-
水能够推动社会的长久发展,是大自然给予人类的珍贵资源. 河流、湖泊、湿地等都是水资源的重要组成部分,它们能够维护生态平衡、保障社会稳定发展. 城市河流则与城市的发展和繁荣与有着密切的关系[1],随着人们生活水平的逐步提升,城市河流除了具备供水、排洪、航运等基础功能外,还应具备美化市容、平衡城市生态环境、排洪防涝、储备水资源等功能[2]. 如今,随着人口的增多、城市化的快速发展,河流生态常面临巨大压力. 为了能够推进可持续发展,城市河流的保护和修复问题备受关注,而有针对性的河流保护和修复方案,不仅能维系大自然平衡,还很大程度的影响城市生活的舒适性[3-4].
水质评价是水情况研究的重要条件,也是反映河流水环境的重要指标[5-6]. 通州地处北京水系流域的下游,是北京水环境监测与保护的重点区域,其河流水质状况直接反映着北京区域水环境质量. 针对通州河流水质进行长时间、多断面的监测分析,既能直观且科学的了解近些年水环境的变化趋势,又有助于了解城市河流管理水平,提高城市河流生态修复的效率,对后续的河流水质监管、水生态治理有着重要指导意义[7-8]. 为了更全面了解通州河流水质的时空变化及治理成效,本研究以通州主要河流的8个断面为例,对2012—2020年间的水质监测数据进行了多元分析:运用单因子水质标识指数法、箱线图法及主成分分析法,对其水质情况进行了综合评价,进一步分析了河流关键污染因素. 以期为城市副中心未来水环境、水生态治理提供有效的数据支撑,推进城市河流生态保护以及环境监督.
-
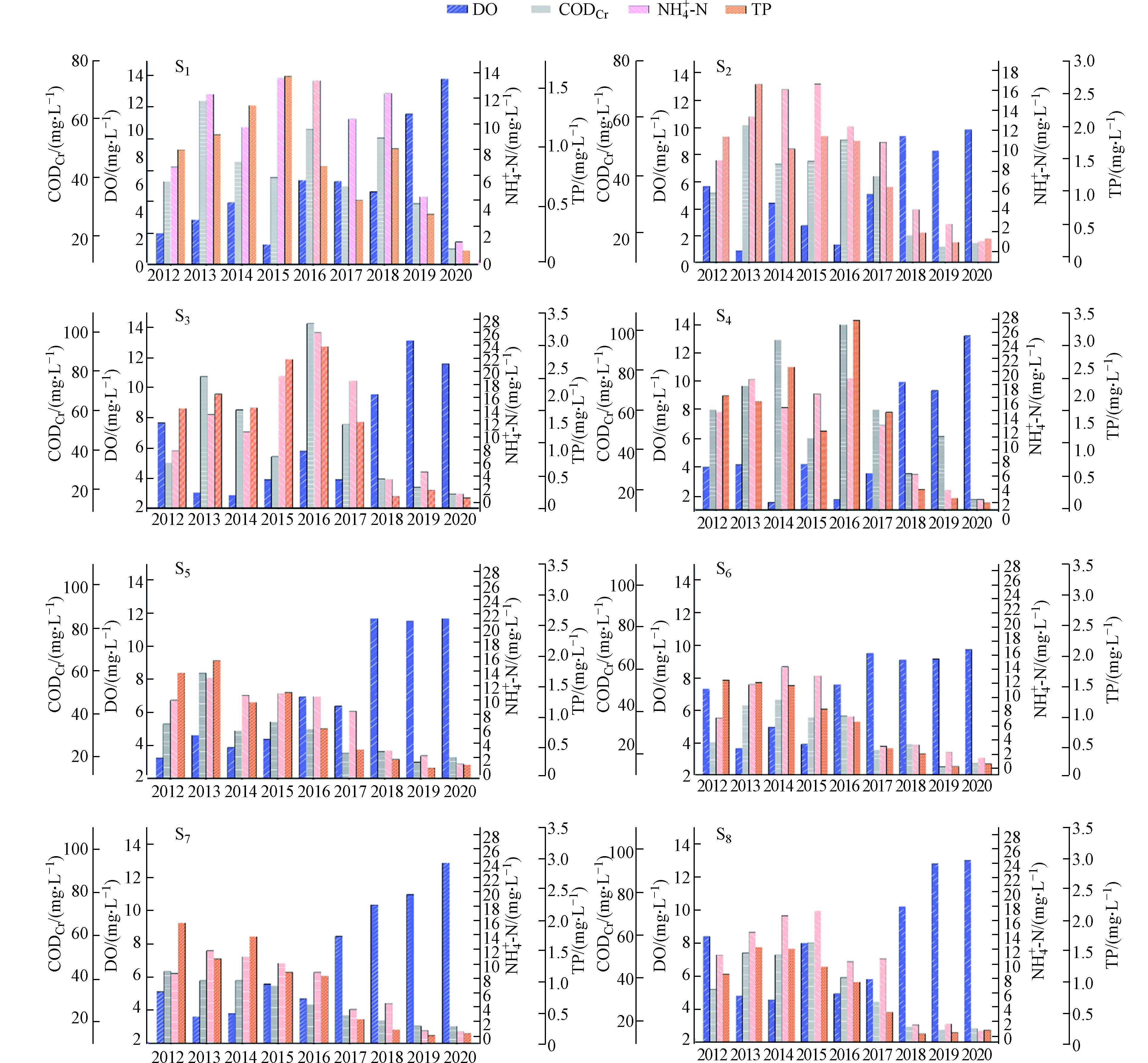
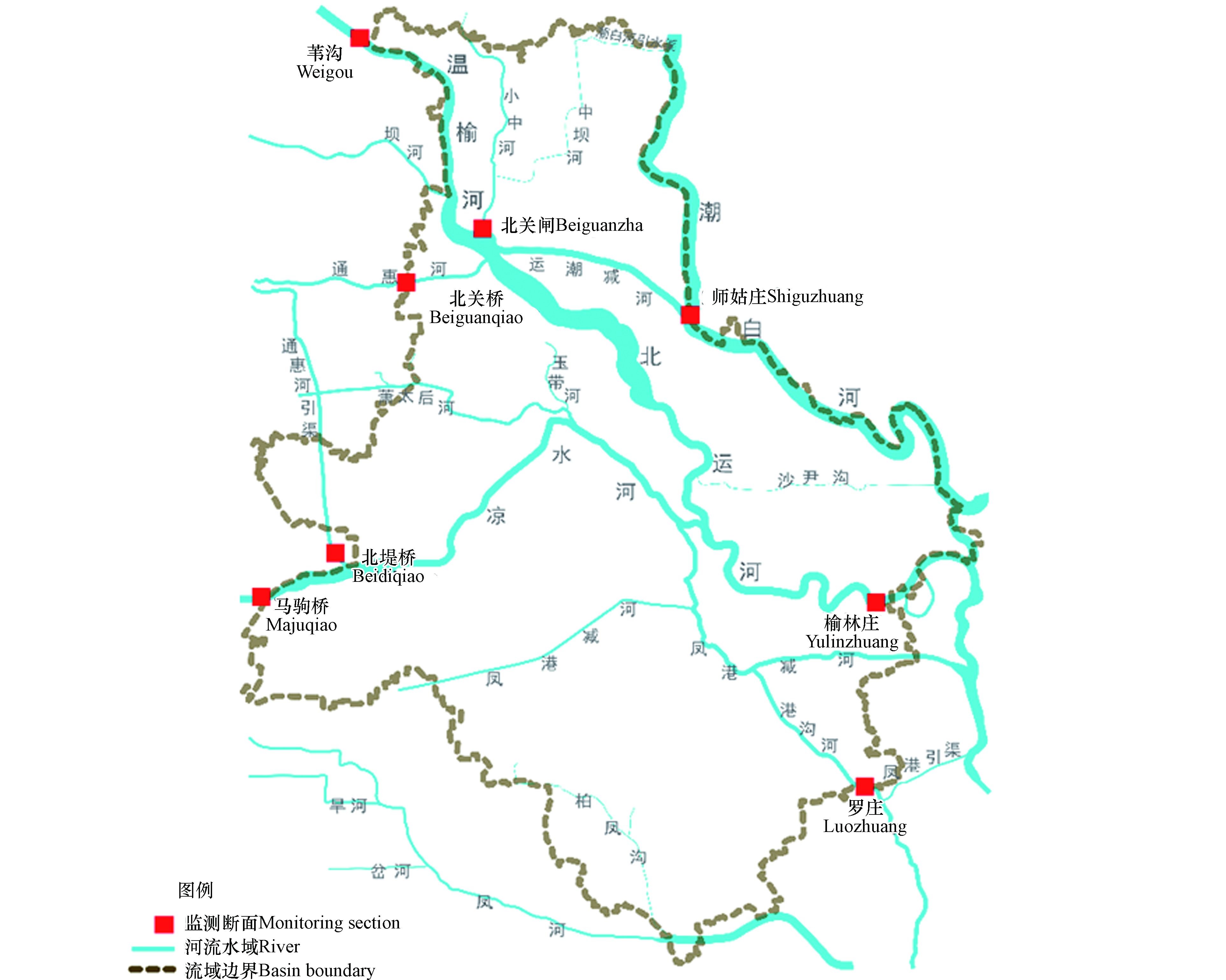
通州区位于北京东南部,地处北京平原东南地势低洼之地,流经北京的河流大多在此处汇集,然后流向河北、天津. 通州区境内有潮白河、北运河两大水系,共大小河流13条[9]. 本研究基于通州河流联通关系,在两大水系中选取了具有代表性的8个关键河流断面为研究对象,即北堤桥S1(通惠河引水渠-凉水河交汇处)、北关桥S2(通惠河入境断面)、罗庄S3(凤港减河出境断面)、马驹桥S4(凉水河入境断面)、师姑庄S5(运潮减河-潮白河交汇处)、苇沟S6(温榆河入境断面)、北关闸S7(温榆河-小中河-北运河交汇处)、榆林庄S8(北运河出境处),各监测断面位置见图1. 对8个断面9年(2012—2020)的监测数据进行综合分析,每年数据分别由丰水期、枯水期和平水期等代表性时间数据构成,(分别为7月份、1月份和10月份,以下简称丰、平、枯).
水质数据来源于北京市水文总站,因监测时间跨度较大、不同监测断面的水质指标有差别等原因,本文选取数据齐全并具有代表性的断面,便于进行水质时空变化的分析. 水质监测指标共包括9项,分别为溶解氧(DO)、化学需氧量(CODCr)、氨氮(NH4+-N)、总磷(TP)、生化需氧量(BOD5)、高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)、粪大肠菌群、硫化物和挥发酚.
-
以9项水质指标为基础,采用单因子水质标识指数法、箱线图法和主成分分析法等3种方法,对通州主要河流水质进行时空特征分析.
单因子水质标识指数法是将监测所得的数据与标准进行对比分类,选择评价结果最差的水质类别作为最终评价结果. 评价标准依据《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838—2002),并按照Ⅲ类标准进行评价[10]. 这种方法一方面可以对水质类别进行标识,另一方面可以对同级别以及不同级别的水质指标,进行横向和纵向的分析比较,从而判断污染程度[11]. 单因子水质标识指数法的具体计算公式如式(1)所示.
其中,Pi代表单因子污染指数,其值越大,表示污染越严重. X1代表第i项的水质分类,X2代表数据在第X1类水质变化区间中所在位置,最终通过公式计算确定;X3代表评价指标的污染程度[12].
箱线图是一种较为直观的数据呈现组合图,常用于数据量较大、组数较多的分析评价中,其优点在于这种方法能较全面的呈现数据分布特征[13]. 在水质分析中,箱线图法即可以根据各箱体之间的长短对比,分析出不同断面间的污染程度差别,又能分析出断面监测数据分布的稳定性[14].
主成分分析法是通过重组、综合变量的方法,将较多的评价运用计算转换为组合指标,这种方法既能减少总体工作量,又能全面客观的反映水质情况和污染原因. 主成分分析法的计算公式如式(2)和式(3)所示.
式中,Fm为主成分得分,Yi为各成分载荷值,Zm为主成分特征值,Xi为标准化后的原始数据,am为各主成分的贡献率,Fs为主成分分析综合得分.
-
单因子评价项目:高锰酸盐指数、溶解氧、化学需氧量、氨氮、总磷、粪大肠杆菌、五日生化需氧量、挥发酚、硫化物. 经计算得到通州地区各断面水质的单项指标X1、X2、X3,然后取9年水质单项指标的平均值,结果如表1[15].
为研究河流水质在时间方面的变化,对8个监测断面在2012—2020年间的4个变化较为明显的水质指标浓度进行分析(图2). 分析结果表明各断面在9年内的主要水质指标变化趋势基本相同. 在2012—2016年间大致呈现上升趋势,2016年后逐渐呈现下降趋势,表明2016年为通州主要河流水质变化的转折点. 其中,各断面的DO指标变化最为明显,总体上在2016年前浓度相对较低,在2016年后浓度明显上升. 各段断面的CODCr、NH4+-N、TP指标则在2016年前相对较高,2016年后明显下降. 这说明2016年之后通州主要河段的水质情况持续好转,相关的水环境保护政策和举措发挥了较好的作用[16-17].
通过分析丰水期、枯水期以及平水期3个水期的时间段单因子污染指数(表1),可看出马驹桥S4、苇沟S6、北关闸S7、榆林庄S8断面溶解氧的最大值均出现在丰水期. 它们的Pi分别为4.51、4.81、4.71、3.90,说明这些断面在丰水期溶解氧的水质类别为4类或者3类. 苇沟S6断面的CODCr污染最大值出现在平水期,Pi为5.52. 北堤桥S1、罗庄S3、北关闸S7断面的CODCr污染最大值出现在枯水期,Pi分别为6.63、6.93、5.92. 北关桥S2丰水期和平水期的CODCr水质指标结果相同,Pi为4.21. 马驹桥S4、师古庄S5和榆林庄S8的枯水期和丰水期的CODCr水质指标结果相同,Pi分别为6.83、5.62和6.13. 除北关桥S2外,各断面的氨氮和总磷最大指标均出现在枯水期. 北关桥S2、罗庄S3、马驹桥S4、师姑庄S5、苇沟S6等5个断面的粪大肠杆菌水质指标最大值均在枯水期,单因子标识指数分别为3.80、3.90、145.89、3.70、3.90. 除了北关桥S2和马驹桥S4,剩余断面的BOD5最大值均出现在枯水期. 总观3个水期中断面的单因子水质指标,可以看出各监测断面丰水期的水质要好于枯水期,这说明除人类活动外,降雨径流也会对河流的水质有所影响. 虽然降雨径流会将径流中的污染物带入河流,从而造成水体污染,但是随着降雨时间的增加,污染物浓度随之降低,与此同时水的流动性变好,故水质呈现好转[18-20].
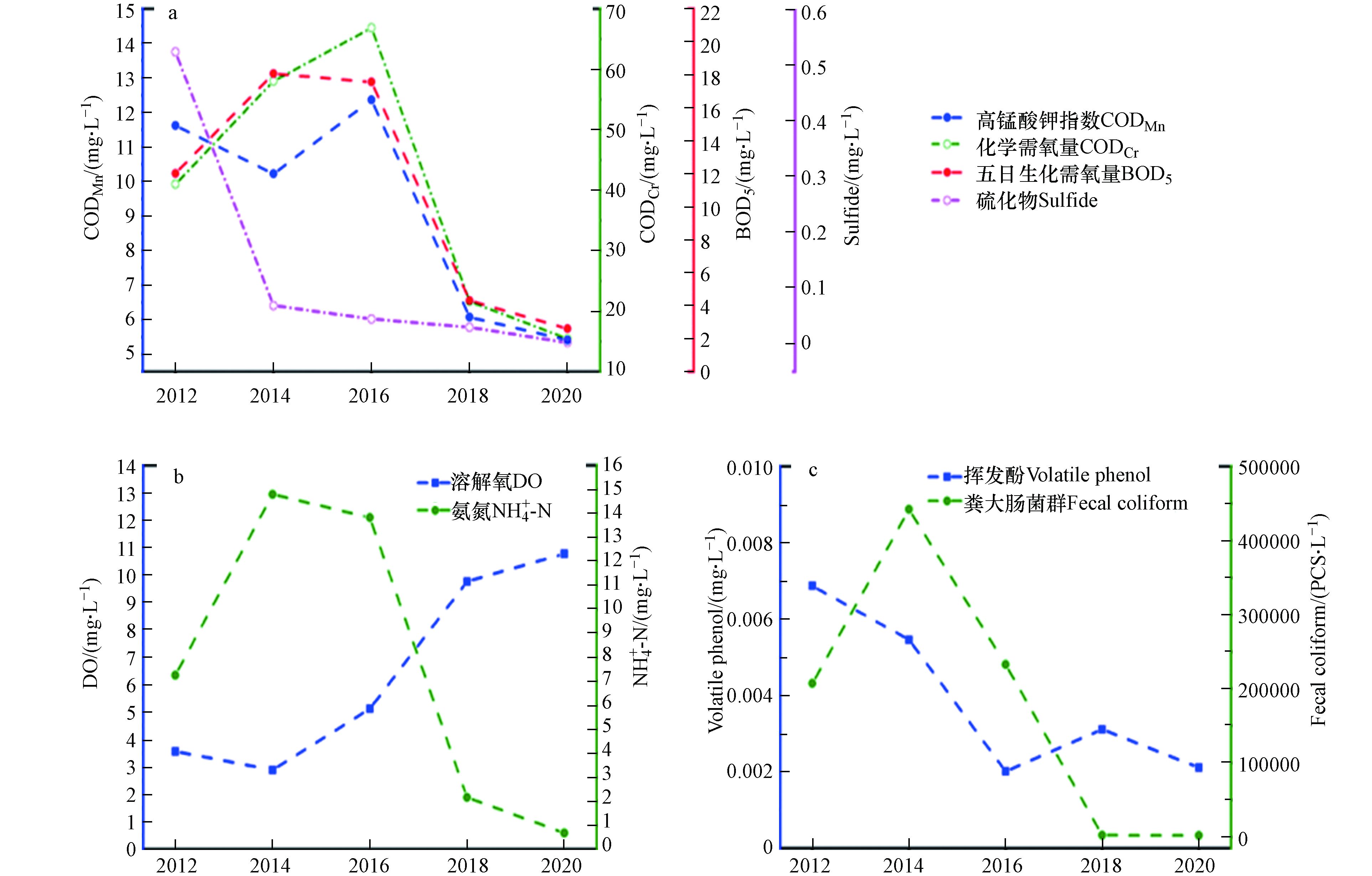
根据表1和图2可看出,通州主要河流水质的空间变化特征. 2012—2016年间北堤桥、北关桥、罗庄、马驹桥断面的溶解氧、化学需氧量、氨氮、总磷水质指标比其他4个断面高. 在2016—2020年间,罗庄、马驹桥断面的水质情况改善明显,北堤桥、北关桥断面的水质情况相对差于其他断面. 通过图1可以看出,北关桥断面是通惠河的入境口,通惠河是北京市东部的河流,承担着北京市区以及东部地区排污泄洪的任务,下游的水质要差于上游[21-22]. 结合相关研究分析可知,这些水质指标主要与河床底泥相关,说明通惠河主要为河床底泥污染[23]. 从图2看出,各段面的氨氮和总磷指标浓度在9年之内都有大幅度下降但还存在超标的现象,说明通州地区河流富营养化的现象普遍存在. 2012—2020年期间,各监测断面的高锰酸盐指数、粪大肠杆菌污染指数、五日生化需氧量、硫化物、挥发酚5个水质指标变化不大,因此综合9年数据进行分析,其中高锰酸盐指数水质指标的最大值出现在罗庄,对应水期为枯水期,单因子水质标识指数为6.13,水质指标远超劣Ⅴ类水质指标,粪大肠杆菌污染指数最大值在马驹桥断面,Pi是145.89,出现时的水期为枯水期,指标严重超标. 通过图1可以看出,此处是凉水河的入境断面,结合相关研究分析可知,这些水质指标主要与人畜粪便和生活污水相关,说明凉水河主要为生活污水污染[23];北堤桥断面的五日生化需氧量污染值最大,Pi数值为7.64,说明此处断面的五日生化需氧量水质指标远超劣Ⅴ类水质指标,受有机物的污染较为严重. 经单因子水质标识指数法分析表明,北堤桥、北关桥、罗庄、马驹桥4个断面挥发酚超过水环境功能区要求,挥发酚不仅对人体身体有极大危害,还对农业和水生植物都有较大伤害性,因此对于挥发酚浓度要严格把控. 挥发酚主要来源于石油化工业以及农药产品中.
根据相关文献可知,北京自2011年转入新工业阶段,并在2013年后大大增加了工业污染治理投资,2017淘汰了污染严重的工业企业,推进非首都功能的疏解[24-25]. 因此,这几处断面挥发酚Pi数值高一方面是由于地面遗撒的石油类产品及园林用农药等随降雨流入河流中造成的水体污染[26-27];另一方面,由图4(c)可以看出,2014年以后挥发酚含量呈现大幅度下降,并在2016年达到Ⅱ类水指标. 由此可以看出,挥发酚Pi数值高的原因在于2012—2016年间的挥发酚浓度过高. 从表1看出各断面的硫化物Pi处于1.10—2.60之间,即X1值为1或2,由此可见硫化物水质指标都在Ⅰ、Ⅱ类水标准范围之中. 综合各项指标总体分析,可看出罗庄和马驹桥断面污染相对严重.
综合分析表明,通州主要河流空间污染特征相似,总体水质在2016年之后呈现好转趋势,且各监测断面丰水期的水质要好于枯水期.
-
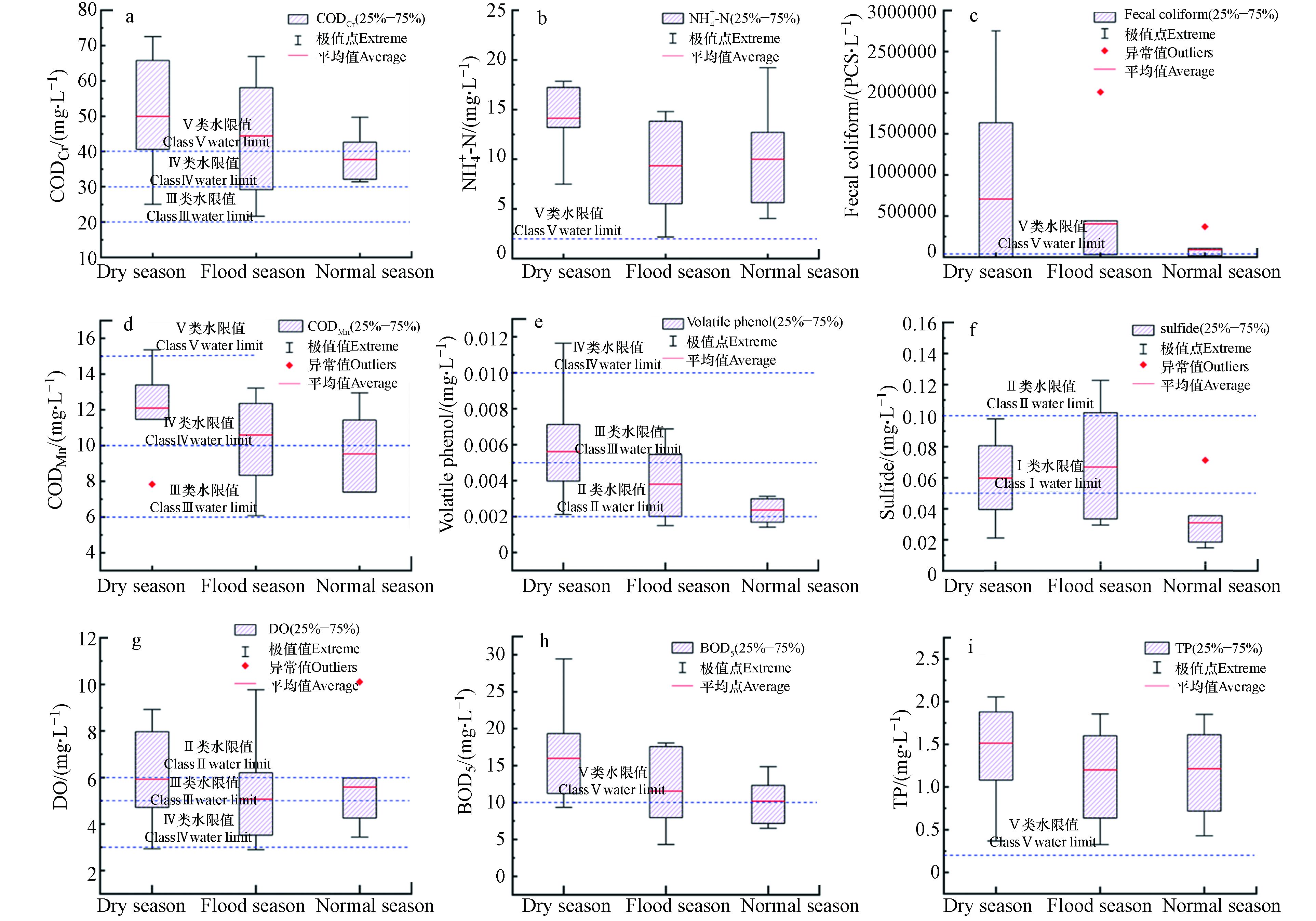
将8个监测断面9年枯水期、丰水期和平水期的平均水质数据输入到origin2018中,制成箱线图,如图3所示. 从图3分析可知,CODCr的平均指标浓度变化次序为:枯水期平均指标浓度>丰水期平均指标浓度>平水期平均指标浓度,污染最大值出现在枯水期,最小值出现在丰水期. 从时间上看,枯水期CODCr在大部分年份中都超过Ⅴ类水质指标限值. 氨氮指标总体浓度均高于Ⅴ类水质标准值,平均指标浓度的变化次序为:枯水期平均指标浓度>平水期平均指标浓度>丰水期平均指标浓度,且在丰水期波动范围更大. TP的情况与氨氮相似,也是远远超出了Ⅴ类水质标准值. 综合来看,各个监测断面N、P总体污染较为严重,存在很大富营养化潜势,需要引起重视[28]. DO枯水期平均指标浓度>平水期平均指标浓度>丰水期平均指标浓度,指标最大值和最小值都出现在丰水期,溶解氧指标大部分时间里都在Ⅲ级水质标准以上. BOD5枯水期平均指标浓度>丰水期平均指标浓度>平水期平均指标浓度,指标最大值出现在枯水期,最小值出现在丰水期,BOD5在大部分时间里也都超过Ⅴ类水质指标限值. CODCr与BOD5浓度较高,说明在监测年限里,监测断面有机物污染比较严重. 粪大肠菌群远超出Ⅴ类水质指标,在丰水期和平水期都出现了浓度特别高的异常值,枯水期的污染更为严重. 在监测时段中,各监测断面硫化物指标浓度相对都很低,基本在Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类的水质标准之间,偶尔在丰水期超出Ⅱ类水质标准. 挥发酚枯水期平均指标浓度>丰水期平均指标浓度>平水期平均指标浓度,在枯水期浓度大部分超出Ⅲ类水质指标限值,而在丰水期和平水期基本符合Ⅲ类水的标准. 高锰酸盐指数大部分时间段里都在Ⅴ类水质标准值以内,其中枯水期平均指标浓度>丰水期平均指标浓度>平水期平均指标浓度,最大值、异常值都出现在枯水期.
综合来看,监测断面的溶解氧、化学需氧量、五日生化需氧量、粪大肠菌群、硫化物、挥发酚等6项水质指标浓度在枯水期和丰水期波动较大,在平水期波动相对较小. 对照各个指标功能区限值可以看出,严重超标的单项指标为总磷、氨氮、粪大肠菌群、化学需氧量和五日生化需氧量,情况较好的指标为高锰酸盐指数、硫化物、挥发酚、溶解氧,由此说明在2012—2020年间通州河流的水质情况较差. 从氨氮、总磷和溶解氧等富营养化相关指标看出,通州河流水体的富营养化较为严重,需要引起重视. 总体而言,监测的9个指标中,只有硫化物的平均指标浓度在丰水期大于其它两个水期,而其余8个指标都是在枯水期的平均浓度更大,与单因子水质指标指数法得出的结论相同. 从图3中还可以看出,水质指标在平水期数据波动较小,在枯水期和丰水期波动较大,且在枯水期容易出现污染浓度大的情况,说明其易受季节气候中雨量变化的影响[22, 29]. 综合分析可看出丰水期水质指标略好于枯水期.
-
利用SPSS2.5软件,对2012年—2020年8个监测断面的9项水质指标数据进行标准化处理,然后对数据进行主成分分析. 其次,再通过降维和相关性分析,得到主成分提取结果,从而定量判断各断面的水质污染主要影响因素,综合得分越高的水质指标,对水体污染贡献率越大. 因丰水期水质指标相对较为稳定,因此选择每个年份的丰水期进行主成分分析.
首先对2012年的丰水期水质进行主成分分析(表2),结果表明前3项的贡献率较大,分别为37.87%、29.88%、20.27%. 由主成分载荷矩阵(表3)可以看出,化学需氧量、总磷、硫化物、五日生化需氧量在第一主成分上有较大载荷. 这主要是因为农业生产中大量使用化肥,从农田排放的氮、磷、硫等,通过农田渗漏进入地表和地下水,成为水体的重要污染源之一[30]. 因此第一主成分体现为农业污水污染. 高锰酸钾指数、溶解氧、氨氮在第二主成分上有较大载荷,由于高锰酸钾和氨氮是水体富营养化和有机物污染主要指标,因此第二主成分体现为富营养化和有机物污染;挥发酚、粪大肠杆菌在第三主成分上有较大载荷,这两种物质主要是生活污水污染的主要指标,因此第三主成分体现为生活污水污染. 通过3个主成分可以反映出通州河流水污染主要以农业污水污染、富营养化、有机物污染和生活污水污染为主[31-32].
利用主成分分析法,依次对2013—2020年丰水期的数据进行分析,根据主成分载荷矩阵和主成分特征值进行计算,得出主成分分析综合得分,得分越高说明水质越差.
由表4可知,各个检测断面的水质时间变化趋势基本相同,各断面主成分分析综合得分总体呈现先升高后降低的趋势,于2016年达到峰值,随后迅速下降. 同时由图4可以看出,丰水期第一主成分中高锰酸钾指数、化学需氧量、五日生化需氧量等因子得分,也呈现先升高后降低趋势,变化特点与各断面主成分分析综合得分变化相同. 这种变化主要是因为2012—2016年通州河流水质的恶化引起了相关部门的关注,政府加强了区域河流的综合整治[33-36],因此各项污染指标自2016年起逐年降低.
由表4分析可知,2016年前马驹桥以及北关桥污染最为严重,这主要是因为这两个点所处的通惠河和凉水河是通州污染最严重的两条河流,但经过治理后水质得到了极大改善[37],因此这两处断面主成分分析综合得分在2016年后逐渐下降. 苇沟闸、北关闸及师姑庄闸主成分分析综合得分总体较低,2016年后得分进一步降低. 这主要因为3处断面地处温榆河、潮白河,这两条河流是通州上游河段,水质一直较好,治理后水质也进一步改善.
总体看来,通州区部分河流的水质指标仍不达标,因此对河流治理应该持续进行,并增加治理效率. 一方面相关部门应该针对当地情况制定相关管理政策,加强河流的空间管控、健全河流保护体系、严格管理河流周边建设活动等;另一方面应该加强河流截污、污水处理、生物治理等相关技术研究,提高河流的承载力和自净能力;还应该拓展水环境保护宣传渠道,提高公民保护意识.
-
本文借助单因子水质标识指数法、箱线图法及主成分分析法等多重分析方法对通州主要河流8个监测断面的水质数据进行了时空分析. 在多样本的分析中,通过对各项指标多角度分析减小偏差,全面探究了通州地区主要河流水质的总体特征和影响水质的主要因素. 具体结论如下:
(1) 通过时间分析可得知,各断面主要水质指标时间变化趋势基本相同,并在2016年出现转折,这主要是因为2016年后相关部门加强了河流治理.
(2) 通过空间分析可知,通州主要河流空间污染特征相似,整体看来下游的水质要差于上游. 通惠河和凉水河总体水质较差,上游的潮白河和温榆河总体水质较好. 通过单因子水质标识指数法对9项水质指标分析后可知,2012—2016年通州河流各指标污染较为严重,2016—2020年通州河流水质情况有所改善,但依然存在氨氮、总磷超标的现象. 综合所有水质指标看来,罗庄和马驹桥断面污染最为严重,需要引起相关部门重视.
(3) 箱线图法分析表明,通州河流在丰水期水质最好,在平水期水质指标波动最小,在枯水期水质指标易超标,这说明气候会对水质产生一定影响. 对照各个指标功能区限值可以看出,总磷、氨氮、粪大肠菌群、化学需氧量和五日生化需氧量等指标超标严重,高锰酸盐指数、硫化物、挥发酚、溶解氧等指标情况较好.
(4) 主成分分析法表明,通州河流丰水期主要受3个主成分影响,其占比分别为37.87%、29.88%、20.27%,其中第一主成分体现为农业污水污染,第二主成分体现为富营养化和有机物污染,因此第三主成分体现为生活污水污染. 主成分分析综合得分表明,通州河流水质呈现时空差异.
基于多元分析的北京市通州区主要河流水质时空变化
Multiple analyses on time-temporal change of water quality in major rivers of Tongzhou, Beijing
-
摘要: 为评估北京市通州区域河流水质时空变化状况,选取该区域主要河流的8个监测断面于2012—2020年间的水质监测数据进行分析。水质监测指标包括溶解氧(DO)、化学需氧量(CODCr)、氨氮(NH4+-N)、总磷(TP)、生化需氧量(BOD5)、高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)、粪大肠菌群、硫化物和挥发酚等9项。借助单因子水质标识指数法、箱线图法及主成分分析法,研究了通州区河水水质时空特征和污染来源。结果表明,通州河流枯水期的水质比丰水期差,下游的水质比上游差,主要污染物有高锰酸盐指数、粪大肠菌群、氨氮、总磷等。这些污染物的类型主要与这些河流所承担的城市排污任务有关。同时从时间上分析,自2016年起通州河流总体水质得到大幅度改善,并持续好转,由此可见近几年通州河流治理效果较好。建议相关管理部门加大对河流、河道、渠道等水系周边环境的修复和建设力度,加强智慧河湖管理平台建设,实现精细化治水、智能化管河。最后,还应拓展宣传渠道,提高市民保护意识,自觉巩固和维护水环境的治理成果。Abstract: To evaluate the rivers of water quality in Tongzhou area, the water quality data of eight monitoring section in Tongzhou’s main rivers during 2012—2020 were selected for analysis. The water quality data include nine indicators like dissolved oxygen (DO), chemical oxygen demand (CODCr), ammonia nitrogen (NH4+-N), total phosphorus (TP), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), permanganate index (CODMn), fecal coliforms, sulfides, volatile phenols and so on. The spatial-temporal features and pollution sources of river’s water quality were analyzed via methods of single factor index, boxplot and principal component analysis. The results demonstrated that the water quality of drought period was worse than that of high flow period toward the rivers, and the water quality of downstream was worse than that of upstream, which could be concluded from the excess of CODMn, fecal coliforms, NH4+-N, TP and others. The main reason of pollution was attribute to municipal sewage discharge. Fortunately, the water quality of most Tongzhou’s rivers has been greatly improved since 2016, which could be attribute to the good governance in recent years. It was suggested that the relevant administrative departments should strengthen the remediation and protection of the surrounding environment of rivers and lakes. And the smart river and lake management platform should also be established to realize refine control and intelligent management of rivers. Finally, the publicity channels should also be expanded and the awareness of public protection should further be improved to maintain the achievements of water environment.
-
Key words:
- major rivers /
- water quality monitoring /
- multiple analyses /
- time-temporal change
-

-
表 1 单因子水质标识指数法对单项指标水质的评价结果
Table 1. Evaluation results of individual index water quality by single factor water quality identification index method
断面
Section时间
Time水质目标
Function高锰酸盐指数
CODMn溶解氧
DO化学需氧量
CODCr氨氮
NH4+-N总磷
TP粪大肠菌群
Fecal coliform五日生化需氧量
BOD5挥发酚
Volatile phenol硫化物
SulfideS1 枯Dry Ⅲ 5.92 3.80 6.63 11.68 12.39 4.21 7.64 4.11 2.60 丰Flood Ⅲ 5.22 2.10 6.03 9.56 8.95 3.60 6.43 3.30 2.60 平Normal Ⅲ 4.91 3.90 5.92 10.67 9.96 4.91 6.33 3.30 1.20 S2 枯Dry Ⅲ 5.12 3.90 5.82 9.26 11.48 3.80 6.23 3.11 1.30 丰Flood Ⅲ 5.22 4.21 4.21 12.29 15.69 3.70 6.23 3.00 2.60 平Normal Ⅲ 5.42 4.21 4.21 11.38 12.69 3.40 6.43 2.00 1.30 S3 枯Dry Ⅲ 6.13 4.91 6.93 16.29 12.99 3.90 7.44 4.41 2.60 丰Flood Ⅲ 5.52 2.30 6.23 9.67 11.68 3.60 6.13 4.21 1.30 平Normal Ⅲ 5.12 4.81 5.92 10.47 12.89 3.70 6.13 2.00 1.10 S4 枯Dry Ⅲ 5.72 4.01 6.83 14.19 16.49 145.89 6.53 4.33 2.60 丰Flood Ⅲ 5.32 4.51 6.83 11.78 14.29 84.99 6.93 3.60 2.40 平Normal Ⅲ 4.71 3.50 6.33 10.27 12.79 21.79 4.41 2.70 1.30 S5 枯Dry Ⅲ 5.12 3.90 5.62 11.78 11.48 3.70 6.13 3.30 1.30 丰Flood Ⅲ 5.01 3.50 5.62 8.85 10.07 3.30 5.72 2.00 1.20 平Normal Ⅲ 4.71 2.10 5.02 8.65 10.57 3.20 5.82 1.00 1.40 S6 枯Dry Ⅲ 5.02 2.00 5.12 9.96 10.87 3.90 6.33 3.30 1.30 丰Flood Ⅲ 4.71 4.81 5.42 8.05 9.47 3.50 5.82 3.30 1.20 平Normal Ⅲ 4.71 2.10 5.52 9.86 10.67 3.30 6.23 3.30 1.10 S7 枯Dry Ⅲ 5.12 2.00 5.92 10.57 12.49 3.20 6.33 3.30 1.20 丰Flood Ⅲ 4.91 4.71 5.32 8.65 9.86 3.90 5.82 3.70 1.10 平Normal Ⅲ 4.51 3.50 4.71 8.65 9.96 3.60 5.52 2.00 1.10 S8 枯Dry Ⅲ 5.12 2.10 6.13 13.19 11.7 3.20 6.43 3.70 2.00 丰Flood Ⅲ 5.01 3.90 6.13 9.06 8.75 3.50 5.82 3.30 2.10 平Normal Ⅲ 4.71 2.40 5.42 10.47 9.86 3.60 5.72 2.00 2.00 表 2 主成分提取结果
Table 2. The principal component extraction results
成分
Components初始特征值
Initial eigenvalue提取载荷平方和
Extract the sum of squares of loads特征值
Eigenvalue贡献率/%
Contribution rate累计贡献率/%
Cumulative contribution rate特征值
Eigenvalue贡献率/%
Contribution rate累计贡献率/%
Cumulative contribution rate1 3.41 37.87 37.87 3.41 37.87 37.87 2 2.69 29.88 67.74 2.68 29.88 67.74 3 1.83 20.27 88.01 1.82 20.27 88.01 4 0.52 5.83 93.85 — — — 5 0.40 4.50 98.35 — — — 6 0.13 1.41 99.76 — — — 7 0.02 0.24 100 — — — 8 0.00 0.00 100 — — — 9 0.00 0.00 100 — — — 表 3 主成分载荷矩阵
Table 3. Principal component load matrix
成分 Components 主成分 Principal components 1 2 3 CODMn 0.65 0.67 −0.14 CODCr −0.30 0.83 0.08 DO 0.82 0.47 0.22 NH4+−N 0.38 −0.74 0.47 TP 0.73 −0.61 0.27 挥发酚 Volatile phenol 0.37 0.53 0.76 硫化物 Sulfide 0.84 −0.16 −0.01 粪大肠菌群 Fecal coliform −0.50 0.18 0.83 BOD5 0.68 0.26 −0.45 表 4 不同年份丰水期监测断面主成分分析综合得分
Table 4. Comprehensive scores of principal component analysis of monitored cross sections in wet seasons of different years
断面Section 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 S1 0.09 −0.32 −0.13 0.86 −0.41 0.79 1.60 1.23 0.95 S2 0.06 0.20 1.84 1.58 0.05 −0.17 −0.03 −0.01 0.00 S3 −0.29 0.97 −1.31 −0.26 1.12 −0.13 −0.61 −0.23 −0.09 S4 0.84 0.11 4.58 0.73 1.06 1.27 −0.25 −0.10 −0.04 S5 −0.21 0.36 −2.05 0.39 −0.40 −0.45 −0.07 −0.03 −0.01 S6 −0.28 −0.60 −1.01 0.28 −0.21 −0.56 −0.02 −0.01 0.00 S7 0.10 −0.53 −0.78 0.29 −0.69 −0.43 −0.27 −0.10 −0.04 S8 −0.26 −0.20 −1.14 2.18 −0.52 −0.31 −0.36 −0.14 −0.05 -
[1] 倪晋仁, 崔树彬, 李天宏, 等. 论河流生态环境需水 [J]. 水利学报, 2002, 33(9): 14-19,26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2002.09.003 NI J R, CUI S B, LI T H, et al. On water demand of river ecosystem [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 33(9): 14-19,26(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2002.09.003
[2] 宋庆辉, 杨志峰. 对我国城市河流综合管理的思考 [J]. 水科学进展, 2002, 13(3): 377-382. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2002.03.019 SONG Q H, YANG Z F. Thinking of integrated management of urban rivers in China [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2002, 13(3): 377-382(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2002.03.019
[3] 赵彦伟, 杨志峰. 河流生态系统修复的时空尺度探讨 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(3): 196-200. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.03.047 ZHAO Y W, YANG Z F. Study on spatial and temporal scale of river ecosystem restoration [J]. Journal of Soil Water Conservation, 2005, 19(3): 196-200(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.03.047
[4] 陈静生, 李荷碧, 夏星辉, 等. 近30年来黄河水质变化趋势及原因分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2000, 19(2): 97-102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2000.02.001 CHEN J S, LI H B, XIA X H, et al. A study on water-quality trend in the Yellow River system from 1960 's to 1990's [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2000, 19(2): 97-102(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2000.02.001
[5] 吴运敏, 陈求稳, 李静. 模糊综合评价在小流域河道水质时空变化研究中的应用 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(6): 1198-1205. WU Y M, CHEN Q W, LI J. Fuzzy comprehensive assessment on spatio-temporal variations of water quality of a small catchment [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(6): 1198-1205(in Chinese).
[6] 李荣昉, 张颖. 鄱阳湖水质时空变化及其影响因素分析 [J]. 水资源保护, 2011, 27(6): 9-13,18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2011.06.003 LI R F, ZHANG Y. Analysis of spatial and temporal variation of water quality and its influencing factors in Poyang Lake [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2011, 27(6): 9-13,18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6933.2011.06.003
[7] 王睿, 左剑恶, 张宇, 等. 北京通州区主要河道水质分析及综合评价[J]. 给水排水, 2020, 56(S1): 724-728, 736. WANG R, ZUO J E, ZHANG Y, et al. Monitoring and comprehensive assessment of water quality of the main rivers in Tongzhou District in Beijing[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2020, 56(Sup 1): 724-728, 736(in Chinese).
[8] 王旭, 王永刚, 武大勇, 等. 北京市河流水生态健康时空异质性及改善路径研究 [J]. 灾害学, 2021, 36(02): 47-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.02.009 WANG X, WANG Y G, WU D Y, et al. Study on spatial otemporal heterogeneity and improvement path of river water ecological health in Beijing [J]. Hazards, 2021, 36(02): 47-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2021.02.009
[9] 芦艳平. 北京通州新城建设中再生水利用规划及其实施 [J]. 水利水电技术, 2012, 43(7): 24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2012.07.007 LU Y P. Planning and implementation of recycled water use in construction of Tongzhou New Town in Beijing [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2012, 43(7): 24-27(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0860.2012.07.007
[10] 徐祖信. 我国河流单因子水质标识指数评价方法研究 [J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 33(3): 321-325. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2005.03.008 XU Z X. Single factor water quality identification index for environmental quality assessment of surface water [J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2005, 33(3): 321-325(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2005.03.008
[11] 林小媛. 水质标识指数法在城市内河水质评价中的应用 [J]. 低碳世界, 2018(2): 24-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2066.2018.02.015 LIN X Y. Application of Water Quality Identification index method in water quality evaluation of urban inland river [J]. Low Carbon World, 2018(2): 24-25(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2066.2018.02.015
[12] 张辉, 杨雄. 单因子水质标识指数法在巢湖流域水质评价中的应用 [J]. 安徽农学通报, 2018, 24(10): 116-119,163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2018.10.048 ZHANG H, YNAG X. Application of single factor water quality identification index method for water quality assessment of Chaohu Lake Basin [J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 24(10): 116-119,163(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7731.2018.10.048
[13] 滕智超, 丁爱中, 李亚惠, 等. 赤水河上游水质时空特征分析及其污染源解析 [J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(3): 322-327. TENG Z C, DING A Z, LI Y H, et al. Sources of water pollution and their spatiotemporal variations in the upper reach of the Chishui River [J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 2016, 52(3): 322-327(in Chinese).
[14] 刘瑶, 于雷, 余向勇, 等. 箱线图在河流水质评价中的应用研究: 2008中国环境科学学会学术年会[C], 中国重庆, 2008. LIU Y, YU L, YU X Y, et al. Application of boxchart in river water quality evaluation: 2008 Annual Conference of Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences [C], Chongqing, China, 2008(in Chinese).
[15] 杨柳, 宋健飞, 宋波, 等. 主要污染物水质标识指数法在河流水质评价的应用 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(11): 239-245. YANG L, SONG J F, SONG B, et al. Primary pollutant water quality identification index method and its application to comprehensive evaluation of river water quality [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(11): 239-245(in Chinese).
[16] 通州区水务局. 立足新起点 创造新成就 努力使通州区水务工作再上新台阶 [J]. 北京水务, 2016(3): 6-7. Tongzhou Distinct Water Authority. Based on a new starting point to create new achievements and efforts to make Tongzhou district water work to a new level [J]. Beijing Water, 2016(3): 6-7(in Chinese).
[17] 吕博. 2015年北京市水务工作会召开 [J]. 北京水务, 2015(1): 7. LU B. The 2015 Beijing water work conference was held [J]. Beijing Water, 2015(1): 7(in Chinese).
[18] 安国英, 郭兆成, 叶佩. 云南大理地区1989—2019年期间气候变化及其对洱海水质的影响 [J]. 现代地质, 2021(35): 1-14. AN G Y, GUO Z C, YE P. Climate change from 1989—2019 in dali, Yunnan province and its impact on water quality in Erhai lake [J]. Modern geology, 2021(35): 1-14(in Chinese).
[19] 高斌, 许有鹏, 陆苗, 等. 高度城镇化地区城市小区降雨径流污染特征及负荷估算 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(8): 3657-3664. GAO B, XU Y P, LU M, et al. Analysis of rainfall runoff pollution and pollution load estimation for urban communities in a highly urbanized region [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(8): 3657-3664(in Chinese).
[20] 张仪, 姜应和, 程静, 等. 基于水质水量监测的武汉市雨水径流污染特征分析 [J]. 水电能源科学, 2022, 40(1): 52-55. ZHANG Y, JIANG Y H, CHENG J, et al. Analysis of pollution characteristics of rainwater runoff in Wuhan City based on water quality and quantity monitoring [J]. Water Resources and Power, 2022, 40(1): 52-55(in Chinese).
[21] 姜娜, 冯绍元, 郑艳侠, 等. 北运河水系通惠河干流水质监测与评价 [J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2012(12): 72-74,81. JIANG N, FENG S Y, ZHENG Y X, et al. Water quality monitoring and evaluation of the Tonghui River in the north canal watershed [J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2012(12): 72-74,81(in Chinese).
[22] 刘波, 张艳, 高静, 等. 北京市通州区农村地下水氨氮浓度及其影响因素 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2006, 23(4): 328-330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2006.04.013 LIU B, ZHANG Y, GAO J, et al. Analysis of NH3-N concentration and the influence factors in ground water in the country of Beijing [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2006, 23(4): 328-330(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2006.04.013
[23] 白文荣. 通惠河下段水环境问题分析 [J]. 北京水务, 2010(1): 41-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4637.2010.01.015 BAI W R. Analysis of the water environment problems in the lower section of the Tonghui river [J]. Beijing Water, 2010(1): 41-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4637.2010.01.015
[24] 郭钧岐, 裴映雪. 改革开放以来北京工业重要政策回顾 [J]. 科技中国, 2019(11): 67-73. GUO J Q, PEI Y X. Review of important industrial policies in Beijing since the reform and opening u [J]. China Scitechnology Business, 2019(11): 67-73(in Chinese).
[25] 江静, 郭伟. 京津冀工业污染治理现状比较及对策研究 [J]. 价值工程, 2016, 35(1): 26-29. JIANG J, GUO W. Research on the actuality comparison and countermeasure of industrial pollution and control in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [J]. Value Engineering, 2016, 35(1): 26-29(in Chinese).
[26] 潘欣荣, 左剑恶, 张宇, 等. 廊坊市区径流污染时空分布特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(2): 795-802. PAN X R, ZUO J E, ZHANG Y, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and source apportionment of runoff pollution in Langfang City [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(2): 795-802(in Chinese).
[27] 刘娇, 吴淑琪, 贾静, 等. 地质环境样品中挥发酚分析现状与进展 [J]. 分析测试学报, 2015, 34(3): 367-374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2015.03.019 LIU J, WU S Q, JIA J, et al. Review on analytical methods of volatile phenols in geoenvironmental samples [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2015, 34(3): 367-374(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2015.03.019
[28] 徐庆勇, 陈忠荣, 杨巧凤, 等. 北京北运河流域平原区地下水水质空间分布特征 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2017, 28(3): 61-65,71. XU Q Y, CHEN Z R, YANG Q F, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of groundwater quality in Beijing north canal watershed [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2017, 28(3): 61-65,71(in Chinese).
[29] 沈琼, 王开颜, 张巍, 等. 北京市通州区地表水中多环芳烃的分布与季节变化 [J]. 环境化学, 2007, 26(4): 523-527. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.04.026 SHEN Q, WANG K Y, ZHANG W, et al. Distribution and seasonal variations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water from Tongzhou district of Beijing [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2007, 26(4): 523-527(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2007.04.026
[30] 夏妍, 彭鹏, 崔凤云, 等. 农业生产对水体环境污染的影响及防治措施 [J]. 环境科技, 2009, 22(S2): 94-95. XIA Y, PENG P, CUI F Y, et al. Effects of agricultural production on water bodies pollution and its measures of pollution control [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2009, 22(S2): 94-95(in Chinese).
[31] 陈志刚. “河长制”下智能视频监测系统研究. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2019CHEN Z G. Research on intelligent video monitoring system“river chief system”. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2019. [32] 王菊思, 赵丽辉, 孙建华. 工业污染源复杂废水体系的水质剖析方法 [J]. 环境化学, 1986, 5(5): 43-49. WANG J S, ZHAO L H, SUN J H. A method for analysis of complex pollutants in wastewater from industrial source [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1986, 5(5): 43-49(in Chinese).
[32] 田颖, 梁云平, 郭婧, 等. “水十条”对北京市地表水环境质量改善分析 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(4): 1-6. TIAN Y, LIANG Y P, GUO J, et al. Analysis on improvement effect of ten-action plan for prevention and control of water pollution on surface water in Beijing [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(4): 1-6(in Chinese).
[33] 姜娜, 冯绍元, 郑艳侠, 等. 北京市北运河流域地表水环境问题分析与治理对策 [J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2010(6): 9-11. JIANG N, FENG S Y, ZHENG Y X, et al. An analysis of problems and countermeasures for the surface water environment pollution of the north canal watershed in Beijing [J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2010(6): 9-11(in Chinese).
[34] 吉利娜, 刘泽娟. 北运河水生态环境保护和修复的实践历程 [J]. 北京水务, 2021(3): 17-21. JI L N, LIU Z J. The practice process of aquatic ecological environment protection and restoration of North Canal [J]. Beijing Water, 2021(3): 17-21(in Chinese).
[35] 王晓琳, 魏宁, 欧芳, 等. 浅析北京市城市污水处理与再生利用 [J]. 市政技术, 2012, 30(2): 89-92,128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7767.2012.02.038 WANG X L, WEI N, OU F, et al. Analysis of Beijing urban sewerage treatment and recycling [J]. Municipal Engineering Technology, 2012, 30(2): 89-92,128(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7767.2012.02.038
[36] 荆红卫, 张志刚, 郭婧. 北京北运河水系水质污染特征及污染来源分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(2): 319-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.02.019 JING H W, ZHANG Z G, GUO J. Water pollution characteristics and pollution sources of Bei Canal River system in Beijing [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(2): 319-327(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.02.019
[37] 李莲芳, 曾希柏, 李国学, 等. 利用模糊综合评判法评价潮白河流域水质 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(2): 471-476. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.02.042 LI L F, ZENG X B, LI G X, et al. Water quality assessment in chaobai river by fuzzy synthetic evaluation method [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2006, 25(2): 471-476(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.02.042
-



 下载:
下载: