-
环境中天然钚(Pu)同位素和137Cs放射性核素的浓度很低,大部分是通过核武器试验、核事故和核燃料后处理释放到环境中[1]. 自全球沉降或其它来源进入水环境后,Pu同位素和137Cs会被水体中的颗粒物吸附而蓄积于沉积物中,其垂直分布可完好保存于沉积序列中,沉积序列中的放射性核素活度反映了各层在沉积时的大气沉降量或其它来源的输入通量,使得沉积物的钚同位素和137Cs的垂直分布与大气沉降或重大环境变化事件密切相关,由此Pu同位素和137Cs在沉积物中的峰值及其它特异值可作为时标定年[2-5]. 同时,137Cs和239+240Pu在沉积物中的浓度和垂直分布特征,除广泛用于定年及评估海洋沉积物的沉积速率外,还可用于考察和评价它们在不同环境条件下和不同时期的迁移行为. 因此,在环境变化过程研究中,人为放射性核素137Cs和239+240Pu除了作为污染事件历史重建的良好指标外,还可以作为了解沉积物混合、水柱中的颗粒清除、水流路径评估等海洋过程的示踪剂[6].
此外,不同来源或事件的Pu同位素具有独特的原子比(如240Pu/239Pu和238Pu/239+240Pu) ,这对放射性污染来源的判断具有重要的参考价值. 例如:大气核试验的240Pu/239Pu原子比为0.18左右[7],武器级240Pu/239Pu原子比较低,在0.01—0.07之间[8],太平洋马绍尔群岛美国核试验基地的核试验(pacific proving grounds, PPG)为0.306—0.36[4]. 因此,根据样品中240Pu/239Pu比值,再结合沉积物中不同深度的Pu同位素活度可大致判断Pu的可能来源. 另外,由于Pu同位素与颗粒物结合能力较137Cs强[1],且239Pu(半衰期为2.41×104 a)和240Pu(半衰期为6.65×103 a)的半衰期也相对较长[9],因此在颗粒较少,并存在生物活动干扰的海洋长时间尺度(如超过百年或千年)的沉积事件研究中,Pu同位素具有补充和替代137Cs作为示踪剂的潜力,加上近年来Pu测定技术水平的提高,使得Pu同位在海洋环境过程的示踪研究中发挥着越来越重要的作用.
海洋中的颗粒物不仅有自生颗粒,还有来自河口径流输入的陆源物质. 在沉积过程中,颗粒物的沉积过程和沉积速率还会受到人为活动、生物扰动及洋流活动的影响,因此沉积物是记录沉积演化信息的档案库[10]. 南沙海域作为半封闭海域,受到黑潮和南海暖流影响,陆海相互作用强烈,是重要的沉积作用区,目前国内对南沙海域的研究主要是围绕表层沉积物展开[11-13]. 因此沉积物岩心的研究数据较为匮乏,这导致了该海域的历史演化数据很难被系统描述,同时,放射性核素污染的可能来源也没有相关数据,如PPG来源的钚是否流入南海,福岛核事故的排放是否污染到南海,这都需要利用相关核素来进行示踪研究. 本文分别测定南沙海域的6个沉积物岩芯不同层段137Cs和239+240Pu的含量,阐明它们随深度变化的特征,通过特征峰所在岩芯深度估算出沉积速率,并与Deng(2021)[14]在南沙海域同一批样品由210Pbex测年法获得的沉积速率对比,探讨整个岩芯形成过程中,环境发生的重要事件,为南沙海域的颗粒物沉积过程的研究、放射性污染的可能来源及环境评价提供参考依据.
-
研究区域采样站位如图1所示. 南沙海域(3°35′—11°55′N,109°30′—117°50′E),东西长约905 km,南北宽约887 km. 其西北与越南相对,东北与菲律宾隔海相望,南部与马来西亚、文莱、印度尼西亚等国沿海相接. 南沙海域呈热带海洋性季风气候,年平均气温超过27 ℃. 南沙海域自南向北由南部大陆架、陆坡和深海盆地组成,形成阶梯式的三级地形[15].
本次实验在南沙海域取样6个岩芯,表1给出了每个取样岩芯的详细信息,沉积物类型主要表现为软泥和粉砂质泥. 根据吴时国等[16]的研究表明,陆坡区域(NS-1、NS-3)的沉积物属于半深海-深海钙质生物碎屑-陆源碎屑沉积,陆架区域(NS-2、NS-4、NS-5、NS-6)的沉积物属于大陆架现代陆源碎屑沉积与陆架残留沉积.
-
2014年5月在南沙海域采用箱式取样器采集了6个沉积物岩芯,岩芯长度在21—35 cm之间,按间隔5 cm左右对每个样品进行切分,用塑料袋封装,然后立即冷冻保存. 带回实验室后,部分样品进行粒度和组成分析,其他样品干燥研磨后,进行137Cs和Pu的分析. 137Cs是使用HPGe γ谱仪(型号:GEM30P4-70,ORTEC,USA)测定其 661.6 keV能量峰,探测效率由实验室无源校准软件 (LabSOCS) 进行校准. Pu同位素的测量参考Zheng and Yamada [17],简要来说,取2—3 g沉积物样品在110—500 ℃的温度下干燥4 h以上,使样品灰化,随后往样品中加入242Pu示踪剂,在电热板上180 ℃条件下用20 mL浓硝酸浸取样品3 h,然后用8 mol·L−1 HNO3溶解样品,煮沸样品3 h后过滤,将滤液蒸发至浆糊状物质出现,用浓硝酸溶解,调节酸度至 8 mol·L−1. 随后加入NaNO2,并在40 ℃的水浴中加热30 min,将Pu的价态调整为Pu4+. 加载到色谱柱(AG 1-X8)上并用60 mL 8 mol·L−1 HNO3洗涤以去除U、Am和Pb、Hg等阳离子基质. 然后用50 mL 10 mol·L−1 HCl洗涤柱子除去Th,用50 mL 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4I-8.5 mol·L−1 HCl洗脱Pu,加入1 mL浓HCl并将洗脱溶液蒸发至干. 加入1 mL 4%HNO3溶解,溶液在柱(AG MP-1M)上洗涤,然后柱子继续用20 mL 8 mol·L−1 HNO3和10 mL 10 mol·L−1 HCl洗涤,溶液中的Pu用16 mL HBr洗脱. 之后,将1 mL浓HNO3添加到溶液中并蒸发至干. 最后使用ICP-MS(Element 2, Thermo Scientific, Bremen, Germany)进行分析.
-
南沙海域6个岩芯采样点的 239+240Pu、137Cs 的活度和240Pu/239Pu的比值如表2所示. 由于沉积物在沉积过程中,会受到压实效应的影响,放射性核素的深度分布特征及计算的沉积速率会有所变化. 表2的校正深度是引用Deng等[14]的同一采样点的数据,在考虑压实效应后,引起的沉积物的密度差异,并进行归一化处理后得到的数据[15].
-
由表2可以看出,6个岩芯中,239+240Pu的活度变化范围为(0.256±0.019)—(0.752±0.078) Bq·kg−1,沉积通量的变化范围为(0.5467±0.052)—(4.377±0.454)Bq·m−2. 其活度最高((0.752±0.078) Bq·kg−1)在NS-2,最低((0.256±0.019) Bq·kg−1)在NS-1. 在NS-2岩芯,239+240Pu的高活度可能是由于该站位距离加里曼丹岛较近,陆源物质的输入和人类活动的干扰所致. 而NS-1出现239+240Pu活度较小,主要原因可能是是采样点水深较大(约1335 m),海水中的颗粒物较少,同时,颗粒物在沉降过程中,沉降时间长,矿化作用明显,因此,Pu同位素较难沉积.
6个岩芯沉积物中, 239+240Pu的活度变化范围类似于南海大陆架北部((0.157±0.005)—(0.776±0.010) Bq·kg−1)[18],小于近岸的南海北部((0.296±0.015)—(1.822±0.206 )Bq·kg−1)[19],大于离岸较远、水深较大的南海盆地(0.002—0.157 Bq·kg−1)[20]. 这种活度大小随离岸距离及水深深度变化的趋势,除受到颗粒沉积动力学过程的影响外,还可能受到南海暖流在冬季沿大陆架向东北方向流动的影响(图1),南海暖流将海南岛的沉积物输送到南海,导致239+240Pu活度在近岸的南海北部较高,大陆架次之,盆地较小[15, 18, 21]. 此外,在水深较浅处,沿岸洋流的下涌和上涌容易在浅层形成泥区,并容易在细颗粒中吸附更多的Pu,增大活度[22].
-
6个沉积岩芯中,137Cs活度的变化范围为(0.758±0.078)—(1.687±0.145)Bq·kg−1,沉积通量的变化范围为(9.203±1.084)—(27.362±2.483)Bq·m−2. 比较6个岩芯后发现,137Cs活度最低值和最高值都在岩芯NS-2,分别为(0.758±0.078) Bq·kg−1和(1.687±0.145) Bq·kg−1,137Cs沉积通量的最高在岩芯NS-2, 为(27.362±2.483) Bq·m−2. 这与岩芯NS-2距离加里曼丹岛较近,陆源物质输入和人类活动干扰的阶段性和突发性有关.
-
240Pu/239Pu原子比随沉积物深度的变化,可以为沉积物测年和沉积物来源的评估提供额外的信息[23]. 该研究区域岩芯沉积物的240Pu/239Pu原子比的变化范围为(0.184±0.020)—(0.201±0.028),平均为0.193±0.025,略高于全球沉降的平均值(0.178±0.019). 表明除了全球沉降外,沉积物中239+240Pu活度和240Pu/239Pu原子比因有其它来源,产生了混合效应,导致增加[24]. 结合水流方向,分析该海域钚的可能来源后,发现尽管 PPG 离南沙海域很远,但PPG中的Pu仍有可能通过洋流输送而沉积到南沙海域[25],具体贡献的比例可以通过两端元法等模型进行计算.
-
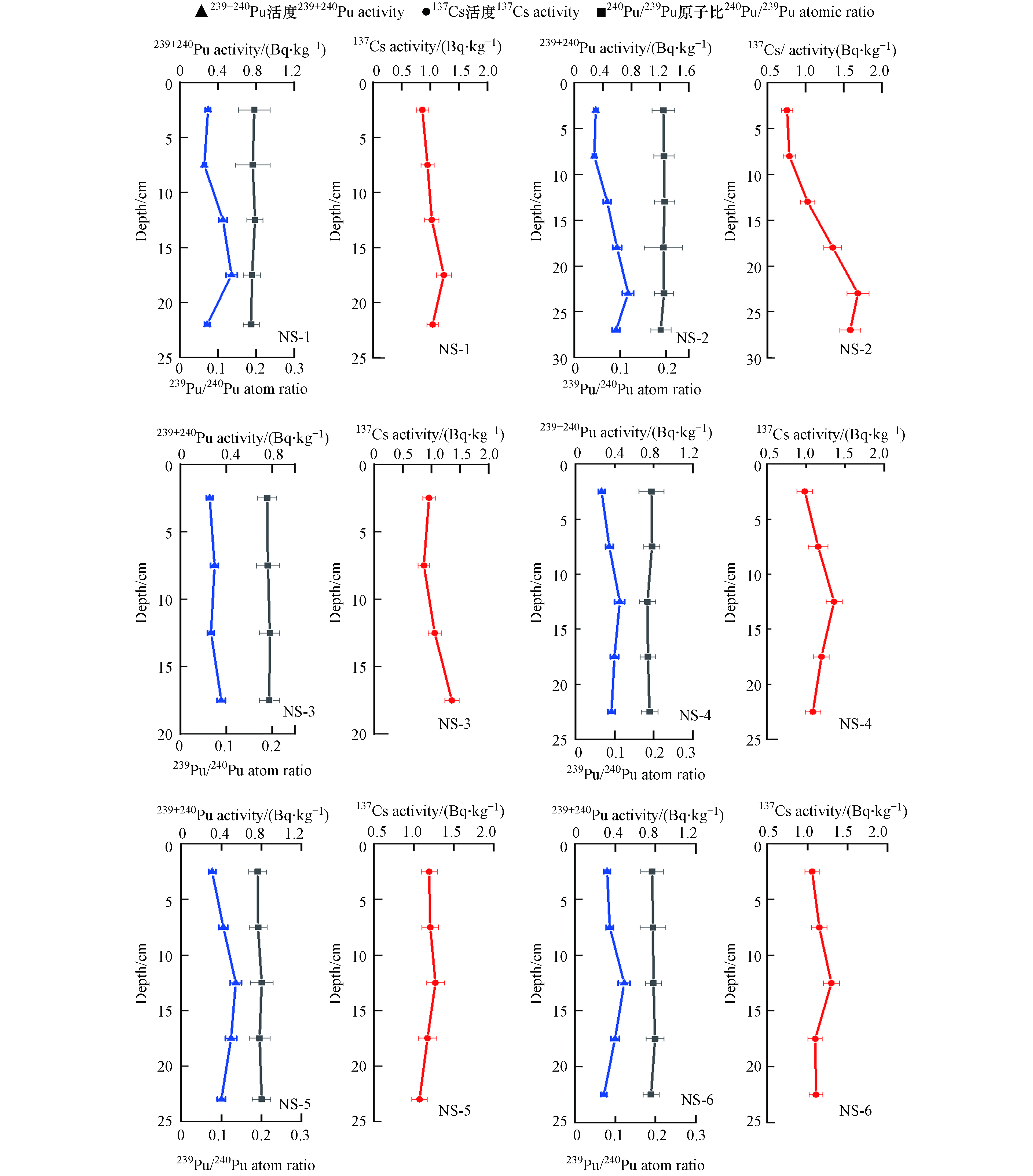
239+240Pu、137Cs等核素的活度随深度的变化反映了这些人工放射性核素的输入和沉积历史[26]. 南沙海域岩芯沉积物样品的239+240Pu、137Cs 的活度和240Pu/239Pu原子比的垂直剖面如图2所示.
图2可以看出, ①除NS-3外,其它5个岩芯239+240Pu和137Cs 活度的蓄积峰都为典型单峰,在垂直分布中有明显的239 + 240Pu和137Cs 的最大峰值,再结合图2各岩芯蓄积峰的240Pu/239Pu原子比,显示出对应于1964年最大沉积量的单峰[23, 27]. ②岩芯NS-3的239+240Pu和137Cs的垂直分布无明显规律,可能是由于岩芯NS-3沉积物采样深度不够,同时样品分样间隔(约5 cm)较大,导致该岩芯239+240Pu和137Cs的垂直分布中蓄积峰不明显;再加上该岩芯处的水深较大,约1537 m,位于深海海底,海洋自生颗粒物在沉积物的来源中占主导地位,而239+240Pu和137Cs随大气沉降进入海水后,绝大部分会停留在海水中,仅非常小的比例能沉降至深海沉积物中,因此沉积物中放射性核素239+240Pu和137Cs无法表现出全球沉降的峰值[5, 10]. ③6个岩芯的240Pu/239Pu原子比值在沉积物岩芯的不同层段基本一致,并且与全球沉降物240Pu/239Pu原子比值(0.18)基本吻合,这表明南沙海域这些沉积物样品中的Pu主要来自于全球沉降,也从侧面证明了可以用最大沉积量的单峰(对应1964年)来计算沉积速率,判断沉积的年代.
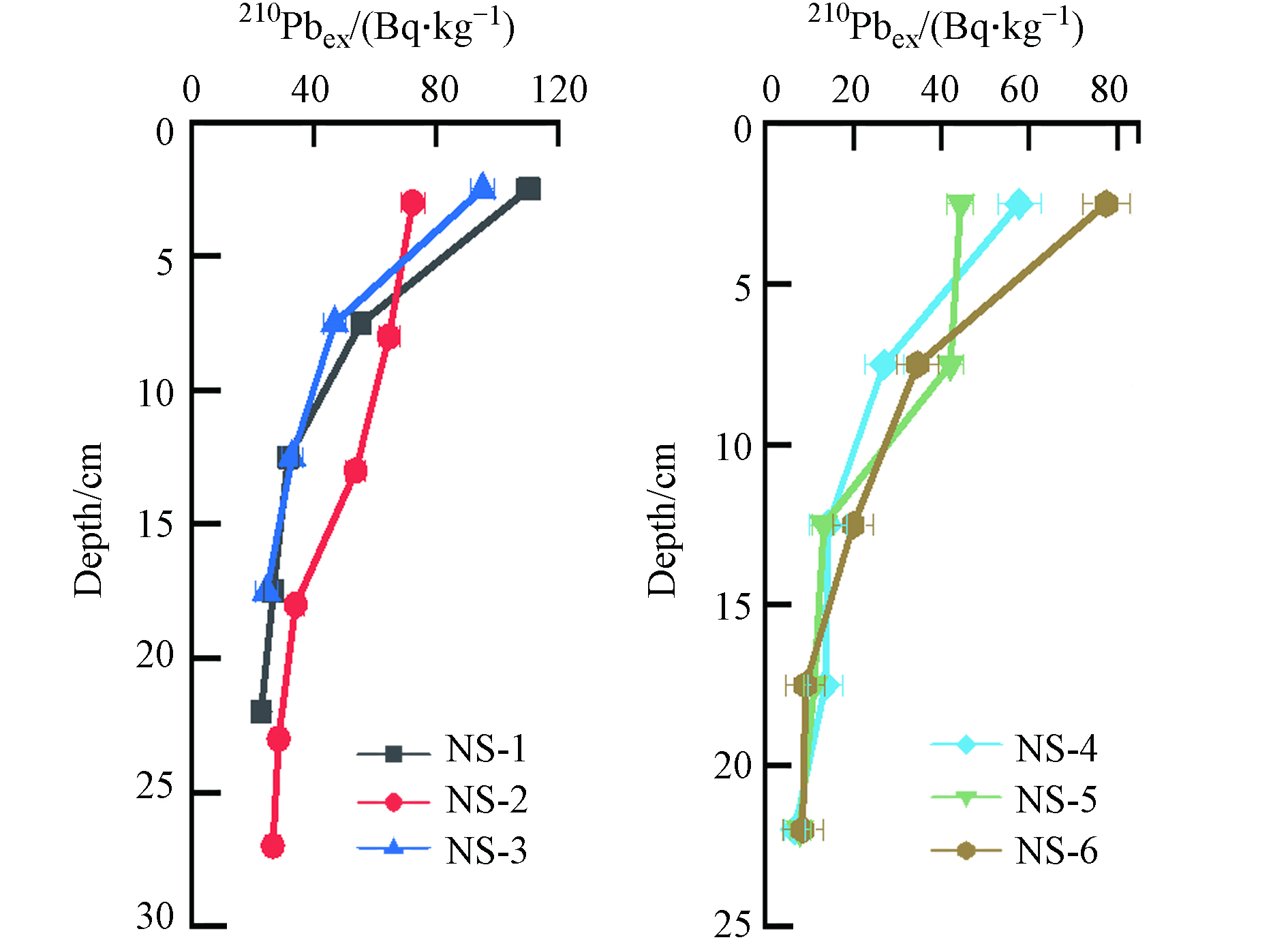
Deng等 [14]在南沙海域同一批样品测得210Pbex活度的垂直剖面分布特征如图3所示. 可以看出,虽然6个岩芯的210Pbex活度大小有一定的差异(其中,NS-1、NS-3较大,其他站位较小),但均呈现出明显的指数衰减趋势,由此可以计算出它们的沉积速率.
-
沉积速率的变化是综合评价区域环境变化的重要指标,放射性核素测年法因计算定量化、精确化和多核素相互印证而得到了快速发展[28-30]. 137Cs法和239+240Pu法通常可以用1963年的峰值和1986年的峰值来确定沉积物中不同深度的年代,计算出平均沉积速率R(cm·a−1)[10, 18-20].
具体计算公式如下,
式中,H为蓄积峰位置的深度(cm),Tc为采样日期(a),Tm为峰值时间(a).
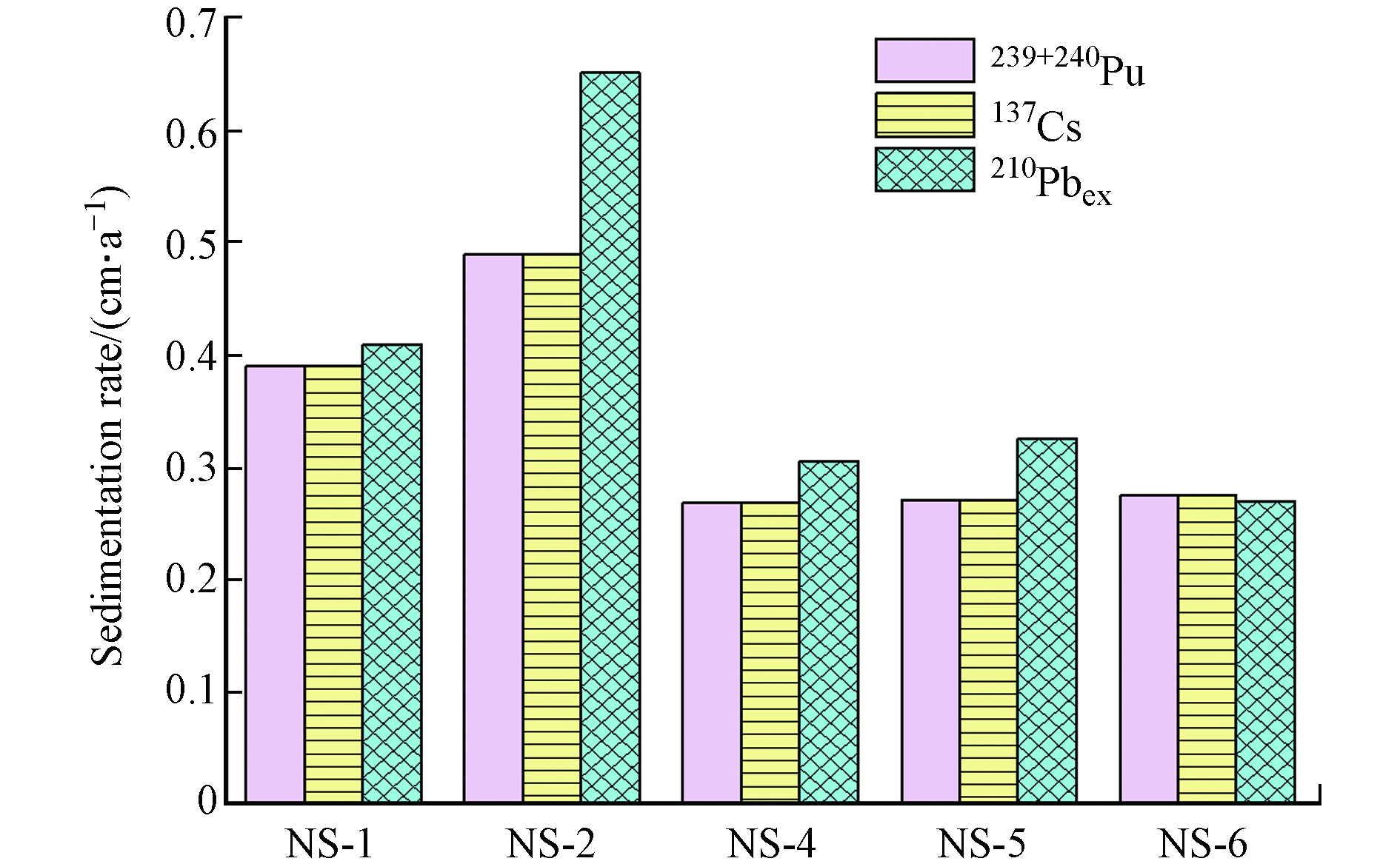
由于NS-3未出现明显的蓄积峰,所以只对剩下5个岩芯进行计算. 结果表明,NS-1—NS-6(NS-3除外)岩芯的平均沉积速率分别为0.390、0.490、0.269、0.271、0.275 cm·a−1. Deng等[14]在南沙海域同一批样品通过210Pbex法计算的NS-1—NS-6岩心的沉积速率分别为 0.385、0.652、0.306、0.326、0.270 cm·a−1 .
图4给出了这5个岩芯的137Cs、239+240Pu法和210Pbex法计算的沉积速率,可以看出,①239+240Pu法得出的沉积速率与137Cs法所得结果基本一致,并与Deng等[14]用210Pbex法计算出的沉积速率基本相符,说明沉积物混合和外界扰动等影响在这5个岩芯影响不大. ②比较这5个岩芯,3种方法所获得NS-2的沉积速率均大于其他4个岩芯,表明,NS-2岩芯由于离岸较近,通过陆地径流或者区域内的海岸侵蚀而输入了较多的颗粒物,这些颗粒物粒级较大,沉降较快. ③对比同一站位不同测定方法的结果发现,除NS-2站位外,3种方法所得结果基本一致,但用210Pbex法测岩芯NS-2的沉积速率远大于其他两种方法的沉积速率,表明在NS-2站位,陆源输入、沉积物混合作用等明显影响了210Pbex法的测定结果,在某些扰动较大的沉积环境中,137Cs 和239+240Pu 法更有优势 (210Pbex定年法的原理是依赖于对每层沉积物210Pb和226Ra的准确测定,计算结果的准确性通常会更易受外界干扰的影响,而137Cs和239+240Pu时标法属于脉冲输入,受沉积物扰动影响较小)[30].
-
中国海域的Pu主要来自1945年以来大气核试验的全球沉降和PPG通过洋流和水团的输入[31]. 由表2可知,南沙海域中沉积物239Pu/240Pu原子比值(平均为0.193±0.025)较高,表明该海域的239+240Pu 既包含有大气的直接沉降,也可能有太平洋马绍尔群岛核试验(PPG)钚的输入[26]. 为了评估 PPG 和全球沉降的来源贡献比例,我们采用了一个简单的两端元混合计算模型[18, 32].
式中,3.67表示239Pu和240Pu活度和原子比之间的换算系数;(Pu)1 和(Pu)2 分别代表由于PPG和全球沉降的239+240Pu贡献存量;R是沉积岩芯的平均240Pu/239Pu原子比;R1是来自 PPG 端元240Pu/239Pu的原子比值0.306—0.36;R2 是来大气沉降端元240Pu/239Pu的原子比值0.18.
结果表明,当R1=0.306时,PPG对南沙海域的贡献为8.94%—15.89%;当R1=0.36时,PPG对南沙海域的贡献为7.15%—12.13%. 总体贡献为7.15%—15.89%(平均约11.29%),小于南海大陆架北部(46%—87%)[18],南海北部(60%—71%)[19]和南海盆地(48%—65%)[20]. 这可能是由于南沙海域海水中悬浮颗粒物浓度较低,生物量较少,导致来自PPG的239+240Pu不能完全被吸附沉降. 剩余的84.11%—92.85%(平均约88.48%)可归因于大气全球沉降.
-
(1)南沙海域6个岩芯中的137Cs的活度范围为(0.758±0.078)—(1.687±0.145) Bq·kg−1,239+240Pu活度范围为(0.256±0.019)—(0.752±0.078) Bq·kg−1 ,240Pu/239Pu原子比范围为(0.184±0.020)—(0.201±0.028).
(2)南沙海域6个岩芯中除NS-3外,其它岩芯的239+240Pu和137Cs垂直分布特征都为典型单峰.
(3)137Cs和239+240Pu法测得的5个岩芯的平均沉积速率范围为0.269—0.490 cm·a−1,与210Pbex法沉积速率(0.270—0.652 cm·a−1)基本相符. 同时,在NS-2站位,210Pbex测得沉积速率远大于其它两种方法所得出的沉积速率.
(4) 用两端元法计算出采样区域沉积物中的钚大部分来源于全球沉降,PPG的贡献为7.15%—15.89 %(平均为11.29%).
南沙海域沉积物239+240Pu和137Cs的分布特 征及环境意义
Distribution characteristics and environmental significance of 239+240Pu and 137Cs in sediments in Nansha Sea area
-
摘要: 放射性核素239Pu、240Pu 和137Cs具有沉积物定年和互相印证的优势,已被广泛运用于沉积速率及放射性物质来源的评估研究中. 本文测量和分析了从南沙海域采集的6个沉积物岩芯中的137Cs 、239 + 240Pu 活度和240Pu/239Pu原子比. 结果表明,南沙海域沉积物中137Cs、239+240Pu活度的变化范围分别为(0.758±0.078)—(1.687±0.145)Bq·kg-1,(0.256±0.019) —(0.752±0.078)Bq·kg-1. 240Pu/239Pu原子比变化范围为(0.184±0.020)—(0.201±0.028),介于全球沉降和太平洋核试验场(PPG) 240Pu/239Pu原子比范围之间,通过两端元法计算出PPG对南沙海域钚(Pu)的相对贡献为7.15%—15.89%(平均为11.29%). 137Cs和239+240Pu活度的垂直分布特征表明,除NS-3岩芯外,其它5个岩芯的137Cs和239+240Pu均为典型的单峰. 239+240Pu法与137Cs法计算的沉积速率基本一致,说明在采样区域,沉积物混合和外界扰动过程对颗粒物沉积影响不大. 在NS-2站位,210Pbex法测得的沉积速率大于其它两种方法的沉积速率,可能是由于NS-2站位离岸较近,人为干扰、沉积物混合作用等其他因素致使210Pbex法测定的结果受到了影响.
-
关键词:
- 沉积速率 /
- 239+240Pu /
- 137Cs /
- 240Pu/239Pu /
- 沉积物岩芯.
Abstract: Radioisotopes 239Pu, 240Pu and 137Cs have the advantages of sediment dating and mutual verification, and have been widely used in the evaluation of deposition rates and sources of radioactive materials. In this paper, the activities of 137Cs, 239 + 240Pu and the atomic ratio of 240Pu/239Pu in six sediment cores collected from Nansha sea area were measured and analyzed. The results show that the variation range of 137Cs, 239+240Pu activity in the sediments of Nansha sea area range from (0.758±0.078)—(1.687±0.145) Bq·kg-1 and (0.256±0.019)—(0.752±0.078) Bq·kg-1. 240Pu/239Pu atomic ratio is (0.184±0.020)—(0.201±0.028), which are between the global subsidence and 240Pu/239Pu atomic ratio of PPG (Pacific Nuclear Test site). Through the two-terminal method, the relative contribution of PPG to plutonium(Pu) in Nansha sea area are calculated to be 7.15%—15.89% (average 11.29%). The vertical distribution characteristics of 137Cs and 239+240Pu activity in sediments show that 137Cs and 239+240Pu are typical single peaks. The sedimentation rates calculated by 239+240Pu method and 137Cs method are basically the same, which indicate that sediment mixing and external disturbance process have little influence on the sedimentation of particles in the sampling area. At NS-2 site, the sedimentation rates measured by 210Pbex method is higher than those by the other two methods, which may be due to the fact that the NS-2 site is close to the shore, so the results of 210Pbex method are affected by human interference, sediment mixing and other factors.-
Key words:
- sedimentation rate /
- 239+240Pu /
- 137Cs /
- 240Pu/239Pu /
- sediment core.
-

-
表 1 岩芯与样品基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of the core and sample
岩芯编号
Core numberNS-1 NS-2 NS-3 NS-4 NS-5 NS-6 采样站位 7°31′19″N,
113°28′7″E4°59′58″N,
113°9′45″E6°27′30″N,
113°0′16″E5°14′41″N,
112°7′27″E5°10′37″N,
110°20′14″E4°50′15″N,
110°26′37″E水深/m 1335 119 1537 123 141 121 岩芯长度/cm 24 29 21 25 26 25 取样层位/cm 0—24 0—29 0—21 0—25 0—26 0—25 表观性状 灰色软泥 粉砂 灰棕色软泥 粉砂质泥 粉砂质泥 粉砂质泥 表 2 南沙海域采样点137Cs与Pu的数据信息(Bq·kg−1)
Table 2. Data Information of 137Cs and Pu at sampling sites in Nansha Sea area(Bq·kg−1)
NS-1 校正深度/cm
Correction depth平均值
Average value0—5.3 5.3—11.9 11.9—16.8 16.8—23.0 23.0—29.5 239+240Pu 0.295±0.028 0.256±0.019 0.451±0.045 0.542±0.058 0.286±0.030 0.366±0.036 137Cs 0.859±0.108 0.948±0.115 1.025±0.124 1.235±0.134 1.038±0.098 1.021±0.116 239Pu/240Pu 0.195±0.041 0.191±0.045 0.197±0.021 0.189±0.022 0.187± 0.021 0.192±0.030 NS-2 校正深度/cm
Correction depth平均值
Average value0—6.2 6.2—10.6 10.6—16.2 16.2—22.0 22.0—28.0 28.0—33.2 239+240Pu 0.298±0.031 0.279±0.027 0.458±0.054 0.597±0.064 0.752±0.078 0.584±0.054 0.495±0.051 137Cs 0.758±0.078 0.789±0.081 1.028±0.095 1.358±0.118 1.687±0.145 1.589±0.138 1.202±0.109 239Pu/240Pu 0.195±0.025 0.196±0.022 0.197±0.022 0.195±0.042 0.196±0.021 0.189±0.022 0.194±0.026 NS-3 校正深度/cm
Correction depth平均值
Average value0—5.2 5.2—10.6 10.6—16.3 16.3—23.3 239+240Pu 0.256±0.028 0.299±0.034 0.268±0.029 0.357±0.038 0.295±0.032 137Cs 0.958±0.109 0.869±0.101 1.058±0.116 1.357±0.124 1.061±0.113 239Pu/240Pu 0.189±0.021 0.191±0.025 0.195±0.022 0.194±0.022 0.192±0.023 NS-4 校正深度/cm
Correction depth平均值
Average value0—5.3 5.3—10.8 10.8—16.6 16.6—22.7 22.7—29.1 239+240Pu 0.267±0.034 0.345±0.039 0.452±0.051 0.398±0.041 0.367±0.037 0.366±0.040 137Cs 0.986±0.098 1.156±0.126 1.358±0.103 1.198±0.098 1.089±0.099 1.157±0.105 239Pu/240Pu 0.194±0.032 0.195±0.021 0.184±0.020 0.185±0.020 0.189±0.021 0.189±0.023 NS-5 校正深度/cm
Correction depth平均值
Average value0—5.3 5.3—10.9 10.8—16.8 16.8—23.0 23.0—30.5 239+240Pu 0.309±0.034 0.421±0.044 0.545±0.058 0.498±0.054 0.402±0.041 0.435±0.046 137Cs 1.189±0.101 1.204±0.106 1.268±0.112 1.168±0.114 1.069±0.094 1.179±0.105 239Pu/240Pu 0.191±0.022 0.192±0.022 0.201±0.028 0.196±0.026 0.201±0.023 0.196 ±0.024 NS-6 校正深度/cm
Correction depth平均值
Average value0—5.3 5.3—11.0 11.0—17.1 17.1—23.4 23.4—29.9 239+240Pu 0.318±0.034 0.345±0.038 0.489±0.058 0.398±0.042 0.287±0.029 0.367±0.040 137Cs 1.058±0.087 1.148±0.098 1.297±0.101 1.098±0.089 1.106±0.088 1.141 ±0.093 239Pu/240Pu 0.192±0.028 0.194±0.032 0.195±0.020 0.199±0.022 0.189±0.020 0.194±0.024 -
[1] LINDAHL P, LEE S H, WORSFOLD P, et al. Plutonium isotopes as tracers for ocean processes: A review [J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2010, 69(2): 73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.08.002 [2] KETTERER M, SZECHENYI S C. Determination of plutonium and other transuranic elements by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: A historical perspective and new frontiers in the environmental sciences [J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2008, 63(7): 719-737. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.04.018 [3] 杨旭, 潘少明, 徐仪红, 等. Pu同位素比值在沉积物测年中的应用 [J]. 海洋通报, 2013, 32(2): 227-234. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.02.017 YANG X, PAN S M, XU Y H, et al. Pu isotope ratios as the geochronometer for sediments [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2013, 32(2): 227-234(in Chinese). doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.02.017
[4] WANG R R, LIU Z Y. Distribution and source of Pu in the sediments of the seas and estuaries of China-a review [J]. Anthropocene Coasts, 2020, 3(1): 53-75. doi: 10.1139/anc-2019-0017 [5] 曾理, 吴丰昌, 万国江, 等. 中国地区湖泊沉积物中137Cs分布特征和环境意义 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2009, 21(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.01.001 ZENG L, WU F C, WAN G J, et al. The distribution characteristic and environmental significance of Cesium-137 deposit profile in Chinese lacustrine sediment [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2009, 21(1): 1-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2009.01.001
[6] GUAN Y J, SUN S Y, SUN S H, et al. Distribution and sources of Plutonium along the coast of Guangxi, China [J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B:Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 2018, 437: 61-65. [7] ROZMARIC M, CHAMIZO E, LOUW D C, et al. Fate of anthropogenic radionuclides (90Sr, 137Cs, 238Pu, 239Pu, 240Pu, 241Am) in seawater in the northern Benguela upwelling system off Namibia [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 286(3): 131514. [8] KELLEY J M, BOND L A, BEASLEY T M. Global distribution of Pu isotopes and 237Np [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 237-238: 483-500. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00160-6 [9] QIAO J X, HOU X L, MIRÓ M, et al. Determination of Plutonium isotopes in waters and environmental solids: A review [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2009, 652(1-2): 66-84. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.03.010 [10] 黄亚楠, 潘少明, 刘志勇. 中国边缘海沉积物中239+240Pu的来源与存量模型 [J]. 地理科学, 2018, 38(11): 1892-1903. HUANG Y N, PAN S M, LIU Z Y. The source and inventory model of 239+240Pu in the sediment cores of the marginal sea of China [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2018, 38(11): 1892-1903(in Chinese).
[11] 赵利, 蔡观强, 钟和贤, 等. 南海北部陆架海域表层沉积物地球化学特征及地质意义 [J]. 地质学刊, 2017, 41(1): 103-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2017.01.103 ZHAO L, CAI G Q, ZHONG H X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of the surface sediments from the continental shelf waters of the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Geology, 2017, 41(1): 103-111(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2017.01.103
[12] 崔振昂, 林进清, 甘华阳, 等. 南海北部湾东部海域表层沉积物地球化学特征 [J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(7): 103-111. CUI Z A, LIN J Q, GAN H Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the surface sediments in the eastern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(7): 103-111(in Chinese).
[13] 赵建如. 南海西北部表层沉积物元素地球化学空间多尺度变化与机制研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016. ZHAO J R. Study on spatial multi-scale variation and mechanism of element geochemistry of surface sediments in northwestern South China Sea[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2016(in Chinese).
[14] DENG S, PENG A G, LIU J, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and organic carbon flux in Nansha Sea area based on 210Pb dating method [J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2021, 329(3): 1167-1181. doi: 10.1007/s10967-021-07911-9 [15] 邓爽, 刘劲, 吴雨田, 等. 南沙海域沉积物226Ra和210Pb的分布特征及环境意义 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2535-2543. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020040401 DENG S, LIU J, WU Y T, et al. Characteristics of distribution and environmental significance of 226Ra and 210Pb in sediments in Nansha Sea area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2535-2543(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020040401
[16] 吴时国, 罗又郎. 南海南部大陆架的残留沉积 [J]. 热带海洋, 1994, 13(3): 47-53. WU S G, LUO Y L. The relict sediments in the south shelf of South China Sea [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1994, 13(3): 47-53(in Chinese).
[17] ZHENG J, YAMADA M. Inductively coupled plasma-sector field mass spectrometry with a high-efficiency sample introduction system for the determination of Pu isotopes in settling particles at femtogram levels [J]. Talanta, 2006, 69(5): 1246-1253. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2005.12.047 [18] WU J W, ZHENG J, DAI M H, et al. Isotopic composition and distribution of Plutonium in northern South China Sea sediments revealed continuous release and transport of Pu from the Marshall Islands [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(6): 3136-3144. [19] WANG R R, LEI L, LI G, et al. Identification of the distribution and sources of Pu in the northern South China Sea: Influences of provenance and scavenging [J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2019, 3(12): 2684-2694. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00245 [20] DONG W, ZHENG J, GUO Q J, et al. Characterization of Plutonium in deep-sea sediments of the Sulu and South China Seas [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2010, 101(8): 622-629. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.03.011 [21] DING Y, BAO X W, YAO Z G, et al. A modeling study of the characteristics and mechanism of the westward coastal current during summer in the northwestern South China Sea [J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2017, 52(1): 11-30. doi: 10.1007/s12601-017-0011-x [22] 杨士瑛, 鲍献文, 陈长胜, 陈菲. 夏季粤西沿岸流特征及其产生机制 [J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2003, 25(6): 1-8. YANG S Y, BAO X W, CHEN C S, et al. Analysis on characteristics and mechanism of current system in west coast of Guangdong Province in the summer [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2003, 25(6): 1-8(in Chinese).
[23] WARNEKE T, CROUDACE I W, WARWICK P E, et al. A new ground-level fallout record of uranium and Plutonium isotopes for northern temperate latitudes [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 203(3-4): 1047-1057. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00930-5 [24] WANG J L, DU J Z, ZHENG J, et al. Plutonium in Southern Yellow Sea sediments and its implications for the quantification of oceanic derived mercury and zinc [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266: 115262. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115262 [25] 黄亚楠, 潘少明. 中国边缘海柱样沉积物中239+240Pu的分布与时标价值 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(3): 1235-1245. HUANG Y N, PAN S M. The dating and distribution of 239+240Pu in the sediment cores of the marginal sea of China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(3): 1235-1245(in Chinese).
[26] ZHUANG Q F, LI G S, WANG F, et al. 137Cs and 239+240Pu in the Bohai Sea of China: Comparison in distribution and source identification between the inner bay and the tidal flat [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 138: 604-617. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.12.005 [27] LIU Z Y, ZHENG J, PAN S M, et al. Pu and 137Cs in the Yangtze River Estuary sediments: Distribution and source identification [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(5): 1805-1811. [28] 赵丽君. 多核素示踪的河口海岸现代沉积物年代学比较研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2018. ZHAO L J. Comparative study on the chronology in the recent sediment of estuary and coast by multi-radionuclides[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2018(in Chinese).
[29] PAN S M, TIMS S G, LIU X Y, et al. 137Cs, 239+240Pu concentrations and the 240Pu/239Pu atom ratio in a sediment core from the subaqueous delta of Yangtze River Estuary [J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2011, 102(10): 930-936. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.05.012 [30] 邓彬彬. 基于210Pb, 137Cs和239+240Pu的不同水环境沉积物年代学比较研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2021. DENG B B. Sedimentary chronology comparison of 210Pb, 137Cs and 239+240Pu in different water environment[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2021(in Chinese).
[31] ZHANG K X, LI G S, PAN S M, et al. Migration path and isotope tracing of 137Cs and 239+240Pu in estuary sediments: A case study of Liao River estuary in China [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2019, 19: 491-500. doi: 10.1007/s11368-018-2092-2 [32] KREY P W. Remote Plutonium contamination and total inventories from Rocky Flats [J]. Health Physics, 1976, 30(2): 209-214. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197602000-00009 -




 下载:
下载: