染物向PMS分子的转移提供了通道,最终实现污染物的降解[81]. 此外,电子转移途径对不同污染物表现出高度选择性,相比苯环等基团,富含电子的苯酚等物质更容易发生直接电子转移而被氧化[78].
-
芬顿反应的原理是在酸性条件下利用Fe2+活化H2O2产生具有强氧化性的·OH对污染物进行降解. 污泥生物炭对污染物有一定吸附能力,同时表面Fe、含氧官能团以及PFRs可作为H2O2的活化位点,参与电子转移,形成吸附-催化协同作用. Luo等研究发现污泥生物炭/H2O2体系对环丙沙星(CIP)的去除率达到70%,其中生物炭对CIP的吸附去除率为27%,PFRs的直接氧化去除率为23%,而由PFRs引发的催化氧化去除率为20%,从而证实了污泥生物炭表面的PFRs在催化H2O2降解CIP的过程中起到重要作用:PFRs既能通过自身氧化性降解部分CIP,也能够通过单电子转移的途径催化H2O2产生·OH[73]. 当使用HNO3对污泥浸渍改性后,生物炭表面的PFRs数量增加且种类发生改变,更有利于对H2O2的活化,对CIP的去除率提升至93%[73] .
除PFRs外,污泥生物炭中自带的Fe在催化芬顿反应中发挥了关键作用,使用含铁污泥制备生物炭或通过负载铁物种的方式均能提高污泥生物炭的催化性能. Li等通过X射线衍射分析出污泥生物炭中Fe的主要存在形式为Fe2P和Fe2O3,在pH为2—4的范围内,浸出的Fe2+和Fe3+能够催化H2O2产生·OH,对CIP的去除率达到80%[82]. Gan等使用芬顿试剂与赤泥对污泥进行调理,制备了富含Fe、Al的污泥生物炭,同时引发均相与非均相芬顿反应对4氯苯酚进行降解,其中生物炭表面的Fe0和Fe0.95C0.05位点通过浸出的Fe2+催化H2O2分解,而FeAl2O4和Fe3O4可直接参与H2O2的分解[72]. 此外,Huang等采用微波热解法制备污泥生物炭,并通过提高微波功率的方式增加了生物炭的比表面积和Fe含量,从而增加了三氯乙烯的去除率[83].
-
过硫酸盐氧化技术的原理是通过催化剂或借助外界能量活化过一硫酸盐(PMS)或过二硫酸盐(PDS)产生更强的氧化性. 在污泥生物炭/PS体系中,污染物的去除机理比较复杂,既包含自由基途径也包含非自由基途径,而污泥的种类与生物炭的制备条件是控制反应机理的主要因素. Wang等在两种不同的污泥生物炭/PMS体系中观察到不同的磺胺甲噁唑(SMX)氧化途径. 未经改性的污泥生物炭虽然存在大量的C=O与石墨碳结构,但由于Fe物种的存在,主要通过自由基途径催化PMS产生·OH和·SO4−;经过赤泥改性的污泥生物炭表面存在大量的氧空位(OV),促进了1O2的生成,主导对SMX的氧化[84]. Wu等探究了两种不同污泥生物炭活化PS降解PN的能力,结果表明来自柠檬酸污水处理厂的污泥生物炭具有丰富的含氧官能团、含氮基团和PFRs,而生活污水厂污泥生物炭具有丰富的金属基团,在中低温(300 ℃、500 ℃)热解时,前者通过含氧官能团和PFRs介导自由基途径表现出相对更高的催化性能,当热解温度达到700 ℃时,随着官能团和PFRs的消失以及碳氮结构的稳定,非自由基途径占据主导,后者由于含有较高的金属含量,产生更多的缺陷结构,从而表现出更高的催化性能[51]. Hu等采用水热联合热解的方法制备污泥生物炭催化剂,发现污泥前驱体的含水率与生物炭中催化活性位点C=O的数量呈正相关,证实了水热预处理能够提高污泥生物炭的催化性能[85]. Wang等分别于300 ℃和800 ℃热解制备了N掺杂污泥生物炭,并用于活化PMS降解SMX,结果表明热解温度主导了SMX的氧化机理. 当热解温度较低时,生物炭的石墨结构发育较差,电子转移途径受到限制,自由基途径占据主导;随着热解温度的升高,生物炭表面的石墨结构形成,以1O2和电子转移为主的非自由基途径占据主导[86].
研究表明,化学活化、金属负载、N掺杂等方式均能提高污泥生物炭对PS的催化性能. Mian等人探究了不同的化学活化方式对污泥生物炭催化性能的影响,发现相比HCl活化,NH4OH与KOH的组合对生物炭催化性能的提升更加明显,改性生物炭具有更大的比表面积以及更高的N含量和C=O数量,使得非自由基途径在催化氧化中占据主导[81]. Fe是最常见的用于催化PS的负载金属,污泥生物炭自身含有丰富的含Fe基团,同时自身也能为Fe的负载提供稳定的载体. Luo等采用共沉淀法制备了负载Fe3O4的磁性污泥生物炭,利用生物炭表面的Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)催化PMS产生·OH和·SO4−,实验结果表明使用载铁生物炭作为PMS催化剂能够将四环素的去除率由76%提升至89%[87]. 研究表明,不同价态的Fe对PS的催化能力存在差异,因此可以通过控制Fe的价态提高生物炭的催化性能[88]. Chen等研究发现,当热解温度由600 ℃提升至1000 ℃时,污泥生物炭中的Fe物种由Fe3O4转化为FeO,催化能力得到提升,且反应过程中的主要自由基由·SO4−转变为·OH[89]. 除Fe外,Mn、Co、Cu等可变价金属也能够通过氧化还原反应促进PS的活化,且多金属共同负载往往具有协同作用[9]. 在N掺杂生物炭/PS体系中,污染物更倾向于通过包括1O2和电子转移在内的非自由基途径发生降解. Zhu等研究发现,相比原生物炭,N掺杂生物炭/PDS体系对污染物的去除率由39.3%提升至100%,证实了含N基团在催化中的重要作用,而更高的热解温度能够促进石墨结构的形成和含N基团的生成,有利于电子转移 [90].
-
臭氧(O3)对有机污染物的氧化受限于溶液的酸碱性和自身的选择性,污泥生物炭具有特定的的表面官能团、石墨C结构和金属基团,可作为增强臭氧氧化的催化剂. Oh等研究发现,使用生物炭基催化剂能够将PN的去除率由28%提升至74%,在O3/生物炭体系中,由含氧官能团催化生成的·OH、1O2和·O2−是主要氧化剂,而石墨C结构增强了污染物向O3的直接电子转移[91]. Zhang等利用焦化废水污泥生物炭催化PN的臭氧氧化,发现随着热解温度的升高,生物炭的催化性能增强,这主要归因于高温热解时C=O等官能团的增加[92].
Fe和Mn等金属及其氧化物也能够作为臭氧氧化的催化位点. Babar等通过浸渍改性的方式增加了生物炭表面Fe的含量,铁改性生物炭参与的非均相臭氧氧化对亚甲基蓝的一小时去除率达到95%,比均相臭氧氧化提升20%,比未改性生物炭体系提升10%[93]. Tian等发现,负载锰氧化物和铁氧化物的生物炭(MnOxBC、FeOxBC)能够将阿特拉津的去除率由48%分别提升至83%和100%,过渡金属改性增加了生物炭表面的路易斯酸位点,促进O3分解产生·OH,而不同价态的金属氧化物也能够促进电子转移过程[94].
-
本文综述了污泥生物炭的原料来源、制备方法、性质以及使用安全性评价,阐述了污泥生物炭相比于传统生物炭的独特性质以及在催化降解污染物中的优势,系统梳理了污泥生物炭的催化机理与应用,证实了发展污泥生物炭是一条行之有效的污泥资源化途径.
目前,有关污泥生物炭催化降解的研究主要集中于对水体中的特定污染物,对多污染物共存体系以及真实水环境应用研究关注较少. 此外,污泥生物炭的稳定性和再生性研究仍需完善,污泥炭化过程中的能耗问题与长期使用过程中的二次污染问题也需引起足够重视. 后续研究应更多关注环境真实污染水体,充分发挥其在环境修复与可持续发展中的内在价值.
污泥生物炭的催化机理及应用研究进展
Mechanism and application for removal of contaminants by sludge-derived biochar catalyst: A review
-
摘要: 污泥衍生的生物炭材料具有丰富的含氮结构和金属元素,可催化过硫酸盐、芬顿、臭氧等体系,实现水体中污染物的有效去除. 系统总结了污泥生物炭的原料种类、制备过程、安全性评价和催化应用,通过探究污泥生物炭作为催化材料的天然性质优势,详细讨论了其在不同体系中的催化机理. 最后,展望了污泥生物炭应用于多种污染物共存体系和真实水环境的未来研究方向,并指出污泥生物炭的稳定性和再生性是制约其发展的重要因素,以期为污泥的资源化利用提供新思路.Abstract: Sludge-derived biochar (SDB) has abundant nitrogenous structures and metal elements that can catalyze persulfate, fenton, and ozone systems to achieve effective removal of pollutants in water. This study provides a systematic overview of the material type, fabrication process, safety assessment, and catalytic application of SDB. By investigating the inherent advantages of SDB as a catalyst, the catalytic mechanism of SDB in different systems was discussed in detail. Finally, the future research directions for the application of SDB in the coexistence system of multiple pollutants and in the real water environment were envisioned, and the stability and renewability of SDB were highlighted as important factors limiting their self-evolution. The objective of this work is to provide new ideas for the utilization of sludge resources.
-

-
表 1 污泥生物炭催化降解水体中污染物的应用
Table 1. Application of sludge derived-biochar catalyst in the degradation of contaminants in water
生物炭
Biochar氧化剂
Oxidation agent污染物
Contaminants去除率/%
Efficiency氧化机理
Oxidation mechanism催化位点
Catalytic sites参考文献
ReferencesBC-Fenton-RM H2O2 4-氯苯酚 100 ·OH Fe0、Fe0.95C0.05、Fe3O4、FeAl2O4 Gan等[72] HNO3 modified-BC H2O2 环丙沙星 93 ·OH C=C、C=O、吡啶N Luo等[73] SBC H2O2 环丙沙星 90 ·OH、·O2− Fe2O3、Fe2P Li等[82] SDBC PMS 磺胺甲噁唑 92.1 ·OH、·SO4−、1O2 Fe物种、OV、C=O、石墨C Wang等[84] SDBC PDS 苯酚 84 ·OH、·SO4−、·O2−、电子转移 PFRs、石墨C、Fe物种 Wu等[51] HSC PMS 磺胺甲噁唑 99.65 ·OH、·SO4−、1O2 C=O Hu等[85] SBC PDS 苯酚 100 ·OH、·SO4−、1O2、·O2− PFRs Wu等[75] MBC PMS 四环素 84 ·OH、·SO4−、1O2、·O2− Fe3O4 Luo等[87] MC600 PDS 2-萘酚 88.7 ·OH、·SO4− Fe物种、C=O、
—OH、—COOHWang等[88] N-BC900 PDS 橙色G 100 1O2、电子转移 C=O、石墨C、含N基团、缺陷结构 Zhu等[90] MS-biochar PDS 四环素 82.24 ·OH、·SO4−、电子转移 石墨C、含N基团、Fe物种 Yu等[12] HS-biochar O3 酮洛芬 99.99 1O2、·O2−、·OH C=O、C=C、
—OHLi等[77] RS−biochar O3 苯酚 99 1O2、·O2−、·OH、电子转移 C=O、—OH、
—COOH、石墨结构、缺陷结构Oh等[91] BC O3 苯酚 95.4 ·O2− C=O Zhang等[92] FeOx/BC O3 阿特拉津 100 ·OH、·O2− FeOx Tian等[94] MnOx/BC O3 阿特拉津 83 ·OH、·O2− MnOx Tian等[94] -
[1] 戴晓虎, 张辰, 章林伟, 等. 碳中和背景下污泥处理处置与资源化发展方向思考 [J]. 给水排水, 2021, 57(3): 1-5. DAI X H, ZHANG C, ZHANG L W, et al. Thoughts on the development direction of sludge treatment and resource recovery under the background of carbon neutrality [J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2021, 57(3): 1-5(in Chinese).
[2] 戴晓虎. 我国污泥处理处置现状及发展趋势 [J]. 科学, 2020, 72(6): 30-34,4. DAI X H. Applications and perspectives of sludge treatment and disposal in China [J]. Science, 2020, 72(6): 30-34,4(in Chinese).
[3] 谭学军, 王磊. 我国重点流域典型污水厂污泥处理处置方式调研与分析 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(14): 1-8. TAN X J, WANG L. Investigation and analysis on the treatment and disposal methods of typical sewage treatment plant sludge in China’s key river basins [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2022, 38(14): 1-8(in Chinese).
[4] 冯逸凡. 市政污泥和工业污泥处置利用技术 [J]. 资源节约与环保, 2020(10): 107-108. FENG Y F. Disposal and utilization technology of municipal sludge and industrial sludge [J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2020(10): 107-108(in Chinese).
[5] 牛亚芬, 帖靖玺. 给水污泥处置现状及资源化利用研究 [J]. 科技创新与应用, 2019(2): 76-78,81. NIU Y F, TIE J X. Study on disposal and resource utilization of water-supplied sludge [J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2019(2): 76-78,81(in Chinese).
[6] CHOI D, OH J I, LEE J, et al. Valorization of alum sludge via a pyrolysis platform using CO2 as reactive gas medium [J]. Environment International, 2019, 132: 105037. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105037 [7] RYU J, HAN Y S, CHO D W, et al. Practical application of PAC sludge-valorized biochars to the mitigation of methyl arsenic in wetlands [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138148. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138148 [8] ZENG H P, QI W, ZHAI L X, et al. Magnetic biochar synthesized with waterworks sludge and sewage sludge and its potential for methylene blue removal [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 105951. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105951 [9] HU J W, ZHAO L, LUO J M, et al. A sustainable reuse strategy of converting waste activated sludge into biochar for contaminants removal from water: Modifications, applications and perspectives [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 438: 129437. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129437 [10] JELLALI S, KHIARI B, USMAN M, et al. Sludge-derived biochars: A review on the influence of synthesis conditions on pollutants removal efficiency from wastewaters [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 144: 111068. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111068 [11] YU Y L, XU Z B, XU X Y, et al. Synergistic role of bulk carbon and iron minerals inherent in the sludge-derived biochar for As(V) immobilization [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 129183. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129183 [12] YU J F, TANG L, PANG Y, et al. Magnetic nitrogen-doped sludge-derived biochar catalysts for persulfate activation: Internal electron transfer mechanism [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 364: 146-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.163 [13] 崔荣煜, 周天水, 王东田, 等. 国内污泥成分特性的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(增刊2): 256-261. CUI R Y, ZHOU T S, WANG D T, et al. Research progress of composition and characteristics of sludge in China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 39(Sup 2): 256-261 (in Chinese).
[14] 张安龙, 潘美玲. 造纸污泥的基础性质及资源化利用 [J]. 纸和造纸, 2011, 30(1): 50-53. doi: 10.13472/j.ppm.2011.01.019 ZHANG A L, PAN M L. Basic properties of paper mill sludge and its utilization [J]. Paper and Paper Making, 2011, 30(1): 50-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.13472/j.ppm.2011.01.019
[15] WANG Z J, MIAO R R, NING P, et al. From wastes to functions: A paper mill sludge-based calcium-containing porous biochar adsorbent for phosphorus removal [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 593: 434-446. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.118 [16] MAN X Y, NING X N, ZOU H Y, et al. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from textile dyeing sludge by ultrasound combined zero-valent iron/EDTA/Air system [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 191: 839-847. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.043 [17] WANG X D, LI C X, LI Z W, et al. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics, chemical speciation and risk evaluation of heavy metals in biochar derived from textile dyeing sludge [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 168: 45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.022 [18] CHEN J L, BAI X Y, YUAN Y, et al. Printing and dyeing sludge derived biochar for activation of peroxymonosulfate to remove aqueous organic pollutants: Activation mechanisms and environmental safety assessment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 136942. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136942 [19] HU G J, LI J B, ZENG G M. Recent development in the treatment of oily sludge from petroleum industry: A review [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 470-490. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.069 [20] DUAN Y H, GAO N B, SIPRA A T, et al. Characterization of heavy metals and oil components in the products of oily sludge after hydrothermal treatment [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127293. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127293 [21] WU Q Y, ZHANG Y, CUI M H, et al. Pyrolyzing pharmaceutical sludge to biochar as an efficient adsorbent for deep removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics from pharmaceutical wastewater: Performance and mechanism [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 426: 127798. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127798 [22] GAO N B, QUAN C, LIU B L, et al. Continuous pyrolysis of sewage sludge in a screw-feeding reactor: Products characterization and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(5): 5063-5072. [23] 赵迎新, 麻泽浩, 杨知凡, 等. 污泥生物炭催化高级氧化过程进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(7): 3984-3994. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-1658 ZHAO Y X, MA Z H, YANG Z F, et al. Progress of advanced oxidation process catalyzed by sludge biochar [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(7): 3984-3994(in Chinese). doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-1658
[24] CHAO C G, CHIANG H L, CHEN C Y. Pyrolytic kinetics of sludge from a petrochemical factory wastewater treatment plant–– a transition state theory approach [J]. Chemosphere, 2002, 49(4): 431-437. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00280-1 [25] SINGH S, KUMAR V, DHANJAL D S, et al. A sustainable paradigm of sewage sludge biochar: Valorization, opportunities, challenges and future prospects [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 269: 122259. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122259 [26] ZHANG X, ZHAO B W, LIU H, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on biochar’s characteristics and speciation and environmental risks of heavy metals in sewage sludge biochars [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2022, 26: 102288. [27] GOPINATH A, DIVYAPRIYA G, SRIVASTAVA V, et al. Conversion of sewage sludge into biochar: A potential resource in water and wastewater treatment [J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 194: 110656. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110656 [28] SUN C, CHEN T, HUANG Q X, et al. Activation of persulfate by CO2-activated biochar for improved phenolic pollutant degradation: Performance and mechanism [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122519. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122519 [29] YU W C, LIAN F, CUI G N, et al. N-doping effectively enhances the adsorption capacity of biochar for heavy metal ions from aqueous solution [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.134 [30] LIAN F, CUI G N, LIU Z Q, et al. One-step synthesis of a novel N-doped microporous biochar derived from crop straws with high dye adsorption capacity [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 176: 61-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.03.043 [31] ZAKER A, CHEN Z, WANG X L, et al. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of sewage sludge: A review [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2019, 187: 84-104. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.12.011 [32] LI J, DAI J J, LIU G Q, et al. Biochar from microwave pyrolysis of biomass: A review [J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2016, 94: 228-244. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.09.010 [33] LIN F, YUAN N N, WU Y G, et al. Evolution of heavy metals leachability and speciation in residues of sewage sludge treated by microwave assisted pyrolysis[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012, 178/179/180/181: 833-837. [34] WANG X D, LI C X, ZHANG B, et al. Migration and risk assessment of heavy metals in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment combined with pyrolysis [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 221: 560-567. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.069 [35] CHEN Y D, WANG R P, DUAN X G, et al. Production, properties, and catalytic applications of sludge derived biochar for environmental remediation [J]. Water Research, 2020, 187: 116390. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116390 [36] ALIPOUR M, ASADI H, CHEN C R, et al. Bioavailability and eco-toxicity of heavy metals in chars produced from municipal sewage sludge decreased during pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2021, 162: 106173. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2021.106173 [37] IHSANULLAH I, KHAN M T, ZUBAIR M, et al. Removal of pharmaceuticals from water using sewage sludge-derived biochar: A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 289: 133196. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133196 [38] MIAN M M, LIU G J, FU B. Conversion of sewage sludge into environmental catalyst and microbial fuel cell electrode material: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666: 525-539. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.200 [39] TOMCZYK A, SOKOŁOWSKA Z, BOGUTA P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects [J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2020, 19(1): 191-215. doi: 10.1007/s11157-020-09523-3 [40] RANGABHASHIYAM S, LINS P V D S, OLIVEIRA L M T M, et al. Sewage sludge-derived biochar for the adsorptive removal of wastewater pollutants: A critical review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 293: 118581. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118581 [41] ZHANG J, JIN J W, WANG M Y, et al. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and rice husk/bamboo sawdust for biochar with high aromaticity and low metal mobility [J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 191: 110034. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110034 [42] QIU J J, HOU H J, LIANG S, et al. Hierarchically porous biochar preparation and simultaneous nutrient recovery from sewage sludge via three steps of alkali-activated pyrolysis, water leaching and acid leaching [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 176: 105953. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105953 [43] ENAIME G, BAÇAOUI A, YAACOUBI A, et al. Biochar for wastewater treatment—Conversion technologies and applications [J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(10): 3492. doi: 10.3390/app10103492 [44] WANG S Z, WANG J L. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by sludge-derived biochar for the degradation of triclosan in water and wastewater [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 356: 350-358. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.062 [45] WEN G, PAN Z H, MA J, et al. Reuse of sewage sludge as a catalyst in ozonation–Efficiency for the removal of oxalic acid and the control of bromate formation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 239/240: 381-388. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.09.016 [46] WANG X D, CHI Q Q, LIU X J, et al. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and environmental risk of heavy metals in pyrolyzed biochar made from hydrothermally treated sewage sludge [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 216: 698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.189 [47] VIJAYARAGHAVAN K. The importance of mineral ingredients in biochar production, properties and applications [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 51(2): 113-139. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2020.1716654 [48] ZHANG R Y, ZHENG X X, ZHANG D Q, et al. Insight into the roles of endogenous minerals in the activation of persulfate by graphitized biochar for tetracycline removal [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 768: 144281. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144281 [49] LIANG J, XU X Y, ZHONG Q J, et al. Roles of the mineral constituents in sludge-derived biochar in persulfate activation for phenol degradation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 398: 122861. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122861 [50] LENG L J, XU S Y, LIU R F, et al. Nitrogen containing functional groups of biochar: An overview [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 298: 122286. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122286 [51] WU W, ZHU S S, HUANG X C, et al. Mechanisms of persulfate activation on biochar derived from two different sludges: Dominance of their intrinsic compositions [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 408: 124454. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124454 [52] WANG J, LIAO Z W, IFTHIKAR J, et al. Treatment of refractory contaminants by sludge-derived biochar/persulfate system via both adsorption and advanced oxidation process [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 185: 754-763. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.084 [53] NIDHEESH P V, GOPINATH A, RANJITH N, et al. Potential role of biochar in advanced oxidation processes: A sustainable approach [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 405: 126582. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126582 [54] FANG G D, GAO J, LIU C, et al. Key role of persistent free radicals in hydrogen peroxide activation by biochar: Implications to organic contaminant degradation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(3): 1902-1910. [55] YANG J, PIGNATELLO J J, PAN B, et al. Degradation of p-nitrophenol by lignin and cellulose chars: H2O2-mediated reaction and direct reaction with the char [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(16): 8972-8980. [56] 韩林, 陈宝梁. 环境持久性自由基的产生机理及环境化学行为 [J]. 化学进展, 2017, 29(9): 1008-1020. doi: 10.7536/PC170566 HAN L, CHEN B L. Generation mechanism and fate behaviors of environmental persistent free radicals [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2017, 29(9): 1008-1020(in Chinese). doi: 10.7536/PC170566
[57] ZHANG Y Z, XU M Q, LIANG S X, et al. Mechanism of persulfate activation by biochar for the catalytic degradation of antibiotics: Synergistic effects of environmentally persistent free radicals and the defective structure of biochar [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 794: 148707. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148707 [58] 阮秀秀, 杜巍萌, 郭凡可, 等. 环境持久性自由基的环境化学行为 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(8): 1780-1788. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017123002 RUAN X X, DU W M, GUO F K, et al. Environmental and chemical behaviors of environmental persistent free radicals [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(8): 1780-1788(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017123002
[59] JIN J W, LI Y N, ZHANG J Y, et al. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on properties and environmental safety of heavy metals in biochars derived from municipal sewage sludge [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 320: 417-426. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.050 [60] PHOUNGTHONG K, ZHANG H, SHAO L M, et al. Leaching characteristics and phytotoxic effects of sewage sludge biochar [J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2018, 20(4): 2089-2099. doi: 10.1007/s10163-018-0763-0 [61] CUI Z L, XU G R, ORMECI B, et al. Transformation and stabilization of heavy metals during pyrolysis of organic and inorganic-dominated sewage sludges and their mechanisms [J]. Waste Management, 2022, 150: 57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2022.06.023 [62] JIN J W, WANG M Y, CAO Y C, et al. Cumulative effects of bamboo sawdust addition on pyrolysis of sewage sludge: Biochar properties and environmental risk from metals [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 228: 218-226. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.103 [63] TONG S R, ZHANG S P, YIN H X, et al. Study on co-hydrothermal treatment combined with pyrolysis of rice straw/sewage sludge: Biochar properties and heavy metals behavior [J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 155: 105074. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105074 [64] ZIELIŃSKA A, OLESZCZUK P. Effect of pyrolysis temperatures on freely dissolved polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) concentrations in sewage sludge-derived biochars [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 153: 68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.118 [65] RAJ A, YADAV A, ARYA S, et al. Preparation, characterization and agri applications of biochar produced by pyrolysis of sewage sludge at different temperatures [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 795: 148722. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148722 [66] TASCA A L, VITOLO S, GORI R, et al. Hydrothermal carbonization of digested sewage sludge: The fate of heavy metals, PAHs, PCBs, dioxins and pesticides [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307: 135997. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135997 [67] WANG F, YIN Z Y, LIU Y R, et al. Changes and release risk of typical pharmaceuticals and personal care products in sewage sludge during hydrothermal carbonization process [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 284: 131313. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131313 [68] COLLIVIGNARELLI M C, CARNEVALE MIINO M, CACCAMO F M, et al. Microplastics in sewage sludge: A known but underrated pathway in wastewater treatment plants [J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(22): 12591. doi: 10.3390/su132212591 [69] NI B J, ZHU Z R, LI W H, et al. Microplastics mitigation in sewage sludge through pyrolysis: The role of pyrolysis temperature [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2020, 7(12): 961-967. [70] XU Z J, BAI X. Microplastic degradation in sewage sludge by hydrothermal carbonization: Efficiency and mechanisms [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 297: 134203. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134203 [71] JI J Q, YUAN X Z, ZHAO Y L, et al. Mechanistic insights of removing pollutant in adsorption and advanced oxidation processes by sludge biochar [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 430: 128375. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128375 [72] GAN Q, HOU H J, LIANG S, et al. Sludge-derived biochar with multivalent iron as an efficient Fenton catalyst for degradation of 4-Chlorophenol [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 725: 138299. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138299 [73] LUO K, YANG Q, PANG Y, et al. Unveiling the mechanism of biochar-activated hydrogen peroxide on the degradation of ciprofloxacin [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 520-530. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.204 [74] DUAN X G, SUN H Q, WANG S B. Metal-free carbocatalysis in advanced oxidation reactions [J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(3): 678-687. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00535 [75] WU W, ZHU S S, HUANG X C, et al. Determination of instinct components of biomass on the generation of persistent free radicals (PFRs) as critical redox sites in pyrogenic chars for persulfate activation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(11): 7690-7701. [76] FANG G D, LIU C, GAO J, et al. Manipulation of persistent free radicals in biochar to activate persulfate for contaminant degradation [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(9): 5645-5653. [77] LI H Q, LIU S J, QIU S W, et al. Catalytic ozonation oxidation of ketoprofen by peanut shell-based biochar: Effects of the pyrolysis temperatures [J]. Environmental Technology, 2022, 43(6): 848-860. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1807610 [78] DUAN X G, SUN H Q, SHAO Z P, et al. Nonradical reactions in environmental remediation processes: Uncertainty and challenges [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 224: 973-982. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.051 [79] CHENG X, GUO H G, ZHANG Y L, et al. Non-photochemical production of singlet oxygen via activation of persulfate by carbon nanotubes [J]. Water Research, 2017, 113: 80-88. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.016 [80] WAN Z H, SUN Y Q, TSANG D C W, et al. Customised fabrication of nitrogen-doped biochar for environmental and energy applications [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 401: 126136. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126136 [81] MIAN M M, LIU G J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by chemically modified sludge biochar for the removal of organic pollutants: Understanding the role of active sites and mechanism [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123681. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123681 [82] LI J, PAN L J, YU G W, et al. The synthesis of heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst using sewage sludge biochar and its application for ciprofloxacin degradation [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 654: 1284-1292. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.013 [83] HUANG Y F, HUANG Y Y, CHIUEH P T, et al. Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of trichloroethylene catalyzed by sewage sludge biochar: Experimental study and life cycle assessment [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 249: 126139. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126139 [84] WANG J, SHEN M, WANG H L, et al. Red mud modified sludge biochar for the activation of peroxymonosulfate: Singlet oxygen dominated mechanism and toxicity prediction [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 740: 140388. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140388 [85] HU W R, TAN J T, PAN G H, et al. Direct conversion of wet sewage sludge to carbon catalyst for sulfamethoxazole degradation through peroxymonosulfate activation [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 728: 138853. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138853 [86] WANG S Z, WANG J L. Nitrogen doping sludge-derived biochar to activate peroxymonosulfate for degradation of sulfamethoxazole: Modulation of degradation mechanism by calcination temperature [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 418: 126309. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126309 [87] LUO X W, SHEN M X, LIU J H, et al. Resource utilization of piggery sludge to prepare recyclable magnetic biochar for highly efficient degradation of tetracycline through peroxymonosulfate activation [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 294: 126372. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126372 [88] WANG X P, GU L, ZHOU P, et al. Pyrolytic temperature dependent conversion of sewage sludge to carbon catalyst and their performance in persulfate degradation of 2-Naphthol [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 324: 203-215. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.101 [89] CHEN Y D, BAI S W, LI R X, et al. Magnetic biochar catalysts from anaerobic digested sludge: Production, application and environment impact [J]. Environment International, 2019, 126: 302-308. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.032 [90] ZHU S S, HUANG X C, MA F, et al. Catalytic removal of aqueous contaminants on N-doped graphitic biochars: Inherent roles of adsorption and nonradical mechanisms [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(15): 8649-8658. [91] OH S Y, NGUYEN T H A. Ozonation of phenol in the presence of biochar and carbonaceous materials: The effect of surface functional groups and graphitic structure on the formation of reactive oxygen species [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(2): 107386. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.107386 [92] ZHANG F Z, WU K Y, ZHOU H T, et al. Ozonation of aqueous phenol catalyzed by biochar produced from sludge obtained in the treatment of coking wastewater [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 224: 376-386. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.07.038 [93] BABAR M, MUNIR H M S, NAWAZ A, et al. Comparative study of ozonation and ozonation catalyzed by Fe-loaded biochar as catalyst to remove methylene blue from aqueous solution [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307: 135738. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135738 [94] TIAN S Q, QI J Y, WANG Y P, et al. Heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of atrazine with Mn-loaded and Fe-loaded biochar [J]. Water Research, 2021, 193: 116860. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.116860 -




 下载:
下载: