-
煤矿开采利用过程中,天然放射性物质所产生的辐射是周边环境辐射的主要来源[1]。据统计,我国煤矸石年排放量达3.8亿t,目前已累计堆放煤矸石总量超过50亿t,规模较大的煤矸石山约1500座,其中有超过300座具有自燃危险[2]。由于矿区大量煤矸石的露天堆放,其中的放射性核素(如铀、钍、镭等)在经风化、雨淋、地表径流等外界作用后,向周边环境迁移、扩散,最后进入水环境和土壤环境中,通过各种途径被人体吸收,威胁人体健康,并对生态环境构成一定威胁[3]。近些年来,有关矿区煤矸石、土壤环境的放射性污染及其风险评价问题一直受到学者的广泛关注。许乃政等[4]对华东地区含煤岩系天然放射性水平进行评价。其中,普通煤田矿区的原煤、煤矸石等固体样品核素238U、232Th、226Ra、40K含量处于正常水平;而石煤矿区的固体样品的238U、226Ra核素富集明显;Zhou等[5]通过对淮南矿区煤矸石进行燃烧模拟实验,研究了煤矸石在燃烧过程中天然放射性核素的富集和挥发,并对其燃烧产物(炉渣)进行取样,结果表明,这些放射性核素主要存在于残渣中,且对周围环境没有造成直接的影响;Seref [6]测定土耳其某燃煤电厂附近土壤U和Th含量,采用土壤地累积指数、富集因子、内梅罗综合污染指数法进行风险评价,结果表明电厂周边土壤基本未受U和Th污染;Liu等[7]报道了华南某铀矿库周围土壤和沉积物中放射性核素的含量分布及来源解析,结果显示238U、226Ra和232Th的最高浓度出现在尾矿砂中,而40K的最高浓度出现在农田中;Belyaeva等[8]研究了埃里温市土壤的放射性污染特征,结果显示以火成岩为主的北部和中部,天然放射性核素水平最高,火力发电厂和金属精炼厂的运营并未影响邻近土壤中放射性核素浓度;张彬等[9]通过估算广东某铀废石堆周边土壤外源U输入通量,并结合放射性核素的逐级提取试验,发现铀废石堆对周边土壤产生了显著的放射性污染,且距废石堆愈近,土壤中外源U的输入通量愈大。
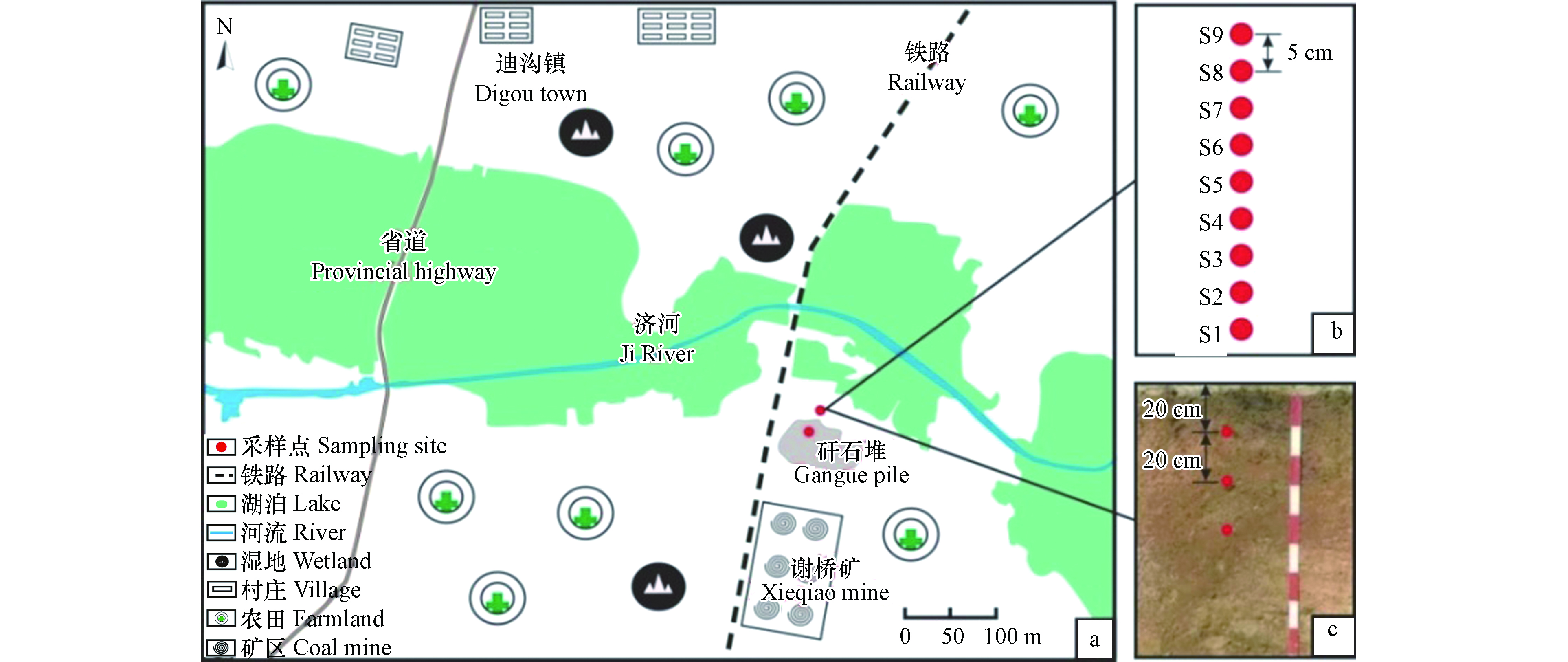
煤炭与很多天然放射性元素伴生,煤矿的开采利用使这些放射性元素随之迁移扩散,煤矸石的长时间堆积也造成这些元素进入周边环境并带来严重的环境污染问题[10]。为评估矸石堆对周边土壤的影响,以谢桥矿区矸石堆及周边土壤为研究对象,测试分析了所堆积煤矸石的物化特性,测定了煤矸石及土壤中放射性核素238U、232Th的活度浓度和赋存形态,并采用地累积指数法对采样点的土壤进行综合评价,研究可为矿区土壤修复提供理论支持。
-
淮南矿区(116°21′21″—117°11′59″E,32°32′45″—33°01′14″N)是我国14个亿吨煤生产基地之一,长期的煤炭开采带来大量的煤矸石堆积。据统计,目前矿区共有煤矸石堆34处,占地面积6.21 km2,占淮南固体废弃物总面积的46.7%[11]。研究区属暖温带半湿润季风气候区,冬季干冷,夏季多雨,降水量年际变化较大。
-
本研究所选取的煤矸石样品来自淮南矿区谢桥煤矿以北1.5 km,大小约为960 m2的矸石场(图1a),煤矸石及周边土壤采样点分布如图1所示。在矸石堆底部采集3份煤矸石样品(记为gs-1、gs-2、gs-3,平行样品)。同时对研究区周边土壤进行采样,因矸石堆周边土壤出现硬化的情况,本次研究以矸石堆为污染源向外辐射,选择一条土壤相对新鲜的路径进行收集,共设置9个采样点(图1b),分别距离矸石堆5、10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45 m,每个采样点土壤分3层采样(图1c),即0—20 cm、20—40 cm、40—60 cm,共采集27个土壤样品。混合均匀后按四分法留取1.5 kg样品,采集后立即用聚乙烯袋封装并注明样品编号。
-
将煤矸石样品自然风干后压制成直径为32 mm和镶边外径为10 mm的圆片试样,运用X射线荧光光谱(XRF)进行主量元素测定[12],矿物成分采用X-射线衍射仪(XRD)分析,所有样品均做3次平行。将采集的样品自然风干后去除砾石、杂草等,过200目筛,称取200 g样品放入γ谱分析专用的样品盒中密封存放,放置4周后测量[13]。根据《土壤中放射性核素的γ能谱分析方法》(GB/T 11743—2013)检测样品中238U和232Th。放射性元素铀、钍的赋存形态采用五步顺序提取法[14],将赋存形态分为离子交换态(F1)、碳酸盐结合态(F2)、铁锰氧化态(F3)、有机结合态(F4)以及残渣态(F5)。提取液中的238U、232Th浓度运用ICAP-Q电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)测定。
-
地累积指数法综合考虑人为活动和自然风化作用等自然因素,评价重金属的污染状况[15-16]。计算公式如下:
式中,Igeo的值表示土壤的污染状况,Ci为元素i的实测含量值,Bq·kg−1,Bi为元素i的参考背景值,Bq·kg−1,本文采用安徽省土壤环境背景值作为参考值[17],1.5为修正系数,污染等级分为7级,如表1所示。
-
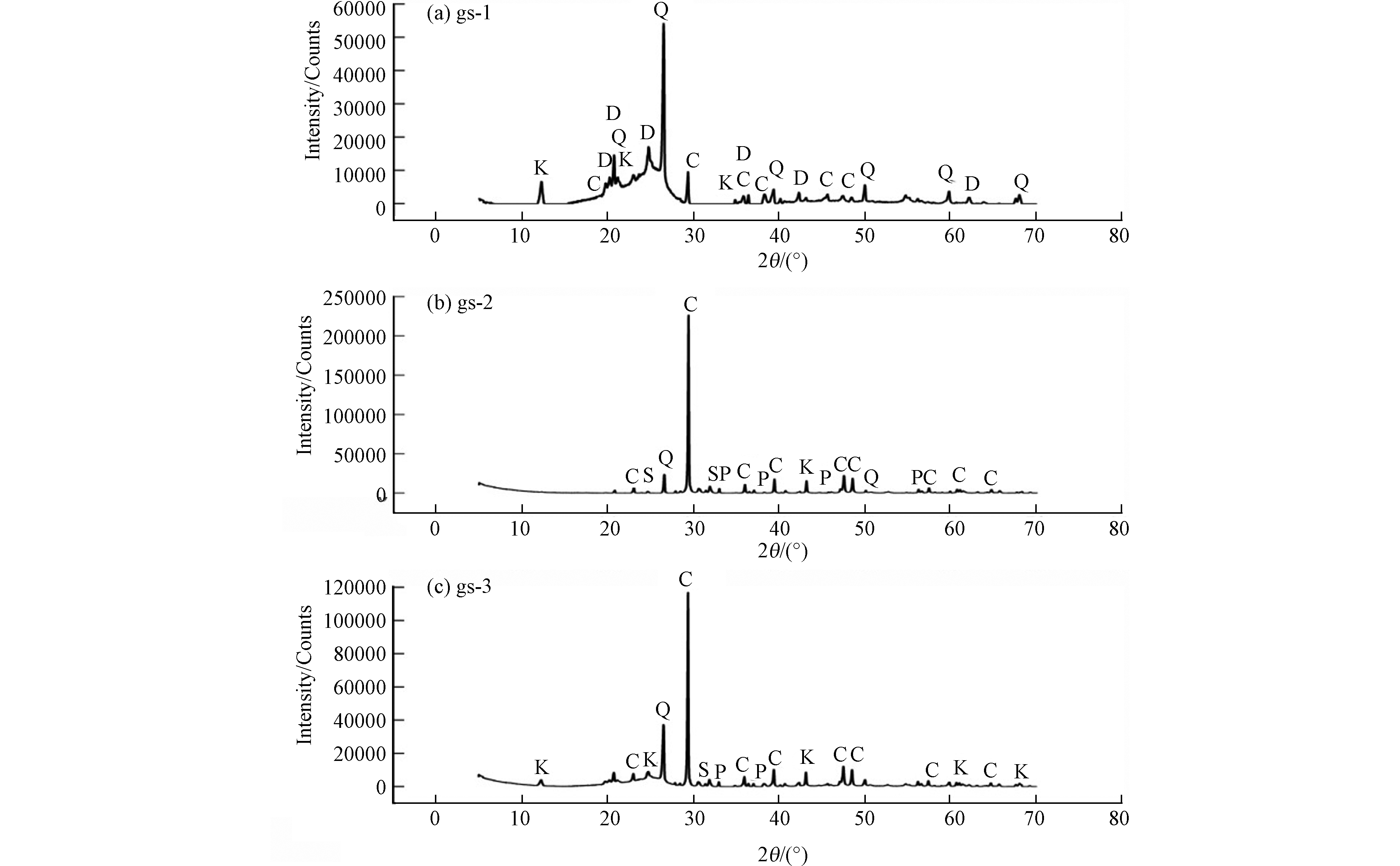
放射性核素在煤矸石中的矿物学、化学性质和赋存形态对其在风化和浸出过程中的后续行为有重要影响[5, 18]。对煤矸石的XRF分析结果显示,煤矸石主要元素为SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO、MgO、K2O、Na2O、TiO2(见表2)。SiO2平均含量较高,达52.41%,其次是Al2O3,含量为25.88%。由Al2O3/SiO2比值小于并接近0.5可知,该矿区煤矸石为主要以粘土矿物为主的岩石,它的矿物成分以高岭石和石英为主[19]。煤矸石中CaO的平均含量为10.15%,与煤矸石中的方解石有关,K2O、TiO2、MgO、Na2O含量分别为0.83%、0.98%、0.90%、1.14%,含量相对较少,在煤矸石中主要以钾长石或云母、金红石、钠长石形式存在[20]。
由图2可知,煤矸石中矿物组成主要以石英、高岭石和方解石为主,其分析结果与XRF测试结果保持一致。李坦夫[21]对淮南矿区煤矸石主要矿物类型研究中也发现淮南矿区煤矸石是以粘土矿物为主的岩石,它的矿物成分以高岭石和石英为主,还有少量伊利石、方解石、黄铁矿、菱铁矿和云母等,验证了这一结论。不同矿物对铀和钍的吸附容量不同,通过煤矸石的矿物成分分析可知,煤矸石中的粘土矿物是吸附铀、钍的关键性矿物,一般来说,伊利石和蒙脱石对铀和钍的吸附能力高于高岭石[22-23],其中铁氧化物的存在对铀、钍的吸附具有积极作用[24]。
-
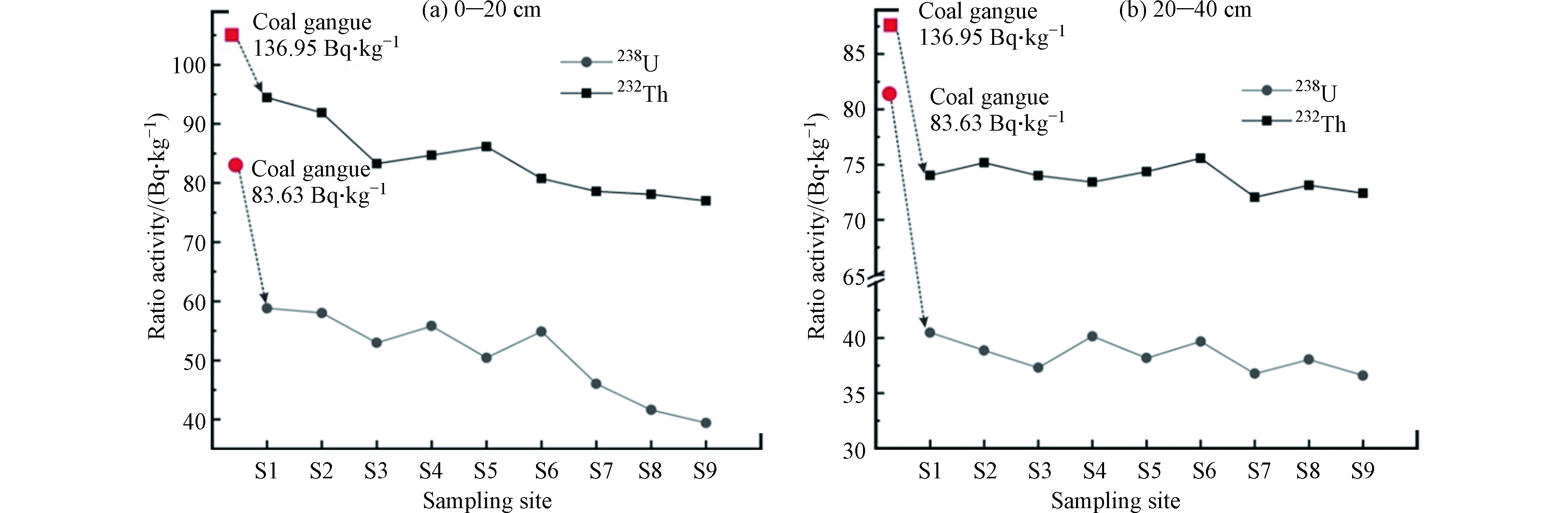
根据矸石堆周边土壤样品中天然放射性核素比活度,按照核素分类,并将0—20 cm、20—40 cm、40—60 cm的3个深度段的数值进行统计,结果列于表3。由表3可知,0—20 cm深度段处天然放射性核素238U、232Th比活度的最大值、最小值、平均值显著高于20—40 cm、40—60 cm深度段。核素238U在0—20 cm、20—40 cm、40—60 cm土壤中平均活度分别为50.89、38.45、32.00 Bq·kg−1,其中0—20 cm土壤中平均活度为安徽省土壤背景值[17](41.4 Bq·kg−1)的1.23倍,20—40 cm、40—60 cm土壤中平均活度未超标;核素232Th在0—20 cm、20—40 cm、40—60 cm土壤中平均活度分别为83.89、73.79、55.40 Bq·kg−1,分别为安徽省土壤背景值(53.1 Bq·kg−1)的1.58、1.39、1.04倍。
由图3可知,整体上核素238U、232Th在0—20 cm土壤中活度最高,在土壤60 cm的深度内,土壤中238U、232Th活度由浅至深逐渐减小,可能是由于矿区堆放的煤矸石经风化、淋滤等自然作用,矸石中的238U、232Th逐渐浸出,经表层土壤的吸附、过滤、络合等作用使得大部分238U、232Th存留在表层土壤中[25],导致深层土壤中238U、232Th活度明显下降。还可能是因为表层土壤植物根系发达,其分泌物可以吸附、包裹铀污染物,使其在根外沉淀下来,因此铀易存留于浅层根系处,不易被深层土壤所吸附[26-27]。
矸石堆放射性核素在环境中大致以纵向和横向两种方式迁移[28],因此除了土壤的深度,样品采集地与矸石堆之间的水平距离也是影响土壤中天然放射性核素比活度的重要影响因素。由于土壤40—60 cm深度段样品距离地表较深,受距离影响较小,本研究只选取0—20 cm、20—40 cm深度段土壤放射性核素比活度进行分析。
图4反应了煤矸石及距矸石堆不同距离处土壤0—20 cm、20—40 cm深度段放射性核素的比活度分布情况。由图4可知,煤矸石样品中238U、232Th平均活度明显高于土壤样品,各采样点的土壤放射性核素在水平方向上存在一定的差异,靠近矸石堆的取样点活度稍偏高,随着地表径流迁移,离矸石堆越近的土壤受核素的影响越大。当距离到达一定值后,水体中的放射性核素被途经的土壤截留,使得输入到下游土壤中的放射性核素的活度呈降低的趋势。Zhou等[29]研究华东某铀矿表层土壤放射性核素污染特征也发现,靠近铀矿场的采样点活度稍偏高,铀矿区附近土壤受到的核素污染相比于其他采样点更严重。
-
煤矸石和土壤中放射性核素的环境影响和生态效应不全取决于其总量,也受控于在介质中的赋存形态,不同化学形态是影响其在土壤中迁移转化能力和生物有效性的重要因素[30]。研究以S3、S6、S9号采样点为例对放射性核素238U、232Th进行水平和纵向形态分析。
-
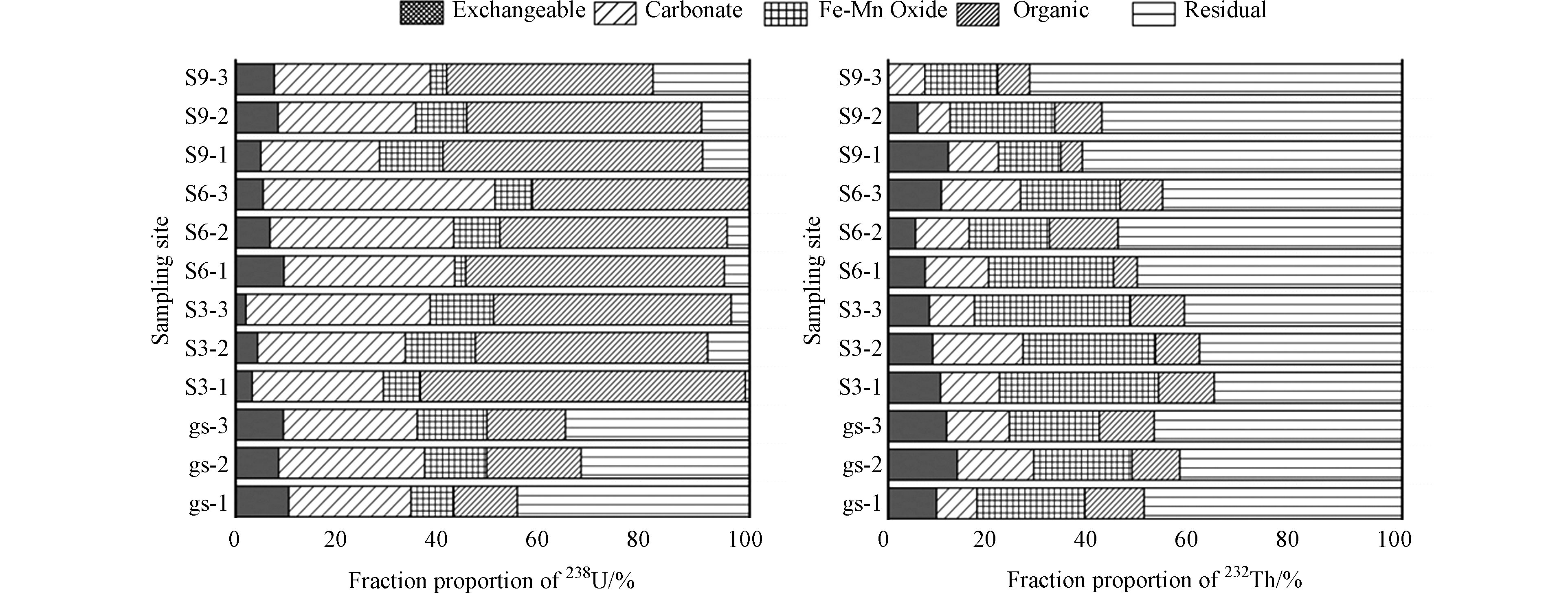
不同深度段放射性核素形态比例统计结果表明(表4),研究区土壤238U各形态按一定比例分布,总体上有机结合态和碳酸盐结合态所占比例相对较高,铁锰氧化态、残渣态次之,离子交换态比例相对较低,而煤矸石样品中238U元素的赋存状态,主要以残渣态和碳酸盐结合态为主,平均占比分别为37.96%和26.08%。
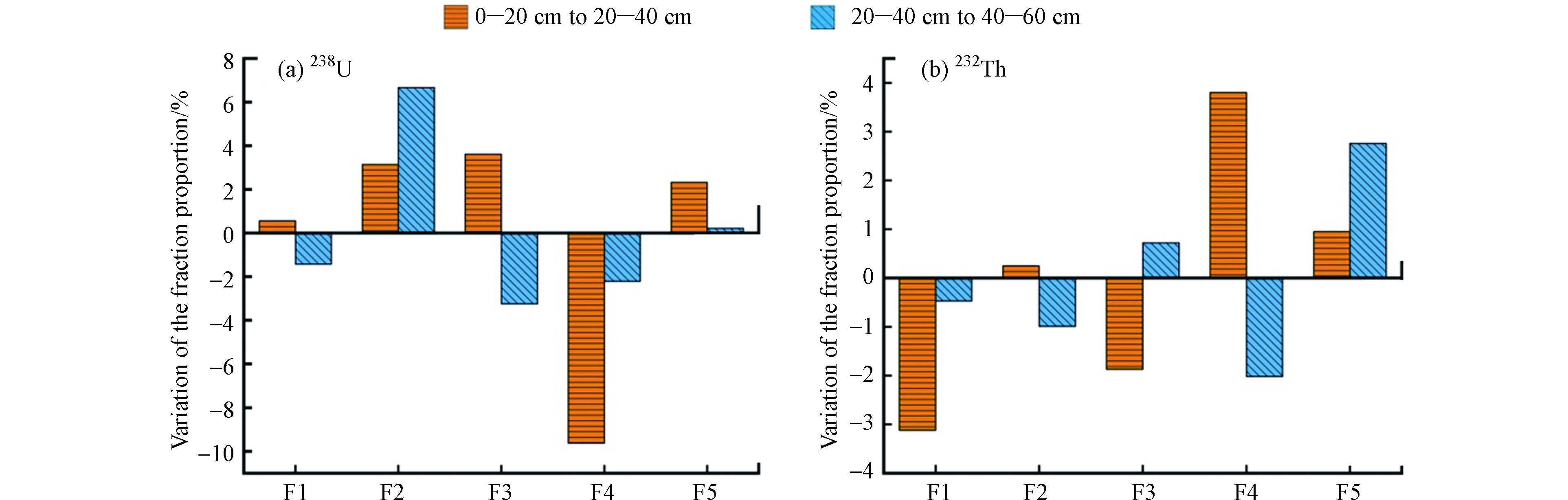
3个深度段对比结果显示,相比于0—20 cm深度段,20—40 cm土壤238U离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化态、残渣态分别增加了0.56%、3.14%、3.61%、2.32%,有机结合态减少了9.63%;相比于20—40 cm深度段,40—60 cm土壤238U离子交换态、铁锰氧化态、有机结合态分别减少了1.43%、3.24%、2.21%,碳酸盐结合态、残渣态增加了6.67%、0.22%[表4和图5(a)]。综上所述,随着采样深度的增加,碳酸盐结合态、残渣态在各剖面土壤中占比呈逐渐增加趋势,而有机结合态比例逐渐下降,其它赋存形态变化规律不明显。
随地表径流迁移的过程中,238U从污染源到土壤的转移可能通过水溶态、胶体、碎屑颗粒等形式[8]。3个土壤剖面样品(S3、S6、S9)中赋存形态主要以有机结合态和碳酸盐结合态为主,表明238U从污染源到土壤的转移可能主要是以有机胶体和水溶态的形式迁移的。研究发现随着采样距离的增加,离子交换态的比例逐渐上升,有机结合态比例逐渐下降,其他形态变化不明显。
-
研究区土壤232Th总体上以残渣态存在,各深度段残渣态比例均在50%以上,其次为铁锰氧化态、碳酸盐结合态、离子交换态、有机结合态。相比于0—20 cm深度段,20—40 cm土壤232Th离子交换态、铁锰氧化态分别减少了3.12%、1.87%,而有机结合态、残渣态增加了3.8%、0.95%;相比于20—40 cm深度段,40—60 cm土壤232Th离子交换态、碳酸盐结合态、有机结合态分别减少了0.47%、0.99%、2.02%,而铁锰氧化态、残渣态增加了0.72%、2.76%(表4)。结合图6(b)可见,随深度增加,土壤232Th碳酸盐结合态比例变化幅度不大,而生态风险较大的离子交换态比例逐渐降低,并在0—20 cm向20—40 cm过渡时变化最为明显。并且随着采样距离的增加,铁锰氧化态所占比例逐渐减少,残渣态的比例逐渐上升,其他形态未体现出明显的变化规律。煤矸石中232Th元素的赋存形态与3个土壤剖面样品(S3、S6和S9)的赋存状态保持一致,主要以残渣态和铁锰氧化态为主,平均占比分别为47.23%和19.20%。
-
本文采用地累积指数法对研究区土壤进行放射性核素污染评价。计算结果见表5,整体上232Th的地累积指数要大于238U,说明232Th在环境中更容易累积。S1—S9号采样点处Igeo(238U)在不同深度段均小于0,表明矸石堆周边土壤并未受到238U这种元素的污染;S1—S6号采样点处Igeo(232Th)在表层土壤(0—20 cm)处于0—1,属于轻微污染,其余深度段并未受到232Th这种元素的污染。由于S1—S6号采样点距离矸石堆相对较近,土壤受到232Th的轻微污染,导致S7-S9号采样点处Igeo(232Th)评价结果低于S1—S6号,因此煤矸石堆放对周边土壤的放射性污染范围主要限定在距矸石堆30 m以内。
-
(1)研究区煤矸石主要为以粘土矿物为主的岩石,而粘土矿物是吸附铀、钍的关键性矿物。
(2)煤矸石样品中238U、232Th平均活度明显高于土壤样品。核素238U在0—20 cm土壤中均值(50.89 Bq·kg−1)为安徽省土壤背景值的1.23倍,核素232Th在0—20 cm、20—40 cm、40—60 cm土壤中均值(83.89、73.79、55.40 Bq·kg−1)分别为安徽省土壤背景值的1.58、1.39、1.04倍。周边土壤238U、232Th活度呈现出与矸石堆距离增加而减小的分布趋势。
(3)土壤样品中238U赋存形态以有机结合态和碳酸盐结合态为主,而232Th总体上以残渣态为主。随土壤剖面由浅至深,238U碳酸盐结合态、残渣态所占比例逐渐增加,而有机结合态逐渐减少,土壤232Th碳酸盐结合态比例变化幅度不大,而生态风险较大的离子交换态比例逐渐降低。
(4)采用地累积指数法对研究区土壤进行放射性核素污染评价,结果表明周边土壤并未受到238U这种元素的污染,而靠近矸石堆的表层土壤(0—20 cm)受到232Th轻微污染。
小尺度矸石堆场及其周边土壤中放射性元素特征分析及风险评价
Characteristic and risk assessment of radioactive elements in small scale gangue dump and surrounding soil
-
摘要: 煤矸石的露天堆放,不仅侵占大量的土地资源,还会带来严重的环境污染问题。为研究煤矸石中放射性核素对周边土壤环境的影响,采集煤矸石及矸石堆周边土壤样品,测试样品中放射性核素238U、232Th的活度浓度,分析煤矸石及周边土壤中放射性核素238U、232Th的分布特征,采用地累积指数法对土壤污染状况进行综合评价。结果表明,矿区煤矸石主要以粘土矿物为主,而粘土矿物是吸附铀、钍的关键性矿物;土壤中放射性元素238U、232Th活度范围分别为31.51—58.81、53.33—94.48 Bq·kg−1,远低于煤矸石,其活度浓度呈现出与矸石堆距离增加而减小的分布趋势;煤矸石中238U、232Th主要以残渣态为主,土壤样品中238U赋存形态以有机结合态和碳酸盐结合态最为突出,而232Th总体上以残渣态为主;地累积指数法评价结果表明,S1-S9号采样点处Igeo(238U)在不同深度段均小于0,表明周边土壤并未受到238U这种元素的污染,而靠近矸石堆的表层土壤(0—20 cm)受到232Th轻微污染,其污染范围限定在距矸石堆30 m以内。Abstract: The open-air stacking of coal gangue not only encroaches on a large amount of land resources, but also brings serious environmental pollution problems. In order to study the influence of radionuclides in coal gangue on the surrounding soil, coal gangue and soil samples were collected in the gangue piles and surrounding areas. The activity concentration and occurrence of radionuclides 238U and 232Th in coal gangue and soil samples were determined. By adopting the geoaccumulation index method, the pollution indices were calculated to assess soil pollution extend. The results showed that the coal gangue in mining area was mainly composed of clay minerals, which were the key minerals to adsorb uranium and thorium; The activity ranges of 238U and 232Th in soil were 31.51—58.81、53.33—94.48 Bq·kg−1, respectively, which were much lower than that of coal gangue. The concentrations of 238U and 232Th in soil showed a decrease trend, with the increase of distance from gangue pile; 238U and 232Th in the coal gangue were mainly residual states. In the soil samples, 238U occurred in organic and carbonate states, while 232Th was mainly in residual state; The geoaccumulation index showed that Igeo (238U) at sampling point S1-S9 was less than 0 in different depth, so the surrounding soil was not polluted by 238U, while the surface soil (0—20 cm) near the gangue pile was slightly polluted by 232Th, and its pollution range was limited to 30 m.
-
Key words:
- gangue pile /
- soil /
- radionuclides /
- occurrence characteristics /
- risk assessment
-

-
表 1 地累积指数评价分级标准
Table 1. Evaluation and classification standard of geological accumulation index method
污染等级 Pollution level 地累积指数 Geoaccumulation index 污染程度 Pollution degree 0 Igeo<0 无污染 1 0≤Igeo<1 轻微污染 2 1≤Igeo<2 轻度污染 3 2≤Igeo<3 中度污染 4 3≤Igeo<4 重度污染 5 4≤Igeo<5 严重污染 6 Igeo≥5 极严重污染 表 2 煤矸石主量元素含量(质量分数,%)
Table 2. Major element content of coal gangue
样品
Sample编号
NumberingSiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 煤矸石 gs-1 52.27 26.12 8.23 9.05 0.87 0.74 1.35 0.99 gs-2 52.4 25.8 7.27 10.22 0.81 0.84 1.23 1.04 gs-3 52.55 25.73 6.45 11.18 1.01 0.92 0.83 0.91 平均值 52.41 25.88 7.32 10.15 0.90 0.83 1.14 0.98 表 3 周边土壤样品中天然放射性核素比活度分析(Bq·kg−1)
Table 3. Analysis of natural radionuclide ratio activity in surrounding soil samples(Bq·kg−1)
核素
Radionuclid深度/cm
Depth平均值
Average中位数
Median最小值
Minimum最大值
Maximum标准差
Standard deviation238U 0—20 cm 50.89 52.97 39.41 58.81 6.66 20—40 cm 38.45 38.18 36.60 40.48 1.35 40—60 cm 32.00 32.13 31.51 32.39 0.34 232Th 0—20 cm 83.89 83.28 77.01 94.48 5.79 20—40 cm 73.79 74.00 72.04 75.57 1.11 40—60 cm 55.40 55.82 53.33 57.75 1.45 表 4 土壤剖面不同深度段238U、232Th各形态比例统计(%)
Table 4. Statistical fraction proportions of 238U and 232Th in different depth sections of soil profile
核素
Radionuclid深度/cm
DepthF1 F2 F3 F4 F5 238U 0—20 5.84 27.28 7.21 54.67 4.99 20—40 6.4 30.42 10.82 45.04 7.31 40—60 4.97 37.09 7.58 42.83 7.53 232Th 0—20 9.72 11.18 22.44 6.54 50.11 20—40 6.6 11.43 20.57 10.34 51.06 40—60 6.13 10.44 21.29 8.32 53.82 表 5 地累积指数法评价结果
Table 5. Evaluation results of geological accumulation index method
核素
Radionuclid采样点
Sampling point地累积指数
Geoaccumulation index采样深度0—20 cm
Sampling depth 0—20 cm采样深度20—40 cm
Sampling depth 20—40 cm采样深度40—60 cm
Sampling depth 40—60 cm238U S1 −0.08 −0.62 −0.58 S2 −0.10 −0.68 −0.58 S3 −0.23 −0.74 −0.58 S4 −0.15 −0.63 −0.59 S5 −0.30 −0.70 −0.59 S6 −0.18 −0.65 −0.60 S7 −0.43 −0.76 −0.61 S8 −0.58 −0.71 −0.62 S9 −0.66 −0.76 −0.62 S1 0.25 −0.11 −0.54 232Th S2 0.21 −0.08 −0.49 S3 0.06 −0.11 −0.51 S4 0.09 −0.12 −0.49 S5 0.11 −0.10 −0.46 S6 0.02 −0.08 −0.51 S7 −0.02 −0.14 −0.56 S8 −0.03 −0.12 −0.57 S9 −0.05 −0.14 −0.58 -
[1] CHAŁUPNIK S, WYSOCKA M, JANSON E, et al. Long term changes in the concentration of Radium in discharge waters of coal mines and Upper Silesian rivers [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2017, 171: 117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.02.007 [2] 李贝. 煤矸石山非控自燃热动力学特征及移热方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2017. LI B. Research on thermodynamic characteristics and heat transfer method of uncontrolled fire in coal gangue dump[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[3] LU Y, YIN W, HUANG L B, et al. Assessment of bioaccessibility and exposure risk of arsenic and lead in urban soils of Guangzhou City, China [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2011, 33(2): 93-102. doi: 10.1007/s10653-010-9324-8 [4] 许乃政, 匡福祥, 叶隽, 等. 华东地区含煤岩系天然放射性水平评价[J/]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(6): 1790-1803. XU N Z, KUANG F X, YE J, et al. Evaluation of natural radioactivity level of coal-bearing strata in the East China[J]. 2021, 48(6): 1790-1803 (in Chinese).
[5] ZHOU C C, LIU G J, WU S C, et al. The environmental characteristics of usage of coal gangue in bricking-making: A case study at Huainan, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 95: 274-280. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.004 [6] TURHAN Ş. Evaluation of agricultural soil radiotoxic element pollution around a lignite-burning thermal power plant [J]. Radiochimica Acta, 2019, 108(1): 77-85. doi: 10.1515/ract-2018-3051 [7] LIU Y Y, ZHOU W B, LIU H Y, et al. Spatial variability and radiation assessment of the radionuclides in soils and sediments around a uranium tailings reservoir, south of China [J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2020, 324(1): 33-42. doi: 10.1007/s10967-020-07077-w [8] BELYAEVA O, MOVSISYAN N, PYUSKYULYAN K, et al. Yerevan soil radioactivity: Radiological and geochemical assessment [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 265: 129173. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129173 [9] 张彬, 冯志刚, 马强, 等. 广东某铀废石堆周边土壤中铀污染特征及其环境有效性 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(1): 156-162. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.01.023 ZHANG B, FENG Z G, MA Q, et al. Pollution characteristics and environmental availability of uranium in the soils around A uranium waste rock pile in Guangdong Province, China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(1): 156-162(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.01.023
[10] 蒋经乾, 劳玉军, 王理, 等. 铀矿山尾矿库区浅层尾砂中核素的垂直分布特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(8): 1561-1563. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.08.2015041601 JIANG J Q, LAO Y J, WANG L, et al. Vertical distribution characteristics of nuculins in shallow tail sands in uranium mines [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(8): 1561-1563(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.08.2015041601
[11] 陈永春, 李守勤, 周春财. 淮南矿区煤矸石的物质组成特征及资源化评价 [J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2011, 23(11): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2011.11.06 CHEN Y C, LI S Q, ZHOU C C. Material composition features and reclaim evaluation of coal gangue in Huainan mining area [J]. Coal Geology of China, 2011, 23(11): 20-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2011.11.06
[12] 李文翠, 于湛, 付玉, 等. 应用XRF与ICP-MS研究陨石样品的元素分布 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(10): 3261-3263. LI W C, YU Z, FU Y, et al. Study on element distribution in meteorite samples by XRF and ICP-MS [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(10): 3261-3263(in Chinese).
[13] BAJOGA A D, AL-DABBOUS A N, ABDULLAHI A S, et al. Evaluation of elemental concentrations of uranium, thorium and potassium in top soils from Kuwait [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2019, 51(6): 1638-1649. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2019.04.021 [14] HU G Q, LIU G J, WU D, et al. Geochemical behavior of hazardous volatile elements in coals with different geological origin during combustion [J]. Fuel, 2018, 233: 361-376. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.069 [15] ODEWANDE A A, ABIMBOLA A F. Contamination indices and heavy metal concentrations in urban soil of Ibadan metropolis, southwestern Nigeria [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2008, 30(3): 243-254. doi: 10.1007/s10653-007-9112-2 [16] 王勤, 彭渤, 方小红, 等. 湘江长沙段沉积物重金属污染特征及其评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 999-1011. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101901 WANG Q, PENG B, FANG X H, et al. Characteristics and assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments from Changsha section of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan Province of China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 999-1011(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101901
[17] 朱锦秋, 邵广南, 江山, 等. 安徽省土壤中天然放射性核素含量调查 [J]. 辐射防护, 1991, 11(4): 291-294. ZHU J Q, SHAO G N, JIANG S, et al. Survey of natural radionuclide contents in soil in Anhui Province [J]. Radialization Protection, 1991, 11(4): 291-294(in Chinese).
[18] KACMAZ H, BURNS P C. Uranyl phosphates and associated minerals in the Koprubasi(Manisa)uranium deposit, Turkey [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 84: 102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.01.001 [19] XU H L, SONG W J, CAO W B, et al. Utilization of coal gangue for the production of brick [J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2017, 19(3): 1270-1278. doi: 10.1007/s10163-016-0521-0 [20] 朱宝忠, 孙运兰, 谢承卫. 不同煅烧温度下贵州兴义煤矸石的光谱学研究 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2008, 33(9): 1049-1052. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2008.09.019 ZHU B Z, SUN Y L, XIE C W. Spectroscopy research on the Guizhou Xingyi gangue of different calcined temperatures [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2008, 33(9): 1049-1052(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2008.09.019
[21] 李坦夫. 淮南矿区煤矸石地球化学特征及利用途径研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2015. LI T F. Environmental geochemistry characteristics and study on the utilizing method of gangue in Huainan mining area[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2015(in Chinese).
[22] XIE Y, CHEN C L, REN X M, et al. Emerging natural and tailored materials for uranium-contaminated water treatment and environmental remediation [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2019, 103: 180-234. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2019.01.005 [23] 郭鹏然, 贾晓宇, 牟德海, 等. 土壤对外源钍的吸附行为表征 [J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(8): 1510-1516. GUO P R, JIA X Y, MU D H, et al. Characterization of adsorption behavior of exogenous thorium on soil [J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(8): 1510-1516(in Chinese).
[24] REILLER P, CASANOVA F, MOULIN V. Influence of addition order and contact time on thorium(Ⅳ)retention by hematite in the presence of humic acids [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(6): 1641-1648. [25] 蒋文波, 高柏, 张海阳, 等. 某铀矿区周边土壤238U和226Ra分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(4): 1799-1805. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.04.034 JIANG W B, GAO B, ZHANG H Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of 238U and 226Ra in soils surrounding a uranium mining area [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(4): 1799-1805(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.04.034
[26] PÉREZ-SÁNCHEZ D, THORNE M C. An investigation into the upward transport of uranium-series radionuclides in soils and uptake by plants [J]. Journal of Radiological Protection, 2014, 34(3): 545-573. doi: 10.1088/0952-4746/34/3/545 [27] 姚高扬, 华恩祥, 高柏, 等. 南方某铀尾矿区周边农田土壤中放射性核素的分布特征 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2015, 31(6): 963-966. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2015.06.025 YAO G Y, HUA E X, GAO B, et al. Distribution characteristics of radionuclides in soils around tailings dump sites of a uranium mining field in South China [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2015, 31(6): 963-966(in Chinese). doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2015.06.025
[28] QIAO P W, LEI M, YANG S C, et al. Development of a model to simulate soil heavy metals lateral migration quantity based on SWAT in Huanjiang watershed, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 77: 115-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.06.020 [29] ZHOU Z K, YANG Z H, SUN Z X, et al. Multidimensional pollution and potential ecological and health risk assessments of radionuclides and metals in the surface soils of a uranium mine in East China [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(2): 775-791. doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02428-x [30] 唐世琪, 刘秀金, 杨柯, 等. 典型碳酸盐岩区耕地土壤剖面重金属形态迁移转化特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(8): 3913-3923. TANG S Q, LIU X J, YANG K, et al. Migration and transformation characteristics and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metal fractions in cultivated land soil profiles at a typical carbonate covering area [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(8): 3913-3923(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: