-
筑牢黄河流域生态安全是保障国家生态安全的重要支撑,而下游冲积平原区是流域内生态脆弱区之一,特别近几十年来随着工业化城镇化发展、气候变化[1]、人类活动[2]等因素影响,带来了水资源短缺、水质恶化等一系列生态环境问题[3]. 同时黄河下游冲积平原区一般工农业发达,是重要农业粮食产区,地下水在工农业和饮用水中扮演者重要角色,对地下水水化学特征及演化机制进行研究,不仅能反映影响地下水化学的各种自然或人为因素,而且对水资源保护与合理开发利用,进而保障生态安全等具有重要意义[4-6]. 德州位于山东省西北部,具有黄河流域下游冲积平原区的典型特征,本次选取了德州市作为代表区开展研究.
目前关于德州市的研究主要集中在浅层地下水水质演化[6]、地面沉降与地下水相关性[7-8]、地下水降落漏斗[9]、深层地下水水化学特征[10]、水位动态[11]等,如贾超等[8]系统研究了鲁西北平原深层地下水降落漏斗现状及地面沉降时空演化,总结了地面沉降与地下水开采的相关性. 赵全升等[6]论述了浅层地下水的水质特征,分析研究了浅层地下水的水质演化. 冯颖等[10]基于多年动态监测研究了德州市深层地下水化学特征及水位动态变化. 纪洪磊等[11]通过分析区内第四纪沉积展布特征,结合二等水准测量数据和分层沉降标数据与地面沉降规律,揭示鲁北平原区地面沉降机理和沉降模式. 为本次研究提供了借鉴,但对德州市地下水水化学特征、演化等尚需开展更深入的研究.
因此,本文通过描述性统计、因子分析、Piper图、Gibbs图、离子比值、矿物饱和指数等方法,对德州市地下水水化学成因进行系统分析,同时结合开采条件下水位变化,分析其生态环境影响. 以期对德州市地下水资源合理开发利用和保护及黄河流域下游水生态环境改善提供借鉴.
-
德州市位于鲁北平原中部,总面积10356 km2,属于黄河下游冲积平原区. 研究区内地势平坦,地面标高自34 m(齐河)降至7 m(庆云东北角),地面坡降为1/1000—1/10000. 德州市属于暖温带半干旱季风气候,多年平均降雨量仅有549.95 mm,多年平均气温13.1℃,地表支流较发达,黄河、徒骇河、卫运河、德惠新河、马颊河、漳卫新河是区内主要河流,除黄河外均属海河水系[10].
德州市属于华北板块,自中生代以来沉积了巨厚的新生界地层,上层主要为第四系一套氧化-还原交替沉积,全新统为冲积湖沼相,其次为冲积-风积及现代河床沉积,厚度超过280 m.而在齐河西南部,厚度仅有170 m左右.
德州市属于典型的黄河下游冲积平原孔隙水水文地质区,具有咸、淡水共存的水环境特征,淡水天然的水环境条件非常敏感和脆弱[10,12]. 区内浅层地下水主要以垂直方向补排为主,大气降水、地表水及灌溉水通过地表以渗入的形式补给浅层地下水,排泄方式以蒸发和开采为主,德州市地下水径流方向为西南—东北,与地表水系径流方向基本一致.
德州市地下水赋存于新生界第四系和新生界明化镇组松散岩的孔隙中,新生代以来由于受阶段性和差异性升降运动的影响,含水层(组)在空间分布上较为复杂,地下水具有明显的分带性,将800 m以浅的地下水分为浅层淡水、中深层咸水、深层淡水等[6]. 浅层淡水多60 m以浅的地下淡水区,含水层底板埋深介于20—60 m之间,岩性以细砂、粉砂为主. 中深层咸水介于60—250 m之间,到以更新统的粉细砂为主,含水层底板多在190—250 m间,该层地下水未利用. 深层地下水分布在咸水层以下,以新近系粉细砂为主. 含水层埋深介于200—800 m之间.
-
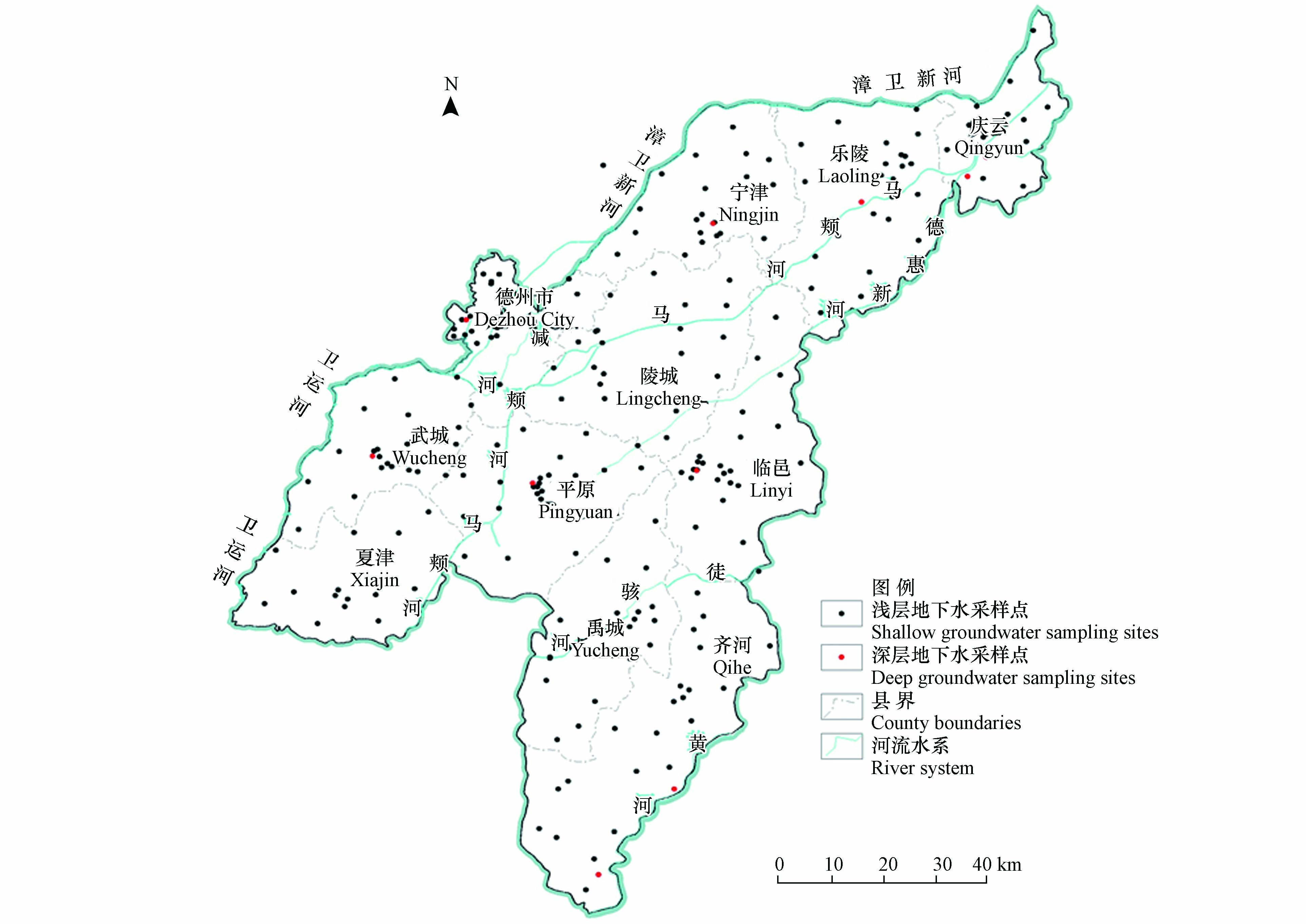
本次采集浅层地下水样品232件,深层地下水11件,共计243件地下水水样点(图1),采样点以民井、机井为主,浅层地下水井深范围为7—60 m,深层地下水井深350—400 m. 现场测试指标如水体温度、pH、电导率、溶解氧、氧化还原电位等使用便携式水质分析仪现场测定,样品采集、测试等方法符合《水质采样样品的保存和管理技术规定》(HJ 493—2009)等规定. 水质化验工作由山东冶金地质总局实验室进行测试,测试方法按照《地下水质检验方法》(DZ/T0064.5—2021)完成,包括主要离子K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−、SO42−、HCO3−、NO3−、Mn2+等,测试方法及检出限见表1.
-
将本次测试取得数据运用Origin2022软件开展描述性统计分析、离子比值系数、Gibbs图、Piper三线图等绘制及分析[5],SPSS26软件进行离子相关性分析,统计主要离子成分、水化学参数分布规律及特征,并进行因子分析,使用PHREEQC软件计算矿物饱和指数,从而对德州市地下水化学特征和演化开展研究.
-
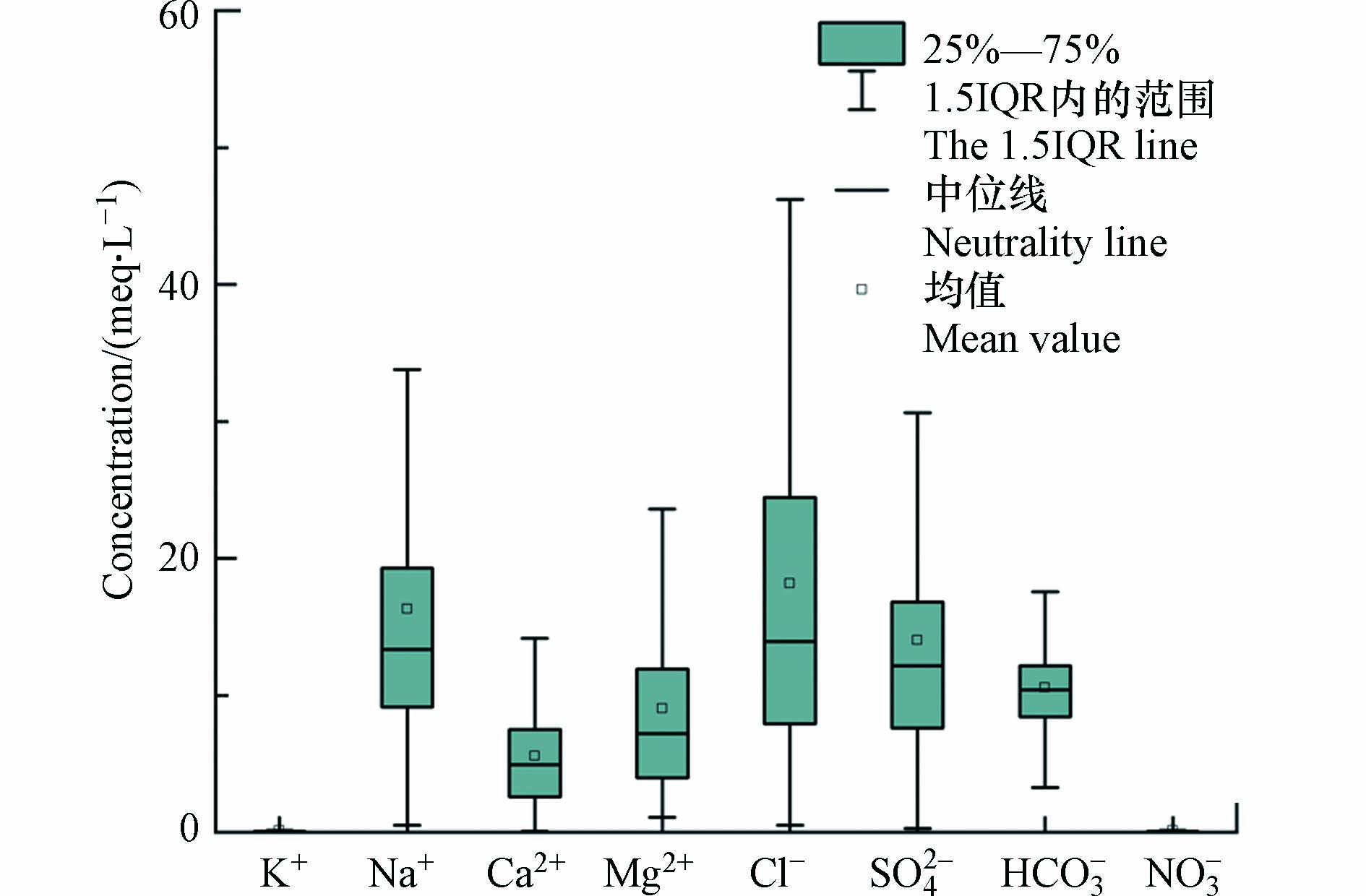
地下水中主要水化学组分指标统计见表2. 研究区浅层地下水pH值介于7.09—8.38之间,深层地下水pH值介于7.59—8.86之间,均属于弱碱性水. 绘制地下水化学参数的箱线图(图2),浅层地下水TDS介于234—28162 mg·L−1之间,深层地下水TDS介于261—2616 mg·L−1之间,主要属淡水、微咸水、咸水范畴. 研究区阳离子当量浓度关系为Na+>Mg2+>Ca2+>K+,以Na+和Mg2+为主,阴离子当量浓度Cl−>SO42−>HCO3−>NO3−,以Cl−、SO42−为主. 通过指标中变异系数可以看出,除pH、K+和HCO3−外,地下水中各离子异系数均较大.
表2可以看出,浅层地下水中各离子含量较高,地下水以Ⅳ类水、Ⅴ类水为主. 德州地区由于地质条件、古地理沉积环境等原因,在800 m以浅咸水区广泛分布,导致相关离子含量超标. 依据《地下水质量标准(GB14848—2017)》,对232组浅层地下水水样进行统计,表3可以看出,主要离子超标率分别为TDS(86.70%)、Na+(77.68%)、F−(70.82%)、Mn2+(86.27%)、SO42−(82.83%)、Cl−(78.54%)、总硬度(64.38%). 最大超标倍数在18—32.7倍,不适宜饮用. 而由于深层地下水氟含量偏高、超采产生的降落漏斗、地面沉降等问题,山东省黄河北部德州、滨州、东营地区均以饮用黄河水为主.
-
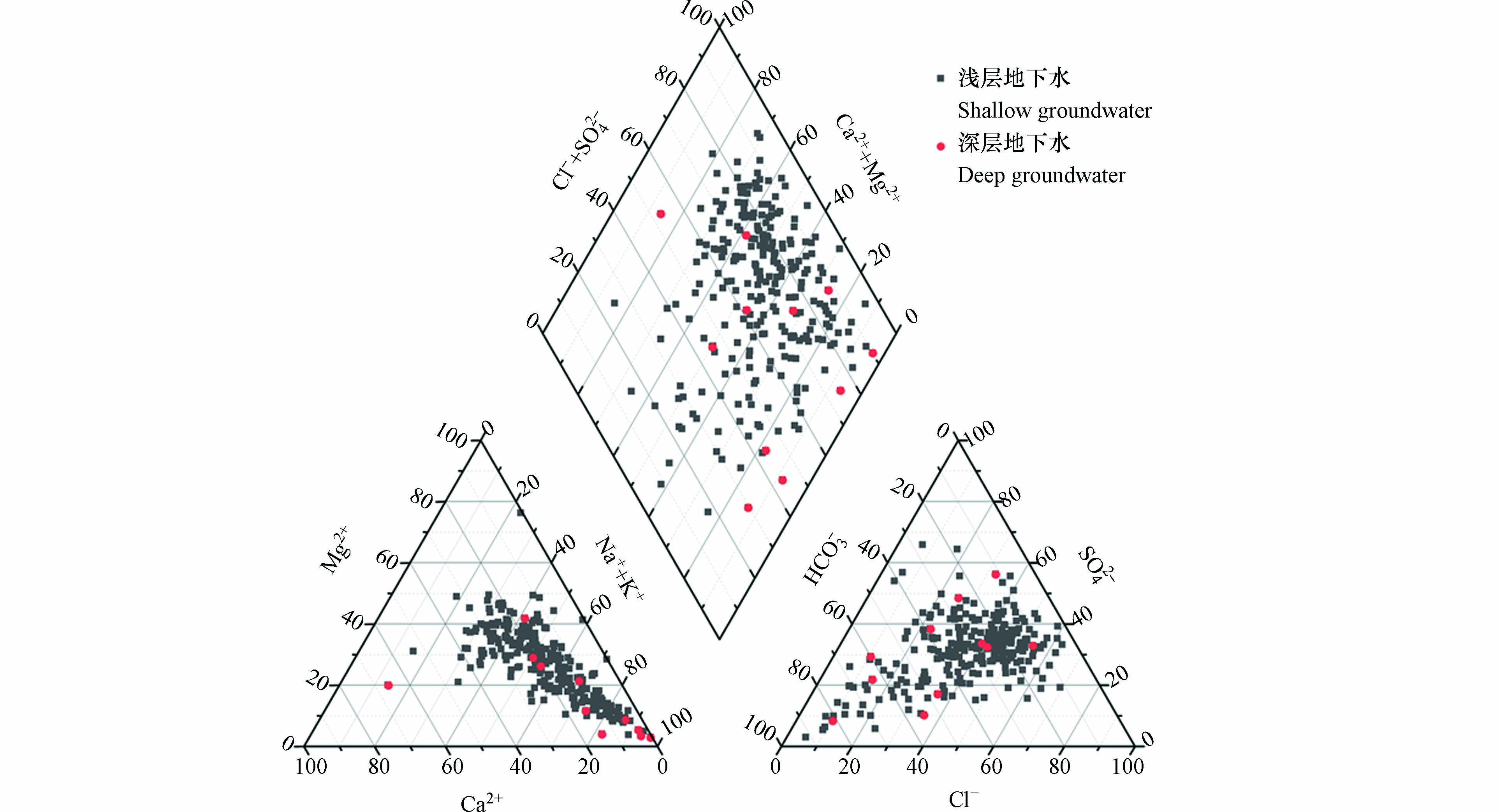
Piper三线图可以不受人为影响的表征地下水中水化学组分及含量分布特征[13-15]. 图3表明,德州市地下水水化学类型较为多样,阳离子主要分布在Na+、Mg2+端,其次为Ca2+端. 阴离子主要则在Cl−,SO42−,HCO3−端分布均较为广泛. 说明在黄河下游地下水各离子来源较为广泛,水化学过程较为复杂. 浅层地下水水化学类型多样,以HCO3·Cl-Ca·Mg型,HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca、HCO3·SO4-Na·Ca型等为主,深层地下水以HCO3·SO4-Na型水为主.
-
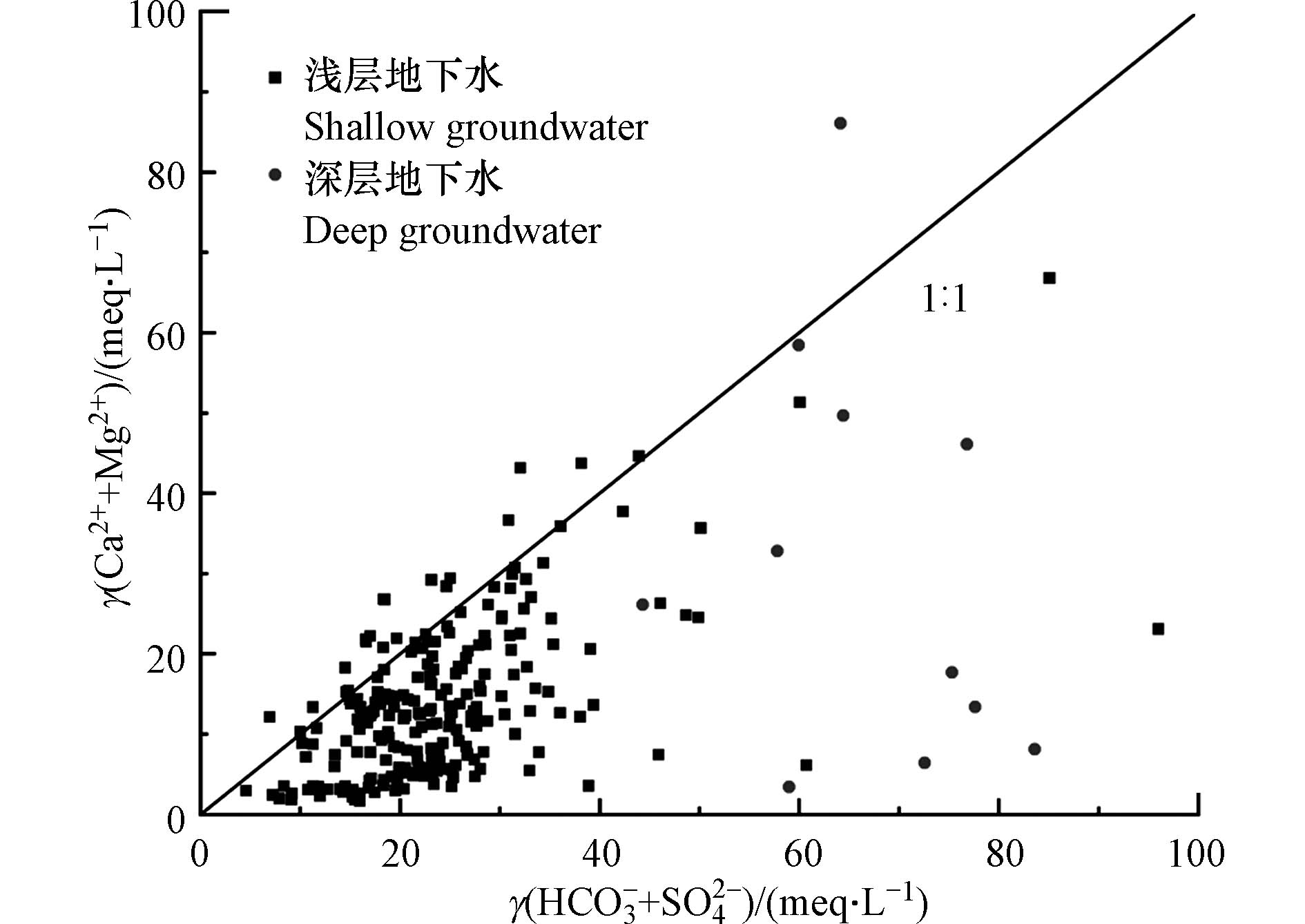
地下水主要离子之间的关系可以通过相关性分析来验证,进而用以推测各离子来源,本文采用Person相关性分析法[5,16],表4为德州市地下水水化学主要组分间的相关关系矩阵,可以看出,除K+离子外TDS与所有离子均呈现显著相关关系,仅Ca2+和HCO3−的相关性不显著,反映了碳酸盐岩的风化溶解对区内地下水形成贡献较小,其他各组分间相关性同样显著. 其中与Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl−和SO42−相关系数达到0.7—0.8以上,表明这5种离子是TDS的主要来源,Na+和Cl−之间相关系数为0.77,说明二者有共同来源,一般可能为蒸发岩的风化溶解,Mg2+、Ca2+均与Cl−和SO42−相关性最高,反映了这4种离子可能来源于硅酸盐岩溶解.
-
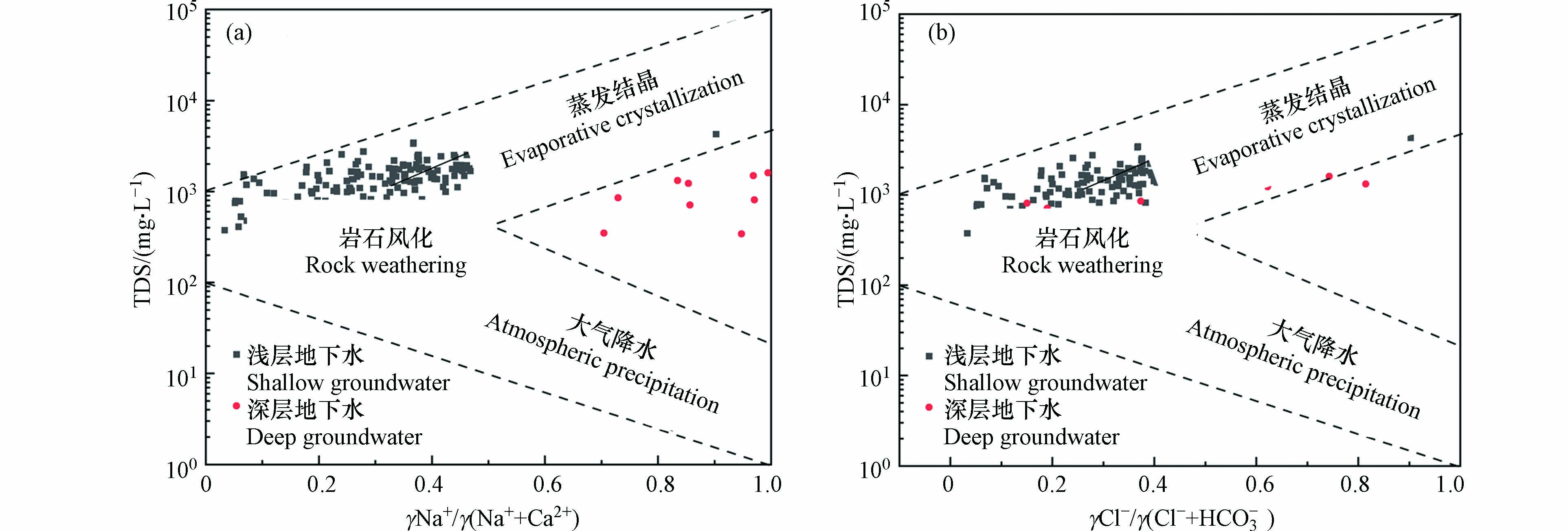
地下水在径流过程中往往伴随着各类岩石矿物的溶解,Gibbs图可宏观地反应水体中主要离子的控制因素[17-19],采用Gibbs图可以判断地下水主要水化学特征形成的控制影响因素,并分析地下水的形成作用. 以TDS(溶解性总固体)作为纵坐标,分别以阳离子Na+/(Na++Ca2+)的质量浓度比和阴离子Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)的质量浓度比值为横坐标,分析各因素在地下水化学组分的形成作用[5,20],根据地下水水化学组分的来源,可分为蒸发结晶、岩石风化溶虑作用和大气降水等三种控制因素[21-22]. 将德州市地下水化学数据绘于Gibbs图中(图4),水样点主要落在岩石风化溶滤作用、蒸发结晶区域内,表明岩石风化溶虑作用、蒸发-浓缩作用共同主导了德州市地下水水文地球化学演化过程,大气降水对地下水化学特征的影响较弱.
-
不同岩石风化溶滤后产生的离子不同,利用端元法进一步探究德州市水文地球化学演化过程中受到不同岩石溶解风化的影响,Mg2+/Na+、Ca2+/Na+和HCO3−/Na+的浓度比值可以将地下水化学组分的来源分为碳酸盐岩、硅酸盐和蒸发岩3种[5,23].图5所示德州市浅层和深层地下水样点均主要落在硅酸盐矿物和蒸发岩矿物风化物间,仅一个深层岩溶裂隙水样点落在碳酸盐岩矿物端. 表明硅酸盐岩和蒸发岩矿物在岩石风化溶虑过程中起主导作用,碳酸盐岩贡献较低.
-
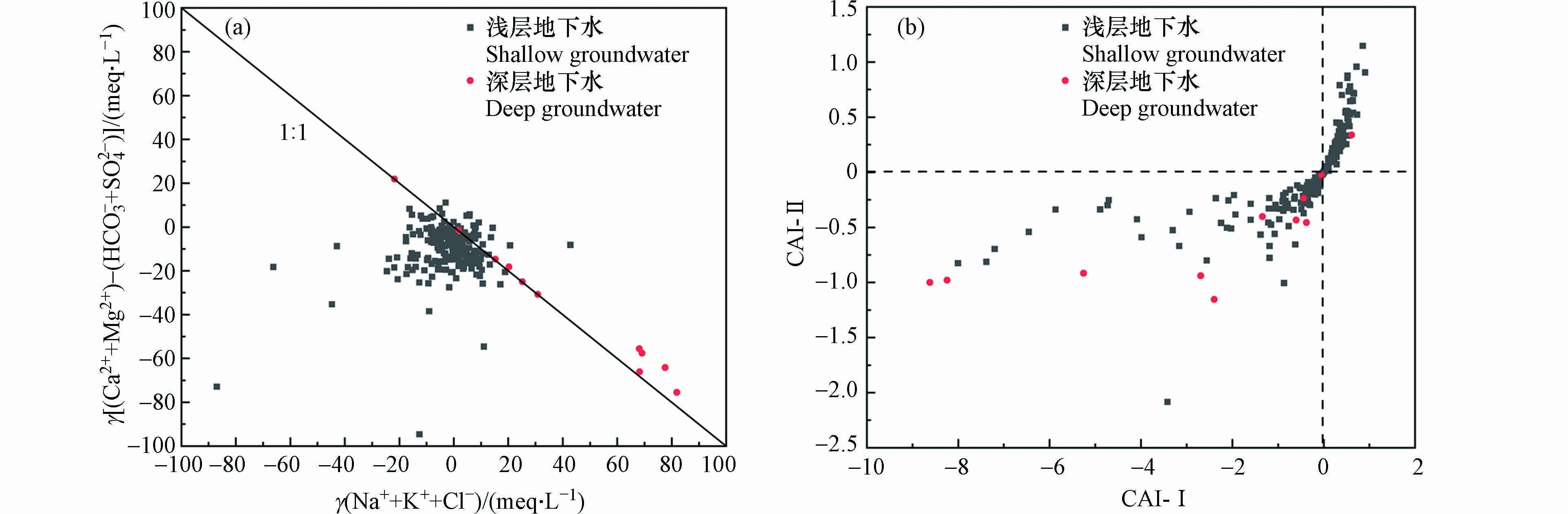
岩石和地下水长期作用过程中,在一定条件下,岩石颗粒携带负电荷会吸附水中的阳离子,而将原有吸附的阳离子释放到水中,转换成地下水化学组分[24-25]. 阳离子交替吸附作用一般使用(Mg2++Ca2+-SO42−-HCO3−)与(Na++K+-Cl−)的摩尔浓度比值关系来表示,若发生阳离子交换作用,两者比值一般在-1 左右[26]. 图6(a)中大部分水样围绕在-1直线周围,深层地下水几乎围绕着-1直线.
表明浅层和深层地下水中均存在阳离子交替吸附作用. 氯碱指数可以用来表示阳离子交替吸附作用的方向和强弱[5]. 图6(b)表明,浅层地下水中阳离子交换较为活跃,正向和反向阳离子交替吸附作用均存在,除齐河县岩溶水水样点为反向交换作用外,深层地下水均发生正向阳离子交替吸附反应.
-
Na+和Cl−的毫克当量比值可反映地下水中Na+和K+的来源[27-29]. 海水和大气降水中的Na+和Cl−浓度比值为0.86,降雨、硅酸盐岩矿物和蒸发岩矿物溶解是地下水中Na+和K+的主要来源[30]. 硅酸盐岩风化溶解产生的Na+与Cl−的比值大于1,而图7(a)Na+/Cl−中有占比一半的水样点位于1:1直线上方,表明地下水中硅酸盐岩矿物溶解为主的水-岩作用,占比约一半的水样点Na+/CL−小于1,表明与蒸发盐岩矿物溶解有关. 同时图7(b)显示大部分水样点Na+浓度明显大于HCO3−,两者共同表明蒸发盐岩矿物和硅酸盐矿物风化溶解主导德州市地下水水文地球化学过程,碳酸盐岩贡献较低.
碳酸盐岩、硅酸盐岩或蒸发盐岩的溶解是地下水中Ca2+、Mg2+的主要来源[31]. (Mg2++Ca2+)与(SO42−+HCO3−)的当量浓度比值可以判定二者来源,图8表明,中部分水样点浓度关系围绕在1:1直线附近,说明地下水中Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于蒸发盐岩矿物(如石膏)的溶解,大部分水样点落在1:1直线下方,证明两种阳离子不足以平衡两种阴离子,需要其他阳离子平衡,说明硅酸盐岩矿物和蒸发盐岩矿物在水岩相互作用中占主导地位.
-
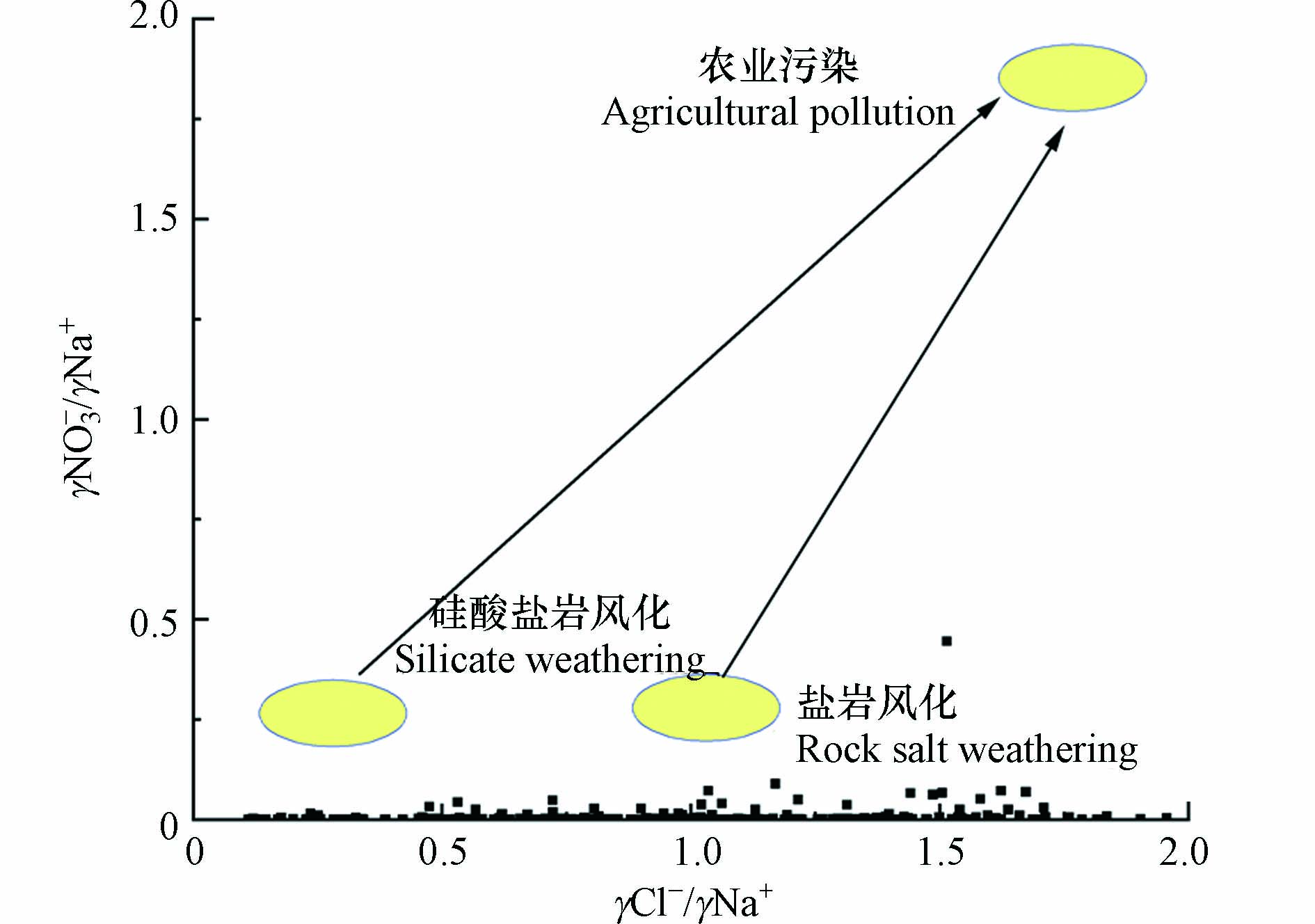
人类活动特别是农业活动对于地下水化学的影响可以通过Cl−/Na+和NO3−/Na+的当量浓度来表示,比值越大表明其受人类活动影响越明显[22、32]. 图9可以看出两者比值均较低,大部分水样点位于硅酸盐岩、盐岩风化端,表明水化学特征受人农业活动影响较小. 而研究区地下水中TDS值普遍偏高,可能与地下水位埋深较浅,水位埋深主要集中在2—8 m的范围内. 地下水蒸发浓缩作用强烈导致,因而水文地球化学过程中蒸发浓缩作用占据重要地位.
-
利用SPSS26软件对水样中9种水化学组分进行因子分析,在因子分析前对各项数据因子分析进行可靠性检验[33],KMO为0.794,Bartlett球度检验显著性为0.000,表明本次数据适合做因子分析. 根据累积方差率提取了2个主因子,如表5所示累积方差率达74.001%,可以反映出德州市地下水中水化学组分的基本信息.
第一主因子F1以Mg2+、Cl−、Na+、Ca2+、SO42−、TDS及总硬度为主,结合上文中分析,主要以蒸发盐岩、硅酸盐岩的风化溶虑作用为主,累积贡献率达62.199%.
第二主因子F2以HCO3−和K+为主,贡献率为11.802%,K+在研究区内含量均较低,贡献率较低,而HCO3−则与该地区已处于黄河流域下游、区内碳酸盐岩仅在齐河沿黄地区隐伏分布有关.
-
将232件浅层地下水和11件深层地下水样品水质数据利用PHREEQC软件计算了各类矿物的矿物饱和指数(SI)[34-35],并分别绘制了浅层和深层地下水矿物饱和指数箱线图,图10可以看出浅层地下水和深层地下水石膏、岩盐等矿物饱和指数均小于0,矿物处于溶解的趋势. 综合上文所述,表明德州市地下水中岩石风化溶解作用占主导地位的是蒸发盐岩岩和硅酸盐矿物,以石膏、岩盐等为主.
-
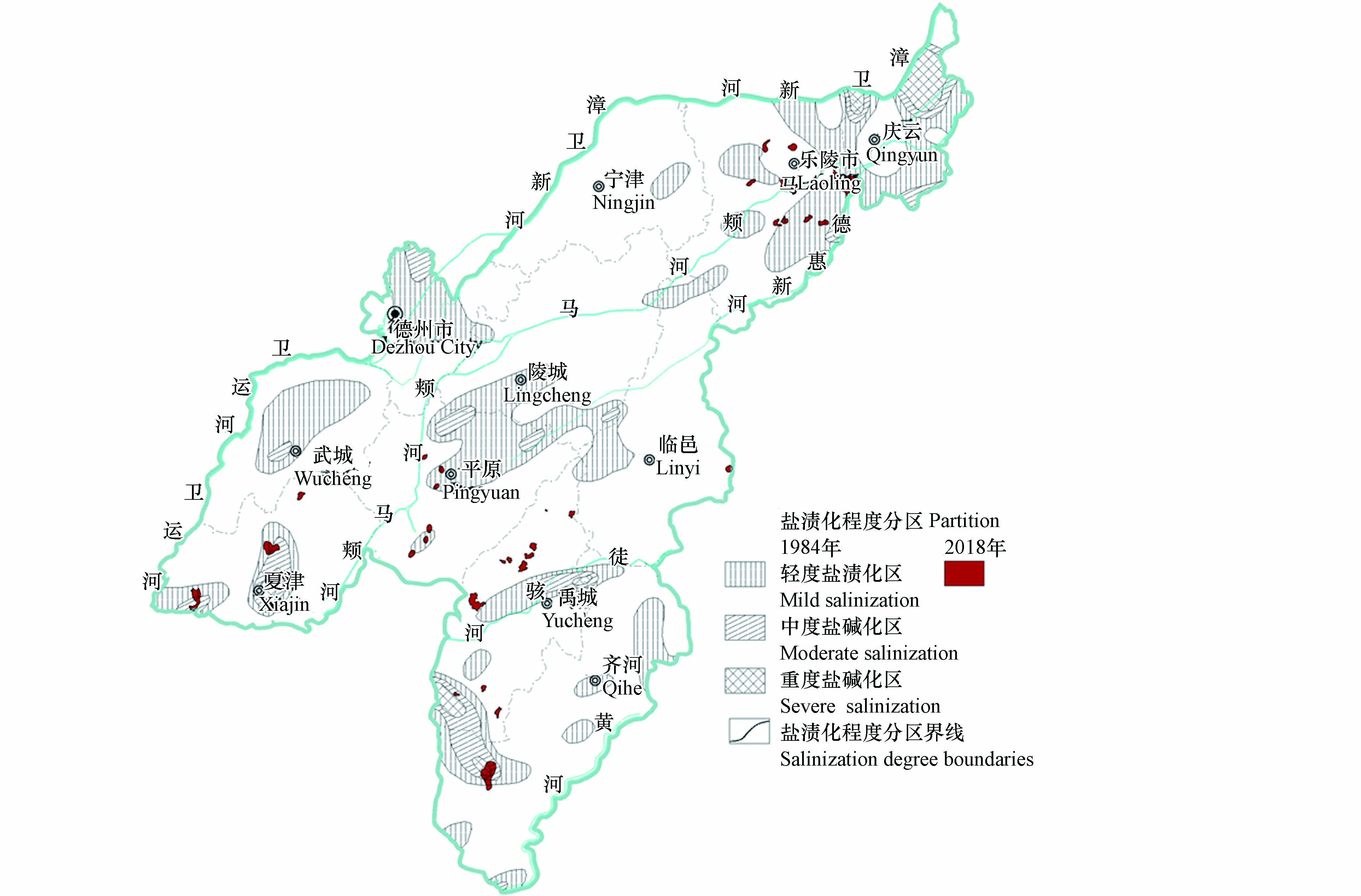
原生沉积环境下,地下水开采量较小,浅层地下水水位保持高位,研究区内蒸发浓缩作用强烈,在复杂的水、土交换条件下,形成了大量的盐渍化土壤. 随着人类活动增加,德州市地下水开采量增加,图11可以看出,自1984年至2020年,德州市地下水浅层孔隙水位变幅介于−10.00—2.75 m之间,总体以下降为主,降幅最大地区分布在夏津苏留庄和宁津大柳镇等传统井灌区,为农业生产活动开采地下水导致. 地下水位升幅区域主要分布在德城区、武城县北部、临邑南部和齐河北部一带,水位回升的原因主要为城市建设占用耕地,地下水开采量减少,外界补给量增加,进而导致水位回升.
随着地下水位下降,地下水演化过程中蒸发浓缩作用减弱,多年来的农灌行为,使得目前研究区的盐渍化土壤有了较大的改善. 图12表明盐渍化减少面积与浅层地下水水位降低有较强的关联性,因此研究区内浅层地下水适宜作为农业灌溉用水,合理开发浅层地下水,控制地下水位可以在一定程度弱化蒸发浓缩作用,对生态环境有一定的有益影响.
-
(1)德州市地下水为弱碱性水,TDS介于234—28162 mg·L−1之间,变化较大,区内占优势的阴、阳离子为Cl−、SO42−和Na+、Mg2+,浅层地下水化学类型复杂,以HCO3·Cl-Ca·Mg型、HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca型、HCO3·SO4-Na·Ca型等为主,深层地下水以HCO3·SO4-Na型水为主.
(2)德州地区地下水化学特征受岩石风化溶滤作用、蒸发浓缩作用、阳离子交换作用的共同影响,以溶滤作用、蒸发浓缩作用为主. 岩石矿物以硅酸盐岩和蒸发岩矿物溶解为主,如盐岩和石膏等. 深层地下水中阳离子交替吸附作用以正向为主,浅层地下水中该反应较为复杂.
(3)SPSS计算显示,德州地区地下水中蒸发盐岩、硅酸盐岩在岩石风化溶滤过程中的贡献率为62.199%,碳酸盐岩风化、其它岩石风化的贡献率约为11.802%.
(4)浅层地下水的合理开发,可以减弱蒸发浓缩作用,在一定程度上改良研究区内的土壤质量,减少区内的盐渍化土地面积,因此合理开发利用浅层地下水用于农业灌溉等,在一定程度上可以有益于生态环境的改善.
黄河流域下游德州地区地下水水化学成因及生态环境影响
Hydrochemical genesis and ecological environment influence of groundwater in dezhou city at lower Yellow River Basin
-
摘要: 德州市位于黄河流域下游平原,是主要农业粮食作物产区,地下水资源影响着农业安全和人民健康安全. 研究地下水化学成因及生态环境影响,对地下水可持续开发利用具有重要意义. 采集243组地下水样品,运用描述性统计分析、因子分析、Piper三线图、Gibbs图及离子比值等方法,结合地质背景条件,运用PHREEQC计算矿物饱和指数,分析区内地下水化学特征及成因,并分析其生态环境影响. 结果表明,德州市地下水为弱碱性水,TDS介于234—28162 mg·L−1之间,区内占优势的阴、阳离子为Cl−、SO42-和Na+、Mg2+,浅层地下水化学类型以HCO3·Cl-Ca·Mg型,HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca、HCO3·SO4-Na·Ca型等为主,深层地下水以HCO3·SO4-Na型水为主. 德州地区地下水化学特征受岩石风化溶滤作用、蒸发浓缩作用、阳离子交换作用的共同影响,以溶滤作用、蒸发浓缩作用为主. 岩石风化溶滤作用以硅酸盐岩和蒸发岩矿物溶解为主. 深层地下水中阳离子交替吸附作用以正向为主,浅层地下水中该反应较为复杂. 德州地区地下水中蒸发盐岩、硅酸盐岩在岩石风化溶滤过程中的贡献率为62.199%,碳酸盐岩风化、其它岩石风化的贡献率约为11.802%. 浅层地下水的合理开发,可以减弱蒸发浓缩作用,在一定程度上改良研究区内的土壤质量,减少区内的盐渍化土地面积,因此合理开发利用浅层地下水用于农业灌溉等,在一定程度上可以有益于生态环境的改善.Abstract: Dezhou City is located in the downstream plain of the Yellow River Basin, which is the main agricultural food crop production area. Groundwater resources affect agricultural safety and people’s health and safety. Studying the hydrochemical genesis and ecological environment influence of groundwater is of great significance to the sustainable development and utilization of groundwater. 243 groups of groundwater samples were collected. Descriptive statistical analysis, factor analysis, Piper diagram, Gibbs diagram and ion ratio methods were used, along with the calculation of mineral saturation index by PHREEQC, combined with the geological background conditions, The chemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the area were analyzed. The results show that: (1) The groundwater in Dezhou City is weak alkaline water, and the TDS was between 234 — 28162 mg·L−1, which changes greatly. The dominant anions and cations in the area were Cl−, SO42− and Na+, Mg2+. The chemical types of shallow groundwater are HCO3·Cl-Ca·Mg, HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca and HCO3·SO4-Na·Ca. The deep groundwater is dominated by HCO3·SO4-Na type water. (2) The chemical characteristics of groundwater in Dezhou area are affected by the combined effects of rock weathering, leaching, evaporation and concentration, and cation exchange. The rock weathering and leaching are mainly the dissolutionof silicate rocks and evaporation rocks. The cation exchange adsorption in deep groundwater is mainly positive, and the reaction in shallow groundwater is more complex. (3) PHREEQC calculation shows that the contribution rate of evaporated salt rock and silicate rock in groundwater in Dezhou area in the process of rock weathering and leaching was 62.199%, and that of carbonate rock weathering and other rock weathering was about 11.802%. (4) Rational exploitation of shallow groundwater can weaken evaporation and concentration, improve soil quality and reduce salinized land area in the study area, therefore, rational exploitation and utilization of shallow groundwater for agricultural irrigation can be beneficial to the improvement of ecological environment to a certain extent.
-

-
表 1 水样测试指标和检出限
Table 1. Water sample test indicators and detection limits
指标
Index检测方法
Detect method检出限
Detection limitpH DZ/T 0064.5-2021 玻璃电极法 — TH DZ/T 0064.15-2021 乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法 3mg·L−1(以CaCO3计) TDS DZ/T 0064.9-2021 重量法 — K+ DZ/T 0064.27-2021 火焰发射光谱法 0.50 mg·L−1 Na+ DZ/T 0064.42-2021 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 0.60 mg·L−1 Ca2+ DZ/T 0064.13-2021 乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法 4 mg·L−1 Mg2+ DZ/T 0064.14-2021 乙二胺四乙酸二钠滴定法 3 mg·L−1 Cl− DZ/T 0064.50-2021 银量滴定法 3 mg·L−1 SO42− DZ/T 0064.64-2021 乙二胺四乙酸二钠-钡滴定法 10 mg·L−1 HCO3− DZ/T 0064.49-2021 滴定法 5 mg·L−1 Mn2+ DZ/T 0064.22-2021 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 0.15 µg·L−1 NO3− DZ/T 0064.59-2021 紫外分光光度法 0.20 mg·L−1 表 2 德州市地下水主要水化学指标质量浓度统计(mg·L−1)
Table 2. Mass concentration statistics of the main hydrochemical indexes(mg·L−1)
pH TH TDS K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- 浅层地下水
SGW均值Mean 7.77 732.38 2321.79 5.98 368.12 111.72 109.3 640.71 680.37 644.69 中值Medium 7.77 631 1930 1.65 303.44 98.1 87.7 487.5 584 629.5 标准差SD 0.23 688.19 2212.67 29.15 351.03 89.98 117.36 638.88 615.3 178.01 最大值Max 8.38 8107 28162 408.6 4317 881 1400 5935 4868 1523 最小值Min 7.09 90 234 0.33 11.92 1.45 11.7 18.7 13.7 173 变异系数CV 0.03 0.94 0.95 4.88 0.95 0.81 1.07 1 0.9 0.28 深层地下水
DGW均值Mean 8.22 236.34 1133.5 2.03 309.95 43.82 34.26 284.28 322.75 384.67 中值Median 8.24 113 1040 1.68 271.06 36.4 12.35 179.5 296.5 396 标准差SD 0.35 309.3 722.29 1.58 194.3 39.77 51.42 277.34 252.49 148.71 最大值Max 8.86 1104 2616 6.24 611 123 187 904 672 644 最小值Min 7.59 45 261 0.87 21.7 2.82 7.4 32.4 35.2 171 变异系数CV 0.04 1.31 0.64 0.78 0.63 0.91 1.5 0.98 0.78 0.39 注:pH和变异系数无量纲. Note:pH and coefficient of variation dimensionless. 表 3 浅层地下水超标组分统计表(mg·L−1)
Table 3. Statistical table of excessive components of shallow groundwater(mg·L−1)
测试指标
Index样品总数
SamplesⅢ类水标准/(mg·L−1)
Standard最大超标倍数
Maximum excess multiple超标率/%
Excessive rateTDS 232 1000 28.1 86.70 Na+ 232 200 21.5 77.68 F- 232 1.00 11.0 70.82 Mn2+ 232 0.1 32.7 86.27 Cl- 232 250 23.7 78.54 SO42- 232 250 19.4 82.83 总硬度(TH) 232 450 18.0 64.38 表 4 黄河流域下游德州地区地下水水化学组分间的相关系数
Table 4. Correlation coefficient between groundwater hydrochemical components in Dezhou area of the lower Yellow River Basin
TDS K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42- HCO3− TDS 1.00 K+ 0.00 1.00 Na+ 0.88* −0.01 1.00 Ca2+ 0.71* −0.04 0.52* 1.00 Mg2+ 0.87* −0.05 0.69* 0.82* 1.00 Cl− 0.92* −0.01 0.77* 0.59* 0.74* 1.00 SO42− 0.86* −0.04 0.67* 0.55* 0.66* 0.90* 1.00 HCO3− 0.18* 0.03 0.23* 0.04 0.16* 0.14* 0.19* 1.00 注:*代表在0.05水平线相关性显著. Note:*Significant correlation at 0.05 level. 表 5 黄河流域下游德州地区地下水组分旋转因子荷载矩阵
Table 5. Rotation Factor Load Matrix of Groundwater Components in Dezhou Area Downstream of the Yellow River Basin
水化学指标
IndexF1 F2 TDS 0.976 0.051 TH 0.923 −0.157 K+ −0.037 0.62 Na+ 0.836 0.153 Ca2+ 0.809 −0.251 Mg2+ 0.926 −0.109 CI− 0.903 0.063 SO42- 0.849 0.101 HCO3− 0.205 0.734 贡献率
(CR)62.199% 11.802% 累积贡献率
(ACR)62.199% 74.001% -
[1] ZHAI Y Z, LEI Y, ZHOU J, et al. The spatial and seasonal variability of the groundwater chemistry and quality in the exploited aquifer in the Daxing District, Beijing, China [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(2): 43. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-4249-9 [2] 吕晓立, 郑跃军, 韩占涛, 等. 城镇化进程中珠江三角洲地区浅层地下水中砷分布特征及成因 [J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(3): 88-98. LÜ X L, ZHENG Y J, HAN Z T, et al. Distribution characteristics and causes of arsenic in shallow groundwater in the Pearl River Delta during urbanization [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(3): 88-98(in Chinese).
[3] 冯娟. 开采条件下德州地区地下水水质演化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011. FENG J. The research on groundwater quality evolution under exploitation conditions in Dezhou[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2011(in Chinese).
[4] 侯国华, 高茂生, 党显璋. 唐山曹妃甸浅层地下水水化学特征及咸化成因 [J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6): 49-57. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.8.10 HOU G H, GAO M S, DANG X Z. Hydrochemical characteristics and salinization causes of shallow groundwater in Caofeidian, Tangshan City [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 49-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.8.10
[5] 彭红霞, 侯清芹, 曾敏, 等. 雷州半岛地下水化学特征及控制因素分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11): 5375-5383. PENG H X, HOU Q Q, ZENG M, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of groundwater in the Leizhou peninsula [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5375-5383(in Chinese).
[6] 赵全升, 冯娟, 安乐生. 德州市浅层地下水水质演化 [J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(5): 1075-1082. ZHAO Q S, FENG J, AN L S. Shallow groundwater quality evolution in Dezhou City [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(5): 1075-1082(in Chinese).
[7] 段晓飞, 孙晓晓, 杨亚宾, 等. 鲁北平原地面沉降现状与机理分析 [J]. 山东国土资源, 2018, 34(10): 86-92. DUAN X F, SUN X X, YANG Y B, et al. Present condition and mechanism analysis on land subsidence in northern Shandong plain [J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2018, 34(10): 86-92(in Chinese).
[8] 贾超, 张少鹏, 孙晓晓, 等. 鲁西北平原地下水开采与地面沉降的相关性 [J]. 中国科技论文, 2021, 16(2): 173-180. JIA C, ZHANG S P, SUN X X, et al. Correlation between groundwater exploitation and land subsidence in northwest plain of Shandong Province [J]. China Sciencepaper, 2021, 16(2): 173-180(in Chinese).
[9] 周晓勇. 德州地区地下水流场参数反演及地层蠕变效应分析研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017. ZHOU X Y. Back analysis of seepage field parameters and research of stratum creep effect in Dezhou City[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017(in Chinese).
[10] 冯颖, 吴清华, 刘帅. 德州市深层地下水水化学动态演化 [J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(4): 51-55. doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.04.007 FENG Y, WU Q H, LIU S. Dynamic evolution of hydrochemistry in deep groundwater in Dezhou City [J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019, 35(4): 51-55(in Chinese). doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.04.007
[11] 纪洪磊, 杨亚宾, 张永伟, 等. 鲁北平原第四纪沉积特征及地面沉降模式分析[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(S1): 241-250. JI H L, YANG Y B, ZHANG Y W, et al. Quaternary sedimentary characteristics and land subsidence model in North Shandong Plain[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(Sup 1): 241-250(in Chinese).
[12] 赵全升, 冯娟, 安乐生. 德州市深层地下水水质演化研究 [J]. 地理科学, 2009, 29(5): 766-772. ZHAO Q S, FENG J, AN L S. Deep groundwater water quality evolution in Dezhou City [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2009, 29(5): 766-772(in Chinese).
[13] 张涛, 蔡五田, 李颖智, 等. 尼洋河流域水化学特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(11): 4537-4545. ZHANG T, CAI W T, LI Y Z, et al. Major ionic features and their possible controls in the water of the niyang river basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(11): 4537-4545(in Chinese).
[14] 冯建国, 赫明浩, 李贵恒, 等. 泰莱盆地孔隙水水化学特征及其控制因素分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2594-2600. FENG J G, HE M H, LI G H, et al. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of porewater in the Tailai Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2594-2600(in Chinese).
[15] 孟舒然, 吕敦玉, 王翠玲, 等. 郑州市中牟县地下水水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(3): 977-986. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010802 MENG S R, LV D Y, WANG C L, et al. Research of groundwater chemical characteristics and controlling factors in Zhongmu County, Zhengzhou City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(3): 977-986(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010802
[16] REN C B, ZHANG Q Q. Groundwater chemical characteristics and controlling factors in a region of northern China with intensive human activity [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(23): 9126. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17239126 [17] 吴起鑫, 韩贵琳, 李富山, 等. 珠江源区南、北盘江丰水期水化学组成特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(7): 1289-1296. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.07.2014120303 WU Q X, HAN G L, LI F S, et al. Characteristic and source analysis of major ions in Nanpanjiang and Beipanjiang at the upper Pearl River during the wet season [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(7): 1289-1296(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.07.2014120303
[18] 孙平安, 于奭, 莫付珍, 等. 不同地质背景下河流水化学特征及影响因素研究: 以广西大溶江、灵渠流域为例 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(1): 123-131. SUN P G, YU S, MO F Z, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors in different geological background: A case study in Darongjiang and Lingqu Basin, Guangxi, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(1): 123-131(in Chinese).
[19] 郑涛, 焦团理, 胡波, 等. 涡河流域中部地区地下水化学特征及其成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(2): 766-775. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202006037 ZHENG T, JIAO T L, HU B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and origin of groundwater in the central Guohe River basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(2): 766-775(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202006037
[20] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry [J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [21] WEI H Y, LIANG X J, LIU S H, et al. Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in Dehui, China [J]. Water, 2020, 12(12): 3378. doi: 10.3390/w12123378 [22] 余东, 周金龙, 魏兴, 等. 新疆喀什地区西部潜水水化学特征及演化规律分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2493-2504. YU D, ZHOU J L, WEI X, et al. Analysis of chemical characteristics and evolution of phreatic water in Western Kashgar Prefecture, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2493-2504(in Chinese).
[23] LIU J T, PENG Y M, LI C S, et al. Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268: 115947. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115947 [24] 张涛, 王明国, 张智印, 等. 然乌湖流域地表水水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4003-4010. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202002080 ZHANG T, WANG M G, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in ranwu lake basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4003-4010(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202002080
[25] 李状, 苏晶文, 董长春, 等. 安徽马鞍山市当涂地区地下水水化学特征及演化机制[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(5) : 1509-1526. LI Z, SU J W, DONG C C, et al. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution mechanisms of the groundwater in Dangtu Area, Maanshan[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(5): 1509-1526(in Chinese),
[26] 崔佳琪, 李仙岳, 史海滨, 等. 河套灌区地下水化学演变特征及形成机制 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4011-4020. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202003150 CUI J Q, LI X Y, SHI H B, et al. Chemical evolution and formation mechanism of groundwater in Hetao irrigation area [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4011-4020(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202003150
[27] MAGARITZ M, NADLER A, KOYUMDJISKY H, et al. The use of Na/Cl ratios to trace solute sources in a semiarid zone [J]. Water Resources Research, 1981, 17(3): 602-608. doi: 10.1029/WR017i003p00602 [28] SAMI K. Recharge mechanisms and geochemical processes in a semi-arid sedimentary basin, Eastern Cape, South Africa [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1992, 139(1/2/3/4): 27-48. [29] 唐金平, 张强, 胡漾, 等. 湔江冲洪积扇地下水化学特征及控制因素分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(7): 3089-3098. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201901006 TANG J P, ZHANG Q, HU Y, et al. Groundwater chemical characteristics and analysis of their controlling factors in an alluvial fan of Jianjiang River [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(7): 3089-3098(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201901006
[30] 余伟, 杨海全, 郭建阳, 等. 贵州草海水化学特征及离子来源分析 [J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(1): 32-41. YU W, YANG H Q, GUO J Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and major ion sources of lake Caohai in Guizhou Province [J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(1): 32-41(in Chinese).
[31] 房丽晶, 高瑞忠, 贾德彬, 等. 草原流域地下水化学时空特征及环境驱动因素: 以内蒙古巴拉格尔河流域为例 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(5): 2161-2169. FANG L J, GAO R Z, JIA D B, et al. Spatial-temporal characteristics of groundwater quality and its environmental driving factors of Steppe Basin—taken Balaguer River Basin of Inner Mongolia for instance [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(5): 2161-2169(in Chinese).
[32] FAN B L, ZHAO Z Q, TAO F X, et al. Characteristics of carbonate, evaporite and silicate weathering in Huanghe River Basin: A comparison among the upstream, midstream and downstream [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 96: 17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.005 [33] 魏善明, 丁冠涛, 袁国霞, 等. 山东省东汶河沂南地区地下水水化学特征及形成机理 [J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(6): 1973-1983. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.021 WEI S M, DING G T, YUAN G X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Yi'nan, East Wenhe River Basin in Shandong Province [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(6): 1973-1983(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.06.021
[34] 王攀, 靳孟贵, 路东臣. 河南省永城市浅层地下水化学特征及形成机制 [J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(6): 2232-2244. WANG P, JIN M G, LU D C. Hydrogeochemistry characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in Yongcheng City, Henan Province [J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(6): 2232-2244(in Chinese).
[35] 于开宁, 田剑, 刘景涛, 等. 兰州市地下水化学特征及演化模拟 [J]. 地质与勘探, 2022, 58(4): 895-904. YU K N, TIAN J, LIU J T, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution simulation of groundwater in Lanzhou City [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2022, 58(4): 895-904(in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: