-
塑料因其轻便、耐用、耐腐蚀、低成本等特点,而被广泛应用于日常生活、工农业生产、高新技术产业等领域。2021年,我国塑料制品累计产量为8004.0万t,累计增长5.9%[1]。塑料产品给人们生活带来极大的便利的同时,也带来的一系列环境问题。使用后的塑料制品由于受到了污染,其回收成本升高、分类难度加大、二次利用价值降低。截止2015年,全世界已经生产了78 亿t废弃塑料,其中仅有不到2%被回收利用[2]。塑料制品带来的各种问题,成为了当前全球关注的热点。微塑料(microplastics, MPs)是指直径小于5 mm的微小塑料颗粒,是由Thompson等[3]在2004年发表的文章中首次提出。这种小尺寸的塑料可以通过陆地、水源和空气传播,并且很难被人为治理[4]。虽然,我国在2020年底实施了“新版限塑令”,即禁止餐饮、零售行业使用不可降解塑料,全面推广可降解塑料的政策,但是一些报道认为,可降解塑料的大规模使用会在环境中引入更多微塑料,从而造成更大的环境负担[5]。
在过去十几年中,微塑料获得了相当大的关注。目前对于微塑料的研究主要集中于海洋、淡水环境以及河道湖泊沉积物、农用土地生态系统,生活污水等,而对大气中的微塑料鲜有研究[6-8]。由于样品收集困难、没有统一、规范的采样标准及前处理方法,所以对大气中微塑料的研究有限,且大部分研究缺乏对比性。微塑料通过大气运输向偏远地区的迁移及其对海洋和陆地生态系统中微塑料的贡献是塑料“源-路径-汇”模型中重要的一个部分[9]。最新的许多研究表明,微塑料可以通过大气运输传播到一些没有人为干扰的未开发地区,如偏远的山地[10-11]、高海拔地区[12-13]、北极地区[14-15]、海洋上空[16-17]、人迹罕至的沙漠[18-19]等。大气运输使得微塑料无处不在,并对人类和生态系统产生了重大影响。对于人体来说,通过呼吸吸入微塑料的量超过通过饮食摄入微塑料的量[20],而微塑料会给人体的呼吸系统造成负担,此外微塑料也可以作为病毒[21]或重金属[22]等其他有害物质的载体,以此对人体造成危害。
大气运输是微塑料转移、汇集过程中,不可忽视的重要环节。本文通过文献收集与分析概述了大气微塑料的采样方式、前处理过程和主要的表征手段。从丰度、物理形态、化学组成三方面介绍了大气中微塑料的赋存特征,同时分析了大气中微塑料可能的来源和迁移规律和健康风险。此外,还讨论了现有的大气微塑料研究方法的适用条件和特点对比,并展望了未来微塑料大气污染的发展方向和亟待解决的问题。
-
对大气微塑料进行文献计量分析,所用的英文文献数据下载自Web of Science (WoS)核心数据库,检索式为“Airborne microplastics OR Atmospheric microplastics OR Suspended microplastics OR atmospheric deposition microplastics OR Microplastics in air”,在检索结果中,按照WoS自有的学科类别进行划分,保留“环境科学”、“海洋淡水生物学”、“工程环境”、“毒理学”和“水资源”等相关学科,检索时间为2022年6月,共有792条检索结果。中文文献下载于中国知网(CNKI),检索词为(主题:微塑料(精确))AND(主题:空气(精确)),共有61条检索结果。利用NoteExpress(版本:3.4.0.8878)统计年发文量和关键词共现关系,选词词频最高的21个关键词,利用Ucient 6.0和Netdraw插件,进行了关键词共现关系分析,分析结果如图1。
在2015年由Dris等[23]发表在期刊Environmental Chemistry上的文章,首次研究了总大气沉降物中的微纤维和微塑料污染。2017年,周倩等[24]发表了首篇研究大气中微塑料的中文文献。虽然对大气微塑料的研究开始较晚,但大气微塑料有望成为微塑料研究的热门领域。通过关键词共现分析得出,目前研究的内容主要集中于大气沉降物、微塑料形态、微塑料的大气迁移,已有许多研究者对国内环境中大气微塑料进行了采样和分析。未来对大气微塑料的研究可能会拓展更多关于微塑料鉴定、毒性、吸入微塑料带来的健康风险、以及微塑料在环境中的老化降解。
-
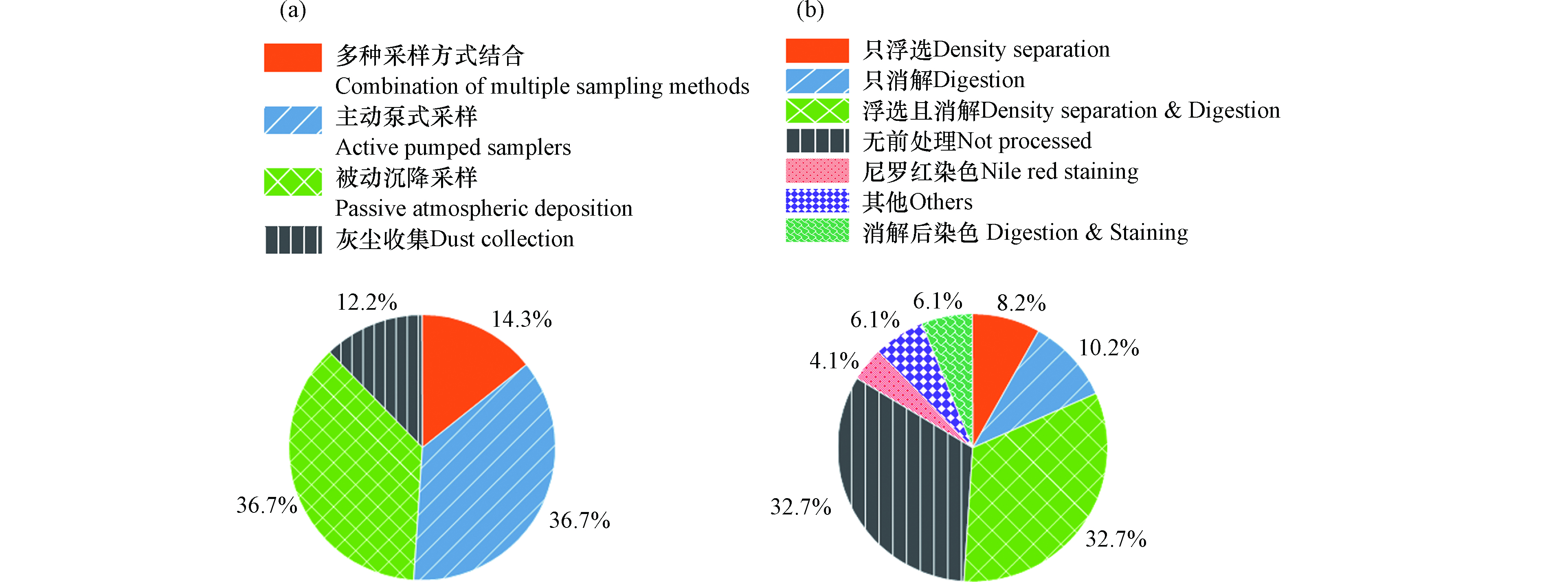
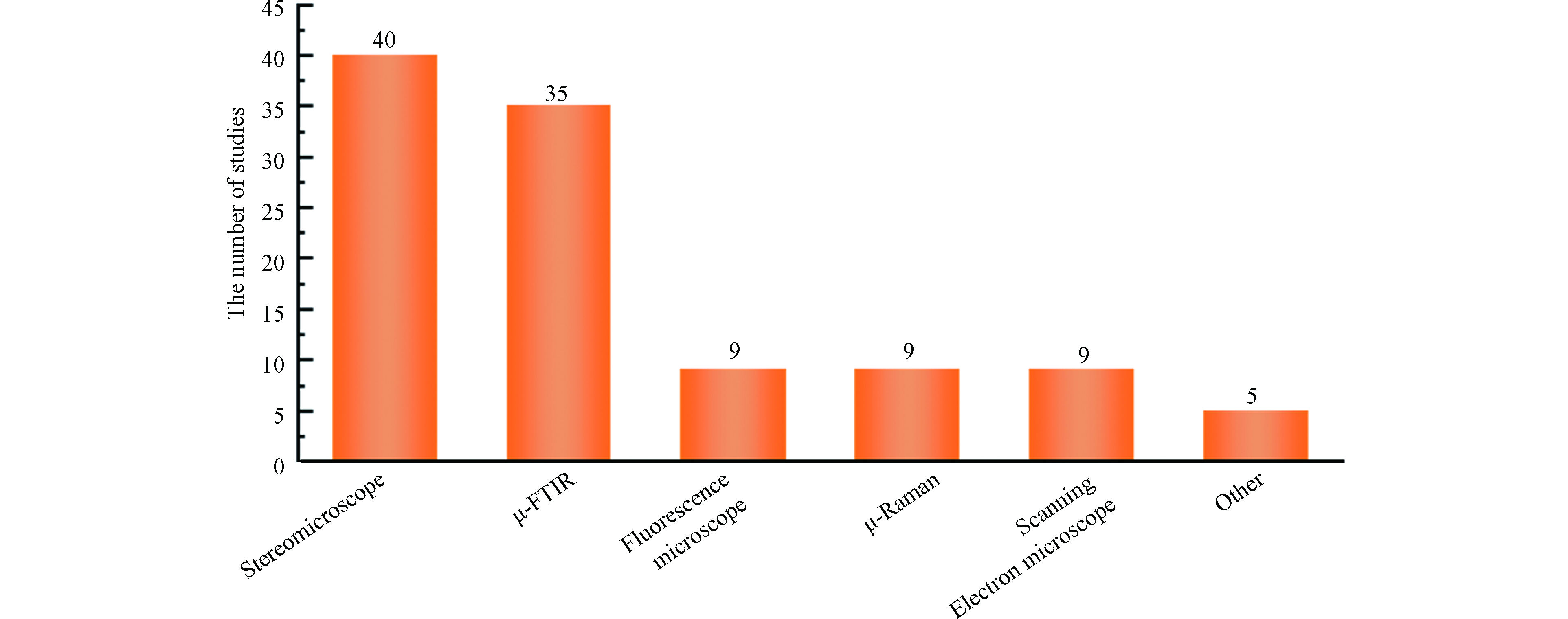
大气微塑料的分析过程包含3个步骤:采样、前处理、定性和定量分析。这一部分参考了49篇关于大气微塑料的研究性文章,统计其中所使用的采样方式、前处理过程和表征手段,并绘图进行分析(图2、3)。
-
大气微塑料分为沉降微塑料和悬浮微塑料。目前没有统一的采样标准,根据研究对象和目的的不同,有被动采样和主动采样两种采样方式。
被动采样用来收集某一时段的总大气沉降物。在忽略再悬浮的条件下,总大气沉降物中的微塑料水平可用于估算大气中的微塑料污染程度。对于一段时期内大气干、湿沉降常用被动沉降采样装置来收集。Dong等[25]使用不锈钢漏斗来收集沉降,将干、湿沉降共同储存在底部的不锈钢桶中。由于装置不需要供电,也不需要频繁维护,所以适合长期和偏远地区的沉降收集。对于室内灰尘和街道上的微塑料沉积物,可以使用刷子将沉积在一定范围地面上的灰尘搜集起来。这种方法搜集成本低且操作简单,但由于灰尘中的微塑料不完全来自大气沉积,因此这些结果不具有可比性,只能作为沉积微塑料结果的补充[26]。
主动采样法是世界范围内用于监测大气污染物的传统方法之一,相比于被动采样,主动采样可以收集到气溶胶中不易沉降的微塑料[27]。主动采样采用泵式大气采样器或者真空吸尘器,以过滤空气的方式采集样品。采样时使用孔径小于2 μm的玻璃纤维或石英纤维滤膜,聚四氟乙烯和尼龙滤膜会对微塑料的鉴别产生干扰。Zhu等[20]采用主动采样的方式,搜集了京津冀和长三角中5个特大城市空气中悬浮微塑料的样品,证明京津冀地区比长三角地区大气微塑料污染严重。Vianello等[28]通过用假人模拟呼吸的方式来采集样品,分析了人在室内环境中微塑料的暴露量。主动采样需要电源和机器定期维护,不适合长时间偏远无人地区的采样,可用于室内采样,或者室外短时间采样。如图2(a)所示,48.9%的研究采用了被动采样的方式,而36.7%的研究采用的主动采样的方式。另外,14.3%的研究使用多种采样方式结合的方法,这有利于进一步研究MPs的来源和迁移动力学,也更有利于不同丰度单位之间的相互转化,可作为未来研究的趋势。进一步的,有必要对采样过程进行统一的规范,提供采样装置和参数值的参考,以提高数据质量和不同研究之间的可比性。
-
前处理的目的是从环境样品中提取出MPs,这一过程使得后续分析鉴定更加方便,准确。空气中MPs样品的前处理方法参考了沉积物、土壤和水中MPs的前处理过程,一般包含浮选、消解两个部分。
浮选过程是利用塑料的密度小于盐溶液的密度这一原理,在样品中加入饱和盐溶液充分混合,使微塑料富集在上清液中,实现微塑料和沉降灰尘的分离。一般采用的饱和盐溶液有NaCl(1.2 g·cm−3)、ZnCl2(1.6 g·cm−3)、NaI(1.8 g·cm−3),目前主要使用ZnCl2溶液作为浮选剂,因为ZnCl2成本相对较低,溶液密度大,可浮选出大多数类型的微塑料[29]。为了提高回收率,一些研究中采样二次浮选。首先用NaCl进行预浮选,再用更高密度的NaI溶液对样品做后续浮选[30]。一方面,预浮选过程减少了NaI的用量,另一方面回收率也从70%提升至99%[31]。
消解过程的目的是去除样品中的有机物,减少干扰,提高检测效率。消解试剂分为四种:酸、碱、氧化剂、酶。在实验过程中,酸、碱会破坏微塑料本身的结构,而酶消解剂反应条件严格,反应速度较慢。实验中常采用的消解试剂有30% H2O2和芬顿试剂(FeSO4溶液与H2O2混合),芬顿试剂是在H2O2的基础上,引入了二价铁离子作为催化剂,大大提高了氧化消解效率。
在采样时间较短、干扰物少的前提下,为了减少在多次转移的过程中MPs的损失和污染,32.7%的研究中取消了前处理过程[32]。同时,样品前处理应与后续表征MPs的手段相匹配,前处理过程不应对后续MPs的表征产生干扰[33],也要尽量避免使用塑料材质的实验用具。因此,对不同前处理方式的回收率对比,提出高效且无干扰的分离、纯化方式也是未来微塑料研究的重点。
-
在采样和前处理过程之后,需要对样品中的MPs进行定性和定量分析,定性分析又可分为物理形态分析和化学成分分析。化学成分分析是为了鉴别MPs的聚合物类型,常用傅里叶红外变换(FTIR)光谱和拉曼(Raman)光谱等化学分析手段[11, 27]。而针对物理形态的表观分析往往针对MPs的粒径、颜色、形态[23, 34]。由于来自环境的样品中成分复杂,单一的分析方法不能全面、可靠鉴别MPs[35],所以常常通过两种以上的分析方法共同鉴别。
(1)视觉分析
视觉分析一般是分析MPs第一步[35],也是最常用最基础的方法[7]。在体式显微镜下,从样品其他成分中分离出疑似MPs的成分,并利用相关软件计数、测量和记录信息,可以直观的得到MPs的粒径、颜色、形态和数量等信息。早期涉及大气微塑料的研究中,存在利用视觉分析结果计算MPs丰度的报道[36]。
然而,这种分析方法不仅费时费力,而且还存在很多缺点。该方法用于粒径较大的微粒和纤维MPs时有效,但小粒径的MPs占据了样本中MPs的绝大多数[37],在目测计数小于100 μm的MPs时容易产生误差。同时,这种方法无法区分合成颗粒和天然颗粒,而且容易受到实验者主观判别的影响,所以常用来与光谱分析法结合使用,互补不足[38]。
在统计中,有10.2%的研究通过使用尼罗红染色的方式来区分天然聚合物和人工合成聚合物[39-40],利用了荧光显微镜来提高视觉分析的效率和准确性。虽然这种方法提高了检测效率,但也不是最理想的鉴别方式。不同的聚合物着色程度并不相同,例如,聚丙烯(PP)和未改性聚乙烯(PE)染色强烈,而聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)或风化聚乙烯在染色后荧光较少。Gabriel等[41]在研究中发现,并不是所有着色的物质都是人工合成聚合物,部分天然有机物质也会被染色,干扰样品检测。虽然,在当下的视觉分析方法无以代之,但在未来,找寻替代视觉分析的方式会成为新的研究趋势。
(2)光谱分析
傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)是用于表征MPs聚合物类型最成熟的分析方法之一,研究者已经通过收集和总结建立了一个完整的用于识别和比较分析的聚合物红外光谱库。通过检测不同红外频率下的样品分子振动强度来获取光谱信息,得到代表对应MPs化学组分的红外光谱图,将微塑料的光谱图与库中已知聚合物的光谱图对比,可以直接匹配构成微塑料的聚合物类型[42]。μ-FTIR是显微镜与傅里叶变换红外光谱仪的结合,它能很好地检测20 μm以上的微塑料[29],目前有许多针对空气中MPs的研究都采用了μ-FTIR的分析方法。μ-FTIR有三种不同的工作模式,分别是透射模式、反射模式、和衰减全反射(ATR)模式,在目前的研究中这三种模式都有涉及[43]。Cai等[44]对东莞的研究采用了反射-μ-FTIR,Wang等[45]对中国南海和东印度洋的研究中使用了透射-μ-FTIR,Ding等[46]对西北太平洋地区的研究使用了ATR-μ-FTIR。
此外,焦平面阵列(FPA)-傅里叶变换红外光谱可以通过对整个平面的样品进行分析成像,最终筛选出其中的MPs颗粒。Vianello等[28]首次将样品封入硒化锌盐窗,通过FPA-FTIR来表征大气中的MPs。尽管FTIR有一些局限性,但它仍然是一种可靠的技术,也是表征从环境中收集的微塑料的最广泛使用的方法。
Raman光谱也被广泛用于微塑料的检测,单波长激光照射到目标样品上后,由于样品的反射、散射和吸收,会产生和检测到不同波长和频率的散射光,利用样品散射光的频率变化进行分析得到分子振动、转动方面的信息,据此分析化合物的种类[47]。在需要分析表面形貌和表面微生物类型时,拉曼光谱无损化学表征的特点占有很大的优势。
近年来有关拉曼光谱检测微塑料的研究越来越多。Marina-Montes[14]利用拉曼光谱首次发现南极地区气溶胶中含有微塑料。Xu等[48]通过表面增强拉曼光谱对小于1 μm的大气MPs样品进行检测。要注意,使用拉曼光谱表征样品时,要保证尽可能去除样品中的杂质有机物,否则背景荧光高,对特征峰的干扰较大。
红外光谱和拉曼光谱都是技术上成熟的方法。红外光谱测定分子的官能团,而拉曼光谱则表征分子骨架,这两种方法相辅相成[49]。但相比于μ-FTIR,拉曼光谱显微镜有更高的空间分辨率(低至0.5—1.0 μm)、宽光谱范围、对非极性官能团的高灵敏度和窄光谱带[37, 50]。所以拉曼光谱只需要少量来自不同环境的微塑料,并产生高度可靠的结果。但与红外技术相比,通过拉曼光谱创建的聚合物光谱库尚未建立,添加剂可能会影响光谱结果的准确性[51]。目前,光谱法作为主流的微塑料表征手段,已经得到了广泛的应用(如图3)。在未来,克服红外光谱和拉曼光谱的局限之处值得进一步研究。
(3)其他分析方法
其他常用的分析方法有热裂解-气相色谱-质谱连用仪(Pyr-GC-MS)和扫描电子显微镜-能谱仪(SEM-EDS)。
Pyr-GC-MS工作时,首先样品会进行热处理,分解所释放出的气态化合物会被收集,并进入气相色谱柱中进行分离,被分离后的各组分进入质谱仪进行成分分析,最后与常见塑料类型的数据库进行比较,从而进行定性、定量分析[52]。这使仪器能够在成分粒径非常小的环境样品中进行识别,但不能分析微塑料的颜色、形状等其他特性。这种分析方法对样品有破坏性,会影响对样品的后续分析[53]。目前,已有色谱分析法应用于分离分析大气中微塑料的实例[54-56],虽然热分析方法很少被用于分析大气微塑料[57],但这种方法是一种十分高效且有潜力的检测方法。
扫描电子显微镜(SEM)有很高的分辨率,可以识别微塑料表面形貌特点,可以判断微塑料的降解方式[58]。在与EDS结合后,用于分析表面元素组成,以此分析微塑料表面附着的重金属或者其他污染物。虽然已有研究使用SEM表征微塑料,但由于SEM仪器的特性,表征前需要在微塑料表面进行溅射喷金处理,在微塑料表面形成导电层,这样可以保护微塑料表面不被SEM发出的电子束破坏。因为制样过程繁琐耗时且成本高,所以SEM不适用于大量微塑料的表征。但已有研究通过深度学习,对扫描电子显微镜照片中不同形状的微塑料进行自动定量和分类,准确率为98.3%[59]。
虽然这些分析方法被用于大气微塑料的检测技术尚不成熟,相信未来在对分析方法的深入研究和仪器附件的开发之后,这些分析手段能有助于大气微塑料的高效分析。
-
根据采样方式的不同,大气中微塑料的量化使用不同的单位。对于被动采样收集的大气沉降物样本,结果以单位面积的沉积速率,即MPs的沉降通量来表示(单位为 个·m−2·d−1),城市中微塑料的沉积通量一般为33—917 个·m−2·d−1。对于通过主动采样泵采集的悬浮颗粒物样本,结果以单位体积进气量所含的微塑料个数,即MPs的浓度来表示(单位为 个·m−3),城市中MPs浓度范围为5.2—505 个·m−3,如表1。在一些研究中,由于MPs粒径小,不采取计数的方式,而是直接通过质量量化。在2020年一项对12个国家室内灰尘的研究中[54],使用了高效液相色谱(HPLC)和电喷雾质谱(ESI-MS)作为分离和分析手段,在所有灰尘样品中都发现了PET(聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯)和PC(聚碳酸酯)塑料,其浓度范围为0.1—120000 μg·g−1。
研究方法会对MPs丰度值有影响。由于大量的小粒径MPs在分析时常常被忽略,在MPs粒径检出限较低的实验中,所得出的实验结果丰度较大。以针对上海地区的研究为例,同样是采用主动采样的方法,在2019年发表的研究中[34],粒径下限为23 μm,平均浓度(1.4±1.4)个·m−3,而在2021年发表的研究中[20],粒径下限为5 μm,平均浓度(267±117)个·m−3,相差了两个数量级。
在海洋上空中的MPs丰度低于城市或郊区的室外空气中MPs丰度。目前对海上的研究有中国东南海域[60](3.9×10−3 个·m−3)、西太平洋[16]((0.6±1.6)×10−1 个·m−3)、珠江口[45]((4.2±2.5)×10−2 个·m−3)、南海((0.8±1.3)×10−2 个·m−3)和东印度洋[45]((4.0±6.0)×10−3 个·m−3),相比中国东南沿海地区城市微塑料的丰度较低。
室内环境的微塑料丰度显著高于室外环境,在Liao等[61]的研究中很直观的验证了这一观点,室内MPs浓度((1583±1180)个·m−3)比室外MPs浓度((189±85)个·m−3)高了一个数量级。室内空气中MPs浓度高主要有两个原因:一是人口密度高,受人为活动影响大,纺织品作为一个产生微塑料的重要源头,其对室内MPs的贡献是很重要的[45]。二是空气流通和向外扩散能力差,沉降下来的MPs很容易在空调等的气流扰动的情况下再悬浮[32]。
总而言之,研究方法会对丰度有很大的影响,这些说明研究者们迫切需要统一微塑料的定量表达形式,规范实验研究的标准方法,并进一步探讨微塑料的时空分布规律。
-
(1)形状
MPs的形状取决于原始聚合材料的形态。空气中微塑料最常见的形状是纤维(fiber)和碎片(fragment),也有研究发现了少量的微珠(microbead)、薄膜(film)和泡沫(foam)。在对中国大连海岸带[62]、河北康保县[63]、东莞[64]、烟台[24]、英国伦敦[15]、中国南海和东印度洋等[60]的研究中纤维作为大气中微塑料的主要存在形态,占MPs总数的60%以上。但也有一些研究得出了不同的结论,在对德国汉堡地区的研究中碎片的含量为95%[65],同样对法国比利牛斯山脉的研究中[65],也得出了碎片占据主要地位的结论。
通过形状可以进行聚合物类别和微塑料来源的初步判断。Cai等[44]检测到样品中的泡沫来自用作包装材料的发泡聚苯乙烯。Liu等[16]首次在海洋空气中检测到微珠,含量为微塑料总量的5%,据其球形外观和黑色,推测这些微珠可能是塑料焚烧产物。同时,空气中纤维微塑料的比例与季节存在一定的相关性,秋冬季气温降低,衣服和毛毯等纤维类纺织品的使用增加,纤维的占比有所上升。形状的不同会影响到大气的空气动力学,从而影响到MPs在空气中的悬浮状态和运动轨迹,因此区分形状对于研究MPs大气运输过程有重要意义。
(2)尺寸
与水环境、沉积物和土壤环境中的微塑料相比,空气中微塑料的尺寸要小得多。尺寸小、质量轻的微塑料更容易悬浮和扩散,尺寸和密度较大的微塑料很难长时间驻留在空气中,且倾向于快速沉降。大部分试验研究结果总结出,随着空气中MPs颗粒尺寸的增加,对应的微塑料数目逐渐减少。在Zhu等[20]对中国5个特大城市的研究中,小于30 μm和30—100 μm范围内的微塑料占总量的绝大多数,分别为61.6%和33.1%,在100—300 μm(4.7%)、300—1000 μm(0.5%)和>1000 μm(0.1%)范围内微塑料丰度要低得多。在对大连海岸带[62]和温州市[61]的研究中,也可以得到类似的结论。
尺寸数据的差异与采样方式和分析方法有关系,主要依赖视觉分析的研究可能存在对小粒径MPs数量的低估[43]。随着分析检测手段的进步,实验中微塑料尺寸的检出限也越来越低,目前,依靠光谱手段的检出限在5 μm左右,大部分研究中大气微塑料的尺寸主要分布在500 μm以下。相比于其他种类的MPs,纤维在一个维度上更长,在大尺寸的微塑料中,纤维的比例最高[61]。小粒径的微塑料可能成为未来微塑料研究的重点,因为,较小的微塑料具有较大的比表面积,表面效应强,更容易吸附其他污染物,且纳米塑料容易被人体通过呼吸道吸入肺部,也更有可能进入体内参与人体内循环,从而,具有更严重的生物毒性效应。
(3)颜色
不同颜色MPs的丰度与研究地区周围人为活动有关,空气中最常见的MPs颜色为黑色(灰色)、和白色(透明)。在布什尔港(伊朗)市区[66]的悬浮粉尘样本中,对MPs的颜色进行讨论,如黑色(21%)、灰色(12%)、白色/透明(39%)、橙色(8%)和红色(20%)。Wang等[45]在珠江口的大气悬浮微塑料样本中,也出现了黑色(37.1%)、白色(12.3%)、棕色(12.4%)、红色(25.3%)、黄色(12.9%)的纤维塑料。在对巴黎大气微塑料的研究中,Dris等[23]指出,由于视觉分析具有一定的主观性,颜色鲜艳(蓝色、红色)的MPs更容易被发现,所以可能存在一定程度的高估。
在分析样品中MPs的来源和潜在附着物和化学成分时,颜色可以起到一定的辅助作用,减少一部分工作量[67]。白色的碎片通常是用于包装材料的聚乙烯,透明材料多为聚丙烯[68]。Matsuguma等[69]提出在实验过程中,MPs可能在紫外线照射或H2O2等氧化消解过程中发生褪色,对最后的结果产生影响。实际上由于氧化能力的限制[38],这一说法有待进一步验证。这也提醒在实验过程中要注意试剂对样品本身的破坏,避免对实验结果产生不良影响。
-
化合物类型是判断污染物最基础、最直观的标准。空气中的MPs是由天然聚合物和人工合成聚合物组成。天然聚合物通常有纤维素和蛋白质。人工合成聚合物的种类很多,目前大气中已经发现的人工聚合物类型有二十多中,最常见的有PET(聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯)、PE(聚乙烯)、PS(聚苯乙烯)、PP(聚丙烯)、PES(聚酯)、PA(聚酰胺)、RY(人造丝)等等。
不同聚合物类型的MPs丰度取决于其需求量和产量[70]。根据Plastics Europe[71]最新的统计结果显示,产出的塑料主要用于包装(40.5%)、建筑(20.4%)、车辆(8.8%)和电子产品(6.2%)等行业,对应各种聚合物的需求比率为:PP(19.7%)、PELD(低密度聚乙烯,17.4%)、PEHD(高密度聚乙烯,12.9%)、PVC(聚氯乙烯,9.6%)、PET(8.4%)、PS(6.1%)。随着可降解塑料的需求量和产量的增加,一些研究在大气MPs中发现PLA(聚乳酸)等可降解塑料[15, 55]。
化合物的类型与形态存在相关关系,Peng[55]在对室内灰尘样品的分析中发现,纤维类MPs中纤维素、PET和PA含量最多,在颗粒MPs中PP和PE所占的比例大。微塑料类型占比也与采样场景相关,Chen[72]在美甲店中对悬浮微塑料的研究中,主要聚合物是丙烯酸(27%),其次是橡胶(21%)和聚氨酯(13%)。Abbasi[73]通过收集表层雪分析尼龙是占比最多的沉降塑料,其次是PP、PET、PS等。
表1列举了近两年大气微塑料研究的赋存特征。到目前为止,没有文献明确对大气样本中聚合物类型的构成的分析进展总结,在以后的研究中可以对聚合物类型的地理分布和不同密度聚合物的大气迁移能力做更进一步的讨论。
-
空气中的微塑料来源广泛,这使得污染物中聚合物种类丰富,对污染物的治理也更加困难。通常空气中微塑料的来源有工农业生产[84],织物的洗涤和晾晒,轮胎、塑料制品的磨损风化[85],街道扬尘[86]和垃圾处理和焚烧[87-88]等。
常见的合成纤维制品、纺织服装可能会导致大气中悬浮微塑料污染。Liu[34]认为用自然阳光干燥的衣服可能是空气中微塑料的重要来源。O'Brien等[89]研究了家用烘干机在工作过程中微塑料纤维的排放,证实机械干燥确实会使微塑料纤维排放到周围的空气中,而且纤维排放量约占被烘干物总质量的1.2‱。刘艳等[90]模拟家庭洗涤过程,结果表明每3 g织物洗涤时释放微塑料数量在1300—1500 根。道路交通也会增加大气微塑料污染。据估计,轮胎磨损产生的颗粒有0.1%—10%会在空气中滞留[91],滞留时长从十几分钟到几小时不等,最大输送距离可达50 km[92]。
对空气中MPs的溯源是全面认识其污染特性的必经之路,而且有助于空气中MPs污染的防治。尽管此过程十分复杂,但大气沉降物中MPs聚合物的类型,所含的添加剂,形态以及颜色等物理外观,与来源具有相关性,从而可以简化溯源过程。在Liu[34]的研究中,从样品的形态特征和化学成分上观察到一些共性,表明空气中的MPs可以通过大气运输从陆地环境输入海洋。空气中大部分的纤维类MPs来自生活中随处可见的纺织品[45]。碎片MPs可能来自包装和可重复使用塑料材料、建筑材料、清洁产品以及广告牌和塑料容器的长时间风化、机械破碎、物理磨损[93]。
-
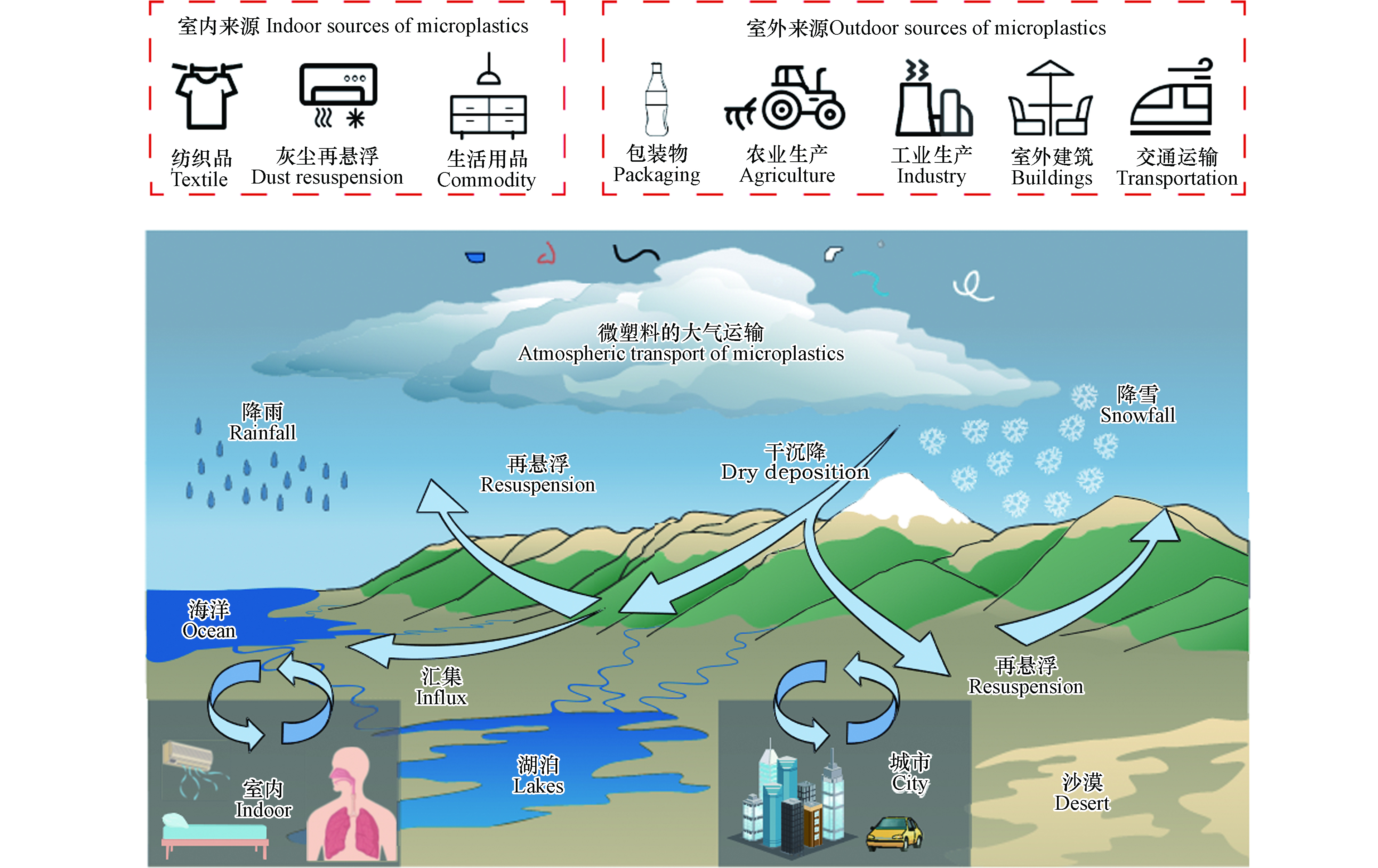
陆地、海洋、河流、湖泊与大气环境之间相互关联,形成了一个MPs的“源-路径-汇”的网络,MPs在几种不同环境之间交换,构成了微塑料在环境中的动态循环[68],如图4。MPs在大气环境中的运动有三种机制:悬浮、运输和沉降。悬浮是由局部空气湍流使得原本静止的MPs随气流一起抬升,进入空气循环。运输是依赖水平方向的气体对流,使得MPs能随空气被运输到更远的地方。沉降是通过降水、重力或者静电引力、吸附、化学作用,使MPs向地面运动。悬浮在空气中的MPs沉积进入陆地或海洋生态系统,也可能通过地表径流汇入水生生态系统。在一定条件下,已经沉降的MPs有可能再次悬浮,如此循环,就可以实现远距离传输。
许多研究已经调查了降水对微塑料沉降效应的影响。在Abbasi[79]对伊朗设拉子市的研究中通过分别对干、湿沉降取样发现,降雨会加速沉降,降水期间收集到的湿沉降中的纤维比相同时间段内收集的干沉降多5—10倍,但干沉降依然占微塑料大气沉降总量的绝大部分。大部分的研究得出,降雨强度不会影响微塑料在大气沉降物中的沉积通量[78],但这一结论依然存在争议,有待进一步调查研究。
许多证据表明,大气运输使得MPs普遍存在于环境中的各个角落。目前很多研究讨论了人迹罕至的地区沉积的MPs,并将这些归因于大气对MPs远距离运输的作用。目前的研究在海洋上空、沙漠、高山、北极、南极、冰川甚至是行星边界层[82]等都发现了MPs的存在,并分析了其迁移轨迹。反向轨迹分析可以有效的分析MPs的远距离运输路径,通过分析采样地的气候类型、风向、风速和颗粒物沉降的速度等,从采样地反推MPs的来源和运动轨迹。通过FLEXPART、HYSPLIT和LAGRANTO等拉格朗日大气模型可以分析大气污染物和微粒的来源位置和传播距离。2019年,Allen等[11]首次尝试通过数学模型解决大气MPs传输动力学问题。
具体而言,目前尚不清楚大气沉降物在多大程度上导致了水体和陆地污染。在这一领域,还需要在空间上,就“源-途径-汇”过程、输运参数以及与气象条件的关系进行更多的研究。
-
要探究微塑料的危害,首先要了解日常生活中人的空气微塑料暴露水平。微塑料的暴露量随着年龄的增长而减少,婴幼儿长期暴露于浓度较高的室内环境,婴儿的暴露量比成人高十倍左右[54]。Liu等[34]估计,上海居民的室外MPs吸入量为21 个·d−1,Vianello等[28]的室内模拟研究表明,成年男性可能在24 h内吸入272 个微塑料颗粒。微塑料暴露水平还受到其他因素影响,Chen等[94]的研究结果显示,空调气流可以促进含MPs的空气与人体的接触,人类暴露风险随空调过滤器使用时间的增加而增加。虽然人体的清除机制会将吸入的大部分微塑料拦截,但已有证据表明在人肺组织存在微塑料[95-96],而吸入的微塑料在肺部积累会增加患慢性肺阻塞等疾病的风险[97]。
尽管已经证实了空气中确实存在微塑料,但吸入微塑料而引起的健康风险尚未确定。微塑料的毒性来源主要包括自身毒性(单体或者聚合物本身),添加剂毒性(阻燃剂、增塑剂和抗氧化剂等),负载化学污染物(重金属和持久性有机污染物)和负载生物污染物(细菌、真菌、病毒),研究者通过细胞的体外培养,讨论了微塑料的细胞毒性机制[98-100]。以PS塑料为例,25 nm的微粒很容易通过非特异性吞噬作用被肺部细胞吸收,造成细胞粉尘过载,氧化应激,代谢紊乱,最终导致炎症甚至其他恶性疾病[101]。但缺少吸入微塑料对生物体内循环过程影响的研究,需要更多的实验数据支撑。
-
本综述通过文献调查,对大气环境中的微塑料的研究现状进行了系统的概述。分别介绍了大气微塑料的采样和前处理方法、表征鉴定技术、物理化学性质、潜在来源和迁移规律。目前,大气环境中的微塑料已经成为微塑料领域的研究热点。但依然存在一些问题有待解决。
(1)目前大气微塑料的研究方法尚未完善,微塑料取样和检测没有统一的操作规范,因此缺乏关于丰度和物化特征的可比数据。针对这些问题,一方面制定操作规范,干、湿沉降分离,主动采样与被动采样的方式相结合,这可以统一丰度表达方式,使研究结果可比性增加。另一方面创新微塑料的表征方法,提高微塑料的检出效率和质量,也是在未来需要解决的问题。
(2)由于研究区主要集中在发达的城市地区,所以对偏远地区微塑料的研究匮乏,特别是一些交通不发达,人烟稀少的地区。所以,在以后的研究中,要在更大范围区域内进行长期监测,这有助于排除区域均一化的影响,更好的评估影响微塑料时空分布的因素。
(3)对于空气中微塑料的来源与运输机制的分析还处于起步阶段。作为一种大气污染物,微塑料远距离运输的潜力巨大,因此可以对污染源及周围很大范围的区域产生影响。我们还需要进行更多的研究去评估大气中微塑料赋存特征与气象因素之间的关系,以此更深入了解微塑料在大气环境中的运输机制和最终去向。
(4)大气微塑料被动物和人类吸入后产生的健康风险研究缺乏系统性,其对植物生长的影响研究尚不多见,这些方面需要进一步研究。在未来需要建立生物模型,通过体内实验探索微塑料与其他污染物结合的毒性机制和联合作用,研究人体吸入后,微塑料的转移轨迹和不同器官的沉积比例。
(5)研究结果要对环保政策的制定有积极的指导作用,同时要投入精力去研究能够替代塑料的生物降解、环境友好的新材料。微塑料的源头控制被认为是防止污染环境的最可持续和有效的手段之一,同时塑料制品的分类回收也是十分有必要的。环保政策应从减少一次性塑料制品的使用和加强回收管理的方面控制微塑料污染。
大气微塑料的分析方法、赋存特征和迁移规律研究进展
Occurrence characteristics, migration, and methodological progress of microplastic in the atmosphere
-
摘要: 微塑料可以进入土壤、淡水、海洋和大气环境,并在不同环境之间动态循环。近期许多研究表明微塑料可以随大气运动进行远距离运输。本文通过文献调研,对大气中微塑料常用的分析方法、物理化学特征、污染来源和迁移规律进行系统性的梳理。结果表明,目前微塑料的表征手段以光谱分析辅助视觉分析法为主。研究区域集中在大型城市及其近郊,形状以纤维和碎片为主,大小主要分布在500 μm以下,颜色以黑、白、透明为主,化合物类型与环境中污染物来源直接相关。大气微塑料的主要来源是纺织品和大块塑料的老化破碎,研究中主要采用HYSPLIT后向轨迹模型,利用气象数据计算污染物迁移路径,来推测其排放源。目前对于大气微塑料研究刚刚起步,研究体系尚未确立,急需确立采样方式和定量分析标准规则,建立高效、低成本的研究方法。Abstract: Microplastics enter soil, freshwater, marine, and atmospheric habitats, where they circulate actively amongst them. Several recent investigations have discovered that microplastics can travel considerable distances in the atmosphere. However, currently research on atmospheric microplastics is in its early stages, with no study framework in place. It is therefore necessary to develop efficient and low-cost research techniques, as well as sample procedures and standard criteria for quantitative analysis. in this study the analysis methodologies, physical and chemical characteristics, pollution sources, and migration laws of microplastics were comprehensively reviewed in the atmosphere of large cities and suburbs using various literature statistics. The results reveal that spectral analysis assisted visual analysis is the primary approach of microplastic characterization. The microplastics found were primarily fiber and debris, with a size distribution of less than 500 μm and a color range of black, white, and translucent. The sources of microplastic pollutants in the environment are thought to be directly tied to compound type, such as textiles, as well as the ageing and shattering of large plastics. Where, the migratory path of pollutants and the source of emissions were detect using widely practiced HYSPLIT backward trajectory model using meteorological data.
-
Key words:
- atmospheric microplastics /
- analysis method /
- transportation rule /
- research progress
-

-
图 4 微塑料的来源与迁移[102]
Figure 4. Source and migration of microplastics
表 1 大气微塑料的赋存特征
Table 1. Occurrence characteristics of atmospheric microplastics
研究地区
Research area尺寸
Size颜色
Color聚合物类型
Polymer type形状
Shape丰度
Abundance参考
Ref.中国 大连海岸带 <1 mm(71.7%) 透明(32.7%)
黑色(29.1%)
蓝色(16.4%)
灰色(12.7%)
红色(5.5%)PET、CP、EPDM、PP、PU、PA、PEA 纤维(98.1%)、碎片(9.1%)、颗粒(1.8%) NA [62] 兰州 50—500 μm(70%) 透明(50%),黑色和蓝色、白色、红色、黄色、绿色 PET,PE,PA,PS,PVC和PMMA 碎片(44.4%)
纤维(47.5%)
泡沫、微球和薄膜353.8 个·m−2·d−1 [74] 河北
康保县<1 mm(41.4%)
1—3 mm(44.0%)
3—5 mm(14.5%)黑色、蓝色、透明、其他 RY(52.5%)
PE(11.5%)
腈纶(3.3%)
PES(26.2%)
PA(1.6%)
PP(3.3%)
PAN(1.6%)纤维(71.1%)
碎片(17.0%)
薄膜(12.0%)(1272.2±
209.1) 个·kg−1
(覆膜农田)
(1024.0±
459.1) 个·kg−1
(无膜农田)[63] 天津 NA NA 纤维素、PET、PA、PP、PE、PLA 纤维、颗粒 (4.1—8.5)×104 个·g−1 [55] 北京
天津
南京
上海
杭州<30 μm(61.6%)
30 −100 μm(33.1%)
100−300 μm(4.7%)
300−1000 μm(0.5%)
>1000 μm(0.1%)NA PET、PA、PE、PS、PP、PVC 碎片(88.2%)
纤维(11.8%)北京(393±112) 个·m−3
天津(324±145) 个·m−3
南京(177±59) 个·m−3
上海(267±117) 个·m−3
杭州(246±78) 个·m−3[20] 上海 主要尺寸范围
2.4—2181.5 μm
其中
<10 μm(21.2%)
>100 μm(11.7%)透明(57.0%)
绿色(15.8%)
蓝色(12.0%)PE(73.8%)
PES(9.2%)
PF(9.0%)
PVC(3.1%)
PP(0.6%)
PU(0.3%)
橡胶(0.2%)碎片(85%) 15.6—93.3 个·m−3 [75] 温州室内 <30 μm(60.4%)
30−100 μm(28.5%)
>100 μm(11%)NA PS、PA、PP、PE、PVC、PET 碎片(89.6%)
纤维(1583±1180) 个·m−3 [61] 温州室外 <30 μm(65.1%)
30−100 μm(29.4%)
>100 μm(5.5%)NA PS、PA、PP、PE、PVC、PET 碎片(94.2%)
纤维(189±85) 个·m−3 广州 57.2%纤维
(0.5—2 mm)
49.4%碎片(100—200 μm)白色(39.8%)
蓝色(28.7%)
红色(13.3%)
绿色(10.1%)
黄色(6.3%)PET、PS、PAN、PP、PA、ALK、EP、ABS 纤维(77.6±19.1%)
碎片(15.9±18.4%)
薄膜(2.1±2.9%)
微珠(4.4±4.9%)51—178
(114±40)个·m−2·d−1[76] 台湾室内 <50 μm(55%)
50—100 μm(36%)
>100 μm(9%)NA PMMA(27%)、
橡胶(21%)、
PU(13%)、PVC(9%)碎片、纤维 (46±55) 个·m−3 [72] 台湾室外 <50 μm(79%)
50—100 μm(21%)NA PMMA(40%)、
橡胶(13%)、PVC(12%)碎片、纤维 (28±24) 个·m−3 太平洋 西北太平洋 10—4556 μm
平均853 μm黑色为主 RY(67%)、PET(23%)、PMMA、PVC、PP、PVA 纤维(88—100%)
碎片(0—8%)
薄膜(0—2%)
颗粒(0—6%)(4.6—64)×10−3
(2.7 ± 1.8)×
10−2 个·m−3[46] 中国南海西北部 平均599±513 μm
<200 μm(28%)
200-500 μm(24%)
500-1000 μm(26%)黑色(28%)
蓝色(20%)
透明(19%)
白色(12%)
棕色(12%)
红色(9%)PES(29%)
RY(19%)
PP(15%)
PE(13%)
PS、PA纤维(65%)
碎片(20%)
颗粒(8%)
碎片(4%)
薄膜(3%)(1.3—6.3)×10−2
(3.5±1.5)×
10−2个·m−3[77] 亚洲 胡志明市 301—4872 μm 红色、蓝色、
绿色、灰色、
黑色PP、PE、PVC 纤维、碎片 71—917 个·m−2·d−1 [78] 亚洲 伊朗布什尔港市 8 μm~1 cm(纤维) 白色(39%)
黑色(21%)
红色(20%)
灰色(12%)
橙色(8%)PET(33%)
PE(29%)
PA(22%)
PS(10%)
PP(6%)碎片(63%)
纤维(27%)
薄膜(10%)5.2 个·m−3 [66] 伊朗设拉子市 市区<100 μm
(31.8%)
山区<100 μm
(74.6%)NA PP(38.2%)
PS(26.5%)
PE(20.5%)
PET(5.9%)
PVC(5.9%)
尼龙(2.9%)纤维(>99%) 1000—
3500个·m−2·month−1
(市区)
200—
600 个·m−2·month−1
(山区)[79] 伊朗布什尔港和设拉子 主要尺寸范围
>1000 μm白色透明(41%)
橙色(24%)
红色(16%)
黑色(9%)
绿色(7%)
紫色(3%)PE(42.0%)
PC(28.0%)
PP(18.6%)
PET(10.0%)
尼龙(1.4%)纤维(85%)
碎片(13%)
薄膜(2%)48.6—139 个·mg−1 [80] 欧洲 波兰格丁尼亚格但斯克湾 75—5000 μm
(纤维)
5—750 μm(碎片)
10—1520 μm
(薄膜)NA PE(41%)
PP(18%)
PE(14%)
PVC(14%)
EPM(9%)
PVA(9%)纤维(60%)
碎片(26%)
薄膜(14%)0—30
(10±8)个·m−2·d−1[81] 西班牙马德里 NA NA PES、PA、PE 碎片(67%) 13.9 个·m−3 [82] 西班牙农村 PES,PA和丙烯酸纤维 纤维(84%) 1.5 个·m−3 德国威悉河
(沉降)<500 μm 灰色(58%)透明(20%)和白色(15%) PP(39%)
PE(17%)
PET, PVC, PS, SI碎片(96.9%)
纤维(2.9%)
微球(0.2%)(99 ± 85) 个·m−2·d−1 [83] 德国威悉河
(悬浮)主要尺寸范围
4—33 μm
其中
<10 μm(67%)白色(82%)
蓝色(5%)
透明(2%)
黑色(2%)PE(78%) 碎片(79%)
微球(21%)(91 ± 47) 个·m−3 注:PET,聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(polyethylene glycol terephthalate);PE,聚乙烯(polyethylene);PC,聚碳酸酯(polycarbonate);PES,聚酯(polyethylene terephthalate);PAN,聚丙烯腈(polyacrylonitrile);RY,人造丝(rayon);EP,环氧树脂(phenolic epoxy resin);ALK,醇酸树脂(alkyd resin);PF,酚醛树脂(phenol-formaldehyde resin);PVC,聚氯乙烯(polyvinyl chloride);PS,聚苯乙烯(polystyrene);PP,聚丙烯(polypropylene);PA,聚酰胺(polyamide);PU,聚氨酯(polyurethane);EPDM,乙烯/丙烯/二烯橡胶共聚物(ethylene/propylene/diene terpolymer);PVA,聚醋酸乙烯酯(polyvinyl acetate);ABS,丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯三元共聚物(abscopolymer);EPM,乙烯-丙烯共聚物(ethylene/propylene copolymer);PMMA,聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(poly(methyl methacrylate));CP,赛璐玢(cellophane);SI,聚硅氧烷(polysiloxane). -
[1] 国家统计局. 国家数据[EB/OL]. [2022-3-24]. [2] RITCHIE H, ROSER M. Plastic Pollution - Our World in Data[EB/OL]. [2022-3-24]. [3] THOMPSON R C, OLSEN Y, MITCHELL R P, et al. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? [J]. Science, 2004, 304(5672): 838. doi: 10.1126/science.1094559 [4] PADHA S, KUMAR R, DHAR A, et al. Microplastic pollution in mountain terrains and foothills: A review on source, extraction, and distribution of microplastics in remote areas [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 207: 112232. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112232 [5] QIN M, CHEN C Y, SONG B, et al. A review of biodegradable plastics to biodegradable microplastics: Another ecological threat to soil environments? [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 312: 127816. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127816 [6] 骆永明, 施华宏, 涂晨, 等. 环境中微塑料研究进展与展望 [J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(13): 1547-1562. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0979 LUO Y M, SHI H H, TU C, et al. Research progresses and prospects of microplastics in the environment [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(13): 1547-1562(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0979
[7] CAN-GÜVEN E. Microplastics as emerging atmospheric pollutants: A review and bibliometric analysis [J]. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 2021, 14(2): 203-215. [8] ALFONSO M B, ARIAS A H, RONDA A C, et al. Continental microplastics: Presence, features, and environmental transport pathways [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 799: 149447. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149447 [9] STUBBINS A, LAW K L, MUÑOZ S E, et al. Plastics in the earth system [J]. Science, 2021, 373(6550): 51-55. doi: 10.1126/science.abb0354 [10] MATERIĆ D, LUDEWIG E, BRUNNER D, et al. Nanoplastics transport to the remote, high-altitude Alps [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 288: 117697. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117697 [11] ALLEN S, ALLEN D, PHOENIX V R, et al. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2019, 12(5): 339-344. doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0335-5 [12] ZHANG Y L, GAO T G, KANG S C, et al. Importance of atmospheric transport for microplastics deposited in remote areas [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 112953. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.121 [13] NEELAVANNAN K, SEN I S, LONE A M, et al. Microplastics in the high-altitude Himalayas: Assessment of microplastic contamination in freshwater lake sediments, Northwest Himalaya (India) [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 290: 133354. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133354 [14] MARINA-MONTES C, PÉREZ-ARRIBAS L V, ANZANO J, et al. Characterization of atmospheric aerosols in the Antarctic region using Raman Spectroscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy [J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2022, 266: 120452. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.120452 [15] BERGMANN M, MÜTZEL S, PRIMPKE S, et al. White and wonderful?Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic [J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(8): eaax1157. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax1157 [16] LIU K, WU T N, WANG X H, et al. Consistent transport of terrestrial microplastics to the ocean through atmosphere [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(18): 10612-10619. [17] TRAINIC M, FLORES J M, PINKAS I, et al. Airborne microplastic particles detected in the remote marine atmosphere [J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2020, 1: 64. [18] ABBASI S, TURNER A, HOSEINI M, et al. Microplastics in the lut and kavir deserts, Iran [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(9): 5993-6000. [19] WANG F, LAI Z P, PENG G Y, et al. Microplastic abundance and distribution in a Central Asian desert [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 800: 149529. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149529 [20] ZHU X, HUANG W, FANG M Z, et al. Airborne microplastic concentrations in five megacities of northern and southeast China [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 55(19): 12871-12881. [21] LIU Q Y, SCHAUER J. Airborne microplastics from waste as a transmission vector for COVID-19 [J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2021, 21(1): 200439. [22] WRIGHT S L, KELLY F J. Plastic and human health: A micro issue? [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(12): 6634-6647. [23] DRIS R, GASPERI J, ROCHER V, et al. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 12(5): 592. doi: 10.1071/EN14167 [24] 周倩, 田崇国, 骆永明. 滨海城市大气环境中发现多种微塑料及其沉降通量差异 [J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(33): 3902-3909. doi: 10.1360/N972017-00956 ZHOU Q, TIAN C G, LUO Y M. Various forms and deposition fluxes of microplastics identified in the coastal urban atmosphere [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(33): 3902-3909(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972017-00956
[25] DONG H K, WANG L X, WANG X P, et al. Microplastics in a remote lake basin of the Tibetan Plateau: Impacts of atmospheric transport and glacial melting[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021: acs. est. 1c03227. [26] AKANYANGE S N, LYU X J, ZHAO X H, et al. Does microplastic really represent a threat?A review of the atmospheric contamination sources and potential impacts [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 777: 146020. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146020 [27] ZHANG Y L, KANG S C, ALLEN S, et al. Atmospheric microplastics: A review on current status and perspectives [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 203: 103118. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103118 [28] VIANELLO A, JENSEN R L, LIU L, et al. Simulating human exposure to indoor airborne microplastics using a Breathing Thermal Manikin [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 8670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45054-w [29] LI J Y, LIU H H, CHEN J P. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection [J]. Water Research, 2018, 137: 362-374. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.056 [30] DI M X, WANG J. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616/617: 1620-1627. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.150 [31] 李昇昇, 李良忠, 李敏, 等. 环境样品中微塑料及其结合污染物鉴别分析研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 960-974. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019102304 LI S S, LI L Z, LI M, et al. Study on identification of microplastics and the combined pollutants in environmental samples [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 960-974(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019102304
[32] ZHANG Q, ZHAO Y P, DU F N, et al. Microplastic fallout in different indoor environments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(11): 6530-6539. [33] dos SANTOS GALVÃO L, FERNANDES E M S, FERREIRA R R, et al. Critical steps for microplastics characterization from the atmosphere [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127668. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127668 [34] LIU K, WANG X H, FANG T, et al. Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 675: 462-471. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.110 [35] SHIM W J, HONG S H, EO S E. Identification methods in microplastic analysis: A review [J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(9): 1384-1391. doi: 10.1039/C6AY02558G [36] DRIS R, GASPERI J, SAAD M, et al. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 104(1/2): 290-293. [37] ARAUJO C F, NOLASCO M M, RIBEIRO A M P, et al. Identification of microplastics using Raman spectroscopy: Latest developments and future prospects [J]. Water Research, 2018, 142: 426-440. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.060 [38] ABBASI S, KESHAVARZI B, MOORE F, et al. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 244: 153-164. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.039 [39] MAES T, JESSOP R, WELLNER N, et al. A rapid-screening approach to detect and quantify microplastics based on fluorescent tagging with Nile Red [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 44501. doi: 10.1038/srep44501 [40] WRIGHT S L, ULKE J, FONT A, et al. Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport [J]. Environment International, 2020, 136: 105411. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105411 [41] ERNI-CASSOLA G, GIBSON M I, THOMPSON R C, et al. Lost, but found with Nile red: A novel method for detecting and quantifying small microplastics (1 mm to 20 μm) in environmental samples [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(23): 13641-13648. [42] WANG W F, WANG J. Investigation of microplastics in aquatic environments: An overview of the methods used, from field sampling to laboratory analysis [J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 108: 195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.08.026 [43] 周帅, 李伟轩, 唐振平, 等. 气载微塑料的赋存特征、迁移规律与毒性效应研究进展 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11): 5027-5037. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.045 ZHOU S, LI W X, TANG Z P, et al. Progress on the occurrence, migration and toxicity of airborne microplastics [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11): 5027-5037(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.11.045
[44] CAI L Q, WANG J D, PENG J P, et al. Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan City, China: Preliminary research and first evidence [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(32): 24928-24935. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0116-x [45] WANG X H, LI C J, LIU K, et al. Atmospheric microplastic over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean: Abundance, distribution and source [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 121846. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121846 [46] DING J F, SUN C J, HE C F, et al. Atmospheric microplastics in the northwestern Pacific Ocean: Distribution, source, and deposition [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 829: 154337. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154337 [47] ROCHA-SANTOS T A P, DUARTE A C. Preface[M]//Characterization and Analysis of Microplastics. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017: xv-xvi. [48] XU G J, CHENG H Y, JONES R, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy facilitates the detection of microplastics <1 μm in the environment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(24): 15594-15603. [49] 杨东琪. 环境样品中微塑料理化特征的检测和表征方法[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2017. YANG D Q. Methods for detecting and representing physical and chemical features of microplastics in environmental samples[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2017(in Chinese).
[50] CABERNARD L, ROSCHER L, LORENZ C, et al. Comparison of Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the quantification of microplastics in the aquatic environment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(22): 13279-13288. [51] HUPPERTSBERG S, KNEPPER T P. Instrumental analysis of microplastics—Benefits and challenges [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 410(25): 6343-6352. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1210-8 [52] la NASA J, BIALE G, FABBRI D, et al. A review on challenges and developments of analytical pyrolysis and other thermoanalytical techniques for the quali-quantitative determination of microplastics [J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2020, 149: 104841. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104841 [53] CHOUCHENE K, NACCI T, MODUGNO F, et al. Soil contamination by microplastics in relation to local agricultural development as revealed by FTIR, ICP-MS and pyrolysis-GC/MS [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 303: 119016. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119016 [54] ZHANG J J, WANG L, KANNAN K. Microplastics in house dust from 12 countries and associated human exposure [J]. Environment International, 2020, 134: 105314. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105314 [55] PENG C, ZHANG X F, ZHANG X Y, et al. Bacterial community under the influence of microplastics in indoor environment and the health hazards associated with antibiotic resistance genes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(1): 422-432. [56] JIMÉNEZ-SKRZYPEK G, ORTEGA-ZAMORA C, GONZÁLEZ-SÁLAMO J, et al. The current role of chromatography in microplastic research: Plastics chemical characterization and sorption of contaminants [J]. Journal of Chromatography Open, 2021, 1: 100001. doi: 10.1016/j.jcoa.2021.100001 [57] GOßMANN I, SÜßMUTH R, SCHOLZ-BÖTTCHER B M. Plastic in the air?!- Spider webs as spatial and temporal mirror for microplastics including tire wear particles in urban air [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 832: 155008. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155008 [58] MBACHU O, JENKINS G, PRATT C, et al. A new contaminant superhighway?A review of sources, measurement techniques and fate of atmospheric microplastics [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2020, 231(2): 85. [59] SHI B, PATEL M, YU D, et al. Automatic quantification and classification of microplastics in scanning electron micrographs via deep learning [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 825: 153903. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153903 [60] WANG X H, LIU K, ZHU L X, et al. Efficient transport of atmospheric microplastics onto the continent via the East Asian summer monsoon [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 414: 125477. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125477 [61] LIAO Z L, JI X L, MA Y, et al. Airborne microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments of a coastal city in Eastern China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 417: 126007. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126007 [62] 涂晨, 田媛, 刘颖, 等. 大连海岸带夏、秋季大气沉降(微)塑料的赋存特征及其表面生物膜特性 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 1821-1828. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108117 TU C, TIAN Y, LIU Y, et al. Occurrence of atmospheric (micro)plastics and the characteristics of the plastic associated biofilms in the coastal zone of Dalian in summer and autumn [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 1821-1828(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108117
[63] TIAN X, YANG M N, GUO Z L, et al. Plastic mulch film induced soil microplastic enrichment and its impact on wind-blown sand and dust [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 813: 152490. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152490 [64] 蔡立奇. 微塑料在不同环境中的污染特征及其降解行为研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2019. CAI L Q. Study on the characteristics of microplastics in different environments and their degradation behaviors[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[65] KLEIN M, FISCHER E K. Microplastic abundance in atmospheric deposition within the Metropolitan area of Hamburg, Germany [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 685: 96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.405 [66] AKHBARIZADEH R, DOBARADARAN S, AMOUEI TORKMAHALLEH M, et al. Suspended fine particulate matter (PM2.5), microplastics (MPs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air: Their possible relationships and health implications [J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 192: 110339. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110339 [67] HARTMANN N B, HÜFFER T, THOMPSON R C, et al. Are we speaking the same language?recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(3): 1039-1047. [68] MUNYANEZA J, JIA Q L, QARAAH F A, et al. A review of atmospheric microplastics pollution: In-depth sighting of sources, analytical methods, physiognomies, transport and risks [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 822: 153339. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153339 [69] MATSUGUMA Y, TAKADA H, KUMATA H, et al. Microplastics in sediment cores from Asia and Africa as indicators of temporal trends in plastic pollution [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2017, 73(2): 230-239. doi: 10.1007/s00244-017-0414-9 [70] 罗犀, 张玉兰, 康世昌, 等. 大气微塑料研究进展 [J]. 自然杂志, 2021, 43(4): 274-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2021.04.006 LUO X, ZHANG Y L, KANG S C, et al. Research progress of microplastics in the atmosphere [J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2021, 43(4): 274-286(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2021.04.006
[71] PLASTICS EUROPE. Plastics - the Facts 2021 • Plastics Europe[EB/OL]. [2022-3-22]. [72] CHEN E Y, LIN K T, JUNG C C, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of airborne microplastics in nail salons [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 151472. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151472 [73] ABBASI S, ALIREZAZADEH M, RAZEGHI N, et al. Microplastics captured by snowfall: A study in Northern Iran [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 822: 153451. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153451 [74] LIU Z, BAI Y, MA T T, et al. Distribution and possible sources of atmospheric microplastic deposition in a valley basin city (Lanzhou, China) [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 233: 113353. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113353 [75] XIE Y C, LI Y, FENG Y, et al. Inhalable microplastics prevails in air: Exploring the size detection limit [J]. Environment International, 2022, 162: 107151. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107151 [76] HUANG Y M, HE T, YAN M T, et al. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a subtropical urban environment [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 126168. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126168 [77] DING Y C, ZOU X Q, WANG C L, et al. The abundance and characteristics of atmospheric microplastic deposition in the northwestern South China Sea in the fall [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2021, 253: 118389. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118389 [78] TRUONG T N S, STRADY E, KIEU-LE T C, et al. Microplastic in atmospheric fallouts of a developing Southeast Asian megacity under tropical climate [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 272: 129874. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129874 [79] ABBASI S, TURNER A. Dry and wet deposition of microplastics in a semi-arid region (Shiraz, Iran) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 786: 147358. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147358 [80] KASHFI F S, RAMAVANDI B, ARFAEINIA H, et al. Occurrence and exposure assessment of microplastics in indoor dusts of buildings with different applications in Bushehr and Shiraz Cities, Iran [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 829: 154651. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154651 [81] SZEWC K, GRACA B, DOŁĘGA A. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the coastal zone: Characteristics and relationship with meteorological factors [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 761: 143272. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143272 [82] GONZÁLEZ-PLEITER M, EDO C, AGUILERA Á, et al. Occurrence and transport of microplastics sampled within and above the planetary boundary layer [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 761: 143213. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143213 [83] KERNCHEN S, LÖDER M G J, FISCHER F, et al. Airborne microplastic concentrations and deposition across the Weser River Catchment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 818: 151812. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151812 [84] CONG Z, KANG S, KAWAMURA K, et al. Carbonaceous aerosols on the south edge of the Tibetan Plateau: Concentrations, seasonality and sources [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 15(3): 1573-1584. doi: 10.5194/acp-15-1573-2015 [85] BAENSCH-BALTRUSCHAT B, KOCHER B, STOCK F, et al. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP) - A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 733: 137823. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137823 [86] 曾永平. 环境微塑料概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 322-329. ZENG Y P. Introduction to microplastics environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020: 322-329(in Chinese).
[87] LI Y W, SHAO L Y, WANG W H, et al. Airborne fiber particles: Types, size and concentration observed in Beijing [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 705: 135967. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135967 [88] HU T Y, HE P J, YANG Z, et al. Emission of airborne microplastics from municipal solid waste transfer stations in downtown [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 828: 154400. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154400 [89] O'BRIEN S, OKOFFO E D, O'BRIEN J W, et al. Airborne emissions of microplastic fibres from domestic laundry dryers [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 747: 141175. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141175 [90] 刘艳, 唐颖, 宋阳, 等. 源于织物洗涤过程的微塑料释放 [J]. 印染, 2021, 47(7): 72-74. LIU Y, TANG Y, SONG Y, et al. Microplastic release from the fabric washing process [J]. China Dyeing & Finishing, 2021, 47(7): 72-74(in Chinese).
[91] SUN J, HO S S H, NIU X Y, et al. Explorations of tire and road wear microplastics in road dust PM2.5 at eight megacities in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153717. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153717 [92] KOLE P J, LÖHR A J, van BELLEGHEM F G A J, et al. Wear and tear of tyres: A stealthy source of microplastics in the environment [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(10): 1265. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14101265 [93] LIU K, WANG X H, WEI N, et al. Accurate quantification and transport estimation of suspended atmospheric microplastics in megacities: Implications for human health [J]. Environment International, 2019, 132: 105127. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105127 [94] CHEN Y X, LI X Y, ZHANG X T, et al. Air conditioner filters become sinks and sources of indoor microplastics fibers [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 292: 118465. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118465 [95] AMATO-LOURENÇO L F, CARVALHO-OLIVEIRA R, JÚNIOR Jr, et al. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 126124. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126124 [96] CHEN Q Q, GAO J N, YU H R, et al. An emerging role of microplastics in the etiology of lung ground glass nodules s [J]. Environmental Sciences Europe, 2022, 34: 25. doi: 10.1186/s12302-022-00605-3 [97] AMATO-LOURENÇO L F, dos SANTOS GALVÃO L, de WEGER L A, et al. An emerging class of air pollutants: Potential effects of microplastics to respiratory human health? [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 749: 141676. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141676 [98] DONG C D, CHEN C W, CHEN Y C, et al. Polystyrene microplastic particles: In vitro pulmonary toxicity assessment [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 385: 121575. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121575 [99] XU M K, HALIMU G, ZHANG Q R, et al. Internalization and toxicity: A preliminary study of effects of nanoplastic particles on human lung epithelial cell [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 694: 133794. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133794 [100] YANG S, CHENG Y P, CHEN Z Z, et al. In vitro evaluation of nanoplastics using human lung epithelial cells, microarray analysis and co-culture model [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 226: 112837. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112837 [101] PRATA J C. Airborne microplastics: Consequences to human health? [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 234: 115-126. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.043 [102] UMCES. Media library · Integration and application network [EB/OL]. [2022-7-20]. -




 下载:
下载: