-
自塑料问世以来,由于其稳定性、轻便性以及较低的价格,经过多年的发展,塑料已经成为生活中不可或缺的一部分. 在已经生产的塑料制品中,约50%是一次性使用的,只有20%至25%的塑料可以长期使用[1]. 尽管存在回收的潜力,但是考虑到经济成本,绝大多数(约92%)的塑料最终在废弃后被填埋或遗弃在自然环境中[1-2]. 近年来,有研究表明海洋已经成为了塑料最大的聚集地,每年有大量的塑料垃圾通过各种途径进入海洋并在海洋环境中累积[3]. 这些塑料垃圾在经历磨损、紫外线作用、微生物降解等过程后,会进一步形成微塑料. 当微塑料进入海洋环境后,容易被浮游生物、鱼类以及哺乳动物等多种海洋生物摄食,对生物体造成物理损伤并抑制生长. 除此之外,微塑料在环境中容易成为其它污染物的载体,如重金属、持久性有机污染物等[4-6],以及微塑料本身在生产过程中添加的增塑剂等. 在微塑料被摄食后,这些污染物可能会随着食物网传递,对生态系统造成不利影响,并可能由于食用海鲜等最终暴露于人体.
除了水体之外,海洋沉积物也被认为是海洋微塑料重要的汇. 漂浮在水体中的微塑料可能在多种因素的作用下发生沉降,水动力、生物摄食以及微生物作用等是影响微塑料下沉速率的主要因素[7]. 微塑料颗粒物表面生物膜的附着和颗粒物间的聚集也会进一步影响微塑料的沉降性能[8]. 有研究发现西班牙地中海沉积物中的微塑料丰度高达900 n·kg−1(干重)[9]. 北太平洋沉积物也发现了一定程度的微塑料[10],表明微塑料可以通过潮流运输到偏远地区,突出了塑料碎片的全球分布. 海洋中微塑料的来源多样,主要包括陆源输入、河流输入、污水排放、海上旅游活动及海洋渔业活动等[11].
目前,关于中国近海养殖海区中微塑料污染的报道较少,茅尾海是一个半封闭式内海,受河流影响较大,同时,茅尾海是一个典型的海水养殖区,长期的渔业养殖活动以及入海河流等为茅尾海带来了一系列的污染问题[12-14],海域内的微塑料污染问题比较明显. 因此本研究通过调查茅尾海水体、沉积物中存在的微塑料的数量、颜色、粒径和类型,了解微塑料在该海域的分布特征,并结合风险评估模型对茅尾海的微塑料污染风险进行初步的评估. 以期科学认识中国近海养殖海区茅尾海的微塑料污染特征,为养殖海域确定其潜在的生态风险提供参考.
-
茅尾海位于钦州湾海域顶部,是半封闭式的内海,其出海口位于海区南部. 该区域东、西、北三面为陆地所环绕,是一个袋状的内海海湾,海域面积约为134 km2. 茅尾海是我国典型的全日潮海区,潮汐性质属非正规全日潮,湾内潮汐日不等现象明显,最大涨落潮差为5.95 m. 该海域独特的地形地貌、水文特征及优良的水质极其适合养殖业的发展,养殖产品主要包括生蚝、青蟹、对虾、石斑鱼等. 其中,生蚝占主要部分,全国超过70%的生蚝产量出自这片海区. 除了养殖活动之外,茅尾海还是著名的风景旅游区[15].
-
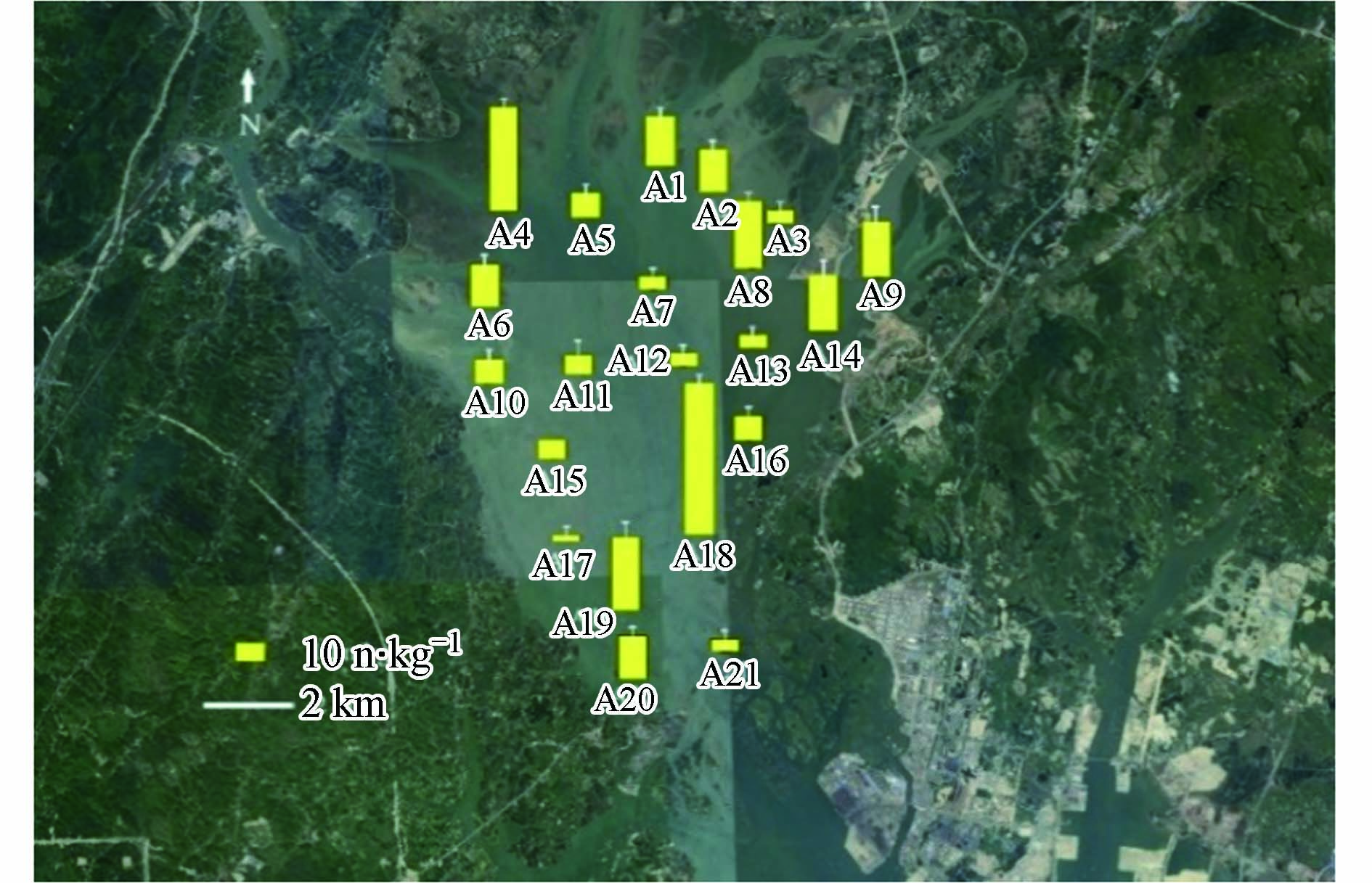
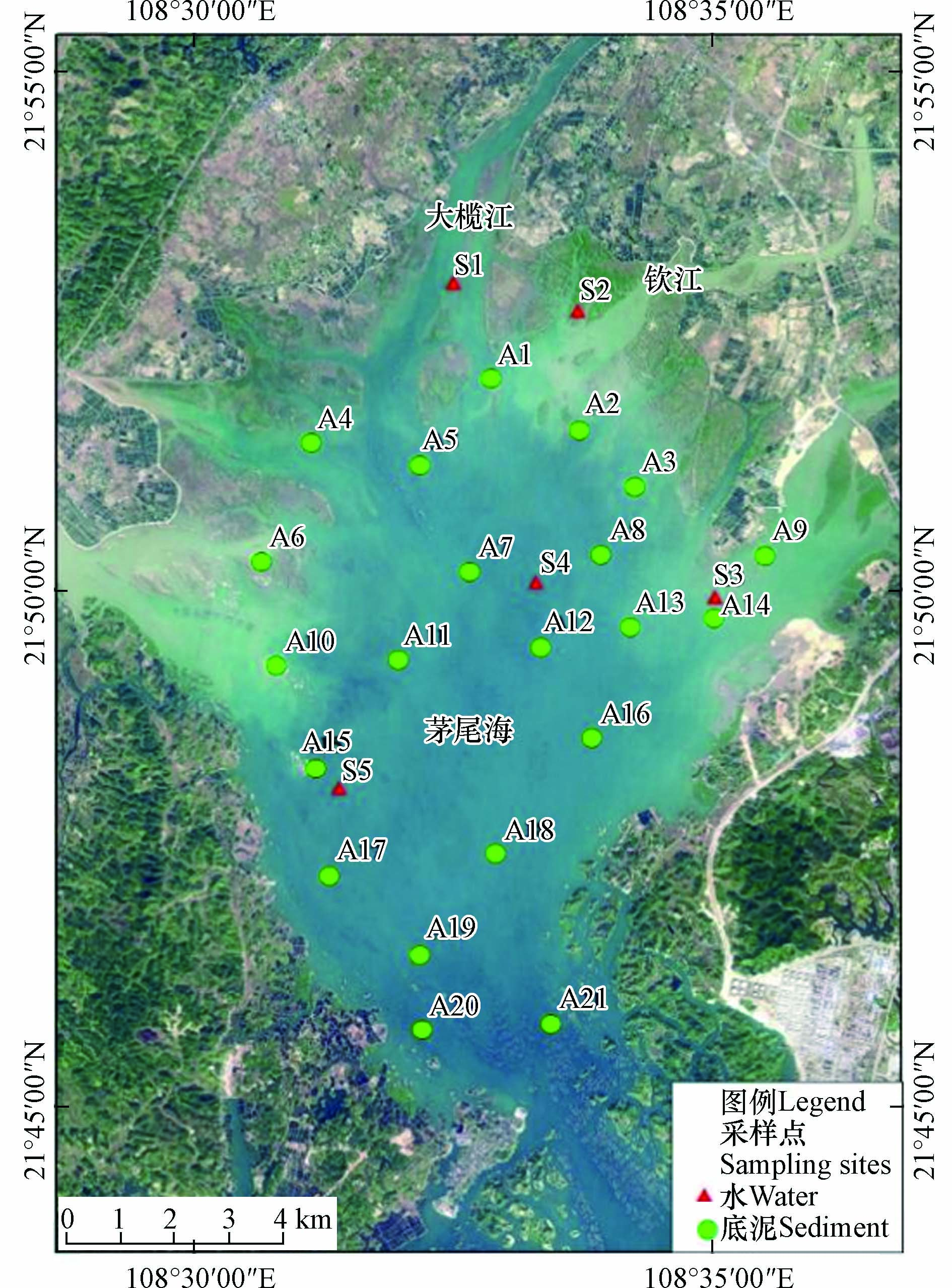
本研究对茅尾海区域进行了水体和沉积物微塑料样品的采集. 水样的采集采用拖网方式,因为茅尾海大部分区域为海水养殖区,分布着养殖用的网箱、蚝排等,为了保证安全,水样的采集只设置了5个采样点. 采样区域位于茅尾海北部钦江入海区域(S1—S3)、中部海域(S4)和南部出口附近水域(S5). 在采集水样时,使用300 μm浮游生物网进行拖网采集,将网固定在距离船舷1 m处,保持航速为1 m·s−1. 网口流量计(Mechanical Flow Meter Model 438 110, HYDRO-BIOS, Germany)被固定在浮游生物网网口中央,在采样前后记录流量计示数,以计算采水体积. 采样结束后利用纯水将收集装置中的残留物冲洗至PP瓶中,置于低温下保存,用于实验室分析. 沉积物使用抓斗式采泥器采集,根据茅尾海的海域环境,在区域内共设置了21个采样点,如图1所示. A1、A2、A4—A6、A9—A10、A13—A15、A17、A19—A21位于茅尾海农渔业区域,A3、A8、A16、A18位于休闲娱乐区域,A7、A12—A13位于茅尾海中部海洋保护区. 在每个采样点,选取表层1 kg样品,保存在铝箔样品袋中,于低温下保存送回实验室分析.
水样及沉积物的处理参照Lin等的方法,并进行改良[16]. 水样在送回实验室之后,通过手持放大镜(放大倍数10倍左右)进行初筛,挑选出较大的微塑料后保存至玻璃培养皿中的滤膜上. 剩余水样首先通过0.45 μm滤膜抽滤后,将滤膜上的残留物转移到1000 mL的烧杯中,加入200 mL 30%过氧化氢,在室温下反应24 h后,加入800 mL饱和氯化钠溶液,经充分搅拌之后,在室温下静置24 h,然后将上清液经0.45 μm滤膜抽滤,将收集了疑似微塑料样品的滤膜置于玻璃培养皿内待测. 采集的沉积物转移到烧杯内后,使用镊子挑出大型的碎石、木头等杂物,在烘箱内使用60 ℃烘干至恒重. 随后将样品破碎并充分混合,每个采样点样品随机称取3份,每份100 g,然后分别置于烧杯中,加入饱和氯化钠溶液1000 mL后,充分搅拌,在室温条件下静置24 h. 随后分离出上清液,借助放大镜初筛后,挑出疑似的微塑料样品保存并去除大型杂物. 剩余水样经0.45 μm滤膜抽滤后,将滤膜上的残留物转移到烧杯中,加入100 mL过氧化氢在室温条件下消解24 h后,再次加入1000 mL饱和氯化钠溶液浮选,使用0.45 μm滤膜抽滤,最终将收集了疑似微塑料样品的滤膜保存在玻璃培养皿中,等待下一步的分析处理. 为了减少误差,对每份样品重复上述步骤3次.
-
将抽滤完成之后的滤膜在恒温干燥箱中以40 ℃干燥24 h后,在配备有成像系统的立式光学显微镜(SAIKEDIGITAL SK2500H,China)下进行统计和筛选. 在观察过程中,滤膜在显微镜下以从左到右呈“Z”字形移动,借助镊子鉴别和挑选疑似的微塑料样品. 在显微镜下,将塑料按照形态分为薄膜、碎片以及纤维等. 通过测量软件统计微塑料的粒径大小,与此同时,也记录微塑料的颜色.
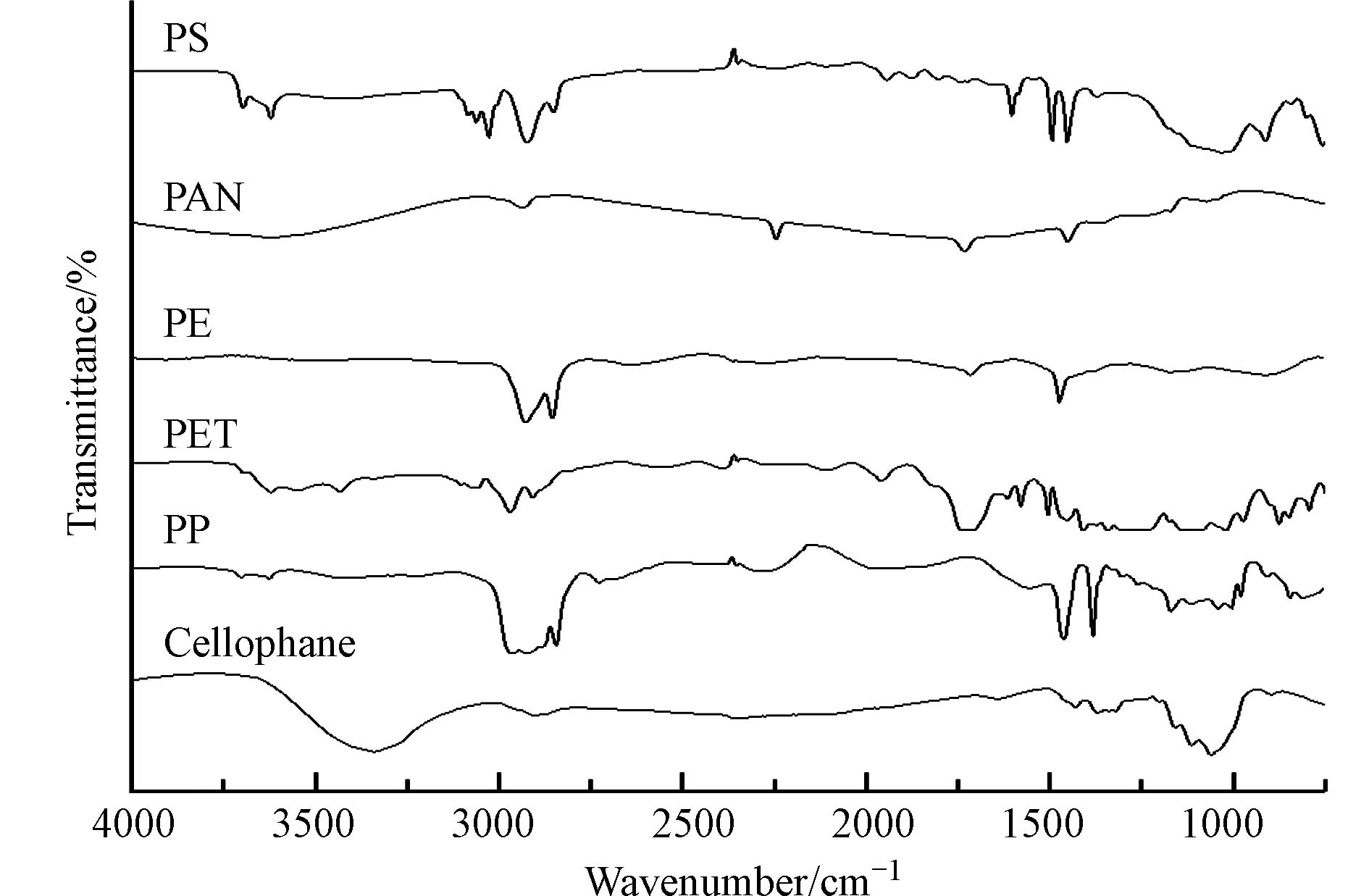
利用配备MCT检测器的傅里叶变换显微红外光谱仪(Nicolet iN 10, Thermo Fisher, USA)测定微塑料的成分. 使用金刚石压池附件测试疑似微塑料样品,测试采用透射方式,测试结果利用OMNIC软件(Thermo Fisher, USA)与谱库内的标准谱图比对,只有匹配度超过70%的结果才被认为是有效的[17-18]. 使用红外检测结果对目检法的结果进行修正,得出每个采样点最终的微塑料统计数.
-
采样系统中的各类设备在使用前用纯水冲洗3次并风干,流量计在实验室进行了校准,样品在转运过程中全程密封保存. 在实验室分析的过程中,操作员穿着棉质实验服并佩戴丁腈手套,同时在桌面放置一张白纸用以评估空气中的微塑料污染. 实验中使用的容器用纯水冲洗3次后烘干,样品在处理间隔时间段内使用铝箔纸覆盖容器口. 对微塑料的整个分析流程进行了两组空白实验,最终并没有发现外源微塑料污染,结果表明微塑料的分析环境是洁净的.
-
本研究参考Xu等[19]和Lithner等[20]提出的微塑料污染风险评估的方法,建立不同类型的微塑料聚合物对生态环境的化学毒性危险指数,以此初步评估中国近海养殖海区茅尾海水体和沉积物中微塑料带来的风险. 使用了以下公式:
其中,T是微塑料污染风险指数,Sn是聚合物危害评分,Pn是采样点每种成分聚合物百分比. 污染程度分类(五类):
$ T $ <10,低风险;10<$ T $ <100,较低风险;101<$ T $ <1000,较高风险;1001<$ T $ <10000,高风险;$ T $ >10000,很高风险[19]. -
利用Excel 2010和SPSS 22.0(IBM, USA)对数据进行统计分析,并使用Origin 2017和ArcGIS 10.2进行绘图. 水和沉积物中的丰度单位分别为n·m−3和 n·kg−1(干重),采用单因素方差分析检验茅尾海沉积物中微塑料丰度之间的差异和茅尾海不同环境介质风险等级之间的差异,采用Pearson相关性分析茅尾海水体和沉积物中微塑料丰度与风险指数间的相关性,所有的结果均以P<0.05判定是否存在显著性.
-
在茅尾海5个采样点采集的水样中均发现了微塑料,水体中的微塑料平均丰度为2.01 n·m−3. 其中,3个位于北部茅尾海入海海区的采样点(S1—S3)水体中微塑料的平均丰度为2.78 n·m−3,而茅尾海中部海区(S4)和南部出海口(S5)水体中的微塑料丰度分别为0.76 n·m−3和0.94 n·m−3(图2 a). 在茅尾海的21个采样点的沉积物中都检测到了微塑料,丰度范围从3.3 n·kg−1至83.3 n·kg−1(干重),平均值为(22.4±19.6)n·kg−1(图2 b). 茅尾海农渔业区域与休闲娱乐区域中的微塑料丰度显著高于中部海洋保护区(P=0.03,P=0.01),微塑料丰度最高值出现在采样点A18,该点位于旅游娱乐区内. 在A17中检测到了微塑料的最低值,该点位于茅尾海西南侧,是茅尾海退潮时主要出海路径.
微塑料在环境中的分布受多种因素的影响,例如天气、周围水域环境和附近的人类活动[21-22]. 在茅尾海区域,人类活动频繁,包括渔业养殖以及旅游活动等. 在这些过程中,受人为或者风力等影响,可能导致塑料袋、塑料瓶、渔业生产用的渔具等大型塑料垃圾被遗弃在海水中,这些塑料垃圾在海水侵蚀等作用下破碎形成微塑料. 采样点S1—S3位于钦江的入海区域,根据以往研究表明,茅尾海入海河流钦江水体中普遍存在微塑料[23],这也可能是北部海域水体中微塑料丰度比另外两个海域高的原因之一. 同时,茅尾海东部存在许多小型岛屿,水流受阻后流速减缓,有利于水体中微塑料的沉降,从而导致微塑料聚集到海底沉积物中. 沉积物中的微塑料丰度呈现出从四周向中心递减的趋势(图3),海区东部沿岸区域的微塑料丰度显著高于西部(P=0.036). 这可能是东部沿岸区域有着主要旅游景点,受到旅游活动的影响以及陆源微塑料的输入. 而西部区域则比较开阔,水流能快速流向出口,水体中微塑料能够快速迁移,不利于微塑料的沉积.
-
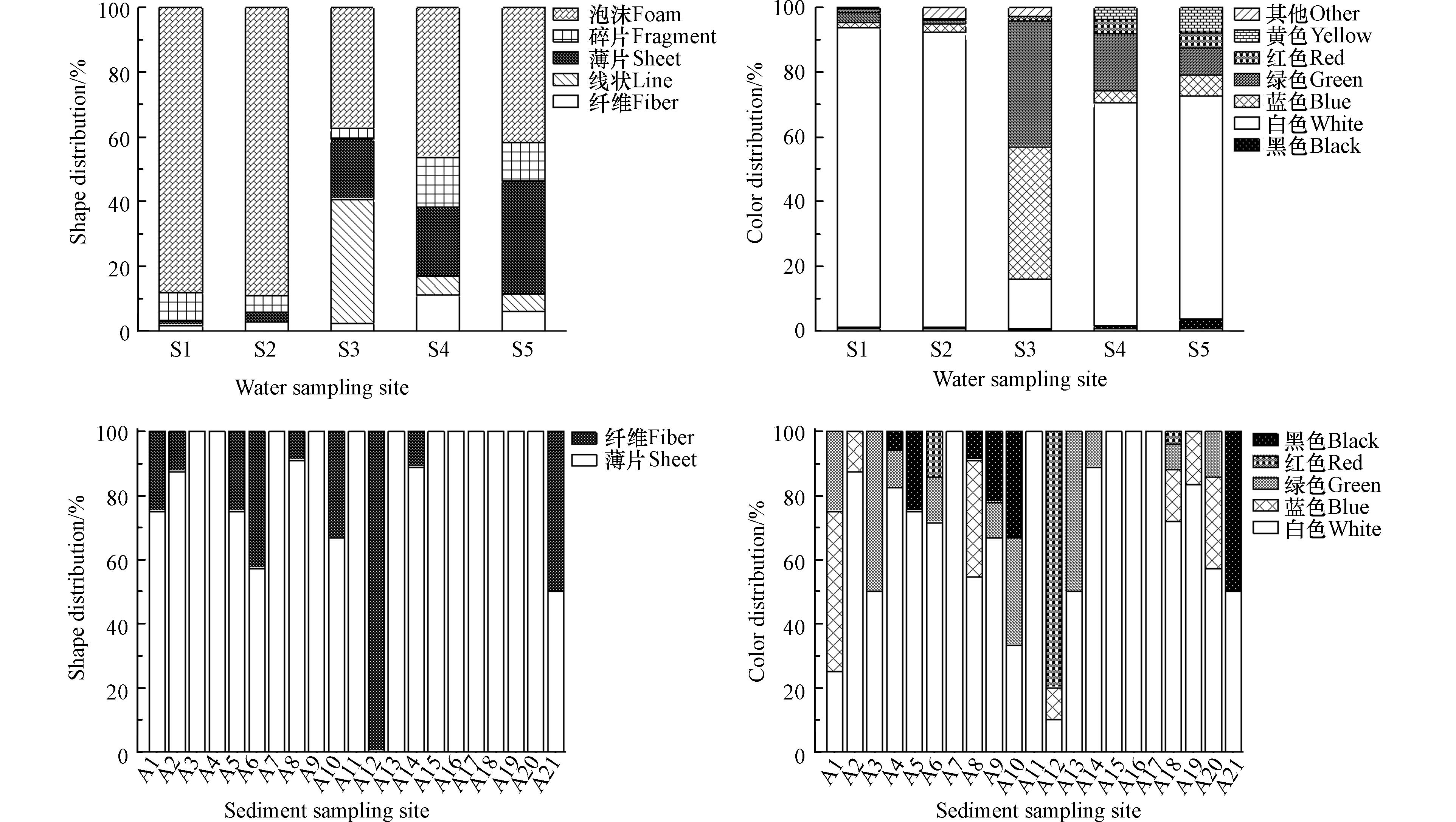
通过显微镜观察,将塑料按照形态分为薄片(sheet)、碎片(fragment)、纤维(fiber)、线状(line)以及泡沫(foam)[24]. 通过分析发现,在茅尾海水体采集的微塑料中,泡沫是5个采样点主要的微塑料类型,其次是薄片、碎片和纤维等. 5个采样点中微塑料的类型基本一致(图4 a)且颜色都以白色为主(图4 b). 在之前的报道中,海洋水体中的微塑料主要为薄片和纤维,泡沫并不是海水中常见的微塑料类型[25]. 但茅尾海水体中泡沫类型占比较大(60.1%),水生环境中的这类微塑料通常与渔业活动有关,用于包装、容器或制作浮力材料等. 茅尾海受养殖业的影响较大,海水养殖活动可能向水体中输入了大量的泡沫碎片.
与水体丰富的微塑料类型相比,在沉积物中微塑料只发现了纤维和薄片两种类型的微塑料(图4 c). 除了S12全部为纤维之外,在其余采样点中,薄片占主要部分,范围从50%至100%. 沉积物中的微塑料的颜色各异(图4 d),其中,薄片主要是白色、蓝色和绿色,而纤维主要是黑色和红色. 在五种微塑料类型中,薄片拥有较大的表面积和相对粗糙的表面,能在短时间内附着更多的微生物,使自身增重而导致沉降[26-27].
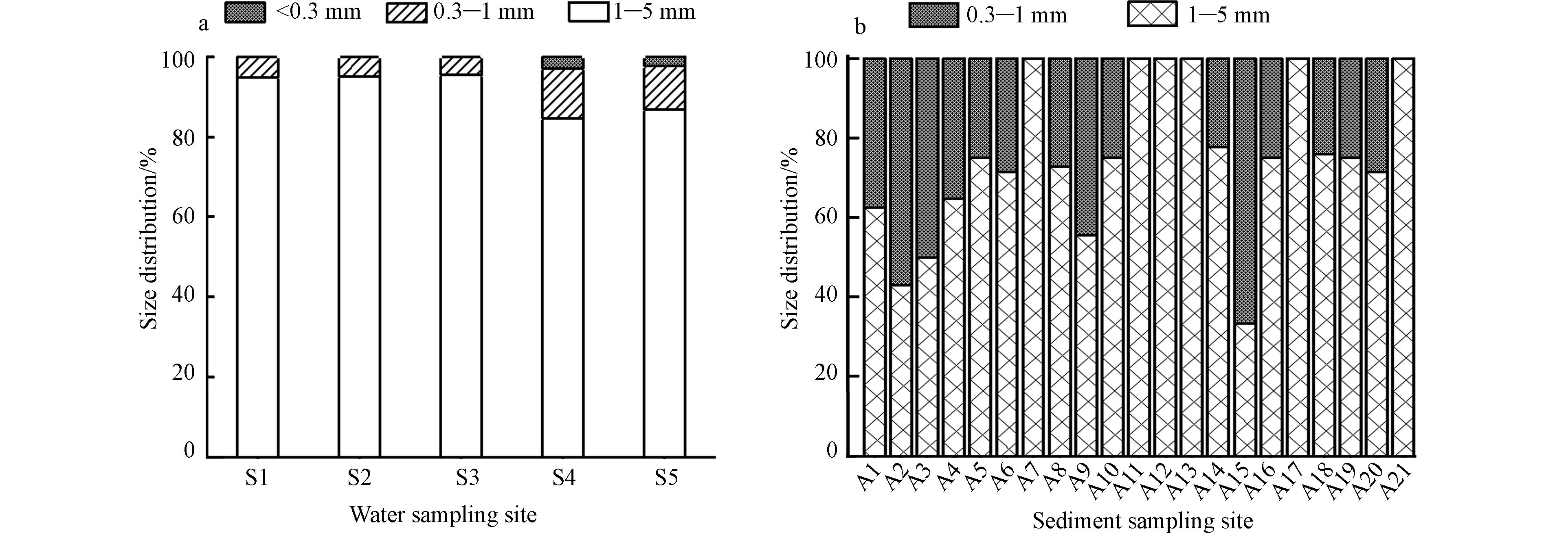
在水体和沉积物样品中,微塑料的粒径趋于一致,1—5 mm范围内的大粒径微塑料占主要部分(33.3%—100%)(图5). 通常,大型塑料在海洋环境中通过机械效应、光氧化和生物降解会逐渐破碎成较小的碎片. 所以在之前大部分的研究中,海水中的微塑料都以小粒径(<1 mm)为主. 比如:在北黄海表层海水和沉积物中,小粒径微塑料占总数的70%以上[28]. 渤海和黄海沉积物中最常观察到微塑料的尺寸小于500 μm[9] . 然而也有研究表明,塑料垃圾进入海洋环境中并不是立刻裂解成微塑料颗粒,往往要经过多重作用才逐渐分解为小粒径颗粒,较大粒径的微塑料颗粒更容易从水体沉降到沉积物中[29-30]. 在本研究中,茅尾海区域可能受到潮流的影响,水体与外海交换频繁,导致这些微塑料在不断地扩散至外海,其停留时间还不足以让其降解成更小的微塑料.
-
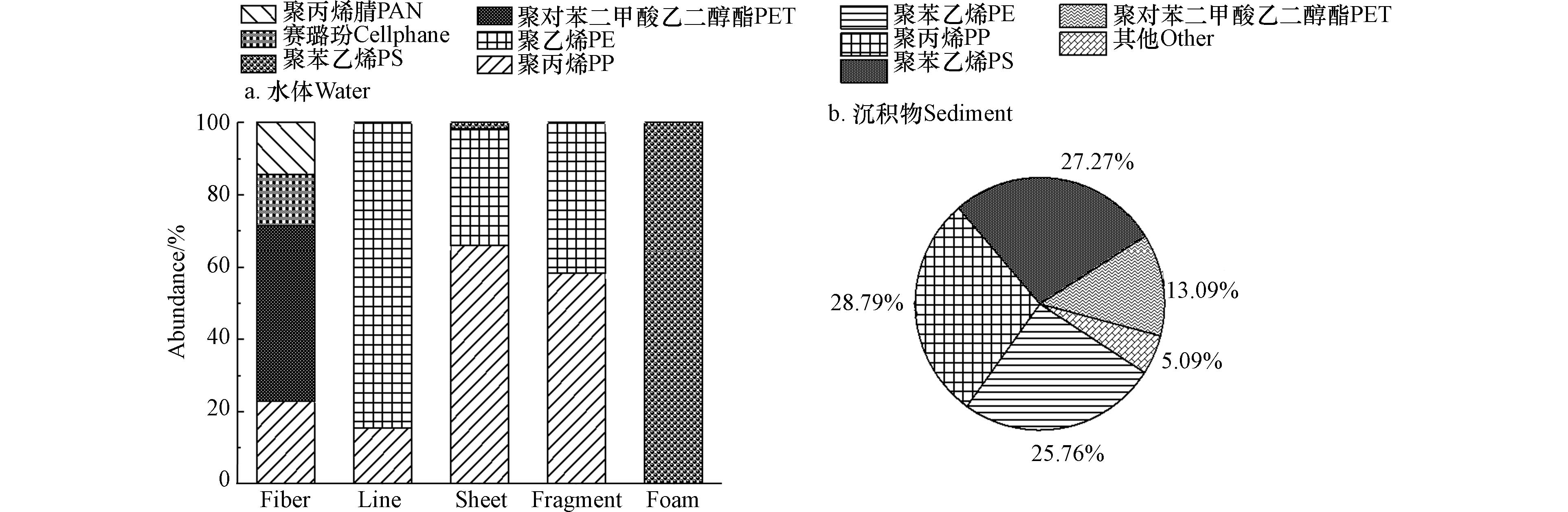
利用傅里叶变换显微红外光谱仪对采集的微塑料样品进行测定,最终的结果显示其中86%为塑料成分. 非塑料的干扰成分主要出现在纤维类的微塑料中,它们最终被鉴定为纤维素. 在水体中共确定了6种不同的微塑料成分(图6 a),包括聚丙烯腈(PAN)、赛璐玢(cellophane)、聚苯乙烯(PS)、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)、聚乙烯(PE)和聚丙烯(PP). 在所有水样中,PP(43.0%)和PE(27.6%)是微塑料的主要成分,因为密度小于水且可以通过海流运输. 纤维的成分相对复杂,主要为PET、PAN和cellophane等,而泡沫的成分都为PS,线状微塑料主要为PE(图7). 沉积物中的微塑料成分与水体中的基本一致,PP(0.89—0.91 g·cm−3)是沉积物中微塑料的主要成分,占比为28.8%,其次是PS(1.04—1.11 g·cm−3)、PE(0.91—0.97 g·cm−3)和PET(1.38 g·cm−3),分别占比27.3%、25.6%和13.1%(图6 b). 其中,薄片的成分相对复杂,而纤维主要为PET. 与低密度微塑料相比,高密度微塑料更容易从水中沉积到沉积物中. 但密度并不是影响微塑料在沉积物分布的唯一因素,微塑料的形状、比表面积以及环境温度、风力等也会影响微塑料的沉降过程[31]. 另外,随着时间的推移,微生物对微塑料的影响会逐渐显现. 微生物大量附着在微塑料表面会改变微塑料的密度以及表面特征,从而改变微塑料在水环境中的分布状态[32].
PP和PE主要在线状、碎片以及薄片型微塑料中检出. 线状微塑料主要为PE,与养殖中使用的塑料绳的成分一致,而泡沫的成分都为PS. 以往研究表明,渔业生产用的渔具中常常包含PP和PE成分,日常生活中常见的包装产品和塑料容器等同样也包含PS成分[33]. 这些塑料制品容易破碎形成微塑料进入海水中. 纤维的成分相对复杂,主要为PET、PAN和Cellophane等,这与常见的纺织产品的成分一致,通常被生产为纤维类产品,这进一步说明了茅尾海中的微塑料有可能来自渔业养殖以及旅游活动.
-
相关聚合物的危害评分如表1所示[20]. 在茅尾海水体中发现了一定程度的赛璐玢(Cellophane),但是其含量较少且缺乏其生态毒性的数据,无法确定其危害评分,所以在计算风险指数时未将其包含在内. 经计算,茅尾海水体和沉积物微塑料污染风险指数和风险等级如表2所示.
依据评价结果,我国典型近海养殖海区茅尾海不同环境介质中存在不同等级的微塑料污染. 茅尾海水体具有较高的生态风险等级,其中S1达到了Ⅳ级(高风险),该点位于茅尾海入海河流钦江河流入海处,各沉积物采样点的风险等级主要集中在Ⅰ—Ⅱ级. 水体和沉积物中微塑料的整体风险评估值分别为361.15和11.82,属于Ⅲ级(较高风险)和Ⅱ级(较低风险),茅尾海水体中微塑料污染风险等级显著高于沉积物(P<0.01). 茅尾海水体中的主要污染因子PAN,具有较高的危害评分,显著影响着水体微塑料污染风险指数. PAN广泛存在于腈纶衣物中,洗涤过程和丢弃的废旧衣物导致衣物上纤维的脱落从而流入到海洋中,造成水体中微塑料的污染,根据Zhang等[23]调查,茅尾海入海河流钦江中广泛存在着成分为PAN的纤维微塑料. 本研究中微塑料的污染水平低于辽河保护区和中国长江口[19, 34],但是高于吉林省查干湖和向海自然保护区[35],属于中等偏低水平. 根据Pearson相关性分析,茅尾海水体和沉积物中微塑料丰度与风险指数间没有相关性(P>0.05),水体与沉积物之间的微塑料污染风险指数也没有相关性(P>0.05),尽管水体与沉积物采样点距离相近,但是T的影响因素主要是微塑料的聚合物类型,由于降解、迁移和沉降,海洋环境各阶段中微塑料的类型会发生变化[35]. 同时,这表明该风险评估模型受到塑料污染物毒性的影响较大,微塑料的高化学毒性会导致高环境风险[17]. 此外,微塑料的污染水平还与茅尾海中微塑料的数量和聚合物类型的数量呈显著性弱相关(P<0.05),因此,仅仅依靠污染程度并不能完全评估研究区域的污染现状. 然而,基于研究区域污染程度高低,可以判别研究区域内高毒性微塑料存在与含量,可以此为根据,探究微塑料污染来源,从源头上控制、治理微塑料污染问题.
目前关于微塑料的生态风险评估尚在起步阶段,没有成熟的风险评价模型评估微塑料的污染风险,并且由于缺乏相关的法律法规管控与监测微塑料污染,海洋中的微塑料丰度与污染程度在逐年增加. 因此应探索建立更为成熟准确的数学模型,评估微塑料对生态环境潜在的健康风险.
-
本研究选取中国近海养殖海区茅尾海作为研究区域,研究了该海域内的微塑料分布特征并初步评估中国近海养殖海区茅尾海水体和沉积物中微塑料的生态风险. 研究得出:
(1)茅尾海水样和沉积物中均发现了微塑料,水体中的微塑料平均丰度为(2.01±1.23)n·m−3,沉积物中微塑料平均丰度为(22.4±19.6)n·kg−1. 茅尾海入海河流钦江中微塑料的输入、渔业养殖活动和旅游活动是茅尾海水体和沉积物中微塑料的重要来源.
(2)由于受到水动力等条件的作用,1—5 mm的微塑料在茅尾海水体、沉积物中都占主要(33.3%—100%). 受渔业养殖活动的影响,泡沫是水体中主要微塑料类型(60.1%),而薄片是沉积物中主要的微塑料类型(50%—100%). 在所有水样中,PP(43.0%)和PE(27.6%)是微塑料的主要成分,纤维的成分主要为PET、PAN和Cellophane等,而泡沫的成分都为PS,线状微塑料主要为PE. PP(28.8%)是沉积物中微塑料的主要成分,其次是PS(27.3%)、PE(25.6%)和PET(13.1%).
(3)通过风险评估模型初步得出,茅尾海微塑料的污染水平属于中等偏低水平. 茅尾海水体中整体微塑料污染风险等级显著高于沉积物,风险指数最高的点在水体采样点S1处(钦江入海处),达到了Ⅳ级(高风险),各沉积物采样点的风险等级主要集中在Ⅰ—Ⅱ级,属于较低风险. 危害评分高的聚合物聚丙烯腈(PAN)是水体中微塑料污染风险的重要来源.
水体及沉积物微塑料污染对近海养殖海区的生态风险
Study on the ecological risk of water and sediment microplastic pollution on offshore marine aquaculture areas
-
摘要: 微塑料在全球海洋水体及沉积物中广泛存在,然而关于近海养殖海区的微塑料污染特征鲜有报道,本研究调查了中国近海养殖海区茅尾海水体和沉积物中微塑料的分布特征并初步对其微塑料污染进行风险评估. 结果表明,茅尾海区域广泛分布着微塑料,茅尾海水体中微塑料的平均丰度为(2.01±1.23) n·m−3,泡沫(60.1%)是主要的类型. 沉积物中的微塑料平均丰度为(22.4±19.6)n·kg−1,薄片(50%—100%)在采样点中占主要部分. 茅尾海水体、沉积物中的微塑料粒径都以1—5 mm为主(33.3%—100%),水体和沉积物中的微塑料主要来自钦江的输入、旅游活动以及海水养殖活动. 通过风险评估模型初步得出,茅尾海区域微塑料的污染水平属于中等偏低水平,水体中微塑料整体污染风险等级显著高于沉积物,生态风险等级分别属于Ⅲ级(较高风险)和Ⅱ级(较低风险). 风险指数最高的点位于茅尾海入海河流钦江入海处,达到了Ⅳ级(高风险),各沉积物采样点的风险等级主要集中在Ⅰ—Ⅱ级,属于较低风险. 危害评分高的聚合物聚丙烯腈(Polyacrylonitrile,PAN)是水体中微塑料污染风险的重要来源.Abstract: Microplastics are widely present in marine waters and sediments worldwide, However, the pollution characteristics of microplastics in offshore aquaculture areas are rarely reported. In this study, the distribution characteristics of microplastics in seawater and sediments in offshore aquaculture areas of Maowei Sea were investigated. Furthermore, a preliminary risk assessment of microplastic pollution was conducted. The results showed that microplastics were widely distributed in the Maowei Sea. The average abundance of microplastics in Maowei Sea was (2.01±1.23) n·m−3. Foam (60.1%) was the dominant type. The average abundance of microplastics in sediments was (22.4±19.6) n·kg−1. Sheet (50%—100%) were the main part in the sampling sites. The particle size of microplastics in seawater and sediment of Maowei Sea is 1—5 mm(33.3%—100%). It was found that the microplastics in the seawater and sediments were mainly from the input of Qinjiang River, tourism activities, and mariculture activities. According to the risk assessment model, the pollution level of microplastics in Maowei Sea is medium to low level. The overall pollution risk level of microplastics in water was significantly higher than that in sediments, belonging to grade Ⅲ(slightly higher risk) and Ⅱ(slightly low risk) respectively. The highest risk index is located in the Maowei Sea into the sea river Qinjiang River into the sea, reached Ⅳ level(high risk), Risk level of each sediment sampling point are mainly concentrated in Ⅰ—Ⅱ level, belongs to low risk. Polymer polyacrylonitrile (PAN) with high hazard score is an important source of microplastic pollution risk in water.
-
Key words:
- Maowei Sea /
- microplastics /
- distribution characteristics /
- ecological risk
-

-
表 1 中国近海养殖海区茅尾海微塑料聚合物的详细信息
Table 1. Detailed information of microplastic polymers in Maowei Sea of China offshore aquaculture area
聚合物
Polymer英文缩写
English abbreviations单体
Monocase密度/(g·cm−3)
Density危害评分
Hazard rating聚乙烯 PE Ethylene 0.89—0.98 11 聚丙烯 PP Propylene 0.85—0.92 1 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯 PET Ethylene glycol 1.38—1.41 4 聚苯乙烯 PS Styrene 1.04—1.1 30 聚丙烯腈 PAN Acrylonitrile 1.184 11521 表 2 茅尾海中微塑料污染风险指数和风险等级
Table 2. Risk index and risk grade of microplastics pollution in Maowei Sea
微塑料污染风险指数
Microplastic pollution risk index风险等级
Risk level采样点
Sampling points<10 Ⅰ S2、S3、A2、A4、A5、A8、A10、A18 10—100 Ⅱ A1、A3、A6、A7、A9、A11、A12、A13、A14、A15、A16、A17、A19、A20、A21 101—1000 Ⅲ S4、S5 1001—10000 Ⅳ S1 -
[1] GEYER R, JAMBECK J R, LAW K L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made [J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(7): e1700782. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700782 [2] KEDZIERSKI M, FRÈRE D, LE MAGUER G, et al. Why is there plastic packaging in the natural environment? Understanding the roots of our individual plastic waste management behaviours [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 740: 139985. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139985 [3] LEBRETON L, SLAT B, FERRARI F, et al. Evidence that the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is rapidly accumulating plastic [J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 4666. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22939-w [4] BRENNECKE D, DUARTE B, PAIVA F, et al. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 178: 189-195. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.12.003 [5] RIOS L M, MOORE C, JONES P R. Persistent organic pollutants carried by synthetic polymers in the ocean environment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(8): 1230-1237. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.03.022 [6] 褚献献, 郑波, 何楠, 等. 微塑料与污染物相互作用的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(2): 427-435. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071502 CHU X X, ZHENG B, HE N, et al. Progress on the interaction between microplastics and contaminants [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(2): 427-435(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071502
[7] VAN CAUWENBERGHE L, VANREUSEL A, MEES J, et al. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments [J]. Environmental Pollution (Barking, Essex:1987), 2013, 182: 495-499. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.013 [8] ALIMI O S, FARNER BUDARZ J, HERNANDEZ L M, et al. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(4): 1704-1724. [9] ALOMAR C, ESTARELLAS F, DEUDERO S. Microplastics in the Mediterranean Sea: Deposition in coastal shallow sediments, spatial variation and preferential grain size [J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2016, 115: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.01.005 [10] MU J L, QU L, JIN F, et al. Abundance and distribution of microplastics in the surface sediments from the northern Bering and Chukchi Seas [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 245: 122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.097 [11] 白璐, 刘宪华, 陈燕珍, 等. 天津近岸海域微塑料污染现状分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(5): 1161-1168. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019062901 BAI L, LIU X H, CHEN Y Z, et al. Current status of microplastics pollution in Tianjin coastal waters [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(5): 1161-1168(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019062901
[12] 韦重霄, 赵爽, 宋立荣, 等. 钦州湾内湾茅尾海营养状况分析与评价研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2017, 42(9): 148-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2017.09.034 WEI C X, ZHAO S, SONG L R, et al. Analysis and assessment of nutrient status in Maowei Sea of inner Qinzhou Bay [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2017, 42(9): 148-153(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2017.09.034
[13] 朱文娟, 黄祥娟, 张栋, 等. 茅尾海养殖区重金属污染调查与评价 [J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2016, 33(2): 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.02.007 ZHU W J, HUANG X J, ZHANG D, et al. The investigation and assessment of heavy metal pollution in the aquiculture area of Maowei Sea [J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2016, 33(2): 36-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.02.007
[14] 廖日权, 许尤厚, 钟秋平, 等. 茅尾海近岸表层沉积物中邻苯二甲酸酯的组成分布特征 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(8): 1342-1347. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.08.013 LIAO R Q, XU Y H, ZHONG Q P, et al. Distribution and chemical composition of phthalic acid esters in surface sediments in Guangxi Maowei Sea littoral [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(8): 1342-1347(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.08.013
[15] 何帅. 茅尾海水质数值模拟及环境容量研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015. HE S. Numerical study on water quality and environmental capacity of Maowei Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015(in Chinese).
[16] LIN L, ZUO L Z, PENG J P, et al. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: A case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou City, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 644: 375-381. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.327 [17] PENG G Y, XU P, ZHU B S, et al. Microplastics in freshwater river sediments in Shanghai, China: A case study of risk assessment in mega-cities [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 234: 448-456. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.034 [18] RODRIGUES M O, ABRANTES N, GONÇALVES F J M, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 1549-1559. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.233 [19] XU P, PENG G Y, SU L, et al. Microplastic risk assessment in surface waters: A case study in the Changjiang Estuary, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 133: 647-654. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.020 [20] LITHNER D, LARSSON Å, DAVE G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(18): 3309-3324. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.038 [21] KUKULKA T, PROSKUROWSKI G, MORÉT-FERGUSON S, et al. The effect of wind mixing on the vertical distribution of buoyant plastic debris [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(7): L07601. [22] BROWNE M A, CRUMP P, NIVEN S J, et al. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: Sources and sinks [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(21): 9175-9179. [23] ZHANG L S, LIU J Y, XIE Y S, et al. Distribution of microplastics in surface water and sediments of Qin river in Beibu Gulf, China[J] Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 708: 135176. [24] ZHANG K, XIONG X, HU H J, et al. Occurrence and characteristics of microplastic pollution in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges reservoir, China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(7): 3794-3801. [25] PENG L C, FU D D, QI H Y, et al. Micro- and nano-plastics in marine environment: Source, distribution and threats - A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 698: 134254. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134254 [26] KLEIN S, WORCH E, KNEPPER T P. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in river shore sediments of the Rhine-main area in Germany [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(10): 6070-6076. [27] HORTON A A, SVENDSEN C, WILLIAMS R J, et al. Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK - Abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 114(1): 218-226. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.004 [28] ZHU L, BAI H Y, CHEN B J, et al. Microplastic pollution in North Yellow Sea, China: Observations on occurrence, distribution and identification [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 636: 20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.182 [29] HUANG Y Z, XIAO X, XU C C, et al. Seagrass beds acting as a trap of microplastics - Emerging hotspot in the coastal region? [J]. Environmental Pollution (Barking, Essex:1987), 2020, 257: 113450. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113450 [30] SONG Y K, HONG S H, JANG M, et al. Combined effects of UV exposure duration and mechanical abrasion on microplastic fragmentation by polymer type [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(8): 4368-4376. [31] SADRI S S, THOMPSON R C. On the quantity and composition of floating plastic debris entering and leaving the Tamar Estuary, Southwest England [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 81(1): 55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.02.020 [32] LOBELLE D, CUNLIFFE M. Early microbial biofilm formation on marine plastic debris [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(1): 197-200. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.10.013 [33] WANG W F, NDUNGU A W, LI Z, et al. Microplastics pollution in inland freshwaters of China: A case study in urban surface waters of Wuhan, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 575: 1369-1374. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.213 [34] 韩丽花. 辽河保护区微(中)塑料的污染特征及生态风险评估研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2020. HAN L H. Occurrences and ecological risks of micro (meso) plastics in Liao River conservation area[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2020(in Chinese).
[35] YIN K, WANG D X, ZHAO H J, et al. Microplastics pollution and risk assessment in water bodies of two nature reserves in Jilin Province: Correlation analysis with the degree of human activity [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 799: 149390. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149390 -



 下载:
下载: