-
室内环境是人类日常生活工作的重要场所,人类长时间都待在室内,因此长期接触室内灰尘物质[1-2]. 同时室外颗粒物通过人类活动、空气循环等途径进入室内,使得室内灰尘成为各种污染物的汇聚点. 其中富集于灰尘中的重金属具有高毒性,难降解性和隐蔽性等特点,可通过呼吸、皮肤接触和手-口摄食等途径进入人体,对人体健康构成潜在危害[3-5]. 随着国民生活水平的不断提高,城市室内灰尘重金属污染越来越受到社会的关注[6-8].
近年来,国内外学者对城市室内不同环境下灰尘重金属的来源与含量[9-10]、时空差异[11]与污染风险[12]等开展大量工作,研究表明室内灰尘Cd、Cu、Zn等元素超标较多具有潜在健康风险[13-15],且人体在室内接受的暴露量较大,约是室外的1000倍[16]. 然而在现有的研究中,多以城市办公、居民区、宿舍等特定室内灰尘研究为主[17-18],缺乏针对城市内高校不同环境下室内灰尘重金属污染和生态健康风险的综合报道.
高校作为一个城市重要的功能区,是学生及教师长期生活学习的场所. 高校师生众多,人群密集且大部分时间在室内活动,室内灰尘重金属将对高校师生健康产生极大影响[19-20]. 此外,师生每天在宿舍、教室、图书馆等不同室内区域活动,关于不同环境下室内灰尘对人体健康危害是否存在差异的研究还不见报道. 因此本文以河南省某高校宿舍、教室、图书馆等室内为例,对其地表灰尘重金属进行测定,并进行生态健康风险评价,旨在保护高校人群身体健康,为高校环境治理提供借鉴.
-
研究高校位于华北平原腹地、河南省东部,属温带季风气候,四季分明,降雨集中于夏季,周围土壤类型为黄潮土[21]. 该校人口分布较为密集,具有一定的代表性. 该高校主体于2003年建成运行,占地面积2000亩,校区有近3000名教职工,以及四万多名全日制本科生和研究生.
-
本研究室内灰尘样品采集时间为2021年春季. 在该校师生正常生活的情况下(避免节假日或大量校外人员来访等导致的异常),选择该校综合教学楼、图书馆、宿舍等6个区域作为采样区,分别在每个样区的不同楼层、角落和地面用小刷子进行灰尘样品采集,总计采集室内灰尘样品44份. 将采集后的样品带回实验室置于通风处,自然风干后,使用100目尼龙筛,去除毛发、纸屑、石砾等杂物后密封保存,每个样品5 g. 同时调查采样区域人员信息、周边环境信息等,并进行详细记录(表1).
-
本研究采用HNO3-HF-HCIO3消解体系[22],在石墨全自动消解仪(ST-60)内进行消解. 样品重金属Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn含量使用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS,美国Thermos Scientific)测定. 为保证实验测定精确度,分析过程中所用试剂均为优级纯,水为二次去离子水;利用空白对照、国家标准土壤样品(GSS-3黄棕壤)和平行样进行质控. 每组样品均重复3次取均值,平行样相对偏差均小于5%,样品加标回收率在92.5%—107.2%之间,符合要求.
-
本研究运用由Tomlinson等从事重金属污染水平的分级研究中提出的污染负荷指数法进行室内灰尘重金属污染评价[23]. 其计算方法如下:
污染系数CFi的计算方法见式(1):
式中,CFi是指元素i的最高污染系数,Ci是指元素i的实测含量,Cj是元素j评价标准,即背景值.
某一点的污染负荷指数计算方法见式(2):
式中:PL1为某一点的元素污染负荷指数;n为评价元素的个数.
某一区域的污染负荷指数e计算方法见式(3):
式中,IPLzone为区域污染负荷指数;n为采样点个数. 污染等级划分参照文献[24]. 本研究采用开封市周边地表灰尘重金属背景值作为重金属的评价标准[25].
-
Hakanson提出的潜在生态风险指数评价法[26]综合考虑 了多种元素的协同作用、环境背景值和环境对于重金属的敏感性等因素来进行评价,可以较好的划分出重金属潜在生态危害程度. 其计算公式为:
式中,RI为重金属综合潜在风险指数 ;Eir为重金属i的单项潜在风险指数;Cir为重金属i的实测浓度;Cin为重金属i的参考值,即背景值;Tir为重金属i的毒性响应系数,6种重金属Cd、Cu、Pb、Ni、Cr和Zn的响应系数分别为30、5、5、5、2、1[27]. Hakanson的Er和RI值是根据8种重金属划分的,在实际应用中要结合研究的实际,不能一味照搬. 因此,本研究结合马建华的方法对Er和RI进行分级[28],潜在生态风险指数划分标准参照文献[9].
-
评估一段时间内发生某种程度有害健康影响的可能性的系统过程称为风险评估. 与每种重金属相关的健康风险的估计是基于对环境中的危险水平以及致癌和非致癌金属的定量评估,通常报告为平均每日剂量(ADD). 本研究根据美国环境保护局(US EPA)修订的健康风险模型进行人体健康风险评价[29-32].
非致癌风险公式如下:
式中,ADDing、ADDinh和ADDder分别表示经手口途径摄入、呼吸摄入和皮肤摄入的日均暴露量(mg·kg−1·d−1);C表示灰尘中的重金属含量(mg·kg−1);IRing和IRinh分别表示手口摄入灰尘速率(mg·d−1)和呼吸摄入灰尘速率(m3·d−1);EF表示年暴露频率(d·a−1);ED表示暴露年限(a);BW表示平均体重(kg);AT表示暴露时间(d);PEF表示颗粒物排放因子(m3·kg−1);SA表示暴露皮肤面积(cm2);SL表示皮肤黏着度(mg·cm−2·d−1);ABS表示皮肤吸收因子,无量纲;CF表示转换系数(kg·mg−1),具体参见表2.
重金属元素Cd、Cr和Ni具有致癌风险,采用以下公式进行计算[20]:
式中,CADDinh表示经呼吸摄入的日均暴露量(mg·kg−1·d−1);AT为致癌的平均暴露时间(d);其它参数含义同上.
式中,HQi为各重金属非致癌健康风险指数;ADDij为非致癌重金属i的第j种暴露途径的日均暴露量(mg·kg−1·d−1);HI为非致癌总风险指数;R为重金属致癌健康风险指数;RfDij为非致癌重金属的第j种暴露途径的参考剂量(mg·kg−1·d−1);SF为致癌重金属呼吸摄入暴露途径的斜率系数(kg·d·mg−1). 各重金属的RfD和SF参考值见表3. 当HI值≤1,表明没有非致癌风险;当HI>1,意味着有非致癌风险[20]. R为多种物质或一种物质多种暴露方式的致癌风险指数;CR为3种致癌重金属综合风险值,当CR<1×10−6时,为无致癌风险,当1×10−6<CR<1×10−4时,为人体可耐受的致癌风险,当CR>1×10−4时,为人体不可耐受的致癌风险[29].
-
对各采样点的灰尘重金属含量进行测定,统计结果见表4. 该高校灰尘中Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn均值分别为1.45、78.25、56.35、34.01、109.44、444.90 mg·kg−1,且平均含量均高于样点所在地开封土壤灰尘背景值,其中Zn的平均含量是背景值的5.76倍. Cd、Cu、Pb和Zn的超标率均超过95%,Cd的超标率高达100%,说明这些重金属在该校室内存在富集. 灰尘Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni和Zn的变异系数在0.1—1,为中等变异,Pb的变异系数为1.03,呈现强变异,表明室内灰尘重金属含量存在空间差异.
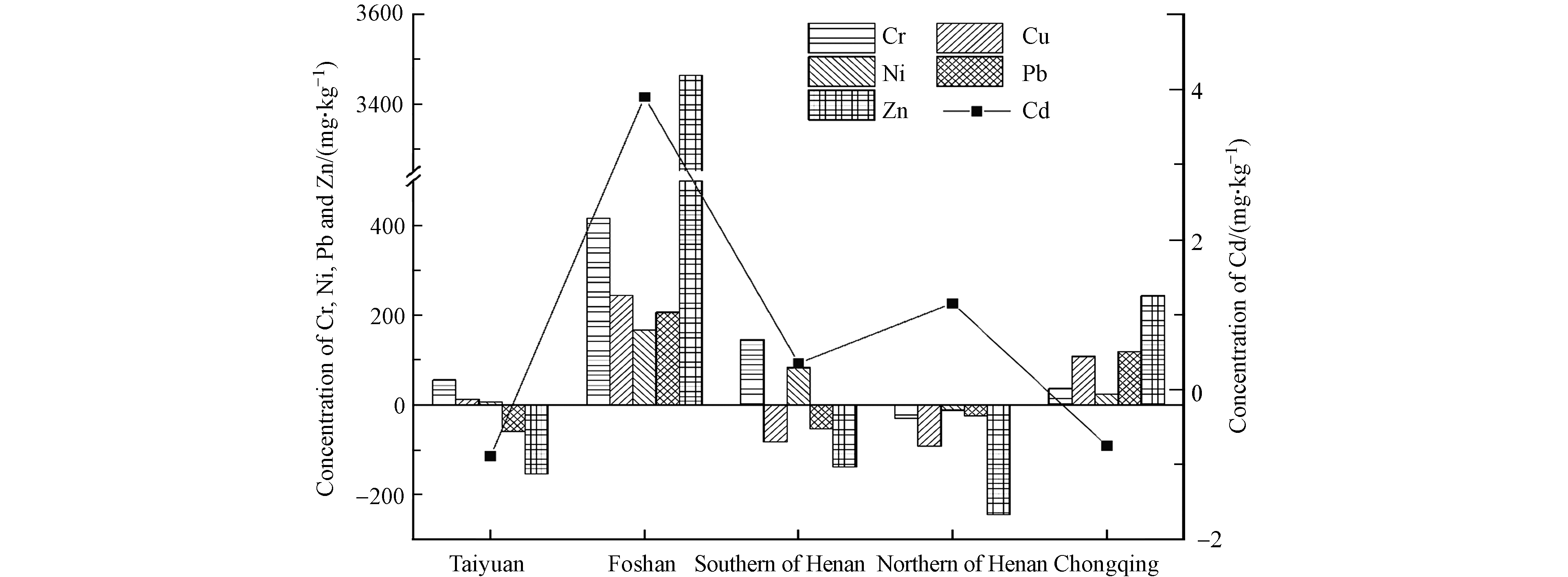
此外,选择太原、佛山、重庆及豫南、豫北不同地域室内灰尘重金属与本研究室内灰尘重金属均值进行比较(图1). 结果表明,相比于太原,本研究Pb、Zn和Cd含量偏高,分别为太原的2.18、1.53、2.59倍. 与豫南地区相比,本研究Cu、Pb和Zn含量偏高,分别为豫南地区的1.86、1.96、1.45倍. 而本研究所在的豫北地区除Cd外,其他元素Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn的平均含量均低于本研究. 但与重金属含量水平较高的佛山和重庆相比,本研究重金属平均含量普遍低于佛山,Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn分别低于佛山2.69、5.32、5.32、4.90、1.89、7.79倍,本研究Cd平均含量高于 重庆,而Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn分别为重庆的60.7%、15.9%、47.4%、40.5%、51.3%.
-
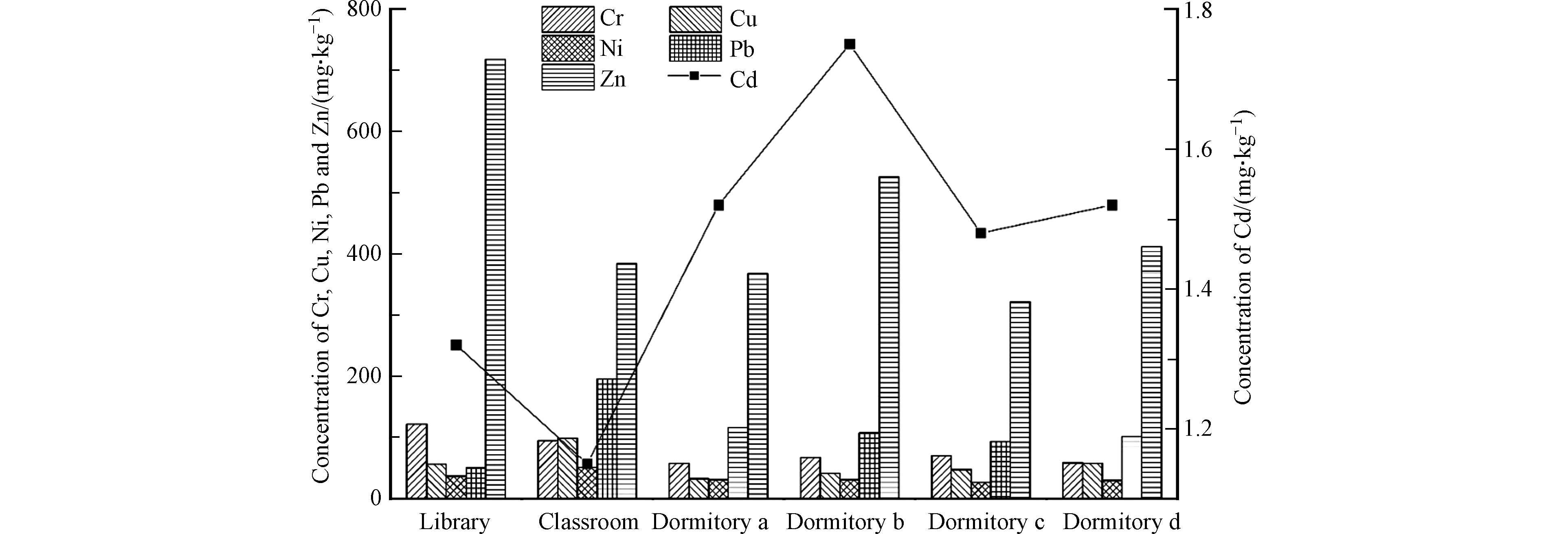
该高校44个采样点分别分布于图书馆(L)、教学楼(C)、宿舍区(DA、DB、DC、DD)3个区域,通过对各个区域6种重金属差异性分析和平均含量进行分析,结果如表5和图2. 3个不同环境室内差异性分析表明,Cr含量在图书馆—宿舍楼和教学楼—宿舍楼以及Pb和Zn含量在图书馆和宿舍楼存在显著性差异(P<0.05),经分析是由于Cr元素在图书馆和教学楼人的个别样点含量较高,Pb和Zn在宿舍楼的个别样点含量较高. 不同 区域采样点的不同重金属污染情况存在一定差异. 其中,宿舍区Cd的平均含量高于图书馆和教学楼,而Cr的平均含量为63.65 mg·kg−1,处于较低水平. Cu在教学楼和图书馆的平均含量分别为98.55 mg·kg−1和56.72 mg·kg−1,Cr为95.07 mg·kg−1和121.78 mg·kg−1,均高于宿舍区的平均含量. 图书馆Zn的含量为717.24 mg·kg−1,分别为宿舍区和教学楼的1.76和1.87倍. Pb的含量在各个区域的大小顺序依次为:教学楼>宿舍区>图书馆.
高校室内重金属来源比较复杂,不仅受到人群活动的影响,还与周围城市交通、建筑施工等不同状况相关密切[36-38]. 在本研究中的6种灰尘重金属Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn的平均含量均明显高于该市(开封)土壤灰尘重金属背景值.
其中,各样点Ni含量仅略高于当地背景值,受人类活动影响较小,而Cd、Zn、Cu、Pb和Cr则与当地背景值相差较大,说明这几种重金属室内含量受到不同程度的来源影响. 通过对6种重金属的相关性进行分析发现(表6),Cr-Cu和Cr-Pb之间存在显著的正相关(P=0.05);Cr-Ni、Cr-Zn和Cu-Ni之间存在显著的正相关(P=0.01),Cd元素与其他元素没有相关性. 表明该校室内灰尘Cu、Ni和Zn可能有相似的来源,Cr和Pb可能有相似的来源. 根据表7主成分分析可知,3个主成分特征值大于1,解释总变量为74.16%,因此,提取3个因子. 第1主成分载荷高的是Cr和Zn,其中Zn的平均值是背景值的5.76倍,并且高于开封市公园地表灰尘值[29],可以排除自然源;有研究表明,交通运输会造成Zn的污染[39-41],Cr和Zn具有相关性;另外,校内包含多条交通道路,且分布在人员活动的主要地点周围,老师及学生驾车、骑车较为频繁,表明Cr和Zn的污染可能来源于交通. 第2主成分载荷较高的是Cu和Ni,李晓燕等发现Cu主要来源于室内油漆涂料、机械磨损和打印机使用等[14]. 该校宿舍每年暑假都会进行白色乳胶漆刷墙,并且教学楼和图书馆经常进行翻新,这些不同装饰材料的风化和脱落增加了室内灰尘重金属的含量,因此,Cu和Ni污染可能主要来源于以装修为主的人为活动. 第3主成分载荷绝对值较高的是Cd和Pb元素,有研究发现办公室内颗粒物的Cd和Pb浓度高于家庭室内[42]. 宿舍、教学楼和图书馆环境相对单一,但人口流动大,且存在各种设备如打印机、图书馆管理设备以及教学设备等,这些设备会发生机械磨损,引起重金属偏高. 因此,Cd和Pb的污染来源主要是以设备使用和消耗磨损为主的人为源.
-
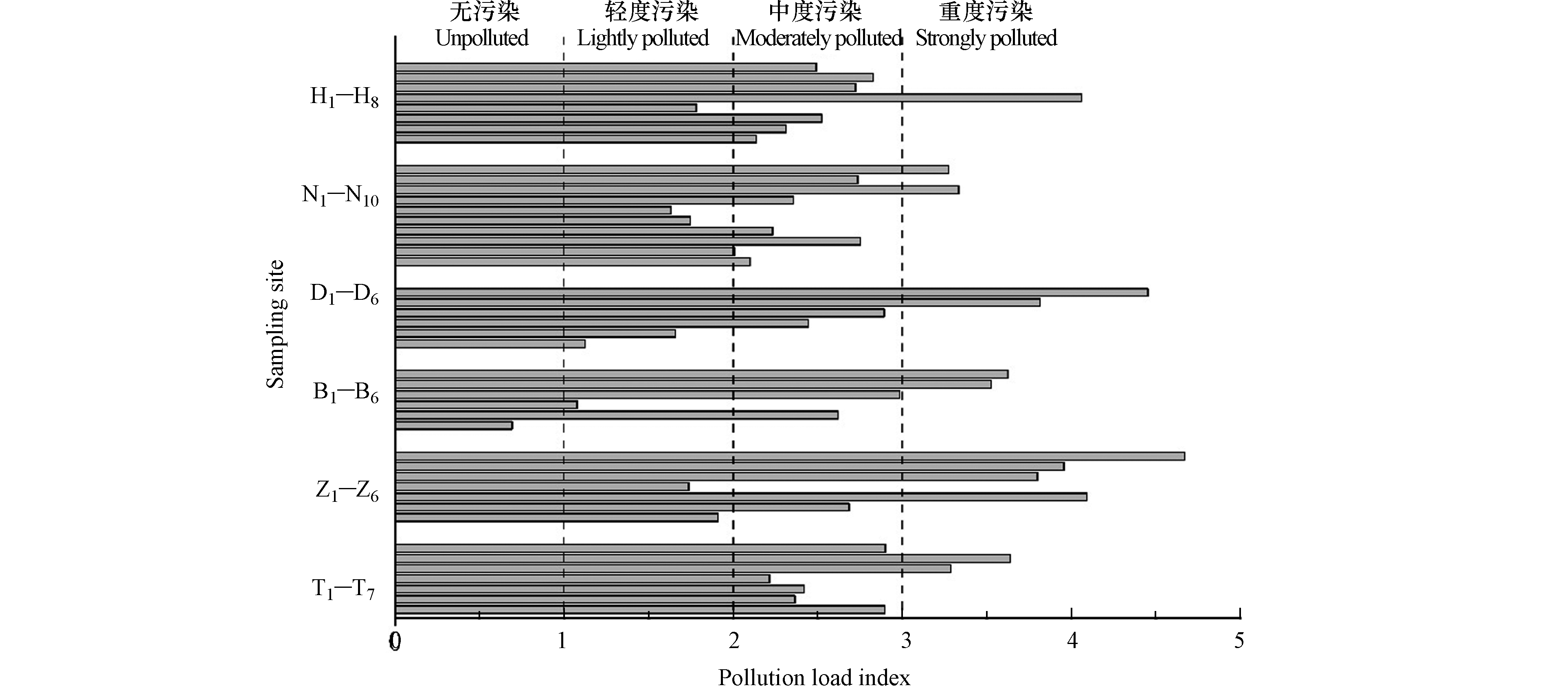
采用污染负荷指数法对该高校灰尘6种重金属污染情况进行评价,所得各样点污染负荷指数最大值为4.45,最小值为0.69,平均值为2.69. 采用污染负荷指数法对44个样点进行分级,结果如图3. 在44个样点中,有43个样点均存在不同程度的污染. 有50%的样点属于中度污染,重度污染的样点为29.5%. 根据区域污染负荷指数公式计算出该高校的区域污染负荷指数为2.52,属于中度污染水平.
通过污染负荷指数法计算公式得出各区域污染负荷指数为:教学楼(3.07)>图书馆(2.78)>宿舍区d(2.54)>宿舍区b(2.46)>宿舍区c(2.35)>宿舍区a(2.05). 图书馆和宿舍区的污染负荷指数均在2—3之间,属于中度污染;而教学楼的污染负荷指数为3.07,属于重度污染. 可见宿舍区的污染负荷指数低于教学楼和图书馆,其中教学楼的污染负荷指数分别是宿舍区a、b、c和d的1.50、1.25、1.31、1.21倍,污染程度相差较大.
-
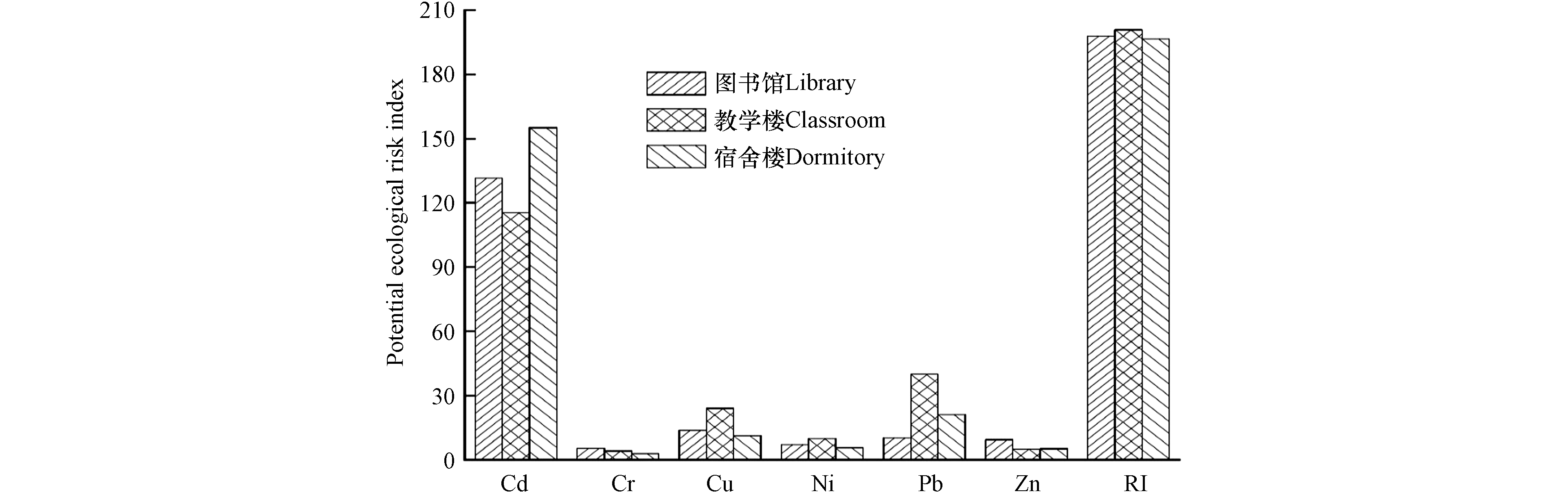
本文以开封市地表灰尘重金属背景值作为参比值[29],利用公式对研究区灰尘重金属潜在生态风险进行计算,所得 单项潜在风险指数值(Er)和重金属综合潜在风险指数值(RI)结果见图4. 该高校室内土壤灰尘中6种重金属的Er平均值大小为:Cd(145.09)>Pb(22.26)>Cu(13.72)>Ni(6.43)>Zn(5.76)>Cr(3.37). Cd元素的单项生态风险指数明显高于其他5种重金属,对综合潜在生态风险的贡献率为73.79%,是最主要的生态风险因子. 根据本研究的潜在生态风险指数划分标准,Cd为高生态风险,其余5种重金属为低生态风险. 从不同室内环境来看,Cd元素的Er值在宿舍楼最高,Cr和Zn元素的Er值在图书馆最高,Cu、Ni和Pb元素的Er值在教学楼最高. 总的来看,综合潜在生态风险指数大小为教学楼(200.90)>图书馆(197.95)>宿舍楼(196.63),均为较高生态风险.
在本研究中,6种重金属在教学楼、宿舍楼和图书馆上有着明显差异. 综合潜在生态风险指数大小为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍楼,均为较高生态风险. 教学楼作为学生、老师上课的主要场所,人员活动最为密集;而图书馆供学生自习、借阅图书的重要场所,往来人员也较为密集,而宿舍区主要是学生休息的场所,人员流动相对不频繁. 因此,造成宿舍楼的RI值低的原因可能是人员活动有关[43].
-
(1) 非致癌健康风险评价
根据公式计算出河南某高校室内灰尘3种暴露途径的非致癌风险和总非致癌风险的指数,结果见表8. 河南省某高校图书馆的为非致癌总风险指数值(HI)大小为Cr>Pb>Cd>Zn>Ni>Cu,HI值均小于标准值1,表明无非致癌健康风险. 从不同暴露途径看,皮肤途径的总HI值>手口途径>呼吸途径,Cr对3种途径的HI值贡献率最高. 教学楼的6种重金属HI值大小为Cr>Pb>Cd>Ni>Cu>Zn,HI值小于1;总HI值的暴露途径大小为手口途径>皮肤途径>呼吸途径. 宿舍楼的重金属HI值大小为Cr>Pb>Cd>Ni>Zn>Cu,HI值小于1;总HI值的暴露途径大小为手口途径>皮肤途径>呼吸途径.
河南省某高校室内灰尘6种重金属的3暴露途径的HQ值和HI值均小于1,表明不存在非致癌健康风险. 从不同暴露途径的HQ值看,6种重金属经呼吸途径摄入的值均最小,Cd和Cr的非致癌风险值暴露途径为皮肤>手口>呼吸;Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn为手口>皮肤>呼吸. 从不同环境室内看,该校的不同场所环境HI值大小为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍,HI值均小于1,对人体基本不会造成健康危害. Cr元素的对HI值贡献仅在综合楼的手口途径小于Pb元素,在其它途径不同环境区的贡献均最大,要注意Cr可能存在潜在的非致癌风险.
(2) 致癌风险评价
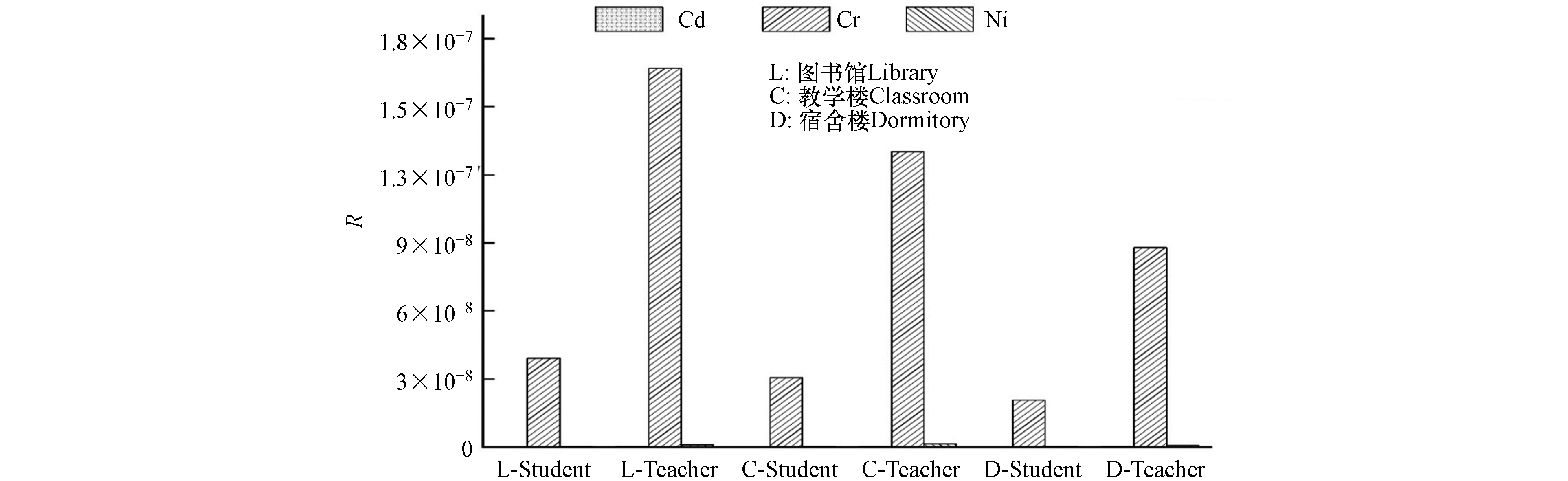
根据致癌风险公式,计算出不同环境室内Cd、Cr和Ni的3种重金属对教师和学生的致癌风险指数和总致癌风险指数,结果见图5. 该高校的致癌重金属元素Cd、Cr和Ni的总致癌风险值均远小于1×10−6的标准值,表明无致癌风险. 从不同室内环境看,该校的总致癌风险值大小为图书馆>教学楼>宿舍;由于教职工暴露年限要高于学生,因此,教职工在3个不同室内环境的致癌风险值均高于学生,但均无致癌风险. 图书馆、教学楼和宿舍楼的3种重金属元素致癌风险指数值(R)大小均为Cr>Ni>Cd. Cd元素R值排序为宿舍楼>图书馆>教学楼;Cr元素R值排序为图书馆>教学楼>宿舍;Ni元素R值排序为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍楼,说明不同元素在不同环境室内的致癌风险程度存在差异.
3个场所和元素的R值均小于标准值,说明3个场所和重金属无致癌风险. 该校的室内灰尘重金属元素不会造成健康危害,但要注意Cr元素可能存在的潜在致癌风险.
该校室内灰尘6种重金属的非致癌人均暴露量大小为手口途径>皮肤途径>呼吸途径,研究结果与蔡云梅等[20]一致. 从不同室内环境看,HI值大小为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍,总致癌风险值大小为图书馆>教学楼>宿舍. 学校及其周边会不定期进行道路整修、操场翻新、跑道铺设以及室内的教室改造、器材引进等措施,这也对学校室内灰尘重金属产生一定影响[44]. 图书馆和教学楼临近校园内的两条主干路,学校教职工和施工的燃油车尾气排放、零部件磨损、汽油泄露等交通产生的Cr很容易飘散或通过人类活动携带进入到室内富集[45],因而图书馆和教学楼的Cr、Cu的含量普遍高于宿舍区;而Cr元素对非致癌风险和致癌风险的贡献最大,贡献率分别达到了65.14%和98.96%. 因此,宿舍楼的非致癌风险和致癌风险均最小. 总体上看,不同环境室内的非致癌和致癌风险指数均对师生的身体健康没有造成危害.
-
有研究发现,大小型仪器、设备的使用会产生一定量的Cd[20],高校内仪器、设备等使用较为频繁,因此导致重金属含量普遍高于背景值;结合图书馆和综合楼与宿舍区之间的差异分析,在宿舍区周围分别存在着施工、绿化程度较低等情况. 宿舍楼c和d位于学校边缘,临近施工工地,建材等产生的重金属元素随空气飘入到宿舍室内;而宿舍楼a和b处于校外,绿化程度等相对较低,且环境较为复杂. 污染负荷指数和潜在生态风险指数均表明,该校的图书馆、教学楼和宿舍楼都存在污染风险,且污染程度为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍楼. 根据人体健康风险,Cr可能存在潜在的非致癌风险和非致癌风险,需要进行防治和治理,因此,给出以下治理建议.
室内环境与室外相比较为稳定,容易造成灰尘重金属的积累. 图书馆和综合楼作为公共场所,一些角落及不容易打扫的地方,灰尘清理周期较长,容易对人体健康产生影响. 因此对于墙角、地毯和桌缝等易造成灰尘积累的地方应当增大清洁力度,提高清洁频率,从而降低室内灰尘含量,减少重金属的累积. 交通源作为重金属的重要来源之一,应当受到重视,校园内适当限制人员活动密集地点车流量,增加其周边绿化程度,可以在一定程度上减少灰尘重金属由交通源进入到室内;机房及其他设备使用房间的设置应尽量远离人员密集的室内,同时根据情况及时处理仪器、设备产生的灰尘,这些也会对室内灰尘重金属含量产生一定的影响. 学校进行楼房维修翻新,使用油漆、涂料和钢材,尽量安排在假期等人员较少时进行. 另外,教学楼作为教师和学生上课的场所,人员流动大,要及时通风、清理等方式减少重金属在室内的含量.
-
(1)该校室内灰尘Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn的平均含量普遍偏高,是该地灰尘重金属背景值的4.80、1.68、2.74、1.30、4.45、5.76倍. 除Cd外,宿舍区其他5种元素低于教学楼和图书馆. Pb、Cu和Ni的均值在教学楼最高,Cd、Cr和Zn均值在图书馆最高.
(2)该校室内灰尘污染负荷指数大小为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍区d>宿舍区b>宿舍区c>宿舍区a,教学楼处于重度污染,图书馆和宿舍为中度污染.
(3)综合潜在生态风险指数大小为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍楼,均为较高生态风险. Cd元素对综合潜在生态风险的贡献率为73.79%,是最主要的生态风险因子.
(4)室内灰尘6种重金属的不同暴露途径和3个不同环境室内的HQ值和HI值均小于1,不存在非致癌健康风险;致癌重金属元素Cd、Cr和Ni的总致癌风险值均远小于1×10−6的标准值,无致癌风险. Cr是最主要的非致癌风险因子(65.4%)和致癌风险因子(98.96%).
河南某高校不同环境室内灰尘重金属污染特征及生态健康风险评价
Pollution characteristics and ecological health risk assessment of heavy metals in indoor dust in different environmental areas of a university in Henan Province
-
摘要: 探讨高校室内灰尘重金属污染情况对于保障师生身体健康具有重要意义. 以河南某高校为研究对象,采集宿舍、图书馆和教学楼等室内44个灰尘样品,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定6种重金属Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb和Zn含量,运用污染负荷指数法和潜在生态风险指数法评价室内灰尘重金属污染程度,利用美国环境保护局(US EPA)开发的人体健康风险评价模型对非致癌和致癌风险进行评价. 结果表明,6种重金属元素的平均含量均高于当地灰尘重金属背景值;教学楼的Pb、Cu、Ni的平均含量较高,Cr、Zn在图书馆含量较高,Cd宿舍区含量较高. 教学楼的污染负荷指数最高,属于重度污染,图书馆和宿舍楼为中度污染. 综合潜在生态风险指数大小为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍楼,均为较高生态风险,其中Cd为最主要的生态风险因子. 不同环境室内的非致癌风险值为教学楼>图书馆>宿舍,总致癌风险值大小为图书馆>教学楼>宿舍,均不存在健康风险;Cr是最主要的非致癌因子(65.4%)和致癌风险因子(98.96%). 本研究揭示了高校不同环境室内灰尘重金属污染情况、生态风险及健康风险状况,为高校室内不同区域重金属污染防治和治理提供了科学依据.Abstract: Studying on the pollution of heavy metals in indoor dust in university has great significance to ensure the health of teachers and students. This research takes a university in Henan Province as the research object, and 44 indoor dust samples were collected from 3 different environmental areas: dormitories, libraries, and classroom. The concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The pollution load index method and potential ecological risk index were used to evaluate the pollution degree of heavy metals in indoor dust. The human health risk evaluation model developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) was used to evaluate the non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks. The results showed that the average contents of six heavy metals were all higher than the background values in local dust and their contents in the dust of different environment had a certain difference. Specifically, the average content of Pb, Cu, and Ni in the classroom, Cr and Zn in the library, and Cd in the dormitory is higher than others. The classroom suffered severe pollution with the highest pollution load index, and the library and dormitory were moderately polluted. In addition, the comprehensive potential ecological risk index in the three different environmental areas all demonstrated high ecological risk, but with different order: classroom > library > dormitory, and Cd is the most important ecological risk factor. The overall order of the non-carcinogenic risk of different environmental areas was classroom > library > dormitory; the total carcinogenic risk decreased in the order of library > classroom > dormitory without health risk. Among all the heavy metals, Cr is the most important non-carcinogenic factor and carcinogenic risk factor, accounting for 65.4% and 98.96%, respectively. This research revealed the pollution characteristics, ecological risk and health risk of heavy metals in indoor dust in different environmental areas of colleges and universities. These findings could provide some reference for the prevention and control of heavy metal pollution in different indoor environment of colleges and universities.
-
Key words:
- university /
- indoor dust /
- heavy metals /
- ecological health risk.
-

-
表 1 河南某高校室内灰尘采样区
Table 1. Indoor dust sampling area of a university in Henan
地点
Location编号
Number人员信息
Personnel information周边环境状况
Surrounding environmental conditions图书馆 T1-T7 本科生、教师及研究生 前后为学校主要活动的两个广场,紧挨两条道路 教学楼 Z1-Z7 本科生、教师及研究生 前方临近广场,两侧分布道路,人员活动密集 宿舍区a B1-B6 本科生 楼下有小吃街,临近居民区和主干道,环境复杂 宿舍区b D1-D6 本科生 周边为居民区,近邻道路,环境复杂 宿舍区c N1-N10 本科生及研究生 处于校内,临近食堂,东侧为施工区 宿舍区d H1-H8 本科生及研究生 靠近学校,临近小吃街,南侧为施工区 表 2 健康风险暴露参数值
Table 2. Human health risk exposure parameter value
表 3 非致癌风险参考剂量值和 致癌风险斜率参考值
Table 3. Non-carcinogenic risk reference dose value and carcinogenic risk slope reference value
元素
ElementRfDij /(mg·kg−1·d−1) SF/(kg·d·mg−1) 手口摄入
Ingest呼吸摄入
Inhale皮肤摄入
Derma呼吸摄入
InhaleCd 1.00×10−3 1.00×10−3 1.00×10−5 6.30 Cr 3.00×10−3 2.86×10−5 6.00×10−5 42.00 Cu 4.00×10−2 4.02×10−2 1.20×10−2 Ni 2.00×10−2 2.06×10−2 5.40×10−3 0.84 Pb 3.50×10−3 3.52×10−3 5.25×10−4 Zn 3.00×10−1 3.00×10−1 6.00×10−2 表 4 灰尘重金属含量统计
Table 4. Statistics of heavy metal content in dust
重金属
Heavy metal背景值/(mg·kg−1)
Background value最小值/(mg·kg−1)
Minimum最大值/(mg·kg−1)
Maximum平均值/(mg·kg−1)
Average变异系数
Coefficient of variation超标率
Standard-exceeding ratioCd 0.30 0.45 3.07 1.45 50.54% 100% Cr 46.51 23.64 173.92 78.25 41.76% 84.10% Cu 20.54 14.15 212.01 56.35 60.68% 95.50% Ni 26.43 4.11 149.08 34.01 72.69% 61.40% Pb 24.58 6.81 787.23 109.44 103.20% 95.50% Zn 77.21 62.34 1306.02 444.90 64.34% 97.70% 注:背景值采用开封市周边地区地表灰尘重金属背景值[25]
Note: the background value is the background value of heavy metals in surface dust around Kaifeng City[25]表 5 图书馆、教学楼和宿舍楼室内灰尘中重金属显著性检验
Table 5. Significance test of heavy metals in indoor dust of library, classroom and dormitory.
元素
Element图书馆-教学楼
Library-classroom图书馆-宿舍楼
Library- dormitory教学楼-宿舍楼
Classroom-dormitory检验方法
Inspection methodCd 0.687 0.451 0.208 LSD Cr 0.053 0.000 0.005 LSD Cu 0.326 0.568 0.177 Tamhane Ni 0.880 0.911 0.589 Tamhane Pb 0.487 0.000 0.778 Tamhane Zn 0.260 0.007 0.916 LSD 表 6 室内灰尘重金属的Pearson相关系数
Table 6. Pearson correlation coefficient of heavy metals in indoor dust
元素
ElementCd Cr Cu Ni Pb Zn Cd 1.00 Cr 0.03 1.00 Cu 0.20 0.31* 1.00 Ni -0.05 0.39** 0.40** 1.00 Pb -0.14 0.36* 0.07 0.28 1.00 Zn 0.09 0.54** 0.04 0.04 0.16 1.00 注:* 在 0.05 水平(双侧)上显著相关,** 在0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关
Note: * is significantly related at the level of 0.05 (both sides), * * is significantly related at the level of 0.01 (both sides)表 7 不同重金属含量主成分中的因子载荷
Table 7. Factor loads of different heavy metal contents in principal components
元素
Element旋转后主成分载荷
Principal component analysis load after rotation第一主成分PCA1 第二主成分PCA2 第三主成分PCA3 Cd 0.148 0.144 0.839 Cr 0.785 0.403 -0.123 Cu 0.055 0.818 0.283 Ni 0.092 0.810 -0.261 Pb 0.377 0.281 -0.592 Zn 0.912 -0.117 0.086 特征值 1.623 1.600 1.226 累计贡献率/% 27.054 53.72 74.156 表 8 不同环境室内灰尘重金属非致癌风险值表
Table 8. Non-carcinogenic risk values of heavy metals in dust from different environmental areas
元素
Element图书馆
Library教学楼
Classroom宿舍楼
DormitoryHQing HQinh HQder HI HQing HQinh HQder HI HQing HQinh HQder HI Cd 1.20×10−3 1.77×10−7 6.02×10−3 7.22×10−3 1.05×10−3 1.55×10−7 5.27×103 6.32×103 1.42×10−3 2.08×107 7.09×103 8.51×103 Cr 3.71×10−2 5.72×10−4 9.27×10−2 1.30×10−1 2.89×10−2 4.46×10−4 7.24×10−2 1.02×10−2 1.95×10−2 3.01×10−4 4.88×10−2 6.86×10−2 Cu 1.30×10−303 1.89×10−7 2.16×10−4 1.52×10−3 2.25×10−3 3.29×10−7 3.75×10−4 2.63×10−3 1.06×10−3 1.55×10−7 1.77×10−4 1.24×10−3 Ni 1.68×10−3 2.4×10−7 3.11×10−4 1.99×10−3 2.34×10−3 3.35×10−7 4.34×10−4 2.78×10−3 1.34×10−3 1.91×10−7 2.48×10−4 1.59×10−3 Pb 1.31×10−2 1.92×10−6 4.38×10−3 1.75×10−2 5.11×10−2 7.47×10−6 1.70×10−2 6.81×10−2 2.69×10−2 3.93×10−6 8.97×10−3 3.59×10−2 Zn 2.19×10−3 3.21×10−7 5.46×10−4 2.74×10−3 1.17×10−3 1.72×10−7 2.92×10−4 1.46×10−3 1.20×10−3 1.77×10−7 3.01×10−4 1.50×10−3 总HI 5.66×10−2 5.75×10−4 1.04×10−1 1.61×10−1 8.68×102 4.54×10−4 9.58×10−2 1.83×10−1 5.14×10−2 3.06×10−4 6.56×10−2 1.17×10−1 -
[1] 曹治国, 董星依, 石玉盟, 等. 3种磷代阻燃剂在室内外灰尘中的粒径分布规律及人体暴露评估 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(7): 2759-2766. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2016.0471 CAO Z G, DONG X Y, SHI Y M, et al. Particle size distribution and human exposure assessment of three organic phosphorus flame retardant in indoor and outdoor dust [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(7): 2759-2766(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2016.0471
[2] 毕珏, 张振宁, 刘雨佳, 等. 高原城市室内灰尘对人角膜上皮细胞损伤研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(7): 3360-3370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.07.041 BI J, ZHANG Z N, LIU Y J, et al. Damage to human corneal epithelial cells caused by indoor dust in plateau city [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(7): 3360-3370(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.07.041
[3] 陈静, 施姜丹, 温勇, 等. 南京室内灰尘与青少年头发指甲中重金属的污染特征研究 [J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 57(3): 451-459. CHEN J, SHI J D, WEN Y, et al. Accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in indoor dust and teenager hair and nails from Nanjing [J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2021, 57(3): 451-459(in Chinese).
[4] 陈琳钰, 陈仙仙, 何欢, 等. 室内灰尘中多环芳烃及其衍生物的赋存与人体暴露研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(2): 404-415. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020062304 CHEN L Y, CHEN X X, HE H, et al. Occurrence and human exposure of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives in indoor dust: A review of recent studies [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(2): 404-415(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020062304
[5] 沈墨海, 王世华, 董文静, 等. 冬季河南省若干城市室内灰尘中重金属的健康风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(10): 2171-2180. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017112301 SHEN M H, WANG S H, DONG W J, et al. Pollution characteristics and health risks of heavy metals in indoor dust from Henan Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(10): 2171-2180(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017112301
[6] 李子夏, 谢娜, 杨芳. 宝鸡市中小学校园室内外灰尘铅暴露及评价 [J]. 地球环境学报, 2018, 9(5): 521-526. doi: 10.7515/JEE182044 LI Z X, XIE N, YANG F. Exposure assessment of environment lead of indoor and outdoor dust in primary and high schools of Baoji [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2018, 9(5): 521-526(in Chinese). doi: 10.7515/JEE182044
[7] 张舒婷, 李晓燕. 城市室内灰尘重金属的水平及来源 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(7): 1201-1207. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.07.024 ZHANG S T, LI X Y. Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in indoor dust of cities [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(7): 1201-1207(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.07.024
[8] 张振宁, 毕珏, 杨丹蕾, 等. 环境浓度下铜锰复合暴露对人角膜上皮细胞的毒性效应 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(2): 458-467. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0230 ZHANG Z N, BI J, YANG D L, et al. Toxic effects of copper and manganese on human corneal epithelial cells at environmental concentrations [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2022, 42(2): 458-467(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0230
[9] TAN S Y, PRAVEENA S M, ABIDIN E Z, et al. A review of heavy metals in indoor dust and its human health-risk implications [J]. Reviews on Environmental Health, 2016, 31(4): 447-456. [10] 耿雅妮, 梁青芳, 杨宁宁, 等. 宝鸡市城区灰尘重金属空间分布、来源及健康风险 [J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(5): 696-706. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2019.47.131 GENG Y N, LIANG Q F, YANG N N, et al. Distribution, sources and health risk assessment of heavy metals in dusts of the urban area of the Baoji City [J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(5): 696-706(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2019.47.131
[11] 姚有如, 方凤满, 朱慧萍, 等. 安徽省部分农村室内灰尘中汞的分布特征与健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(2): 282-288. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.02.2016053002 YAO Y R, FANG F M, ZHU H P, et al. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of mercury in indoor dust of some rural areas of Anhui Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(2): 282-288(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.02.2016053002
[12] 黄浩, 徐子琪, 严俊霞, 等. 太原市城乡居民区采暖季室内灰尘中重金属的污染特征及其生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(5): 2143-2152. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008045 HUANG H, XU Z Q, YAN J X, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk evaluation of indoor dust from urban and rural areas in Taiyuan City during the heating season [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(5): 2143-2152(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008045
[13] 曹治国, 余刚, 吕香英, 等. 北京市典型室内外灰尘中重金属的粒径和季节变异特征及人体暴露评估 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(4): 1272-1278. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.04.011 CAO Z G, YU G, LÜ X Y et al. Particle size distribution, seasonal variation characteristics and human exposure assessment of heavy metals in typical settled dust from Beijing [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(4): 1272-1278(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.04.011
[14] 李晓燕, 汪浪, 张舒婷. 城市室内灰尘重金属水平、影响因素及健康风险: 以贵阳市为例 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(8): 2889-2896. LI X Y, WANG L, ZHANG S T. Level and the courses of heavy metals and its risk assessment in indoor dust of city: Take Guiyang as a case [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(8): 2889-2896(in Chinese).
[15] 李良忠, 胡国成, 张丽娟, 等. 矿区家庭灰尘中重金属污染及其潜在生态风险 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(4): 1230-1238. LI L Z, HU G C, ZHANG L J, et al. The pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of the heavy metals in household dusts from mineral areas [J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(4): 1230-1238(in Chinese).
[16] HWANG H M, PARK E K, YOUNG T M, et al. Occurrence of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in indoor dust [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 404(1): 26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.05.031 [17] 刘晓途, 彭长凤, 陈达, 等. 广州地区室内灰尘中典型非邻苯增塑剂的污染特征与暴露风险 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(8): 3676-3681. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202012117 LIU X T, PENG C F, CHEN D, et al. Characterization and exposure risk assessment of non-phthalate plasticizers in house dust from Guangzhou [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(8): 3676-3681(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202012117
[18] 曹治国, 王萌萌, 王小颍, 等. 办公室地面灰尘中PAHs污染的时间变化规律及人体健康风险 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2018, 13(3): 209-219. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20171129001 CAO Z G, WANG M M, WANG X Y, et al. Time variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in floor dust from office and corresponding human health risks [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2018, 13(3): 209-219(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20171129001
[19] 樊馨瑶, 卢新卫, 刘慧敏, 等. 西安市高校校园地表灰尘重金属污染来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(8): 3556-3562. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201912041 FAN X Y, LU X W, LIU H M, et al. Pollution and source analysis of heavy metal in surface dust from Xi'an university campuses [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(8): 3556-3562(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201912041
[20] 蔡云梅, 黄涵书, 任露陆, 等. 珠三角某高校室内灰尘重金属含量水平、来源及其健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(9): 3620-3627. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201703256 CAI Y M, HUANG H S, REN L L, et al. Levels, sources, and health risk assessments of heavy metals in indoor dust in a college in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(9): 3620-3627(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201703256
[21] 马玉凤, 李双权, 杜军, 等. 河南黄土研究进展 [J]. 地域研究与开发, 2021, 40(4): 171-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2021.04.030 MA Y F, LI S Q, DU J, et al. Research progress of loess study in Henan Province [J]. Areal Research and Development, 2021, 40(4): 171-180(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2021.04.030
[22] 徐伊莎, 夏新, 李欣, 等. 消解体系对土壤重金属测定的影响 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(5): 66-69,154. XU Y S, XIA X, LI X, et al. Effect of digestion systems on determination of heavy metals in soil [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(5): 66-69,154(in Chinese).
[23] TOMLINSON D L, WILSON J G, HARRIS C R, et al. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index [J]. Helgolä nder Meeresuntersuchungen, 1980, 33(1): 566-575. [24] 祝培甜, 赵中秋, 陈勇, 等. 江苏省某镇土壤重金属污染评价 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(4): 2535-2541. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201601016 ZHU P T, ZHAO Z Q, CHEN Y, et al. Evaluation of soil heavy metals pollution in a town, Jiangsu Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(4): 2535-2541(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201601016
[25] 马建华, 董运武, 陈彦芳. 开封市周边地区地表灰尘重金属背景值研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(5): 1798-1806. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0477 MA J H, DONG Y W, CHEN Y F. Background values of heavy metals in surface dusts in the vicinity of Kaifeng, Henan Province [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(5): 1798-1806(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0477
[26] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [27] 王小莉, 陈志凡, 魏张东, 等. 开封市城乡交错区农田土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 513-522. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017072407 WANG X L, CHEN Z F, WEI Z D, et al. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment in agricultural soils located in the peri-urban area of Kaifeng City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 513-522(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017072407
[28] 马建华, 韩昌序, 姜玉玲. 潜在生态风险指数法应用中的一些问题 [J]. 地理研究, 2020, 39(6): 1233-1241. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020190632 MA J H, HAN C X, JIANG Y L. Some problems in the application of potential ecological risk index [J]. Geographical Research, 2020, 39(6): 1233-1241(in Chinese). doi: 10.11821/dlyj020190632
[29] 段海静, 蔡晓强, 阮心玲, 等. 开封市公园地表灰尘重金属污染及健康风险 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(8): 2972-2980. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.08.033 DUAN H J, CAI X Q, RUAN X L, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and its health risk of surface dusts from parks of Kaifeng, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(8): 2972-2980(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.08.033
[30] BUX R K, HAIDER S I, MALLAH A, et al. Spatial analysis and human health risk assessment of elements in ground water of District Hyderabad, Pakistan using ArcGIS and multivariate statistical analysis [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 210: 112915. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112915 [31] 万千, 赵静, 韦旭, 等. 电子废弃物拆解车间灰尘中重金属污染特征及职业人群健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(3): 883-892. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020110901 WAN Q, ZHAO J, WEI X, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in the dust from e-waste dismantling workshop and health risk assessment of occupational population [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(3): 883-892(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020110901
[32] USEPA. Supplemental guidance for developing soil screening levels for superfund sites[R]. Washington, DC: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, 2002. [33] 张双银, 吴琳娜, 张广映, 等. 都柳江上游沿岸喀斯特地区土壤重金属污染及健康风险分析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(7): 421-433. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0474 ZHANG S Y, WU L N, ZHANG G Y, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution analysis and health risk assessment in Karst areas along the upper reaches of the Du Liujiang River [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2022, 42(7): 421-433(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0474
[34] HAN Q, WANG M S, CAO J L, et al. Health risk assessment and bioaccessibilities of heavy metals for children in soil and dust from urban parks and schools of Jiaozuo, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 191: 110157. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110157 [35] 李晓燕, 谢馨洁. 我国西南三市家庭灰尘重金属水平及差异 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(2): 365-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.02.025 LI X Y, XIE X J. A study on heavy metals in household dusts in 3 cities in Southwestern China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(2): 365-371(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2013.02.025
[36] HOU S N, ZHENG N, TANG L, et al. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018 [J]. Environment International, 2019, 128: 430-437. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.04.046 [37] CHEN X D, LU X W. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in topsoil from an area in Xi’an City, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 151: 153-160. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.01.010 [38] LU X W, PAN H Y, WANG Y W. Pollution evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal in roadway dust from a resource-typed industrial city in Northwest China [J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2017, 8(3): 587-595. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2016.12.019 [39] 杨明航, 李旭, 王玥, 等. 某燃煤电厂周边地表灰尘重金属空间分布、源解析及健康风险评价 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(8): 176-182. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2022.215 YANG M H, LI X, WANG Y, et al. Spatial distribution, source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface dust around a coal - fired power plant [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(8): 176-182(in Chinese). doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2022.215
[40] 陈轶楠, 马建华. 河南省某市驾校地表灰尘重金属污染及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(8): 3017-3026. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2016.0010 CHEN Y N, MA J H. Assessment of pollution and health risks of heavy metals in surface dusts from driving schools in a city of Henan, China [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(8): 3017-3026(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2016.0010
[41] 张鹏岩, 康国华, 庞博, 等. 宿鸭湖沉积物重金属空间分布及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(5): 2125-2135. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201610116 ZHANG P Y, KANG G H, PANG B, et al. Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Suya Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(5): 2125-2135(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201610116
[42] ABDUL-WAHAB S A, YAGHI B. Total suspended dust and heavy metal levels emitted from a workplace compared with nearby residential houses [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(5): 745-750. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.10.017 [43] 马建华, 朱玉涛. 嵩山景区旅游活动对土壤组成性质和重金属污染的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(3): 955-965. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.03.007 MA J H, ZHU Y T. Impacts of tourist activities on components, properties and heavy metal pollution of soils in the Songshan scenic area [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(3): 955-965(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.03.007
[44] PRAGG C, MOHAMMED F K. Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust from an industrial estate in Trinidad, West Indies [J]. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 2020, 30(3): 336-343. doi: 10.1080/09603123.2019.1609657 [45] 李军, 李开明, 位静, 等. 兰州BRT沿线站台灰尘及其两侧绿化带土壤重金属污染及健康风险评价 [J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(2): 228-240. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.025 LI J, LI K M, WEI J, et al. Contaminations and health risks of heavy metals from the roadside greenbelt soils and dust along the BRT platform in Lanzhou [J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(2): 228-240(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.025
-



 下载:
下载: