-
近年来,随着我国城市化和工业化进程的快速发展,各种环境污染物的排放量急剧增长,致水环境中污染物的种类和数量也持续增加. 水环境质量的不断恶化,给水生生态系统带来不良影响,同时对人类健康构成潜在威胁,严重制约着社会经济的可持续发展.
研究发现,氧化应激是机体受到有害因素作用后的共同反应机制,许多疾病的发生与机体的氧化应激有关[1]. 生物体在一些环境污染物(如重金属、农药、持久性有机污染物、纳米粒子、药物和个人护理用品等)短期胁迫下便可使体内活性物质 (reactive species, RS) 产生增多,当过量的RS超过了机体抗氧化防御系统的清除能力时,会引起机体产生氧化应激反应,造成DNA/RNA、蛋白质等生物分子的氧化损伤,从而导致机体代谢紊乱,诱发疾病[2−3]. 因此,利用氧化应激评价环境污染物的毒性影响,有助于深入了解环境污染物的致病机理,为污染物的监控预警以及疾病的预防提供科学依据[4−5].
斑马鱼 (Danio rerio) 属辐鳍亚纲 (Actinopterygii) 、鲤科 (Cyprinidae) 、短担尼鱼属 (Danio) ,繁殖力强,繁殖周期短,对毒物的刺激十分敏感,具有高度保守的基因组和信号传导通路,与人类基因高度同源[6−7],目前已被广泛应用于生态毒理学相关研究领域,同时也是分子遗传学、发育生物学中常用的模式生物[8−9]. 本文基于重金属、农药和新兴污染物等常见环境污染物对斑马鱼引起的氧化应激反应进行综述,并对该领域未来的研究方向进行展望.
-
机体在正常新陈代谢过程中会产生一定量的活性氧 (reactive oxygen species, ROS) 和活性氮 (reactive nitrogen species, RNS) . ROS是一类较基态氧活泼的含氧基团,包括自由基如羟基 (OH·) 、超氧阴离子 (O2·-) 以及非自由基如过氧化氢 (H2O2) . RNS是一氧化氮 (NO) 与ROS反应产生的一类具有高度氧化活性的自由基和硝基类衍生物,包括 NO、氮氧阴离子 (NO−) 等[10]. 适量的ROS和RNS在生物体内发挥着重要作用,如细胞信号传递和机体免疫,但过量的ROS和RNS会造成机体损害.
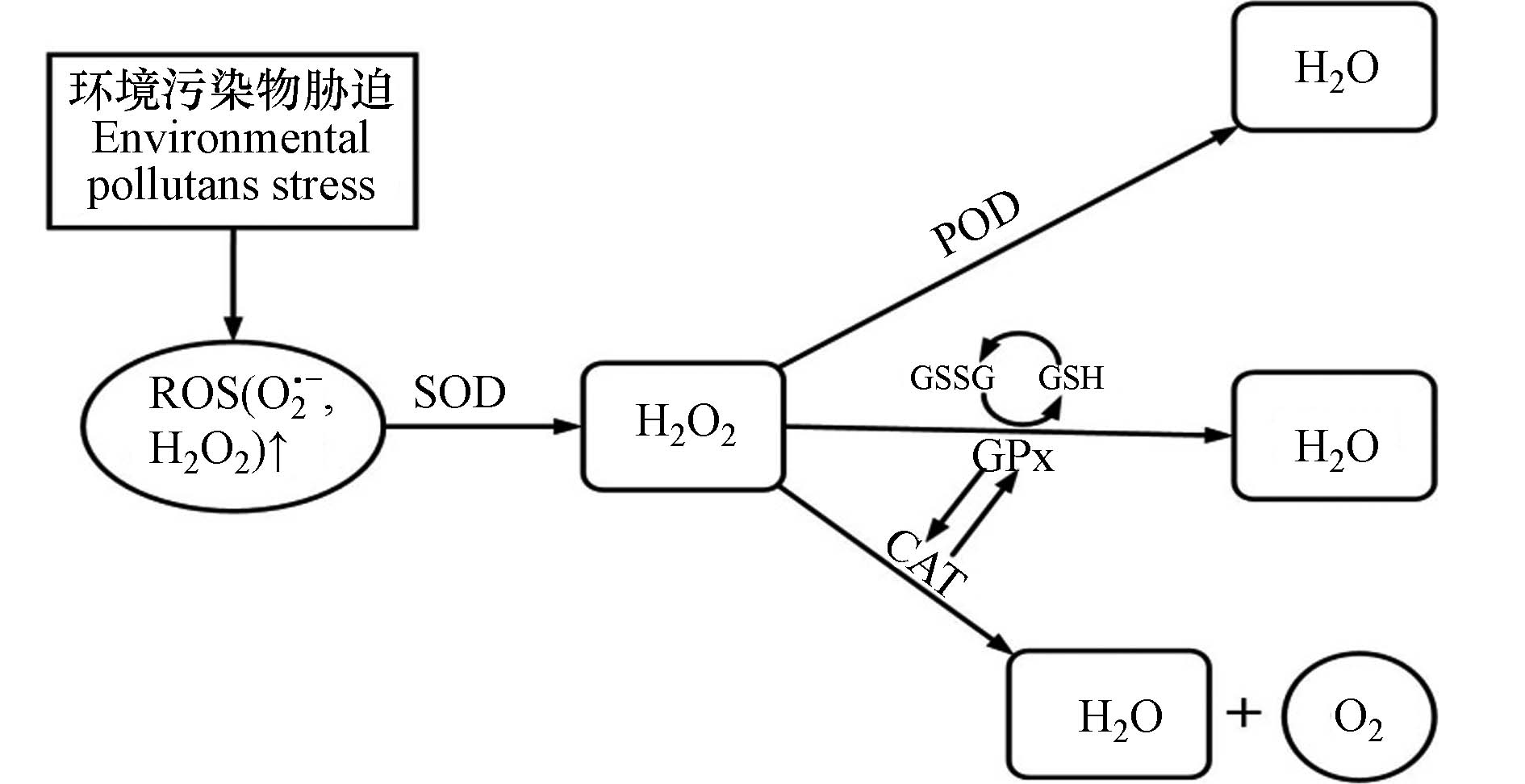
抗氧化防御系统是为了清除体内过量ROS和RNS而自发形成的一种解毒机制,使得ROS和RNS的产生和清除处于动态平衡状态,其主要由抗氧化酶 (如超氧化物歧化酶 (SOD) 、过氧化氢酶 (CAT) 、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 (GPx) 、过氧化物酶 (POD) 等) 以及抗氧化小分子 (如还原型谷胱甘肽 (GSH) 、β-胡萝卜素 (维生素B) 、抗坏血酸 (维生素C) 等) 构成[11]. SOD是抗氧化防御系统的第一道防线,对ROS具有高亲和力,能使O2·-转化为O2和H2O2. 根据不同的金属辅助因子,SOD可分为Cu/Zn-SOD,Mn-SOD和Fe-SOD等,它们有助于防止金属催化的OH·的形成. CAT可以催化H2O2分解反应生成H2O和O2,每分钟可以分解约600万个H2O2分子. 迄今为止,CAT已受到广泛研究,包含300多种类型,如单功能过氧化氢酶、双功能过氧化氢酶和含锰过氧化氢酶等. GPx、POD是生物体内重要的抗氧化酶,均可清除体内的H2O2,在保护机体免受自由基损伤(尤其是脂质过氧化)方面发挥重要作用. GSH是一种水溶性的低分子量抗氧化剂,可维持机体的正常免疫功能,其含量是衡量机体抗氧化能力大小的重要因素. 同时,不同抗氧化酶和抗氧化小分子之间存在联合作用,机体对氧化胁迫的响应是抗氧化系统各成分共同作用的结果,如CAT与GPx可共同作用清除H2O2、并相互影响,具有一定的互补性;GSH可与谷胱甘肽硫转移酶 (GST) 相互协调以有效清除生理性或病理性的氧自由基[12−13](图1).
当体内ROS和RNS的产生清除失衡,机体便会出现氧化应激,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量强氧化性中间产物,引发脂质过氧化、基因突变、蛋白质失活等损伤.
生物膜上的不饱和脂肪酸极易被氧化,当ROS和RNS攻击生物膜时,会引起脂质过氧化反应. MDA是脂质过氧化作用最常见的降解产物之一,能与蛋白质和DNA等大分子形成共价加合物,在糖尿病和神经退行性疾病等多种疾病的发生中发挥作用. 此外,MDA的产生可影响线粒体呼吸链复合物及线粒体内关键酶活性、加剧膜的损伤、放大ROS的作用,因而MDA可以反映机体脂质过氧化速率和强度,是反映氧化损伤最常用的指标之一[2, 14].
DNA与ROS的相互作用可引起DNA-蛋白质交联、糖和碱基修饰产物的形成、链内和链间交联、单链或双链断裂,造成DNA损伤,进而增加机体患癌症、心血管疾病和神经退行性疾病等多种疾病的风险. 在 DNA 碱基中,鸟嘌呤因其最低的氧化还原电位和最高的氧化性而对氧化敏感,当ROS攻击鸟嘌呤碱基第8位碳原子时,可生成8-羟基脱氧鸟苷(8-OHdG). 8-OHdG目前已成为DNA氧化损伤中最有效的生物标志之一[3, 15].
蛋白质因其在细胞、血浆和组织中的丰富性以及与各种氧化剂的高反应速率而成为ROS的重要靶标. 蛋白质与ROS的相互作用可导致氨基酸侧链或蛋白质骨架的氧化、羰基衍生化合物的形成以及蛋白质-蛋白质交联. 其中,蛋白质羰基常被用作蛋白质氧化损伤的生物标记物[15].
机体内的抗氧化防御系统在保护机体免受氧化损伤的过程中起着重要作用. 为了维持机体的正常生理功能,抗氧化防御系统通过阻止或延缓相关底物发生不必要的氧化从而严格控制RS的量,确保机体中“氧化还原稳态”的保持[16−17]. 在环境污染物胁迫下,当机体抗氧化防御系统无法控制RS的过量产生时,机体内氧化和抗氧化平衡态被打破,进而引起生物体发生氧化应激,抗氧化系统各成分和氧化代谢产物可以作为氧化应激的生物标志物利用,用以评价机体的健康状况及获得对环境风险的早期预警信号[18−19].
-
重金属污染较为隐蔽,且周期长,大多具有不可逆性. 当河流、湖泊和海洋等水体受到重金属污染时,会使水质剧烈恶化,对水生动物造成巨大威胁,并可通过生物富集和生物放大作用对人类健康带来严重损害[20]. 研究表明,多种重金属可诱导斑马鱼机体氧化应激的发生,本文主要介绍了环境中较普遍、毒性较强的几种重金属或类金属(镉、铅、汞、砷、铬)[21−22].
-
Cd是一种生物毒性极强的重金属元素,半衰期长,可在生物体内大量蓄积. 较低浓度Cd暴露对成年斑马鱼便具有急性致死效应 (96h-LC50为5 mg·L−1) . 亚致死浓度的Cd暴露可致使斑马鱼大脑、卵巢和肝脏中多种抗氧化酶活性改变,造成脂质过氧化,破坏细胞膜结构[23]. 有研究报道,Cd引起的生物氧化应激可能是由转录因子2 (Nrf2) /抗氧化反应元件 (ARE) 和金属硫蛋白转录因子1 (MTF-1) /金属反应元件 (MRE) 调控[24]. 斑马鱼肝细胞系 (ZFL) 是体外检测和细胞成像的模型细胞系,能准确评估潜在污染物的风险,已被广泛应用于水环境Cd污染的监测评估中. Morozesk等[25]采用ZFL探索了Cd暴露对机体氧化应激的效应,发现Cd暴露使ZFL中CAT及GST活性降低,金属硫蛋白含量和脂质过氧化程度加剧,并引起遗传损伤. Kwok等[26]研究发现,Cd暴露使ZFL中谷胱甘肽还原酶 (GR) 活性上调,MDA含量增加,并引起细胞凋亡.
在抗氧化物对Cd毒性干预作用研究中,锌 (Zn) 被认为是重要的抗氧化剂,Zn能在Cd诱导的机体氧化应激中发挥保护作用,进而降低Cd毒性[27−28]. Chouchene等[29]发现,在Zn干预后,Cd暴露下斑马鱼胚胎表现出的形态异常,生长延迟及高死亡率均有所下降,推测Zn通过影响机体氧化应激反应发挥保护作用. Wang等[30]将斑马鱼置于0和200 mg·L−1 Zn溶液中预暴露8周,然后分别转移至不同浓度的 Cd溶液中继续暴露4 d,发现Zn预暴露通过增强机体抗氧化防御能力显著降低了Cd暴露造成的脂质过氧化. Zn暴露对于生物体的保护作用提示在进行包括Cd在内的重金属毒性评价时,生物体的过往抗氧化物暴露史是需考虑的因素.
-
Pb广泛存在于环境中,难以降解,可造成生物体血液、肾脏及神经系统损害[31]. Pb暴露可导致生物体内ROS过量产生,从而诱导氧化应激,这被认为是Pb对生物体产生神经毒性、肝毒性、肾毒性等多种毒性的重要机制之一[32]. Park等[33]采用斑马鱼研究了温度改变对Pb暴露毒性的潜在影响,发现在热应激 (34 ℃) 条件下Pb显著诱导抗氧化系统相关基因 (SOD、CAT) 表达上调,并加重细胞损伤. 因此,在研究水体污染物的生物毒性影响时,应考虑气候变化(特别是温度)对水环境中污染物毒性的潜在影响.
此外,由于Pb2+很难从体内完全清除,且目前的主要治疗方法(使用乙二胺四乙酸二钠钙、二巯基丁二酸等的螯合疗法)存在较为严重副作用,寻找能减轻或消除Pb2+毒性的药物或补充剂尤为重要. 有研究发现菊苣酸对斑马鱼发育初期的Pb2+毒性具有较强保护作用,这主要是通过减轻Pb2+引起的氧化损伤,恢复BV-2细胞的细胞周期而实现[34].
-
Hg是一种广泛而持久存在的有毒重金属污染物,可对人体的神经系统、肾、肝脏等产生严重的损害作用. 水环境中的Hg可通过抑制水生动物抗氧化酶活性来影响其防御系统,引起机体损伤[35]. Zhang等[36]发现Hg暴露可对斑马鱼胚胎抗氧化酶 (CAT、GST、GPX) 活性、GSH、MDA含量以及编码抗氧化蛋白 (cat1、sod1、gstr、gpx1a、nrf2、keap1) 的mRNA水平等构成影响,引起死亡率和畸形率增加、体长缩短和孵化延迟等发育损伤,并诱导免疫毒性. 同时,Hg对生物抗氧化系统的影响存在性别差异. Hg暴露可诱导成年雄性斑马鱼睾丸中SOD和CAT活性,上调sod1和cat1的表达水平,并引起脂质过氧化以及病理学损伤,而雌性斑马鱼卵巢中SOD、CAT活性及其mRNA表达则相对稳定,提示雄性斑马鱼可能比雌性斑马鱼更易受到Hg污染威胁[37].
-
As是一种广泛分布于自然界中的有毒类金属元素. 环境中的As暴露可通过以下方式引起机体发生氧化应激: (1) As代谢产生的ROS诱导机体出现氧化应激; (2) As与GSH结合,谷胱甘肽二硫化物 (GSSG) 含量增加,耗尽机体内源性抗氧化剂,导致氧化应激[38]. 长期以来,As介导的氧化应激被认为是As毒性的重要机制[39]. Delaney等[40]发现,亚砷酸钠能同时诱导斑马鱼机体氧化应激和内质网应激,并认为两种应激相关通路之间的相互干扰是亚砷酸钠诱导肝毒性的基础.
世界卫生组织规定饮用水的As标准限制为10 mg·L−1,然而,在许多发展中国家,50 mg·L−1的As被认为是饮用水的可接受水平[41]. 有研究表明,即使是50 mg·L−1的As,其毒性也足以在斑马鱼中引起显著的氧化应激[42]. 近年来,水环境中低剂量的As暴露毒性受到广泛关注. Sun等[43]发现,低浓度 (≤150 mg·L−1) 的As2O3可诱导斑马鱼胚胎SOD活性升高,影响Cu/Zn-SOD和Mn-SOD的mRNA 转录水平,斑马鱼胚胎进而通过调节金属硫蛋白1 (MT1) 和热休克蛋白70 (HSP70) 的转录水平以对抗由As2O3引起的氧化应激,但低浓度的As仍可造成脂质过氧化等氧化损伤. Dong等[44]发现,暴露于低浓度的As2O3中不仅会诱导斑马鱼胚胎出现氧化应激,还可进一步损害斑马鱼的生长发育,诱导细胞凋亡.
-
Cr及其化合物被广泛应用于皮革、印染和不锈钢等工业生产中,是重要的环境污染物之一. Cr在自然界中主要以三价铬 (Cr (Ⅲ) ) 和六价铬(Cr (Ⅵ) )存在. Cr (Ⅲ) 毒性较小,是人体代谢所必须的元素,而Cr (Ⅵ) 对肝、肾、神经系统等具有广泛毒性作用[22],氧化应激被认为是Cr (Ⅵ) 毒性作用的关键环节之一. Cr (Ⅵ) 暴露引起的持续氧化应激在多个转录因子(NF-κB、AP-1、p53和HIF-1) 的激活、细胞周期的调节和细胞凋亡的诱导中起关键作用,进而导致肝、肾毒性[45]. 近年来,Cr (Ⅵ) 诱导的神经毒性、免疫毒性与氧化应激的相关性在斑马鱼模型得到初步证实. Shwa等[46]发现环境相关浓度 (2 mg·L−1) 的Cr可造成斑马鱼脑中CAT活性上升,GSH和MDA含量升高,诱导神经毒性,抗氧化相关蛋白 (Nrf2, NQO1, HO-1) 的表达表明其毒性机制可能与Nrf2-ARE信号通路有关. Jin等[23]发现斑马鱼胚胎暴露于Cr (Ⅵ) 后,影响斑马鱼胚胎SOD、GPx和GST的活性及相关基因的转录水平,出现脂质过氧化,造成免疫毒性. 虽然目前初步证实氧化应激是Cr (Ⅵ) 诱导多种毒性的关键机制,但仍需进一步寻找相关的毒性靶点. 重金属致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究汇总见表1.
-
我国目前是全球最大的农药生产国和使用国,农药污染形势极为严峻. 农药可通过干湿沉降、地表径流、土壤淋溶等多种途径进入水环境,对水生生态系统造成严重破坏. 目前,关于农药胁迫对斑马鱼氧化应激的研究主要集中于杀菌剂、杀虫剂、除草剂(表2).
-
三唑类杀菌剂是一类有机杂环类化合物,具有广谱性,高效性,内吸传导性强等特点,既能防病治病,又能调节作物生长,是目前使用面较广的一类药剂[47]. 典型的三唑类杀菌剂有戊唑醇、丙环唑和苯醚甲环唑等,因其具有低生物降解性和易在环境中转移等特点,能在环境中长期存在,对生态环境系统和人类健康构成严重威胁. Li等[48]发现,在低浓度戊唑醇胁迫下,成年斑马鱼肝脏中的多种酶活性 (SOD、CAT、POD和GST) 均显著增加,凋亡基因 (bax, caspase-8) 表达上调,导致肝损伤. Zhao等[49]发现,丙环唑诱导斑马鱼氧化状态失衡,胚胎中ROS含量上升,GPx和CAT活性显著上调,造成脂质过氧化和细胞凋亡. Zhu等[50]发现,苯醚甲环唑造成了斑马鱼体内ROS的过度积累和抗氧化酶 (SOD、CAT和GST) 的抑制,触发细胞凋亡,诱发心血管毒性;抗氧化剂 N-乙酰-L-半胱氨酸可以显著逆转氧化应激并减轻苯醚甲环唑诱导的心血管异常.
甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂是继三唑类杀菌剂后又一广泛使用的杀菌剂. 甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂对细菌毒性机制主要是通过结合在线粒体复合体Ⅲ的细胞色素Qo位点来阻断电子传递链,抑制线粒体的呼吸,从而导致ATP合成的损失,造成氧化损伤[51]. Li等[52]将斑马鱼胚胎暴露于三种甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂(吡唑醚菌酯,肟菌酯和啶氧菌酯)中96 h,发现3种甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂均诱导斑马鱼体内ROS和MDA含量增加,抑制了SOD活性和GSH含量,同时改变Mn-SOD的mRNA水平,诱导胚胎发生氧化应激并引起免疫毒性. Han等[53]将斑马鱼暴露于甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂嘧菌酯中,发现ROS在斑马鱼肝脏中积累显著增多,肝脏SOD,CAT和GST活性受到诱导,脂质过氧化程度加剧;并且不同性别斑马鱼表现出不同的敏感性,与雄性斑马鱼相比,雌性斑马鱼表现出更高的ROS敏感性,这可能与雌激素通过增强抗氧化酶相关基因的表达来发挥保护作用有关. 因此,应用斑马鱼评价甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂的氧化应激效应时,应考虑性别差异. Mao等[54]在开展甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂吡唑醚菌酯对斑马鱼毒性影响研究时发现,除性别差异外,吡唑醚菌酯杀菌剂对斑马鱼不同生命阶段的氧化应激效应也有差异,对成年斑马鱼的潜在不利影响相对较低,对斑马鱼胚胎/幼鱼的影响更为显著.
-
氯氰菊酯 (CYP) 是一种拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂,被广泛应用于害虫防治,是淡水生态系统中常见的污染物[55]. Paravani等[56-57]发现CYP可使斑马鱼鳃SOD和CAT活性显著上升,引起Mn-sod-cat基因mRNA水平显著上调,并出现DNA损伤. 高效氯氰菊酯 (β-CYP)是CYP的一种高效异构体,对多种生物具有潜在的免疫毒性及神经毒性,且具有显著的对映选择性[58]. Mu等[59]研究将成年斑马鱼分别置于β-CYP对映体和β-CYP外消旋体中,结果表明在0.1 mg·L−1浓度下,1R-cis-aS和1R-trans-aS对映体及β-CYP外消旋体能显著诱导肝脏脂质过氧化,但只有1R-cis-aS引起脑脂质过氧化;而暴露于1S-cis-aR和1S-trans-aR对映体的斑马鱼则未观察到明显的氧化应激. 因此,在进行β-CYP环境风险评估时,β-CYP对成年斑马鱼氧化应激影响应考虑该农药的对映选择性.
在杀虫剂造成氧化应激的干预保护研究中,Han等[60]发现褪黑素 (MLT) 能通过抑制杀虫剂介导的斑马鱼氧化应激来有效的保护斑马鱼免受杀虫剂诱导的发育神经毒性和细胞凋亡.
此外,斑马鱼抗氧化活性系统在吡虫啉[61]、毒死蜱[62]等杀虫剂农药毒性评价中也得到广泛的应用,这些农药均可对斑马鱼抗氧化酶产生诱导或抑制效应,造成氧化损伤,且肝脏是主要的靶器官.
-
百草枯是一种速效触杀灭生性除草剂,易溶于水,有腐蚀性,毒性强,除草效果极佳,是世界上使用最广泛的除草剂之一,被认为是一种典型的氧化应激触发物[63]. Wang等[64]将斑马鱼暴露于百草枯后,发现斑马鱼体内MDA含量和CAT活性显著上升,抗氧化酶相关基因 (sod1、sod2等) 及Nrf2信号通路被激活,并认为斑马鱼是研究百草枯诱导氧化应激机制和筛选有效抗氧化剂的有效模式生物.
乙草胺是我国用量最大的农药之一,具有较高的水溶性,在水环境中被广泛检出,研究表明,乙草胺能显著激活生物体肝脏氧化应激[65]. Zhang等[66]研究发现长期高剂量乙草胺暴露可降低斑马鱼卵巢的抗氧化能力,破坏卵巢的功能;乙草胺浓度越高,暴露时间越长,斑马鱼抗氧化能力越差;诱导氧化应激可能是乙草胺影响鱼类卵巢发育的机制之一. 农药致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究汇总见表2.
-
新兴污染物 (emerging contaminants, ECs) 是指尚未受到相关政策法规限制,浓度普遍较低且监测方法有限,对环境和人类健康具有潜在严重危害的污染物[67]. 新兴污染物的环境污染及生态毒理效应已成为全球所面临的重大环境问题之一. 近年来,在环境污染物胁迫对斑马鱼氧化应激效应的研究领域,研究者们不再局限于重金属、农药等常见的环境污染物,开始关注持久性有机污染物、纳米粒子、药品及个人护理品等新兴污染物的毒性影响[68](表3).
-
POPs是具有持久性、生物积累性和高毒性,能够进行长距离迁移并对人类健康和生态环境具有严重危害的有机污染物[69]. 水体是POPs在环境中迁移转化的重要介质,水环境中的POPs可对水生生物产生毒害作用[70].
多氯联苯 (PCBs) 又称氯化联苯,是斯德哥尔摩公约优先禁止的持久性有机污染物之一,是水环境中广泛分布的典型持久性有机污染物[71]. PCBs暴露能够引起机体氧化应激的产生. Liu等[72]将斑马鱼胚胎暴露于3,3',4,4',5-五氯联苯中,发现斑马鱼体内MDA含量增加,抗氧化酶 (Cu/Zn-Sod、CAT、GPx) 活性下降. PCBs暴露诱导的氧化应激被认为与芳烃受体 (AHR) 的激活有关,AHR激活后可导致细胞色素P4501A (CYP1A) 的表达增加,从而诱导ROS产生[73].
有研究发现,机体暴露于PCBs后,维生素E的细胞水平会降低,维生素E作为抗氧化物质可对PCBs造成的毒性损伤具有保护作用[74]. Na等[75]将斑马鱼胚胎暴露于3,3',4,4',5-五氯联苯中,并使用维生素E进行干预,发现维生素E能通过诱导热休克蛋白 (HSC70) 和SOD2的表达并抑制芳烃受体 2 (AHR2) 和 CYP1A 的表达有效发挥抗氧化作用.
全氟辛烷磺酸 (PFOS) 曾被广泛应用于纺织、食品包装及电镀行业,具有神经毒性、内分泌毒性、和生殖毒性[76]. 近年来,鉴于对动物和人类的潜在毒性,PFOS已被许多国家禁止使用,由半衰期相对较短的氯代多氟烷基醚磺酸盐 (F-53B) 、全氟壬烯氧基苯磺酸钠 (OBS) 等作为PFOS的替代品. 但目前对PFOS替代品的排放和处置缺乏限制,导致其广泛存在于水环境中,应充分关注其潜在的生态环境风险[77−78]. Wu等[79]将斑马鱼幼鱼暴露于F-53B溶液中48 h,发现F-53B对斑马鱼的毒性效应与PFOS类似,在斑马鱼幼鱼中具有生物累积性和持久性,环境相关浓度便可诱导氧化应激反应,CAT、SOD、Cu/Zn−SOD和GST活性降低,GPx活性升高,脂质过氧化程度加剧. Zou等[80]发现,OBS对斑马鱼幼鱼的氧化应激效应与PFOS相当,其机制可能均与Nrf2-ARE信号通路有关.
二噁英化合物属于典型的持久性有机污染物,其中以2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并二恶英 (TCDD) 毒性最强. TCDD暴露能导致生物体内氧自由基的过度生成,出现氧化应激[81]. 聂芳红等[82]将斑马鱼暴露于TCDD中,发现受试斑马鱼受到过多氧自由基的攻击,肝脏MDA含量增加,SOD和GST活性降低,从而造成机体损伤.
多溴二苯醚 (PBDEs) 是广泛用于家具、汽车和建材生产的溴化阻燃剂. Meng等[83]发现2,2',4,4'-四溴联苯醚 (BDE-47) 和2,2',4,4',5,5-六溴二苯醚 (BDE-153) 能诱导斑马鱼肝细胞SOD和CAT活性显著升高,出现氧化应激并进一步造成DNA损伤和细胞凋亡.
-
现今,纳米材料在电子、化工、生物医药等诸多领域发挥重要作用,了解其对环境及生物体的潜在安全性变得至关重要[84]. 相关研究表明,氧化应激可能在纳米粒子毒性作用中发挥关键作用[85]. Tang等[86]发现长期暴露于二氧化钛纳米粒子 (TiO2-NPs) 可使斑马鱼肝脏、肠道和鳃中SOD、CAT和GST的活性均显著上升以对抗不良反应,但这些酶活性的上升仍不足以抵消过量的ROS,最终斑马鱼出现氧化损伤,其中以肝脏和鳃更为明显. 这与Sarasamma等[87]将斑马鱼暴露于C70纳米颗粒的毒性研究结果类似.
同时,纳米粒子同其他污染物的联合暴露可能存在协同效应. Du等[88]发现PFOS和氧化锌纳米颗粒 (ZnO-NPs) 联合暴露导致斑马鱼体内ROS含量、GPx活性和MDA含量明显升高,氧化应激相关的基因如Cat、Gpx1a和Sod1显著下调;联合暴露比单独暴露可能更易引起严重的氧化应激和氧化损伤.
此外,不同粒径的纳米颗粒对斑马鱼氧化应激效应不同. Zhu等[89]将斑马鱼暴露于不同粒径的SiO2纳米粒子溶液中,发现15 nm处理组的SiO2积累量明显高于30 nm组,且15 nm SiO2比30 nm SiO2对斑马鱼幼鱼的ROS水平、抗氧化系统和脂质过氧化的影响更为显著,表明小粒径纳米可引起更严重的氧化应激.
-
PPCPs主要是指各种常用药物(如抗生素、结核药等)与护理用品(如香料、化妆品等)及其代谢产物在内的一系列化学物质,多种PPCPs在浓度极低时便可对生物产生急性和慢性毒性作用[90].
Zou等[91]发现抗结核药异烟肼能显著提高斑马鱼幼鱼体内ROS和MDA的含量,降低SOD的活性,异烟肼诱导斑马鱼幼鱼产生的氧化应激是其具有发育毒性的重要原因之一. Félix等[92]发现麻醉药氯胺酮胁迫导致斑马鱼胚胎中SOD、CAT、GSSG活性均受到影响,Sod1和Cat基因表达显著上调. 氯胺酮主要通过参与斑马鱼胚胎中的p53依赖性途径诱导氧化应激,而氧化应激是氯胺酮对斑马鱼具有致畸性的重要原因. Liang等[93]发现烟酸诺氟沙星 (NOR-N) 暴露提高了斑马鱼幼鱼体内SOD、CAT和GPx的活性及MDA含量,并上调相关基因mRNA水平,引起发育毒性及免疫毒性. Pavla等[94]探讨了抗生素恩诺沙星对斑马鱼的毒性影响,发现暴露3 d时斑马鱼体内的GPx和GST活性便出现了变化,高浓度组 (500 μg·L−1) 脂质过氧化程度加剧;但暴露7 d起,所有抗氧化酶活性或脂质过氧化程度趋于正常;暴露14 d后,抗氧化酶基因的mRNA表达也恢复正常,这表明斑马鱼幼鱼抗氧化防御系统可能有能力在短时间内适应恩诺沙星的胁迫.
三氯生因具有良好的广谱抗菌性能而被广泛应用于洗衣粉、肥皂、牙膏等个人护理产品中,常在环境和生物体中被频繁检出. Gyimah等[95]将斑马鱼暴露于三氯生中,发现斑马鱼体内多种抗氧化酶活性显著降低,MDA、8-OHdG和蛋白质羰基等氧化损伤标记物的含量显著增加,脑和肝脏是主要的靶器官. 王凡等[96]发现较高浓度三氯生显著影响了斑马鱼卵巢抗氧化 (SOD、CAT、GPx1a和MT-2) 和凋亡 (Bcl-2、p53和Bax) 相关基因的表达,从而产生了氧化损伤,加速细胞凋亡的发生. 可见,三氯生的潜在生态风险不容忽视. 新兴污染物致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究汇总见表3.
此外,还有研究者对微囊藻毒素、微塑料、内分泌干扰物等其他常见新兴环境污染物致斑马鱼氧化应激效应进行了研究,见表4.
-
随着科学技术和社会经济的快速发展,越来越多的化学物质被人们排放到水环境中,水环境污染问题日趋严重,对水生生物和人类健康构成严重威胁. 氧化应激是水环境污染物致机体损伤的重要机制,通过对水环境污染物致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究,有助于早期预警并预防水环境污染物引起的机体损伤,为探索更有效的防治水环境污染物危害的方法和技术奠定基础. 目前,关于环境污染物致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究还不够系统和深入,限制着对环境污染物致病机理的认识,今后可进一步从以下几方面展开研究:
(1) 在当前的环境污染中,环境污染物的暴露往往不是单一出现的,更多是以联合暴露的形式威胁环境安全和人类健康,目前的研究局限于传统的环境污染物联合暴露对机体氧化应激的影响,且联合暴露的污染物数量种类较少,这与实际情况不符. 同时,环境污染物毒性影响易受到环境因素 (如温度、pH等) 的影响,基于斑马鱼机体氧化应激反应关注不同环境因素下的污染效应将更具现实意义.
(2) 环境污染物致斑马鱼不同性别、不同器官、不同生长发育阶段氧化应激效应的差异目前仍缺乏系统性的研究,同时这些变化趋势的解释还局限于推理和猜测,需要开展更多的研究来阐明确切的影响机制.
(3) 新兴环境污染物在多种环境介质中被广泛检出,分析其生物可利用性及在不同条件下的实际暴露水平、探明其对斑马鱼机体氧化应激的效应,寻找有效的监测评价生物标记物,应受到更多的关注.
(4) 在抗氧化物质的研究中,Zn、菊苣酸、VC[104]、白藜芦醇[105]、岩藻多糖[106]等物质虽已明确对斑马鱼机体氧化应激具有保护作用,但作用机制尚不明确. 寻求更多、更为有效的抗氧化剂,并明确其作用机制是预防、治疗生物体受到氧化损伤的关键途径.
常见环境污染物致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究进展
Research progress on oxidative stress induced by common environmental pollutants in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
-
摘要: 近年来,随着我国城市化和工业化进程的快速发展,水环境污染问题日趋严重,对生态环境和人类健康构成潜在威胁. 氧化应激是机体促氧化物产生和清除之间出现失衡的一种状态,被认为是影响许多疾病发生发展的重要因素,是水环境污染物对生物体产生毒性的重要途径之一. 本文基于重金属、农药和新兴污染物等常见环境污染物对斑马鱼所产生的氧化应激反应进行综述,以期为开展污染物损伤生物体的监控预警及疾病预防提供一定参考依据.Abstract: In recent years, with the rapid development of urbanization and industrialization, the problem of water environment pollution has become increasingly serious, which poses a potential threat to the ecological environment and human health. Oxidative stress is a state of imbalance between the production and removal of prooxidants, which is considered to be an important factor affecting the occurrence and development of many diseases and one of the important ways for water environmental pollutants to produce toxicity to organisms. In this paper, the oxidative stress reactions of zebrafish caused by common environmental pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and emerging pollutants were reviewed to provide some reference for the monitoring and early warning of pollutant damage organisms and disease prevention.
-
Key words:
- environmental pollutants /
- zebrafish /
- oxidative stress
-

-
表 1 重金属致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究
Table 1. Studies on oxidative stress of zebrafish by heavy metals
污染物
Pollutants生长发育时期或模型
Growth period or model浓度
Concentration暴露时间
Exposure time氧化应激
Oxidative stress毒性效应
Toxic effects参考文献
ReferencesCd 肝细胞系 1、5 、10 mg·L−1 24 h CAT↓ GST↓ MDA↑ 遗传损伤 [25] 肝细胞系 0.229、0.458 、0.917 mg·L−1 24 h GR↑ 细胞凋亡 [26] Pb 胚胎 2、7、10 μg·L−1 7 d SOD↑ CAT↑ 细胞凋亡 [33] Hg 胚胎 1、4、16 μg·L−1 7 d CAT↑ GST↑ GPx↓ GSH↑ MDA↑ 发育毒性、免疫毒性 [36] 成鱼(雄/雌) 15、30 μg·L−1 30 d 雄:SOD↑ CAT↑ GSH↑ MDA↑
雌:GPx↓ GSH↓生殖毒性 [37] As 幼鱼 25、50、75 、 150 mg·L−1 120 h SOD↑ MDA↑ 脂质过氧化 [43] 成鱼 10、50、100 、150 mg·L−1 28 d SOD↑ CAT↑ MDA↓ 发育毒性、细胞凋亡 [44] Cr 成鱼 2 mg·L−1 60 d CAT↑ GSH↑ MDA↑ 细胞凋亡、神经毒性 [45] 胚胎 0.882、2.942、8.825 mg·L−1 96 h SOD↑ GPx↓ GST↑ Cu/Zn-Sod↑ Mn-Sod↑ Cat↑ GPx↑ 免疫毒性 [23] 注:正体字母代表酶或小分子,斜体字母代表基因.
Note: normal letters represent enzymes or small molecules, and italic letters represent genes.表 2 农药致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究
Table 2. Studies on oxidative stress of zebrafish by pesticides
污染物
Pollutants生长发育
时期或模型
Growth period
or model浓度
Concentration暴露时间
Exposure time氧化应激
Oxidative stress毒性效应
Toxic effects参考文献
References戊唑醇 成鱼 0.18、0.92 、 1.84 mg·L−1 28 d SOD↑ CAT↑ POD↑ GST↑ 细胞凋亡、肝脏毒性 [48] 丙环唑 胚胎 0.5、2 、5 mg·L−1 96 h ROS↑ GPx↑ CAT↑ MDA↑ 细胞凋亡、免疫毒性 [49] 苯醚甲环唑 胚胎 0.3、0.6 和1.2 mg·L−1 96 h ROS↑ SOD↓ CAT↓ GST↓ 细胞凋亡、心血管毒性 [50] 甲氧基丙烯
酸酯类杀菌
剂曲霉素胚胎 30—105 mg·L−1 96 h ROS↑ SOD↓ MDA↑ GSH↓ 免疫毒性 [52] 成鱼
(雄/雌)1、10、100 μg·L−1 28 d 雄:ROS↑ SOD↑↓ CAT↑ GST↑ MDA↑
雌:ROS↑ SOD↓ CAT↑ GST↓↑ MDA↑遗传毒性 [53] 幼鱼/成鱼(雄/雌) 25、50、75 、 150 mg·L−1 96 h/28 d 幼鱼:CAT↑ POD↑ GST↑ MDA↑
成鱼(雄):SOD↓ CAT↑↓ POD↑↓ GST↓↑ MDA↑
成鱼(雌):SOD↑↓CAT↑↓↑ POD↑ GST↓↑ MDA↑发育毒性 [54] 氯氰菊酯 成鱼 0.3、0.6 μg·L−1 12 d SOD↑ CAT↑ 遗传毒性 [56-57] 吡虫啉 成鱼 2 mg·L−1 28 d ROS↑ SOD↑↓ GST↑↓ CAT↑ MDA↑ 遗传毒性 [61] 毒死蜱 成鱼 30、100、300 μg·L−1 21 d SOD↓ GST↓ GPx↓ GSH↓ MDA↑ 消化道毒性 [62] 百草枯 幼鱼 100 mg·L−1 72 h CAT↑ MDA↑ 细胞凋亡 [64] 乙草胺 成鱼 1、10、100 μg·L−1 21 d SOD↑ CAT↑ GPx↑ 发育毒性 [66] 表 3 新兴污染物致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究
Table 3. Studies on oxidative stress of zebrafish by emerging pollutants
污染物
Pollutants生长发育时
期或模型
Growth period
or model浓度
Concentration暴露时间
Exposure
time氧化应激
Oxidative stress毒性效应
Toxic effects参考文献
References3,3',4,4',5-五氯联苯 胚胎 16、32、64、128 μg·L−1 7 d Cu/Zn-Sod↓ CAT↓ GPx↓ MDA↑ 发育毒性 [72] 氯代多氟烷基醚磺酸盐 幼鱼 10、100 mg·L−1 72 h SOD↓ Cu/Zn-Sod↓ CAT↓ GST↓ GPx↑ GSH↓ MDA↑ 脂质过氧化 [79] 2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并二恶英 成鱼 0.1、0.2、0.4、0.8 μg·L−1 5 d SOD↓GST↓ MDA↑ 脂质过氧化 [82] 多溴二苯醚 成鱼 5、50、500 μg·L−1 15 d SOD↑ CAT↑ 细胞凋亡、遗传毒性 [83] 二氧化钛纳米粒子 成鱼 10、50、100 mg·L−1 7 d SOD↓ CAT↓ GSTs↓ MDA↑ 脂质过氧化 [86] C70纳米颗粒 幼鱼/成鱼 0.5 、 1.5 mg·L−1 14 d ROS↑ SOD↑ MDA↑ 神经毒性 [87] 异烟肼 幼鱼 1、2、4、6、8、16 mmol·L−1 72 h ROS↑ SOD↓ MDA↑ Sod1↓ 发育毒性 [91] 氯胺酮 胚胎 50、70、90 mg·L−1 24 h ROS↑ SOD↑ CAT↑ GSSG↑ Sod1↑ Cat↑ 细胞凋亡 [92] 烟酸诺氟沙星 胚胎 0.002、0.2、1、5、25 mg·L−1 96 h SOD↑ CAT↑ GPx↑ MDA↑ 发育毒性、免疫毒性 [93] 恩诺沙星 幼鱼 5、10、500 μg·L−1 14 d GPx↓ GST↑ MDA↑ 脂质过氧化 [94] 三氯生 成鱼 50、100、150 μg·L−1 30 d SOD↓ CAT↓ GPx↓ GSH↓ GSSH↓ GR↓ MDA↑ 8-OHdG↑ 蛋白质羰基↑ 遗传毒性 [95] 成鱼 0.034、0.068 mg·L−1 42 d SOD↓ CAT↓ GPx1a↑↓ MT-2↑ 细胞凋亡 [96] 注:正体字母代表酶或小分子,斜体字母代表基因.
Note: normal letters represent enzymes or small molecules, and italic letters represent genes.表 4 其他新兴环境污染物致斑马鱼机体氧化应激的研究
Table 4. Studies on oxidative stress of zebrafish by other emerging pollutants
污染物
Contaminants研究方法
Method斑马鱼氧化应激效应
Effects of pollutants on the oxidative stress of zebrafish参考文献
References微囊藻毒素 雌性斑马鱼暴露于微囊藻毒素7 d 卵巢中SOD、CAT和GPx活性及mRNA水平皆上调,MDA含量增加,出现生殖毒性. [97] 成年斑马鱼暴露于微囊藻毒素7 d 低浓度组 (50 μg·kg−1) 抗氧化酶活性及其mRNA水平皆上调,出现轻微肝损伤,高浓度组(200 μg·kg−1) 抗氧化酶活性及其mRNA水平皆下调,出现严重的肝损伤. [98] 微塑料 成年斑马鱼暴露于聚苯乙烯微塑料中7 d 肝脏中SOD和CAT活性皆上升,出现肝脏炎症和脂质积累. [99] 成年斑马鱼暴露于聚苯乙烯微塑料中21 d 肠道中SOD和CAT活性皆上升,出现肠道炎症. [100] 氧化石墨烯 成年斑马鱼暴露于氧化石墨烯14 d 肝脏中MDA含量、SOD和CAT活性增加,GSH含量降低,出现组织损伤及肠道炎症. [101] 双酚S 成年斑马鱼暴露于双酚S 75 d 长期暴露于双酚S可能会通过诱导大脑氧化应激造成斑马鱼出现焦虑和恐惧反应. [102] 四溴双酚A 斑马鱼胚胎暴露于四溴双酚A 72 h 四溴双酚A浓度高于0.1 mg·L−1时,SOD、CAT和GPx的酶活性出现降低;在1 mg·L−1浓度时,SOD、CAT和GPx1a的基因表达也出现显著降低. 出现细胞凋亡及心脏毒性. [103] 注:正体字母代表酶或小分子,斜体字母代表基因.
Note: normal letters represent enzymes or small molecules, and italic letters represent genes. -
[1] FORMAN H J, ZHANG H Q. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy [J]. Nature Reviews Drμg Discovery, 2021, 20(9): 689-709. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1 [2] WANG F, XU R, ZHENG F, et al. Effects of triclosan on acute toxicity, genetic toxicity and oxidative stress in goldfish (Carassius auratus) [J]. Experimental Animals, 2018, 67(2): 219-227. doi: 10.1538/expanim.17-0101 [3] ZHANG Y X, GUO P Y, WU Y M, et al. Evaluation of the subtle effects and oxidative stress response of chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol, and florfenicol in Daphnia magna [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 575-584. doi: 10.1002/etc.4344 [4] 蒋安祺, 刘慧, 王为木. 纳米ZnO对中华圆田螺的氧化应激效应 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(4): 892-897. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.04.2016102505 JIANG A Q, LIU H, WANG W M. Oxidative stress of nano ZnO on Cipangopaludina cahayensis [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(4): 892-897(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.04.2016102505
[5] 殷健. 重金属对斑马鱼的毒性效应及作用机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2014: 19-22. YIN J. Studies on toxic effect and mechanism of heavy metals on zebrafish[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2014: 19-22(in Chinese).
[6] HOWE K, CLARK M D, TORROJA C F, et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome [J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 498-503. doi: 10.1038/nature12111 [7] LEE J G, CHO H J, JEONG Y M, et al. Genetic approaches using zebrafish to study the microbiota-gut-brain axis in neurological disorders [J]. Cells, 2021, 10(3): 566. doi: 10.3390/cells10030566 [8] XU C, TU W Q, DENG M, et al. Stereoselective induction of developmental toxicity and immunotoxicity by acetochlor in the early life stage of zebrafish [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 164: 618-626. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.004 [9] HOLTZMAN N G, IOVINE M K, LIANG J O, et al. Learning to fish with genetics: A primer on the vertebrate model Danio rerio [J]. Genetics, 2016, 203(3): 1069-1089. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.190843 [10] LU Q R, SUN Y Q, ARES I, et al. Deltamethrin toxicity: A review of oxidative stress and metabolism [J]. Environmental Research, 2019, 170: 260-281. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.045 [11] WINZER K. Oxidative stress in the marine environment-prognostic tools for toxic injury in fish liver cells[D]. Amsterdam: Universität Amsterdam, 2001: 19-23. [12] VAN DER OOST R, BEYER J, VERMEULEN N P E. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2003, 13(2): 57-149. doi: 10.1016/S1382-6689(02)00126-6 [13] 余晓玲. 猪场废水中四环素类抗生素对斑马鱼抗氧化效应毒理研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2019: 11-13. YU X L. Toxicological study on antioxidant effects of tetracycline antibiotics on zebrafish in swine wastewater[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019: 11-13(in Chinese).
[14] LU D L, MA Q, SUN S X, et al. Reduced oxidative stress increases acute cold stress tolerance in zebrafish [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A:Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 2019, 235: 166-173. [15] DEMIRCI-ÇEKIÇ S, ÖZKAN G, AVAN A N, et al. Biomarkers of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense [J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2022, 209: 114477. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2021.114477 [16] PICKERING A D. Rainbow trout husbandry: Management of the stress response [J]. Aquaculture, 1992, 100(1/2/3): 125-139. [17] 黄钰清, 杨燕宁. 氧化应激在糖尿病性角膜病变中的研究进展 [J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2022, 22(3): 399-402. HUANG Y Q, YANG Y N. Research progress of oxidative stress in diabetic keratopathy [J]. International Eye Science, 2022, 22(3): 399-402(in Chinese).
[18] ALMEIDA J A, DINIZ Y S, MARQUES S F G, et al. The use of the oxidative stress responses as biomarkers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to in vivo cadmium contamination [J]. Environment International, 2002, 27(8): 673-679. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00127-1 [19] 王晓蓉, 罗义, 施华宏, 等. 分子生物标志物在污染环境早期诊断和生态风险评价中的应用 [J]. 环境化学, 2006, 25(3): 320-325. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.03.016 WANG X R, LUO Y, SHI H H, et al. Application of molecular biomarkers in early diagnosis and ecological risk assessment for water and soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2006, 25(3): 320-325(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2006.03.016
[20] GASMI T, KHOUNI I, GHRABI A. Assessment of heavy metals pollution using multivariate statistical analysis methods in Wadi El Bey (Tunisia) [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2016, 57(46): 22152-22165. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2016.1147377 [21] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 关于进一步加强重金属污染防控的意见[EB/OL]. [2022-03-07]. [22] 洪亚军, 冯承莲, 徐祖信, 等. 重金属对水生生物的毒性效应机制研究进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(11): 1-9. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201911001 HONG Y J, FENG C L, XU Z X, et al. Advances on ecotoxicity effects of heavy metals to aquatic organisms and the mechanisms [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(11): 1-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201911001
[23] JIN Y X, LIU Z Z, LIU F, et al. Embryonic exposure to cadmium (II) and chromium (VI) induce behavioral alterations, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 2015, 48: 9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2015.01.002 [24] CHEUK W K, CHAN P C Y, CHAN K M. Cytotoxicities and induction of metallothionein (MT) and metal regulatory element (MRE)-binding transcription factor-1 (MTF-1) messenger RNA levels in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) ZFL and SJD cell lines after exposure to various metal ions [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2008, 89(2): 103-112. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.06.006 [25] MOROZESK M, FRANQUI L S, PINHEIRO F C, et al. Effects of multiwalled carbon nanotubes co-exposure with cadmium on zebrafish cell line: Metal uptake and accumulation, oxidative stress, genotoxicity and cell cycle [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 202: 110892. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110892 [26] KWOK M L, CHAN K M. Oxidative stress and apoptotic effects of copper and cadmium in the zebrafish liver cell line ZFL [J]. Toxicology Reports, 2020, 7: 822-835. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.06.012 [27] 吴丰昌, 冯承莲, 曹宇静, 等. 锌对淡水生物的毒性特征与水质基准的研究 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2011, 6(4): 367-382. WU F C, FENG C L, CAO Y J, et al. Toxicity characteristic of zinc to freshwater biota and its water quality criteria [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2011, 6(4): 367-382(in Chinese).
[28] 储蓄, 张军霞, 王晶. 动物氧化应激及其营养调控措施研究进展 [J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2021, 52(12): 3346-3356. doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.012.003 CHU X, ZHANG J X, WANG J. Research progress of animal oxidative stress and its nutritional regulation [J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2021, 52(12): 3346-3356(in Chinese). doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2021.012.003
[29] CHOUCHENE L, KESSABI K, GUEGUEN M M, et al. Interference with zinc homeostasis and oxidative stress induction as probable mechanisms for cadmium-induced embryo-toxicity in zebrafish [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(26): 39578-39592. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-18957-x [30] WANG C C, SI L F, GUO S N, et al. Negative effects of acute cadmium on stress defense, immunity, and metal homeostasis in liver of zebrafish: The protective role of environmental zinc dpre-exposure [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 222: 91-97. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.111 [31] 郭晖, 庄静静. 3种水生植物对铅污染水体的抗性研究 [J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2019, 39(2): 52-59. GUO H, ZHUANG J J. Resistance of 3 aquatic plants to lead polluted water [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 39(2): 52-59(in Chinese).
[32] LOPES A C B A, PEIXE T S, MESAS A E, et al. Lead exposure and oxidative stress: A systematic review [J]. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2016, 236: 193-238. [33] PARK K, HAN E J, AHN G, et al. Effects of thermal stress-induced lead (Pb) toxicity on apoptotic cell death, inflammatory response, oxidative defense, and DNA methylation in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2020, 224: 105479. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105479 [34] MU Y, YU J Q, JI W H, et al. Alleviation of Pb2+ pollution-induced oxidative stress and toxicity in microglial cells and zebrafish larvae by chicoric acid [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 180: 396-402. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.040 [35] 鲍虞园, 叶国玲, 钟金香, 等. Hg2+对中国鲎幼体急性毒性及MT的诱导效应 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(6): 300-307. BAO Y Y, YE G L, ZHONG J X, et al. Acute toxicity of Hg2+ to and associated metallothionein induction in Tachypleus tridentatus larvae [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(6): 300-307(in Chinese).
[36] ZHANG Q F, LI Y W, LIU Z H, et al. Exposure to mercuric chloride induces developmental damage, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in zebrafish embryos-larvae [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2016, 181: 76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.10.029 [37] ZHANG Q F, LI Y W, LIU Z H, et al. Reproductive toxicity of inorganic mercury exposure in adult zebrafish: Histological damage, oxidative stress, and alterations of sex hormone and gene expression in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2016, 177: 417-424. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.06.018 [38] XU M C, RUI D S, YAN Y Z, et al. Oxidative damage induced by arsenic in mice or rats: A systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2017, 176(1): 154-175. doi: 10.1007/s12011-016-0810-4 [39] MONDAL P, SHAW P, DEY BHOWMIK A, et al. Combined effect of arsenic and fluoride at environmentally relevant concentrations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain: Alterations in stress marker and apoptotic gene expression [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 269: 128678. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128678 [40] DELANEY P, RAMDAS NAIR A, PALMER C, et al. Arsenic induced redox imbalance triggers the unfolded protein response in the liver of zebrafish [J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2020, 409: 115307. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115307 [41] SMITH A H, SMITH M M H. Arsenic drinking water regulations in developing countries with extensive exposure [J]. Toxicology, 2004, 198(1/2/3): 39-44. [42] SARKAR S, MUKHERJEE S, CHATTOPADHYAY A, et al. Low dose of arsenic trioxide triggers oxidative stress in zebrafish brain: Expression of antioxidant genes [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 107: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.05.012 [43] SUN H J, ZHANG J Y, WANG Q, et al. Environmentally relevant concentrations of arsenite induces developmental toxicity and oxidative responses in the early life stage of zebrafish [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 113022. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113022 [44] DONG W Q, SUN H J, ZHANG Y, et al. Impact on growth, oxidative stress, and apoptosis-related gene transcription of zebrafish after exposure to low concentration of arsenite [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 211: 648-652. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.010 [45] YAO H, GUO L, JIANG B H, et al. Oxidative stress and chromium (VI) carcinogenesis [J]. Journal of Environmental Pathology, Toxicology and Oncology:Official Organ of the International Society for Environmental Toxicology and Cancer, 2008, 27(2): 77-88. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.v27.i2.10 [46] SHAW P, MONDAL P, BANDYOPADHYAY A, et al. Environmentally relevant concentration of chromium induces nuclear deformities in erythrocytes and alters the expression of stress-responsive and apoptotic genes in brain of adult zebrafish [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 703: 135622. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135622 [47] 农琼媛, 覃礼堂, 莫凌云, 等. 抗生素与三唑类杀菌剂混合物对羊角月牙藻的长期毒性相互作用研究 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(4): 140-149. NONG Q Y, QIN L T, MO L Y, et al. The toxic interactions of long-term effects involving antibiotics and triazole fungicides on Selenastrum capricornutum [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(4): 140-149(in Chinese).
[48] LI S Y, JIANG Y, SUN Q Q, et al. Tebuconazole induced oxidative stress related hepatotoxicity in adult and larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 125129. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125129 [49] ZHAO F, CAO F, LI H, et al. The effects of a short-term exposure to propiconazole in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(30): 38212-38220. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09968-7 [50] ZHU J S, LIU C L, WANG J Y, et al. Difenoconazole induces cardiovascular toxicity through oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 216: 112227. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112227 [51] HNÁTOVÁ M, GBELSKÁ Y, OBERNAUEROVÁ M, et al. Cross-resistance to strobilurin fungicides in mitochondrial and nuclear mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae [J]. Folia Microbiologica, 2003, 48(4): 496-500. doi: 10.1007/BF02931331 [52] LI H, CAO F J, ZHAO F, et al. Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity induced by three strobilurins (pyraclostrobin, trifloxystrobin and picoxystrobin) in zebrafish embryos [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 207: 781-790. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.146 [53] HAN Y N, LIU T, WANG J H, et al. Genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by the fungicide azoxystrobin in zebrafish (Danio rerio) livers [J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2016, 133: 13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.03.011 [54] MAO L G, JIA W, ZHANG L, et al. Embryonic development and oxidative stress effects in the larvae and adult fish livers of zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to the strobilurin fungicides, kresoxim-methyl and pyraclostrobin [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729: 139031. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139031 [55] 潘宏伟. 斑马鱼对溴氰菊酯、氯化镉胁迫的行为响应及机制分析[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2019: 67-72. PAN H W. Behavioral response and mechanism analysis of zebrafish (Danio rerio) under deltamethrin and cadmium chloride stress[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2019: 67-72(in Chinese).
[56] PARAVANI E V, SIMONIELLO M F, POLETTA G L, et al. Cypermethrin: Oxidative stress and genotoxicity in retinal cells of the adult zebrafish [J]. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 2018, 826: 25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2017.12.010 [57] PARAVANI E V, SIMONIELLO M F, POLETTA G L, et al. Cypermethrin induction of DNA damage and oxidative stress in zebrafish gill cells [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 173: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.004 [58] 高越, 赵劲宇, 张鹏九, 等. 苹果园施用高效氯氰菊酯对施药人员的暴露量及健康风险评估 [J]. 农药, 2021, 60(1): 38-41. doi: 10.16820/j.cnki.1006-0413.2021.01.010 GAO Y, ZHAO J Y, ZHANG P J, et al. Risk assessment of human exposure to Beta-Cypermethrin during application in apple orchard [J]. Agrochemicals, 2021, 60(1): 38-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.16820/j.cnki.1006-0413.2021.01.010
[59] MU X Y, SHEN G M, HUANG Y, et al. The enantioselective toxicity and oxidative stress of beta-cypermethrin on zebrafish [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 229: 312-320. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.088 [60] HAN J J, JI C, GUO Y C, et al. Mechanisms underlying melatonin-mediated prevention of fenvalerate-induced behavioral and oxidative toxicity in zebrafish [J]. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A, 2017, 80(23/24): 1331-1341. [61] GE W L, YAN S H, WANG J H, et al. Oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by imidacloprid in zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(6): 1856-1862. doi: 10.1021/jf504895h [62] WANG X Y, SHEN M L, ZHOU J J, et al. Chlorpyrifos disturbs hepatic metabolism associated with oxidative stress and gut microbiota dysbiosis in adult zebrafish [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2019, 216: 19-28. [63] GAAIED S, OLIVEIRA M, LE BIHANIC F, et al. Gene expression patterns and related enzymatic activities of detoxification and oxidative stress systems in zebrafish larvae exposed to the 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 224: 289-297. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.125 [64] WANG Q, LIU S, HU D Y, et al. Identification of apoptosis and macrophage migration events in paraquat-induced oxidative stress using a zebrafish model [J]. Life Sciences, 2016, 157: 116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.06.009 [65] 蒋青桃, 宋仙平, 张锋, 等. 乙草胺对雄性小鼠GC-1精原细胞的毒性研究 [J]. 职业与健康, 2020, 36(21): 2920-2926. doi: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2020.0800 JIANG Q T, SONG X P, ZHANG F, et al. Toxicity of acetochlor on GC-1 spermatogonia cells of male mice [J]. Occupation and Health, 2020, 36(21): 2920-2926(in Chinese). doi: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2020.0800
[66] ZHANG Y Y, XUE W, LONG R Z, et al. Acetochlor affects zebrafish ovarian development by producing estrogen effects and inducing oxidative stress [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(22): 27688-27696. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09050-2 [67] 朱炳宇, 周博, 李查德邓, 等. 生物监测在新兴污染物研究中的应用及进展 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2019, 36(5): 460-465. doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2019.05.022 ZHU B Y, ZHOU B, LI C D D, et al. Application and development of biological monitoring in study of emerging contaminants: a review of recent studies [J]. J Environ Health, 2019, 36(5): 460-465(in Chinese). doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2019.05.022
[68] 中国科学院生态环境中心. 典型污染物的环境暴露与健康危害机制 [J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2016, 31(Z2): 158-162. Ecological Environment Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Environmental exposure and health hazard mechanism of typical pollutants [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, 31(Z2): 158-162(in Chinese).
[69] 阮挺, 江桂斌. 发现新型环境有机污染物的基本理论与方法 [J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(11): 1328-1336. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.20200915004 RUAN T, JIANG G B. Basic theory and analytical methodology for identification of novel environmental organic pollutants [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(11): 1328-1336(in Chinese). doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.20200915004
[70] 周海龙, 张林宝, 廖春阳, 等. 持久性有机污染物对水生动物芳香烃受体通道的毒理机制及其早期监测 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2010, 5(1): 9-17. ZHOU H L, ZHANG L B, LIAO C Y, et al. Advances on toxicological mechanism of AhR pathway and early biomonitoring of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in aquatic animals [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2010, 5(1): 9-17(in Chinese).
[71] NAGAYAMA J, TSUJI H, IIDA T, et al. Immunologic effects of perinatal exposure to dioxins, PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in Japanese infants [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 67(9): S393-S398. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.134 [72] LIU H, NIE F H, LIN H Y, et al. Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress, and related gene expression induced by dioxin-like PCB 126 in zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Environmental Toxicology, 2016, 31(3): 295-303. doi: 10.1002/tox.22044 [73] SCHLEZINGER J J, WHITE R D, STEGEMAN J J. Oxidative inactivation of cytochrome P-450 1A (CYP1A) stimulated by 3, 3', 4, 4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl: Production of reactive oxygen by vertebrate CYP1As [J]. Molecular Pharmacology, 1999, 56(3): 588-597. doi: 10.1124/mol.56.3.588 [74] TERAOKA H, DONG W, TSUJIMOTO Y, et al. Induction of cytochrome P450 1A is required for circulation failure and edema by 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in zebrafish [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2003, 304(2): 223-228. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00576-X [75] NA Y R, SEOK S H, BAEK M W, et al. Protective effects of vitamin E against 3, 3', 4, 4', 5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126) induced toxicity in zebrafish embryos [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2009, 72(3): 714-719. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.09.015 [76] ZHENG X M, LIU H L, SHI W, et al. Effects of perfluorinated compounds on development of zebrafish embryos [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2011, 19(7): 2498-2505. [77] CHEN H, HAN J B, ZHANG C, et al. Occurrence and seasonal variations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) including fluorinated alternatives in rivers, drain outlets and the receiving Bohai Sea of China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 1223-1231. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.068 [78] SHI Y L, SONG X W, JIN Q, et al. Tissue distribution and bioaccumulation of a novel polyfluoroalkyl benzenesulfonate in crucian carp [J]. Environment International, 2020, 135: 105418. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105418 [79] WU Y M, DENG M, JIN Y X, et al. Uptake and elimination of emerging polyfluoroalkyl substance F-53B in zebrafish larvae: Response of oxidative stress biomarkers [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 215: 182-188. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.025 [80] ZOU Y L, WU Y M, WANG Q Y, et al. Comparison of toxicokinetics and toxic effects of PFOS and its novel alternative OBS in zebrafish larvae [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 265: 129116. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129116 [81] KERN P A, FISHMAN R B, SONG W, et al. The effect of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on oxidative enzymes in adipocytes and liver [J]. Toxicology, 2002, 171(2/3): 117-125. [82] 聂芳红, 孔庆波, 刘连平, 等. 两种二噁英类化合物对斑马鱼肝脏MDA、SOD和GST的影响 [J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2009, 28(2): 210-213. NIE F H, KONG Q B, LIU L P, et al. Effects of two DLCs on hepatic MDA, SOD and GST in zebrafish [J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2009, 28(2): 210-213(in Chinese).
[83] MENG S L, CHEN X, GYIMAH E, et al. Hepatic oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in adult zebrafish following sub-chronic exposure to BDE-47 and BDE-153 [J]. Environmental Toxicology, 2020, 35(11): 1202-1211. doi: 10.1002/tox.22985 [84] 张章, 唐天乐, 唐文浩. 人工纳米材料对斑马鱼生态毒理效应研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2016, 11(5): 14-23. ZHANG Z, TANG T L, TANG W H. Research progress in ecotoxicological effects of engineered nanomaterials on zebrafish [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2016, 11(5): 14-23(in Chinese).
[85] CLEMENTE Z, CASTRO V, JONSSON C, et al. Ecotoxicology of nano-TiO2 an evaluation of its toxicity to organisms of aquatic ecosystems [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2012, 6: 33-50. [86] TANG T, ZHANG Z, ZHU X. Toxic effects of TiO2 NPs on zebrafish [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 6(4): 523. [87] SARASAMMA S, AUDIRA G, SAMIKANNU P, et al. Behavioral impairments and oxidative stress in the brain, muscle, and gill caused by chronic exposure of C70 nanoparticles on adult zebrafish [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(22): 5795. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225795 [88] DU J, CAI J, WANG S T, et al. Oxidative stress and apotosis to zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and ZnO nanoparticles [J]. International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, 2017, 30(2): 213-229. [89] ZHU B, HE W, HU S, et al. The fate and oxidative stress of different sized SiO2 nanoparticles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 225: 705-712. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.091 [90] YU X, SUI Q, LYU S G, et al. Do high levels of PPCPs in landfill leachates influence the water environment in the vicinity of landfills? A case study of the largest landfill in China [J]. Environment International, 2020, 135: 105404. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105404 [91] ZOU Y, ZHANG Y, HAN L W, et al. Oxidative stress-mediated developmental toxicity induced by isoniazide in zebrafish embryos and larvae [J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology:JAT, 2017, 37(7): 842-852. doi: 10.1002/jat.3432 [92] FÉLIX L M, VIDAL A M, SERAFIM C, et al. Ketamine induction of p53-dependent apoptosis and oxidative stress in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 201: 730-739. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.049 [93] LIANG X M, WANG F LI K B, et al. Effects of norfloxacin nicotinate on the early life stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio): Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2020, 96: 262-269. [94] SEHONOVA P, TOKANOVA N, HODKOVICOVA N, et al. Oxidative stress induced by fluoroquinolone enrofloxacin in zebrafish (Danio rerio) can be ameliorated after a prolonged exposure [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2019, 67: 87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2019.02.002 [95] GYIMAH E, DONG X, QIU W H, et al. Sublethal concentrations of triclosan elicited oxidative stress, DNA damage, and histological alterations in the liver and brain of adult zebrafish [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(14): 17329-17338. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08232-2 [96] 王凡, 牛晓莹, 刘飞, 等. 三氯生对斑马鱼卵巢抗氧化和凋亡相关基因表达的影响 [J]. 淡水渔业, 2020, 50(1): 3-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2020.01.001 WANG F, NIU X Y, LIU F, et al. Effect of triclosan on expression of antioxidant and apoptosis-related genes in ovary of Danio rerio [J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2020, 50(1): 3-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2020.01.001
[97] HOU J, LI L, XUE T, et al. Damage and recovery of the ovary in female zebrafish i. p.-injected with MC-LR [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2014, 155: 110-118. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.06.010 [98] HOU J, LI L, XUE T, et al. Hepatic positive and negative antioxidant responses in zebrafish after intraperitoneal administration of toxic microcystin-LR [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 120: 729-736. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.079 [99] LU Y F, ZHANG Y, DENG Y F, et al. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effects in liver [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(7): 4054-4060. [100] QIAO R X, SHENG C, LU Y F, et al. Microplastics induce intestinal inflammation, oxidative stress, and disorders of metabolome and microbiome in zebrafish [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 246-253. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.245 [101] CHEN M J, YIN J F, LIANG Y, et al. Oxidative stress and immunotoxicity induced by graphene oxide in zebrafish [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2016, 174: 54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.02.015 [102] SALAHINEJAD A, ATTARAN A, NADERI M, et al. Chronic exposure to bisphenol S induces oxidative stress, abnormal anxiety, and fear responses in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 750: 141633. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141633 [103] WU S M, JI G X, LIU J N, et al. TBBPA induces developmental toxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in embryos and zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio) [J]. Environmental Toxicology, 2016, 31(10): 1241-1249. doi: 10.1002/tox.22131 [104] XIANG Q Q, XU B F, DING Y L, et al. Oxidative stress response induced by butachlor in zebrafish embryo/larvae: The protective effect of vitamin C [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2018, 100(2): 208-215. doi: 10.1007/s00128-017-2245-9 [105] GIORDO R, NASRALLAH G K, AL-JAMAL O, et al. Resveratrol inhibits oxidative stress and prevents mitochondrial damage induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(11): 3838. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113838 [106] OH J Y, KIM E A, KANG S I, et al. Protective effects of fucoidan isolated from celluclast-assisted extract of Undaria pinnatifida sporophylls against AAPH-induced oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo zebrafish model [J]. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 25(10): 2361. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102361 -



 下载:
下载:

