-
水库沉积物作为水环境中有机质的埋藏和贮存场所,是水生态系统的重要组成部分[1],沉积物中的碳、氮、磷等生源要素是指示水域生产力、营养盐水平的有效指标,直接反映了水体的污染状况[2]. 沉积物有机质分解过程在消耗水的溶解氧的同时,还会向水体释放大量的碳、氮、磷、硫等营养盐[3],并通过沉积物-水界面的物质交换过程,改变氮、磷营养盐在生态系统中的循环,对水体富营养化水平产生重要影响[4]. 水库在发电、航运、渔业以及供水等方面具有重要功能,水库的水环境保护及水生态安全维护成为目前和今后的主要任务,研究水库中沉积物的碳、氮、磷含量的时空分布特征,有助于了解水库的营养状况及水体氮、磷污染生态风险,为保障水库供水安全等方面提供科学依据[5]. 此外,通过对沉积物指标的分析还可以重建水域环境的演变过程以及其对人类活动的响应,以便揭示水体富营养化的演化规律[6].
江西柘林水库,又名柘林湖、庐山西海,是长江中游鄱阳湖流域的大型峡谷型旅游性水库,由人工拦截鄱阳湖五大支流之一的“修河”而成. 作为江西省最大的人工湖,不仅是江西省九江市重要的饮用水水源地,也是沿湖城乡生活污水和工业污水的主要纳污水体[7]. 此外,作为庐山西海5A级风景名胜区和鱤国家级水产种质资源保护区的所在地,还被国家环保总局列入了中国重要湿地名录名单,在水源涵养、洪水调蓄、旅游开发、渔业养殖以及生物多样性保护等方面均具有重要的生态作用[8]. 随着沿湖工、农业以及旅游业的迅速发展,入库的氮磷负荷不断增加,库区的水生态环境也发生了新的改变,尽管柘林水库整体呈中营养状态,但部分水域的浮游植物优势种主要以蓝藻门的微囊藻和长孢藻属为主,有爆发蓝藻水华的风险[7-9]. 近年来有关柘林水库的研究主要集中在水质、浮游植物、底栖动物以及鱼类等方面[10-13],未见有关柘林水库沉积物研究的报道.
为了解柘林水库表层沉积物的污染现状,本研究基于柘林水库4个季度33个监测点的表层沉积物调查数据,分析了沉积物中总氮、总磷和有机质含量的时空分布特征,基于相关性分析和C/N比值解析了沉积物有机质的来源,并以综合污染指数法和有机污染指数法分别评价了表层沉积物的污染现状,以期为柘林水库水生态环境的管理和保护提供科学数据支撑.
-
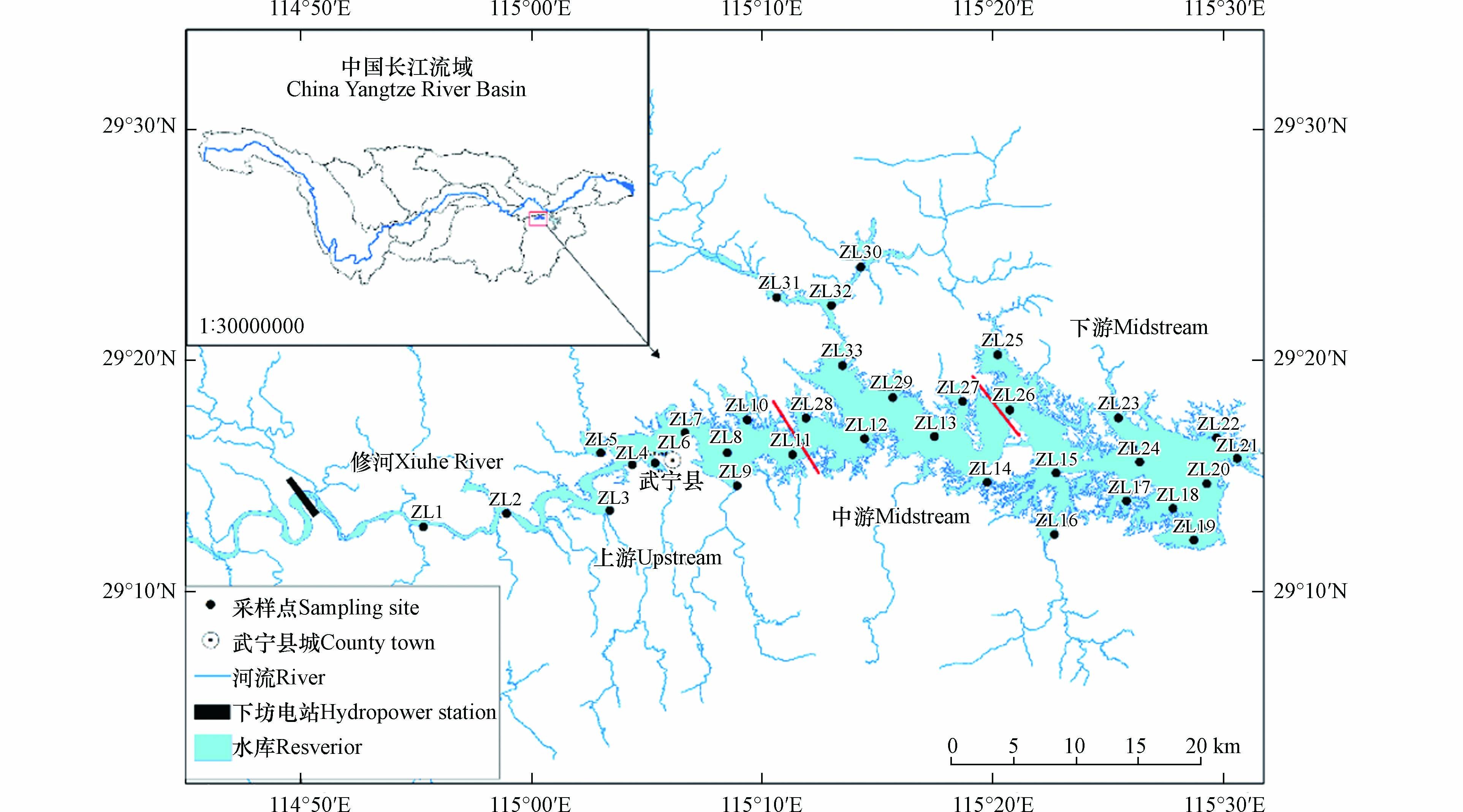
柘林水库位于修河流域(E 115°04′―115°40′, N 29°03′―29°27′),水库坝址以上汇水区域9340 km2,水域面积308 km2,总容量79.2亿m3,正常水位65 m,平均水深16.3 m,最大水深45 m,流域内大小支流有603条,库区内岛屿3亩以上的有1667个[14]. 柘林水库属亚热带季风气候,四季分明,雨水充沛,但季节分布不均匀,流域年平均降水量为1611.8 mm,一般4―7月为丰水期,10―1月为枯水期[15].
-
根据柘林水库的生态环境及水文特点,参照《水库渔业资源调查规范(SL167—2014)》在上、中、下游设置共33个采样点,采样点分布如表1和图1所示. 分别于2020年10月(秋季)、2021年1月(冬季)、4月(春季)和7月(夏季)使用1/16 m2的彼得森抓斗式采泥器分季度采集表层沉积物样品,立即装入清洁的聚乙烯自封袋,并冷冻保存带回实验室用于沉积物总氮(TN,mg·kg−1)、总磷(TP,mg·kg−1)和有机质(OM,%)含量的测定,采样过程参照《HJ494—2009 采样技术规范》进行.
-
采用凯氏定氮法、碱熔-钼锑抗分光光度法和重铬酸钾容量法测定TN、TP和OM的含量,相关操作分别参照标准《HJ 717—2014》、《HJ 632—2011》以及《水和废水监测分析方法(第四版)》.
-
目前国内外对沉积物的污染状况评价一般采用综合污染指数法和有机污染指数法,其中综合污染指数法是表层沉积物的TN和TP污染程度为基础,再计算综合污染指数(FF),进行综合污染程度评价,虽然综合指数法相比单一指数更能反映沉积物的客观污染情况,但忽略有机质指标,因此,有必要采用有机质污染指数法(OI)进一步评价沉积物的污染现状. 其计算公式如下:
式中,Si为因子i(TN或TP)的标准指数,Si>1,表示因子i含量超过标准值,Ci为因子i的实测值,CS为因子i的评价标准值,其中TN和TP的CS值[16]分别取1000 mg·kg−1, 420 mg·kg−1. FF为综合污染指数,F为STN和STP的平均值,Fmax为STN和STP中的最大值;OI、OC和ON分别表示有机污染指数,有机碳和有机氮,单位均为%. 沉积物FF和OI的评价参照包宇飞等[16]进行,评价标准如表2所示.
-
Excel 2016 软件和R 4.2.1软件用于数据的统计分析,使用R软件的“multcomp”包对不同采样位置、季节以及的TN、TP、OM、N/P以及C/N的差异进行单因素方差分析和多重比较,差异显著水平为P<0.05. 使用R 4.2.1软件的 “ggcorrplot”包进行Pearson相关性分析,P<0.05,表示相关性显著,P<0.01,表示相关性极显著. 首先使用ArcGis10.2软件对33个监测点4个季度的污染物指数的平均值进行正态分布检验,再用“普通克里金”法进行空间插值分析和绘图,采样点位分布图的绘制也在ArcGis10.2软件完成,其他图表的绘制在R 4.2.1软件里用“ggplot2”包完成.
-
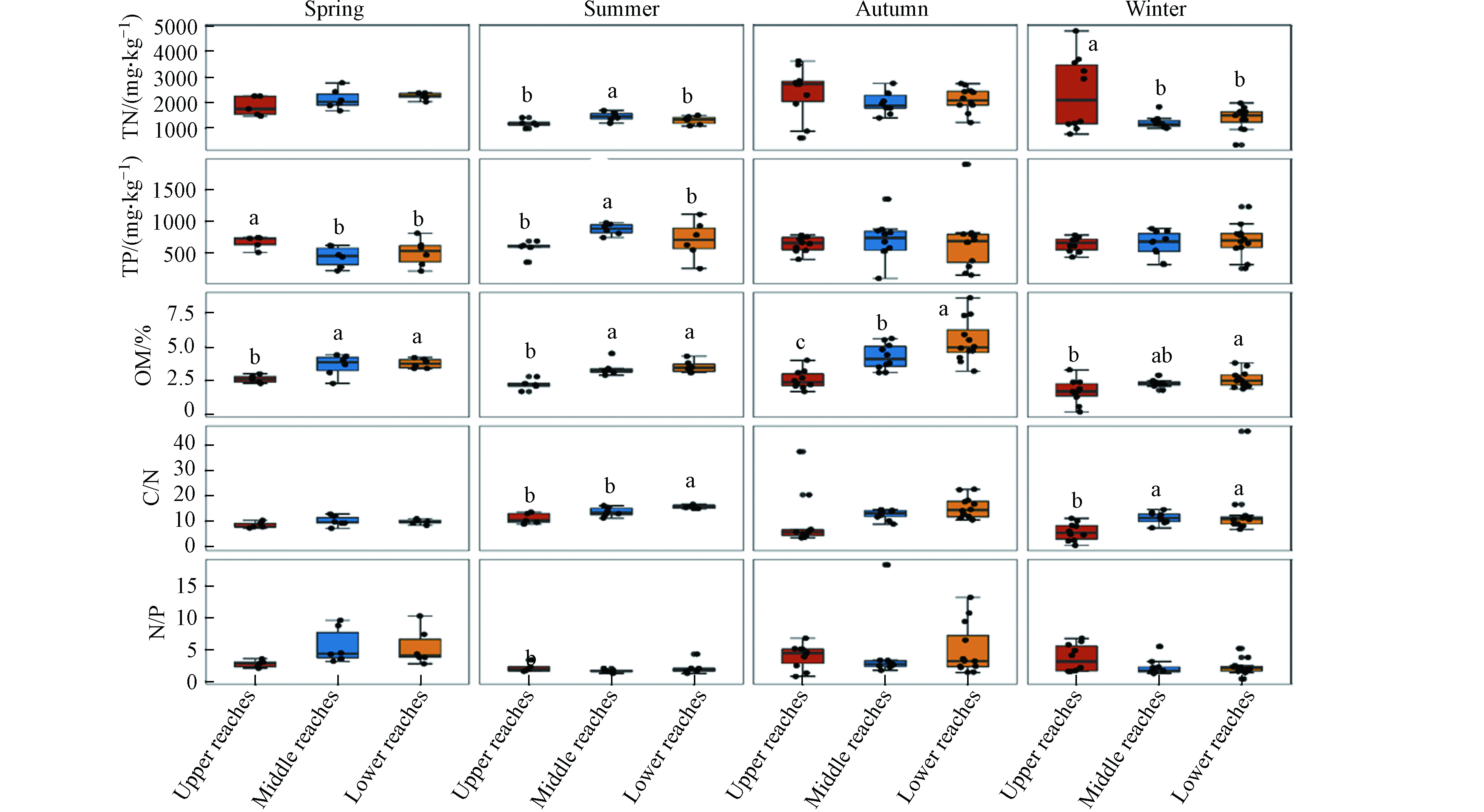
柘林水库表层沉积物TN、TP、OM、C/N和N/P的变化范围分别为334―4800 mg·kg−1、98―1900 mg·kg−1、0.2%―8.6%、0.33―45.52和0.43―18.27,均值1832.6 mg·kg−1、657.5 mg·kg−1、3.2%、11.51和3.49(表3). 湖库沉积物的时空分布受到内源和外源因素的共同影响,比如水动力作用会影响外源输入的污染物的沉降和再悬浮过程[17]. 研究发现柘林水库沉积物TN在上游最高为(2088.4±1086.6) mg·kg−1,但与上、中、下游间的差异均不显著(P>0.05),这可能与点源氮的输入有关[18],柘林水库的主要来水水源为上游的修河,年均来水量为80.6 ×108 m3,随之携带的污染物进入水体后不断沉积,导致沉积物氮负荷升高[19],此外,上游区域的ZL4#―ZL8#采样点靠近武宁县城,接纳了更多的城市生活污水,也导致了这些采样点的TN含量更高. 而位于上游修河的ZL3#采样点TN含量最高为4800 mg·kg−1,分析可能与该采样点附近的采砂活动有关. 与TN相比,水库沉积物TP与内源浮游生物的沉降密切相关[20],柘林水库中、下游沉积物TP含量((667.3±259.9)mg·kg−1、(660.1±335.6)mg·kg−1)均高于上游((632.7±116.2)mg·kg−1),这可能与建在下游的大坝有关,坝前悬浮物中的营养物质不断累积,导致TP含量升高,这与江雪等[21]对天津于桥水库沉积物磷的赋存特征的研究结果一致. 沉积物TN、TP的时空分布还与水草存在与否密切有关,随水草生物量的增加,氮含量升高,磷含量降低[22],而柘林水库的水生植物主要分布在上游修河[23],这也是上游沉积物TN含量高、TP含量低的原因之一.
沉积物OM是反映湖库有机质营养程度的重要指标,其来源主要分为内源输入和外源汇入两个途径[24]. 柘林水库沉积物OM总体上在下游(3.9%)显著高于上游(2.2%),且与中游间的差异不显著(P>0.05),这可能与水库周边的土地利用现状和水上的人类活动干扰的影响密切相关[25]. 王书锦等[26]研究表明,洱海流域的罗时江河口湿地Ⅱ区沉积物OM含量高于Ⅰ区,而调查发现,相比Ⅰ区,Ⅱ区是旅游观光船的主要运行区域,船运带来水体扰动促进了该区域沉积物对OM的吸附,无独有偶,柘林水库作为庐山西海5A级国家风景名胜区的主体部分,以发展生态旅游业为主[23],较中、上游区域,下游区域的水上观光旅游、船运等活动更为频繁,因此下游区域的沉积物OM含量更高. 此外,下游更高土地利用率和更多样化的土地利用类型,也促进了沉积物对OM的吸附[27].
季节上(图2),4个季度的N/P在上中下游间的差异均不显著(P > 0.05),但TN、TP和OM含量均具有明显的季节差异,其中在春季,上游TP和OM分别为 (670.6±102.6) mg·kg−1、2.6%±0.3%,TP显著高于中、下游(P < 0.05),OM显著低于中、下游(P < 0.05);在夏季,中游TN((1453.3±180.5)mg·kg−1)、TP((875.8±90.6)mg·kg−1)显著高于上、下游(P > 0.05),上游OM(2.2%±0.4%)和C/N(10.99±2.14)显著低于下游(P < 0.05);在秋季,上、中、下游的OM差异显著(P < 0.05),下游(5.4%±1.6%)>中游(4.3%±1.0%)>上游(2.6%±0.7%),TN在上游最高、TP中游最高而C/N则在下游最高,分别为(2391.1±993.4) mg·kg−1、(711.1±322.4)mg·kg−1和15.24±4.29;在冬季,与中下游相比,上游TN显著较高、OM和C/N显著较低,分别为(2355.9±1440.5)mg·kg−1、1.7%±0.9%和5.73±2.13. 秋季下游OM(5.4%±1.6%)显著高于中(4.3%±1.0%)和上游(2.6%±0.7%).
总体上,夏季TP((727.4±207.0)mg·kg−1)显著高于其他季节。夏季多雨使得因地表径流进入水体的大量颗粒物作为磷的载体而大量沉积[28],导致沉积物TP含量显著升高. 秋季TN含量较高((2159.4±854.0)mg·kg−1),且冬季((1639.1±688.2)mg·kg−1)高于夏季((1322.5±542.7)mg·kg−1),这可能柘林水库的水文条件有关,相比夏季,冬季的水流缓慢有利于氮污染物的沉积[29];而冬季较低水温也会导致沉积物N素的循环过程慢于夏季[30]. 秋季的OM(4.2%±1.7%)显著高于其他季节,分析认为,秋季是柘林水库旅游的旺季,旅游活动干扰强度的变化也进一步引起了沉积物OM差异. 此外,研究还发现,相比其他区域(表4),位于库湾的TP((726.1±331.9)mg·kg−1)和OM(3.7%±1.5%)均显著较高(P<0.05),分析认为这可能与库湾内的网箱养殖和休闲鱼排有关. 据统计[23],截止至2013年,柘林水库库湾的网箱养殖面积有65.93 km2,占湖区面积的20%,尽管近年来受环保政策影响,库湾的网箱也明显减少,但随着休闲渔业发展,库湾的休闲垂钓筏排数量也在不断增多,导致输入库湾的有机质负荷增多,沉积物OM含量也更高,有研究表明[31],受养殖活动的影响,太湖的沉积物OM含量更是增加了593%.
与国内不同湖库表层沉积物TN、TP、OM含量相比(表5). 柘林水库表层沉积物TN与清林径水库[32](1645 mg·kg−1)相当,但高于其他湖库. TP则与山美水库[33](642 mg·kg−1)相当,低于黄柏河梯级水库[16] (3840 mg·kg−1)、三峡水库[34] (1014 mg·kg−1)和金盆水库[35] (1131 mg·kg−1). 与同处江西省的其他15座典型[36]水库相比,柘林水库沉积物TN、TP含量均处于较高水平,分析认为这可能与水库的规模、淤积形式等有关. 柘林水库属大型峡谷型水库,汇水面积9340 km2,入库河流多,营养盐负荷高,且非点源污染已成为柘林水库区域污染的重要来源[37]. 此外,柘林水库的库湾多,水体的滞留时间较长,更加有利于污染物的沉积[38-39],这也可能是柘林水库沉积物TN、TP含量较高的原因之一. 柘林水库OM均值为3.2%,与国内其他湖、水库相比,柘林水库有机质含量处于中等水平,与山美水库[33](3.3%)、丹江口水库[40](2.9%)、三峡水库[34](2.8%)和于桥水库[41] (3.6%)相当,显著低于金盆水库[35](7.0%)但显著高于鄱阳湖[42](1.6%).
-
生源要素的比值反映了其营养来源[43],研究发现(表6),柘林水库表层沉积物的OM与TP和C/N均呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),相关系数均为0.21,但与TN相关性不显著(P > 0.05). C/N与OM呈显著负相关(P < 0.05),与TN呈极显著负相关(P < 0.01),相关系数别为0.45和−0.53,表明沉积物OM与TP有一定的同源性,但与TN的来源不一致,这也进一步证实了柘林水库沉积物TN和TP的来源存在差异. 沉积物对TN和TP 的吸附不仅受沉积物理化参数的影响,还与沉积物OM含量有关,有研究表明[44],长江中下游湖泊表层沉积物对磷的吸附量与沉积物OM含量呈显著的正相关关系,这可能也是导致柘林水库沉积物TP和OM在时空分布具有一致性的重要原因. 沉积物OM与TN相关性不显著,表明它们的来源可能不一致,C/N与OM和TP的相关性显著,但与TN呈显著负相关,与TP呈显著正相关,这也进一步说明了柘林水库沉积物OM可能与TP具有相同的来源但与TN不同. 而柘林水库沉积物TN与TP 的相关性不显著(r=0.04,P > 0.05),反映了TN与TP 在来源存在一定差异性,毛亮等[45]对湖南省的大通湖沉积物氮、磷耦合特征的研究也得到了类似的结果.
C/N是识别沉积物有机污染来源及生物种类的重要依据,其值越大,陆源输入的有机质成分就越大[46]. 调查期间,柘林水库C/N均值为11.51,超过56.1% 采样点的C/N值在10―20之间,表明水生生物和陆生生物是其沉积物有机质的主要来源,这与鄱阳湖流域的里湖水库、赣江流域的金盘水库以及饶河流域的大口坞水库的研究结果一致[36]. 此外,研究还发现,C/N值的最大和最小值分别为0.33和45.33,分别出现在上游的ZL6#采样点和下游的ZL18#采样点,而ZL18#采样点位于坝前的深水区,厌氧的环境促进了沉积物的反硝化作用进程,降低了沉积物TN的含量[37],这与该采样点具有最低的沉积物TN含量(344 mg·kg−1)的结果一致. 由图2可知,柘林水库沉积物C/N也呈现一定时空异质性,下游(13.80)显著较高,且均高于12,表明陆源有机质是柘林水库下游沉积物OM的重要来源[47]. 此外,在夏、秋季,下游C/N高于中上游,而且夏季和秋季分别有88.2%和71.9%的采样点的C/N值大于10,说明夏、秋季沉积物输入了更多的陆源有机质,分析认为夏、秋季正处雨季,库区水位随降雨增多升高,陆生植物的残枝败叶因淹没进入水体,导致陆源性有机质的输入量增加[16].
-
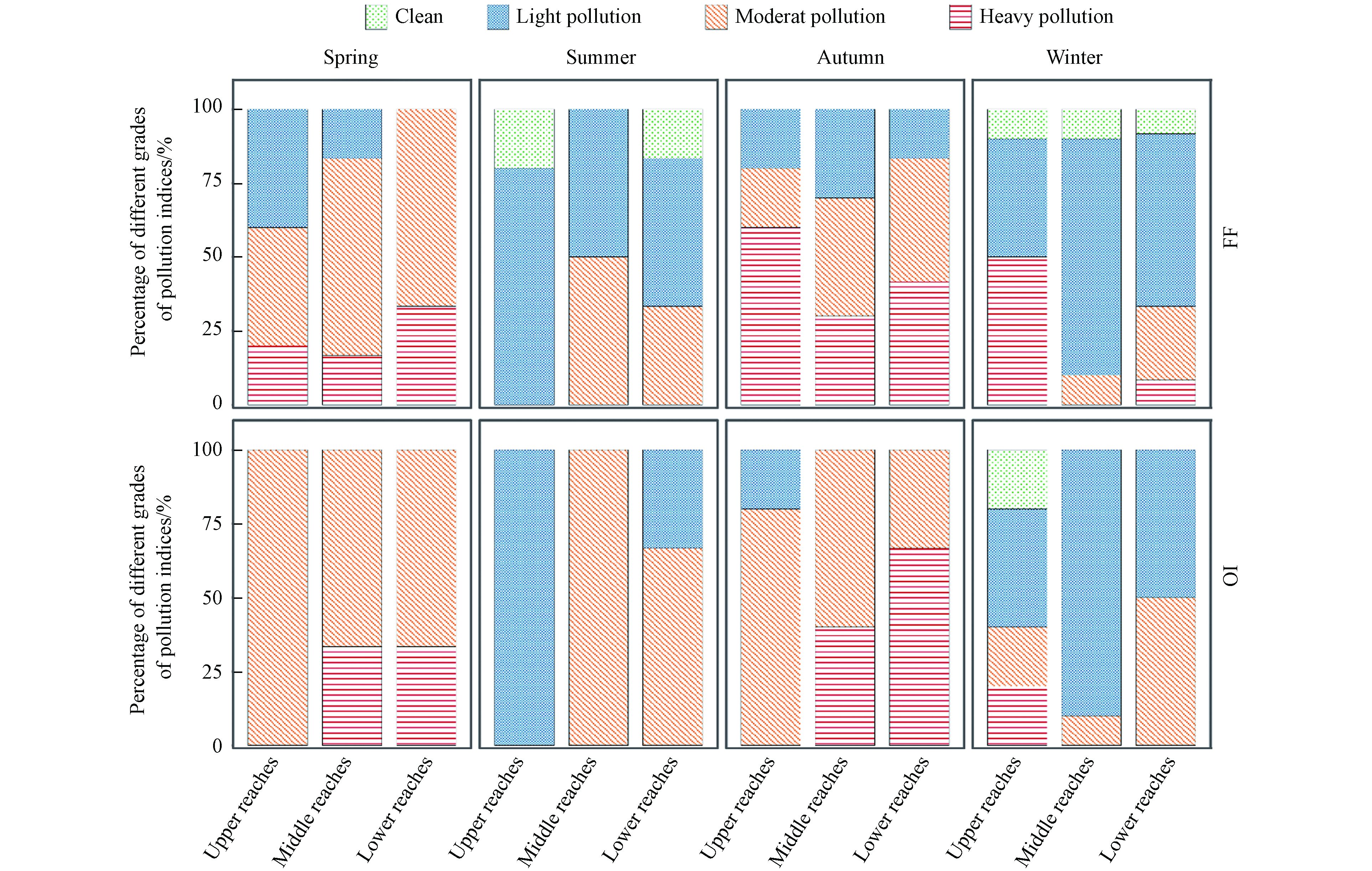
相比湖泊,有关水库沉积物污染状况的研究较少,而且评价方法也尚无统一的标准[48],主要有单因子指数法、综合污染指数法、有机质污染指数法、内梅罗综合指数法以及模糊数学综合评价法等[49],调查期间,柘林水库沉积物STN、STP、FF和OI指数的范围分别为1.32―3.66、0.65―1.85、1.30―3.11和0.18―0.78,均值分别为1.91、1.11、1.76和0.35,表明柘林水库表层沉积物处于中等污染等级(图3).
本研究分别运用综合污染指数法和有机质污染指数评价了柘林水库沉积物的污染现状,总体上(表7),以综合污染指数FF评价,轻度污染占比最高为39.8%,中度-重度污染的占比超过55%,清洁等级占比最低仅为5.1%. 以有机物污染指数OI评价,69.4%的采样点为中度-重度污染,轻度和清洁等级的占比分别为28.6%和2.0%.
与其他季节相比(图4),秋季FF和OI污染等级达到中度—重度污染的比例显著较高,特别是中、下游的有机质污染水平均为中度-重度污染,这可能与秋季频繁的旅游活动,比如传统节日中秋节和国庆节更是旅游活动的旺季. 此外,夏季的多雨天气,导致水体中的营养盐在秋季沉积也可能是秋季污染水平较高的原因之一. 在空间上,55%以上的采样点的污染等级已经达到中度—重度污染水平,其中TN的重度污染的占比最高为31.63%,与江西其他水库相比,柘林水库沉积物TN污染等级更高[33],尤其是在上游修河和武宁县城区域,将近50 %的采样点都属于重度污染水平,其生态风险不容忽视. 就TP而言,库湾区域重度污染水平的比例达到了33.3%,存在内源磷释放的潜在风险,因此应该控制库湾内的养殖网箱和休闲垂钓鱼排的规模. 此外,下游区域77.8%采样点的有机质污染指数超过0.5,说明下游有机质污染风险较高,这可能与下游风景区内频繁的水上旅游活动有关,为了降低剧烈扰动对有机质的影响,建议更换快艇为静缓型的游船.
-
(1) 调查期间,柘林水库沉积物TN、TP和OM均呈现一定的时空异质性. 空间上,TP和OM表现为中、下游>上游,库湾>库心、入库河口,TN则为上游>中、下游,入库河口>库心、库湾. 季节上, TN和OM秋季较高,TP则在夏季较高.
(2) 柘林水库沉积物OM与TP有一定的同源性,但与TN的来源不一致. 沉积物有机质具有混合来源. 空间上,陆源有机质是下游和库湾的主要来源;季节上,水生生物是春季和冬季的主要来源.
(3) 柘林水库表层沉积物总体上处于中度污染水平,具有一定的生态污染风险. 上游TN生态风险较高;下游和库湾的TP和OM污染风险更高. 建议对加强上游县城周边的污水排放治理、控制库湾内养殖网箱和垂钓鱼排数量、科学调整下游水上旅游路线和船只类型.
柘林水库表层沉积物氮、磷、有机质的时空分布及污染评价
Temporal-spatial distribution and pollution assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir
-
摘要: 柘林水库是鄱阳湖流域的大型峡谷型水库,具有水源涵养、洪水调蓄、旅游开发、渔业养殖以及生物多样性保护等重要生态功能. 研究其表层沉积物营养盐和有机质的污染特征,对了解其污染生态风险、揭示富营养化的演化规律具有重要意义. 于2020年9月、2021年1月、4月和7月对33个监测点的表层沉积物(0―10 cm)进行季度采样,分析了沉积物总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)和有机质(OM)的时空分布格局及相关性,并分别运用综合污染指数法(FF)和有机质污染指数法(OI)对其污染现状进行评价. 结果表明,柘林水库表层沉积物TN、TP和OM含量范围分别为334―4800 mg·kg−1、98―1900 mg·kg−1和0.2%―8.6%,均值分别为1832.6 mg·kg−1、657.5 mg·kg−1和3.2%,且呈现一定的时空异质性. Pearson相关分析表明,柘林水库沉积物OM与TP、C/N均呈显著正相关(P<0.05),相关系数分别为0.21和0.45,但OM与TN、TP与TN的相关性均不显著(P>0.05),表明沉积物OM与TP有一定的同源性,但与TN的来源不一致. 沉积物来源分析表明,柘林水库沉积物有机质具有混合来源,春季和冬季沉积物有机质来源以水生生物为主,下游和库湾区域的陆源输入有机质的贡献则更大. STN、STP、FF和OI指数的范围分别为1.32―3.66、0.65―1.85、1.30―3.11和0.18―0.78,均值分别为1.91、1.11、1.76和0.35,表明柘林水库表层沉积物处于中等污染等级,具有一定的生态污染风险.Abstract:
Zhelin Reservoir is a large canyon reservoir in Poyang Lake basin, which plays an important ecological role in water conservation, flood control, tourism development, fishery culture and biodiversity protection. It is of great significance to study the pollution characteristics of nutrients and organic matter in surface sediments to understand the risk of ecological pollution and reveal the evolution law of eutrophication. The spatial and temporal distribution patterns of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP) and organic matter (OM) in the surface sediments (0―10 cm) were analyzed with samples collected from 33 monitoring sites in September 2020, January, April and July 2021. The pollution status was evaluated by single, comprehensive and organic matter pollution index, respectively. Results showed that: TN, TP and OM in the surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir showed certain spatial-temporal heterogeneity, and ranged from 334―4800 mg·kg−1, 98―1900 mg·kg−1 and 0.2%―8.6% with mean values of 1832.6 mg·kg−1, 657.5 mg·kg−1 and 3.2%, respectively. Pearson correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between OM and TP with the correlation coefficients of 0.21 and 0.45, respectively (P < 0.05), but no significant correlation between OM and TN, TN and TP in sediments of Zhelin reservoir (P > 0.05), indicating that OM and TP had certain homology, but the source of TN was not consistent. Further analysis showed that the organic matter in the sediments of Zhelin Reservoir had mixed sources, the main source of sediment organic matter was aquatic organisms in the spring and winter, while the contribution of terrigenous material inputs to OM was larger in the Lower reaches and reservoir bay. The pollution indices of STN, STP, FF and OI ranged from 1.32―3.66, 0.65―1.85, 1.30―3.11 and 0.18―0.78, with mean values of 1.91, 1.11, 1.76 and 0.35, respectively, indicating that there was certain ecological pollution risk in the surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir with the moderate pollution grade. -
Key words:
- surface sediments /
- nutrients /
- temporal-spatial distribution /
- pollution assessment /
- Zhelin Reservoir.
-

-
表 1 柘林水库表层沉积物采样点分布情况
Table 1. Sampling site and season of surface sediments in Zhelin Reservoir
采样点
Sampling
site采样位置
Sampling
location采样区域
Sampling
area采样季节 Sampling season 采样点周围情况描述
Description of sampling
site春季
Spring夏季
Summer秋季
Autumn冬季
WinterZL1 上游 入库河流或河口 + + 修水河段、砂质为主,
采砂作业活动频繁ZL2 + + + + ZL3 + + + + ZL4 上游 入库河流或河口 + + 靠近武宁县城,接纳工农业生产和
城镇居民生活污水ZL5 库湾 + + ZL6 入库河流或河口 + + ZL7 库心区域 + + + + ZL8 库心区域 + + ZL9 入库河流或河口 + + + + ZL10 上游 库湾 + + + + 潘龙岗库湾 ZL11 上游 库心区域 + + + + 库心 ZL12 中游 库心区域 + + 罗坪镇 ZL13 库心区域 + + + + ZL14 中游 库湾 + + + + 扬州乡 ZL27 中游 库湾 + + + + 八里棚库湾 ZL28 中游 库湾 + + + + 河口库湾 ZL29 库心区域 + + 巾口乡 ZL30 中游 入库河流或河口 + + 鲁溪镇双溪河 ZL31 中游 入库河流或河口 + + 横路镇株林河 ZL32 中游 入库河流或河口 + + + + 两河交汇 ZL33 中游 入库河流或河口 + + + + 红岩潭大桥附近 ZL15 下游 库湾 + + + + 瓜源河、花源谷风景区、
阳光照耀29度度假区ZL16 入库河流或河口 + + + + ZL17 库湾 + + ZL18 下游 库心区域 + + 司马旅游码头、观光塔、
滨湖栈道、玻璃桥等ZL19 库湾 + + + + ZL20 下游 库心区域 + + + + 瑶池湾国际垂钓中心、民宿、
民俗文化村等ZL21 库湾 + + ZL22 库湾 + + ZL23 下游 库湾 + + + + 西海渔村风景区 ZL24 库心区域 + + ZL25 下游 库湾 + + + + 官莲乡巾口大桥附近 ZL26 下游 库心区域 + + 墨斗山观湖岛景区 注:“+”表示在该季节采样. “+” represent sampling in this season. 表 2 沉积物综合污染指数和有机污染指数评价标准
Table 2. Assessment standards of surface sediments comprehensive pollution index (FF) and organic pollution index (OI)
级别
Level综合污染指数
FF有机质污染指数
OI评价等级
GradeⅠ <1.0 <0.05 清洁 Clean Ⅱ 1.0≤FF≤1.5 0.05≤OI<0.20 轻度污染 Light pollution Ⅲ 1.5<FF≤2.0 0.20≤OI<0.5 中度污染 Moderate pollution Ⅳ >2.0 ≥0.5 重度污染 Heavy pollution 表 3 柘林水库表层沉积物TN、TP、OM 、C/N和N/P的空间分布
Table 3. Spatial patterns of TN, TP, OM, C/N and N/P in surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir
总氮/(mg·kg−1)
TN总磷/(mg·kg−1)
TP有机质/%
OM碳氮比
C/N
氮磷比
N/P上游 2088.4±1086.6 632.7±116.2 2.2±0.8c 8.40±6.79b 3.37±1.75 中游 1676.8±490.4 667.3±259.9 3.4±1.0ab 11.84±2.32a 3.40±3.33 下游 1757.9±549.5 660.1±335.6 3.9±1.5a 13.80±6.64a 3.69±2.99 全库 1832.6±754.4 654.1±257.8 3.2±1.4b 11.51±6.04a 3.49±2.78 注:同列的不同字母表示差异显著,P<0.05.
Note: Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences, P<0.05表 4 柘林水库表层沉积物TN、TP、OM的区域分布
Table 4. Area patterns of TN, TP and OM in surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir
总氮/ (mg·kg−1)
TN总磷/(mg·kg−1)
TP有机质/%
OM入库河口 1948.6±915.2 567.1±201.8b 2.9±1.3b 库心 1757.4±772.2 654.6±196.9b 3.0±1.2b 库湾 1802.8±589.6 726.1±331.9a 3.7±1.5a 注:同列的不同字母表示差异显著,P<0.05.
Note: Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences, P<0.05表 5 柘林水库表层沉积物TN、TP、OM的特征及与其他湖库的对比
Table 5. Characteristics of TN, TP and OM of surface sediments in Zhelin Reservoir and their comparison with other lakes and reservoirs
所处省份
Province湖库名称
Name总氮/(mg·kg−1)
TN总磷/(mg·kg−1)
TP有机质/%
OM文献来源
Reference江西 鄱阳湖 1340 460 1.6 王圣瑞等[42] 湖北 黄柏河梯级水库 1500 3840 4.6 包宇飞等[16] 江西 江西15座典型水库 951 609 2.6 胡强等[36] 福建 山美水库 1180 642 3.3 邱祖凯等[33] 陕西 金盆水库 1132 1131 7.0 王亚平等[35] 河南 丹江口水库 1340 570 2.9 李冰等[40] 广东 清林径水库 1645 232 1.9 兰建洪等[32] 重庆 三峡水库 903 1014 2.8 封丽等[34] 天津 于桥水库 1365 480 3.6 吴光红等[41] 江西 柘林水库 1833 658 3.2 本研究 表 6 柘林水库表层沉积物TN、TP、OM、C/N和 N/P相关性(n=98)
Table 6. Pearson correlation between TN, TP, OM,C/N and N/P in surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir (n=98)
指标
Parameters总氮
TN总磷
TP有机质
OM碳氮比
C/NTP 0.04 1 OM 0.17 0.21* 1 C/N −0.53** 0.14 0.45** 1 N/P 0.45** −0.64** 0.21* −0.2 表 7 柘林水库表层沉积物污染等级评价
Table 7. Pollution grade assessment on surface sediments of Zhelin Reservoir
综合污染指数 FF 有机质污染指数 OI 点位数量
Sampling sites number占比/%
Percentage点位数量
Sampling sites number占比/%
Percentage清洁 5 5.1 2 2.0 轻度污染 39 39.8 28 28.6 中度污染 30 30.6 50 51.0 重度污染 24 24.5 18 18.4 -
[1] RUBIO-PORTILLO E, VILLAMOR A, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ V, et al. Exploring changes in bacterial communities to assess the influence of fish farming on marine sediments [J]. Aquaculture, 2019, 506: 459-464. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.03.051 [2] WU M, HUANG S L, WEN W, et al. Nutrient distribution within and release from the contaminated sediment of Haihe River [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(7): 1086-1094. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60491-3 [3] SHEN Q S, LIU C, ZHOU Q L, et al. Effects of physical and chemical characteristics of surface sediments in the formation of shallow lake algae-induced black bloom [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 25(12): 2353-2360. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60325-8 [4] ZHANG Y, SONG C L, JI L, et al. Cause and effect of N/P ratio decline with eutrophication aggravation in shallow lakes [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 627: 1294-1302. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.327 [5] 潘雄, 顾文俊, 李欢, 等. 洪湖沉积物碳氮磷分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 长江科学院院报, 2021, 38(8): 41-46. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200640 PAN X, GU W J, LI H, et al. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in sediments of Honghu Lake: Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(8): 41-46(in Chinese). doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200640
[6] CUNDY A B, CROUDACE I W, CEARRETA A, et al. Reconstructing historical trends in metal input in heavily-disturbed, contaminated estuaries: Studies from Bilbao, Southampton Water and Sicily [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2003, 18(2): 311-325. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00127-0 [7] 戴国飞, 刘慧丽, 张伟, 等. 江西柘林湖富营养化现状与藻类时空分布特征 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2015, 27(2): 275-281. doi: 10.18307/2015.0211 DAI G F, LIU H L, ZHANG W, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of algae and eutrophic status of Lake Zhelin, Jiangxi Province [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2015, 27(2): 275-281(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2015.0211
[8] 刘慧丽, 廖兵. 柘林湖湖泊生态环境问题及保护对策 [J]. 江西科学, 2013, 31(1): 48-52,128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3679.2013.01.013 LIU H L, LIAO B. The major eco-environmental problems and its protection countermeasures in Zhelin Lake [J]. Jiangxi Science, 2013, 31(1): 48-52,128(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3679.2013.01.013
[9] 张毅鸽, 王一郎, 杨平, 等. 江西柘林湖水华蓝藻: 长孢藻(Dolichospermum)的形态多样性及其分子特征 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(4): 1076-1087. doi: 10.18307/2020.0416 ZHANG Y G, WANG Y L, YANG P, et al. Morphological diversity and molecular characteristics of bloom forming Dolichospermum species in Lake Zhelin, Jiangxi Province [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(4): 1076-1087(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0416
[10] 孟子豪, 李学梅, 王旭歌, 等. 网箱养殖对柘林水库氮磷营养盐时空分布的影响-以太阳山库湾为例 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(9): 2832-2840. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021022204 MENG Z H, LI X M, WANG X G, et al. Influence of cage fish-farming on tempo-spatial distribution of nitrogrn and phosphorus in Zhelin Reservior: A case study of Taiyangshan Bay [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(9): 2832-2840(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021022204
[11] 曾旻, 廖兵, 安长廷, 等. 江西柘林水库大型底栖动物群落结构 [J]. 南昌大学学报(理科版), 2014, 38(5): 506-510. doi: 10.13764/j.cnki.ncdl.2014.05.021 ZENG M, LIAO B, AN C T, et al. Community structure of macrozoobenthos in Zhelin Reservoir of Jiangxiprovince [J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Natural Science), 2014, 38(5): 506-510(in Chinese). doi: 10.13764/j.cnki.ncdl.2014.05.021
[12] 陈康, 孟子豪, 李学梅, 等. 江西柘林水库鱼类群落结构及功能多样性分析 [J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(11): 4592-4602. CHEN K, MENG Z H, LI X M, et al. Community structure and functional diversity of fishes in Zhelin Reservoir, Jiangxi Province [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 4592-4602(in Chinese).
[13] 陈康, 孟子豪, 李学梅, 等. 鄱阳湖流域柘林水库秋季浮游植物群落结构及其构建过程驱动机制 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2022, 34(2): 433-444. doi: 10.18307/2022.0206 CHEN K, MENG Z H, LI X M, et al. Phytoplankton community structure and driving mechanism of its construction process in autumn in Zhelin Reservoir, Lake Poyang Basin [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2022, 34(2): 433-444(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2022.0206
[14] 樊华, 陈然, 刘志刚. 柘林水库水环境容量及水污染控制措施研究 [J]. 人民长江, 2009, 40(24): 39-40,43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2009.24.013 FAN H, CHEN R, LIU Z G. Study on environmental capacity and water pollution control measures of Zhelin Reservoir [J]. Yangtze River, 2009, 40(24): 39-40,43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2009.24.013
[15] 王怀清, 彭静, 赵志强, 等. 江西柘林水库集水区近50年气候干湿状况研究 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2011, 20(6): 723-728. WANG H Q, PENG J, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Dryness/wetness status research in upper reaches of Zhelin Reservoir in last 50 years [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2011, 20(6): 723-728(in Chinese).
[16] 包宇飞, 胡明明, 王殿常, 等. 黄柏河梯级水库沉积物营养盐与重金属分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1005-1016. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.013 BAO Y F, HU M M, WANG D C, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of nutrients and heavy metals in sediments of the cascade reservoirs in Huangbai River [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(5): 1005-1016(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.013
[17] 孙小静, 秦伯强, 朱广伟, 等. 持续水动力作用下湖泊底泥胶体态氮、磷的释放 [J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(6): 1223-1229. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.06.010 SUN X J, QIN B Q, ZHU G W, et al. Release of colloidal N and P from sediment of lake caused by continuing hydrodynamic disturbance [J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(6): 1223-1229(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.06.010
[18] COOPER S R, MCGLOTHLIN S K, MADRITCH M, et al. Paleoecological evidence of human impacts on the Neuse and Pamlico estuaries of North Carolina, USA [J]. Estuaries, 2004, 27(4): 617-633. doi: 10.1007/BF02907649 [19] 周子振, 黄廷林, 章武首, 等. 柘林水库污染物来源及水体分层对水质的影响 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2016, 48(2): 93-99. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2016.02.016 ZHOU Z Z, HUANG T L, ZHANG W S, et al. Pollution sources and the stratification effects on water quality of Zhelin Reservoir [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016, 48(2): 93-99(in Chinese). doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.2016.02.016
[20] 杨洋, 刘其根, 胡忠军, 等. 太湖流域沉积物碳氮磷分布与污染评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(12): 3057-3064. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0710 YANG Y, LIU Q G, HU Z J, et al. Spatial distribution of sediment carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus and pollution evaluation of sediment in Taihu Lake Basin [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(12): 3057-3064(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0710
[21] 江雪, 文帅龙, 姚书春, 等. 天津于桥水库沉积物磷赋存特征及其环境意义 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(3): 628-639. doi: 10.18307/2018.0305 JIANG X, WEN S L, YAO S C, et al. Environmental significance of phosphorus existing forms in the sediments of Yuqiao Reservoir in Tianjin [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(3): 628-639(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2018.0305
[22] HORPPILA J, NURMINEN L. Effects of different macrophyte growth forms on sediment and P resuspension in a shallow lake [J]. Hydrobiologia, 2005, 545(1): 167-175. doi: 10.1007/s10750-005-2677-9 [23] 刘慧丽, 戴国飞, 张伟, 等. 鄱阳湖流域大型湖库水生生态环境变化及驱动力分析: 以柘林湖为例 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2015, 27(2): 266-274. doi: 10.18307/2015.0210 LIU H L, DAI G F, ZHANG W, et al. Analysis of the water ecological environment changes of the large lakes and driving factors in Lake Poyang Basin: A case study of Lake Zhelin [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2015, 27(2): 266-274(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2015.0210
[24] WANG S R, ZHENG B H, CHEN C, et al. Thematic issue: Water of the Erhai and Dianchi lakes [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(5): 3685-3688. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4727-6 [25] 叶宏萌, 杨浩, 袁旭音, 等. 基于流域沉积物氮磷形态的生态风险评价: 以沙溪流域为例 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(12): 3471-3479. YE H M, YANG H, YUAN X Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment based on nitrogen and phosphorus forms in watershed sediments: A case study of the Shaxi Watershed, Fujian [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(12): 3471-3479(in Chinese).
[26] 王书锦, 刘云根, 张超, 等. 洱海流域入湖河口湿地沉积物氮、磷、有机质分布及污染风险评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(1): 69-77. doi: 10.18307/2017.0108 WANG S J, LIU Y G, ZHANG C, et al. Distribution and pollution risk assessment of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in inlet rivers of Erhai Basin [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2017, 29(1): 69-77(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2017.0108
[27] 谌欣, 黄细嘉, 王佳. 生态湖泊型风景区旅游用地集约利用评价与优化研究: 以九江市庐山西海为例 [J]. 河南农业, 2021(6): 61-64. CHEN X, HUANG X J, WANG J. Evaluation and optimization of intensive use of tourism land in ecological lake scenic spot: A case study of Zhelin Reservoir, Jiujiang [J]. Agriculture of Henan, 2021(6): 61-64(in Chinese).
[28] 车霏霏, 陈俊伊, 王书航, 等. 南湖水系水-沉积物磷时空分布、影响因素及控制对策 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(6): 928-935. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200068 CHE F F, CHEN J Y, WANG S H, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution, influencing factors and control strategies of phosphorus in water-sediment of Nanhu Lake water system [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2020, 10(6): 928-935(in Chinese). doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200068
[29] 刘欢, 孔维苇, 王晓锋, 等. 重庆梁滩河表层沉积物氮形态时空特征及影响因素 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(6): 332-341. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.06.047 LIU H, KONG W W, WANG X F, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics and influencing factors of nitrogen morphology in surface sediments of Liangtan River, Chongqing [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(6): 332-341(in Chinese). doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.06.047
[30] 卓海华, 邱光胜, 翟婉盈, 等. 三峡库区表层沉积物营养盐时空变化及评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(12): 5020-5031. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705127 ZHUO H H, QIU G S, ZHAI W Y, et al. Evaluation of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of nutrients in surface sediment in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(12): 5020-5031(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201705127
[31] 杨清心, 李文朝. 东太湖围网养鱼后生态环境的演变 [J]. 中国环境科学, 1996, 16(2): 101-106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.1996.02.005 YANG Q X, LI W C. Environmental changes since foundation of pen-fish-farming in East Taihu Lake [J]. China Environmental Science, 1996, 16(2): 101-106(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.1996.02.005
[32] 兰建洪, 刘丰, 郭晓玮, 等. 清林径水库表层沉积物营养盐分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2021, 19(2): 269-275. doi: 10.13244/j.cnki.jiwhr.20190176 LAN J H, LIU F, GUO X W, et al. Pollution characteristics and evaluation of nutrients in surface sediments of Qinglinjing Reservoir [J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2021, 19(2): 269-275(in Chinese). doi: 10.13244/j.cnki.jiwhr.20190176
[33] 邱祖凯, 胡小贞, 姚程, 等. 山美水库沉积物氮磷和有机质污染特征及评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(4): 1389-1396. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.04.025 QIU Z K, HU X Z, YAO C, et al. Pollution characteristics and evaluation of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter in sediments of Shanmei Reservoir in Fujian, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(4): 1389-1396(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.04.025
[34] 封丽, 李崇明, 张韵, 等. 三峡水库运行期支流沉积物营养盐污染评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(12): 151-157. FENG L, LI C M, ZHANG Y, et al. Nutrients distribution and pollution evaluation for top-layer sediments in tributaries of Three Gorges Reservoir during water storage period [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(12): 151-157(in Chinese).
[35] 王亚平, 黄廷林, 周子振, 等. 金盆水库表层沉积物中营养盐分布特征与污染评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(3): 659-665. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.03.2016071305 WANG Y P, HUANG T L, ZHOU Z Z, et al. Distribution and pollution evaluation of nutrients in surface sediments of Jinpen Reservoir [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(3): 659-665(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.03.2016071305
[36] 胡强, 吴晓彬, 王姣, 等. 江西省典型水库沉积物碳、氮、磷分布及污染评价 [J]. 江西水利科技, 2021, 47(3): 214-218. HU Q, WU X B, WANG J, et al. Distribution and pollution evaluation of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in typical reservoirs in Jiangxi Province [J]. Jiangxi Hydraulic Science & Technology, 2021, 47(3): 214-218(in Chinese).
[37] 刘慧丽, 冯明雷, 熊鹏. 柘林湖非点源入湖负荷估算及对策研究 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(4): 1670-1673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.04.103 LIU H L, FENG M L, XIONG P. Non-point source into lake load estimation and countermeasure research on Zhelin lake [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(4): 1670-1673(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.04.103
[38] WANG M, CHEN H, YU Z C, et al. Carbon accumulation and sequestration of lakes in China during the Holocene [J]. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21(12): 4436-4448. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13055 [39] ZHU Y Y, SHAN B Q, HUANG J Y, et al. In situ biochar capping is feasible to control ammonia nitrogen release from sediments evaluated by DGT [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 811-821. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.06.007 [40] 李冰, 王亚, 郑钊, 等. 丹江口水库调水前后表层沉积物营养盐和重金属时空变化 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3591-3600. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201801003 LI B, WANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Temporal and spatial changes in sediment nutrients and heavy metals of the Danjiangkou Reservoir before and after water division of the mid-route project [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(8): 3591-3600(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201801003
[41] 吕豪朋, 申丽娜. 天津于桥水库流域河流表层沉积物中碳·氮·磷分布及污染评价 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(27): 98-102, 167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.27.031 LV H P, SHEN L N. Distribution characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous of river surface and pollution status evaluation of sediments in Yuqiao Reservoir Basin, Tianjin [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(27): 98-102, 167(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.27.031
[42] 王圣瑞, 倪栋, 焦立新, 等. 鄱阳湖表层沉积物有机质和营养盐分布特征 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2012, 2(1): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2012.01.005 WANG S R, NI D, JIAO L X, et al. Space-time variety of organic matter and nutrient in surface sediments from Poyang Lake [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2012, 2(1): 23-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2012.01.005
[43] ANDREWS J E, GREENAWAY A M, DENNIS P F. Combined carbon isotope and C/N ratios as indicators of source and fate of organic matter in a poorly flushed, tropical estuary: Hunts bay, Kingston harbour, Jamaica [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 46(5): 743-756. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1997.0305 [44] 王圣瑞, 金相灿, 赵海超, 等. 长江中下游浅水湖泊沉积物对磷的吸附特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2005, 26(3): 38-43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.03.009 WANG S R, JIN X C, ZHAO H C, et al. Phosphate adsorption characteristics onto the sediments from shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Environmental Science, 2005, 26(3): 38-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.03.009
[45] 毛亮, 罗丛强, 石彭灵, 等. 湖泊水、沉积物氮磷的空间分析及其耦合特征研究: 以大通湖为例 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(5): 952-959. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20170400104 MAO L, LUO C Q, SHI P L, et al. Spatial analysis and coupling characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in water and sediment—a case study in Datong Lake [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(5): 952-959(in Chinese). doi: 10.11693/hyhz20170400104
[46] DAN S F, LIU S M, YANG B, et al. Geochemical discrimination of bulk organic matter in surface sediments of the Cross River Estuary system and adjacent shelf, South East Nigeria (West Africa) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 678: 351-368. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.422 [47] KU H W, CHEN Y G, CHAN P S, et al. Paleo-environmental evolution as revealed by analysis of organic carbon and nitrogen: A case of coastal Taipei Basin in Northern Taiwan [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2007, 41(2): 111-120. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.41.111 [48] 黄廷林, 刘飞, 史建超. 水源水库沉积物中营养元素分布特征与污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(1): 166-172. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.01.022 HUANG T L, LIU F, SHI J C. Distribution characteristics and pollution status evaluation of sediments nutrients in a drinking water reservoir [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(1): 166-172(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.01.022
[49] 祁艳丽, 唐永杰, 蔡树伯, 等. 淡水湖泊沉积物污染评价方法比较: 以北大港水库为例 [J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2016, 27(6): 26-30, 38. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2016.06.05 QI Y L, TANG Y J, CAI S B, et al. Comparison of evaluation methods of the freshwater lake sediment pollution: A case study of Beidagang Reservoir [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2016, 27(6): 26-30, 38(in Chinese). doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2016.06.05
-



 下载:
下载: