-
水环境中重金属存在隐蔽性、稳定性、易富集和难降解等特点,容易通过饮水途径在人体内富集,从而危及人体健康[1-2],其来源主要有自然来源和人为来源,前者包括地质侵蚀、风化等自然过程,后者包括矿业活动、金属加工、工业和生活废水排放、化石燃料燃烧、农药和化肥的不恰当施用等人类活动[3-5]. 20世纪70年代以来,国内外学者从重金属形态分析、空间分布及来源、迁移与积累和污染效应等多方面对水体中重金属进行了研究[6-11],如王漫漫[8]、钟明[9]、旷攀[10]和谭冰[11]等分别对太湖流域、沙颍河流域、贵州普定水库和洋河流域万全段地表水体和沉积物中重金属污染和生态风险进行了评价,均有效支撑了当地水资源的科学管理.
近年来,云贵地区地表水中重金属的环境影响得到了越来越多学者的关注. 刘伟等 [12]的研究探讨了贵州麻江县煤矿集中开采区摆沙河流域地表水重金属污染特征,马先杰等[13]的研究对贵州8个典型锰矿区地表水及表层沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险进行了评价,熊燕等[14]的研究则对南盘江流域(云南段)水系沉积物中重金属含量分布特征及其污染状况进行了分析,均发现不同地区地表水中重金属存在不同程度的富集,而矿业活动是地表水和水系沉积物中重金属富集的主要来源. 珠江流域地表水中重金属污染情况也是学者关注的重点之一,杨思林等[15]的研究认为珠江流域的水体和土壤均有不同程度的重金属污染,且下游流域污染较上游严重. 姚波等[16]和陈晓鸿等[17]的研究对珠江流域上游云贵地区和南盘江流域曲靖段农田土壤重金属的污染特征进行了分析,发现土壤中重金属污染也不容忽视.
小黄泥河地处珠江源区、云贵两省交界地带,为全国重要江河水功能区,同时也是云贵重要的矿业活动区,对珠江源的保护有着重要的现实意义. 目前,关于小黄泥河流域的研究相对较少,李继平等[18]和肖文博等[19] 的研究探讨了小黄泥河水资源合理配置和利用的方法,涂春霖等[20]的研究分析了小黄泥河流域地表水的水化学特征及控制因素,但关于其重金属的研究还鲜有涉及,基于此,本研究对小黄泥河流域地表水中重金属的空间分布特征及来源进行解析,并对其污染水平进行综合评价,以期为小黄泥河流域水环境综合治理提供科学依据.
-
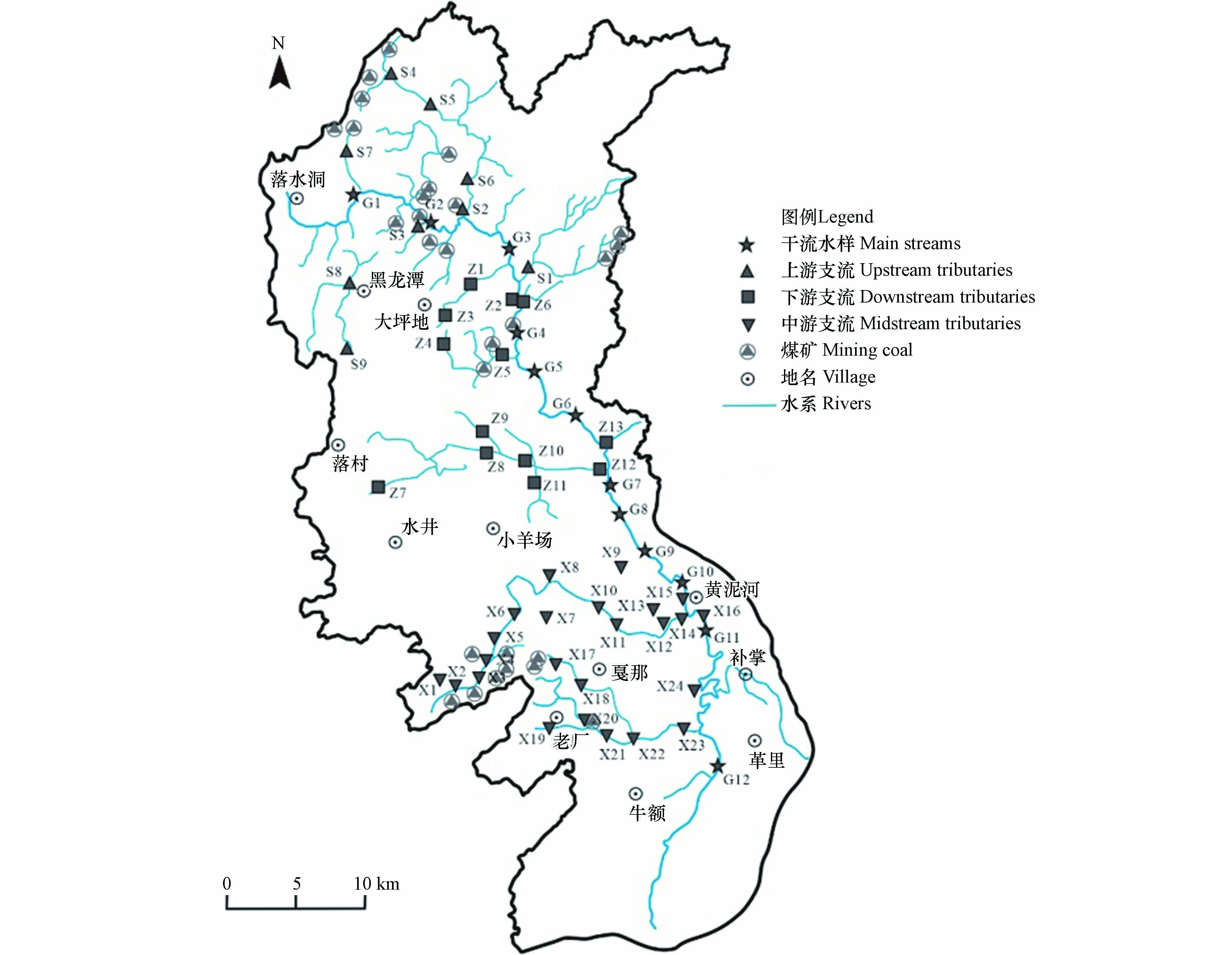
小黄泥河流域位于云贵高原向广西丘陵过渡的斜坡地带,其地理位置:东经104°23′37" — 104°47′58",北纬25°3′59"— 25°40′28",为珠江流域上游南盘江的二级支流. 小黄泥河干流河长98.7 km,流域面积约1 446 km2(图1). 流域水资源较丰富,多年平均流量42.6 m3·s−1,年径流量13.4亿m3. 该区地处亚热带高原型季风气候区,多年平均气温16.2 ℃,年平均降雨量为1384 mm [18-19]. 总体地势北高南低,高程1152 — 2355 m,自上游至下游,河床坡降逐渐降低. 河流两岸多为坡耕地,水土流失相对严重. 流域内矿产资源丰富,有煤矿、砂石矿、石膏矿、锑矿、萤石矿等,其中煤矿主要位于流域上游和下游地区,砂石矿等主要分布于中游一带,锑矿和萤石矿见于下游支流. 目前主要开采矿种为煤矿,其他矿种均已关闭. 小黄泥河及其支流沿岸多有洗煤厂和煤矸石等分布,对沿河生态环境安全和居民生活都造成了潜在的威胁.
-
在小黄泥河流域布置了58个采样点,对其干流和主要支流均进行了控制,其中矿业活动和城镇区域加密布样,并于2020年9 — 10月进行系统的水样采集工作,采集干流水样12件(G1 — G12),上游支流水样9件(S1 — S9),中游支流水样13件(Z1 — Z13),下游支流水样24件(X1 — X24),采样点位置如图1所示. 使用500 mL聚乙烯塑料瓶进行采样,采样前先用蒸馏水把聚乙烯塑料瓶清洗干净,采样时再用水样润洗3 次,水样采集一般在水面10 cm以下,现场用便携式多参数水质测定仪(DZB-718型)测定pH、水温(T)等参数,用于分析锰、铜、铅、锌、镉的水样加入5 mL浓硝酸酸化至 pH<2,用于分析总铁和砷的水样原样保存,送国土资源部成都矿产资源监督检测中心检测,其中锰、铜、铅、锌、镉和总铁用电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定,砷用原子荧光法测定. 在进行水样分析时,采用加标回收方式进行质量监控,采用重复分析方法控制样品分析的精密度,水样分析结果显示加标回收率和合格率均为100%.
-
研究采用内梅罗综合污染指数法评价小黄泥河流域地表水重金属污染等级. 内梅罗综合污染指数法能够反映水体重金属污染现状及各种重金属对复合污染的不同贡献,并甄别出主要污染物,是水体重金属污染评价的常用方法[12, 21-22].
单因子污染指数:
多因子综合污染指数:
式中,Ci为重金属i的实测浓度,Si为相应的水质标准,这里采用《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838—2002)中的Ⅲ类水质标准作为参比标准,重金属金属Fe和Mn参考《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838—2002)中集中式生活饮用水地表水源地补充项目标准限值;max(Pi)为重金属单因子污染指数的最大值;ave(Pi)为各金属单因子污染指数的平均值. 地表水中重金属的污染评价标准如表1所示.
-
地表水中重金属对人群造成健康风险的途径有饮用途径、呼吸途径和接触途径,但呼吸途径与接触途径和饮用途径健康风险存在2—3级数量级的差距,这里忽略不计,仅考虑重金属通过饮用途径对人群造成的健康风险程度,包括针对成人和儿童的致癌物(As和Cd) 评价模型和非致癌物( Fe、Mn、Cu、Zn 和Pb) 评价模型[23-25]. 其中致癌风险评价模型表达式如下:
若结果>0. 01,则按高剂量暴露计算:
非致癌风险评价模型表达式如下:
总健康风险评价公式如下:
式中,Ri和Hi分别为化学致癌物和非致癌物i经饮水暴露产生的人均年致癌风险(a−1),Di为有毒物质i经饮水暴露的单位体重日均暴露剂量[mg·( kg·d)−1];qi为化学致癌物i经饮水暴露摄入的致癌系数[mg·( kg·d)-1],RFDi为非致癌物i饮水途径的日均推荐剂量[mg·( kg·d) -1],70 为平均寿命(a). 致癌物和非致癌物评价模型参数值见表2.
饮水途径日均暴露剂量Di计算公式如下:
式中,w为日均饮水量,成人为1.5 L·d−1,儿童为1.0 L·d−1;Ci为污染物i饮水途径的质量浓度,单位为mg·L−1;A 为人均的人体体重, 成人取64.3 kg,儿童取22.9 kg [23,26].
-
本研究数据采用Excel 2016进行处理和统计分析,利用SPSS19. 0 进行Pearson相关分析和因子分析,采用软件Mapgis6.7和Arcgis 10.7 制作图件.
-
小黄泥河流域地表水中pH值和重金属浓度统计特征见表3.
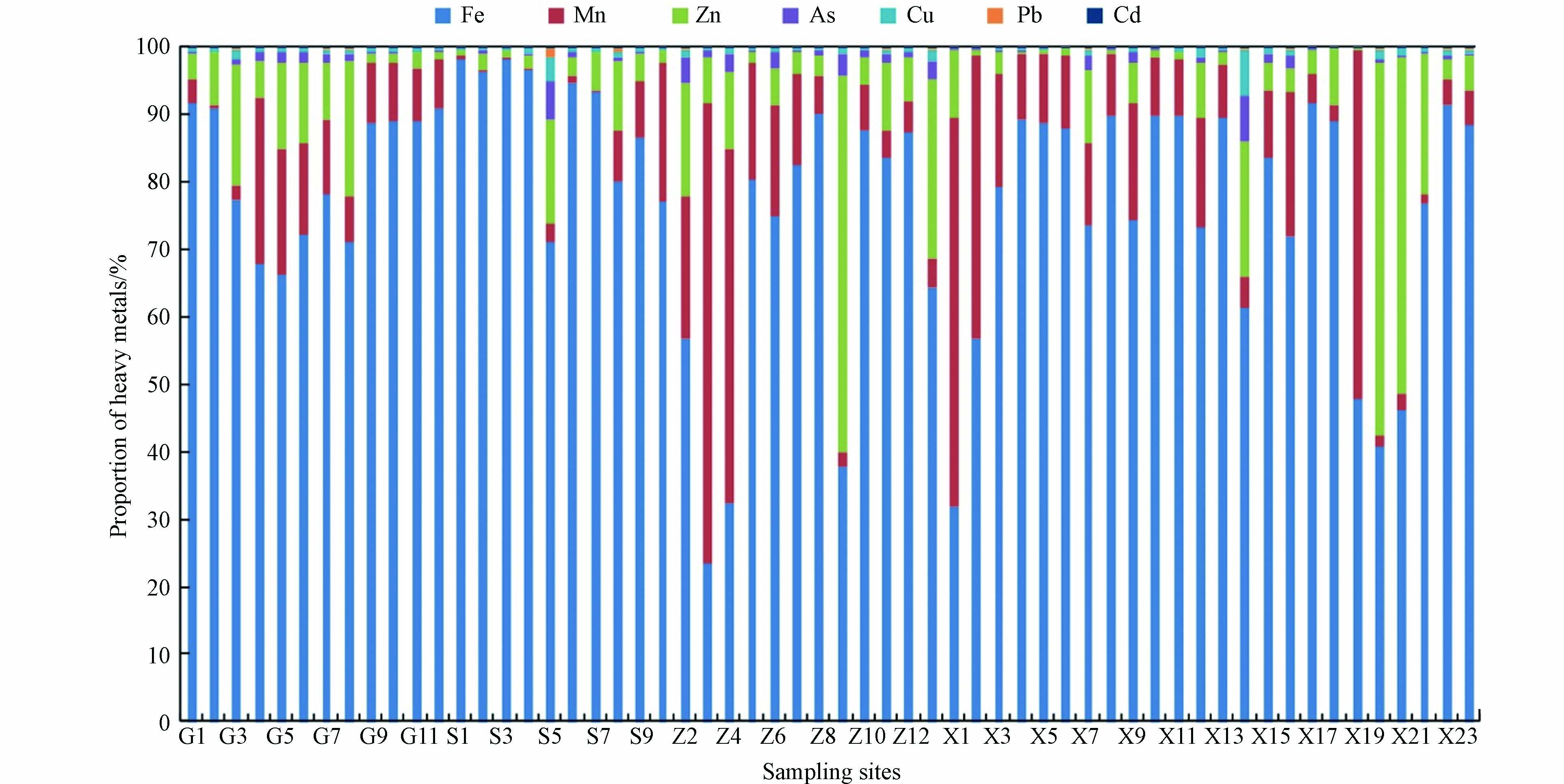
流域内河水pH值变化范围6.48 — 9.14,均值为7.98,总体偏碱性,变异系数为5.34%,在流域范围内较稳定. 7种重金属除Fe和Mn外,其他重金属浓度均较低,各重金属平均浓度顺序为:Fe(810.66 μg·L−1)>Mn(126.90 μg·L−1)>Zn(24.71 μg·L−1)>As(2.45 μg·L−1)>Cu(2.33 μg·L−1)>Pb(0.43 μg·L−1)>Cd(0.03 μg·L−1),除Fe和Mn的平均浓度超过《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838—2002)中地表水源地标准限值外,其他重金属浓度均远低于地表水Ⅲ类水质标准. 从统计数据看(表3、图2),流域内Fe浓度为17.1 — 6471 μg·L−1,均值为810.66 μg·L−1,最大浓度和最小浓度之间相差378.42倍,占7种重金属总量的23.56% — 98.38%,均值为77.17%;Mn浓度为0.96 — 1201 μg·L−1,均值为126.9 μg·L−1,最大浓度和最小浓度之间相差132.19倍,占重金属总量的0.18% — 68.21%,均值为12.27%;Zn浓度为3.35 — 142 μg·L−1,均值为24.71 μg·L−1,占重金属总量的0.33% — 55.98%,均值为8.81%,三者占重金属总量的95%以上,而其他重金属浓度均较低,总体占重金属总量的0.11% — 13.76%,均值仅为1.77%.
与云贵地区及珠江流域其他河湖相比(表4),小黄泥河流域地表水中Fe和Mn浓度较高,高于柳江流域和贵州红枫湖均值,但低于贵州典型煤矿集中开采区摆沙河流域的均值;Zn浓度高于柳江、龙江和西江干流均值,与东江和贵州红枫湖相当,远低于贵州摆沙河流域和东江淡水河流域均值;Cu、As和Pb浓度略高于龙江和西江干流,低于东江和柳江流域均值;Cd浓度较低,与西江干流相当,但远低于贵州普定水库、红枫湖和柳江流域的均值.
变异系数(CV)表明了每个样本间元素的离散程度,可以更好地反映数据的离散性. 一般CV<10%的为弱变异水平,10%≤CV≤100%的为中等变异水平,CV>100%为强变异水平[2]. 小黄泥河流域地表水中各重金属变异系数均较高,其排序为Mn>Fe>Pb> As>Cu>Zn>Cd,在流域范围内均达到了强变异水平,表明各重金属元素的空间分布均极不均匀. 其中干流各重金属变异系数范围为31.42% — 71.02%,均值为50.04%;上游支流变异系数范围为25.06% — 106.84%,均值为62.63%;中游支流变异系数范围为41.36% — 158.26%,均值为82.45%;下游支流变异系数范围为98.81% — 143.00%,均值为105.20%,变异系数表现为下游支流>中游支流>上游支流>干流,从上游支流到下游支流变异程度逐渐增强,反映了不同河段重金属具有不同的来源.
-
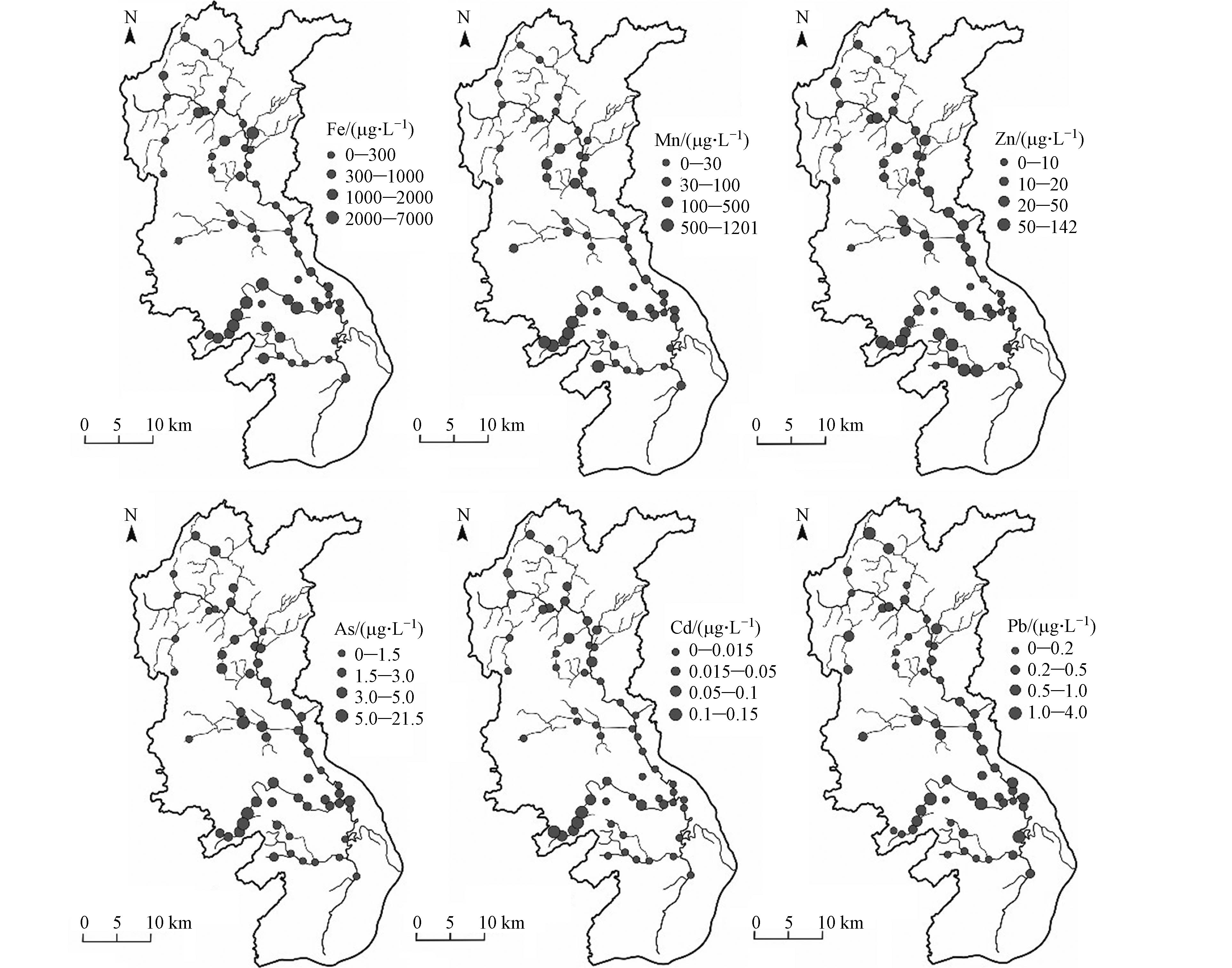
小黄泥河流域地表水中各重金属浓度分布在空间上表现出不同的特征(图3),下游支流中各重金属浓度均较高,该区为矿业集中区,煤矿、锑矿、萤石矿等均有分布,矿业废水通过各种途径进入到地表水中,导致各重金属浓度均较高. 从各重金属浓度分布来看,Fe和Mn的高值点主要位于上游支流和下游支流,Fe平均浓度为下游支流>上游支流>中游支流>干流,Mn平均浓度为下游支流>中游支流>干流>上游支流,其中下游支流Fe、Mn浓度最高,平均浓度分别为1429.50 μg·L−1和254.97 μg·L−1,为标准限值的4.77倍和2.55倍,需要引起相应重视. 其他各重金属浓度均没有超标现象,Zn平均浓度表现为下游支流>中游支流>干流>上游支流,其变异程度均不高,表明Zn的空间分布较为均匀. Cu、As、Cd和Pb浓度均较低,远低于标准限值,且其相对高值点均位于下游支流,暗示这几个重金属之间可能具有相同的来源.
-
地表水中重金属浓度的相关性可以判断重金属的来源是否相同,如果不同重金属浓度之间相关性显著,则说明它们可能具有相似的来源或迁移途径[28, 30]. 小黄泥河流域地表水中重金属浓度之间的Pearson相关系数结果见表5. 结果显示,Fe和Cu之间相关性最强(P<0.01),相关系数为0.87;Cu和Cd,Cu和As,Fe和Cd,Fe和As之间相关性也较高(P<0.01),相关系数分别为0.78、0.71、0.71和0.70,As和Cd相关系数也较高,为0.60(P<0.01),表明这4种重金属可能有相同的来源. Mn是流域内地表水中浓度较高的重金属,其与Fe、Cd、Cu和As之间也具有较显著的相关性(P<0.01),相关系数分别为0.60、0.64、0.44和0.44,表明Mn与这几个重金属也可能存在同源性. Zn与Cd表现出弱相关,相关系数为0.32(P<0.05),与其他重金属相关性均较弱,说明其来源与其他重金属不同. Pb与Cu相关性较高,为0.52(P<0.01),与Fe和Cd弱相关(P<0.05),相关系数分别为0.38和0.33,暗示其可能存在不同的来源.
-
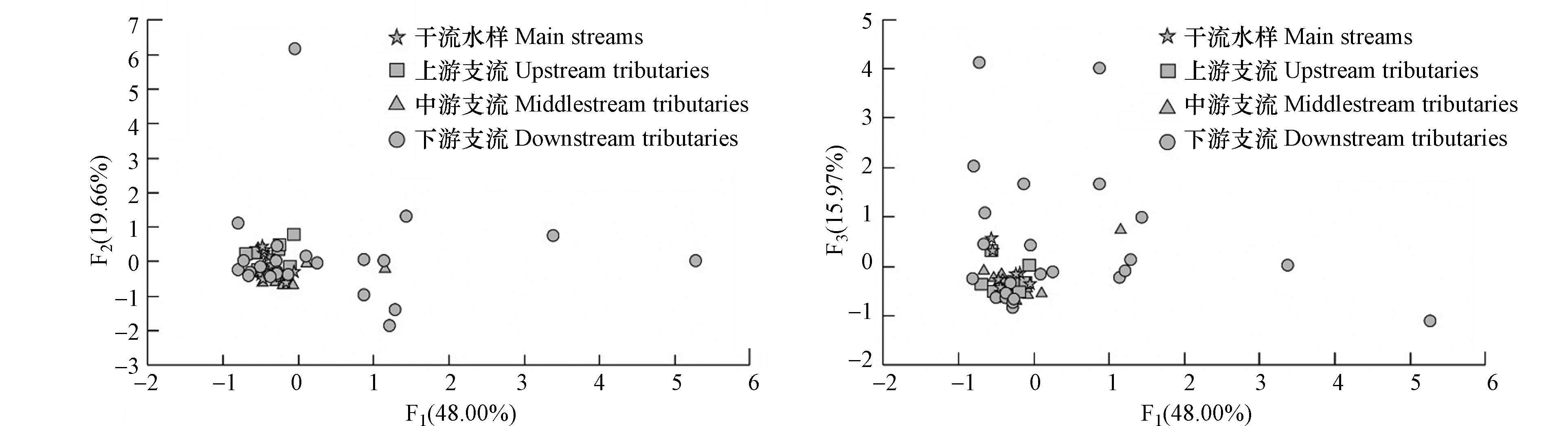
因子分析广泛应用于水质的时空变化和污染源识别的研究中[31]. 对数据进行KMO和Bartlett’s 球形检验,KMO检验值为0.685,Bartlett’s 球形检验具有显著性,满足因子分析要求. 采用主成分分析法,在经方差极大正交旋转后,提取得到特征值大于1的3个公因子,累积贡献率可达83.63%(表6),基本反映了7 种重金属的来源情况. 计算各采样点每个公共因子的因子得分,其得分高低可以反映该点受公共因子的影响作用程度的大小[32],同时绘制3个公因子得分变量的散点图(图4).
由图4和表6可知,F1因子的贡献率为48%,主要载荷为Fe、As、Cd、Cu和Mn,相互之间均具有较强相关性,表明这5种重金属可能有共同的来源. F1得分高值点主要位于下游支流(图4),推测受到了采煤活动的影响. 小黄泥河流域各重金属元素变异性均较高,且从上游支流到下游支流变异性逐渐增强. 研究区为云贵重要的采煤基地,含煤地层主要为龙潭组,煤层及其夹矸中富含黄铁矿和菱铁矿[33-36],导致该区采煤废水中含有大量的Fe和Mn,排放到地表水中后引起地表水Fe和Mn浓度的增加,这与刘伟等[12]的研究一致,表明地表水中Fe、Mn主要来源于采煤废水. 同时,云贵地区煤中As、Cd和Cu也有较高的含量[37-39],如秦身钧[38]的研究发现盘州市地区煤中As高度富集,Cu轻度富集,两者含量明显高于中国煤均值;杨建业[39]的研究认为贵州普安矿区煤中As、Cd、Cu、Pb和Zn等显著富集,其中As、Cd、Pb和Zn主要赋存在黄铁矿中,而Cu主要存在于高岭石中等. 也有学者研究认为,酸性矿山排水常含有高浓度的Fe,并富集Cd、Pb、As、Cu和Zn等重金属[40],与本次研究的结果一致,表明采煤活动是地表水中高浓度重金属的主要来源. F2因子的贡献率为19.66%,主要载荷为Pb和Cu,二者呈显著相关. 研究表明[41-42],Pb和Cu是交通污染的标志性元素,汽车轮轴轴承摩擦、制动衬面摩擦等均会释放Pb和Cu. 小黄泥河沿岸路网发达,车辆往来频繁,释放出的重金属通过大气沉降进入地表水中,导致其浓度增加,因此认为F2代表了道路交通的影响. F3因子的贡献率为15.97%,主要载荷为Zn. Zn与其他重金属相关性均较差(表5),表明Zn的来源与其他重金属有所不同. 研究区除含煤地层外,还有大范围碳酸盐岩分布,面积达70%左右. 在区域上,研究区位于以发育碳酸盐岩型铅锌矿床为特色的黔西北铅锌成矿区 [43-44],碳酸盐中具有较高Zn含量. 从Zn的空间分布来看,其高值点位于中游和下游的碳酸盐岩分布区,推测Zn可能来源于碳酸盐岩的风化过程,因此认为F3代表了地质背景的影响.
由此可见,研究区地表水中重金属浓度主要受到采煤活动、道路交通和地质背景的控制,其贡献率分别为48.00%、19.66%和15.97%,其中Fe、As、Cd和Mn主要来源于采煤活动,Pb主要来源于道路交通的输入,Zn主要受地质背景的控制,Cu则受到采煤活动和道路交通的综合影响. 而采煤活动是小黄泥河流域地表水中重金属最重要的来源.
-
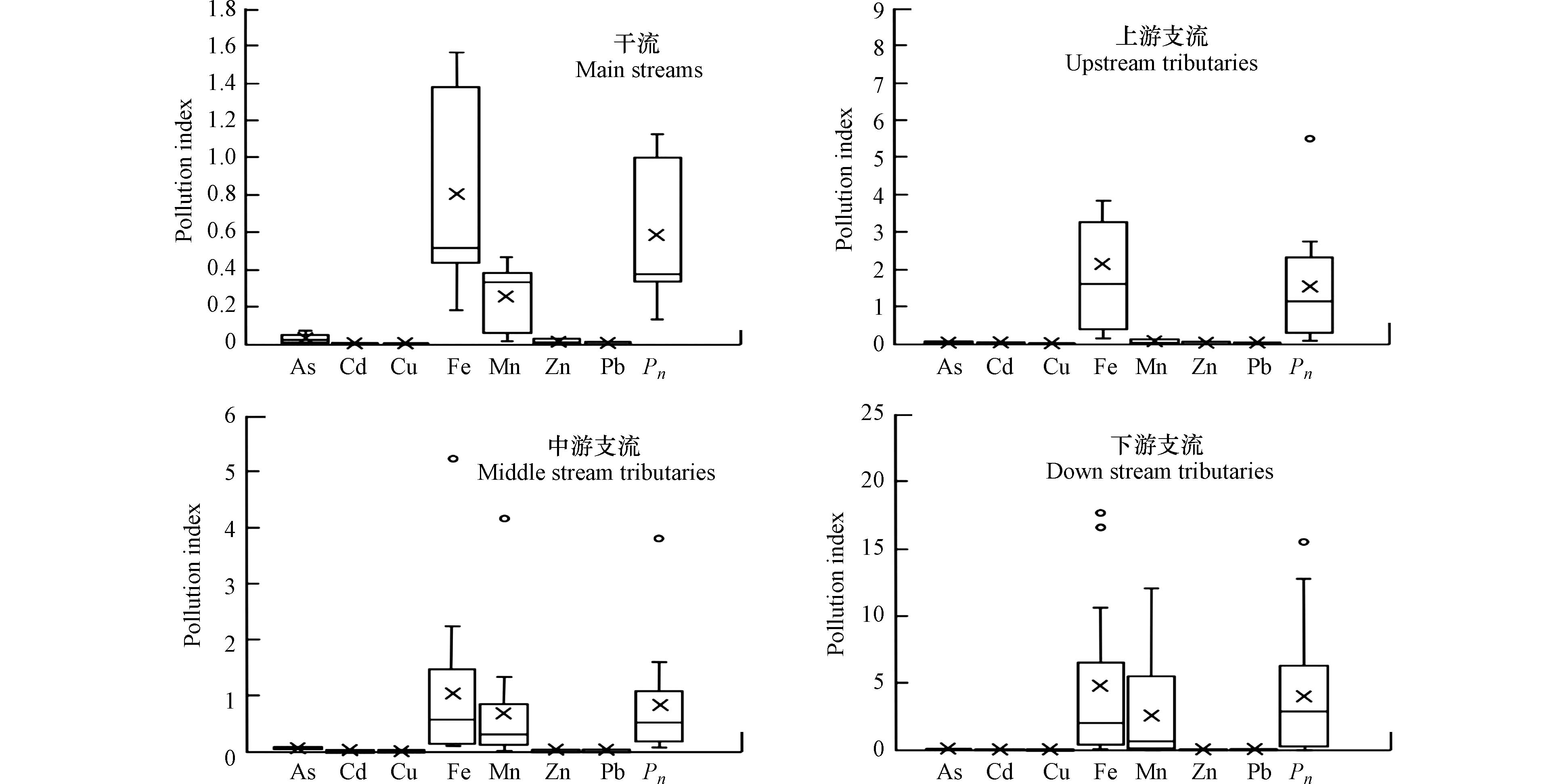
小黄泥河流域地表水重金属单因子和综合污染指数评价结果如图5所示,除Fe和Mn外,其他重金属(As、Cd、Cu、Zn、Pb)单因子污染指数均远小于1,不存在污染风险.
Fe和Mn的单因子污染指数较高,且在不同区域支流中表现出不同的特征. Fe单因子污染指数为0.06—21.57,均值为2.70,各区域支流均存在不同程度的污染,总体污染程度下游支流>上游支流>中游支流>干流;Mn单因子污染指数为0.01—12.01,均值为1.27,中下游支流存在一定程度的污染,上游支流和干流相对安全. 综合污染指数评价结果表明,干流水质总体优于支流,干流综合污染指数为0.13—1.12,均值为0.58,上游、中游和下游各支流综合污染指数分别为0.10—5.50、0.07—3.81和0.04—15.53,均值分别为1.53、0.85和3.98,下游支流为高度污染,上游支流为轻度污染,中游支流也处于警戒线以上,均主要受到Fe和Mn的影响.
-
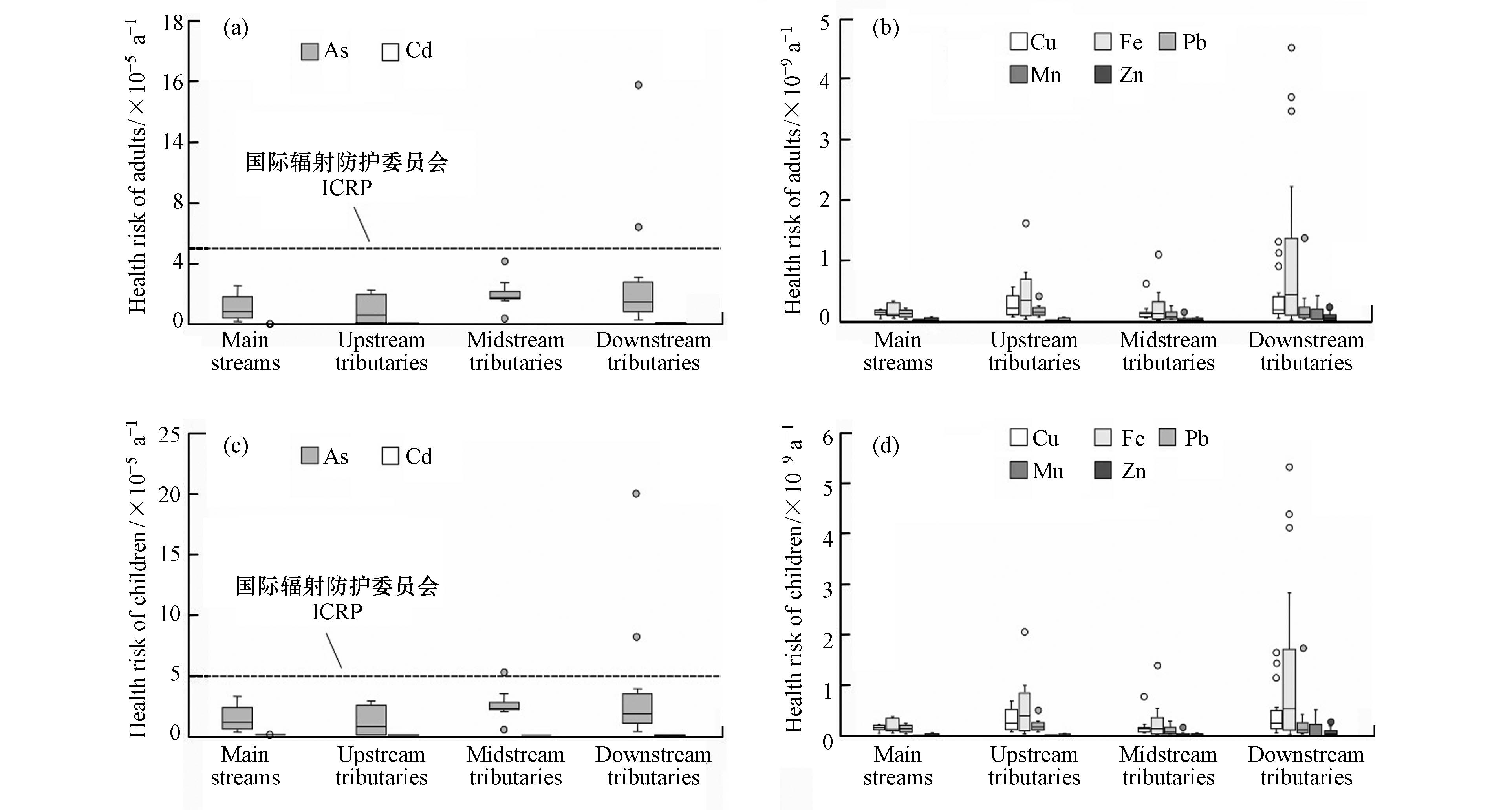
根据小黄泥河流域地表水体中重金属浓度数据,计算出重金属的成人和儿童人均年致癌风险和非致癌风险值(表7),并绘制不同干支流化学致癌物和化学非致癌物健康危害风险箱型图(图6),结果表明,化学致癌物(As和Cd)通过饮水途径的健康风险值明显高于化学非致癌物(Cu、Pb、Fe、Mn和Zn),儿童的健康风险明显高于成人,与前人的研究结果一致[6, 23-24]. 各重金属在地表水中所致健康风险值大小次序为:As>Cd>Fe>Cu>Pb>Zn>Mn,其中As的健康风险值最高,成人和儿童的健康风险值分别为0.06×10−5—15.8×10−5 a−1和0.07×10−5—20.1×10−5 a−1,其高值点主要位于下游支流. 以国际辐射防护委员会ICRP最大可接受风险值5×10−5 a−1 (取lg值为−4.3)为基准,下游支流有2个点位As的健康风险已高于最大可接受风险值,需要引起重视. 致癌物Cd及非致癌物Cu、Pb、Fe、Mn和Zn的成人和儿童健康风险值均远低于最大可接受风险值,对流域内人群不产生健康危害. Fe和Mn虽在流域地表水中浓度较高,但由于其为非致癌物,致癌强度系数较低[6],所以健康风险值也相对较低.
在空间分布上,As、Mn和Zn的健康风险值为下游支流>中游支流>干流>上游支流,Cd和Pb的健康风险值为下游支流>上游支流>干流>中游支流,Cu和Fe的健康风险值为下游支流>上游支流>中游支流>干流,下游支流风险值最高,推测受到了矿业活动的影响. 总风险值主要由As贡献,故其空间分布和As一致. 需要注意的是,本次主要讨论了重金属通过饮水途径对成人和儿童健康产生危害的风险,但事实上当地居民并不直接饮用河流中的水,而呼吸和皮肤接触等其他暴露途径的影响基本可忽略不计,因此实际风险可能会相对更低.
总体来看,小黄泥河流域主要污染重金属为Fe和Mn,但其并不对人体构成健康危害;As的健康风险值较高,但在流域内并不存在污染,表明小黄泥河流域河水中重金属的健康风险总体可控. 但另一方面,虽然Fe和Mn的个人健康风险值较低,不构成致癌风险,但摄入过量的Fe和Mn也会对人体健康造成极大伤害[45],因此也需要注重地表水中Fe和Mn的监测和防治. 由前述分析可知,地表水中Fe和Mn主要来源于采煤活动,如煤矿矿井水的不当排放、煤粉尘的沉降和煤矸石的淋溶等,并可能通过落水洞、溶井等对地下水造成影响,进而危及居民的饮用水安全. 因此,要加强源头治理,对不当排放的矿井水进行监管,对沿沟谷河流堆放的煤矸石进行清理等,减少污染来源,为小黄泥河水环境的健康保驾护航.
-
(1)云贵高原小黄泥河流域地表水中重金属平均浓度顺序为:Fe>Mn>Zn>As>Cu>Pb>Cd,除Fe和Mn的平均浓度超过《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838—2002)中地表水源地标准限值外,其他重金属浓度均远低于地表水Ⅲ类水质标准,其中Fe、Mn和Zn占重金属总量的95%以上. 流域内各重金属变异系数均较高,其排序为Mn>Fe>Pb>As>Cu>Zn>Cd,在流域范围内均达到了强变异水平,空间分布极不均匀,下游支流各重金属浓度均较高.
(2)相关性分析显示Fe、Cd、Cu、As和Mn之间具有较强的相关性,因子分析也表明Fe、As、Cd、Cu和Mn具有相同的来源,主要受到采煤活动的影响,而Pb和Zn则分别受控于道路交通输入和地质背景.
(3)小黄泥河流域地表水中Fe和Mn的单因子污染指数较高,而其他重金属总体上不存在污染风险. Fe在干支流均存在不同程度的污染,Mn在中下游支流存在一定程度的污染. 干流水质总体优于支流,下游支流为高度污染,上游支流为轻度污染,中游支流也处于警戒线以上,均主要受到Fe和Mn的影响.
(4)重金属健康风险评价结果显示,儿童的重金属健康风险明显高于成人. 各重金属在地表水中所致个人风险值大小次序为:As>Cd>Fe>Cu>Pb>Zn>Mn,除部分点位As的个人健康风险超过了最大可接受风险值外,其余重金属的个人健康风险值均远低于最大可接受风险值.
云贵高原小黄泥河流域重金属分布特征及健康风险评价
Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in Xiaohuangni River Basin on Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau
-
摘要: 小黄泥河为珠江源区南盘江流域主要支流之一,也是云贵高原重要的江河水功能区,查明小黄泥河流域地表水重金属分布特征、污染程度和健康风险,可以为珠江源区的生态环境保护提供有力支撑. 系统采集小黄泥河干流及支流河水样品,对河水样品中重金属Fe、Mn、Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和类金属As进行测定,并采用内梅罗综合污染指数法和健康风险评价模型,对小黄泥河流域地表水中的重金属进行污染评价和健康风险评价. 结果表明,小黄泥河流域河水中重金属平均浓度顺序为:Fe(810.66 μg·L−1)>Mn(126.90 μg·L−1)>Zn(24.71 μg·L−1)>As(2.45 μg·L−1)>Cu(2.33 μg·L−1)>Pb(0.43 μg·L−1)>Cd(0.03 μg·L−1),其中Fe和Mn两种重金属存在超标现象,其他重金属均未出现超标现象. 相关性分析及因子分析表明,地表水中7种重金属元素主要受到采煤活动、道路交通和地质背景3个因素的控制,其贡献率分别为48.00%、19.66%和15.97%. Fe和Mn的单因子污染指数较高,存在不同程度的污染,而其他重金属总体上不存在污染风险. 综合污染指数评价结果显示,干流水质总体优于支流,下游支流为高度污染,上游支流为轻度污染,均主要受到Fe和Mn的影响. 地表水中重金属产生的健康风险总体可控,其大小依次为As>Cd>Fe>Cu>Pb>Zn>Mn,除下游支流部分点位As的健康风险高于最大可接受风险值外,致癌物Cd及非致癌物Cu、Pb、Fe、Mn和Zn的健康风险均远低于最大可接受风险值.Abstract: The Xiaohuangni River is one of the main tributaries of the Nanpan River Basin in the source area of the Pearl River, and it is also an important river water function area in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. The identification of the distribution characteristics, pollution levels and health risks of heavy metals in the surface water of the Xiaohuangni River basin can provide strong support for the protection of the source area of the Pearl River. The samples of main stream and tributaries of Xiaohuangni River were collected to determine the concentrations of Fe, Mn, Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd and metalloid of As in the water. The Nemerow index method and health risk assessment model were applied to assess the degree of contamination and health risk of heavy metals in surface water. The results show that the average concentration of each heavy metals can be ranked as Fe(810.66 μg·L−1)>Mn(126.90 μg·L−1)>Zn(24.71 μg·L−1)>As(2.45 μg·L−1)>Cu(2.33 μg·L−1)>Pb(0.43 μg·L−1)>Cd(0.03 μg·L−1), in which Fe and Mn are the main excessive heavy metals, and other heavy metals do not exceed the standard. Correlation analysis and factor analysis show that the seven heavy metals are mainly affected by coal mining activities, traffic sources and geological background, and their contribution rates are 48.00%, 19.66% and 15.97%, respectively. According to single factor pollution index, Fe and Mn have different degrees of pollution, while other heavy metals generally are pollution-free. And according to the comprehensive pollution index, the water quality of the main stream is better than that of the tributaries, the downstream tributaries are highly polluted and the upstream tributaries are slightly polluted, both are mainly affected by Fe and Mn. The health risk caused by heavy metals in the surface water is generally controllable, and the health risk value of each heavy metals can be ranked as As > Cd > Fe > Cu > Pb > Zn > Mn. Except that the health risk of As at some points of downstream tributaries is higher than the maximum acceptable risk value, the health risk of carcinogen Cd and non-carcinogens Cu, Pb, Fe, Mn and Zn are far lower than the maximum acceptable risk value.
-

-
表 1 重金属污染评价标准
Table 1. Evaluation criteria for heavy metal pollution
Pi Pn 污染程度
Degree of contaminationPi ≤ 1 Pn ≤ 0.7 安全 1< Pi ≤ 2 0.7 < Pn ≤ 1 警戒 2<Pi≤ 3 1<Pn≤ 2 轻度污染 Pi > 3 Pn > 2 高度污染 表 2 重金属毒理学参数
Table 2. Toxicological parameters of the heavy metals
化学致癌物
Carcinogenqi/[mg·(kg·d)−1] 化学非致癌物
Non-carcinogenRFDi/[mg·(kg·d) −1] As 15 Fe 0.7 Cd 6.1 Pb 0. 001 4 Cu 0. 005 Zn 0. 3 Mn 1.4 表 3 小黄泥河流域重金属质量浓度统计特征1)
Table 3. Statistical characteristics of heavy metal concentration in Xiaohuangni River basin
样点
Samples统计参数
Statistical parameterspH As Cd Cu Fe Mn Zn Pb 干流
Main streams
(N=12)最小值 7.21 0.25 0.02 0.36 55.09 1.50 3.35 0.07 最大值 8.48 3.47 0.06 1.96 469.00 46.90 43.20 0.59 平均值 8.01 1.60 0.02 1.39 241.66 25.93 16.35 0.34 标准偏差 0.34 1.08 0.01 0.44 145.85 16.08 11.61 0.17 变异系数 4.20 67.90 53.52 31.42 60.35 62.00 71.02 49.89 上游支流
Upstream tributaries
(N=9)最小值 7.68 0.08 0.02 0.62 40 1.5 5.35 0.16 最大值 8.44 3.09 0.03 5.70 2306.58 15.2 29.18 1.17 平均值 7.98 1.26 0.02 2.55 639.71 5.18 14.05 0.49 标准偏差 0.24 1.19 0.01 1.66 683.49 5.01 7.26 0.28 变异系数 3.03 94.31 25.06 65.15 106.84 96.64 51.70 58.33 中游支流
Midstream tributaries
(N=13)最小值 7.11 0.51 0.015 0.51 27.8 1.45 7.06 0.1 最大值 8.45 5.66 0.09 6.31 1567 416 41 0.71 平均值 7.77 2.67 0.02 1.46 311.75 67.92 18.67 0.26 标准偏差 0.39 1.10 0.02 1.47 410.53 107.48 10.11 0.19 变异系数 5.01 41.36 96.23 100.64 131.68 158.26 54.13 72.31 下游支流
Downstream tributaries
(N=24)最小值 6.48 0.4 0.015 0.41 17.1 0.96 3.99 0.11 最大值 8.86 21.5 0.15 13.4 6471 1201 142 3.94 平均值 8.06 3.19 0.04 3.19 1429.50 254.97 36.16 0.54 标准偏差 0.50 4.20 0.04 3.37 1806.85 330.83 35.73 0.78 变异系数 6.16 131.43 100.39 105.67 126.40 129.75 98.81 143.00 全流域
Whole basin
(N=58)最小值 6.48 0.075 0.015 0.362 17.1 0.96 3.35 0.069 最大值 9.14 21.5 0.15 13.4 6471 1201 142 3.94 平均值 7.98 2.45 0.03 2.33 810.66 126.90 24.71 0.43 标准偏差 0.43 2.94 0.03 2.51 1323.39 244.77 26.11 0.54 变异系数 5.34 120.13 104.67 107.87 163.25 192.89 105.67 125.39 地表水水质标准 6—9 50 5 1000 300 100 1000 50 pH为无量纲,其他指标为μg·L−1,变异系数为%.
pH is dimensionless, other indicators are μg·L−1, and the coefficient of variation is %.表 4 小黄泥河流域地表水重金属浓度均值与其它水体比较(μg·L−1)
Table 4. Comparison of heavy metal concentrations in surface water of Xiaohuangni River basin with other water bodies
Fe Mn Zn Cu As Cd Pb 本研究 810.66 126.9 24.71 2.33 2.45 0.03 0.43 贵州普定水库[10] ─ ─ ─ 3.332 0.036 0.334 4.97 贵州摆沙河流域[12] 68479 2745 184 ─ 11.1 ─ ─ 贵州红枫湖[27] 247 42 33.1 1.24 ─ 0.11 4.63 东江淡水河流域[28] ─ 305.00 151.5 67.5 ─ ─ 15 东江[28] ─ 145 30 8 ─ ─ 8.5 柳江流域[26] 150. 85 45. 75 10. 78 17. 78 0. 99 1. 28 2. 44 龙江中下游[29] ─ ─ 2.39 0.90 1.31 0.05 0.34 西江干流中下游[29] ─ ─ 3.14 1.28 1.66 0.03 0.35 注:—表示无数据. —no data. 表 5 小黄泥河流域地表水重金属浓度相关关系1)
Table 5. Correlation coefficients between major ions of river water in Xiaohuangni River basin
As Cd Cu Fe Mn Zn Pb As 1 Cd 0.60** 1 Cu 0.71** 0.78** 1 Fe 0.70** 0.71** 0.87** 1 Mn 0.44** 0.64** 0.44** 0.60** 1 Zn 0.03 0.32* 0.15 0.22 0.19 1 Pb 0.13 0.33* 0.52** 0.38** 0.11 0.01 1 **表示在0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关,*表示在 0.05 水平(双侧)上显著相关.
** means significant correlation at the 0.01 level (two-sided), * means significant correlation at the 0.05 level (two-sided).表 6 研究区水样旋转成分矩阵
Table 6. Rotational composition matrix of water samples
F1 F2 F3 As 0.86 0.04 −0.17 Cd 0.81 0.26 0.30 Cu 0.79 0.52 0.03 Fe 0.86 0.33 0.12 Mn 0.76 −0.12 0.23 Zn 0.10 0.01 0.97 Pb 0.12 0.96 0.01 特征值 3.36 1.38 1.12 贡献率/% 48.00 19.66 15.97 累积贡献率/% 48.00 67.66 83.63 表 7 饮水途径化学致癌物质和化学非致癌物质所致健康危害风险值(a−1)
Table 7. Health risk caused by chemical carcinogens and non-carcinogens via drinking water(a−1)
重金属
Heavy metals项目 干流(N=12)
Main steams上游支流(N=9)
Upstream tributaries中游支流(N=13)
Midstream tributaries下游支流(N=24)
Downstream tributaries成人
Adults儿童
Children成人
Adults儿童
Children成人
Adults儿童
Children成人
Adults儿童
Children致癌风险 As(×10−5) 范围 0.18—2.54 0.23—3.25 0.06—2.27 0.07—2.9 0.38—4.15 0.48—5.3 0.29—15.8 0.37—20.1 均值 1.17 1.49 0.93 1.18 1.96 2.5 2.34 2.99 Cd(×10−8) 范围 4.47—16.4 5.71—20.9 4.47—10.1 5.71—12.9 4.47—26.8 5.71—34.2 4.47—44.7 5.71—57.1 均值 6.21 7.93 7.35 9.39 6.19 7.9 13.2 16.8 非致癌风险 Cu(×10−10) 范围 0.35—1.92 0.45—2.45 0.61—5.58 0.77—7.12 0.50—6.17 0.64—7.87 0.40—13.1 0.51—16.7 均值 1.36 1.73 2.49 3.18 1.42 1.82 3.12 3.98 Pb(×10−10) 范围 0.24—2.06 0.31—2.63 0.55—40.7 0.70—5.19 0.35—24.8 0.45—3.16 0.38—13.8 0.49—17.6 均值 1.19 1.52 1.7 2.17 0.92 1.17 1.9 2.42 Fe(×10−10) 范围 0.39—3.27 0.49—4.18 0.28—16.1 0.36—20.6 0.20—10.9 0.25—14.0 0.12—45.2 0.15—57.7 均值 1.69 2.15 4.47 5.7 2.18 2.78 9.98 12.7 Mn(×10−12) 范围 0.52—16.4 0.67—20.9 0.50—5.31 0.67—6.77 0.51—145 0.65—185 0.34—419 0.43—535 均值 9.05 11.6 1.81 2.31 23.7 30.3 89 114 Zn(×10−12) 范围 5.46—70.4 6.96—89.8 8.71—47.5 11.1—60.7 11.5—66.8 14.7—85.3 6.5—231 8.3—295 均值 26.6 34 22.9 29.2 30.4 38.8 58.9 75.2 总风险(×10−5) 范围 0.19—2.55 0.24—3.25 0.06—2.28 0.08—2.91 0.38—4.15 0.48—5.3 0.30—15.8 0.38—20.2 均值 1.18 1.5 0.93 1.19 1.96 2.51 2.35 3 -
[1] YUAN G L, LIU C, CHEN L, et al. Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(1): 336-345. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.039 [2] 张伟燕, 马龙, 吉力力·阿不都外力, 等. 博尔塔拉河地表水重金属来源分析及其污染评价 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(7): 100-106. ZHANG W Y, MA L, JILILI Abuduwaili, et al. Source analysis and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface water of Bortala River, Northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(7): 100-106(in Chinese).
[3] 温泉, 赵艳民, 曹伟, 等. 潮白河中游沉积物中重金属分布、来源及生态风险评估 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(3): 599-607. WEN Q, ZHAO Y M, CAO W, et al. Distribution characteristics, sources and potential ecological risks of heavy metal pollution in the middle reaches of chaobai river [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(3): 599-607(in Chinese).
[4] YANG Q Q, LI Z Y, LU X N, et al. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 642: 690-700. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.068 [5] OUYANG W, WANG Y D, LIN C Y, et al. Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 637/638: 208-220. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.434 [6] 刘昭, 周宏, 曹文佳, 等. 清江流域地表水重金属季节性分布特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1): 175-183. LIU Z, ZHOU H, CAO W J, et al. Seasonal distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of Qingjiang River [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1): 175-183(in Chinese).
[7] 陈俊华, 章艳红, 沈威, 等. 抚河南昌段重金属空间分布特征及来源分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11): 4936-4944. CHEN J H, ZHANG Y H, SHEN W, et al. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in Nanchang section of the Fuhe River [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11): 4936-4944(in Chinese).
[8] 王漫漫, 陆昊, 李慧明, 等. 太湖流域典型河流重金属污染和生态风险评估 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(10): 2025-2035. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.10.2016022301 WANG M M, LU H, LI H M, et al. Pollution level and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in typical rivers of Taihu Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(10): 2025-2035(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.10.2016022301
[9] 钟明, 万云, 万安, 等. 沙颍河流域沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(7): 1857-1864. ZHONG M, WAN Y, WAN A, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Shaying River [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(7): 1857-1864(in Chinese).
[10] 旷攀, 李秋华, 金爽, 等. 贵州高原普定水库水环境重金属的时空分布特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(3): 576-588. KUANG P, LI Q H, JIN S, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of heavy metals in water environment of Puding Reservoir in Guizhou Province and risk assessment [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(3): 576-588(in Chinese).
[11] 谭冰, 王铁宇, 朱朝云, 等. 洋河流域万全段重金属污染风险及控制对策 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(2): 719-726. TAN B, WANG T Y, ZHU Z Y, et al. Risk assessment and countermeasures of heavy metals pollution in Wanquan segment of Yanghe River [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(2): 719-726(in Chinese).
[12] 刘伟, 刘胜华, 秦文, 等. 贵州煤矿集中开采区地表水重金属污染特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(7): 1788-1799. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019042903 LIU W, LIU S H, QIN W, et al. The characteristics of heavy metals pollution in surface water at the intensive coal mining area in Guizhou [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(7): 1788-1799(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019042903
[13] 马先杰, 陆凤, 陈兰兰, 等. 贵州锰矿区地表水体重金属污染及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(11): 191-197. MA X J, LU F, CHEN L L, et al. Heavy metal pollution of surface water-bodies in guizhou's Manganese mining areas: Characteristics and ecological risk assessment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(11): 191-197(in Chinese).
[14] 熊燕, 宁增平, 刘意章, 等. 南盘江流域(云南段)水系沉积物中重金属含量分布特征及其污染状况评价 [J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(2): 171-178. XIONG Y, NING Z P, LIU Y Z, et al. Distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in sediments in the nanpan river basin (Yunnan section) [J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(2): 171-178(in Chinese).
[15] 杨思林. 珠江上游沉积物与土壤金属元素地球化学特征研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2014. YANG S L. Study on geochemical characteristics of metal elements in sediments and soil in the upper reaches of Pearl River[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[16] 姚波, 杨爱萍, 陈华毅, 等. 珠江流域上游云贵地区农田土壤重金属污染状况及其风险性分析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(10): 2259-2266. YAO B, YANG A P, CHEN H Y, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution and risk assessment of agricultural soils in the Yunnan-Guizhou area, Upper Pearl River Basin [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(10): 2259-2266(in Chinese).
[17] 陈晓鸿, 李强, 喇优抓. 南盘江流域曲靖段土壤及农作物中重金属污染特征与生态风险评价 [J]. 安徽农学通报, 2020, 26(15): 126-132. CHEN X H, LI Q, LA Y Z, et al. The pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the crops and soils from the Qujing section of the nanpan river [J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 26(15): 126-132(in Chinese).
[18] 李继平, 姚章民. 小黄泥河流域水资源供需分析及合理配置探讨 [J]. 人民珠江, 2003, 24(5): 21-23. LI J P, YAO Z M. Supply and demand analysis and rational allocation of water resources in Xiaonihe River Basin [J]. Pearl River, 2003, 24(5): 21-23(in Chinese).
[19] 肖文博, 王保华, 贺庆峰. 小黄泥河洪水资源利用研究 [J]. 人民珠江, 2015, 36(6): 9-11. XIAO W B, WANG B H, HE Q F. Research on utilization of flood resources in Xiao huangni river [J]. Pearl River, 2015, 36(6): 9-11(in Chinese).
[20] 涂春霖, 尹林虎, 和成忠, 等. 珠江源区小黄泥河流域地表水水化学组成特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 1885-1897. TU C L, YIN L H, HE C Z, et al. Hydrochemical composition characteristics and control factors of xiaohuangni river basin in the upper Pearl River [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 1885-1897(in Chinese).
[21] 蔡永兵, 孙延康, 孟凡德, 等. 典型金矿区入湾河流重金属的时空分布特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1167-1178. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020110602 CAI Y B, SUN Y K, MENG F D, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in a river flowing into the bay in a typical gold mining area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1167-1178(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020110602
[22] 何宇, 洪欣, 闭潇予, 等. 九洲江流域水环境重金属污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(1): 240-253. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020062812 HE Y, HONG X, BI X Y, et al. Characteristics and sources of heavy metal pollution in water environment of Jiuzhou River Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(1): 240-253(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020062812
[23] 王若师, 许秋瑾, 张娴, 等. 东江流域典型乡镇饮用水源地重金属污染健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(9): 3083-3088. WANG R S, XU Q J, ZHANG X, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in typical township water sources in Dongjiang River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(9): 3083-3088(in Chinese).
[24] 林曼利, 桂和荣, 彭位华, 等. 典型矿区深层地下水重金属含量特征及健康风险评价: 以皖北矿区为例 [J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(5): 589-598. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.05.09 LIN M L, GUI H R, PENG W H, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in deep groundwater from different aquifers of a typical coal mining area: A case study of a coal mining area in northern Anhui Province [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2014, 35(5): 589-598(in Chinese). doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.05.09
[25] ADIMALLA N. Groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and potential health risks assessment: A case study from semi-arid region of south India [J]. Exposure and Health, 2019, 11(2): 109-123. doi: 10.1007/s12403-018-0288-8 [26] 张清华, 韦永著, 曹建华, 等. 柳江流域饮用水源地重金属污染与健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(4): 1598-1607. ZHANG Q H, WEI Y Z, CAO J H, et al. Heavy metal pollution of the drinking water sources in the Liujiang River Basin, and related health risk assessments [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4): 1598-1607(in Chinese).
[27] 田林锋, 胡继伟, 秦樊鑫, 等. 重金属元素在贵州红枫湖水体中的分布特征 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(3): 481-489. TIAN L F, HU J W, QIN F X, et al. Distribation of heavy metal elements in the water body from Lake Hongfeng [J]. China Environmental Science, 2011, 31(3): 481-489(in Chinese).
[28] 王丽, 陈凡, 马千里, 等. 东江淡水河流域地表水和沉积物重金属污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(9): 1671-1684. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.09.2015012703 WANG L, CHEN F, MA Q L, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water and sediment in Danshui River of Dongjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(9): 1671-1684(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.09.2015012703
[29] 文泽伟. 龙江—柳江—西江流域的水化学特征和重金属污染研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016. WEN Z W. Study on hydrochemistry characteristics and heavy metal pollution in the Longjiang-Liujiang-Xijiang watershed[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese).
[30] ZHOU J, FENG K, PEI Z P, et al. Pollution assessment and spatial variation of soil heavy metals in Lixia River Region of Eastern China [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2016, 16(3): 748-755. doi: 10.1007/s11368-015-1289-x [31] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 等. 毕节市北部岩溶地下水水化学特征及影响因素的多元统计分析 [J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4): 1446-1456. YUAN J F, DENG G S, XU F, et al. The multivariate statistical analysis of chemical characteristics and influencing factors of Karst groundwater in the northern part of Bijie City, Guizhou Province [J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(4): 1446-1456(in Chinese).
[32] 沈杨, 何江涛, 王俊杰, 等. 基于多元统计方法的地下水水化学特征分析: 以沈阳市李官堡傍河水源地为例 [J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 440-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.024 SHEN Y, HE J T, WANG J J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater based on multivariate statistical analyses: Taking the liguanpu ripanian wellhead area in Shenyang City for example [J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(2): 440-447(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.02.024
[33] 田利, 谢红东, 张学东. 贵州盘县土城向斜南西翼二叠系龙潭组地球化学特征及意义 [J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2014, 26(7): 15-20,32. TIAN L, XIE H D, ZHANG X D. Permian Longtan formation geochemical characteristics and significance in southwest limb of Tucheng syncline, Panxian, Guizhou [J]. Coal Geology of China, 2014, 26(7): 15-20,32(in Chinese).
[34] 周逃涛, 张晓丽, 齐亚林, 等. 滇东老厂地区龙潭组页岩矿物组成特征及脆性分析 [J]. 矿产与地质, 2019, 33(04): 670-675. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2019.04.013 ZHOU T T, ZHANG X L, QI Y L, et al. Mineral composition and brittleness analysis of shale of Longtan Formation in Laochang area, East Yunnan [J]. Mineral resources and geology, 2019, 33(04): 670-675(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2019.04.013
[35] 孙国敏, 王春雷, 张淑霞. 黑龙江省地表水铁锰超标成因分析 [J]. 东北水利水电, 2013, 31(4): 34-35,40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2013.04.016 SUN G M, WANG C L, ZHANG S X. Cause analysis of excessive iron and Manganese in surface water of Heilongjiang Province [J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast China, 2013, 31(4): 34-35,40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2013.04.016
[36] 林德洪, 刘汉武, 史绪山. 贵州鬃岭煤矿区水环境污染特征及成因分析 [J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(5): 186-195. LIN D H, LIU H W, SHI X S. Characteristics and cause analysis of water pollution in zongling coal mining area, Guizhou [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 28(5): 186-195(in Chinese).
[37] 陆青锋, 吴士豪, 秦身钧, 等. 贵州盘县矿区煤中伴生元素的地球化学特征 [J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2017, 45(10): 169-175. LU Q F, WU S H, QIN S J, et al. Geochemical features of associated elements in coal from Panxian Minefield of Guizhou [J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2017, 45(10): 169-175(in Chinese).
[38] 秦身钧, 高康, 王金喜, 等. 黔西南盘县火烧铺和金佳矿区晚二叠世煤中伴生元素的地球化学特征 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(6): 1507-1516. QIN S J, GAO K, WANG J X, et al. Geochemistry of the associated elements in the Late Permian Coal from the Huoshaopu and Jinjia Mines, Southwestern Guizhou [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(6): 1507-1516(in Chinese).
[39] 杨建业. 贵州普安矿区晚二叠世煤中微量元素的质量分数和赋存状态 [J]. 燃料化学学报, 2006, 34(2): 129-135. YANG J Y. Contents and occurrence modes of trace elements in the Late Permian coals from Puan Coalfield, Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2006, 34(2): 129-135(in Chinese).
[40] 李学先. 酸性矿山废水影响下喀斯特流域水文地球化学特征及演化规律研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018. LI X X. Study on hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution rules of Karst Basin under the effects of acid mine waste water[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2018(in Chinese).
[41] 王增辉. 鲁西南平原区大气干湿沉降元素输入通量及来源浅析: 以巨野县为例 [J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4): 839-846. WANG Z H. An analysis of the input flux and source of elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of southwest plain of Shandong: A case study of Juye County [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4): 839-846(in Chinese).
[42] 郭锋, 申慧芳, 樊文华. 大同市矿区中学地表灰尘重金属粒级效应及健康风险评估 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(1): 162-166. GUO F, SHEN H F, FAN W H. Particle size distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metal of surface dust in middle school of mining district in Datong City [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(1): 162-166(in Chinese).
[43] 韩润生, 吴鹏, 张艳, 等. 西南特提斯川滇黔成矿区富锗铅锌矿床成矿理论研究新进展 [J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(2): 554-573. HAN R S, WU P, ZHANG Y, et al. New research progress in metallogenic theory for rich Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Triangle (SYGT) area, southwestern Tethys [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(2): 554-573(in Chinese).
[44] 熊伟, 程鹏林, 周高, 等. 黔西北铅锌成矿区成矿金属来源的铅同位素示踪 [J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(4): 425-429. XIONG W, CHENG P L, ZHOU G, et al. The origin of ore-forming metals in northwestern Guizhou Pb-Zn metallogenic district constrained by Pb isotopes [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(4): 425-429(in Chinese).
[45] 马金凤. 微量元素铁与一些疾病关系的研究 [J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 1999, 16(3): 72-74. MA J F. Study on the relationship between trace iron and some diseases [J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 1999, 16(3): 72-74(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: