-
浮游生物是湖泊水库等水体中水生生物的重要组成部分,在水域生态系统的能量流动、物质循环和信息传递中起着至关重要的作用[1-2]. 一方面,作为水生态系统的初级生产者,浮游生物在湖泊水库生态系统中扮演着重要角色;另一方面,由于自身对环境因子变化响应敏感且迅速,浮游生物可作为反映水质变化的“指示剂”和水质评估的依据[3]. 因此,关注浮游生物的群落组成及变化对于揭示湖泊富营养化水平以及水质变化具有重要作用[4-5].
东平湖作为山东省第二大淡水湖泊,是黄河下游唯一重要蓄滞洪区、南水北调的重要枢纽、京杭大运河的重要节点,其水质质量对黄河流域的环境保护和高质量发展具有重要影响. 近年来,受流域内污染物输入以及南水北调东线工程影响,东平湖水质以及浮游生物群落发生明显变化[6-7]. Liu等[8]利用多元统计方法探讨了东平湖表层沉积物中硅藻类群与环境变量的关系,结果显示2014年东平湖全年均处于富营养化状态,生态污染较为严重. 董贯仓等[9]研究发现,东平湖水体多以蓝藻门、绿藻门及硅藻门为优势种,东平湖调水工程可通过物质带入影响水质,进而引起浮游植物量的升高. 辛未等[10]采用多样性指数法等生态评价法对2016—2017年东平湖水质与生物多样性进行评价,结果表明,东平湖浮游植物优势种群共计14种(属),以蓝藻门的伪鱼腥藻(Pseudoanabaena sp.)、拟浮丝藻(Planktothricoides sp.)为主,东平湖水质总体处于中污染水平. 高雯琪等[11]探究了调水后东平湖浮游动物时空响应,结果表明,东平湖水体多以桡足类(Copepoda, Cop.)、枝角类(Cladocerans, Cla.)及轮虫(Rotifers)为优势种,调水在一定程度上影响了东平湖浮游动物的群落结构,是东平湖浮游动物出现小型化趋势的可能原因之一,同时调水也有利于东平湖的水质改善. 然而,目前有关东平湖浮游生物的研究成果主要侧重于浮游植物或浮游动物单一群落,有关东平湖浮游植物与浮游动物两者相结合的研究较少.
本研究在前人的研究基础上,综合运用Shannon多样性指数法、Pielou均匀度指数法、优势度指数法、Margalef丰富度指数法等多种生态评价法以及Pearson相关性分析法与冗余分析法(RDA)等多元统计方法,分析东平湖秋季浮游植物以及浮游甲壳动物群落结构特征,探讨东平湖浮游生物群落结构的环境驱动因子,以期为东平湖湖区水质污染的治理与防控以及保障用水安全提供理论参考.
-
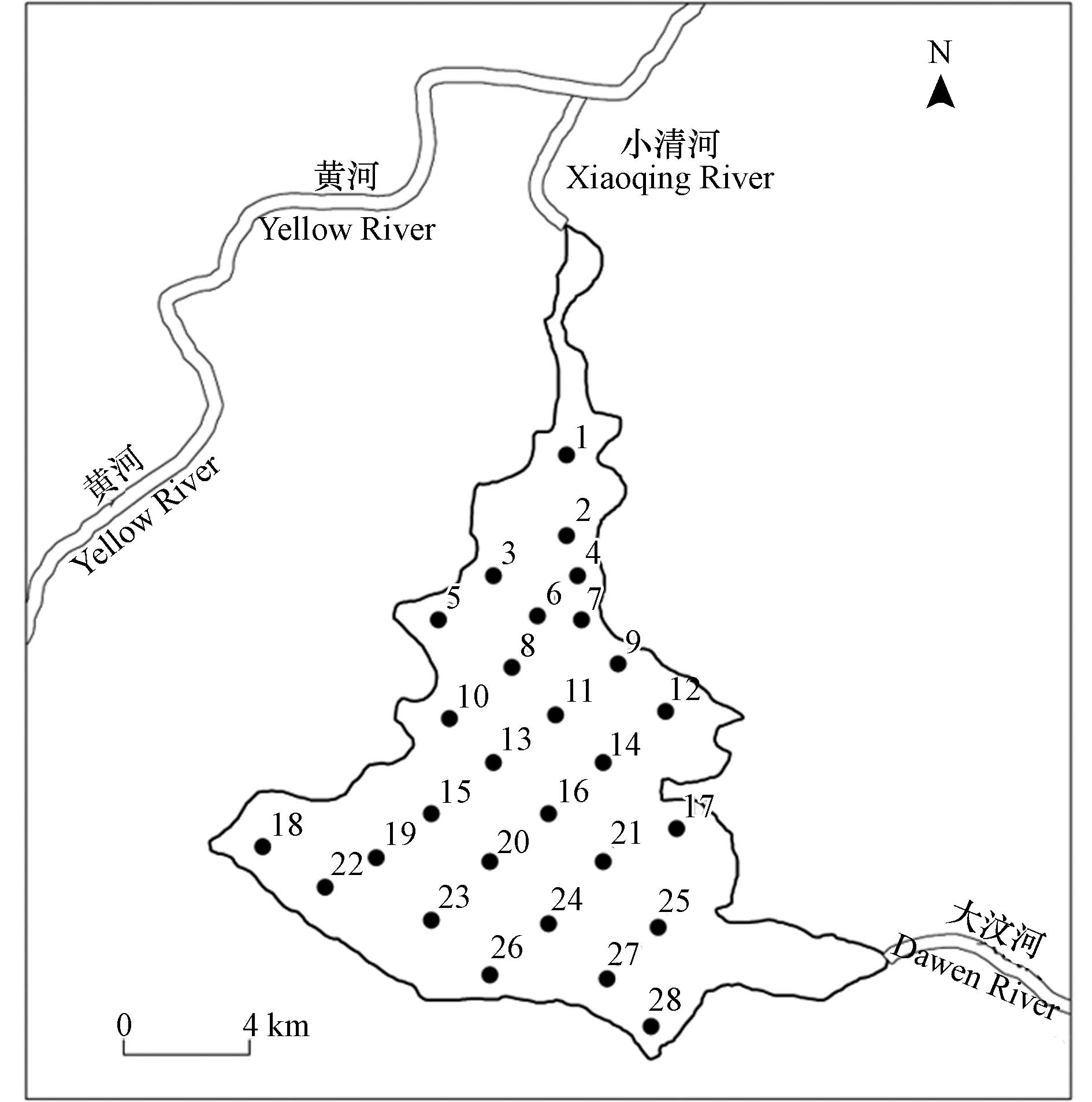
东平湖(116°00′—116°30′ E、35°30′—36°20′ N)位于山东省泰安市东平县,是山东省第二大淡水湖,黄河下游仅存的天然湖泊. 东平湖北与黄河通过小清河连接,东与主要补给源大汶河相连,且除特殊年份湖区开闸泄洪以及南水北调蓄水外,大汶河是湖区唯一入湖径流(图1). 东平湖总面积627 km2,分为新、老两个湖区. 老湖区面积209 km2,常年蓄水,即一般所称的东平湖,其中水域面积124 km2,多年平均水深2—4 m,是典型的浅水湖泊;新湖区为滞洪区,面积418 km2,大部分为农耕地,除特殊洪水年份,常年无水[6,12]. 本文研究区域为常年蓄水的老湖区.
东平湖属温带大陆性半湿润季风气候区,四季分明. 湖区水生植被丰富,其中以菹草、菱角等分布面积较广,且主要分布于湖区北部及东岸地带[13-14]. 丰富的水生植被为淡水鱼类、虾、蟹等提供了充足的食物以及多变的栖息环境,使得东平湖成为山东省重要的水产生产基地. 2002年,国务院正式批复《南水北调总体规划》,东平湖被确定为南水北调东线工程最后一个调蓄湖和胶东地区输水干线工程的起点湖;2013年,东平湖作为南水北调东线调蓄湖泊开始调水,且调水时间为每年12月至次年5月. 自此,东平湖对保障华北和胶东地区用水安全起到至关重要的作用.
-
于2021年9月底对全湖进行采样. 结合东平湖地理环境特征以及均匀性原则,全湖共设置采样点28个(图1). 各采样点样品采集包括水样及浮游生物(浮游植物与浮游甲壳动物)样品. 水样采集采用分层取样法,将水样按实际水深分为上、中、下层,用5 L采水器分别在3个层位上取样后混合均匀. 其中,取500 mL水样送至实验室进行水质指标检测;取1 L水样于聚乙烯瓶中,加入10 mL鲁哥试剂避光静置72 h,虹吸上清液浓缩至30 mL,用于浮游植物定量分析. 浮游甲壳动物定量采集使用5 L采水器分别在上、中、下层采集共15 L水,并过25号浮游生物网,将滤出液收集于聚乙烯小瓶中加入4%甲醛溶液保存. 浮游植物与浮游动物采集样液沉淀浓缩后分别使用0.1 mL和1 mL计数框进行镜检、计数和鉴定.
本研究分析的主要水质指标有总氮(TN)、硝态氮(NO3--N)、亚硝态氮(NO2--N)、氨氮(NH4+-N)、总磷(TP)、磷酸盐(PO4−-P)、叶绿素(Chl.a)、悬浮物浓度(SS)等. 水样的预处理及分析均参照国家相关标准方法. 其中,TN和TP浓度均采用过硫酸盐氧化法并通过紫外分光光度计UV-2450(HJ 636-2012)比色测定,NH4+-N浓度采用纳氏试剂光度法(HJ 535-2009)测定,NO3−-N浓度采用紫外分光光度法(HJ 636-2012)测定,NO2−-N浓度采用重氮-偶合分光光度法测定,Chl.a浓度采用热乙醇法提取,PO4−-P浓度采用钼蓝法测定,SS采用过滤-称重法测定,CODMn采用高锰酸钾指数法测定,总有机碳(TOC)浓度采用外加热-重铬酸钾氧化法测定. 透明度(SD)采用塞式罗盘测定,水温(Tem)、溶解氧(DO)、pH、盐度(Sal)、氧化还原电位(ORP)及电导率(SPC)等采用水质多参数仪(YSI-MP556)现场测定.
-
本文主要采用综合营养状态指数(TLI)[15]对水质进行综合评价.
-
采用Shannon-Wiener多样性指数[16]、Pielou均匀度指数[17]、优势度指数[18]、Margalef丰富度指数[19]分析东平湖浮游生物群落特征.
生物多样性是群落的主要特征之一,Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')能够反映出群落结构的复杂程度,指数越大,表明群落结构越复杂和稳定;Pielou 均匀度指数(J)指一个群落或生境中全部物种个体数目的分配状况,能够反映出各物种个体数目分配的均匀程度,指数越大,则群落越稳定,多样性越高;优势度指数(Y)是在群落的类群组成基础上进一步推算出来以表达群落组成状况的指标,指数越大,优势生物的生态功能越突出;Margalef丰富度指数(D)描述群落中所含物种丰富程度的数量指标,指数越大,群落丰富度越高. 各指数计算公式分别为:
式中,fi为物种i出现的频率,ni为物种i的个体数,N为全部样品的总个体数,S为样品中浮游植物物种总数,
$ {P}_{i} $ 为第 i 种生物的个体数与总体数的比值. 取优势度 Y ≥ 0.02 的物种作为优势种. 各生物多样性指数评价标准[3,10]如表1所示. -
采用SPSS 25.0软件基于Pearson相关性分析法对浮游生物群落结构特征与环境因子进行相关性分析,并运用R语言软件包进行绘图. 利用CANOCO 5.0软件包对浮游生物及环境因子进行去趋势对应分析(DCA),以探究显著影响浮游生物群落结构时空格局的驱动因子. DCA分析中,当4个轴中梯度最大值超过4,属于单峰型模型,使用典范对应分析(CCA);如果小于3,属于线性模型,使用冗余分析(RDA).
-
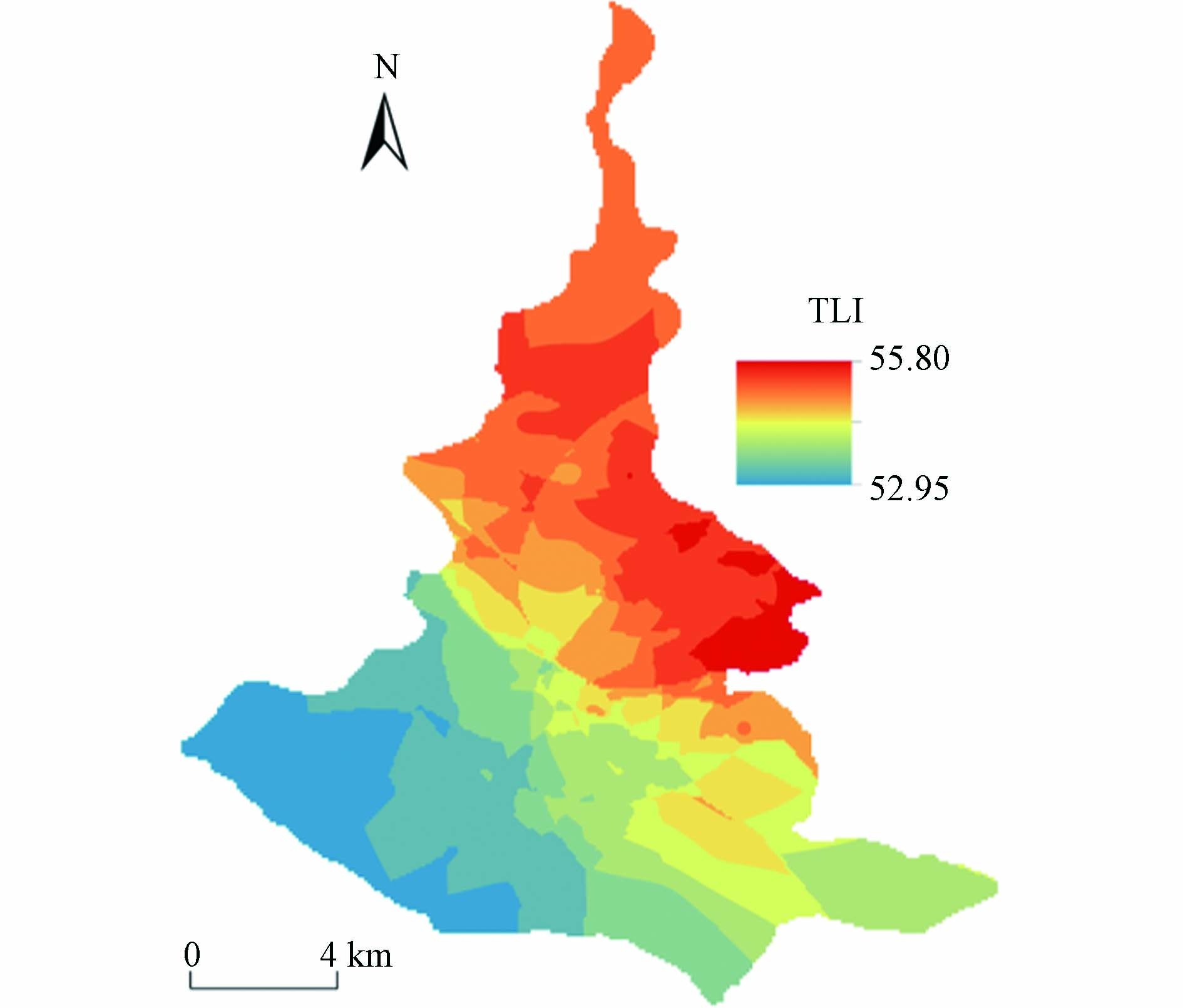
就全湖平均水平而言,东平湖秋季各水质因子平均浓度分别为3.14 mg∙L−1(TN)、2.40 mg∙L−1(NO3--N)、0.20 mg∙L−1(NH4+-N)、0.14 mg∙L−1(TP)、3.30 mg∙L−1(CODMn)、11.90 mg∙m−3(Chl.a)、0.12 mg∙L−1(NO2--N)、0.02 mg∙L−1(PO4−-P)、9.04 mg∙L−1(DO)、4.95 m(Depth)、0.73 m(SD)、9.01 mg∙L−1(TOC)、7.71(pH)、22.72 ℃(Tem)、0.83 mS∙cm−1(SPC)、271.54 mV(ORP)及0.43‰(Sal). 此外,东平湖秋季综合营养状态指数(TLI)全湖变化范围为51.05—62.26,平均值为54.31,呈轻度富营养化状态. 这与2010(TLI = 58,轻度富营养化)、2011(TLI = 50.97,轻度富营养化)、2012(TLI = 52.33,轻度富营养化)、2015(TLI = 53.83,轻度富营养化)、2017(TLI = 52.51,轻度富营养化)及2019(轻度富营养化)秋季水体营养状态相差不大[9,20-22],较2006—2010年(轻度富营养至中度富营养)较好[23]. 就空间分布而言,东平湖秋季TLI以湖区东北部较高,湖区西南部水平较低(图2).
-
本次共检出浮游植物8门73种(属). 其中,绿藻门(Chlorophyta, Chl.)种类最多,鉴定出32种,占总种数的43.8%;蓝藻门(Cyanophyta, Cya.)15种,占种类总种数的20.5%;硅藻门(Bacillariophyta, Bac.)14种,占总种数的19.2%;裸藻门(Euglenophyta, Eug.)、甲藻门(Pyrroptata, Pyr.)、金藻门(Chrysophyta, Chr.)、隐藻门(Cryptophyta, Cry.)与黄藻门(Xanthophyta, Xan.)种类数较少,分别为4种、4种、2种、1种与1种. 由于绿藻、蓝藻、硅藻 3 个门类浮游植物种类数之和超过浮游植物种类总数的80%,东平湖秋季浮游植物种类组成为绿藻-蓝藻-硅藻型.
东平湖秋季浮游植物生物密度(M)为2.30×108 cells∙L−1,其中蓝藻门的密度最大(M = 7.76×107 cells∙L−1),占比达33.71%,其次是绿藻门(M = 7.68×107 cells∙L−1)、硅藻门(M = 6.42×107 cells∙L−1)和隐藻门(M = 7.36×106 cells∙L−1),占比分别为33.37%、27.87%和3.20%. 甲藻门(M = 1.71×106 cells∙L−1)、金藻门(M = 1.09×106 cells∙L−1)、裸藻门(M = 7.46×105 cells∙L−1)、黄藻门(M = 7.20×105 cells∙L−1)的密度相对较小,占比分别为0.74%、0.47%、0.32%及0.31%. 此次监测中,容易引发蓝藻水华的微囊藻属的藻密度(M = 1.63×105 cells∙L−1)较低,且颤藻(M = 1.11×106 cells∙L−1)、束丝藻(M = 7.47×105 cells∙L−1)等常见的有害产毒蓝藻的藻密度也较低.
从东平湖秋季浮游植物生物密度的空间分布来看(图3),各样点间浮游植物密度变化范围为3.31×106—1.40×107 cells∙L−1,其中以湖区东部及东北沿岸密度较高,湖区中部与西部密度较低,且最高值与最低值相差4倍左右.
一般认为,水体营养水平状况对浮游植物种类和密度影响较大[24]. 本研究中,东平湖秋季水体TLI自湖区东北部向西南部逐渐减小(图2),使得浮游植物生物密度以湖区东北部较高、中西部较低. 东平湖秋季浮游植物结构空间差异较小,全湖浮游植物群落主要以蓝藻门、硅藻门和绿藻门为主,与辛未等[10]2016年监测结果一致. 其中,湖区北部及西南部多以蓝藻门为主,且湖区北部隐藻门等具有一定比重,多样性较为丰富,湖区南部主要以绿藻门为主,湖区东南部硅藻门占比较高,湖心区三者占比较为均衡.
以优势度Y ≥ 0.02为评价标准,本文计算了东平湖秋季浮游植物优势种及优势度值(表2). 东平湖秋季表现出多个优势种的群落结构,采样周期内浮游植物优势种共3门9种,主要为绿藻门、硅藻门和蓝藻门. 其中,绿藻门优势种数量占比最高(44.4%),蓝藻门的伪鱼腥藻(Pseudoanabaena spp.)优势度最大(Y = 0.205),其次为小环藻(Cyclotella spp.)、栅藻(Scendesmus sp.)、平裂藻 (Merismopedia sp.)、镰形纤维藻(Ankistrodesmus falcatus)、针杆藻(Synedra spp.)、小球藻(Chlorella spp.)、色球藻(Chroococcus spp.)与衣藻(Chlamydomonas spp.).
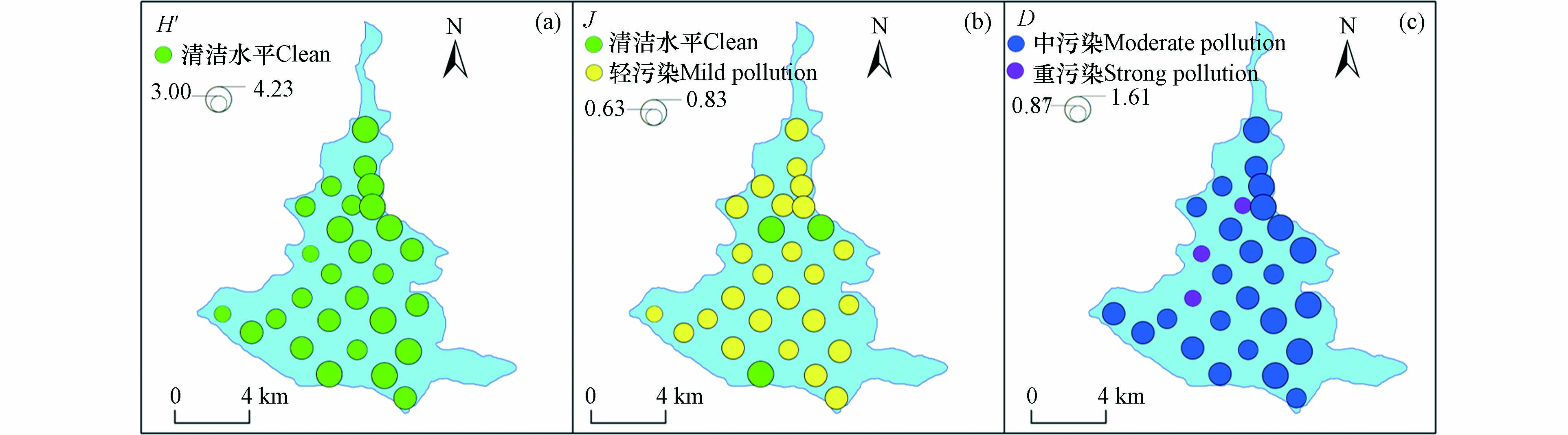
根据式(2)—(4),本文分别计算东平湖秋季各采样点浮游生物的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')、Pielou均匀度指数(J)及Margalef丰富度指数(D),各指数空间分布特征如图4所示. 总体而言,各指数评价结果存在差异. 东平湖秋季浮游植物H' 指数变化范围为3.00—4.23,均值为3.70,评价结果为清洁水平(图4a);浮游植物J指数均值为0.75,评价结果为清洁-轻污染水平(图4b);浮游植物D指数变化范围为0.88—1.61,均值为1.29,评价结果为中污染水平(图4c).
通过与前人研究进行对比,21世纪以来东平湖秋季浮游植物优势物种、生物量(B)以及H'指数如表3所示. 近年来,东平湖秋季浮游植物优势种群组成处于相对稳定的状态,即主要以蓝藻门、绿藻门及硅藻门为主,同时出现蓝藻门的伪鱼腥藻、绿藻门的小球藻、硅藻门的小环藻及针杆藻为优势种的频次较高. 本研究中,东平湖秋季浮游植物生物量为9.02 mg∙L−1,略高于2013年秋季(5.97 mg∙L−1)[25]与2017年秋季(6.42 mg∙L−1)[9],明显低于2007年秋季(23.52 mg∙L−1)[26],时间变化上总体呈先下降后上升的趋势. 2013年以来,东平湖作为南水北调东线工程调蓄水库开始蓄水,为确保北调水质,其上游调蓄湖泊加大了对水质的管理[27],使得注入东平湖的水质较好,东平湖水体富营养化程度有所降低[21,23],浮游植物生物量也随之降低.
-
本次共检出浮游甲壳动物2门10种(属),其中桡足类(Copepoda, Cop.)3种,枝角类(Cladocerans, Cla.)7种,分别占总种数的30%与70%. 浮游甲壳动物密度与生物量分别为3.34×103 cells∙L−1与6.00×103 mg∙L−1. 其中,桡足类的密度最大(M = 2.04×103 cells∙L−1),占比达60.26%,枝角类(M =1.34×103 cells∙L−1)占比为39.74%. 浮游甲壳动物生物密度以湖区中部与西北部较高,湖区东部、南部沿岸生物密度较低(图5). 浮游甲壳动物H'变化范围为0.26 — 1.98,均值为1.76,J变化范围为0.13 — 0.95,均值为0.76,D指数变化范围为0.41 — 0.93,均值为0.61,分别对应中污染、清洁以及重污染水平. 这主要是由于本次实验中浮游植物检测物种数多于浮游甲壳动物,使得浮游植物评价结果较优于浮游动物.
浮游甲壳动物密度与水体营养水平以及浮游植物密度等关系密切[31]. 一方面,某些浮游动物(如桡足类)喜生活在富营养水体中[32];另一方面,浮游植物作为浮游动物的主要食物来源,对于浮游动物群落的分布具有重要影响[33]. 当浮游植物的丰度增加到一定程度时,充足的食物来源为浮游动物的生长繁殖提供有利条件,浮游动物的密度也随之增加;当浮游植物的丰度达到较高值时,对水体的SD、DO等因子产生一定影响,导致浮游动物密度下降[34]. 本研究中,浮游甲壳动物生物密度空间分布与TLI和浮游植物生物密度空间分布存在差异,即浮游甲壳动物集中分布于浮游植物生物密度与TLI较低的湖区中部以及西部地区,而非浮游植物与TLI较高的湖区东部与东北沿岸(图2). 这可能是由于东平湖秋季浮游植物的丰度达到较高值,对水体的溶解氧等环境因子产生一定影响,从而使得在浮游植物较丰富的湖区东部浮游甲壳动物生长受到抑制.
此次监测中浮游甲壳动物优势种共计2门4种(属),其中剑水蚤(Cyclops)优势度最高(Y = 0.305),其次为象鼻溞 (Bosmina spp.)、无节幼体(Nauplius)和网纹溞属 (Ceriodaphnia)(表2). 高雯琪等[11]对2016年秋季浮游动物优势种研究发现,东平湖水体多以桡足类、枝角类及轮虫为优势种,其中主要以真剑水蚤、剑水蚤、四齿单趾轮虫等为主;侯莉等[29]对2020年东平湖生物多样性研究发现,东平湖浮游动物主要以广布中剑水蚤、桡足幼体、无节幼体、汤匙华哲水蚤、枝角幼体、秀体溞、长额象鼻溞、针簇多肢轮虫、矩形龟甲轮虫等为优势种. 结合本研究来看,近年来东平湖秋季浮游甲壳动物优势种群组成主要以桡足类的剑水蚤为主,表明该种群变化一直处于相对稳定的状态.
-
通过对东平湖秋季浮游植物9个优势物种以及浮游甲壳动物4个优势物种进行DCA分析,由于排序轴梯度长度最大值小于3,因此本文采用线性模型(RDA)对东平湖秋季浮游生物群落特征的环境驱动因子进行分析. 通过对13个优势物种与TN、TP、Tem、DO等10个环境因子以及生物多样性指数、生物量(B)等进行RDA排序分析,采用蒙特卡拟合方法分别对浮游植物、浮游甲壳动物与环境因子间关系进行显著性检验,分析结果如图6所示.
对浮游植物而言,轴Ⅰ和轴Ⅱ分别解释了36.49%和3.47%的浮游植物优势种与环境因子关系;对浮游甲壳动物而言,轴Ⅰ和轴Ⅱ分别解释了18.55%和4.90%的优势种与环境因子关系,表明本次排序分析较好地解释了优势种与环境因子的关系. 经过筛选,对浮游植物及浮游甲壳动物群落结构多样性变化起重要作用的环境影响因子分别为TN与DO. 其中,TN解释率为 15.3%(P = 0.024,F = 4.7),DO解释率为14.4%(P = 0.03,F = 4.1). TN作为浮游植物生长繁殖的必需物质,影响着浮游植物的生长及生物量. 本研究中TN与衣藻等优势代表物种以及浮游植物群落的密度和生物量具有较高正相关性(图7),表明水体中TN浓度的增加会导致浮游植物密度的升高、浮游植物生物量增加及群落丰富度的增加. DO与pH、PO4--P具有协同影响作用,三者主要对象鼻溞等代表物种的密度及浮游甲壳动物生物量、物种数和浮游植物密度总量等指标产生较高正相关影响(图6),对浮游甲壳动物丰度及生物量的变化起重要作用.
-
通过对东平湖2021年9月份全湖28个采样点进行水样采集与检测,采用综合营养状态指数法、生态多样性指数法、相关性分析法以及冗余分析法等多种分析方法,本文系统分析了东平湖秋季浮游植物与浮游甲壳动物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的关系. TLI全湖平均值为54.31,呈轻度富营养化状态,且空间分布呈自湖区东北部向西南部逐渐递减趋势. 此次共检出浮游植物8门73种(属),浮游甲壳动物2门10种(属),其中浮游植物主要以绿藻、蓝藻和硅藻为主,浮游甲壳动物为桡足类和枝角类. 浮游植物生物密度空间分布与TLI相似,呈湖区东部与东北岸较高、中西部较低格局. 以优势度 Y ≥ 0.02 为评价标准,东平湖秋季表浮游植物优势种共9种,以蓝藻门的伪鱼腥藻(Pseudoanabaena spp)优势度最大(Y = 0.205),浮游甲壳动物优势种为4种,以剑水蚤(Cyclops)优势度最高(Y = 0.305). 东平湖秋季浮游植物Shannon-Wiener 多样性指数、Pielou均匀度指数以及Margalef 丰富度指数分别为3.70、0.75与1.29,其生态多样性污染评价结果分别为清洁水平、轻污染水平与中污染水平. 通过对浮游生物优势物种与环境因子以及生物多样性指数进行RDA排序分析与相关性分析,结果显示,TN与DO分别为影响东平湖浮游植物与浮游甲壳动物生长的主要环境驱动因子.
东平湖秋季浮游生物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系
Plankton community characteristics and its relationship with environmental factors in the autumn of Dongping Lake, China
-
摘要: 作为黄河下游仅存天然湖泊以及南水北调东线工程重要枢纽,东平湖生态环境安全对黄河流域生态环境保护与中国北方供水安全起到重要作用. 为明确东平湖秋季浮游生物群落结构特征及环境驱动因子,于2021年9月对全湖28个采样点进行水样采集与检测,并采用综合营养状态指数法、生态多样性指数法、相关性分析法以及冗余分析法等多种分析方法进行了分析研究. 此次研究共检出浮游植物8门73种(属),浮游甲壳动物2门10种(属),其中浮游植物主要以绿藻、蓝藻和硅藻为主,浮游甲壳动物主要以桡足类和枝角类为主. 浮游植物中,蓝藻门的伪鱼腥藻(Pseudoanabaena spp.)优势度最大(Y = 0.205),浮游甲壳动物中则以剑水蚤(Cyclops)优势度最高(Y = 0.305). 东平湖秋季浮游植物生物密度空间分布与综合营养状态指数(TLI)具有较强相关性,高值均分布于湖区东部与东北岸,而湖区中、西部较低. 浮游植物Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Pielou均匀度指数以及Margalef丰富度指数分别为3.70、0.75与1.29,其生态多样性污染评价结果分别为清洁水平、轻污染水平与中污染水平. 冗余分析结果表明,TN为影响东平湖浮游植物生长的主要环境驱动因子,DO为影响东平湖浮游甲壳动物生长的主要环境驱动因子.Abstract: As the only natural lake in the lower Yellow River and an important hub of the eastern route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, its ecological environment security has great impacts on the ecological environment protection in the Yellow River basin and the security of water supply in the northern China. In order to clarify the plankton community characteristics and its environmental driving factors in the autumn of Dongping Lake, water samples from 28 sampling sites were collected in September 2021, and the comprehensive trophic level index method, ecological diversity index method, correlation analysis and redundancy analysis were used. In this study, a total of 73 taxa of phytoplankton (genera or species) in 8 phyla and 10 taxa of crustacean zooplankton (genera or species) in 2 phyla were identified among which Chlorophyta, Cyanophyta and Bacillariophyta were the main phytoplankton, and Copepoda and Cladocerans were the main crustacean zooplankton. Among phytoplankton, Pseudoanabaena spp had the highest dominance (Y = 0.205), and Cyclops had the highest dominance (Y = 0.305) in crustacean zooplankton. The comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) and the spatial distribution of the biological density of phytoplankton in the autumn of Dongping Lake was strongly correlated, with high values in the east part and northeast bank of the lake and low values in the center and west lake areas. The Shannon-Wiener diversity index, Pielou evenness index and Margalef richness index of phytoplankton were 3.70, 0.75 and 1.29, corresponding to the pollution conditions of clean, light pollution and moderate pollution, respectively. Redundancy analysis revealed that TN and DO were the main environmental driving factors affecting the growth of phytoplankton and crustacean zooplankton, respectively, in the autumn of Dongping Lake.
-
Key words:
- Dongping Lake /
- plankton /
- community characteristics /
- environmental driving factor.
-

-
表 1 不同生物多样性指数评价标准
Table 1. Evaluation criteria of different biodiversity indices
H' 水质类型
Water qualityJ 水质类型
Water qualityD 水质类型
Water qualityH' > 3 清洁水平 J > 0.8 清洁水平 D > 4 清洁水平 2 ≤ H' ≤ 3 β -中污染型 0.5 ≤ J ≤ 0.8 轻污染型 3 ≤ D ≤ 4 轻度污染型 1 ≤ H' ≤ 2 α -中污染型 0.3 ≤ J ≤ 0.5 β -中污染型 1 ≤ D ≤ 3 中度污染型 H' < 1 重污染型 0.1 ≤ J < 0.3 α -中污染型 0 ≤ D < 1 重度污染型 表 2 东平湖秋季浮游生物优势种与优势度
Table 2. Dominant species and degree of dominance for plankton in autumn of Dongping Lake
优势种(属)
Dominant speciesY 浮游植物 蓝藻门 色球藻 (Chroococcus spp.) 0.045 平裂藻 (Merismopedia sp.) 0.058 伪鱼腥藻 (Pseudoanabaena spp.) 0.205 绿藻门 小球藻 (Chlorella spp.) 0.046 衣藻 (Chlamydomonas spp.) 0.022 镰形纤维藻 (Ankistrodesmus. falcatus) 0.054 栅藻 (Scendesmus sp.) 0.085 硅藻门 小环藻 (Cyclotella spp.) 0.184 针杆藻 (Synedra spp.) 0.051 浮游动物 桡足类 无节幼体 (Nauplius) 0.296 剑水蚤 (Cyclops) 0.305 枝角类 象鼻溞 (Bosmina spp.) 0.298 网纹溞属 (Ceriodaphnia) 0.095 表 3 21世纪以来东平湖秋季浮游植物群落特征对比
Table 3. Comparison of phytoplankton community characteristics in the autumn of Dongping Lake since 21 century
时间
Years优势种
Dominant speciesB/ (mg∙L−1) H' 2007[26] 主要优势种群为蓝藻门、绿藻门、硅藻门及隐藻门 23.52 2.60 2007[28] 以蓝藻门的色球藻和席藻为主 — 1.73 2010[29] 伪鱼腥藻、尖尾蓝隐藻、卷曲纤维藻 — — 2010[20] 伪鱼腥藻、尖尾蓝隐藻、镰形纤维藻 — 3.9 2011[20] 伪鱼腥藻、依沙束丝藻、针形纤维藻 — 3.1 2012[20] 伪鱼腥藻、依沙束丝藻、尖针杆藻 — 3.7 2013[25] 色球藻、席藻、小球藻及针杆藻 5.97 1.49 2016 — 2017[10] 伪鱼腥藻、蓝纤维藻、拟浮丝藻、鱼腥藻、平裂藻、巨颤藻、浮丝藻、细小平裂藻、
束丝藻、泽丝藻、席藻、四尾栅藻、湖生卵囊藻、纤维藻— 2.73 2017[9] 漂浮泽丝藻、色球藻、小球藻、小环藻、舟形藻、针杆藻、普通黄丝藻 6.42 1.76 2020[30] 小环藻、平裂藻、颗粒直链藻 — — 2021(本研究) 伪鱼腥藻、小环藻、栅藻、平裂藻、镰形纤维藻、针杆藻、小球藻、色球藻及衣藻 9.02 3.7 -
[1] MARCHETTO A, PADEDDA B M, MARIANI M A, et al. A numerical index for evaluating phytoplankton response to changes in nutrient levels in deep Mediterranean reservoirs [J]. Journal of Limnology, 2009, 68(1): 106. doi: 10.4081/jlimnol.2009.106 [2] 秦伯强, 高光, 朱广伟, 等. 湖泊富营养化及其生态系统响应 [J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(10): 855-864. doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-10-855 QIN B Q, GAO G, ZHU G W, et al. Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(10): 855-864(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-10-855
[3] 王雅雯, 李迎鹤, 张博, 等. 嘉兴南湖不同湖区浮游动植物群落结构特征与环境因子关系 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(6): 3106-3117. WANG Y W, LI Y H, ZHANG B, et al. Structural characteristics of zooplankton and phytoplankton communities and its relationship with environmental factors in different regions of Nanhu Lake in Jiaxing City [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(6): 3106-3117(in Chinese).
[4] 符哲, 郭晶, 黄代中, 等. 洞庭湖的富营养演变特征及影响因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(8): 2636-2645. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042005 FU Z, GUO J, HUANG D Z, et al. The evolution and influencing factors of eutrophication in Dongting Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(8): 2636-2645(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021042005
[5] 姜登岭, 赵昊, 邬喜红, 等. 嘉兴城市河网区高、低水位期浮游植物群落及其与环境因子的典范对应分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(9): 2540-2550. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020040804 JIANG D L, ZHAO H, WU X H, et al. Model correspondence analysis of phytoplankton community and its environmental factors at high and low water levels in urban river network area of Jiaxing City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(9): 2540-2550(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020040804
[6] CHEN Y Y, CHEN S Y, YU S Y, et al. Distribution and speciation of phosphorus in sediments of Dongping Lake, North China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 72(8): 3173-3182. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3223-8 [7] ZHANG Y H, HUANG, L L, ZHANG Z B, et al. Assessment of nutrients and organic matter in sediments of Dongping Lake, China [J]. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 2016, 25(4): 2269-2277. [8] LIU S S, YAO M, CHEN S Y, et al. Surface sediment diatom assemblages response to water environment in Dongping Lake, North China [J]. Water, 2021, 13(3): 339. doi: 10.3390/w13030339 [9] 董贯仓, 冷春梅, 丛旭日, 等. 南水北调东线工程运行3年后东平湖浮游植物群落特征及环境驱动因子 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2022, 34(1): 61-73. doi: 10.18307/2022.0107 DONG G C, LENG C M, CONG X R, et al. Phytoplankton community and driving environmental factors in Lake Dongping after 3 years implementation of the east route of South-to-North Water Diversion Project [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2022, 34(1): 61-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2022.0107
[10] 辛未, 高雯琪, 夏文彤, 等. 调水后东平湖浮游植物群落结构及水质生物评价 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2022, 38(1): 145-156. XIN W, GAO W Q, XIA W T, et al. Phytoplankton community structure and bioassessment of water quality in Dongping Lake after water diversion [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2022, 38(1): 145-156(in Chinese).
[11] 高雯琪, 辛未, 夏文彤, 等. 东平湖浮游动物对南水北调东线运行的时空响应 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2022, 38(1): 114-123. GAO W Q, XIN W, XIA W T, et al. Spatio-temporal responses of zooplankton to the operation of the eastern route of the south-to-north water diversion project in Dongping Lake [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2022, 38(1): 114-123(in Chinese).
[12] CHEN Y Y, CHEN S Y, LIU J Z, et al. Environmental evolution and hydrodynamic process of Dongping Lake in Shandong Province, China, over the past 150 years [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 68(1): 69-75. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1716-x [13] DENG H G, ZHANG J, CHEN S Y, et al. Metal release/accumulation during the decomposition of Potamogeton crispus in a shallow macrophytic lake [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 42: 71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2015.07.004 [14] YU Q Z, MICKLER R A, LIU Y J, et al. Remote sensing of Potamogeton crispus L. in Dongping Lake in the North China plain based on vegetation phenology [J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2020, 48(4): 563-573. doi: 10.1007/s12524-020-01103-w [15] 丁洋, 赵进勇, 张晶, 等. 松花湖水质空间差异及富营养化空间自相关分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(5): 2232-2239. DING Y, ZHAO J Y, ZHANG J, et al. Spatial differences in water quality and spatial autocorrelation analysis of eutrophication in Songhua Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(5): 2232-2239(in Chinese).
[16] Shannon C E, Weaver W. The mathematical Theory of Communication [J]. Philosophical Review, 1949, 60(3): 144. [17] PIELOU E C. Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession [J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1966, 10(2): 370-383. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90133-0 [18] MCNAUGHTON S J. Relationships among functional properties of Californian grassland [J]. Nature, 1967, 216(5111): 168-169. [19] 白海锋, 王怡睿, 宋进喜, 等. 渭河陕西段浮游动物群落结构时空特征及其驱动因子 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(8): 1602-1610. BAI H F, WANG Y R, SONG J X, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and driving factors of zooplankton community structure in the Shaanxi section of Weihe River, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2022, 41(8): 1602-1610(in Chinese).
[20] 路学堂. 东平湖浮游植物群落结构与驱动因子及蓝藻水华可能性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2013. LU X T. The research on phytoplankton community, driving environmental factors and the possibility of cyanobacterial bloom in Dongping Lake, China[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2013(in Chinese).
[21] 胡尊芳, 宋印胜, 孙建峰, 等. 东平湖枯丰水期水质健康风险评价 [J]. 水电能源科学, 2016, 34(9): 31-34. HU Z F, SONG Y S, SUN J F, et al. Water quality health risk assessment of Dongping Lake in dry and wet seasons [J]. Water Resources and Power, 2016, 34(9): 31-34(in Chinese).
[22] 陈豪, 徐洪增, 路民, 等. 东平湖水体营养化状况综合评价 [J]. 人民黄河, 2022, 44(1): 83-88. CHEN H, XU H Z, LU M, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of water trophication status in Dongping Lake [J]. Yellow River, 2022, 44(1): 83-88(in Chinese).
[23] 刘红彩. 东平湖水环境状况与影响因素研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2012. LIU H C. The research of water environment condition and the influencing factor of Dongping Lake[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2012(in Chinese).
[24] 韦丽琼, 郭芳, 姜光辉. 广西武鸣盆地岩溶泉口浮游生物群落对水环境变化的响应 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2022, 34(3): 777-790. doi: 10.18307/2022.0307 WEI L Q, GUO F, JIANG G H. Responses of plankton community to water environment changes in Karst springs in Wuming Basin, Guangxi Province [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2022, 34(3): 777-790(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2022.0307
[25] 冷春梅, 董贯仓, 王亚楠, 等. 南水北调运行初期东平湖浮游植物群落特征分析 [J]. 水产学杂志, 2019, 32(1): 22-27. LENG C M, DONG G C, WANG Y N, et al. Phytoplankton community structure characteristics in Dongping Lake in initial stages of south-to-north water transfer project [J]. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2019, 32(1): 22-27(in Chinese).
[26] 王志忠, 巩俊霞, 陈述江, 等. 东平湖水域浮游植物群落组成与生物量研究 [J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 8(5): 235-240,1. WANG Z Z, GONG J X, CHEN S J, et al. Studies on community characteristics and biomass of phytoplankton in Dongping Lake [J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 8(5): 235-240,1(in Chinese).
[27] 王一舒, 逄勇, 罗缙, 等. 南水北调东线(江苏段)水质变化趋势分析 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2014, 25(4): 104-107. WANG Y S, PANG Y, LUO J, et al. Analysis of change tendency of water quality in east line of south-to-north water diversion project of Jiangsu section [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2014, 25(4): 104-107(in Chinese).
[28] 冷春梅, 巩俊霞, 王亚楠, 等. 东平湖2007年浮游植物调查及分析 [J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(4): 513-516. LENG C M, GONG J X, WANG Y N, et al. Analysis of phytoplankton biological quantity in Dongping Lake in 2007 [J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 40(4): 513-516(in Chinese).
[29] TIAN C, LU X T, PEI H Y, et al. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton and its relationship with the environmental factors in Dongping Lake, China [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(3): 2627-2645. doi: 10.1007/s10661-012-2736-4 [30] 侯莉, 张玲玲, 张倩. 东平湖水生生物资源调查与评估 [J]. 绿色科技, 2022, 24(2): 52-55. HOU L, ZHANG L L, ZHANG Q. Investigation and assessment of aquatic biological resources in Dongping Lake [J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 52-55(in Chinese).
[31] 林青, 由文辉, 徐凤洁, 等. 滴水湖浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系 [J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(23): 6918-6929. LIN Q, YOU W H, XU F J, et al. Zooplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Dishui Lake [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(23): 6918-6929(in Chinese).
[32] 谢海莎, 邵瑞华, 王际焱, 等. 延河丰水期浮游生物群落分布及其与环境因子的关系 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2022, 48(1): 108-114. XIE H S, SHAO R H, WANG J Y, et al. Relationship between distribution of plankton community and environmental factors in Yanhe River during wet season [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2022, 48(1): 108-114(in Chinese).
[33] LÉVESQUE S, BEISNER B E, PERES-NETO P R. Meso-scale distributions of lake zooplankton reveal spatially and temporally varying trophic cascades [J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2010, 32(10): 1369-1384. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbq064 [34] 徐梅, 吴芳仪, 刘靓靓, 等. 焦岗湖浮游甲壳动物群落结构的季节动态 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(5): 1254-1262. XU M, WU F Y, LIU J J, et al. Seasonal variation of community structure of crustacean zooplanktons in Lake Jiaoganghu [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(5): 1254-1262(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: