-
全球水资源中只有2.5%是由淡水组成的,淡水中只有大约5%或世界总水域的0.15%可供直接利用,其余的则包含在极地冰川或高海拔冰川中. 目前,全球淡水储量正在迅速枯竭,对世界上许多人口稠密的地区将产生严重影响. 随着科技和人类社会的快速发展,当前人类日常生活和工农业生产赖以生存的水资源大量充斥着人类活动而产生的化学污染物,所含有的化学品数量己多达100,000种以上,大多具有强毒性大、含量低、生物富集等特点,其危害已引起了国际环境科学界乃至公众的广泛关注. 但是,药物与个人护理品类作为与人类接触最为频繁、用量最大的化学品,特别是与人们生活及生产密切相关并且广泛应用的抗生素类药物长期被公众所忽视[1-2].
抗生素药物的种类、产量与用量在近年来不断增加,药品管理的混乱和盲目使用致使药物的滥用问题日益凸显,由此造成的基因抗性增强等问题也较为显著[3]. 抗生素类药物多数在人和动物体内不能被完全吸收,大部分以原形和代谢产物通过粪便和尿液直接排入环境,通过城市污水处理厂并经过多年积累,造成环境水体中的抗生素含量急剧增加,最终造成环境的污染. 同时,抗生素可通过饮用水源进入人体,进一步威胁人类的身体健康,如果不加以处理,将会对环境带来严重的后果[4-5]. 传统的水处理方法难以处理完全使之达到排放要求,如抗生素的生物毒性让生物处理手段变得困难,物理吸附方法虽可去除此类物质,但后续的进一步处理仍存在问题,化学氧化法需要投入大量的化学试剂等等问题[6-8]. 因此,越来越多的经济、社会、法律和环境压力要求利用对于环境中的抗生素类药物采用“最佳可用技术”,而不需要过多的成本,并追求“无污染的性能”,即“零污染处理”,因此寻找一种低能耗,高效率的废水处理方法是当前环保工作者的重要课题.
电催化氧化技术是基于传统电化学处理方式,经过国内外学者的进一步改善,由于电力系统的成熟,该技术逐步进入到大众视野. 电催化氧化法的主要原理是在电场的作用下,借助电场产生大量活性极强的•OH,与有机化合物发生加成、取代、电子转移、断键等电子转移反应,将废水中难降解的大分子有机物降解为小分子物质,直到完全矿化为CO2、水和无机离子等[9],因此,国内外研究学者把电催化氧化水处理技术被称为重要的“环境友好”(Environment Friendly Technology)水处理技术[10]. 电催化氧化技术具备易于控制、条件温和、自动化操作、高效低耗能等特点,利用电场作用使污染物分解或者转化来达到水净化的目的,具有明显的技术优势,成为目前水中有机污染物处理的重要处理手段[11-13].
-
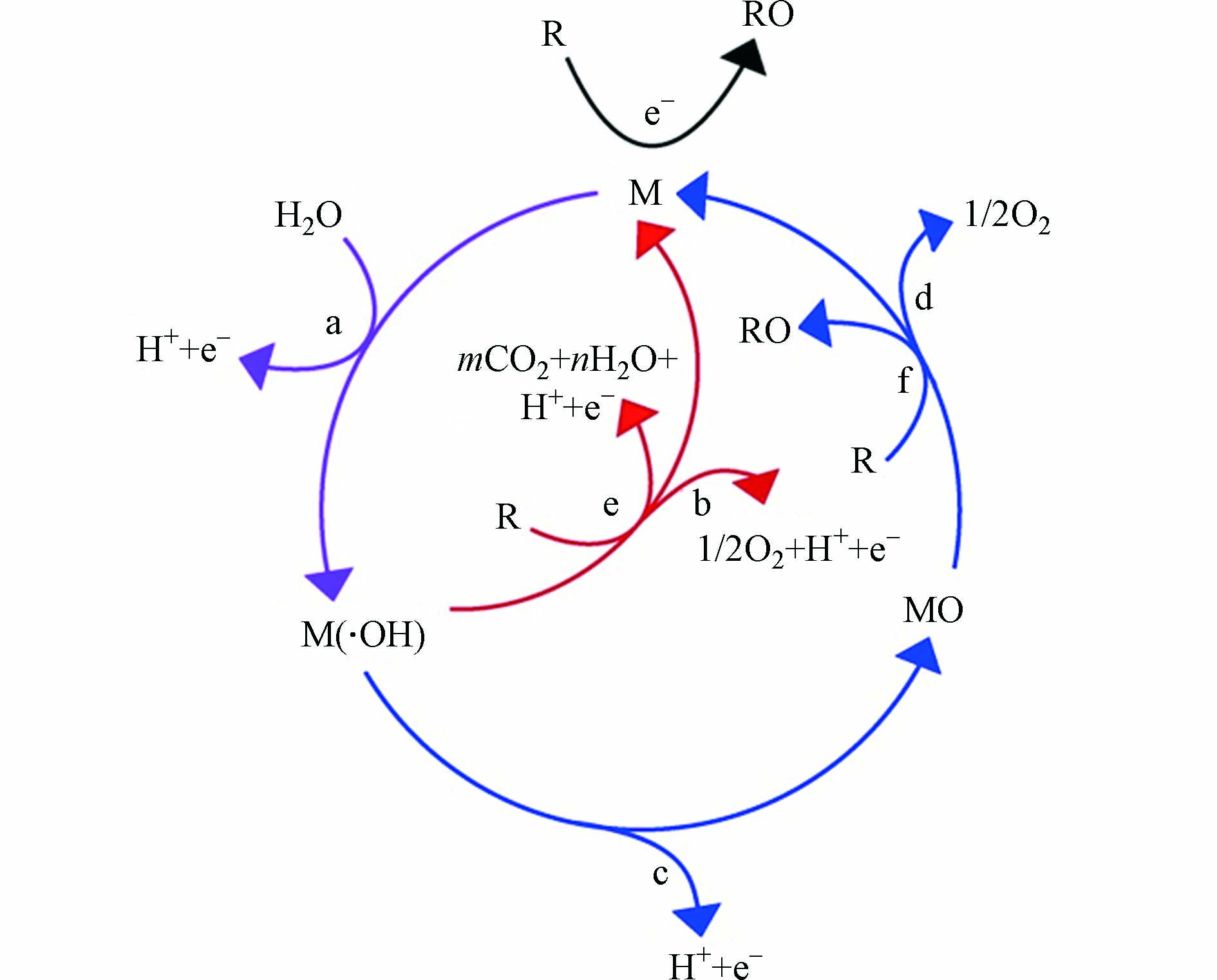
电催化氧化技术被认为是一种高效的水处理技术手段,通过直接或间接产生强氧化性物质与有机污染物进行作用,将其部分转化或最终彻底矿化为CO2和H2O,具有氧化性强、操作简便、环境友好等一系列特点,成为当前环境工作者研究的一大热点[14-17]. 电催化氧化除在阳极表面直接氧化有机污染物外,还伴随着着强氧化剂的产生,这些氧化剂可作用于阳极表面并将氧化过程扩展到本体溶液[18]. 在大多数提出的描述有机污染物氧化的机制中,污染物通常在阳极表面上通过生成的强氧化性的羟基自由基(•OH)进行矿化,•OH的存在形式取决于所使用的阳极材料及其固有的电催化氧化性能. 具体来说,阳极M上最初通过水分子的放电过程形成吸附的•OH,即,M(•OH);接下来,有机污染物R与M(•OH)进行作用,将R矿化为CO2和H2O,同时,在R的电化学降解过程中,生成的M(•OH)还可以进一步发生分解生成O2,这是整个过程的副反应,具体如式1—4所示[18].
根据电化学氧化反应的机制,具有低析氧过电位的阳极,例如Pt、RuO2、IrO2、石墨或碳,表现出“活性”行为,其析氧电位通常低于1.8 V vs. SHE,仅允许有机物部分氧化,对于活性电极来说,在活性电极表面上形成更高价的金属氧化物(MO),•OH以化学吸附的形式存在于电极的晶格(MO)当中,此后,MO将继续与有机物反应达到转化污染物的目的,具体路径为c,f,同时,在电催化过程中往往伴随着析氧副反应(b,d)的发生,在一定程度上降低了电极表面电催化氧化有机物的电流效率;具有高析氧过电位的非活性阳极,如PbO2、BDD和SnO2,•OH一般地以物理性吸附的形式存在于非活性电极,这意味着电极与羟基自由基的相互作用力较弱,自由基与电极的附着力不强,•OH可脱离电极表面自由地与有机污染物反应. 在非活性电极表面,物理性吸附•OH继续与溶液中的有机污染物进行作用,将有机物转化为其他物质或者完全矿化为CO2和H2O,具体路径为a、b、e,如图1所示[19]. 基于以上阐述,析氧反应发生的难以程度直接影响电催化过程的有机物的矿化和析氧反应进行程度. 当阳极材料的析氧电位较低时,析氧反应在有机物降解过程中占主导地位. 相反,当析氧过电位高时,析氧反应难以发生,有机物的降解过程容易发生,可提高有机物矿化的电流效率. 一般来说,阳极析氧电位越高,M(•OH)与阳极表面的相互作用越弱,对有机污染物氧化的化学反应性越高,因此,高析氧电位的研究材料一直称为电催化氧化有机污染物的重要目标[14, 20- 21].
除了基于氧气析出反应生成强氧化性•OH活性物质外,近年来还发展了其他的间接电氧化活性物种的电催化氧化机理[22-23]. 在含氯离子的废水中,除以上涉及的•OH活性物种外,活性氯物种也是电催化氧化技术中生成的传统、应用最广泛的氧化剂之一. 溶液中自然存在或人工添加的氯化物会在阳极表面参与阳极氧化反应,Cl−转化为ClO−,促进活性氯物种的形成,其主要以气态Cl2、HClO或ClO−的形式存在,最终对溶液中的污染物进行氧化降解[24]. 相关研究表明,溶液中的活性离子的形式受到溶液pH值的影响较大,在酸性和强碱性溶液体系中,主要以氯气和OCl−形式存在;二在偏碱性和中性溶液中,则以HOCl形式存在. 同时,在含高氯离子浓度溶液中,电催化氧化技术最为适合采用的阳极材料通常为DSA阳极.
通过自由基和非自由基反应方式电化学生成的活性硫物种(SO4•−和S2O82−)是电催化氧化有机污染物的另一种新的降解机制[25-26]. 目前,活性硫物种的产生主要通过直接添加过硫酸盐或硫酸盐活化的方式得到. 在有机物的处理过程中,一般选用导电性和丰度较高的硫酸盐作为支持电解质,因此硫酸盐活化相比直接添加过硫酸盐更具备吸引力. 在硫酸盐介质中,SO4•−和S2O82−主要通过以下3种途径产生[25, 27]:
(1) SO42−的直接氧化
(2) SO42−和电产生活性 •OH的反应
(3) 电产生SO4•−重组为S2O82−,同时S2O82−可在阳极材料上进一步活化为SO4•−
-
电催化氧化过程中,有机污染物的电催化氧化反应主要在阳极材料上进行,阳极材料作为整个电催化氧化反应的主要发生场所,其自身性质直接决定了电催化氧化机理和动力学过程[28-29]. 目前,许多阳极材料被开发出来用于电催化氧化有机污染物的阳极氧化过程,主要包含金属Pt、形稳型阳极、掺硼金刚石、碳质材料及亚氧化钛阳极等,典型的特点及效果如表1所示.
-
Pt是一类在电化学研究中被广泛用作电极材料,具有良好的导电性和化学稳定性,是首次被用作氧化有机污染物的阳极材料. Pt阳极的析氧过电位相对较低,在0.5 M H2SO4中的约为1.7 V vs. SHE,可以以低电流效率实现有机污染物的选择性转化[30]. Goyal等[31]研究了Pt阳极对双氯芬酸的降解,有机物的降解反应遵循伪一级动力学,实验结果表明,最初无色的双氯芬酸溶液在300 mA的中性缓冲液(pH=6.5)中降解,180 min后逐渐变为深棕色,持续电解至结束(360 min),有机物的总有机碳减少了46%. 然而,由于Pt阳极的电催化性能较弱,难以实现有机物的完全矿化,并且价格因素及表面钝化膜的形成因素使其在实际系统中难以应用.
-
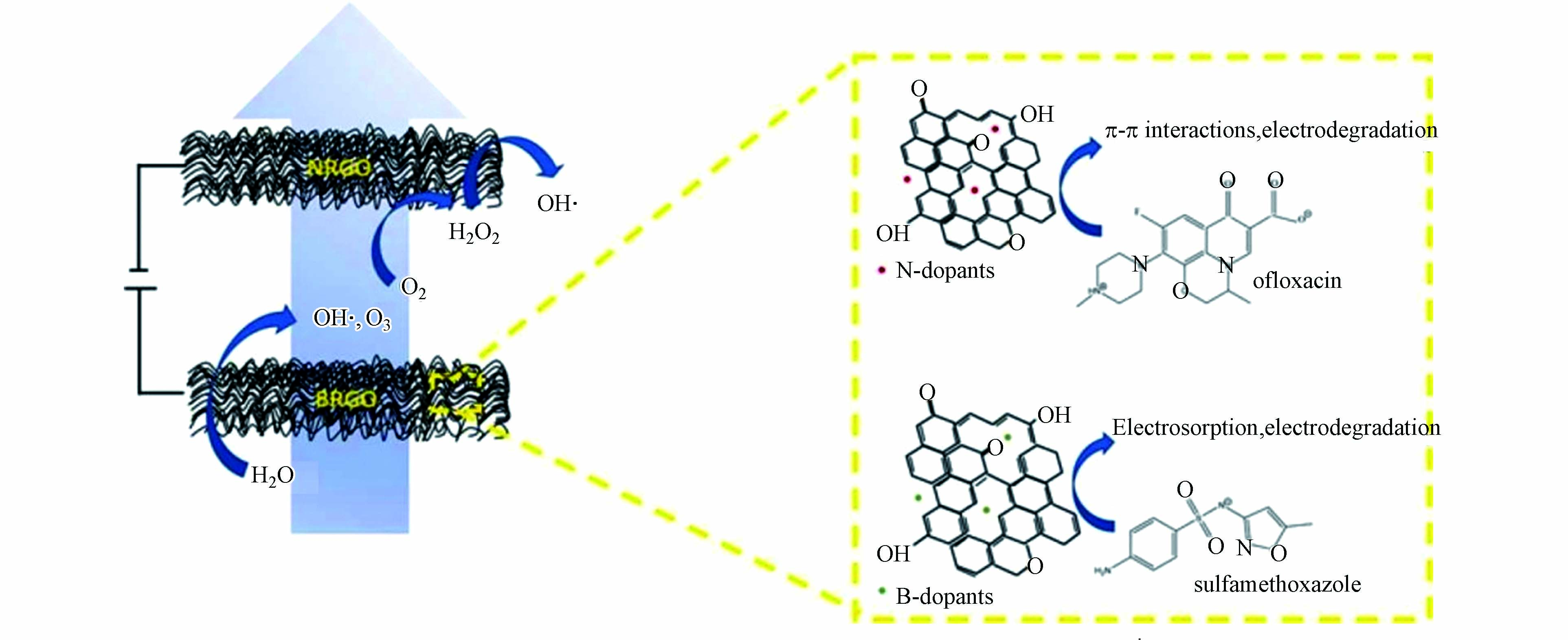
碳质材料具有良好导电性、成本低、高比表面积、对有机污染物亲和度好以及良好的电催化性能,是一种应用前景广阔的材料,除石墨电极外,许多其他碳质材料已广泛用于去除有机污染物,主要包括活性碳纤维、碳毡和碳纳米管等[32-34]. Natalia Ormeno-Cano等[35]采用硼和氮原子掺杂的石墨烯海绵作为阳阴极构建了流通式电化学反应器,用于在低电导率支持电解质中去除抗生素类污染物(磺胺甲恶唑、甲氧苄啶、氧氟沙星和红霉素),如图2所示,研究结果显示,与还原的氧化石墨烯显示出强π-π相互作用的抗生素(氧氟沙星)的去除效果不受传质的限制,并且在所研究的电解质流速范围内,抗生素的去除效率可达到80%以上,在较高的流速条件下,高电流密度下产生的气泡对于抗生素的去除产生不利影响. 此外,活性碳材料也可在三维反应器中充当反应性粒子[36- 37],但是,作为阳极材料的碳质材料中的碳元素容易氧化分解,因此碳素电极在氧析出条件下极易被腐蚀,同时碳素电极存在强度较低等问题,这是未来碳素材料需重点解决的关键问题.
-
在钛基上涂覆具有电催化性能的金属氧化物的电极,称为形稳阳极(dimensionally stable anode,DSA),其以良好的稳定性和电催化活性得到了极大的关注. DSA阳极可根据电催化过程的要求,合理地调节材料的物质组成和电子结构,实现电催化性能和寿命的显著提升,目前DSA阳极材料主要包含SnO2、PbO2、RuO2、IrO2、Ta2O5等及其复合物[38-41]. PbO2是DSA阳极中的典型代表,对于PbO2阳极电催化活性性能调控的策略主要包含制备条件优化、异质原子掺杂、基体适配、表面浸润状态调控等[42-46]. Xia等[47]制备了Co元素掺杂PbO2电极,Co掺杂相比未掺杂的Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3/α,β-PbO2电极具有更致密表面、更小晶体尺寸、高析氧电位和羟基自由基的产生效率等优异特点,在最佳操作参数0.1 mol·L−1 Na2SO4,诺氟沙星浓度50 mg·L−1,pH=5,电流密度20 mA·cm−2条件下,抗生素诺氟沙星在电解60 min后的浓度、化学需氧量和总有机碳去除率分别达到85.29%、43.65%和41.89%,同时,经过处理的诺氟沙星溶液对费氏弧菌的毒性评估迅速下降到无毒,表明诺氟沙星的电化学氧化是降低其对环境生态系统毒性的有效方法. 但是,PbO2电极在电化学降解污染物过程中可能伴随着金属Pb的溶出,因此在选择阳极过程中需综合考虑成本、性能和环境等因素.
-
掺硼金刚石(BDD)电极具有使用寿命长、强度大、电催化活性高,在高电位下依旧能稳定使用,不会大量吸附有机物而被污染等优点,因此,BDD电极由于其自身优异的物理和化学性质,被认作为电催化氧化水中有机污染物最为理想高效的电极材料[14, 48-49]. BDD的制备需要借助特定的化学气相沉积技术,沉积过程中的实验参数直接影响BDD薄膜电极的自身性质,主要包括基体类型、薄膜厚度、晶粒大小、表面粗糙度、硼掺杂度和石墨化程度等[50-52]. Santos等[51]研究了微米和纳米金刚石电极对于抗生素环丙沙星的电催化氧化性能,研究发现,通过调控沉积过程的CH4/H2率可制备得到不同晶粒尺寸的BDD电极;得益于较高的sp2含量、高硼掺杂度和提升的表面积,纳米金刚石电极相对于微米金刚石电极具有更快的环丙沙星去除动力学,最佳的降解实验条件为电流密度40 mA·cm−2,环丙沙星浓度15 mg·L−1. 目前,研究者一般认为低硼掺杂量和高sp3/sp2率有利于BDD电极表面电化学活性物质的产生,加快BDD电极的电催化降解过程,但对于不同的电解液体系和电催化氧化机理,其具体的影响机制还有待进一步考证. 但是,由于作为沉积BDD的Si基体脆性大及导电性差,Nb,Ta和W的价格昂贵,以上均不适合作为工作应用的理想基体材料. 此外,BDD沉积需要借助化学气相沉积方法,整体成本较高,限制了其在废水处理领域上的应用与发展,因此,如何得到低价格、高质量的大面积BDD电极是其有效实际用于电催化氧化领域的最大挑战.
-
亚氧化钛(TinO2n-1)是对一系列非化学计量式钛氧化物的统称,其通式为TinO2n-1(4≤n≤10)[53],TinO2n-1电极具有导电性高、耐腐蚀性强、析氧电位高和成本相对低廉的特点,且TinO2n-1的导电性与n值有关,Ti4O7导电率最高可达1500 S·cm−1;目前,TinO2n-1常用于电催化降解水中的药物及个人护理品、全氟化合物、偶氮染料等有机污染物,是目前较具有应用前景和研究较多的阳极材料之一[54]. 亚氧化钛通常由地球上最丰富的原料之一的TiO2制得,来源丰富[55],然而,TinO2n-1电极的制备通常采用真空热压或等离子喷涂工艺,技术成本较高[56]. 此外,污染物向电极表面的传质过程是限制污染物电催化降解的重要因素,研究发现电解液流通穿过电极可以加速污染物向电极表面的传质,进而促进污染物的降解并增加电流效率[57-58]. 为了降低TinO2n-1电极的制作成本并增强有机污染物向TinO2n-1电极表面的传质动力学,研究者采用提拉浸渍-氢热还原法制备TinO2n-1多孔膜电极,并以TinO2n-1多孔膜电极为基础构建流通式-电催化氧化系统,同时揭示了TinO2n-1多孔膜电极的催化机制. Zeng等[59]利用阳极氧化和电化学还原方法在多孔钛膜制备了一种基于还原型TiO2纳米管阵列膜(RTNA/TM),阳极氧化处理在钛基板上原位形成均匀的纳米管,之后通过电化学还原将部分Ti4+离子转化为Ti3+离子,一维的TiO2纳米管和还原处理提高了磺胺甲恶唑的去除效率(86.1%),降低了电催化氧化过程的能耗(0.55 kWh·m−3),与批处理模式相比,在流通模式下运行的RTNA/TM显著提高了磺胺甲恶唑的去除性能,甚至优于BDD电极,如图3所示,并且,电化学氧化过程中的作用机理为•OH自由基起主要作用,直接电子转移发挥次要作用. 尽管TinO2n-1材料具有优越的电化学性能,但其商业化应用过程限制因素依然较多.
-
单个有机废水处理方法对污染物的去除效率低且成本难以控制等因素,限制了单独处理技术的广泛应用. 相对于其它水处理技术来说,电催化氧化技术具有操作方便,设备简单,投资少和适用性广等技术优势,但面临着过程消耗电能大、运行费用过高和电流效率低等限制. 为了进一步提高有机物的电催化效率和降低过程中能耗,许多科研人员将电化学氧化技术与其它处理技术集成组合,协同促进电催化过程动力学[60-61],这对电化学氧化技术的工业可行性及实用性提供是一条切实可行的路线,在抗生素类废水的处理上取得了较好的效果.
-
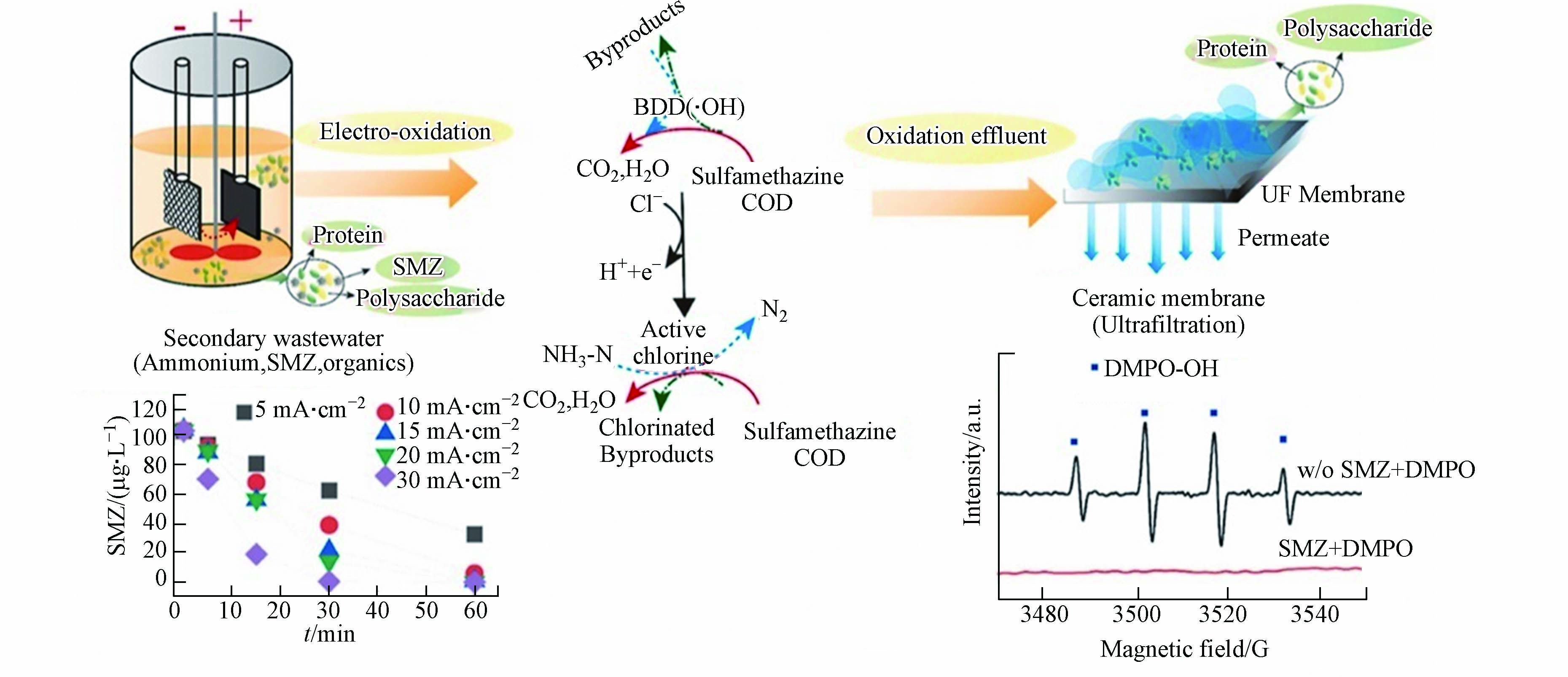
电化学氧化-物理联合技术是近年来开展来的一种新型联合水处理技术. 常规的物理处理主要通过吸附、絮凝、膜分离技术等实现物相分的分离,难以完全降解有机污染物[62]. 例如,吸附法借助吸附材料的高比表面积提供位点吸附污染物,是目前最常见的物理水处理方法. 由于吸收容量限制,吸附材料在吸收饱和后效率会迅速降低,在吸附过程中容易产生大量的难处理污泥,无法继续循环利用,限制了吸附技术在废水处理中的应用;膜分离技术很难适用于浓度较高的工业有机废水,并且膜块常存在污染、结垢、堵塞等弊端,需时常进行清洗或更换,增加了整体的运行成本. 电化学氧化-物理联合处理技术利用电化学氧化法对废水进行初步预处理,再用物理处理方法进一步的提高处理效率[32, 60, 63-64]. Liang等[65]结合BDD电催化氧化-纳滤陶瓷膜系统对废水中的抗生素磺胺甲嘧啶进行处理,电催化氧化过程中产生的大量的•OH和H2O2可实现有效的磺胺甲嘧啶去除,在高电流密度(30 mA·cm−2)和短电解时间(60 min)下发现磺胺甲嘧啶可完全消除;电化学氧化技术可显著提高COD的去除效率,但氨氮去除率并未提高,由于纳滤膜对于氨氮的有效排斥作用,可从渗透物中去除了大量的氨氮和一些其他离子,同时降低了电导率(小于9 μS·cm−1). 此外,纳滤膜表面可形成多孔、均匀、致密的生物污垢层,与控制条件下相比,提升了其长期运行(240 h)的渗透通量(25.1%),结果如图4所示[66].
-
单纯的电催化氧化过程产生的强氧化性物种往往比较单一,如羟基自由基、活性氯和活性硫等,从而导致有机化合物的降解,实现的电化学动力学速率较为缓慢;在过程中向体系用引入其他能源辅助手段,如O3、氧化试剂、紫外灯照射UV和超声波等是当前增强电催化氧化效率的最经常采用的手段[67-71]. 在一定的活化条件下,过硫酸盐能够在电场作用下产生出羟基自由基以及硫酸根自由基,理论上可以去除绝大部分的有机物[72]. Song等[33]研究了包含多壁碳纳米管、石墨、黑炭和颗粒活性炭在内的各种碳阳极电化学活化过二硫酸盐(PDS)以降解抗生素磺胺甲恶唑. 碳阳极的磺胺甲恶唑的降解在电化学活化PDS作用下表现出双重动力学:诱导阶段和快速衰减阶段. 碳阳极电化学活化PDS对磺胺甲恶唑的降解率提高了约15—35倍,是碳/PDS体系的30-130倍,同时,非自由基氧化、•OH和SO4•共同促成了磺胺甲恶唑的电化学降解. Ennouri等[67]研究了紫外光照射下BDD电极电化学氧化氯霉素(CHL)的组合高级氧化工艺,具体评估了主要工艺参数(电流密度、pH、温度和氯化物浓度)对CHL降解和矿化的影响,在BDD上进行3 h的紫外辅助阳极氧化可以使CHL完全降解并矿化,生成的氯化物可以光诱导形成自由基物质的前体进一步加速CHL氧化过程,在最佳条件下(300 mA·m–2、0.01 mol·L−1 NaCl、pH=10),CHL可在处理150 min后完全去除,180 min内CHL的矿化率达到了95%,所获得的结果表明,电化学-紫外照射可能代表了一种有前途的方法来处理含有CHL或其他持久性有机物的废水.
-
生物处理技术是利用微生物降解废水中的污染物作为自身的营养处理有机废水的方式,具有较大的发展空间[73]. 具体过程中,生物处理技术将复杂的大分子有机物经厌氧微生物代谢后经厌氧发酵氧化为小分子有机物,虽然该过程中COD去除效率不高,但可以使大量大分子有机物转化成更易处理的小分子有机物,提高有机废水的可生化性. 但对于被有机化合物污染的废水的处理,生物氧化虽然是最便宜的工艺,但有毒或生物难降解分子的存在可能会阻碍这种方法,因此提出生物氧化法与电化学的方法组合使用,能以更低廉高效的方法达到对水中污染物的处理[74-77]. Li等[78]构建了一种新型电化学膜生物膜反应器(EMBfR)用于去除磺胺嘧啶(SDZ),同时抑制抗生素抗性基因的增长. 结果表明,EMBfR可实现了94.9%的SDZ去除率,显著高于未施加电场的对照膜生物膜反应器(MBfR)(44.3%)或没有生物膜的电解反应器(77.3%). 此外,EMBfR中抗性基因的相对丰度仅为MBfR中的32.0%,表明EMBfR中抗性基因的产生受到明显抑制,具体的作用机制与电场存在下微生物群落结构的变化导致潜在的芳香降解微生物富集和电化学和生物过程之间的协同效应导致的SDZ在EMBfR中的独特降解途径,结果如图5所示.
-
Fenton 氧化法是一种传统有效的污水处理方法,其原理主要是Fe2+催化分解H2O2产生•OH. 由于Fenton氧化法降解效率高,操作简单,且加入的H2O2增加了溶液中的溶解氧,因此有着广泛的应用. 但是大量研究发现,Fenton氧化法处理有机污染物的限制在于溶液的pH体系[79-80]. 当溶液酸性较强时,Fe2+/Fe3+配合物的形态受到直接地影响,易生成大量铁泥沉淀,抑制•OH的生成,同时过程氧气的析出最终导致有机物的矿化效率[81],因此,反复酸碱环境调整是该过程必不可少的关键步骤.
一般来说,电催化氧化机理为阳极产生羟基自由基电化学矿化有机污染物,阴极部分主要进行为氢气析出反应. 当氧气注入到阴极表面后,可以存在以下反应:
碳毡、氧气扩散阴极、活性碳纤维或石墨阴极被用作常见的反应(14)的阴极材料. 当向溶液中引入Fe2+后,存在以下芬顿反产生强氧化性羟基自由基过程[82]:
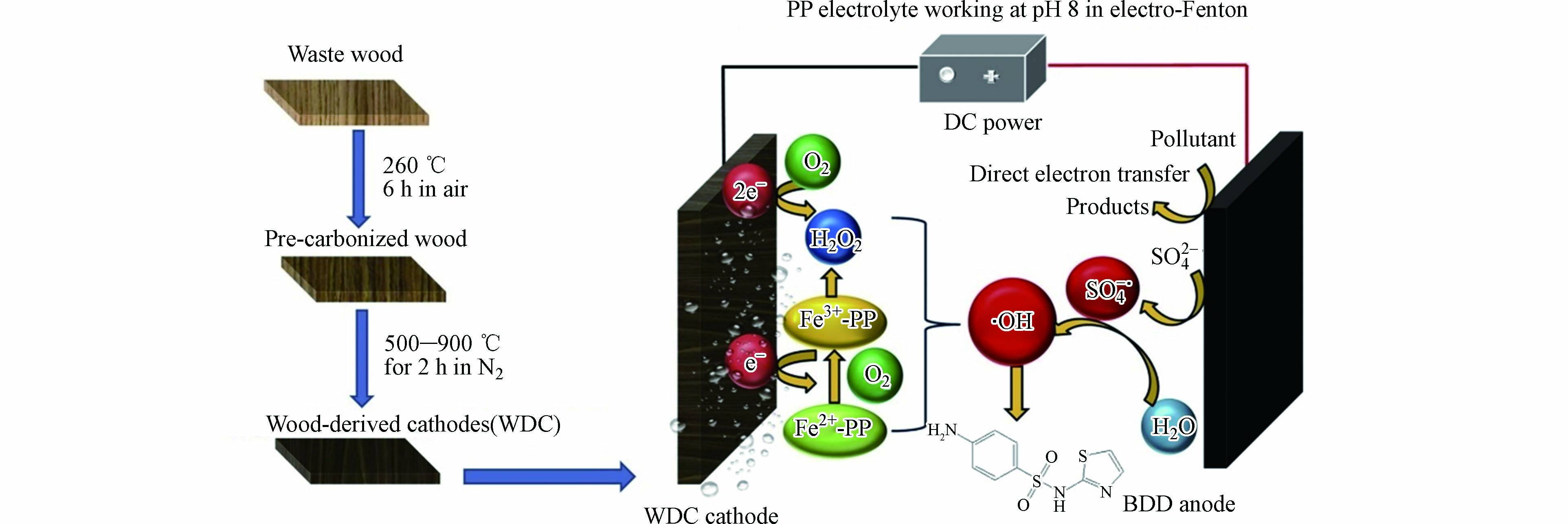
由此衍生出电-芬顿技术应用于电化学氧化水中有机污染物为增强电催化氧化过程提供了一种新的途径. 当采用氧气扩散阴极作为阴极材料时,阳极电化学氧化与阴极芬顿反应协同矿化有机污染,达到增强电催化氧化动力学的目的[83-86]. Deng等[87]利用回收的木材废料,通过简单一步热解制造制备生物质衍生的多孔碳阴极(WDC)材料,以BDD作为阳极,在焦磷酸盐(PP)电解质中对磺胺噻唑(STZ)电芬顿处理,通过对热解温度、施加电流和电解质等因素优化考察探索对于H2O2积累能力的影响规律. 结果表明,在900 °C下制备的 WDC阴极由于其较大的电活性表面积(28.81 cm2)而实现了最高的H2O2积累(3 h内为13.80 mg·L–1),与传统电解液相比,PP降低了溶液中H2O2的分解速率,导致H2O2积累量增加. 由于在溶液中形成Fe2+-PP配合物,PP允许在pH值为8时运行电芬顿反应,此外,Fe2+-PP能够激活氧产生•OH,通过这种方式,STZ的降解通过4个主要途径发生:1) 来自 Fe2+-PP 配合物的•OH自由基;2) 通过来电芬顿反应的•OH自由基,3) BDD的表面电产生的•OH自由基;4) BDD表面激活的SO4•-,以上强氧化性物质协同加速对有机物进行矿化作用,结果如图6所示.
除了以上的组合工艺以外,目前报道的组合工艺层出不穷,这里就不一一列举,但以上组合工艺的最后目的均是提升有机污染物的去除效率,扬长避短,发挥各自优势,因此,电化学氧化组合工艺在以后的研究和应用中将大有用途.
-
抗生素类药物是目前水环境中出现的一类新兴有机污染物,具有难自然降解、环境刺激性、生物毒性及耐药性等特点,如何高效去除水环境中抗生素类污染物是近年来环境工作者重点探讨的研究内容. 电催化氧化技术作为一种高效的水处理技术,在近年来的实践中被证明在处理抗生素类污染物方面是行之有效的,但也存在一些问题和挑战. (1) 作为整个氧化反应的反应场所,阳极材料直接关乎电催化氧化性能,但是目前能够被工程实用化的阳极材料依然有限,主要和电极寿命、成本和实用化等因素有关,因此,加大阳极材料的开发与改进,设计制备价格适合、电催化活性高、稳定性优良的电极材料依然是阳极材料开发和应用的重要内容;(2) 为了最大限度地发挥阳极材料的性能,有必要对降解过程中的关键操作参数进行探讨,如支持电解质、pH、有机物性质、反应器内部传质动力学等,有助于认识电催化氧化过程动力学,此外,建立物质降解过程动力学模型有利于反向指导阳极材料的定向设计;(3) 电催化氧化技术目前仍是以结果为导向为主的科学,具体涉及的电催化氧化机理在近年来有了一定的认识,如何通过先进的分析方法,如原位光谱技术等,认清电催化氧化机理是研究者进一步需要解决的问题,降解过程中可能产生的毒性更强的中间产物往往会对人类造成更大的危害,如何避免抗生素类污染物在降解过程中的生物的毒性是未来电催化氧化处理有机污染物需要深思的一个重要挑战;(4) 电催化氧化技术依然面临着高能耗的问题,从工业和实际应用来看,进一步开发电催化氧化法与其它方法联用技术降低过程能耗. 此外,可将电催化氧化技术与可再生能源结合(例如,风能,波能,太阳能和地热能能量)结合,充分利用可再生能源的能量输入解决当前的高能耗问题,这是未来电催化氧化技术的重要方向,也是目前科研工作者重点探讨的重要途径.
电催化氧化技术降解水中抗生素类污染物研究进展
Recent developments of electrochemical oxidation in degradation of emerging antibiotic pollutants
-
摘要: 医疗行业的快速发展和抗生素的滥用导致的水污染日益严重,水环境中残留的新兴抗生素类污染物已成为当今社会面临的最严峻挑战之一,将对人类健康带来极大危害. 电催化氧化技术作为水处理技术中的绿色环保技术,近年来在国内外受到众多环境保护工作者的关注,越来越多地被广泛地用于处理含新兴抗生素类有机污染物的水体. 本文首先阐述了电催化氧化技术对于有机污染物的电催化反应机理,重点介绍了电催化氧化技术降解水中抗生素类污染物采用的阳极材料的研究进展及发展状况,总结了阳极材料用于处理抗生素类污染物的降解效果及部分改性手段,此外,还对于当前电催化氧化联合技术处理水中抗生素类污染物的情况进行了系统的总结,最后对电催化高级氧化技术在未来抗生素类污染物的发展进行了展望.Abstract: The rapid development of the medical industry and the abuse of antibiotics have led to increasingly serious pollution of water body. Emerging antibiotic residues presented in the water environment have become one of the most severe challenges, which will bring great harm to human health. As a green environmental protective technology in wastewater treatment technologies, electrocatalytic oxidation technique has attracted extensively attentions from many environmental workers at home and abroad in recent years, which has been increasingly adopted to treat wastewater containing emerging antibiotics pollutants. The paper firstly expounds the electrocatalytic reaction mechanism of electrocatalytic oxidation technology for organic pollutants, and focuses on the research progress of anode materials employed in electrocatalytic oxidation technology for elimination of emerging antibiotics pollutants. In addition, the current situation of the combined electrocatalytic oxidation technologies to treat antibiotic pollutants are systematically summarized. Finally, the development of electrocatalytic advanced oxidation technology for elimination of emerging antibiotic pollutants in the future is prospected.
-

-
表 1 电催化氧化有机污染采用的阳极材料类型及特点
Table 1. Features and types of anode materials in electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants
电极材料
Types of anode materials析氧电位
Oxygen evolution potential电催化活性
Electrocatalytic activity特点
FeaturesRuO2-TiO2 1.4—1.7 V vs SHE 
使用贵金属,价格高,活性低 IrO2-Ta2O5 1.5—1.8 V vs SHE 使用贵金属,价格高,活性低 Pt 1.7—1.9 V vs SHE 贵金属,价格高,钝化膜生成 PbO2 1.8—2.0 V vs SHE 活性适中,成本低,离子溶出 SnO2-Sb2O5 1.9—2.2 V vs SHE 导电性差,催化活性适中 BDD 2.2—2.6 V vs SHE 催化活性高,大面积制备困难,成本高 亚氧化钛 ~2.6 V vs SHE 催化活性高,原料丰富,制作成本高 -
[1] dos SANTOS A J, KRONKA M S, FORTUNATO G V, et al. Recent advances in electrochemical water technologies for the treatment of antibiotics: A short review [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 26: 100674. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2020.100674 [2] 刘玉灿, 朱玉良, 纪现国, 等. 水中药物和个人护理品分析方法研究进展 [J]. 化学通报, 2022, 85(2): 228-234. LIU Y C, ZHU Y L, JI X G, et al. Research progress in determination methods of pharmaceutical and personal care products in water [J]. Chemistry, 2022, 85(2): 228-234(in Chinese).
[3] CHENG D L, NGO H H, GUO W S, et al. A critical review on antibiotics and hormones in swine wastewater: Water pollution problems and control approaches [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 387: 121682. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121682 [4] 曲有鹏, 吕江维, 冯玉杰, 等. 硼掺杂金刚石薄膜电极降解青霉素G钠废水机制 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2020, 52(6): 119-125. QU Y P, LU J W, FENG Y J et al. Degradation mechanism of penicillin G sodium wastewater at boron-doped diamond electrodes [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020, 52(6): 119-125(in Chinese).
[5] KOVALAKOVA P, CIZMAS L, MCDONALD T J, et al. Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 251: 126351. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126351 [6] 姜记威, 张诗轩, 曾文炉, 等. 生物炭基材料在抗生素废水处理中的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(S2): 389-401. JIANG J W, ZHANG S X, ZENG W L, et al. Research progress on biochar-based materials for the treatment of antibiotic wastewater[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(Sup 2): 389-401(in Chinese).
[7] OBEROI A S, JIA Y Y, ZHANG H Q, et al. Insights into the fate and removal of antibiotics in engineered biological treatment systems: A critical review [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(13): 7234-7264. [8] XIANG Y J, XU Z Y, WEI Y Y, et al. Carbon-based materials as adsorbent for antibiotics removal: Mechanisms and influencing factors [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 237: 128-138. [9] 李金城, 宋永辉, 汤洁莉. 电化学氧化法去除兰炭废水中COD和NH3-N [J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2): 697-705. LI J C, SONG Y H, TANG J L. Removing of COD and NH3-N from blue-coke wastewater by electrochemical oxidation [J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(2): 697-705(in Chinese).
[10] COMNINELLIS C. Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1994, 39(11/12): 1857-1862. [11] 王超, 姚淑美, 彭叶平, 等. 高级氧化法处理抗生素废水研究进展 [J]. 化工环保, 2018, 38(2): 135-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.02.002 WANG C, YAO S M, PENG Y P, et al. Research progresses on treatment of antibiotics wastewater by advanced oxidation process [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2018, 38(2): 135-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.02.002
[12] WANG J L, ZHUAN R. Degradation of antibiotics by advanced oxidation processes: An overview [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 701: 135023. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135023 [13] CHOUDHARY V, VELLINGIRI K, THAYYIL M I, et al. Removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions by electrocatalytic degradation [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2021, 8(5): 1133-1176. doi: 10.1039/D0EN01276A [14] MARTÍNEZ-HUITLE C A, PANIZZA M. Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2018, 11: 62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2018.07.010 [15] MARTÃNEZ-HUITLE C A, FERRO S. Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: Direct and indirect processes [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2006, 35(12): 1324-1340. doi: 10.1039/B517632H [16] QIAO J, XIONG Y Z. Electrochemical oxidation technology: A review of its application in high-efficiency treatment of wastewater containing persistent organic pollutants [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 44: 102308. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102308 [17] 王慧晴, 李燕, 司友斌, 等. 电催化氧化降解水体中抗生素磺胺 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(3): 779-787. WANG H Q, LI Y, SI Y B, et al. Electro-catalytic oxidative degradation of sulfonamide in water [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(3): 779-787(in Chinese).
[18] JIANG Y Y, ZHAO H T, LIANG J, et al. Anodic oxidation for the degradation of organic pollutants: Anode materials, operating conditions and mechanisms. A mini review [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2021, 123: 106912. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2020.106912 [19] HE Y P, LIN H B, GUO Z C, et al. Recent developments and advances in boron-doped diamond electrodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 212: 802-821. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.11.056 [20] SHESTAKOVA M, SILLANPÄÄ M. Electrode materials used for electrochemical oxidation of organic compounds in wastewater [J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2017, 16(2): 223-238. doi: 10.1007/s11157-017-9426-1 [21] HU Z Z, CAI J J, SONG G, et al. Anodic oxidation of organic pollutants: Anode fabrication, process hybrid and environmental applications [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 26: 100659. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2020.100659 [22] WANG J L, WANG S Z. Reactive species in advanced oxidation processes: Formation, identification and reaction mechanism [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 401: 126158. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126158 [23] SRIVASTAVA V, SURESH KUMAR M, NIDHEESH P V, et al. Electro catalytic generation of reactive species at diamond electrodes and applications in microbial inactivation [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 30: 100849. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100849 [24] SANTOS G O S, EGUILUZ K I B, SALAZAR-BANDA G R, et al. Understanding the electrolytic generation of sulfate and chlorine oxidative species with different boron-doped diamond anodes [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 857: 113756. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113756 [25] DIVYAPRIYA G, NIDHEESH P V. Electrochemically generated sulfate radicals by boron doped diamond and its environmental applications [J]. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2021, 25(3): 100921. doi: 10.1016/j.cossms.2021.100921 [26] de FREITAS ARAÚJO K C, da SILVA D R, dos SANTOS E V, et al. Investigation of persulfate production on BDD anode by understanding the impact of water concentration [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2020, 860: 113927. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.113927 [27] SHIN Y U, YOO H Y, AHN Y Y, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of organics in sulfate solutions on boron-doped diamond electrode: Multiple pathways for sulfate radical generation [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 254: 156-165. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.04.060 [28] 赵媛媛, 王德军, 赵朝成. 电催化氧化处理难降解废水用电极材料的研究进展 [J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(7): 1125-1132. ZHAO Y Y, WANG D J, ZHAO C C. Progress in electrode materials for refractory wastewater treatment by electro-catalytic oxidation [J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(7): 1125-1132(in Chinese).
[29] 李晓良, 王雪, 邱晓鹏, 等. 高活性阳极制备及阿莫西林降解中的毒性效应 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(2): 727-734. LI X L, WANG X, QIU X P, et al. Preparation of high active anode and its toxicity in amoxicillin degradation [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(2): 727-734(in Chinese).
[30] BRITO L R D, GANIYU S O, dos SANTOS E V, et al. Removal of antibiotic rifampicin from aqueous media by advanced electrochemical oxidation: Role of electrode materials, electrolytes and real water matrices [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 396: 139254. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139254 [31] BRILLAS E, GARCIA-SEGURA S, SKOUMAL M, et al. Electrochemical incineration of diclofenac in neutral aqueous medium by anodic oxidation using Pt and boron-doped diamond anodes [J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 79(6): 605-612. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.03.004 [32] TAN T Y, ZENG Z T, ZENG G M, et al. Electrochemically enhanced simultaneous degradation of sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin and amoxicillin from aqueous solution by multi-walled carbon nanotube filter [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 235: 116167. [33] SONG H R, YAN L X, JIANG J, et al. Enhanced degradation of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole by electrochemical activation of PDS using carbon anodes [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 344: 12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.050 [34] ZHANG Y Y, WANG A M, REN S Y, et al. Effect of surface properties of activated carbon fiber cathode on mineralization of antibiotic cefalexin by electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton treatments: Mineralization, kinetics and oxidation products [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 221: 423-432. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.016 [35] ORMENO-CANO N, RADJENOVIC J. Electrochemical degradation of antibiotics using flow-through graphene sponge electrodes [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 431: 128462. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128462 [36] SHI H M, GAO M, XU Z C, et al. Long-term performance of granular activated carbon electrode system for the removal of amoxicillin [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 46: 102397. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102397 [37] 程佳鑫, 李荣兴, 杨海涛, 等. 三维电催化氧化处理难生化降解有机废水研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(1): 288-304. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020082804 CHENG J X, LI R X, YANG H T, et al. Review of three-dimensional electrodes for bio-refractory organic wastewater treatment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(1): 288-304(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020082804
[38] 石秋俊, 刘安迪, 唐柏彬, 等. Ni掺杂Sb-SnO2瓷环粒子电极电催化氧化磺胺嘧啶 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(4): 1725-1733. SHI Q J, LIU A D, TANG B B, et al. Electrocatalytic oxidation of sulfadiazine with Ni-doped Sb-SnO2 ceramic ring particle electrode [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(4): 1725-1733(in Chinese).
[39] JIN H C, ZHANG X J, YU Y, et al. High-performance Ti/IrO2-RhOx-TiO2/α-PbO2/β-PbO2 electrodes for scale inhibitors degradation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 435: 135167. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135167 [40] DONG H, CHI W Q, GAO A, et al. Electrochemical degradation of tetracycline using a Ti/Ta2O5-IrO2 anode: Performance, kinetics, and degradation mechanism [J]. Materials, 2021, 14(15): 4325. doi: 10.3390/ma14154325 [41] POINTER MALPASS G R, de JESUS MOTHEO A. Recent advances on the use of active anodes in environmental electrochemistry [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 27: 100689. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100689 [42] FENG J Q, TAO Q B, LAN H, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of sulfamethoxazole by nitrogen-doped carbon nanosheets composite PbO 2 electrode: Kinetics and mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 286(Pt 2): 131610. [43] YANG C, FAN Y A, SHANG S S, et al. Fabrication of a permeable SnO2-Sb reactive anodic filter for high-efficiency electrochemical oxidation of antibiotics in wastewater [J]. Environment International, 2021, 157: 106827. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106827 [44] WANG Q, TU S Q, WANG W Y, et al. Optimized Indium modified Ti/PbO2 anode for electrochemical degradation of antibiotic cefalexin in aqueous solutions [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 628: 127244. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127244 [45] 李晓良, 路思佳, 郑兴, 等. 活性碳纤维修饰PbO2电极的制备及其对阿莫西林的降解解毒研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(10): 3985-3992. LI X L, LU S J, ZHENG X, et al. Fabrication of PbO2 electrode modified by activated carbon fiber and its degradation and detoxification of amoxicillin [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(10): 3985-3992(in Chinese).
[46] 岳文清, 倪月, 孙则朋, 等. 改性钛基PbO2电极对有机污染物的降解性能: 以甲基橙和4-硝基苯酚为例 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2): 706-716. YUE W Q, NI Y, SUN Z P, et al. Degradation of organic pollutants by modified titanium based PbO2 electrode: Taking methyl orange and 4-nitrophenol as examples [J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(2): 706-716(in Chinese).
[47] XIA Y J, YAN Y, HU L B, et al. Enhanced mechanism of electrochemical oxidation of antibiotic norfloxacin using a Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3/α, β-Co-PbO2 electrode [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(10): 106510. doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ac2927 [48] DAVIDE C, MARCO P. Application of boron-doped diamond electrodes for electrochemical oxidation of real wastewaters [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 30: 100844. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100844 [49] NIDHEESH D P V, DIVYAPRIYA D G, OTURAN D N, et al. Environmental applications of boron-doped diamond electrodes: 1. applications in water and wastewater treatment [J]. ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6(8): 2124-2142. doi: 10.1002/celc.201801876 [50] HE Y P, ZHAO D D, LIN H B, et al. Design of diamond anodes in electrochemical degradation of organic pollutants [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2022, 32: 100878. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100878 [51] dos SANTOS A J, FORTUNATO G V, KRONKA M S, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of ciprofloxacin in different aqueous matrices using synthesized boron-doped micro and nano-diamond anodes [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 204: 112027. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112027 [52] YANG W L, TAN J L, CHEN Y H, et al. Relationship between substrate type and BDD electrode structure, performance and antibiotic tetracycline mineralization [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 890: 161760. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161760 [53] SCIALDONE O, GALIA A, SABATINO S. Abatement of Acid Orange 7 in macro and micro reactors. Effect of the electrocatalytic route [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 148/149: 473-483. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.11.005 [54] SEIBERT D, ZORZO C F, BORBA F H, et al. Occurrence, statutory guideline values and removal of contaminants of emerging concern by Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 748: 141527. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141527 [55] GENG P, SU J Y, MILES C, et al. Highly-ordered magnéli Ti4O7 nanotube arrays as effective anodic material for electro-oxidation [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 153: 316-324. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.178 [56] HUANG D H, WANG K X, NIU J F, et al. Amorphous Pd-loaded Ti4O7 electrode for direct anodic destruction of perfluorooctanoic acid [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(17): 10954-10963. [57] LIU S Q, WANG Y, ZHOU X Z, et al. Improved degradation of the aqueous flutriafol using a nanostructure macroporous PbO2 as reactive electrochemical membrane [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 253: 357-367. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.09.055 [58] MONTEIL H, PECHAUD Y, OTURAN N, et al. Pilot scale continuous reactor for water treatment by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: Development of a new hydrodynamic/reactive combined model [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 404: 127048. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127048 [59] ZENG W C, LIANG H, ZHANG H, et al. Efficient electrochemical oxidation of sulfamethoxazole by a novel reduced TiO2 nanotube arrays-based flow-through electrocatalytic membrane [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 289: 120720. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120720 [60] GANESAN S, AMIRTHALINGAM M, ARIVALAGAN P, et al. Absolute removal of ciprofloxacin and its degraded byproducts in aqueous solution using an efficient electrochemical oxidation process coupled with adsorption treatment technique [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 245: 409-417. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.092 [61] 张腾云, 范洪波, 廖世军. 联合电催化氧化处理难降解有机废水研究进展 [J]. 工业水处理, 2009, 29(6): 1-4. ZHANG T Y, FAN H B, LIAO S J. Research progress in the combined electro-catalytic oxidation technologies for treating refractory organic wastewater [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2009, 29(6): 1-4(in Chinese).
[62] 蒋宗宏, 陈淼, 李心清, 等. 改性生物炭对水体中抗生素的去除研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(12): 3846-3860. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020080202 JIANG Z H, CHEN M, LI X Q, et al. Research progress on the removal of antibiotics in water by modified biochar [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(12): 3846-3860(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020080202
[63] WANG X Y, LI F X, HU X M, et al. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes coupled with membrane filtration for degrading antibiotic residues: A review on its potential applications, advances, and challenges [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 784: 146912. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146912 [64] DU X, YANG W P, ZHAO J, et al. Peroxymonosulfate-assisted electrolytic oxidation/coagulation combined with ceramic ultrafiltration for surface water treatment: Membrane fouling and sulfamethazine degradation [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 235: 779-788. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.035 [65] SONG Y, XIAO M Y, LI Z Y, et al. Degradation of antibiotics, organic matters and ammonia during secondary wastewater treatment using boron-doped diamond electro-oxidation combined with ceramic ultrafiltration [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 286: 131680. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131680 [66] DU X, MO Z Y, LI Z Y, et al. Boron-doped diamond (BDD) electro-oxidation coupled with nanofiltration for secondary wastewater treatment: Antibiotics degradation and biofouling [J]. Environment International, 2021, 146: 106291. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106291 [67] RAWDHA E, ROBERTO L, ANTONIO Z, et al. Degradation of chloramphenicol in water by oxidation on a boron-doped diamond electrode under UV irradiation [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 41: 101995. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.101995 [68] GUO H, LI D S, LI Z, et al. Promoted elimination of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole in water using sodium percarbonate activated by ozone: Mechanism, degradation pathway and toxicity assessment [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 266: 118543. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118543 [69] PATIDAR R, SRIVASTAVA V C. Mechanistic insight into ultrasound-induced enhancement of electrochemical oxidation of ofloxacin: Multi-response optimization and cost analysis [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 257: 127121. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127121 [70] HASSANI A, MALHOTRA M, KARIM A V, et al. Recent progress on ultrasound-assisted electrochemical processes: A review on mechanism, reactor strategies, and applications for wastewater treatment [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 205: 112463. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112463 [71] 刘晨, 梁吉艳, 孟静, 等. 光助电催化氧化降解水体中甲硝唑的实验研究 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2020, 46(5): 93-98. LIU C, LIANG J Y, MENG J, et al. Experimental study on degradation of metronidazole in water by photoassisted electrocatalytic oxidation [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2020, 46(5): 93-98(in Chinese).
[72] YU S, ZHANG R R, DANG Y, et al. Electrochemical activation of peroxymonosulfate at Ti/La2O3-PbO2 anode to enhance the degradation of typical antibiotic wastewater [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 294: 121164. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121164 [73] CHEN M, XU J, DAI R B, et al. Development of a moving-bed electrochemical membrane bioreactor to enhance removal of low-concentration antibiotic from wastewater [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 293: 122022. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122022 [74] MOUSSET E, TRELLU C, OLVERA-VARGAS H, et al. Electrochemical technologies coupled with biological treatments [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 26: 100668. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2020.100668 [75] CHENG D L, NGO H H, GUO W S, et al. Removal process of antibiotics during anaerobic treatment of swine wastewater [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 300: 122707. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122707 [76] GANZENKO O, HUGUENOT D, van HULLEBUSCH E D, et al. Electrochemical advanced oxidation and biological processes for wastewater treatment: A review of the combined approaches [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(14): 8493-8524. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-2770-6 [77] 曲有鹏, 吕江维, 董跃, 等. 电催化-生物电化学耦合系统处理青霉素废水的机制 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(5): 2378-2384. QU Y P, LÜ J W, DONG Y, et al. Mechanisms of penicillin wastewater treatment by coupled electrocatalytic and bioelectrochemical systems [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(5): 2378-2384(in Chinese).
[78] LI Z Y, DAI R B, YANG B C, et al. An electrochemical membrane biofilm reactor for removing sulfonamides from wastewater and suppressing antibiotic resistance development: Performance and mechanisms [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 404: 124198. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124198 [79] ZHANG Y, ZHOU M H. A critical review of the application of chelating agents to enable Fenton and Fenton-like reactions at high pH values [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 362: 436-450. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.035 [80] SIRÉS I, BRILLAS E. Upgrading and expanding the electro-Fenton and related processes [J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 27: 100686. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2020.100686 [81] BRILLAS E, GARCIA-SEGURA S. Benchmarking recent advances and innovative technology approaches of Fenton, photo-Fenton, electro-Fenton, and related processes: A review on the relevance of phenol as model molecule [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 237: 116337. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116337 [82] EL-GHENYMY A, GARRIDO J A, CENTELLAS F, et al. Electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton degradation of sulfanilic acid using a boron-doped diamond anode and an air diffusion cathode [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2012, 116(13): 3404-3412. doi: 10.1021/jp300442y [83] ZAZOU H, OTURAN N, SÖNMEZ-ÇELEBI M, et al. Mineralization of chlorobenzene in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton processes using Pt or BDD anode and carbon felt cathode [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 774: 22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.04.051 [84] OZCAN A, ÖZCAN A, DEMIRCI Y. Evaluation of mineralization kinetics and pathway of norfloxacin removal from water by electro-Fenton treatment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 304: 518-526. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.105 [85] WANG A M, ZHANG Y Y, HAN S S, et al. Electro-Fenton oxidation of a β-lactam antibiotic cefoperazone: Mineralization, biodegradability and degradation mechanism [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 270: 129486. [86] AHMAD D, IGNASI S, NIHAL O, et al. Electrochemical treatment of the antibiotic sulfachloropyridazine: Kinetics, reaction pathways, and toxicity evolution [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(7): 4074-4082. [87] DENG F X, OLVERA-VARGAS H, GARCIA-RODRIGUEZ O, et al. Waste-wood-derived biochar cathode and its application in electro-Fenton for sulfathiazole treatment at alkaline pH with pyrophosphate electrolyte [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 377: 249-258. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.077 -



 下载:
下载: