-
环氧树脂是一种热固性高分子聚合物,通常为环氧氯丙烷与双酚A或多元醇的缩聚产物. 因其具有良好的绝缘性、耐腐蚀性、密封性和高黏结强度等性能[1-3],作为涂料、胶黏剂、浇铸料等已广泛应用于电器、电机和电子元器件中[4-5]. 有机含卤化合物(主要是有机氯化物和有机溴化物)已作为阻燃剂广泛应用于各种塑料制品、玩具和电子产品中,是目前应用最为广泛的一类阻燃剂[6]. 含卤化合物在燃烧过程中产生的有毒酸性气体会对人的呼吸系统造成影响;废弃的聚合物因不完全燃烧会产生强致癌性的二噁英类物质,而二噁英具有高富集性和迁移性,且难以降解,属于持久性有机污染物(POPs),对环境和人体的健康均会构成潜在危害[7-8]. 卤素的限制和控制使用成为世界各国的共识,同时也促进了“无卤素”材料的推广应用. 欧盟于2006年实施了《关于在电子电气设备中限制使用某种危险物的指令》(RoHS指令),对用于阻燃剂的多溴联苯和多溴联苯醚进行了限量使用的规定[9];国际电工技术委员会颁布了EN61249-2-21限量标准,对电子产品材料、玩具中卤素的含量进行了明确的规定:氯和溴的含量均不超过900 mg· kg−1,溴和氯总量不超过1500 mg· kg−1 [7,10],符合要求的材料称为“无卤素”材料. 因此准确测定相关产品和元器件中的卤素对于产品出口和质量检测具有非常重要的意义.
离子色谱法是一种快速准确的卤素测定方法,而聚合物中卤素不能直接进行测定,需要通过一定的前处理手段将其转化为无机阴离子. 最常见的聚合物中卤素的前处理方法有氧弹燃烧法[3,6-8,11-14]和高温燃烧裂解法[15],氧弹燃烧法是在密闭容器(氧弹)中充入高压氧气,经点燃后将聚合物进行燃烧分解,样品中卤素转化为卤化氢,被吸收液吸收后进行离子色谱的测定. 与早期的氧瓶燃烧法相比,氧弹燃烧法能够使样品燃烧更完全,样品的燃烧损失小,不容易受到污染,操作过程安全可靠. 但该方法自动化程度低,样品测定周期长,燃烧后卤素离子容易吸附在氧弹装置内壁及点火线上,需要仔细冲洗. 高温燃烧裂解法是采用一种高温燃烧裂解炉及吸收装置,将样品通过石英舟推入到裂解炉的石英管中,在氧气和水蒸气的混合气流中进行高温氧化燃烧、裂解及气化,同时进行水蒸气吸收并通过吸收瓶收集冷凝液,将聚合物中的氯、溴等卤素转化为阴离子,将吸收液直接导入离子色谱仪即可实现聚合物中卤素的快速测定. 该方法操作简单、灵敏度高、可实现与离子色谱的联用,已用于植物油[16]、纺织品[17]、炭黑[18]和水泥[19]中氟、氯、溴等的测定,但对于环氧树脂中氯和溴的同时测定未见报道.
本研究采用高温燃烧裂解法进行环氧树脂的样品前处理,对影响高温燃烧裂解参数进行了选择优化,通过与离子色谱的在线联用实现环氧树脂中氯和溴的快速测定,并与传统的氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法进行了比较和方法确认. 该方法将自动化的高温燃烧裂解与配备预浓缩柱的离子色谱相结合,进一步降低了氯和溴的检出限,操作简单,准确度高,可用于相关产品的快速检测和批量产品的质量控制.
-
在线燃烧离子色谱:930 Combustion IC PP(AJ)型,瑞士万通公司;该仪器包括燃烧模块(德国耶拿公司)、920型样品吸收模块、930型离子色谱分析模块、MagIC Net 控制软件和自动进样器. 燃烧模块温度调节范围从室温至1050 ℃,控温精度±1 ℃. 氧弹燃烧装置及其附件(充氧装置等)购自于湖南长沙仪器厂;ICS-5000+型离子色谱仪,美国Thermo公司. XP205型电子天平,瑞士Mettler Toledo公司,最大称样量220 g,最小分度0.01 mg. Milli-Q Integral超纯水系统,德国Merck公司.
GBW(E) 080268氯离子溶液标准物质,浓度为1000 µg· mL−1,相对扩展不确定度为0.7%(k=2);GBW 06205溴化钾中溴成分分析标准物质,溴含量67.150%,扩展不确定度0.014%(k=2);GBW (E) 080549水中氟溶液标准物质,浓度为1000 µg· mL−1,相对扩展不确定度为1%(k=2);GBW (E) 080266水中硫酸根溶液标准物质,浓度为1000 µg· mL−1,相对扩展不确定度 为0.7%(k=2);4种标准物质均购自于中国计量科学研究院. 测定前,以GBW 06205溴化钾中溴成分分析标准物质配制成浓度100 µg· mL−1的溴离子标准溶液. 所有溶液均采用超纯水进行配制. ERM-EC680k和ERM-EC681k低密度聚乙烯标准物质购自于欧盟委员会联合研究中心标准物质与测量研究院(IRMM),ERM-EC680k中氯和溴的标准值分别为:(102.2±3.0) mg· kg−1、(96±4) mg· kg−1;ERM-EC681k中氯和溴的标准值分别为:(800±50) mg· kg−1、(770±40) mg· kg−1. 无水碳酸钠、碳酸氢钠购自于德国Merck公司;硫酸,优级纯,购自于国药集团化学试剂有限公司;过氧化氢,BVIII级,购自于北京化学试剂研究所. 高纯氧气和氩气:纯度≥99.99%. 环氧树脂为白色粉末状固体,由山东非金属材料研究所提供.
-
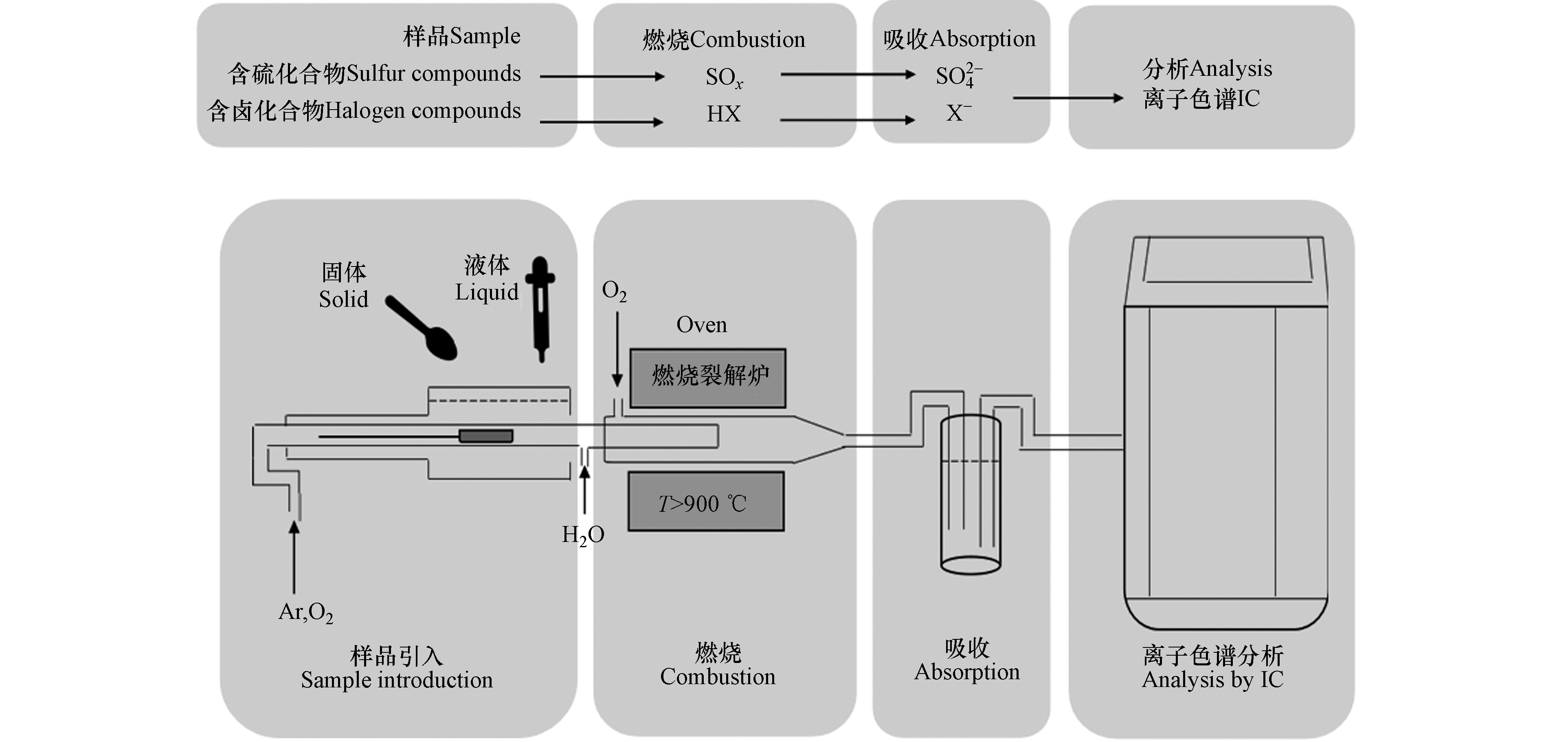
在线燃烧离子色谱法的原理是:环氧树脂样品在经自动进样器推进高温燃烧裂解炉后,首先在氩气氛围下发生热分解,随后在氧气和水蒸气的混合气流中氧化燃烧、裂解及气化,形成卤化氢气体,由氩气载带进入吸收装置,由过氧化氢吸收液吸收,环氧树脂中的氯、溴等卤素转化为阴离子,将吸收瓶收集的冷凝液直接导入离子色谱仪,通过建立的标准曲线,以峰面积对样品中的氯和溴进行定量分析. 在线燃烧离子色谱结构及原理图见图1.
标准曲线:配制含有氟、氯、溴、硫酸根离子的混合标准溶液以考察离子色谱的分离能力,其中4种离子的浓度分别为1.00、2.50、0.50、5.00 mg·L−1. 测定时通过精密加液器自动注入不同体积的混合标准溶液(最低浓度点进样体积为200 µL),标准曲线中氯离子浓度分别为0.10、0.25、0.50、1.25、2.50 mg· L−1,溴离子浓度分别为0.02、0.05、0.10、0.25、0.50 mg·L−1. 经离子色谱分离后,以峰面积对标准溶液浓度绘制标准曲线.
为保证样品在进入燃烧裂解炉后不发生爆燃,且在热分解后充分氧化燃烧、裂解及气化,首先对氩气和氧气的流速进行调整和优化,经综合考虑,最终设定的氧气流速为300 mL·min−1,氩气流速为100 mL·min−1. 准确称取(4—7)mg环氧树脂样品(精确至 0.01 mg)于石英样品舟中,为促进样品完全燃烧,尽量将样品置于样品舟中间位置,然后放入自动进样器. 设定燃烧裂解炉及离子色谱条件,直接检测样品中氯和溴的含量. 为降低空白影响,石英样品舟在进样燃烧前,需置于马弗炉中在800 ℃下灼烧2 h. 通过建立的标准曲线以及样品称样量、吸收液体积和吸收液进样体积,仪器自动给出样品中的卤素含量. 仪器测定参数如下:
燃烧炉燃烧温度:1030 ℃;燃烧时间:400 s;冷却时间:400 s;氧气流速:300 mL·min−1;氩气流速:100 mL·min−1;吸收液:100 mg·L−1过氧化氢,吸收液体积:6 mL;燃烧离子色谱再生液:100 mmol·L−1硫酸. 色谱柱:Metrosep A Supp 5(5 µm,150 mm×4.0 mm);预浓缩柱:Metrosep A PCC1 HC/4.0;淋洗液:3.2 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3和1.0 mmol·L−1 NaHCO3混合溶液;柱温:30 ℃;淋洗液流速:0.7 mL·min−1;进样量:50 µL或200 µL;检测器:电导检测器.
-
称取0.3 g(精确至0.0001 g)的环氧树脂样品于铂坩埚中,将坩埚放入氧弹内环中,事先在氧弹底部加入5 mL吸收液(0.45 mol·L−1 Na2CO3和0.08 mol·L−1 NaHCO3混合溶液),在铂丝圈内插入2 mm宽的滤纸为点火线,另一端插入样品中,向氧弹内通2 min高纯氧气以除去大部分氮气,盖上弹盖拧紧,慢慢往弹内冲氧至3.0 MPa. 将拧紧的氧弹置于水浴中,检查是否漏气,然后在8 V电压下点燃样品. 在水浴中放置30 min后,再打开放气阀慢慢放气,放气时间控制在约15 min. 打开氧弹盖,把氧弹内吸收液转移至250 mL容量瓶中,用近沸的超纯水仔细洗涤氧弹的各部件及内表面,合并所有溶液,定容. 以单点比对法对样品进行离子色谱测定,峰面积定量. 离子色谱条件如下:
色谱柱:AS23(5 µm,250 mm×4. 0 mm),美国Thermo公司;吸收液:0.45 mol·L−1 Na2CO3和0.08 mol·L−1 NaHCO3混合溶液;淋洗液:4.5 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3和0.8 mmol·L−1 NaHCO3混合溶液;淋洗液流速:1.0 mL·min−1. 检测器:电导检测器;进样量:25 μL.
-
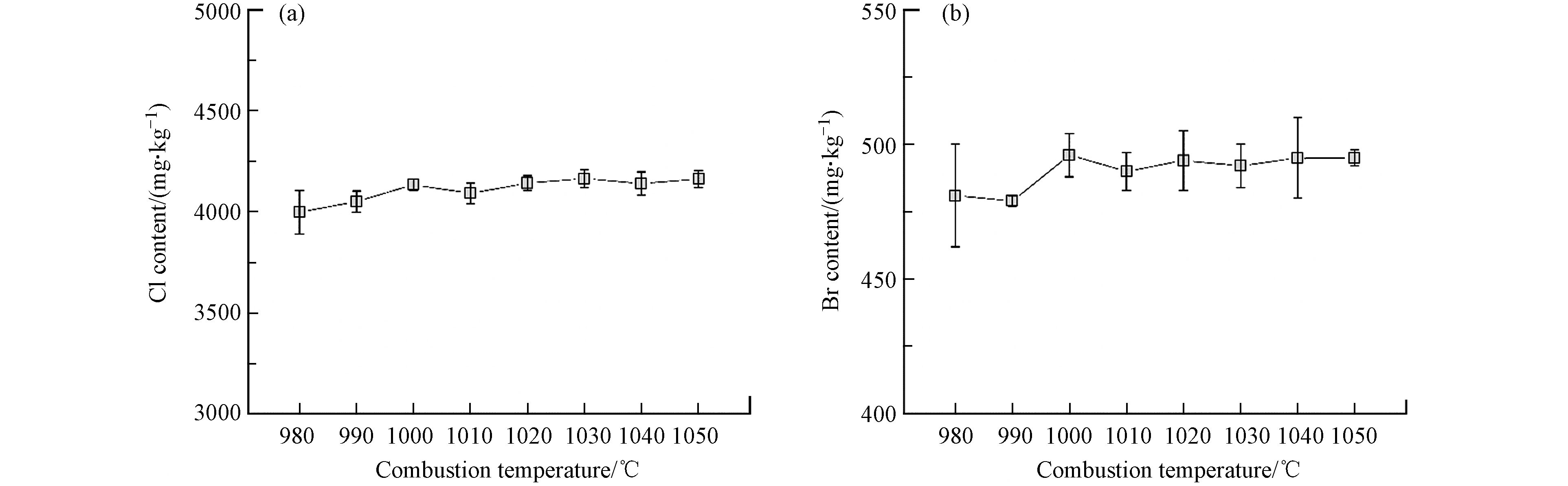
高温燃烧裂解的作用是将样品完全燃烧,从而使样品中的卤化物完全分解并被吸收液吸收. 燃烧温度过低,则样品燃烧不完全,而燃烧温度过高时,容易导致样品表面在极短的时间内快速发生碳化,不利于样品的热分解,因此需要较长的燃烧时间才能保证样品的充分燃烧. 因此,每间隔10 ℃、考察了980—1050 ℃温度范围内燃烧温度下环氧树脂中氯和溴的含量,结果见图2.
从图2可见,随着燃烧温度的升高,环氧树脂中氯和溴的含量逐渐增大,当燃烧温度大于1000 ℃时,氯和溴的测定值基本保持不变,说明能够实现样品的完全燃烧. 由于燃烧温度过高会缩短石英燃烧管的使用寿命,综合考虑燃烧效果和燃烧管使用寿命,最终选择的燃烧温度为1030 ℃.
-
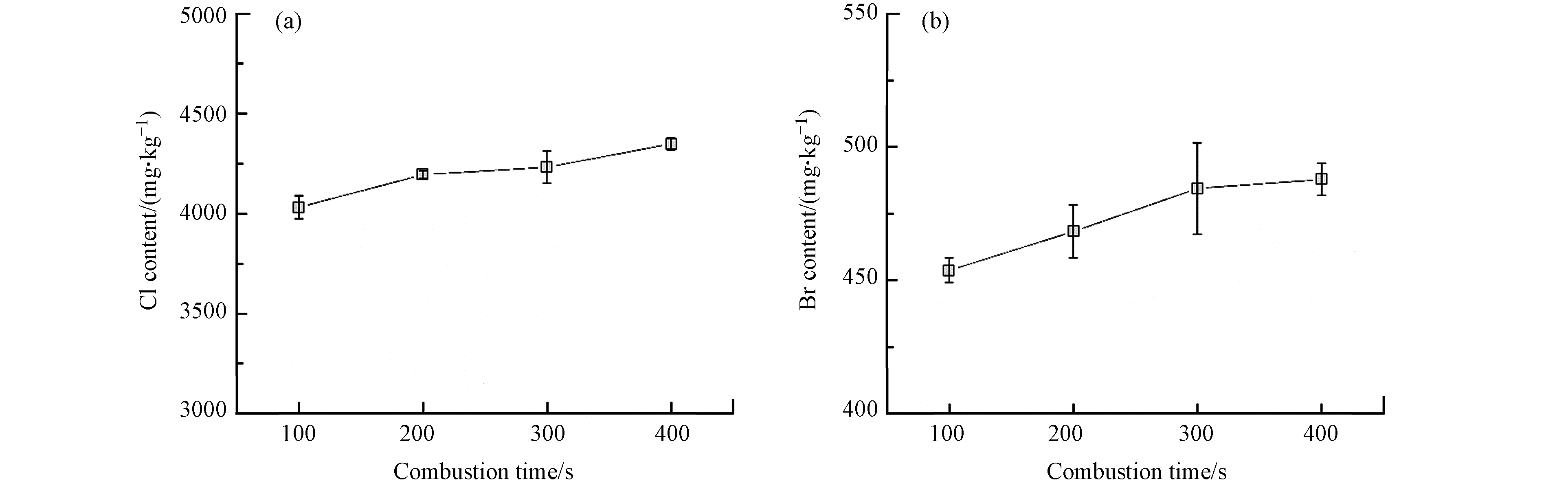
燃烧时间也是影响燃烧效果的重要参数,分别考察了在100 、200 、300、400 s时氯和溴的测定结果. 从图3可见,在1030 ℃燃烧温度下,随着燃烧时间的延长,氯和溴的含量逐渐增大,当燃烧时间达到400 s,测定值最大. 因仪器可设置的最长燃烧时间为400 s,最终选择的燃烧时间为400 s.
-
首先对环氧树脂中氯和溴进行初步测定,发现该样品中氯的含量较高,标准曲线氯离子的浓度范围为(0.10—2.50)mg·L−1,溴离子的浓度范围为(0.02—0.50)mg·L−1;另外,电子天平的最小分度为0.01 mg,应保证称量引入的不确定度在千分位,因此综合考虑标准溶液的线性范围和称量不确定度,最终选择环氧树脂样品的称样量在(4—7)mg,EC680k的称样量为(14—17)mg,吸收液的进样体积则分别为50 µL和200 µL.
-
在保证样品充分燃烧、卤化物完全转化为卤素离子的前提下,应确保卤素被吸收液完全吸收,这也是影响回收率的重要因素. 分别考察了吸收液体积为4、5、6 mL时环氧树脂样品的测定结果. 从图4可以看出,吸收液体积对氯和溴含量测定结果的影响差别不大,吸收液体积为6 mL时,氯和溴的含量稍高,因此最终选择吸收液的体积为6 mL.
-
在优化的实验条件下,对一系列不同浓度的混合标准溶液进行测定,采用最小二乘法以色谱峰面积(y)对氯和溴离子的浓度(x)进行线性拟合,得到线性回归方程. 结果表明,氯离子浓度在(0.10—2.50) mg·L−1、溴离子浓度在(0.02—0.50)mg·L−1范围内,线性相关系数(r2)大于0.9999. 根据3倍和10倍信噪比分别计算氯和溴离子的仪器检出限(LOD,S/N=3)和定量下限(LOQ,S/N =10). 按照样品称样量5 mg、吸收液体积为6 mL进行计算,该方法对于氯和溴的检出限分别为:0.17 mg· kg−1和0.78 mg· kg−1,定量下限分别为:0.55 mg· kg−1和2.60 mg· kg−1(见表1).
-
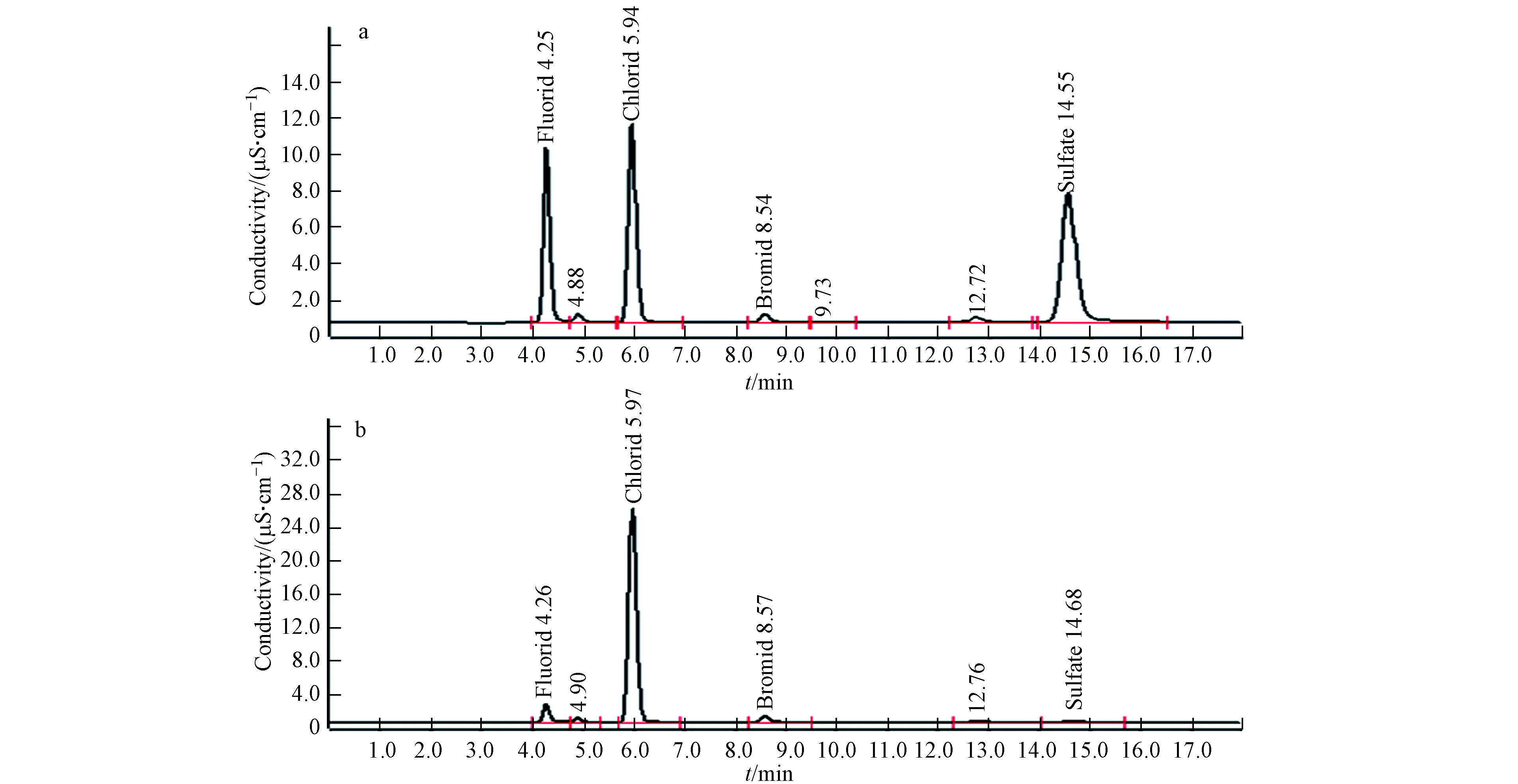
采用优化好的在线燃烧离子色谱法和氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法分别测定了环氧树脂中氯和溴的含量. 为保证测定结果的准确可靠,分别采用EC680k和EC681k作为质控样品进行方法验证. 另外,在线燃烧离子色谱法测定前,首先采用标准溶液进行了离子色谱测定部分的重复性考察,对氯和溴浓度分别为0.50 mg· L−1和0.10 mg· L−1的标准溶液重复进样5次,测定结果的精密度分别为0.62%和1.08%,说明离子色谱测定部分重复性良好,在此基础上再开始样品的测定. 测定过程中,每间隔4个样品进行EC680k的测定,以校正仪器漂移. 氧弹燃烧-离子色谱中,由于氧弹装置的内壁、铂金坩埚及电极等部件极易吸附氯和溴,因此在样品转移过程中采用近沸的去离子水反复冲洗氧弹上述部件[7],为保证充分洗涤和转移,最终的定容体积为250 mL. 在线燃烧离子色谱法测定EC680k中氯和溴的结果(平均值±标准偏差,n=3)分别为:(104.2±2.2)mg· kg−1、(98.1±3.0)mg· kg−1;氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法测定EC681k中氯和溴的结果(平均值±标准偏差,n=3)分别为:(795±10)mg· kg−1、(749±10)mg· kg−1,两种方法测定结果均与标准物质的标准值较为符合,折算成氯和溴的回收率分别在99.3%—102%和97.2%—102%. 两种方法对环氧树脂的测定结果见表2,在线燃烧离子色谱法标准曲线和样品的色谱图见图5.
由表2可以看出,两种方法测定氯的结果一致,说明高温燃烧裂解和氧弹燃烧两种样品前处理方式,均能实现环氧树脂的完全燃烧,即对于氯的回收率一致;在线燃烧离子色谱法测定溴的结果与氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法相比偏低约5%,但在进行EC680k测定时,测定结果与标准值一致,说明对于溴含量高的样品,高温燃烧裂解-离子色谱测定的回收率稍低于氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法,因此在进行在线燃烧离子色谱测定时,需采用基体相同或相近的标准物质进行质控和方法确认. 另外,由图5可见,在线燃烧离子色谱法在17 min即可实现样品的分离测定,采用自动进样器的情况下,除第一个样品需要约35 min的测定时间外,其余样品的测定时间约为20 min,因此与传统的氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法相比,大大缩短了分析时间,重复性好、灵敏度高、准确度较高,能够满足日常检测的需求.
-
本文建立了在线燃烧离子色谱同时测定环氧树脂中氯和溴的分析方法,通过对燃烧温度、燃烧时间、吸收液体积、氧气和氩气流速、称样量等条件的选择优化,实现了环氧树脂的高温裂解燃烧并被吸收液充分吸收,通过与氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法比较,证明了该方法准确可靠,对于氯和溴的回收率较高. 预浓缩柱的使用,进一步提高了离子色谱测定方法的灵敏度,有望用于低含量氯和溴的测定. 在线燃烧离子色谱法操作简单、自动化程度高、重复性好,具有较高的准确度,适合于批量样品中氯和溴的含量筛查和多批次产品的质量控制.
在线燃烧离子色谱法测定环氧树脂中的氯和溴
Determination of chlorine and bromine in epoxy resins by online combustion ion chromatography
-
摘要: 建立了在线燃烧离子色谱同时测定环氧树脂中氯和溴的分析方法. 采用高温裂解炉与离子色谱的在线联用装置,通过对样品进行高温燃烧裂解和气化,以100 mg·L−1过氧化氢为吸收液,将产生的卤化氢气体吸收并转化为无机阴离子,离子色谱法进行样品的测定,以氯和溴的峰面积外标法进行定量. 对影响燃烧效果和测定结果准确度的因素如燃烧时间、燃烧温度、吸收液体积、称样量、氧气和氩气流速等条件进行了选择优化. 在(0.10—2.50)mg·L−1和(0.02—0.50)mg·L−1范围内,氯和溴离子的线性相关系数(r2)大于0.999,该方法对于氯和溴的定量下限分别为0.55 mg·kg−1和2.60 mg·kg−1. 采用建立的方法分别对环氧树脂和EC680k低密度聚乙烯标准物质中的氯和溴进行测定,并与传统的氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法进行了比较. 结果表明:在线燃烧离子色谱法对于环氧树脂中氯和溴测定结果的相对标准偏差分别为1.28% 和2.29%,测定值与氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法基本一致,EC680k的测定结果与标准值符合,证明该方法具有良好的准确度和精密度. 该方法准确度和灵敏度高、重复性较好,能够满足批量树脂类样品中氯和溴的含量筛查和多批次产品的质量控制.Abstract: A method for the simultaneous determination of chlorine and bromine in epoxy resins by online combustion ion chromatography was developed. High-temperature pyrolysis furnace coupled with ion chromatography was used to decompose and gasify the samples at high temperature, and hydrogen peroxide (100 mg·L−1) was used as absorbent. The resulting hydrogen halide gas was absorbed and transformed into inorganic halogen anions, and the samples were separated and determined by ion chromatography, which was quantified by an external standard method using the peak area of chlorine and bromine. Parameters that affect the combustion effect and the accuracy of the results such as combustion time, combustion temperature, the volume of the absorption liquid, sample weight, and the flow rate of oxygen and argon were optimized. In the range of (0.10—2.50) mg·L−1 and (0.02—0.50) mg·L−1, the linear correlation coefficient (r2) of chlorine and bromine was greater than 0.999. The limits of quantitation of this method for chlorine and bromine was 0.55 mg·kg−1 and 2.60 mg·kg−1, respectively. Chlorine and bromine in epoxy resins and EC680k low-density polyethylene certified reference materials were determined by the established method, and the results were compared with the traditional oxygen bomb combustion-ion chromatography. The results showed that the relative standard deviations of chlorine and bromine in epoxy resins were 1.28% and 2.29%, respectively, which were consistent with the results of oxygen bomb combustion-ion chromatography, the determination results of EC680k wee in accordance with the certified value, which proves that the method has good accuracy and precision. The method has high accuracy, sensitivity and repeatability, and can meet the requirements of screening chlorine and bromine content in batch samples and quality control of multi-batch products.
-
Key words:
- online combustion ion chromatography /
- epoxy resins /
- chlorine /
- bromine
-

-
表 1 氯和溴离子的保留时间、线性、检出限和定量下限(mg·L−1)
Table 1. Retention time, linearity, detection limits (LOD) and quantitation limits (LOQ) of chlorine and bromine (mg·L−1)
分析物
Analyte保留时间/min
Retention time线性方程
Regression equation线性相关系数r2 线性范围
Linear rangeLOD LOQ Cl 5.94 y=0.4160+0.0137x 0.9999 0.10—2.50 2.64 8.83 Br 8.54 y=0.0120+0.0047x 0.9992 0.02—0.50 2.34 7.80 表 2 样品测定结果 (mg· kg−1,n=6)
Table 2. Results of the samples (mg· kg−1, n=6)
测定结果
Analyte在线燃烧离子色谱法
Online combustion-ion chromatography氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法
Oxygen bomb combustion-ion chromatography氯 溴 氯 溴 1 4301 482 4332 493 2 4352 465 4357 505 3 4235 471 4341 512 4 4273 490 4356 511 5 4341 492 4222 511 6 4218 488 4303 510 平均值 4287 481 4319 507 RSD /% 1.28 2.29 1.19 1.44 -
[1] BUCKNALL C B, GILBERT A H. Toughening tetrafunctional epoxy resins using polyetherimide [J]. Polymer, 1989, 30(2): 213-217. doi: 10.1016/0032-3861(89)90107-9 [2] FANG C, GUAN D B, YAO W G, et al. Studies on mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy resin modified by fluorine-containing silicone [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 401/402/403: 713-716. [3] 汪丽, 余小岚, 黄滨, 等. 氧弹燃烧法测定环氧树脂中氮含量 [J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 48(3): 139-141. WANG L, YU X L, HUANG B, et al. Determination of nitrogen contents of epoxy resins by oxygen bomb combustion and oxygen bottle combustion [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2009, 48(3): 139-141(in Chinese).
[4] 范亚平, 任天斌, 黄艳霞, 等. 水性环氧树脂涂料及其固化机理的研究 [J]. 涂料工业, 2006, 36(7): 17-21. FAN Y P, REN T B, HUANG Y X, et al. Study on waterborne epoxy resin coatings and its curing mechanism [J]. Paint & Coatings Industry, 2006, 36(7): 17-21(in Chinese).
[5] 马明, 闵红, 周宇艳, 等. 顶空-气相色谱-负化学离子源质谱法测定水性环氧树脂涂料中表氯醇 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(5): 1017-1019. MA M, MIN H, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Determination of epichlorohydrin in waterborne epoxy resin coatings by headspace-gas chromatography-negative chemical ion source mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(5): 1017-1019(in Chinese).
[6] 巩东侠, 刘肖, 江海飞, 等. 氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法测定电子元器件中的卤素 [J]. 岩矿测试, 2009, 28(6): 545-548. GONG D X, LIU X, JIANG H F, et al. Determination of halogen in electronic components by oxygen bomb-ion chromatography [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2009, 28(6): 545-548(in Chinese).
[7] ZHANG S, ZHAO T B, WANG J, et al. Determination of fluorine, chlorine and bromine in household products by means of oxygen bomb combustion and ion chromatography [J]. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 2013, 51: 65-69. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bms108 [8] 童国璋, 徐哲明. 氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法测定高分子聚合物的卤素[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011, 34(增刊1): 268-270. TONG G Z, XU Z M. Determination of halogen in the polymer by ion chromatography with oxygen bomb combustion[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 34 (Sup 1): 268-270(in Chinese).
[9] The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2002/95/EC: on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment[R]. 2003. [10] International Electrotechnical Commission. Reinforced base materials, clad and unclad non-halogenated epoxide woven E-glass reinforced laminated sheets of defined flammability (vertical burning test), copper-clad[R]. 2003. [11] 何晓俊, 刘奇祥, 庞承焕, 等. 离子色谱法测定塑料中卤素准确性研究 [J]. 现代塑料加工应用, 2021, 33(6): 32-34. HE X J, LIU Q X, PANG C H, et al. Study on accuracy of ion chromatography for determination of halogens in plastics [J]. Modern Plastics Processing and Applications, 2021, 33(6): 32-34(in Chinese).
[12] 马志斌, 王淑杰, 张磊. 氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法测定电子产品中的卤素 [J]. 分析仪器, 2012(6): 36-38. MA Z B, WANG S J, ZHANG L. Determination of halogen in electric products by ion chromatography [J]. Analytical Instrumentation, 2012(6): 36-38(in Chinese).
[13] 涂建国, 司亚春. 氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法测定电子电气产品中卤素[J]. 化学分析计量, 2014, 23(增刊1): 29-31. TU J G, SI Y C. Determination of halogen in electrical and electronic products by oxygen bomb–ion chromatography[J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2014, 23(Sup 1): 29-31(in Chinese).
[14] 叶晨, 曾文法, 杨俊明. 氧弹燃烧-离子色谱法测定塑胶中卤素 [J]. 广州化工, 2013, 41(8): 136-138,220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2013.08.051 YE C, ZENG W F, YANG J M. Determination of halogen in plastic by oxygen bomb-ion chromatography [J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2013, 41(8): 136-138,220(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2013.08.051
[15] 高欢, 卫碧文, 杨荣静等. 自动裂解-离子色谱联用技术测定电子电气产品中卤素和硫 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(5): 1051-1052. GAO H, WEI B W, YANG R J, et al. Determination of halogen and sulfur in electronic and electrical products by automatic pyrolysis-ion chromatography [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(5): 1051-1052(in Chinese).
[16] CHIVARZIN M E, REVELSKYN I A, NIKOSHINA A V, et al. New approach to the fast screening of plant oil samples for F-, Cl-, Br- and S-organic compounds on the trace level [J]. Talanta, 2016, 150: 113-117. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.002 [17] 曹丽华, 丁友超, 张秀等. 高温燃烧-水蒸气吸收-离子色谱法测定纺织品中的有机卤化物 [J]. 分析测试学报, 2022, 41(2): 234-241. CAO L H, DING Y C, ZHANG X, et al. Determination of organic halides in textiles by ion chromatography method with high temperature combustion and water vapor absorption [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2022, 41(2): 234-241(in Chinese).
[18] 梁晨, 张锦梅, 郑秀瑾等. 在线燃烧-离子色谱法测定炭黑中氯和溴的含量 [J]. 理化检验-化学分册, 2019, 55(11): 1345-1348. LIANG C, ZHANG J M, ZHENG X J, et al. IC determination of chlorine and bromine in carbon black with on-line combustion [J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2019, 55(11): 1345-1348(in Chinese).
[19] 王碗, 刘肖, 蔡亚岐, 等. 自动快速燃烧炉-离子色谱联用技术检测水泥等建材中的氯 [J]. 分析试验室, 2007, 26(12): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2007.12.003 WANG W, LIU X, CAI Y Q, et al. Determination of chloride in some building materials by automatic quick furnace-ion chromatography [J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2007, 26(12): 10-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2007.12.003
-



 下载:
下载: