-
随着社会经济的快速发展,人类对矿产资源及各类人工合成化学品的消费数量大量增加. 而高强度的人类活动常常导致各类污染物输入水体,包括现有污水处理工艺未能去除的污染物[1-2],突发水污染事件中单次大量输入的污染物[3-5],生产活动中的非目标污染物[6-7]等,各类污染物的大量输入使得水生态环境面临前所未有的压力. 输入水体的污染物可被水体悬浮物吸附逐渐沉降于河床或通过絮凝沉降等突发环境事件应急处置措施短时间内沉降于河床[8-10],汇入沉积物环境. 部分污染物通过沉积物的生物或化学过程降解,但仍有大量的难以降解的金属污染物、有机污染物长期累积在河床沉积物中. 而当水体外在环境条件(如pH、水温、流量等)发生改变时,沉积物中的污染物可能重新释放进入水体[11-12],此时,沉积物成为水体的二次污染源. 沉积物在源与汇的转化之间可能对生物群落乃至整个水生态系统造成危害[13-15].
针对污染物进入沉积物带来的环境风险和生态风险,化学分析是了解沉积物污染程度和生物毒性最基础的工作,其结果直接提供了沉积物中各类元素成分和污染物的含量[16],而生物毒性测试则被认为是判断沉积物中的污染物对生物影响的更为直接且可靠的方法[17-18],因此生物毒性测试在沉积物污染的生态风险评价中逐渐运用. 本文梳理了水生生物毒性测试在沉积物污染评价中的应用,指出了水生生物测试应用于沉积物毒性研究的重要性,并针对目前不同学者的研究,从沉积物基质、受试生物、毒性测试终点3个方面对水生生物测试技术应用的方法学进行了总结归纳,并为今后的发展方向进行了展望,以期为沉积物生物毒性测试标准方法的建立提供参考.
-
在20世纪60—70年代开始,有学者关注到沉积物污染及其对水生生物的毒性影响[19-21],在进行城市河道疏浚底泥的化学分析时,发现其中含有大量且成分复杂的化学污染物,对其毒性感到担忧[22],并且逐渐认识到仅开展沉积物成分与含量的化学分析难以说明沉积物中污染物对生物的具体影响. 因此基于生物毒性测试的技术方法逐渐成为评估沉积物中污染物毒性效应的有效手段[23],并由此发展了多种关于沉积物质量评价的方法和相关研究.
-
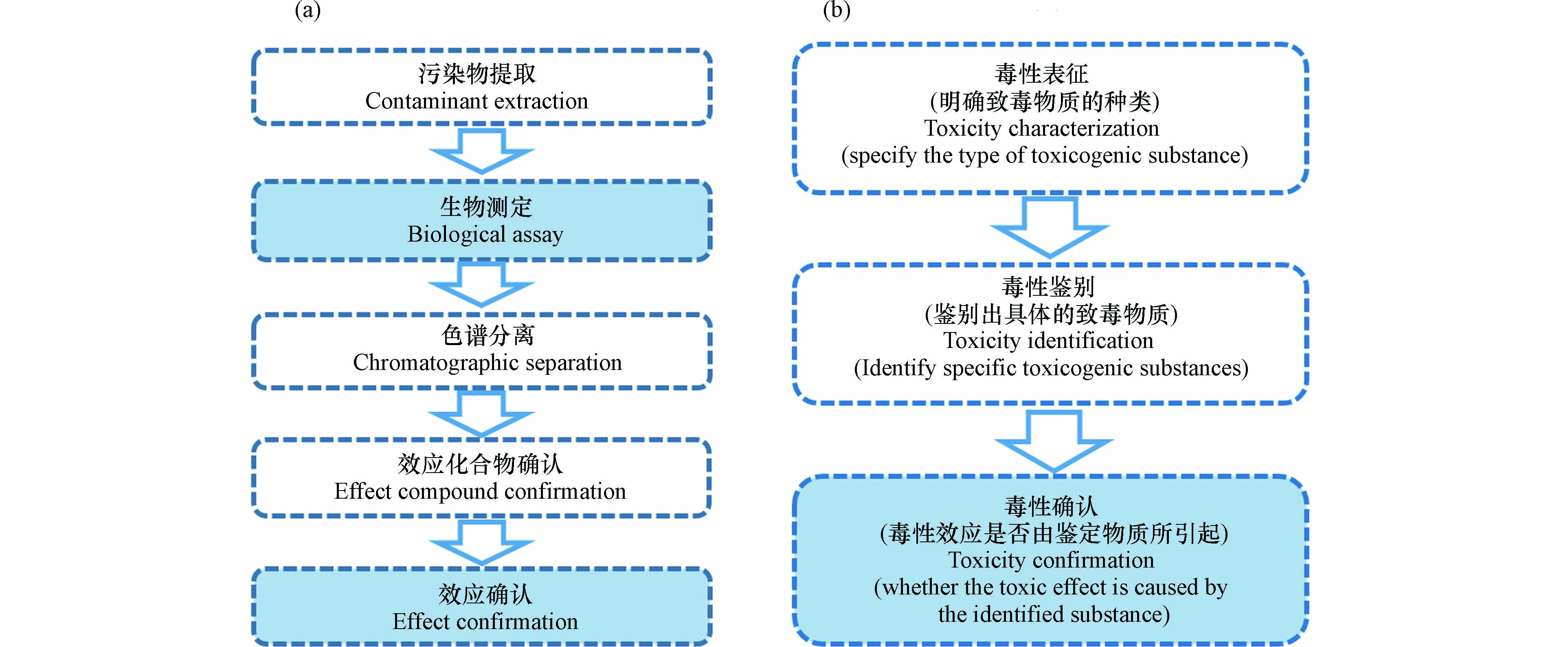
对于成分复杂的沉积物环境,单纯的化学分析或是生物测试对于评价沉积物的毒性都是不够的. 效应导向分析(effect-directed analysis,EDA)[24]和沉积物毒性鉴别评价(toxicity identification evaluation,TIE)[25]将沉积物环境的污染状况与生物效应相关联,又可筛查出污染沉积物中的致毒因子,是评价沉积物毒性的重要研究手段. 两种方法的具体操作流程如图1所示.
EDA是一套仅针对有机污染物的分析测试方法,它综合运用了生物测试与化学分析,污染物经提取后运用一种或多种生物测试方法检测样品可能导致的生物效应,然后经过组分分析等步骤鉴定出主要的效应化合物,最后通过污染物与生物间的剂量-效应关系检验化学测定结果[26-28]. TIE起初是由美国环保局(U S EPA)于1984年提出的用于工业废水和生活污水中毒性物质鉴别与评价的一套完整方案,随后其应用到沉积物重污染物的毒性鉴别评价中. 其操作方法与EDA较为相似,不过所能鉴别的污染物种类较EDA更为丰富,包含了氨氮、重金属、有机物等. 首先通过生物测试检测毒性的有无或大小,最后结合化学分析测定致毒污染物的身份及含量情况[29]. 在沉积物毒性物质鉴别应用中逐渐发展了沉积物孔隙水TIE和全沉积物TIE,使鉴定结果更加准确,也使更多的水生生物类群用于TIE的毒性检测中. 两种方法中生物毒性的测试均是重要的操作步骤,沉积物TIE主要采用活体水生生物测试,不同营养级的模式生物在TIE的发展中逐渐被运用. 而EDA除了可以应用水生生物毒性效应测试外,应用更多的则是体外生物测试,例如特异性效应,如遗传毒性、致突变性、芳香烃受体效应、内分泌干扰效应等. 整体来说,水生生物毒性测试在沉积物毒性评价中是十分关键的内容.
-
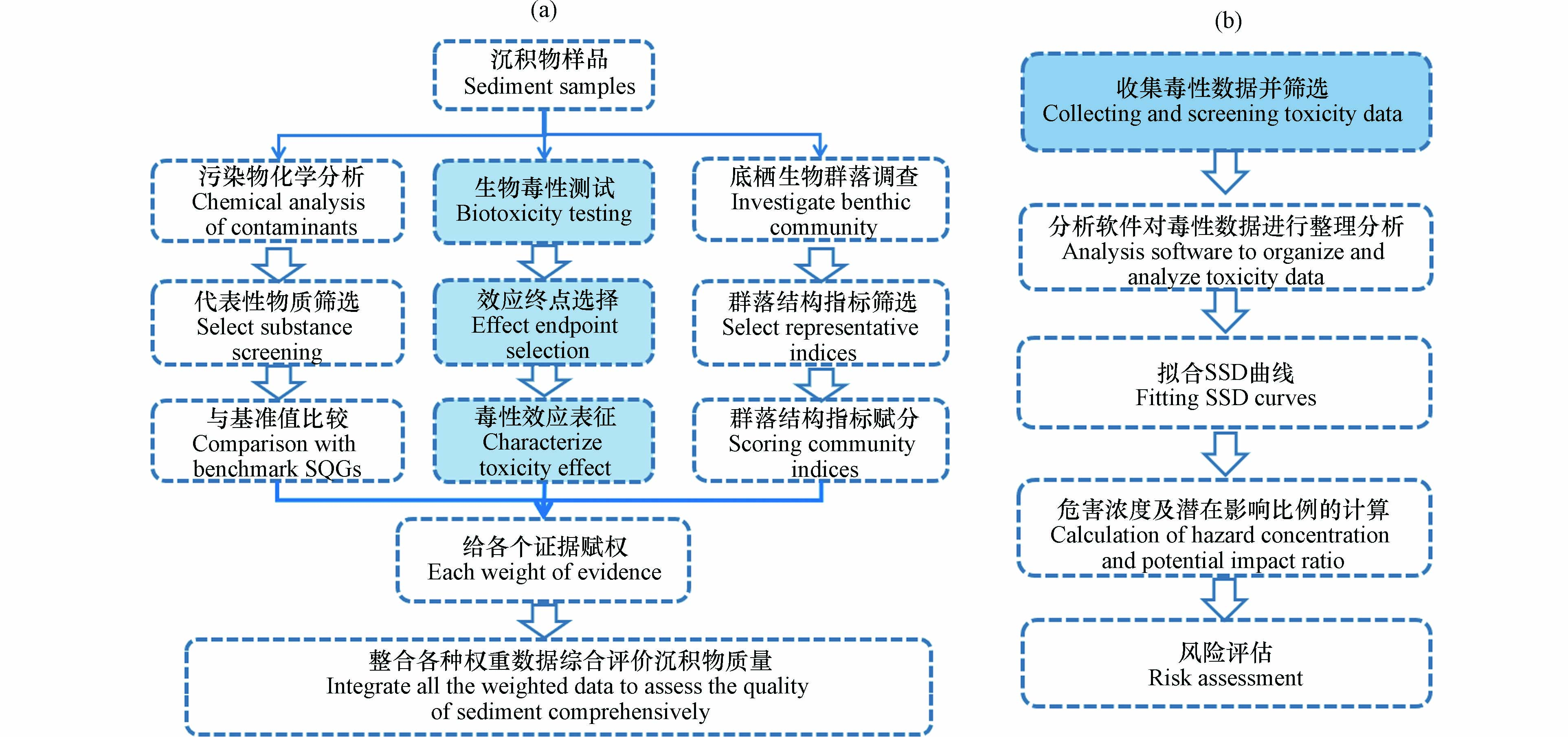
随着对沉积物污染问题的研究,陆续形成不同的沉积物风险评价方法,如地累积指数法、富集系数法、潜在生态风险系数法、风险评价码、重金属-硫化物(AVS-SEM)差值法等,这些评价方法均基于沉积物中污染物的化学分析. 物种敏感性分布法(species sensitivity distributions,SSD)[30]和证据权重法(weight of evidence,WOE)[31]则是基于沉积物中污染物毒性研究的较为经典的沉积物风险评价方法,两种方法的具体操作流程如图2所示.
SSD是表征特定污染物在沉积物中对生物的生态风险的方法,集合毒性实验数据信息,模拟不同物种对环境中污染物的敏感度,预测可保护大多数物种的环境浓度,从而保护生态系统的结构和功能[32]. WOE采取综合评价的策略对沉积物质量进行评价,整合了沉积物化学分析、毒性实验和底栖生物群落结构调查的证据线索,利用信息处理与解译方法得出科学全面的沉积物污染评价结论[33]. 美国、加拿大、荷兰和英国等国家已经把证据权重法应用到官方的受污染沉积物风险评价指南中[34-36]. 获取生物毒性数据是SSD评估的首要任务,进行水生生物毒性测试则是获取毒性数据的唯一渠道,U S EPA要求构建SSD曲线需满足3门8科水生生物的毒性数据,欧洲委员会则要求至少8科10种生物的毒性数据. 在对沉积物进行综合评价的WOE方法中,生物毒性测试的结果是一条重要的证据线索,对评价结果起到了重要支撑作用.
-
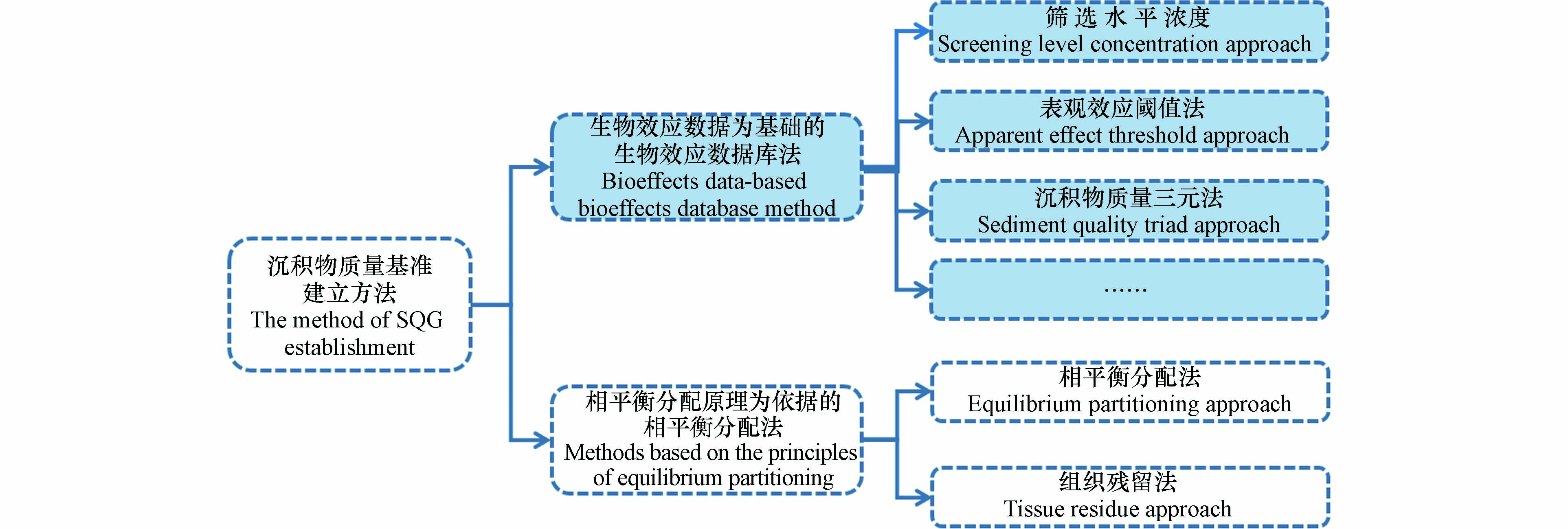
为科学有效地评价和治理沉积物污染逐渐发展起来了沉积物质量基准(sediment quality guideline,SQG),是指特定的化学物质在沉积物中不对底栖水生生物或其他有关水体功能产生危害的实际允许值[37-39]. 沉积物质量基准研究方法有10余种,钟文珏等[40]根据理论基础可分为两大类:一类是以生物效应数据为基础的生物效应数据库法;第二类是以相平衡分配原理为依据的相平衡分配法,如图3所示. 近年来我国已在太湖、鄱阳湖等大型湖泊及海河、辽河、长江等流域[41-46]开展沉积物环境基准值研究. 基于生物效应数据库法能够充分利用广泛多样的生物毒性效应数据而备受关注,然而在国内的发展却受到限制,主要由于我国开展的关于污染沉积物生物效应的研究仍较少,导致水生生物毒性效应数据不足. 因此利用水生生物毒性测试手段,获取沉积物中各类污染物的毒性数据可为我国全面建立沉积物质量基准奠定基础.
-
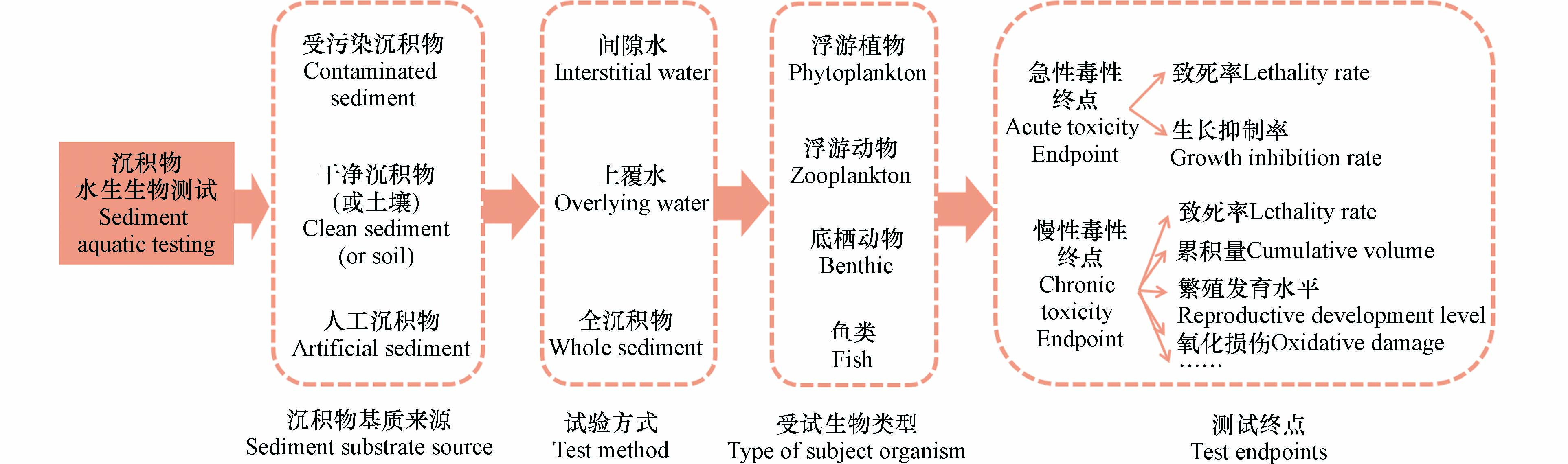
水生生物是研究沉积物污染物毒性时的首选生物类型,因此如何对沉积物进行处理、如何筛选受试生物、如何确定毒性测试终点十分重要. 经济合作与发展组织(OECD)已发布使用带丝蚓(Lumbriculus)和摇蚊(Chironomid)为受试生物的沉积物生物毒性测试技术规范[47-49],而我国尚未正式出台沉积物生物毒性的测试技术规范或标准方法,沉积物生物毒性测试技术标准化的建立有助于推动沉积物环境污染治理与修复的发展. 根据大部分学者的研究,文章从沉积物基质、受试生物选择和测试终点3部分内容对沉积物毒性的水生生物测试方法进行梳理概括,如图4所示.
-
沉积物生物毒性测试的基质主要包括直接采集受污染沉积物、干净沉积物(或土壤)以及人工配制沉积物进行加标染毒3种,研究人员基于不同的分析目的采用不同的基质开展毒性测试.
-
采用受污染沉积物进行生物毒性试验,其结果直接反映了调查区域沉积物污染的生物效应[50]. 裴舟韬等[51]利用大型溞为受试生物,以常州市典型城市黑臭水体为对象,对污染河流治理前后沉积物毒性变化进行了监测,所获得的沉积物毒性变化数据对河道治理手段和效果评价提供了科学依据. Massei等[52]采集了瑞典博特尼亚湾的3个污染地点的沉积物,进行了斑马鱼胚胎的急性毒性测试,暴露在污染沉积物下的胚胎可以观察到特定的脊髓畸形和孵化延迟. 现场采集的沉积物开展生物毒性测试更具现实意义,受污染的沉积物组分复杂多变,毒性效应不止由单一污染物所引起,如果想要获取沉积物的主要致毒污染物信息,则需借助EDA和TIE两种方法对污染物进行筛查. 布吉红等[45,53]在研究辽河支流表层沉积物的毒性现状时,将污染沉积物经预处理后采集间隙水进行了摇蚊幼虫10 d活体毒性测试,又结合沉积物毒性鉴别评价(TIE)方法甄别出辽河不同支流的主要污染因子. 基于受污染沉积物的水生生物毒性测试结果对于评价污染沉积物的生态风险具有重要意义
-
通过已知浓度的单一毒物或添加特定性质的沉积物进行生物测试可以确定“毒物剂量-生物效应”间的关系,加标法制备的沉积物基质在研究特定的污染物在沉积物中的归趋和生物学毒性效应时具有明显的优势. 首先需要选取干净的沉积物或土壤(即其中所含受试污染物的本底浓度不会对受试生物产生毒害作用的沉积物),然后按照试验所需掺入受试污染物进行水生生物的毒性测试. 韩雨薇等[54]在研究沉积物中金属Pb和Cd对河蚬的毒性效应中,由于较难获得重金属本底值较低的天然沉积物,便采用洁净的农田土壤加标的方式模拟天然沉积物进行试验. Yang 等[55]研究了水生生物群落对沉积物中Cu的敏感性响应,所用沉积物采集于未受污染地区的湿地土壤,在实验室进行加标染毒. 但值得注意的是,虽然此种方法采用的沉积物相对“清洁”,但仍需要在进行试验时做好对照组试验,有必要时需要对沉积物中其他组分进行掩蔽处理,以保证试验结果的准确性. 此外,在沉积物加标过程中针对不同加标物的理化特征选择不同的加标方式:当加标物为可以溶于水的物质(如水溶性农药、重金属等),可制备一定浓度的储备液,按试验所需加入沉积物中;而当加标物为微溶甚至不溶于水的物质(如部分痕量有机物、油类等),则需特定的介质辅助加标,比如甲醇、乙醇、丙酮等有机溶剂,加标后需要将有机溶剂挥发干净,避免对试验产生干扰. 大量试验结果表明,污染物加标的方法可以得到所需合理范围内的污染物浓度梯度,明确地指示污染物的剂量-效应关系,其结果丰富了不同污染物的毒性数据库,而且准确的毒性结果对于SQG的建立具有重要意义.
-
天然的沉积物和土壤是一种复杂的基质,长久暴露在环境中不可避免的含有一些痕量的污染物或其他复杂化学成分,采用各种实验室材料,如沙子、高岭土、磨细泥炭等所配制的人工沉积物避免了天然沉积物或土壤中的污染物[56],在实际的沉积物生物测试中同样具有广泛的应用. OECD和U S EPA发布过配制人工沉积物进行的毒性试验的相关规范[47,57],文婷等[58]参照了OECD的方法配制出人工沉积物,考察加入四氧化三铁纳米颗粒后对斑马鱼胚胎发育和氧化应激水平的影响. 相较于天然沉积物,人工沉积物可根据试验所需更加灵活地调节粒度大小、有机物含量等沉积物的性质,然而人工沉积物与各类型污染物的结合特性、氧化还原条件、微生物组合方面与天然沉积物的差异目前仍有待进一步研究.
-
不同的生物类群由于其生存环境、生理特征、营养等级、生命周期、污染物耐受性等的差异,对于沉积物中的各类污染物可能具有不同的“剂量-效应”关系,在沉积物生物毒性测试中,受试生物选择的一般原则包括:在环境中在广泛存在且具有重要生态价值、对污染物具有较高敏感性、在实验室中易于培养等[59]. 沉积物毒性的水生生物测试中常用的受试生物包括浮游植物、底栖生物、浮游动物和鱼类.
-
浮游植物是原生生物界一类能够进行光合作用的真核生物,是水体中的初级生产者[60]. 由于其生长繁殖快速、对水体污染物敏感等特点,常被用于各类污染物的毒理学试验. 对于常规的以水为介质或是沉积物提取间隙水、上覆水的毒性测试,利用浮游植物进行试验十分便捷有效. 邓惜汝等[61]选择了铜绿微囊藻、普通小球藻和梅尼小环藻进行了慢性毒性测试,通过藻类生长抑制试验测定了林丹和毒死蜱两种农药对藻类的毒性效应,结果表明两种农药对3种藻的生长存在不同程度的抑制效应,且质量浓度越高抑制效应越强. 由于浮游植物生长受水体浊度影响较大,水体浊度升高对浮游植物的生长具有一定的负面影响,且无法统计浮游植物的生长状况,因此在“藻类固定化”的概念被提出前,浮游植物只被用于间隙水、上覆水等水相的毒性试验,藻类固定化扩大了浮游植物在沉积物毒性试验中的应用范围. Moreira等[62]试验证明,三角褐指藻用4.9%海藻酸盐和4%的锶溶液制备的固定化藻球是最稳定、最适合微藻生长. Zhang等[63]改进优化了藻类固定化方法,使用淡水绿藻制备出海藻酸钠-钙藻球,置于沉积物-水体系中进行毒性测试,后加入3%柠檬酸钠溶液溶解藻球计数. 有研究认为,由于藻球内藻类生长较弱,敏感性降低,限制了固定化藻球的应用,从而提出了“底泥固定化”的方法. Pei等[64]利用冻干沉淀物和3%(W/V)海藻酸盐混合制成固定化底泥,在4%(W/V) CaCl2溶液中硬化,试验表明底泥固定后,污染物的扩散能力没有降低. 底泥固定化的思路拓宽了以浮游植物为受试生物的沉积物毒性测试方法的选择.
-
浮游动物是一类经常在水中营浮游性生活,且本身不能制造有机物的异养型无脊椎动物和脊索动物幼体的总称,是中上层鱼类和其他经济动物的重要饵料[65]. 卤虫和溞类动物是水体中典型的浮游动物,采用浮游动物进行生物毒性测试具有繁殖周期短、实验室易培养、产仔量多等优势[66]. 研究中多将浮游动物用于沉积物提取液的毒性的检测. 李纯厚等[67]选用浮游桡足类群体和卤虫进行疏浚淤泥溶出液对海洋浮游动物的毒性测试,试验结果表明一定温度条件下溶出液对受试生物有致毒作用. 范文宏等[68]将采集于北京密云水库内湖的沉积物加标染毒后提取出上覆水,在上覆水中加入50只大型溞进行上覆水体系暴露试验,暴露于上覆水体系中的大型溞体内的生物积累量和金属硫蛋白(MT)含量随沉积物Cd含量的升高而升高. 实际上,浮游动物在水相和水土接触界面均可进行生存活动,而且摄食、生长等活动离不开沉积物环境,因此在考察沉积物间隙水、上覆水毒性,以及进行全沉积物的毒性测试,浮游动物均可被应用,且全沉积物体系的毒性测试更好地模拟了现实环境. Li等[13]以大型溞作为受试生物,考察了上覆水与水-沉积物共存两种体系中金属镉(Cd)的毒性状况,以生物积累量、金属硫蛋白含量以及死亡率作为考察指标,分析讨论了水体沉积物中重金属对生物毒性的作用机制.
-
底栖动物是指栖息于水域底内或底表的动物,是水生生物中的一个重要生态类群,是鱼类和鸟类等食物链中消费者的食物来源[69]. 水体中的沉积物为众多底栖动物提供生产的场所,底栖动物主要以沉积物中的有机颗粒为食,沉积物环境质量是底栖动物的种类和数量的重要影响因素. OECD出台的沉积物生物毒性测试技术规范中的受试生物均是底栖动物,可见选取底栖生物作为沉积物毒性研究的受试生物对揭示污染物在水生态系统中的迁移转化过程及其对人类健康的影响都具有极其重要的研究意义[70]. 摇蚊幼虫是底栖动物的代表性生物之一,在水体中分布广泛. 邓鑫等[71]研究了加标水体和沉积物中Cd2+对伸展摇蚊幼虫和黄色羽摇蚊幼虫的急性(96 h)和慢性(20 d)毒性,观测指标为死亡率、羽化率、羽化时间和口器畸形率. 毒性测试结果和指标监测表明伸展摇蚊对沉积物中镉污染的敏感性要高于黄色羽摇蚊. Martinez等[72]将摇蚊幼虫分别暴露在3种不同浓度的Cd和Cu加标的沉积物中,考察了摇蚊的生长发育反应以及口器畸形率,证明金属Cd和Cu都会对摇蚊幼虫产生致畸作用. 水丝蚓[70]、虾[73]和一些双壳类动物[74]也是常被应用于毒理学测试中的水生底栖动物. 底栖动物类群多用于全沉积体系的毒性测试,可直接暴露于沉积物环境与污染物直接接触,这也是底栖动物较其他生物类群在沉积物毒测试应用中的优点.
-
鱼类是水生食物链中最高等级的生物,对有毒有害物质十分敏感,同时,由于其作为重要的水产品,与人类健康的关系十分密切,可对其进行充分的解剖观察、开展不同组织器官的污染物累积化学分析等[75],因此在各类环境毒理学试验中都被频繁选用. 在通常认知中,鱼类只生活于水中,所以试验相多为上覆水或间隙水,选择全沉积物相做毒性测试的较少. 然而,Camargo等[76]的研究认为,由于鱼类产卵是在沉积物表面进行的,鱼类数量的下降或许与沉积物毒性有关. 另外水动力学条件改变引起沉积物上浮,这些沉积物有极大可能性会被鱼类摄入. 鱼类作为受试生物在沉积物毒性研究中具有极强重要性. 俞云鹏[77]采集了湛江近海样点滨湖公园附近海域沉积物,使用超声波提取技术和硅胶柱净化法相结合来制备沉积物多氯联苯(PCBs)的提取物,将斑马鱼暴露在不同染毒浓度和不同时间的PCBs提取物中,试验证明沉积物提取物中的PCBs能引起斑马鱼肠道的病变并造成肠道微生物菌群的组成和丰度的改变. 文婷等[58]就沉积物中四氧化三铁纳米颗粒(Fe3O4 NPs)的安全阈值开展研究,将2 hpf(受精后时间,小时)的斑马鱼胚胎暴露在含有不同浓度Fe3O4 NPs的沉积物中,96 hpf后考察对斑马鱼胚胎发育和氧化应激水平的影响. 泥鳅以底泥中的腐屑为食,是水环境中典型的底栖鱼类,已经被广泛用来作为监测水体沉积物污染程度的敏感指示生物,赵艳民等[78]以泥鳅死亡率、血液红细胞数量、红细胞体积、红细胞微核率和核异常率作为测试指标,考察了镉加标沉积物对其的毒性状况. 斑马鱼作为模式生物在各类环境污染物的毒性研究中已相当成熟,但是基于沉积物毒性的研究却是缺乏的,泥鳅与水体中其他常见的鱼类相比具有不一样的生活习性,十分适合作为全沉积物体系毒性测试的模式生物,可以进行更加深入的研究. 另外可考虑选取其他国内本土的鱼种进行深入的研究,扩大鱼类作为沉积物毒性测试的模式生物种类数量.
-
水生生物测试沉积物毒性的终点可分为急性毒性测试和慢性毒性测试,二者在受试生物的暴露时间、效应终点和效应指标方面存在区别,因此选择合理的试验终点也是进行毒性测试的关键. 与水体毒性测试类似,沉积物毒性测试中试验终点和效应终点也与受试生物的选择有关,表1中归纳了不同研究者进行沉积物毒性实验的常用受试物种以及测试时间及效应终点等内容. 浮游植物和浮游动物类群生物的生命周期一般较短,选其进行急性毒性测试的较多,而多数底栖动物和鱼类生物的生命周期相对较长且体型较大,更加利于考察生长代谢、基因表达和繁殖水平等慢性毒性的效应终点,因此在慢性毒性测试中更倾向于选择这两类生物.
急性毒性测试较慢性毒性测试在受试生物的暴露时间上有明显的缩短,一般为24 h、48 h、72 h、96 h等,对于生命周期较长的受试生物,急性毒性的暴露时间可能也会有相应的延长. 效应终点一般为存活(死亡率、存活率)和生长(体重、体长、生长率、生物量等)两种,常用的效应指标有LC50、EC50等. 钟文珏等[79]研究了沉积物中芘对花翅羽摇蚊幼虫和淡水单孔蚓两种淡水底栖动物的急慢性毒性效应,其中对花翅羽摇蚊幼虫进行96 h急性毒性测试,LC50为189 mg·kg−1干重,淡水单孔蚓对芘的耐受力较强,急性毒性测试测得了芘对淡水单孔蚓体表损伤(包括尾部发白、尾部凹陷及自断)14 d-EC50为222 mg·kg−1干重. 考察沉积物中污染物对受试生物的致死率是最基础但极具意义的工作,设置不同毒性浓度梯度对沉积物加标染毒进行急性毒性测试可以快速获得某一类污染物在沉积物中的毒性数据,这是急性毒性测试的主要优势.
然而,有研究指出,衡量生存影响的短期暴露通常只能用于识别高浓度或高毒性的污染沉积物[80]. 对于沉积物中毒性较低的污染物或者含量较低的污染物,只有通过慢性毒性测试才能反映出污染物对水生生物的影响. 慢性毒性测试的暴露时间通常大于一周,甚至可长达1—2个月. 慢性毒性测试效应终点除存活和生长两类外,还包括繁殖(孵化率、孵化时间、性别比等),常用的效应指标有MATC、EC10、EC20、NOEC、LOEC等. 韩雨薇等[81]以泥鳅死亡率、鳃部渗血率和体质量变化为测试的效应终点,研究了沉积物中Pb、Cd对泥鳅的慢性毒性影响. 另外,随着研究的深入,慢性试验终点所考察的指标上升到基因表达、酶活性等分子水平,Boulanger等[82]在研究加拿大境内圣路易斯湖沉积物污染时,将受精后的斑马鱼胚胎分别暴露于受污染和不受污染的沉积物中,与多环芳烃、多氯联苯、二噁英和呋喃几种污染物反应有关的基因在暴露于污染沉积物中有着更高水平的表达,也表明该地点沉积物可能对生命早期阶段的鱼类产生有害影响. 慢性毒性测试的优势主要在于能够帮助说明沉积物中污染物对受试生物的致死原因,生理生化、生长代谢、基因表达等指标的考察解释了污染物对受试生物的影响机理,将沉积物毒理学的发展推向了更高的水平.
-
面对沉积物环境的复杂多变、各类新型污染物的出现以及我国关于淡水沉积物环境质量标准的缺乏,水生生物测试在沉积物质量评价中发挥了重要作用,并且应有更加深入的发展. 以下将从3个方面对水生生物毒性测试的应用与发展进行讨论与展望.
(1) 文章所讨论的水生生物测试是一种体内生物测试,而体外生物测试则是指在体外培养从通常的生物学环境中分离出的生物体组分进行的实验,包括细胞毒性、遗传毒性以及重组受体报告基因细胞实验. 体内生物测试优点在于可以选择不同营养级的代表性水生生物进行毒性试验,全面反映沉积物中污染物质对生物的胁迫效应情况. 一方面受试生物的培养对实验室要求严格、对实验人员的专业要求较高以及实验方法未全面进行标准化,另一方面越来越重视受试生物的伦理学问题,限制了水生生物毒性测试在沉积物质量评价中的发展. 因此,在对沉积物进行水生生物的毒性测试时,应选取适当的受试生物,最好将体外生物测试与体内生物测试相结合,试验结果相互补充,以对沉积物毒性进行客观、全面地评价,为沉积物环境中污染物的精准管控提供重要依据.
(2) 我国目前对于各类水生生物的毒性数据较为缺乏. 物种敏感性分析(SSD)将污染物现状与水环境中的生物毒性效应结合,在沉积物生态风险评价中有着广泛应用,也是推导沉积物质量基准的常用方法. SSD的应用需要获取一定量的水生生物毒性数据,在国内学者的研究中,绝大多数污染物对水生生物的毒性数据来自于U S EPA的ECOTOX数据库或国际农药行动联盟建立的PAN农药数据库,而国内水生生物对污染物的毒性数据较为缺乏. 因此,在未来发展中应建立充实不同类型污染物、不同营养等级水生生物的毒性数据库,立足中国沉积物环境污染问题,注重本土受试物种的标准化,保证毒性数据准确性,有助于建立我国的沉积物质量基准.
(3) 随着对水体沉积物的不断深入研究发现,例如微塑料、纳米材料等越来越多的非传统污染物出现在沉积物中,污染物间的相互作用让沉积物环境的污染物毒性效应更加复杂化. 利用水生生物测试沉积物中新型污染物的毒性效应正处于起步阶段,在未来应用中应重视污染物间的拮抗、协同作用,发展新型污染物的毒性效应的测试方法,了解更多种类污染物对水生生物的毒性机理,推动沉积物污染治理领域的深入发展.
水生生物毒性测试用于沉积物评价的研究进展
Advances in aquatic biotoxicity testing for sediment evaluation
-
摘要: 针对沉积物污染问题的研究目前已建立了不同的评价方法与体系,目前常用的结合生物毒性测试的有效应导向分析(EDA)、沉积物毒性鉴别评价(TIE)、证据权重法(WOE)、物种敏感性分布法(SSD)和沉积物质量基准(SQG)等,这些方法在河流、湖泊等水体沉积物中污染物毒性效应表征及沉积物质量评价方面有重要应用. 本文指出水生生物毒性测试应用的重要性,根据不同学者的研究内容归纳了水生生物毒性测试的方法学,对沉积物进行水生生物毒性测试的基质处理包括直接采用污染沉积物、洁净沉积物加标以及人工配置沉积物,受试生物主要包括浮游植物、浮游动物、底栖动物和鱼类,毒性试验终点包括急性毒性终点和慢性毒性终点;最后指出水生生物测试存在的问题,并对沉积物质量评价未来发展方向进行展望,以期为我国沉积物生物毒性测试标准方法的建立提供参考.Abstract: Various evaluation methods have been developed for the risk assessment of sediment contamination, involving effect-directed analysis (EDA) for biological toxicity testing, sediment toxicity identification evaluation (TIE), weight-of-evidence (WOE), species sensitivity distribution (SSD), sediment quality benchmark (SQG), etc. These methods have been widely applied in toxic effects characterization of contaminants in river and lake sediments as well as in sediment quality evaluation. Aquatic biotoxicity test plays an important role in the above mentioned evaluation methods. In this review, methodology of aquatic biotoxicity testing in different studies were summarized, including treatment of testing substrates, selection of test organisms, and the test endpoints. 3 types of testing substrates were introduced, which were directly use of contaminated sediment, clean sediment spiking, and artificial sediment. 4 groups of widely used tested organisms, phytoplankton, zooplankton, benthic animals and fish, were elaborated. And 2 kinds of test endpoints, acute toxicity endpoints and chronic toxicity endpoints were summarized. Moreover, some problems of aquatic biotoxicity testing, and future development of sediment quality evaluation were discussed, hope to provide some reference in the standard methods establishment for sediment biotoxicity testing in China.
-
Key words:
- sediment toxicity /
- biotoxicity /
- aquatic organisms /
- contaminants.
-

-
表 1 沉积物水生生物毒性测试常见受试生物及其测试终点
Table 1. Commonly used tested organisms in sediment toxicity tests and the test endpoints
受试生物类型
Subject
organism type污染物类型
Pollutant type沉积物基质
Sediment substrate受试生物
Subject organism测试时长
Test Duration测试终点
Test endpoints参考文献
References浮游植物 Cu、农药 干净沉积物加标 羊角月牙藻 72 h 生长抑制 [55] Cu 干净沉积物加标 小球藻 72 h 生长量 [60] 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 光合藻类 96 h 生长抑制 [83] 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 小球藻、斜生栅藻 96 h 生长抑制 [84] 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 小球藻 96 h 生长抑制 [85] 浮游动物 Cd 干净沉积物加标 蚤状溞 7 d、72 h 死亡率 [86] Cu 干净沉积物加标 大型溞 48 h 死亡率 [16] 重金属 受污染沉积物 大型溞 96 h 生长抑制 [85] 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 卤虫 96 h 中毒症状反应、死亡率 [67] 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 卤虫、猛水溞、大型溞 96 h 死亡率 [87] Cd 干净沉积物加标 大型溞 72 h 生物累积、金属硫蛋白含量、死亡率 [13] 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 卤虫 7 d 卤虫体长、酶活性 [88] 底栖动物 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 桡足类动物 7 d 繁殖力 [77] 无机硒 干净沉积物加标 霍甫水丝蚓 14 d、60 d 生理指标 [89] 氯代阻燃剂 干净沉积物加标 中华圆田螺 32 d 生物积累、氧化应激效应 [90] 重金属 受污染沉积物 双壳类动物 28 d 总抗氧化能力(TAOC)、脂质过氧化(MDA)、溶酶体膜稳定性测定 [91] 重金属 受污染沉积物 摇蚊幼虫 14 d、10 d 死亡率、羽化率 [92] 多环芳烃、
重金属受污染沉积物 太平洋牡蛎 24 h至幼虫孵化 生物积累、金属硫蛋白含量 [93] 氨 干净沉积物加标 淡水贻贝 96 h、10 d 生长量 [94] Cd 干净沉积物加标 铜锈环棱螺 21 d 生物累积、抗氧化酶活性 [95] 五氯酚 干净沉积物加标 淡水单孔蚓 96 h、10 d、14 d、
21 d、28 d存活数、个体体重、体表损伤情况 [96] 重金属 受污染沉积物 河蚬 60 d 软体肌肉组织重金属含量 [97] 鱼类 Zn、Cd 干净沉积物加标 泥鳅 21 d 死亡率、体重变化、渗血率 [45] 四氧化三铁
纳米颗粒干净沉积物加标 斑马鱼胚胎 96 hpf 胚胎发育、氧化应激水平 [58] 综合毒性 污染沉积物 斑马鱼胚胎 5 d 死亡率、基因表达 [82] 汞 受污染沉积物 青鳉鱼胚胎和仔鱼 24 h、48 h、
96 h 、21 d仔鱼畸形率和死亡率、
胚胎孵化率和孵化时间、
胚胎畸形率和胚胎死亡率[98] 农药 干净沉积物加标 太阳鱼、斑马鱼、
食蚊鱼、麦穗鱼96 h 死亡率 [99] 综合毒性 受污染沉积物 斑马鱼胚胎 96 h 致畸性、遗传毒性等 [100] -
[1] WANG Y W, LI X M, LI A, et al. Effect of municipal sewage treatment plant effluent on bioaccumulation of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the recipient water [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(17): 6026-6032. [2] 王杜珈, 何帅, 周小霞. 污水处理厂不同单元工艺水中重金属及其纳米颗粒的分布 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7): 3358-3365. WANG D J, HE S, ZHOU X X. Distribution of heavy metals and their corresponding nanoparticles in different treatment unit processes in the sewage treatment plant [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(7): 3358-3365(in Chinese).
[3] MA Q L, YAO L A, GUO Q W, et al. Long-term impact of accidental pollution on the distribution and risks of metals and metalloids in the sediment of the Longjiang River, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(2): 1889-1900. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10505-9 [4] ZHAO X M, YAO L A, MA Q L, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of cadmium in water and sediment in Longjiang River, China: Implication on water quality management after pollution accident [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 194: 107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.127 [5] QU J H, MENG X L, YE X Q, et al. Characteristic variation and original analysis of emergent water source pollution accidents in China between 1985 and 2013 [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(19): 19675-19685. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7164-5 [6] 师荣光, 周启星, 蔡彦明, 等. 天津郊区土-水界面污染流多环芳烃的污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2010, 30(4): 874-881. SHI R G, ZHOU Q X, CAI Y M, et al. Contamination characteristics and source analyses of PAHs in contaminated flows from soil-water interfaces of Tianjin Suburban Areas, China [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2010, 30(4): 874-881(in Chinese).
[7] 赵建亮, 应光国, 魏东斌, 等. 水体和沉积物中毒害污染物的生态风险评价方法体系研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2011, 6(6): 577-588. ZHAO J L, YING G G, WEI D B, et al. Ecological risk assessment methodology of toxic pollutants in surface water and sediments: A review [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2011, 6(6): 577-588(in Chinese).
[8] 郎庆成, 张玲, 赵斌, 等. 重金属污染事件应急处理技术探讨: 以广西龙江镉污染事件为例 [J]. 再生资源与循环经济, 2012, 5(3): 39-40. LANG Q C, ZHANG L, ZHAO B, et al. Analysis on emergency management of heavy metal pollution incidents: A case study on Guangxi Longjiang cadmium pollution [J]. Recyclable Resources and Circular Economy, 2012, 5(3): 39-40(in Chinese).
[9] 邴永鑫, 卓琼芳, 黄大伟, 等. 某尾矿库泄漏次生突发水环境锑污染事件的应急处置 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(9): 2888-2894. BING Y X, ZHUO Q F, HUANG D W, et al. Emergency disposal of a sudden water environmental accident with antimony pollution caused by leakage of tailings pond [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(9): 2888-2894(in Chinese).
[10] 陈思莉, 黄大伟, 张政科, 等. 流域突发水污染事件应急处置工程削污技术 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(7): 2233-2238. CHEN S L, HUANG D W, ZHANG Z K, et al. Pollution reduction technologies for emergent water pollution disposal in river basins [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(7): 2233-2238(in Chinese).
[11] 卓琼芳, 许振成, 虢清伟, 等. 聚铝混凝沉淀物含镉絮体稳定性评估[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(S1): 245-248. ZHUO Q F, XU Z C, GUO Q W, et al. Estimation of the stability of cadmium flocs[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(Sup 1): 245-248(in Chinese).
[12] 柳王荣, 虢清伟, 杨仁斌, 等. 镉污染应急处置含镉絮体稳定性实验研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(5): 1797-1801. LIU W R, GUO Q W, YANG R B, et al. Experimental studies on stability of flocs from cadmium pollution emergency treatment [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(5): 1797-1801(in Chinese).
[13] LI X M, PENG W H, JIANG Y Y, et al. The Daphnia magna role to predict the cadmium toxicity of sediment: Bioaccumlation and biomarker response [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 138: 206-214. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.002 [14] BROOKS B W, TURNER P K, STANLEY J K, et al. Waterborne and sediment toxicity of fluoxetine to select organisms [J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 52(1): 135-142. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00103-6 [15] YI X Y, LI H Z, MA P, et al. Identifying the causes of sediment-associated toxicity in urban waterways in South China: Incorporating bioavailability-based measurements into whole-sediment toxicity identification evaluation [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2015, 34(8): 1744-1750. doi: 10.1002/etc.2970 [16] CAIRNS M A, NEBEKER A V, GAKSTATTER J H, et al. Toxicity of copper-spiked sediments to freshwater invertebrates [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1984, 3(3): 435-445. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620030308 [17] PICONE M, BERGAMIN M, LOSSO C, et al. Assessment of sediment toxicity in the Lagoon of Venice (Italy) using a multi-species set of bioassays [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 123: 32-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.09.002 [18] SIMPSON S L, CAMPANAO, HO K T. Marine ecotoxicology [M]. Academic Press: San Diego, USA, 2016: 199-237. [19] 范成新, 刘敏, 王圣瑞, 等. 近20年来我国沉积物环境与污染控制研究进展与展望 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2021, 36(4): 346-374. FAN C X, LIU M, WANG S R, et al. Research progress and prospect of sediment environment and pollution control in China in recent 20 years [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2021, 36(4): 346-374(in Chinese).
[20] OLIFF W D, BERRISFORD C D, TURNER W D, et al. The ecology and chemistry of sandy beaches and nearshore submarine sediments of Natal-Ⅱ: Pollution criteria for nearshore sediments of the Natal coast [J]. Water Research, 1967, 1(2): 131-146. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(67)90080-2 [21] WOODIN S A. Polychaete abundance patterns in a marine soft-sediment environment: The importance of biological interactions [J]. Ecological Monographs, 1974, 44(2): 171-187. doi: 10.2307/1942310 [22] BURTON G A. Assessing the toxicity of freshwater sediments [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1991, 10(12): 1585-1627. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620101204 [23] BURTON A G, PITT R, CLARK S. The role of traditional and novel toxicity test methods in assessing stormwater and sediment contamination [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2000, 30(4): 413-447. doi: 10.1080/10643380091184228 [24] BRACK W. Effect-directed analysis: A promising tool for the identification of organic toxicants in complex mixtures? [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2003, 377(3): 397-407. doi: 10.1007/s00216-003-2139-z [25] U S. EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Sediment Toxicity Identification Evaluation (TIE) Phase Ⅰ Ⅱ and Ⅲ Guidance Document[S]. Washington DC: Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology, EPA/600/R-07/080, 2007. [26] BRACK W, AIT-AISSA S, BURGESS R M, et al. Effect-directed analysis supporting monitoring of aquatic environments—An in-depth overview [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 544: 1073-1118. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.102 [27] 曲广波, 史建波, 江桂斌. 效应引导的污染物分析与识别方法 [J]. 化学进展, 2011, 23(11): 2389-2398. QU G B, SHI J B, JIANG G B. Development and application of effect-directed analysis in environmental research [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2011, 23(11): 2389-2398(in Chinese).
[28] 马千驰, 刘艳娜, 史建波, 等. 生物效应导向的污染物分析研究新进展 [J]. 中国科学:化学, 2018, 48(10): 1195-1206. doi: 10.1360/N032018-00092 MA Q C, LIU Y N, SHI J B, et al. Effect-directed analysis in environment research: Current status and future challenges [J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2018, 48(10): 1195-1206(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N032018-00092
[29] 王子健, 骆坚平, 查金苗. 水体沉积物毒性鉴别与评价研究进展 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2009, 31(12): 35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.12.023 WANG Z J, LUO J P, ZHA J M. A review on progress of sediment toxicity identification and evaluation [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2009, 31(12): 35-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.12.023
[30] POSTHUMA L, SUTER G W, TRAAS T P. Species sensitivity distributions in ecotoxicology[M]. Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, USA, 2002, 3-10. [31] HOPE B K, CLARKSON J R. A strategy for using weight-of-evidence methods in ecological risk assessments [J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment:An International Journal, 2014, 20(2): 290-315. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2013.781849 [32] 曾勇, 孙霄, 赖雨薇, 等. 基于物种敏感性分布的多环芳烃水生态系统风险评价方法与应用 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(5): 235-243. ZENG Y, SUN X, LAI Y W, et al. Aquatic ecosystem risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons based on species sensitivity distribution [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(5): 235-243(in Chinese).
[33] 蒋宇霞, 刘有胜, 应光国. 沉积物质量综合评价及应用证据权重法的案例分析 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(3): 71-82. JIANG Y X, LIU Y S, YING G G. Integrated sediment quality assessment: A case study based on weight of evidence approach [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(3): 71-82(in Chinese).
[34] U S EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Guidelines for ecological risk assessment[S]. EPA/630/R-95/002F, 1998. [35] Science Advisory Board for Contaminated Sites in British Columbia. Guidance for a weight of evidence approach in conducting detailed ecological risk assessments (DERAs) in British Columbia[S]. Bellevue: Exponent, 2010. [36] Environment Agency. Ecological Risk Assessment: A public consultation on a framework and methods for assessing harm to ecosystems from contaminants in soil[S]. Bristol: Environment Agency, 2003. [37] SMITH S L, MACDONALD D D, KEENLEYSIDE K A, et al. A preliminary evaluation of sediment quality assessment values for freshwater ecosystems [J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 1996, 22(3): 624-638. doi: 10.1016/S0380-1330(96)70985-1 [38] CHAPMAN P M. Sediment quality criteria from the sediment quality triad: An example [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1986, 5(11): 957-964. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620051104 [39] BURTON J A. Sediment quality criteria in use around the world [J]. Limnology, 2002, 3(2): 65-76. doi: 10.1007/s102010200008 [40] 钟文珏, 曾毅, 祝凌燕. 水体沉积物质量基准研究现状 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2013, 8(3): 285-294. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20111113003 ZHONG W J, ZENG Y, ZHU L Y. Current research status of sediment quality criteria [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2013, 8(3): 285-294(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20111113003
[41] ZHU L, LIU J W, XU S G, et al. Deposition behavior, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in reservoir sediments of Northeast China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 142: 454-463. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.039 [42] 曾毅, 钟文珏, 祝凌燕, 等. 太湖地区全沉积物毒性识别评估研究 [J]. 中国科学:化学, 2012, 42(8): 1234-1241. doi: 10.1360/032011-859 ZENG Y, ZHONG W J, ZHU L Y, et al. Toxicity identification evaluation(TIE) on the whole sediments collected from Taihu Lake, China [J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2012, 42(8): 1234-1241(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/032011-859
[43] 熊捷迁, 弓晓峰, 江良, 等. 鄱阳湖水体沉积物中Zn、Cd对底栖生物的毒性效应及基准验证 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(6): 1687-1700. doi: 10.18307/2021.0607 XIONG J Q, GONG X F, JIANG L, et al. Toxic effects of zinc and cadmium on the benthic organisms in sediments of Lake Poyang and verification of quality guideline [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2021, 33(6): 1687-1700(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2021.0607
[44] 王利娜, 周俊丽, 赵艳芳, 等. 海河流域中部表层沉积物中重金属分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 水资源保护, 2021, 37(5): 147-152. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2021.05.022 WANG L N, ZHOU J L, ZHAO Y F, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments in the middle of Haihe River Basin [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2021, 37(5): 147-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2021.05.022
[45] 布吉红, 陈辉辉, 许宜平, 等. 辽河表层沉积物重金属生态风险与综合毒性表征 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2014, 9(1): 24-34. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20130117001 BU J H, CHEN H H, XU Y P, et al. Ecological risk of interstitial water heavy metals and toxicity characterization of surface sediments in branches of Liaohe River [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2014, 9(1): 24-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20130117001
[46] 徐泽锋, 赵晓丽, 赵建, 等. 长江流域沉积物重金属污染特征及优控因子筛选[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(S1): 101-109. XU Z F, ZHAO X L, ZHAO J, et al. Inspiration for priority control of heavy metals in sediments of Yangtze River Basin[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2020, 50(Sup 1): 101-109(in Chinese).
[47] OECD(Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development). OECD guides for the testing of chemicals, sediment-water chironomid toxicity test using spiked sediment 218[S]. 2004. [48] OECD. Test No. 225: Sediment-water Lumbriculus toxicity test using spiked sediment[S]. 2007. [49] OECD. Test No. 233: Sediment-water Chironomid life-cycle toxicity test using spiked water or spiked sediment[S]. 2010. [50] ZHANG Y F, SPADARO D A, KING J J, et al. Improved prediction of sediment toxicity using a combination of sediment and overlying water contaminant exposures [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266: 115187. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115187 [51] 裴舟韬, 徐柔柔, 高月香, 等. 城市黑臭河道治理前后沉积物对大型溞的毒性变化监测与评价 [J]. 环境监控与预警, 2020, 12(4): 6-11. PEI Z T, XU R R, GAO Y X, et al. Toxicity changes of urban black and odorous river sediment on Daphnia magna before and after remediation [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2020, 12(4): 6-11(in Chinese).
[52] MASSEI R, HOLLERT H, KRAUSS M, et al. Toxicity and neurotoxicity profiling of contaminated sediments from Gulf of Bothnia (Sweden): A multi-endpoint assay with Zebrafish embryos [J]. Environmental Sciences Europe, 2019, 31: 8. doi: 10.1186/s12302-019-0188-y [53] 布吉红, 陈辉辉, 许宜平, 等. 河流表层沉积物活体毒性甄别和毒性因子初探 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(10): 2885-2891. BU J H, CHEN H H, XU Y P, et al. Exploration of toxicity factor and in vivo toxicity identification evaluation of surface sediments [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(10): 2885-2891(in Chinese).
[54] 韩雨薇, 张彦峰, 陈萌, 等. 沉积物中重金属Pb和Cd对河蚬的毒性效应研究 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(4): 129-137. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20150120003 HAN Y W, ZHANG Y F, CHEN M, et al. Toxicity of Pb/Cd-spiked freshwater sediments to Corbicula fluminea [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(4): 129-137(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20150120003
[55] YANG J H, XIE Y W, JEPPE K, et al. Sensitive community responses of microbiota to copper in sediment toxicity test [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2018, 37(2): 599-608. doi: 10.1002/etc.3980 [56] BIHANIC F L, PERRICHON P, LANDI L, et al. Development of a reference artificial sediment for chemical testing adapted to the MELA sediment contact assay [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2014, 21(24): 13689-13702. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-2607-3 [57] U S EPA. Methods for measuring the toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates[R]. 1994. [58] 文婷, 隋彦伯, 周雅娜, 等. 人工沉积物中四氧化三铁纳米颗粒对斑马鱼胚胎发育和氧化应激水平的影响 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2021, 16(6): 191-200. WEN T, SUI Y B, ZHOU Y N, et al. Effects of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on development and oxidative stress in zebrafish embryo exposed to artificial sediment [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2021, 16(6): 191-200(in Chinese).
[59] 赵中华, 张路, 于鑫. 水体沉积物毒性的评价方法 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2007, 24(5): 360-363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2007.05.034 ZHAO Z H, ZHANG L, YU X. Methods for sediment toxicity evaluation [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2007, 24(5): 360-363(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2007.05.034
[60] 刘国光, 王莉霞, 徐海娟, 等. 水生生物毒性试验研究进展 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2004, 21(6): 419-421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2004.06.033 LIU G G, WANG L X, XU H J, et al. The progress of aquatic toxicity test [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2004, 21(6): 419-421(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2004.06.033
[61] 邓惜汝, 鲜啟鸣, 孙成. 林丹、毒死蜱对淡水藻类毒性效应的比较研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(3): 472-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.03.016 DENG X R, XIAN Q M, SUN C. Toxic effects of Lindane and Chlorpyrifos on freshwater algae [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(3): 472-476(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.03.016
[62] MOREIRA S M, MOREIRA-SANTOS M, GUILHERMINO L, et al. Immobilization of the marine microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum in alginate for in situ experiments: Bead stability and suitability [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2006, 38(1/2): 135-141. [63] ZHANG L J, YING G G, CHEN F, et al. Development and application of whole-sediment toxicity test using immobilized freshwater microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2012, 31(2): 377-386. doi: 10.1002/etc.734 [64] PEI Z T, XU R R, LIU H Y, et al. Development and application of a novel whole sediment toxicity test using immobilized sediment and Chlorella vulgaris [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 189: 109979. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109979 [65] 张艳, 郑琳, 陈碧鹃, 等. 悬浮物对浮游植物和浮游动物的急性毒性效应 [J]. 渔业科学进展, 2014, 35(2): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2014.02.003 ZHANG Y, ZHENG L, CHEN B J, et al. Acute toxicological effects of suspended solids on phytoplankton and zooplankton [J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2014, 35(2): 16-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2014.02.003
[66] NEBEKER A V, CAIRNS M A, GAKSTATTER J H, et al. Biological methods for determining toxicity of contaminated freshwater sediments to invertebrates [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1984, 3(4): 617-630. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620030412 [67] 李纯厚, 林燕棠, 杨美兰, 等. 南方某港疏浚淤泥溶出液对海洋浮游动物的毒性实验 [J]. 热带海洋, 1998, 17(1): 71-77. LI C H, LIN Y T, YANG M L, et al. Toxicity tests of sludge solution from a port of South China Sea to marine zooplankton [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1998, 17(1): 71-77(in Chinese).
[68] 范文宏, 段勇, 林爽, 等. 水体沉积物结合态镉对大型溞(Daphnia magna)的生物毒性研究 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2009, 4(4): 544-551. FAN W H, DUAN Y, LIN S, et al. The biotoxicity of cadmium associated with fresh-water sediment to the Daphnia magna [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2009, 4(4): 544-551(in Chinese).
[69] WU M C, DAHMS H U, LIU C H, et al. Estuarine sediment toxicity testing with an indigenous subtropical amphipod [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 162: 111797. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111797 [70] 沈洪艳, 张红燕, 刘丽, 等. 淡水沉积物中重金属对底栖生物毒性及其生物有效性研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(1): 272-280. SHEN H Y, ZHANG H Y, LIU L, et al. Bio-Toxicity and bioavailability of metal-spiked freshwater sediments to benthic invertebrates [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(1): 272-280(in Chinese).
[71] 邓鑫, 周祥, 刘志红, 等. Cd2+对伸展摇蚊及黄色羽摇蚊幼虫的毒性效应研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(9): 1640-1645. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.09.002 DENG X, ZHOU X, LIU Z H, et al. Toxic effects of cadmium on larvae of Chironomus riparius and Chironomus flaviplumus [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(9): 1640-1645(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.09.002
[72] MARTINEZ E A, MOORE B C, SCHAUMLOFFEL J, et al. Morphological abnormalities in Chironomus tentans exposed to cadmium—and copper-spiked sediments [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2003, 55(2): 204-212. doi: 10.1016/S0147-6513(02)00136-7 [73] ECHOLS B S. Toxicity evaluation of Louisiana nearshore marsh sediments following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 168: 112380. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112380 [74] BOUR A, HAARR A, KEITER S, et al. Environmentally relevant microplastic exposure affects sediment-dwelling bivalves [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236: 652-660. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.006 [75] HALLARE A V, SEILER T B, HOLLERT H. The versatile, changing, and advancing roles of fish in sediment toxicity assessment—a review [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2011, 11(1): 141-173. doi: 10.1007/s11368-010-0302-7 [76] CAMARGO J B D A, CRUZ A C F, CAMPOS B G, et al. Use, development and improvements in the protocol of whole-sediment toxicity identification evaluation using benthic copepods [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 91(2): 511-517. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.10.015 [77] 俞云鹏. 湛江近海沉积物PCBs对斑马鱼肠组织结构、微生物和细胞因子的影响[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2018. YU Y P. Effect of PCBs extracted from sediments in Zhanjiang offshore on histological structure, microflora and cytokines of zebrafish intestine[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2018(in Chinese).
[78] 赵艳民, 张雷, 秦延文, 等. 镉“加标”沉积物对泥鳅(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)生物毒性研究 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2011, 6(1): 80-86. ZHAO Y M, ZHANG L, QIN Y W, et al. Bio-toxicity of cadmium-spiked sediments to Misgurnus anguillicaudatus [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2011, 6(1): 80-86(in Chinese).
[79] 钟文珏, 张瑜, 祝凌燕. 沉积物中芘对淡水底栖动物的急慢性毒性效应 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(7): 2765-2772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.07.043 ZHONG W J, ZHANG Y, ZHU L Y. Acute and chronic toxic effects of Pyrene on the benthic organisms in sediments [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(7): 2765-2772(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.07.043
[80] BETTINETTI R, GIAREI C, PROVINI A. Chemical analysis and sediment toxicity bioassays to assess the contamination of the River Lambro (Northern Italy) [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2003, 45(1): 72-78. doi: 10.1007/s00244-002-0126-6 [81] 韩雨薇, 钟文珏, 张彦峰, 等. 沉积物中Pb和Cd对泥鳅的毒性效应及其基准阈值的验证 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(7): 1078-1084. HAN Y W, ZHONG W J, ZHANG Y F, et al. Toxicities of Pb/Cd-spiked freshwater sediments to Misgurnus anguillicaudatus and assessment of Pb/Cd sediment quality guidelines [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(7): 1078-1084(in Chinese).
[82] BOULANGER E, BARST B D, ALLOY M M, et al. Assessment of environmentally contaminated sediment using a contact assay with early life stage zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 659: 950-962. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.265 [83] 王子健, 马梅, 杜青, 等. 乐安江鄱阳湖河口沉积物样品生态效应的初步评价 [J]. 环境化学, 1993, 12(5): 342-346. WANG Z J, MA M, DU Q, et al. Preliminary ecotoxicological assessment of sediment samples from lean river estuary near Poyang Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1993, 12(5): 342-346(in Chinese).
[84] 马梅, 童中华, 王怀瑾, 等. 乐安江水和沉积物样品的生物毒性评估 [J]. 环境化学, 1997, 16(2): 167-171. MA M, TONG Z H, WANG H J, et al. Assessing the biological toxicity of water and sediment from lean river [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1997, 16(2): 167-171(in Chinese).
[85] 王翔, 聂湘平, 黄卓尔, 等. 广州城市河涌沉积物浸出液对水生生物的急性毒性 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2006, 1(2): 180-185. WANG X, NIE X P, HUANG Z E, et al. Toxicity of the lixivium of the sediment from 6 streams of Guangzhou to aquatic organisms [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2006, 1(2): 180-185(in Chinese).
[86] MORAN P W, NOWELL L H, KEMBLE N E, et al. Influence of sediment chemistry and sediment toxicity on macroinvertebrate communities across 99 wadable streams of the Midwestern USA [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599/600: 1469-1478. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.035 [87] 修瑞琴, 许永香, 高世荣, 等. 环境生物测试技术对沉积物的毒性评价研究 [J]. 卫生研究, 1994, 23(1): 14-17. doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.1994.01.005 XIU R Q, XU Y X, GAO S R, et al. Toxicity evaluation of sediments by environmental bioassay techniques [J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 1994, 23(1): 14-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.1994.01.005
[88] 晁敏, 伦凤霞, 王云龙, 等. 长江口南支沉积物对卤虫的毒性效应研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(5): 1020-1024. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.05.003 CHAO M, LUN F X, WANG Y L, et al. Study on the sediments toxicity of south branch of Yangtze River Estuary to Artemia salina [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(5): 1020-1024(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.05.003
[89] 李潇, 李丹, 罗艺璇, 等. 沉积物中无机硒对霍甫水丝蚓的生物效应研究 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2021, 16(3): 208-217. LI X, LI D, LUO Y X, et al. Biological effects of inorganic selenium in sediments on Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2021, 16(3): 208-217(in Chinese).
[90] 周珊珊, 董敏峰, 张莉娜. 沉积物中的得克隆在中华圆田螺体内的积累及氧化应激效应 [J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2019, 47(4): 457-461. ZHOU S S, DONG M F, ZHANG L N. Bioaccumulation and oxidative stress of sediment-bounded dechloraneplus in Cipangopaludina chinensis [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2019, 47(4): 457-461(in Chinese).
[91] AMATO E D, MARASINGHE WADIGE C P M, TAYLOR A M, et al. Field and laboratory evaluation of DGT for predicting metal bioaccumulation and toxicity in the freshwater bivalve Hyridella australis exposed to contaminated sediments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 243: 862-871. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.004 [92] ZHANG Y F, HAN Y W, YANG J X, et al. Toxicities and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake, China, based on sediment quality guidelines [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 62: 31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.08.002 [93] GEFFARD O, GEFFARD A, HIS E, et al. Assessment of the bioavailability and toxicity of sediment-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals applied to Crassostrea gigas embryos and larvae [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2003, 46(4): 481-490. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00451-4 [94] NEWTON T J, ALLRAN J W, O'DONNELL J A, et al. Effects of ammonia on juvenile unionid mussels (Lampsilis cardium) in laboratory sediment toxicity tests [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2003, 22(11): 2554-2560. doi: 10.1897/02-342 [95] 龙奕, 刘珊珊, 王萌, 等. 纳米Al2O3和Cd联合暴露对铜锈环棱螺体内Cd的生物积累和抗氧化酶活性的影响 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2): 216-223. LONG Y, LIU S S, WANG M, et al. Effects of Cd and Al2O3-NPs co-exposure on bioaccumulation of Cd and antioxidase enzyme activities in Bellamya aeroginosa [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 216-223(in Chinese).
[96] 钟文珏, 张瑜, 韩雨薇, 等. 沉积物中五氯酚对底栖生物的急慢性毒性效应 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(1): 297-304. ZHONG W J, ZHANG Y, HAN Y W, et al. Acute and chronic toxic effects of pentachlorophenol on the benthic organisms in sediments [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(1): 297-304(in Chinese).
[97] 丁园, 赵帼平, 刘运坤, 等. 污泥重金属在河蚬体内富集及毒性研究 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2014, 36(6): 1393-1397. DING Y, ZHAO G P, LIU Y K, et al. Accumulation and toxicity characteristics of heavy metal in sewage sludge contained in Corbicula fluminea [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2014, 36(6): 1393-1397(in Chinese).
[98] 林晶, 闫海鱼, 荆敏, 等. 河流汞污染对青鳉鱼早期发育的毒性影响 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(5): 1706-1714. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202005.002 LIN J, YAN H Y, JING M, et al. Toxic effects of river mercury contamination on early development of Oryzias latipes [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(5): 1706-1714(in Chinese). doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202005.002
[99] 赵颖. 淡水鱼类对3种农药的敏感性分布(SSDs)初探[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. ZHAO Y. Tentative exploration of sensitivity distribution (SSDs) on freshwater fish to 3 kinds of pesticides[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013(in Chinese).
[100] BOEHLER S, STRECKER R, HEINRICH P, et al. Assessment of urban stream sediment pollutants entering estuaries using chemical analysis and multiple bioassays to characterise biological activities [J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2017, 593-594: 498-507. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.209 -



 下载:
下载: