-
工业发展过程中产生的危险废物通常具有腐蚀性、毒性、反应性或感染性等一种或多种特性,不仅对当地环境造成影响,严重时可危害人类健康. 目前,危险废物的处理方式有填埋、焚烧、固化和化学处理等,处置过程中难免会产生各种二次污染物,并通过大气和水等环境介质进入到土壤中,对土壤、地下水及周边生态环境造成影响[1-3]. 危险废物处置利用单位对本场地和周边用地的生态环境影响具有长期性和隐蔽性,一旦造成污染后往往影响范围较广、难以修复,且可能通过植物吸收等途径在食物链中积累[4]. 因此,关注危废处置场地环境现状十分必要. 近年来,随着危险废物处置利用技术的不断推广应用,危险废物处置利用企业引起的潜在环境污染问题越来越受到人们的广泛关注,尤其以危废焚烧源的排放、危废填埋源对周边生态环境和人体健康影响、危废收集利用企业运行中的二次污染影响等问题引起国内外学者的极大兴趣[5-7]. 有研究表明,危废处置场周边土壤重金属污染情况与危废处置方式密切相关,其中焚烧造成的污染最为严重[8-10]. 但同时也存在另一种观点认为处置场周边土壤重金属的污染并非主要受处置方式的影响,其它外部影响也较为显著且不同重金属主要污染源也有所差异[11-12].
目前,危废处置相关研究多聚焦于单一处置方式下的影响,对各类处置方式以及多种方式复合影响的对比评估研究较少. 本文以上海市6家4种类型危废处置利用企业周边表层(0—20 cm)土壤为研究对象,采用地累积指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法、主成分分析和潜在生态风险指数法,对研究区域表层土壤重金属分布累积情况、可能的来源及潜在生态风险进行分析评价,对比分析其累积特征,明确重金属对不同危废处置方式累积响应,分析其潜在生态风险差异,以期为危废处理处置企业污染风险管控提供参考.
-
上海位于长三角地区,地势平坦,属于亚热带海洋季风气候区,雨量充沛,土壤类型主要为水稻土、灰潮土和滨海盐土等. 上海市人口密集,拥有如汽车制造、石油化工、钢材制造、电子产品制造业等多样的行业门类. 城市发展的同时不可避免的产生大量危险废物,也带来了一定的土壤环境质量问题. 本文选取上海6家典型危废处置企业周边作为研究区域(表1),6家企业涉及垃圾填埋,医废、危废、工业固废焚烧处理,废旧电子元器件回收处理等工艺,其中单纯垃圾填埋企业1家(TM)、填埋焚烧混合处理工艺企业1家(HH)、单纯焚烧处理工艺2家(FS)、危废回收再利用企业2家(HS). 本研究依据《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166—2004)在6家企业周边进行布点采样,共布设70个点位,另在各企业周边选取历史上主要作为绿地使用、无工业生产活动的区域设置背景对照监测点位(6个). 每个采样点采集表层(0—20 cm)土壤密封于PVC袋中,每个样品均采用梅花布点法采集5个等容小样混合而成.
-
样品采集带回实验室后,去除植物残屑和砂砾,室温自然风干,研磨过100目筛. Hg、Sb和As 的测定参照《土壤和沉积物 汞、砷、硒、铋、锑的测定微波消解/原子荧光法》(HJ 680—2013),Cu、Ni的测定参照《土壤和沉积物 铜、锌、铅、镍、铬的测定火焰原子吸收分光光度法》(HJ 491—2019),Pb、Cd的测定参照《土壤质量 铅、镉的测定 石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法》(GB/T 17141—1997). 每个样品测定3次,平行样本间的相对标准偏差≤5%,同时采用同种方法检测空白样品. 每批样品均使用重金属标准溶液进行质量控制,回收率在90%—110%范围内.
-
地累积指数法(geo-accumulation index, Igeo)[13]是普遍用于研究重金属污染程度的定量指标[14-15].
式中,Igeo为地累积指数,
$ {C}_{i} $ 为重金属污染物实测值(mg·kg−1);$ {C}_{\mathrm{s}}^{i} $ 为重金属污染物背景值(mg·kg−1),本研究以采样背景对照点检测值为参照标准. 分级标准:Igeo≤0 无污染;0<Igeo≤1 轻-中度污染;1<Igeo≤2 中度污染;2<Igeo≤3 中-强度污染;3<Igeo≤4 强度污染;4<Igeo≤5 强-极强度污染;Igeo>5 极强度污染. -
内梅罗综合污染指数法(Nemerow integrated pollution index, NIPI)是在单因子污染指数评价的基础上,通过对平均值和最大值的归纳处理,进行综合评价的方法[16]. 采用内梅罗综合污染指数法进行土壤重金属污染的生态评价,可以全面反映重金属的综合污染水平,而且还能突出污染程度最严重的重金属元素对环境的有害影响[17-18]. 计算公式如下:
其中,
式中,
$ {P}_{\mathrm{综}} $ 为内梅罗综合污染指数;$ {P}_{i} $ 为土壤重金属$ i $ 的单因子指数;$ {C}_{i} $ 为重金属$ i $ 的实测浓度(mg·kg−1);$ {C}_{\mathrm{s}}^{i} $ 为重金属$ i $ 的背景浓度(mg·kg−1);$ {P}_{i\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $ 为重金属单因子指数的最大值;$ {P}_{i\mathrm{a}\mathrm{v}\mathrm{e}} $ 为重金属单因子指数的算术平均值. 内梅罗综合污染指数法分级标准: P综≤0.7 清洁;0.7< P综≤1.0 预警;1.0< P综≤2.0 轻度污染;2.0< P综≤3.0 中度污染;P综>3.0重度污染. -
潜在生态风险指数法(comprehensive potential ecological risk index, RI)由瑞典科学家Håkanson[19]提出,该方法同时考虑各重金属元素在环境中的含量、生态环境效应和它们对环境的毒性差异,定量评估重金属可能引起的生态环境风险,被广泛应用于土壤和沉积物重金属潜在生态风险评价[20-21]. 计算公式如下:
式中,RI为重金属综合潜在风险指数;
${E}_{\mathrm{r}}^{i} $ 为土壤中重金属i对应的单项潜在生态风险指数;Ci为重金属i在土壤环境中的浓度值(mg·kg−1);$ {C}_{\mathrm{s}}^{i} $ 为重金属i的含量标准值或地球化学背景值(mg·kg−1),本研究选用采样背景值;Ti为土壤中重金属i所对应的毒性响应系数. 潜在生态风险评价分级标准见表2. -
数据采用Microsoft Excel 2016土壤样品中重金属含量进行描述性统计分析及制图,使用Origin 2018进行图表的绘制. 采用SPSS 26软件对数据进行Pearson相关性分析和主成分分析.
-
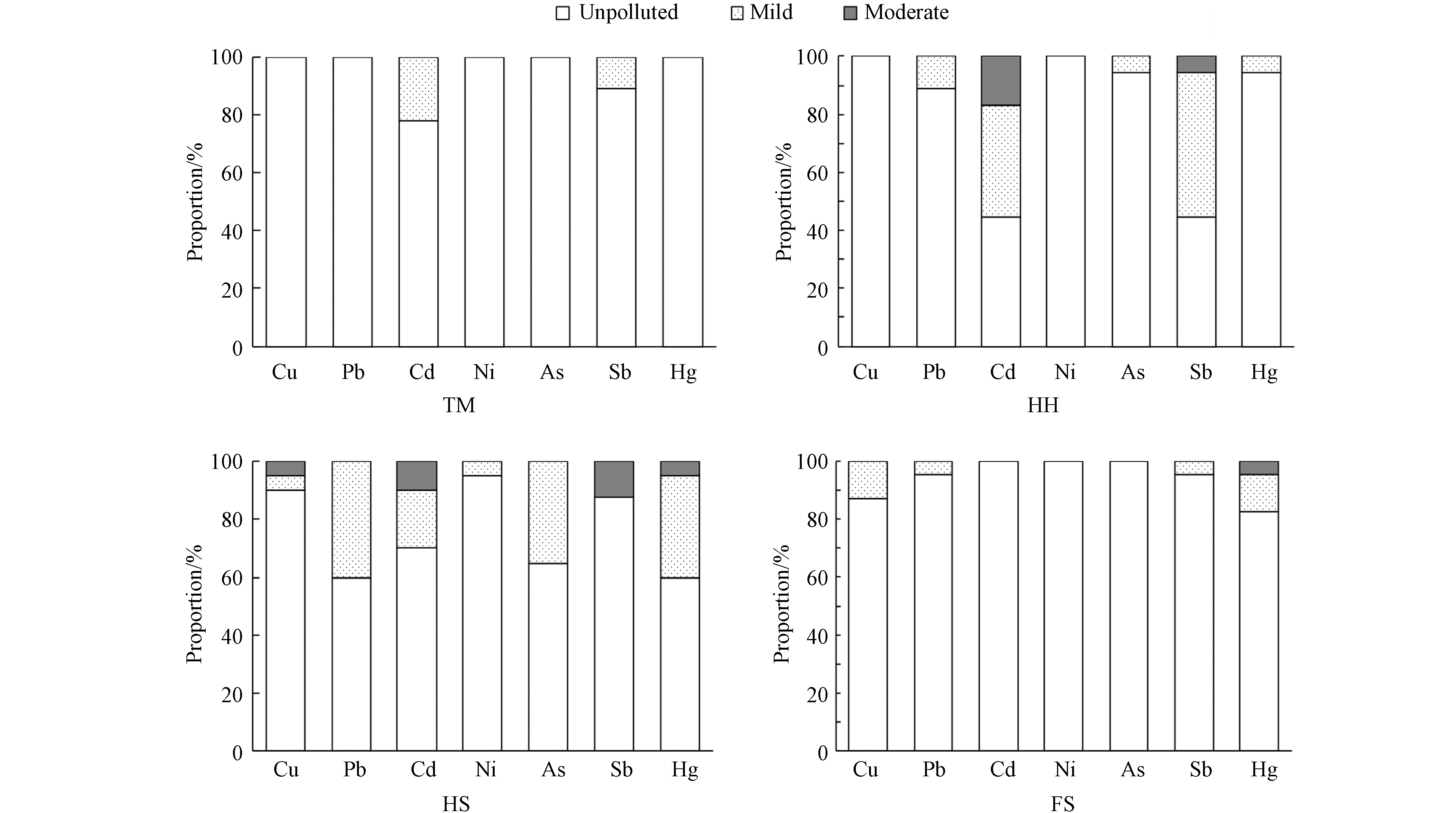
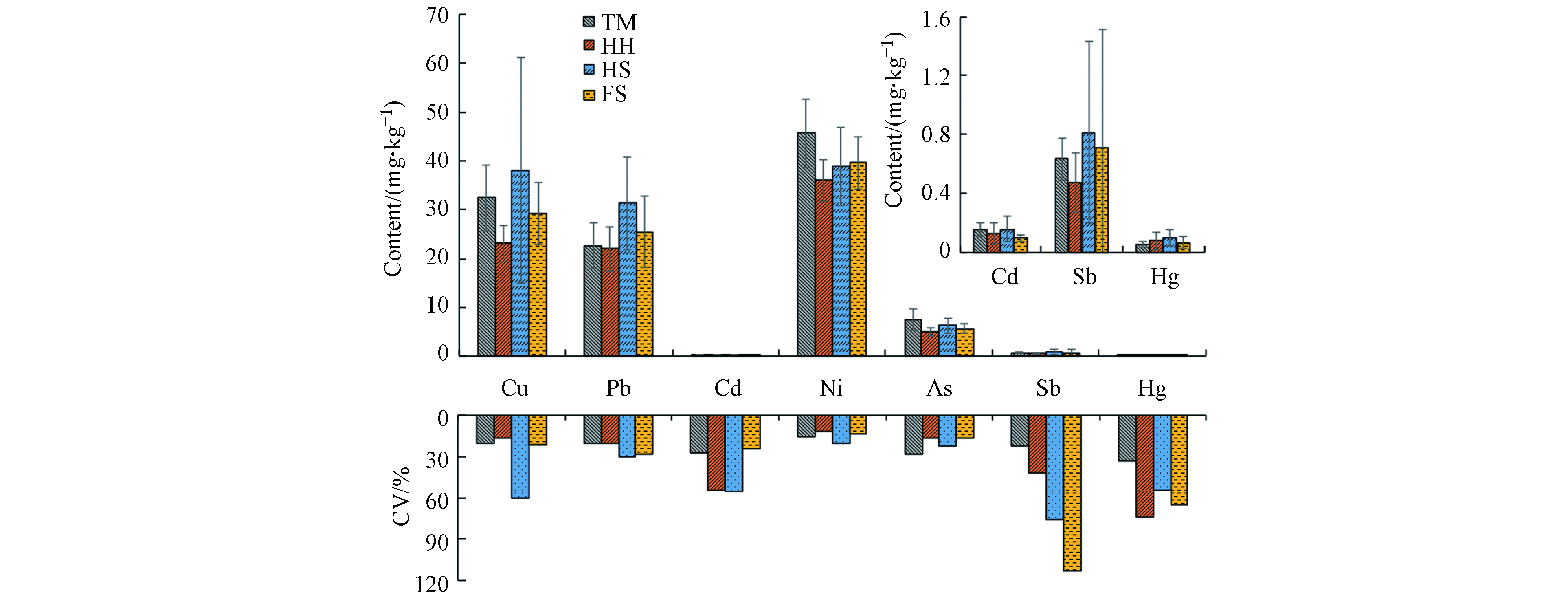
典型危废处置利用企业周边表层土壤重金属Cu、Pb、Cd、Ni、As、Sb检出率均为100%,其平均含量分别为30.63、25.92、0.13、39.30、5.89、0.64 、0.08 mg·kg−1(表3). 重金属Ni和Sb的平均值和中位值均小于土壤背景值,Cu、Pb和Cd 3种重金属的平均值均大于背景值,分别是背景值的1.10、1.099、1.20倍,表明Cu、Pb和Cd均存在不同程度的累积,且Cd的累积程度最大. 7种重金属中Sb含量的最大值超背景值倍数最高,达到4.79倍,其次为Cu、Cd和Hg. 变异系数反映了重金属的空间变化程度,重金属Sb的变异系数(89%)最大,Hg(65%)和Cd(51%)的变异系数也相对较高,均达到了强变异(>50%)等级[22],表明Sb、Hg和Cd在研究区域表层土壤中的空间分布极不均匀,可能存在由外源物质输入的点源污染.
HS周边土壤中Cu、Pb、Sb和Hg含量相对高于TM、HH和FS(图1),且此4种重金属变异系数均大于50%,表明Cu、Pb、Sb和Hg在HS周边土壤中分布不均匀,企业生产活动可能对其周边部分点位土壤造成了Cu、Pb、Sb、Hg的累积. TM周边土壤中Ni和As含量相对较高,但其变异系数较小(分别为15.5%和28.5%),表明TM对其周边影响不明显. 此外,HH周边土壤中Cd和Hg、FS周边土壤中Sb和Hg变异系数均大于50%,表明HH和FS周边土壤中Hg、Cd或Sb 可能受到企业生产的影响. 综上,TM对其周边土壤影响较小,HH、HS和FS生产可能对其周边土壤造成部分重金属的累积.
-
由图2可知,研究区域整体上,7种重金属地累积指数的平均值均小于0,即单个重金属因子在研究区域未呈现污染现象. 但是,在HH周边表层土壤中Cd和Sb以及HS周边表层土壤中Cd的地累积指数平均值>0,处于轻-中等累积. TM周边土壤存在部分点位Cd(22.2%)和Sb(11.1%)处于轻-中等累积(图3),结合点位信息,存在累积的点位与企业有河流相隔,猜测非企业影响,可能源自其它外源因素. 含量统计所提TM周边土壤相对较高的Ni和As含量,并不存在累积,可能源于土壤异质性. HH周边,除Cd和Sb外,Pb、As和Hg也存在少量轻-中等累积点位,而Cd和Sb均有55.6%的点位存在累积,尤其是Cd有16.7%的点位达到中等累积. HS周边土壤重金属整体上处于无累积水平,然而7种重金属均有一定比例的点位处于轻-中等累积(图3),甚至中等累积水平,尤其是Cu、Cd、Sb和Hg,中等累积的点位占比分别为5%、10%、12.5%和5%. FS周边存在1个点位的Hg达到中等累积,少量点位Cu、Pb、Sb和Hg轻-中等累积. 综合来看,HS周边7种重金属累积程度明显高于其它3种处置工艺企业,HH周边重金属Pb、Cd、As、Sb和Hg累积程度也较高,表明相较于填埋和单纯焚烧处置企业,回收利用和混合处置工艺企业周边表层土壤可能受到人为活动影响更大. 国内外已有很多研究表明垃圾焚烧厂会对周边土壤造成明显污染[8-9,23],焚烧过程中重金属可随焚烧烟气排放进入大气中,并伴随干湿沉降进入周边土壤,由于烟气的长期排放及重金属的难迁移性,造成土壤中重金属的累积. 对电子废物回收处理场地相关研究表明,电子废物在拆解、融化、燃烧、处置等过程中容易造成周边土壤重金属污染[24-27].
-
4种类型危废处置利用企业周边土壤重金属的内梅罗综合污染指数(P综)范围为1.13—1.84(表4),均处于轻度污染水平,其中HS内梅罗综合指数(1.84)最高,其次为HH(1.73). 所有点位的P综均大于0.7,表明企业周边均存在不同程度的污染. 整体上,有66%—74%的点位处于轻度污染水平,HS和HH周边分别存在10%和11%的点位土壤达到重度污染等级,从单因子指数结果分析,主要贡献因子为Cd、Sb、Cu和Hg. TM周边土壤均为轻度污染及以下水平,FS周边无重度污染土壤. 综合来看,HS和HH周边土壤重金属污染相对较为严重. 结合研究企业基本情况进一步分析发现,HH处置的危废类型较多,包括医疗危废、工业危废、一般工业固废等,涉及含铜、砷、镉、锑、汞、铅、镍等废物,且年处理量较大;HS处置危废的包括含金属(主要为金、银、铅、铜、铁、镍)废液回收在生产、废旧电子器件处理等,因此这两类危废处置企业周边表层土壤污染相对严重与企业生产活动有关.
-
不同重金属之间相关性分析有助于辨识重金属来源,因此本研究对7种重金属进行Pearson相关性分析,结果如表5所示,TM周边土壤中Cu、Cd、Ni、As、Sb和Hg等 6种重金属均为两两显著正相关关系(P<0.05),且Pb与Cu、As、Hg呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),表明7种重金属具有同源性;HH周边Pb、Cd、Hg和Sb显著正相关,具有同源性;HS周边Cd、Ni、As、Sb、Hg和Pb显著正相关,具有同源性;FS周边Cu、Pb、Ni、As和Sb显著正相关,而Hg与其它6种重金属相关性均不显著,说明FS周边Hg与Cu、Cd、Ni、As、Sb、Pb来源不同.
-
4类危废处置企业周边土壤重金属数据KMO效度检验值均>0.6,且均通过Bartlett球形检定(P<0.001),主成分分析结果具有统计学意义,分析结果如表6所示. TM提取1个主成分,累积方差贡献率为81.21%,基本反映所有数据主要信息,即表明其周边重金属具有同源性,与相关性分析结果相同. 结合土壤重金属含量统计结果,表明TM没有对其周边土壤造成明显污染.
HH和FS周边均提取3个主成分,但各主成分重金属的载荷不尽相同,表明填埋焚烧复合处置和单纯焚烧处置企业周边土壤重金属污染来源不一致. HH第一主成分中,Cu、Pb、Cd和Sb有较高的正载荷,结合前文土壤重金属含量统计,Cu未发生累积,而Pb、Cd和Sb含量均高于背景值,尤其Cd和Sb存在中度累积,结合采样点位置,Cd和Sb均累积的样点分布在企业四周,靠近公路、填埋区、焚烧线或医塑处理车间,而Pb累积的点位位于企业焚烧线的主导风向上,表明Pb、Cd和Sb的累积主要受人为源污染影响. 研究表明,Cu和Cd被归到同一主成分时,可视为人为活动在区域尺度上的影响[28],机械设备加工、交通运输以及焚烧废气排放均可向周边排放Pb、Cd和Cu[9,29]. 以上表明主成分1是自然源和人为活动(包括焚烧废气排放沉降、填埋及交通运输等)综合影响. As和Hg在主成分1和2中均占有一定的载荷,Hg是焚烧废气排放的重要标识性污染物之一[23,30],As累积的点位位于企业主导风向且距离稍远的农田中,农业活动过程中农药和磷肥的施用是导致农田土壤As累积的主要原因[31],而As在主成分2有较高负载荷,因此主成分2主要反映焚烧过程的影响. 主成分3方差贡献率为14.54%,Ni具有较高正载荷,研究报道,Ni是我国城市土壤污染程度最低的重金属之一,Ni的含量变化主要由成土过程引起[9],因此主成分3代表成土母质. 综上,HH周边人为活动(不只是焚烧废气排放)是造成土壤重金属Pb、Cd、Sb和Hg的累积主要因素. FS主成分1的贡献率为44.42%,Cu、Pb、Ni、As和Sb具有较高正载荷,根据前文统计结果,Ni、As均不存在累积,Cu、Pb和Sb存在部分点位累积,且5种重金属显著正相关,作为焚烧废气排放的重要标识性污染物之一的Pb[30]在企业主导风向范围内有点位累积,Cu的累积点位分布于企业北部、西部和东北部,机械设备加工、交通运输以及焚烧废气排放均可向周边排放Pb和Cu[9,29],因此,主成分1反映自然源和人为源综合影响. 主成分3方差贡献率为14.85%,Hg具有较高正载荷,Hg存在中等累积,且与其余6种重金属均显著不相关,表明Hg与其它几种重金属来源不同,研究表明Hg是焚烧废弃排放的标志物,表明主成分3代表焚烧废气排放影响,综上,人为活动造成了FS周边土壤重金属Cu、Pb、Sb和Hg的累积,其中焚烧废气排放沉降造成了Hg的中等程度累积.
HS提取2个主成分,主成分1贡献率达80.95%,Cu、Pb、Cd、Ni、As和Sb均有极高正载荷,考虑到HS主要处置含Cu、Pb、Ni废液和废旧电子器件,因此主成分1代表人为生产活动影响,即HS周边土壤重金属污染主要是企业生产活动造成的. Hg在主成分2中具有较高正载荷,且Hg与Pb、Cd、As呈显著正相关,Cu和Ni是非挥发性物质,Hg、Cd、Pb和As同属于挥发性物质,研究发现,电子废物倾倒场、拆解区周围土壤中重金属Pb、Ni、Cu、As和Cd污染严重[6,32-35],因此猜测主成分1反映企业存储处置危废时废液泄露或废旧电子元件拆解过程中的直接影响,主成分2反映企业回收加工处置过程中产生的二次污染,且危废泄露造成的污染程度远大于二次污染.
-
上海市典型危废处置利用企业周边表层土壤综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)平均值为118.84(表7),处于轻微潜在生态风险,但其最大值高达329.92,处于强生态风险等级. RI值变化范围较大,部分点位风险较强,可能存在集中处置区域导致局部污染严重的现象. 7种重金属中,Cd和Hg潜在生态危害较大,最大值均处于强生态风险等级.
4类危废处置企业中,HS周边表层土壤潜在生态风险最高(RI=151.87,表8),接近于中度生态风险,Cd和Hg处于中度生态风险等级,Er平均值分别为53.72和57.28;HH周边表层土壤Cd处于中度生态风险等级,Er平均值为54.76. 4类危废处置企业周边综合潜在生态风险主要来自Cd和Hg,Cd和Hg对RI的贡献率高达67.18%—75.42%(图4),HH周边土壤中Cd对RI的贡献率最高,FS周边Hg对RI的贡献率最高,TM和HS周边Cd和Hg对RI的贡献率相当. TM周边所有监测点位均属于轻微生态风险等级,FS周边亦有95%的监测点位属于轻微生态风险等级,HS周边有45%的点位处于中度生态风险等级.
-
(1)土壤中Cu、Pb和Cd存在不同程度的累积,且Cd的累积程度最大. 4种类型危废处置利用企业周边土壤重金属整体上处于轻度污染水平,但填埋焚烧复合处置和危废回收处置企业周边污染程度相对较高,分别有11%和10%的点位达重度污染等级,存在局部风险过重的情况.
(2)不同危废处置利用企业周边重金属污染分布和来源不尽相同. 危废填埋焚烧复合处置企业周边重金属Pb、Cd、Sb和Hg的累积主要源于人为活动(包括填埋、焚烧废气排放沉降和交通运输等);危废焚烧处置企业周边部分点位土壤重金属Cu、Pb、Sb和Hg的累积主要有人为活动造成,其中Hg主要受焚烧废气排放沉降的影响;危废回收利用企业周边土壤重金属Cu、Pb、Cs、Ni、As和Sb主要受生产过程中危废的直接影响,Hg可能来源于二次污染.
(3)研究区域潜在生态风险主要来自Cd和Hg,两种金属均有达到强生态风险等级. 危废回收利用处置企业周边土壤潜在生态风险程度最高,其次为填埋焚烧复合处置企业.
典型危废处置利用企业周边土壤重金属分布特征、来源及风险评价
Distribution characteristics, sources analysis and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils surrounding typical hazardous waste disposal and utilization plants
-
摘要: 为探讨典型危险废物处置企业周边表层土壤重金属的分布特征和污染来源,以上海市4种典型危险废物处置利用企业周边土壤为研究对象,采集并检测表层土壤中7种重金属(Pb、Hg、Cd、Ni、Sb、Cu、As)的含量. 运用地累积指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法和潜在生态风险指数法评价重金属污染特征,采用多元统计方法分析重金属来源. 结果表明,研究区域土壤中Cu、Pb和Cd存在不同程度的累积,且Cd的累积程度最大;4种类型危废处置利用企业周边土壤重金属整体上处于轻度污染水平,但填埋焚烧复合处置和危废回收处置企业周边分别有11%和10%的点位达重度污染等级. 潜在生态风险评价结果显示,研究区域7种重金属的综合潜在风险指数均值为118.84,其中Cd和Hg的贡献率最高,危废回收利用处置企业周边土壤潜在生态风险程度最高,其次为填埋焚烧复合处置企业,应予以重视.Abstract: In order to explore the distribution, sources and potential ecological risk in the surface soils surrounding the hazardous waste disposal and utilization plants, four typical hazardous waste disposal and utilization plants in Shanghai were selected in this study, and the contents of seven heavy metals (Pb、Hg、Cd、Ni、Sb、Cu、As) in the surface soils were determined. Geo-accumulation index, Nemerow comprehensive pollution index and potential ecological risk index were used to assess the pollution characteristics. Multivariate statistical analysis was used to investigate the pollution sources in the study area. The results showed that Cd was the primary pollutant, followed by Cu and Pb. The heavy metals in the soil surrounding the four types of hazardous waste disposal and utilization plants were at the level of slight pollution as a whole. However, 11% and 10% of the points around landfill incineration complex treatment plant and hazardous waste recycling plant reached the level of heavy pollution, respectively. The mean value of the potential ecological risk index of the seven heavy metals was 118.48, among which Cd and Hg contributed more. The potential ecological risk assessment showed that the risk of soils surrounding the hazardous waste recycling plant was the highest, followed by landfill incineration complex treatment plant, deserving much attention.
-

-
表 1 研究区域基本情况
Table 1. The general situation of disposal plants
研究区域
Study area处置工艺
Disposal method处置类型
Types of hazardous waste年处理量/万t
Annual disposal capacity点位数
Number of sampling pointsTM 填埋 生活垃圾、危废 已封场 9 HH 填埋、焚烧、回收利用 医废、危废、工业固废 15 18 HS 回收再生产 含金属废液、电子元件 2.6(HS1), 1(HS2) 20 FS 焚烧 危废、工业固废 3.4(FS1), 3.58(FS2) 23 表 2 土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价分级标准
Table 2. Classification criterion and potential ecological risk index of heavy metals
级别
Pollution levels$ {\mathit{E}}_{\mathit{r}} $ RI 轻微生态风险 $ {E}_{\mathrm{r}} $ RI<150 中度生态风险 40≤ $ {E}_{\mathrm{r}} $ 150≤RI<300 强生态风险 80≤ $ {E}_{\mathrm{r}} $ 300≤RI<600 强烈生态风险 160≤ $ {E}_{\mathrm{r}} $ RI≥600 极强生态风险 $ {E}_{\mathrm{r}} $ 表 3 危废处置利用企业周边表层土壤重金属含量统计结果(n=70)
Table 3. Descriptive statistics for heavy metals in soil in the study area (n=70)
重金属元素
Elements最小值/ (mg·kg−1)
Minimum最大值/ (mg·kg−1)
Maximum平均值/ (mg·kg−1)
Average中位值/ (mg·kg−1)
Median标准偏差/ (mg·kg−1)
Standard deviation变异系数/%
Coefficient of variation背景值/ (mg·kg−1)
BackgroundCu 16.00 133.00 30.63 29.00 14.17 46 27.83 Pb 14.30 63.90 25.92 25.55 7.96 31 23.83 Cd 0.05 0.40 0.13 0.12 0.07 51 0.11 Ni 28.00 68.00 39.30 38.00 6.72 17 41.33 As 3.59 11.40 5.89 5.69 1.48 25 5.66 Sb 0.23 4.21 0.64 0.53 0.57 89 0.73 Hg 0.02 0.28 0.08 0.07 0.05 65 0.07 表 4 研究区土壤重金属的内梅罗综合污染指数评价特征值统计表
Table 4. Eigenvalue statistics of integrated pollution index of heavy metals in the study area
P综
Integrated pollution index不同污染等级点位占比/% Proportion of each pollution level 清洁
Clean预警
Precautionary轻度污染
Slightly polluted中度污染
Moderately polluted重度污染
Heavily pollutedTM 1.13 0.00 33.33 66.67 0.00 0.00 HH 1.73 0.00 5.56 66.67 16.67 11.11 HS 1.84 0.00 5.00 70.00 15.00 10.00 FS 1.28 0.00 17.39 73.91 8.70 0.00 表 5 重金属之间的相关性关系
Table 5. Pearson correlation coefficients of heavy metals in study area
企业
Plants重金属
ElementsCu Pb Cd Ni As Sb Hg TM
n=9Cu 1 Pb 0.800** 1 Cd 0.814** 0.549 1 Ni 0.898** 0.486 0.805** 1 As 0.945** 0.821** 0.691* 0.832** 1 Sb 0.865** 0.622 0.788* 0.761* 0.824** 1 Hg 0.897** 0.910** 0.667* 0.705* 0.910** 0.730* 1 HH
n=18Cu 1 Pb 0.799** 1 Cd 0.621** 0.664** 1 Ni 0.316 0.381 0.095 1 As 0.535* 0.415 0.361 0.258 1 Sb 0.429 0.686** 0.589* 0.613** 0.245 1 Hg 0.270 0.339 0.569* 0.218 0.018 0.531* 1 HS
n=20Cu 1 Pb 0.896** 1 Cd 0.369 0.554* 1 Ni 0.900** 0.863** 0.349 1 As 0.694** 0.823** 0.503* 0.814** 1 Sb 0.985** 0.977** 0.937** 0.942** 0.868** 1 Hg 0.204 0.572** 0.616** 0.154 0.448* 0.254 1 FS
n=23Cu 1 Pb 0.784** 1 Cd 0.286 0.267 1 Ni 0.454* 0.526** 0.129 1 As 0.453* 0.528** -0.202 0.511* 1 Sb 0.556** 0.750** 0.459* 0.124 0.184 1 Hg 0.003 0.104 -0.046 0.132 -0.073 0.053 1 表 6 研究区表层土壤重金属元素主成分分析结果
Table 6. Principal component analysis for heavy metals in surface soils from the study area
研究区域
Plants项目
ItemsPC1 PC2 PC3 研究区域
Plants项目
ItemsPC1 PC2 PC3 TM Cu 0.988 − − HH Cu 0.812 −0.368 −0.147 Pb 0.823 − − Pb 0.886 −0.135 −0.049 Cd 0.841 − − Cd 0.803 0.100 −0.468 Ni 0.873 − − Ni 0.538 0.096 0.803 As 0.958 − − As 0.539 −0.667 0.041 Sb 0.888 − − Sb 0.821 0.331 0.268 Hg 0.925 − − Hg 0.575 0.650 −0.235 特征值 5.685 − − 特征值 3.675 1.149 1.018 方差贡献率% 81.210 − − 方差贡献率% 52.498 16.416 14.540 累计贡献率% 81.210 − − 累计贡献率% 52.498 68.914 83.454 HS Cu 0.951 −0.211 − FS Cu 0.864 0.016 −0.081 Pb 0.997 0.071 − Pb 0.946 0.012 0.035 Cd 0.961 0.239 − Cd 0.378 0.759 −0.035 Ni 0.946 −0.249 − Ni 0.640 −0.417 0.149 As 0.922 −0.107 − As 0.603 −0.652 −0.198 Sb 0.984 −0.103 − Sb 0.739 0.476 −0.002 Hg 0.362 0.931 − Hg 0.078 −0.039 0.985 特征值 5.667 1.057 − 特征值 3.109 1.403 1.040 方差贡献率% 80.951 15.102 − 方差贡献率% 44.417 20.038 14.851 累计贡献率% 80.951 96.053 − 累计贡献率% 44.417 64.455 79.306 表 7 研究区域重金属潜在生态风险评价
Table 7. Assessment of the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soil
Er RI Cu Pb Cd Ni As Sb Hg 最小值 3.23 2.38 15.00 3.54 5.34 1.66 5.50 51.23 最大值 23.89 13.41 150.00 8.23 21.41 27.73 136.64 329.92 平均值 5.75 5.75 42.23 4.86 11.82 8.08 40.35 118.84 标准差 2.58 1.94 26.96 0.89 2.87 5.55 27.03 49.30 对RI贡献率% 4.84 4.84 35.54 4.09 9.95 6.80 33.95 表 8 不同类型危废处置利用企业周边土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价特征值
Table 8. Eigenvalue statistics of potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soil surrounding different types of hazardous waste disposal enterprises
危废处置企业
PlantsEr RI Cu Pb Cd Ni As Sb Hg 平均值 TM 5.34 4.61 34.07 5.02 9.55 8.15 36.08 102.82 HH 5.02 5.78 54.76 4.10 11.14 12.82 24.77 118.39 HS 6.60 7.54 53.72 4.73 14.17 7.83 57.28 151.87 FS 5.73 4.60 25.63 5.51 11.22 4.43 39.49 96.62 生态
风险
等级
比例/%轻度 TM 100 100 66.67 100 100 100 66.67 100 HH 100 100 44.44 100 100 100 94.44 77.78 HS 100 100 40.00 100 100 100 35.00 55.00 FS 100 100 95.65 100 100 100 65.22 95.65 中度 TM 0 0 33.33 0 0 0 33.33 0 HH 0 0 38.89 0 0 0 0 22 HS 0 0 40.00 0 0 0 35.00 45.00 FS 0 0 4.35 0 0 0 26.09 4.35 强 TM 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 HH 0 0 16.67 0 0 0 5.56 0 HS 0 0 20.00 0 0 0 30.00 0 FS 0 0 0 0 0 0 8.70 0 -
[1] CHAUDHARY R, NAIN P, KUMAR A. Temporal variation of leachate pollution index of Indian landfill sites and associated human health risk [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(22): 28391-28406. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12383-1 [2] RIMMER D L, VIZARD C G, PLESS-MULLOLI T, et al. Metal contamination of urban soils in the vicinity of a municipal waste incinerator: One source among many [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 356(1/2/3): 207-216. [3] ZHANG H, HE P J, SHAO L M. Flow analysis of heavy metals in MSW incinerators for investigating contamination of hazardous components [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(16): 6211-6217. [4] HUANG J, HUANG B T. Study on the impact of the soil and shallow groundwater quality by a hazardous waste incinerator in Shanghai [J]. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 569(1): 012031. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/569/1/012031 [5] 辛宝平, 王佳. 涉重危废概念的提出及其资源化利用 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(1): 1-9. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202111146 XIN B P, WANG J. Scientific definition of hazardous wastes containing heavy metals and their resource utilization [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2022, 16(1): 1-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202111146
[6] DUTTA D, GOEL S, KUMAR S. Health risk assessment for exposure to heavy metals in soils in and around E-waste dumping site [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(2): 107269. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.107269 [7] WANG C, SHAO N N, XU J Y, et al. Pollution emission characteristics, distribution of heavy metals, and particle morphologies in a hazardous waste incinerator processing phenolic waste [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 388: 121751. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121751 [8] 倪晓坤, 封雪, 于勇, 等. 典型固废处理处置场周边土壤重金属污染特征和成因分析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(9): 2146-2156. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0504 NI X K, FENG X, YU Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in soils surrounding a typical solid waste disposal plant [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(9): 2146-2156(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0504
[9] 吕占禄, 张金良, 陆少游, 等. 某区生活垃圾焚烧发电厂周边及厂区内土壤中重金属元素的污染特征及评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(5): 2483-2492. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201810030 LÜ Z L, ZHANG J L, LU S Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in surface soil around a municipal solid waste incineration power plant [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(5): 2483-2492(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201810030
[10] FERRÉ-HUGUET N, NADAL M, MARI M, et al. Monitoring metals near a hazardous waste incinerator. Temporal trend in soils and herbage [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2007, 79(2): 130-134. doi: 10.1007/s00128-007-9086-x [11] 冯经昆, 钟山, 孙立文, 等. 重庆某垃圾焚烧厂周边土壤重金属污染分布特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(6): 969-975. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.06.005 FENG J K, ZHONG S, SUN L W, et al. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metal contamination in soil surrounding a municipal solid waste incineration plant in Chongqing [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(6): 969-975(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.06.005
[12] WEI J X, LI H, LIU J G. Heavy metal pollution in the soil around municipal solid waste incinerators and its health risks in China [J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 203: 111871. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111871 [13] MÜLLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River [J]. Geology Journal, 1969, 2: 108-118. [14] ĆUJIĆ M, DRAGOVIĆ S, ĐORĐEVIĆ M, et al. Environmental assessment of heavy metals around the largest coal fired power plant in Serbia [J]. CATENA, 2016, 139: 44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2015.12.001 [15] MOR S, VIG N, RAVINDRA K. Distribution of heavy metals in surface soil near a coal power production unit: Potential risk to ecology and human health [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2022, 194(4): 1-20. [16] 彭驰, 何亚磊, 郭朝晖, 等. 中国主要城市土壤重金属累积特征与风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 1-10. PENG C, HE Y L, GUO Z H, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of major cities in China [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 1-10(in Chinese).
[17] QIN J Q, HUANG X L. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in sediments of the Xiling channel inland waterway Guangdong Province [J]. Asian Agricultural Research, 2019, 11: 40-49. [18] 邓海, 王锐, 严明书, 等. 矿区周边农田土壤重金属污染风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(4): 1127-1137. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071601 DENG H, WANG R, YAN M S, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil around mining area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(4): 1127-1137(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020071601
[19] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [20] KE X, GUI S F, HUANG H, et al. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 175: 473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.029 [21] JIANG Y X, CHAO S H, LIU J W, et al. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 168: 1658-1668. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.088 [22] WANG Y Z, DUAN X J, WANG L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: Case study in Jiangsu Province [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 710: 134953. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134953 [23] 钟山, 高慧, 张漓衫, 等. 平原典型垃圾焚烧厂周边土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(1): 164-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.01.024 ZHONG S, GAO H, ZHANG L S, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metal in soils surrounding a typical municipal solid waste incineration plant [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(1): 164-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.01.024
[24] CHEN H R, WANG L, HU B F, et al. Potential driving forces and probabilistic health risks of heavy metal accumulation in the soils from an e-waste area, southeast China [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 289: 133182. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133182 [25] ZHANG Q, YE J J, CHEN J Y, et al. Risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in soils of an abandoned e-waste site in China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 185: 258-265. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.11.003 [26] WONG M H, WU S C, DENG W J, et al. Export of toxic chemicals - A review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 149(2): 131-140. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.01.044 [27] LI W L, A CHAL V. Environmental and health impacts due to e-waste disposal in China - A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 737: 139745. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139745 [28] LV J S, LIU Y, ZHANG Z L, et al. Factorial kriging and stepwise regression approach to identify environmental factors influencing spatial multi-scale variability of heavy metals in soils [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 387-397. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.065 [29] 韩玉丽, 邱尔发, 王亚飞, 等. 北京市土壤和TSP中重金属分布特征及相关性研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(1): 146-155. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.01.022 HAN Y L, QIU E F, WANG Y F, et al. Study on heavy metals distribution and correlation in soil and TSP of Beijing [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(1): 146-155(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.01.022
[30] 赵曦, 黄艺, 李娟, 等. 大型垃圾焚烧厂周边土壤重金属含量水平、空间分布、来源及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(6): 1013-1021. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.06.016 ZHAO X, HUANG Y, LI J, et al. Environmental levels, spatial distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soils surrounding a large solid waste incinerator [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(6): 1013-1021(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.06.016
[31] 戚洁, 王美娥, 汪自强, 等. 北京市近郊区土壤砷累积特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(8): 2849-2854. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.08.048 QI J, WANG M E, WANG Z Q, et al. Accumulation characteristics of arsenic in suburban soils of Beijing [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(8): 2849-2854(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2012.08.048
[32] 万千, 赵静, 韦旭, 等. 电子废弃物拆解车间灰尘中重金属污染特征及职业人群健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(3): 883-892. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020110901 WAN Q, ZHAO J, WEI X, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in the dust from e-waste dismantling workshop and health risk assessment of occupational population [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(3): 883-892(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020110901
[33] LEUNG A O W, DUZGOREN-AYDIN N S, CHEUNG K C, et al. Heavy metals concentrations of surface dust from e-waste recycling and its human health implications in southeast China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(7): 2674-2680. [34] WU Y Y, LI Y Y, KANG D, et al. Tetrabromobisphenol A and heavy metal exposure via dust ingestion in an e-waste recycling region in Southeast China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 541: 356-364. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.038 [35] TZORAKI O, ZKERI E, LASITHIOTAKIS M, et al. Trace metals’ contamination in water and soils in the vicinity of a small-medium waste electrical and electronic equipment recycling plant [J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2020, 39(3): e13343. -



 下载:
下载: