-
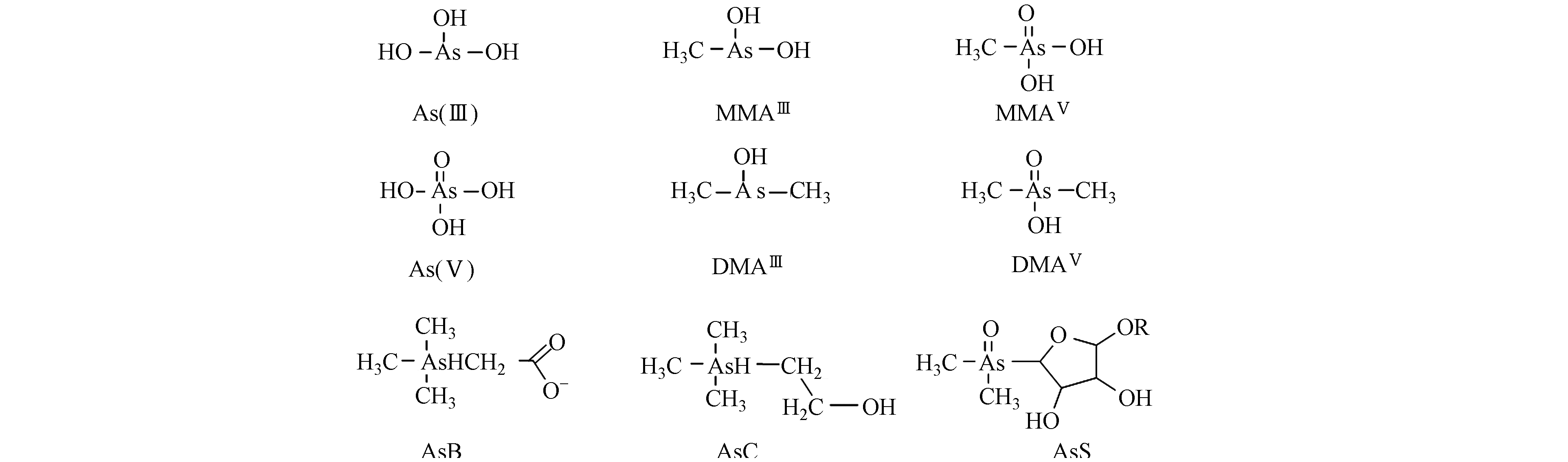
砷是全球水生生态系统的重要污染物,是一种能通过地质过程或人类活动在水生环境中释放的有毒元素,一些人类活动如过矿石冶炼、煤炭燃烧加剧了自然环境中的砷浓度[1 − 3]. 环境中的砷可分为无机砷和有机砷,无机砷主要包括砷酸盐(As(Ⅴ))、亚砷酸盐(As(Ⅲ)),有机砷主要包括砷甜菜碱(AsB)、砷胆碱(AsC)、甲基砷酸(MMA)及其甲基化砷复合物(MMAⅢ、MMAⅤ)、二甲基砷酸(DMA)及其二甲基化砷复合物(DMAⅢ、DMAⅤ)、砷糖(AsS)和砷脂(AsL)[4]. 砷在水生生物中的赋存形态(图1)因不同的水生生物而有所不同,水生生物普遍对砷具有较高的累积能力,可通过摄食、皮肤渗透或者黏膜吸收砷,并能通过主动运输进入细胞[5],吸收的砷会对机体造成不良影响,如中毒、免疫紊乱、组织损伤以及细胞死亡[6],而其毒性大小又与存在形态有关,由半数致死剂量(LD50)确定的不同形态的砷毒性顺序为As(Ⅲ)>As(Ⅴ)>MMAV>DMAV>AsS>AsC>AsB[7 − 8],通常而言,无机砷毒性高于有机砷毒性,As(Ⅲ)毒性高于As(Ⅴ),但在比较各种砷化合物对人肝细胞毒性实验时发现,毒性顺序为DMAⅢ≫As(Ⅲ)>MMAⅢ>As(Ⅴ)>MMAⅤ=DMAⅤ[9 − 10],因此,砷对生物体的毒性作用引起了全球范围内的关注.
无机砷可在水生环境中经水生生物及微生物代谢转化形成多种形态的砷,这些形态的砷毒性小于原有的无机砷毒性[11],说明砷在形态上的转化可能是砷的一个重要解毒机制,因此,关于砷毒性及其代谢转化的关系一直是重要的研究领域. 孟加拉国、印度、美国、阿根廷、智利、中国等都遭到了由砷污染造成的健康问题[12],作为一种自然污染物,砷已被证明对人类健康造成不利影响,其中无机砷可导致皮肤癌、肺癌、膀胱癌、神经退行性等疾病[13],已被国际癌症研究中心(IARC)列为Ⅰ类致癌物[14]. 有研究表明,砷暴露与神经退行性等疾病发病率增加有关,然而其毒性致病机理尚不清楚,因此国内外大量研究者采用动物模型研究神经退行性等疾病(如阿尔兹海默症、帕金森等)或缓解此类疾病的药物,同时,近年来有许多砷与微生物的研究值得关注. 在医学研究中发现,肠道微生物与砷代谢有着极大的相关性;在环境学方面,砷的微生物参与了全球砷的生物化学循环过程,能吸收转化环境中的砷,一定程度上降低了环境中的砷污染,具有极大的生物治理潜力[15 − 17]. 因此,近年来,有大量关于砷在小鼠/大鼠、人体、微生物中的代谢毒理情况的研究,可为人类流行病学、毒理学和生态环境研究奠定坚实的基础.
全球水生生态系统中的砷在不同水生生物中的生物累积、生物转化、产生的毒性及毒理效应的过程是复杂的,不同的水生生物对砷的耐受程度不同,不同形态的砷对水生生物产生的毒性也不同,因此,砷在水生生物中的生物累积、生物转化及毒理效应受到国内外研究者持续而广泛的关注,大量实验研究集中砷在水生生物、小鼠/大鼠、人体、微生物中的代谢毒理学,本文将重点对这一系列热点问题展开综述,可为进一步阐明砷在不同生物中的累积转化过程及毒理学效应,为研究者深入探索该领域提供一定的参考.
-
通常来说,鱼类处于水生食物链的顶端,在正常的新陈代谢中会从食物、水、底泥环境中不可避免地累积重金属元素,因此,鱼类常被用做极具代表性的生物标志物,从而评价鱼类生活环境的金属水平. 淡水生物和海水生物的砷形态形成有所不同,鱼和贝类中砷形态和含量随着个体的种类和采样面积存在显著差异,砷甜菜碱(AsB)是鱼类中的主要砷形态[18].
无机砷对水生生物有剧毒,但膳食无机砷暴露对鱼类的慢性影响尚不清楚. 为了解慢性砷暴露下鱼类中砷的累积情况,Chen等[19]对淡水青鳉(Oryzias mekongensis)进行一项为期28 d的慢性无机砷膳食暴露(As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)),发现经同浓度(1.3 mmol·L−1)的As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)分别暴露后,淡水青鳉组织中砷的生物累积浓度先增后减,而这两种浓度先增后减的时间存在一定的差异性. Di等[20 − 21]在对鲫鱼(Carassius auratus)进行一项为期40 d的慢性无机砷(As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ))食物相暴露研究中也发现了类似的相关性,在分别暴露相同浓度(50 μg·g−1)的As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)后,测定鲫鱼肝脏及全身肌肉中As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)和AsB的累积情况,在鲫鱼肝脏中,AsB在暴露过程中比例呈上升趋势(34%—66%),As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)比例在暴露过程中逐渐下降(84%—91%). 在对鲫鱼肌肉组织中砷累积情况的研究发现,经As(Ⅲ)暴露的鲫鱼肌肉中检测到更高比例的AsB,两种无机砷累积的减少与其转化为无毒的AsB的增加有关,相比于As(Ⅴ),As(Ⅲ)更容易转化为AsB. 在暴露的食物相中,As(Ⅲ)的生物利用度低于As(Ⅴ),这可能是由于As(Ⅲ)通过鲫鱼肌肉组织的能力较低。而在这项研究[21]中发现, 鲫鱼肌肉组织含有大量的As(Ⅲ),说明As(Ⅴ)能大量转化为As(Ⅲ),从而累积在鲫鱼肌肉组织中.
另外,砷在鱼类各组织中的累积情况不同,且不同品种间累积情况存在差异. Kim等[22]对幼年岩鱼进行水环境砷暴露20 d,发现在幼岩鱼组织中砷的累积顺序大小为肝>肾>脾>鳃>肠>肌肉. Kumar等[23]采用亚砷酸钠对鲶鱼(Clarias batrachus)进行为期60 d的暴露,最后发现砷在鲶鱼各组织中的累积情况为肝脏>血液>肌肉>皮肤>大脑. Juncos等[24]发现,克里奥尔鲈鱼、虹鳟鱼、褐鳟鱼不同组织累积砷浓度大为肾脏>肝脏>鳃>肌肉. 作为高等物种水生食物的重要来源,水环境中的无脊椎动物易富集砷[25],鱼类存在于水生食物链的顶端,在捕食这些无脊椎动物时同时摄入砷[26]. 大量的研究表明,AsB是这些鱼类组织中砷的主要存在形态,而无机砷(As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ))和有机砷(MMA、DMA、AsC)占总砷的比例相对较少. 这些砷形态在鱼体内累积、储存、进一步转化,通过食物链传递,产生生物放大作用,累积至人体中,对生物与人类健康产生潜在危害[27 − 28],因此,鱼类是人类砷暴露的重要来源.
-
甲壳类、双壳类水生动物由于自身滤食性的特点,易富集重金属元素,AsB是最主要的砷形态[29]. 例如,Zhang等[30]在对中国南方湛江河口地区的甲壳类动物中的砷含量测定发现,AsB占所有砷化物的80.6%—98.8%. Hong等[29]对韩国浦项市高度工业化地区中水生生物中的砷累积研究中发现,在蟹类和虾类中AsB占总砷浓度的88%,相比之下,甲壳类、双壳类水生动物中累积的砷浓度高于鱼类. 另外,甲壳类水生动物不同组织对砷的累积情况有所不同,Devesa等[31]测定克氏原螯虾整个生物体及其各个部分的总砷和砷形态的浓度,发现无机砷占总砷的18%—34%,不同部位的砷浓度与克氏原螯虾的部位有关,其中肝胰腺的总砷及无机砷含量最高,尾巴中的总砷和无机砷含量最低. 同样地,Liao等[32]将南美白对虾分别暴露于不同浓度的As(Ⅲ)中21 d,发现肝胰腺也是南美白对虾体内累积砷的主要组织,总砷和无机砷的累积浓度同暴露浓度呈正相关. 而累积高砷浓度的肝胰腺会对甲壳类动物的繁殖产生影响,这与Yamaguchi等[33]发现砷对野生淡水蟹的性腺发育有影响的研究结果一致.
人群通过膳食摄入鱼类、甲壳类、双壳类及其制品,可使砷在消费者体内蓄积暴露,而甲壳类、双壳类水生动物则经代谢转化形成大量的AsB,以其作为机体内主要的砷形态,使机体免受毒性更高的无机砷的损害作用,这可能是水生生物的一种自我保护机制. 同时,对于甲壳类水生动物的研究发现,不同种类和不同组织中砷的累积情况均不同,但大部分甲壳类水生动物的肝胰腺中都累积了大量的砷,这或许是因为肝胰腺作为甲壳动物最重要的组成部分,具有免疫砷毒性及解毒作用.
-
除鱼类、甲壳类、双壳类水生动物易累积环境中的砷外,水生环境中的藻类同样暴露于重金属污染中,易累积砷,研究发现大型藻类对砷具有较高的累积速率和对金属的亲和力,可以高度暴露于砷的污染中[34]. 但影响海藻中砷累积的因素有很多,例如,藻类的种类、环境中的砷浓度、藻类的收获时间、藻类对养分的吸收程度和环境中的温度状况. 虽然海藻中的有机砷含量高于无机砷,但由于海藻中的无机砷比有机砷毒性更大,因此研究海藻中的无机砷比有机砷更为广泛[7]. 对海藻累积砷的研究过程中发现,海藻酸盐是褐藻活细胞中最丰富的多糖,能吸收环境中的重金属和类金属[35],导致褐藻中累积砷. 而外界磷酸盐(
${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ )的浓度也可能促进海藻对砷的吸收,因为磷酸盐(${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ )和砷酸盐As(Ⅴ)结构相似,它们具有几乎相同的pKa值,相似的带电氧原子以及相似的热化学半径,因而藻类不能区分这两者[36 − 38],并且随着环境中${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ 浓度的增加,微藻对砷的吸收会受到抑制[39],这可能是由于${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ 浓度的增加会减少细胞膜上As(Ⅴ)转运体的数量或者是其与As(Ⅴ)竞争细胞质As(Ⅴ)还原酶上的砷结合位点[40].另外,在研究藻类中砷的生物累积时也发现加入外源物质纳米二氧化钛可通过影响细胞表面的疏水性、细胞膜的完整性和迁移率来影响砷在藻类中的累积[41],加入纳米二氧化钛可显著促进淡水藻类铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)中As(Ⅴ)的累积和斜生栅藻(Scenedesmus obliquus)中As(Ⅲ)的累积[42]. 作为水生生态系统的重要组成部分,藻类在海洋生态系统砷循环中扮演重要角色,能累积高浓度的无机砷,可以极大降低环境中的砷浓度,因此纳米离子与砷污染物共同累积砷的研究需要更多的关注,以发现更多水生植物对砷的高效解毒途径.
水产品由于味道鲜美,营养丰富,同时作为人类优质蛋白的重要来源,深受消费者的青睐,而水产品由于自身易累积重金属的特点,经食物链传递累积至人体中,易造成潜在健康危害,因此有大量对水产品中重金属污染情况并做出膳食健康评价的研究,表1为国内外部分地区近10年来对不同水产品中砷的累积监测情况.
水产品是我国重点出口的产品,由于所处的自然环境、养殖使用的化学物质及自身特性易累积重金属,经人类摄入造成食品安全问题,因此世界各国组织十分重视水产品中重金属污染物含量问题,出台了相关技术控制法规和标准,如国际食品法典委员会(Codex Alimentarius Commission,CAC)、欧盟、美国、日本、韩国、澳大利亚等都对水产品中重金属污染物出台相关标准和技术法规[54]. 全球各地水生生物生长的水域环境不同,各国消费水产品的情况不同,砷限量值也存在差异,CAC、欧盟、日本、韩国、孟加拉国等均未规定水产品中总砷/无机砷限量值,而澳大利亚规定鱼类、甲壳类、软体动物无机砷限量值分别为2.0、2.0、1.0 mg·kg−1,国内对砷限量值参照GB 2762—2017《食品安全国家标准 食品污染物限量》,规定水产动物及其制品(鱼类及其制品除外)、鱼类及其制品的无机砷含量分别不能高于0.5 mg·kg−1、0.1 mg·kg−1 [55],印度尼西亚则对海藻及鱼类及其制品的总砷做出最大限量规定,分别为1.0 mg·kg−1和2.0 mg·kg−1[56],美国对甲壳类和贝类中总砷限量值分别不得超过76 mg·kg−1和86 mg·kg−1(表2). 相比澳大利亚及美国的标准,中国对水产品中砷限量更严. 大量的基础科学研究表明,砷在不同水生生物中的赋存形态不同,产生的毒性作用也不同,而国外大部分国家却未对砷做出限量规定,对于各国砷限量差异问题,笔者认为有必要继续完善水产品中砷限量指标,不仅要根据各类水产品生长环境及其自身特性进行研究评估,还要继续研究不同水生生物的砷毒理学效应,有必要细化水产品分类,根据各类水产品中无机砷与总砷占比情况,毒性特点设定更加科学合理的砷限量值.
-
水生生物易累积砷,并造成一定的毒性作用,环境中的砷进入水生生物体内,经转化代谢作用降低了砷的毒性. 在研究水生生物中砷的生物转化时发现,水生生物对砷的生物转化包括无机砷的生物转化和有机砷的生物转化,水生动物主要吸收无机砷,随后将无机砷氧化或还原,或者通过甲基化生成有机砷形式[58]. 在砷的生物转化过程中,无机砷化合物被细菌、藻类、真菌和人类甲基化,并在甲基化过程中产生甲基化产物MMA和DMA,这些甲基化砷是慢性砷暴露的最终代谢物和标志物,转化过程如下:
As(Ⅴ)→As(Ⅲ)→MMAⅤ→MMAⅢ→DMAⅤ[59]
生物甲基化是无机砷的一种解毒过程,其终产物为甲基化的无机砷,如MMAⅤ和DMAⅤ,可通过尿液排泄,MMAⅢ不能经由尿液排出体外,而是作为一种中间产物留在体内,其具有比其他无机砷更高的毒性,这可能是砷致癌的原因[60].
一些研究发现,经As(Ⅴ)暴露后的鱼体组织中能检测到更多经As(Ⅲ)直接暴露后的As(Ⅲ),因此,推测As(Ⅴ)能大量转化为As(Ⅲ),并广泛分布在鱼肌肉中. 而As(Ⅴ)的强还原能力可解释在实验暴露结束后鱼类组织中并未检测到As(Ⅴ)的原因,这表明,大量的As(Ⅴ)可能在鱼肌肉中分布前就已经转化为As(Ⅲ). 除此之外,As(Ⅲ)转化为AsB的能力高于As(Ⅴ)[21],因此,As(Ⅴ)还原为As(Ⅲ)可能是水生生物的一种解毒过程. 尽管As(Ⅲ)的毒性强于As(Ⅴ),但是As(Ⅴ)在转化为As(Ⅲ)后,As(Ⅲ)与肽结合、转化为低毒甚至无毒的有机砷, 以及经细胞排出过程中都能降低As(Ⅲ)的毒性. 另外,少数砷形态可能通过其他方式解毒,如通过与金属硫蛋白的结合以及一些甲壳类动物的退壳行为、遗传行为[61 − 62].
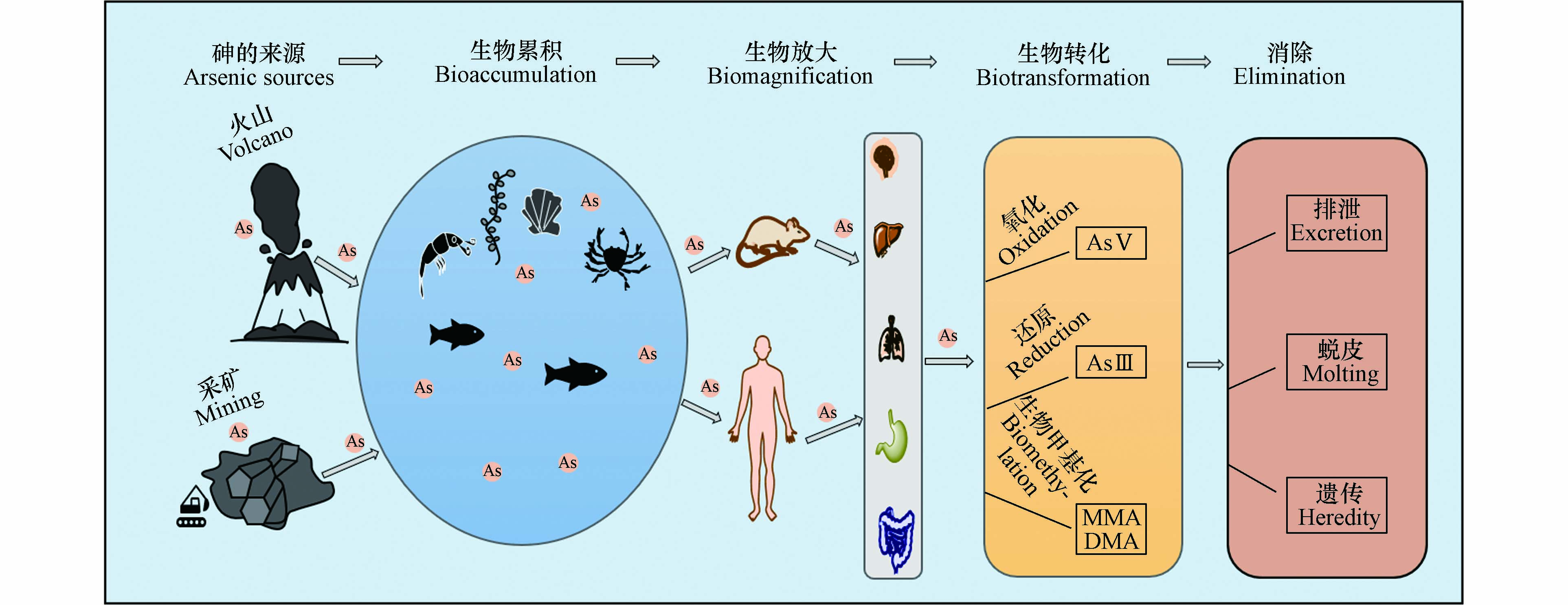
砷在水生生物体内的生物转化一直是关注的热点,水生生物可以将As(Ⅴ)还原为As(Ⅲ),随后甲基化为MMA和DMA,机体体内存在多种对砷转化代谢过程,如细胞的排泄作用、退壳行为、遗传行为、与机体内的各种金属肽结合、转化为无毒或毒性更低的有机砷. 图2为砷在生物体内的累积转化代谢过程.
-
砷易累积在水生生物体内,参与全球水生生态系统中的砷循环,由天然形成和人类生产过程中产生的砷易累积在水生生物体内,可通过改变机体内的各种酶和代谢物,导致机体发生组织、代谢上的紊乱[63],既能降低砷对机体的毒性又能导致机体遭受更大的毒性,并且不同的砷形态对不同水生生物产生的毒性不同. 例如,Rahman等[64]对小球藻(Chlorella sp. strain CE-35)、浮萍(Lemna disperma)、水蚤(Ceriodaphnia cf. dubia)的3种淡水生物进行As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)和DMA毒性大小比较,结果发现As(Ⅲ)对浮萍的毒性最大,对小球藻的毒性最小,As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)对水蚤的毒性相当,DMA对浮萍和水蚤的毒性最小. 另外,环境中的磷浓度、pH值、盐度和溶解有机物(DOM)水平等均会影响砷对水生生物的毒性[62]. He等[65]研究不同pH下明亮发光杆菌(Photobacterium phosphoreum)、大型水蚤(Daphnia magna)、斑马鱼(Danio rerio)的3种水生生物中的砷毒性,发现不同pH下这3种水生生物受到砷毒性的大小随pH的变化存在生物特异性. Rahman等[64]对3种淡水浮游生物的毒性试验中发现,As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)对小球藻和浮萍的毒性与培养基中磷酸盐(PO43-)浓度有关,小球藻具有将As(Ⅴ)还原为As(Ⅲ)的能力,这种途径可能是小球藻对砷的耐受机制,以降低As(Ⅴ)对机体的毒性. 由于生物体通过磷酸盐转运体吸收As(Ⅴ),通过甘油蛋白吸收As(Ⅲ),因此不同的转化途径可能导致不同的砷毒性[66]. 尽管砷对淡水浮游植物的毒性因浮游植物种类的不同而有极大差异,但大部分毒性生物测定表明,As(Ⅴ)比As(Ⅲ)对淡水浮游植物的毒性更大,而As(Ⅲ)对海洋浮游植物毒性更大. 尽管As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)在淡水系统中占主导地位,但砷形态对水生生物的毒性由于与水中磷酸盐等化学物质相互作用而变得更为复杂,这些化学物质会影响As(Ⅴ)的生物利用度和吸收[39],而As(Ⅲ)具有更高的生物利用度,因此,As(Ⅲ)比As(Ⅴ)对海洋浮游植物的毒性更大.
在淡水和海水中,水生生物体内的主要砷形态为AsB,这表明水生生物为保护自身机体免遭更大的毒性作用,可以高毒的无机砷最终转化为几乎无毒的AsB. 另外,不同形态的砷对不同的水生生物具有不同的毒性,对于砷产生毒性差异的原因可能是由于生物体自身因素,如摄取砷的途径、代谢途径及机体自身对重金属的解毒机制上的差异性,以及非生物因素,如砷的暴露浓度、暴露时间、暴露介质中的pH、PO43-水平等.
-
砷在全球水生生态系统内循环,通过食物链传递,产生生物放大作用,对不同的生物体产生不同的毒性,鱼类、甲壳类、双壳类水生动物易累积砷,通过食物链传递,最终累积到人体中,对人类健康造成了潜在危害,因此,砷对人体的代谢毒性受到了广泛的研究. 为了解膳食摄入砷对不同生物体的毒理学作用,研究者们通常采用小鼠/大鼠模拟不同生物体体内砷代谢情况,测定小鼠/大鼠各器官中砷形态,同时收集它们的排泄物以反映砷的代谢毒理学效应. 例如,王旭等[67]对81只大鼠进行4种砷形态(As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)、MMA、DMA)为期28 d的动物代谢实验,发现这4种砷形态的主要排出方式为粪便和尿液,少部分仍保留在血液中. 赵梦醒等[68]研究海带中砷元素在大鼠消化系统和血液中的形态变化,发现随着海带中砷形态在大鼠体内代谢,除大鼠血液中的砷形态无变化外,海带中的砷形态在消化系统中的形态和含量均发生变化. 于霄云等[69]探讨外源性谷胱甘肽(GSH)和亚硒酸钠对饮水砷暴露小鼠肝、肾和血中砷代谢的影响,发现GSH组小鼠肝中和血液中DMA含量和总砷含量均高于对照组,GSH组小鼠肝中砷一甲基化率和二甲基化率与砷组小鼠对应的甲基化率比较升高,因此,对小鼠给予外源性GSH可以促进无机砷在小鼠体内甲基化代谢.
慢性砷暴露会导致小鼠代谢紊乱,如葡萄糖代谢受损和能量消耗减少,在慢性砷暴露对小鼠皮层和血清代谢组学的影响实验中发现,慢性砷暴露可通过干扰皮层和血清氨基酸类代谢和三羧酸循环、神经递质合成障碍以及干扰能量代谢而影响中枢神经系统功能[70 − 71]. 另外,亚慢性砷暴露对小鼠大脑组织神经递质代谢酶及其受体基因表达谱有所影响,对小鼠进行As2O3和锑(Sb)的共同暴露会导致小鼠氧化应激、肝组织脂质代谢紊乱和脂肪变性,这可能是肝组织中线粒体吞噬和线粒体通路凋亡的重要驱动因素,而这种线粒体吞噬和凋亡极大程度上诱导细胞死亡[72]. As2O3可能导致小鼠大脑组织部分神经递质的合成和分解代谢酶基因表达下调,且干扰其部分受体基因的表达[73]. 在对小鼠进行慢性饮水无机砷暴露时发现小鼠体内无机砷代谢产物的蓄积与分布具有明显的组织和区域特异性,由于无机砷代谢产物具有不同的毒性,推测膀胱和脑组织可能是慢性无机砷暴露发挥毒性最重要的靶器官,而详细机制仍需进一步探讨[74]. 目前众多研究选择小鼠/大鼠作为砷形态致毒机制研究的主要对象,而其准确致毒机制仍然不是十分清楚,虽然小鼠/大鼠常被用做毒理学研究,但由于砷在生物体内的代谢物及砷本身都会与细胞内外大分子发生作用,且小鼠/大鼠与人体内的的砷代谢机制仍有很大差别[75],因此,未来对砷代谢机制仍然需要大量研究.
-
小鼠/大鼠组织器官中的砷经代谢后极大降低了砷对机体的毒性,目前研究者对砷在小鼠/大鼠体内的毒性研究取得了一定的成果,无机砷已被列入Ⅰ类致癌物,对人体具有一定的致畸致癌性,而有机砷则被认为毒性较小,但大量的研究发现小鼠/大鼠中的砷经代谢后,器官组织中能检测到大量的DMA,而DMA作为无机砷的主要代谢产物本身具有独特的毒性,研究发现在小鼠和大鼠的肺以及人肺细胞中的DMA会诱导器官特异性损伤,造成DNA单链断链,造成这种损伤的主要原因是DMA的过氧自由基和肺内组织产生活性氧[76 − 77],DMA染毒后可使小鼠骨髓细胞有丝分裂指数明显上升,造成DNA单链断裂,而DMA的进一步代谢产物二甲基砷化物能与氧分子反应产生活性氧,使得DNA链上的C8位鸟嘌呤碱基被羟基自由基和单线态氧攻击生成8-羟基脱氧鸟苷(8-OHdG),导致DNA氧化损伤[78]. 虽然DMA是有机砷形态,其毒性远低于无机砷毒性,但仍然不能忽视其毒性作用.
亚慢性砷暴露对小鼠不同的组织造成不同程度的影响,砷在小鼠各个器官组织中的代谢及毒性情况有所不同. 为了解膳食慢性砷暴露对生物体脑组织的影响,王琛绯等[16]对小鼠进行食物慢性砷暴露,结果发现,小鼠的脑组织中仅能检测到低毒的DMA和部分未知砷,这可能是小鼠为保护自身机理正常运行而仅允许毒性较低的DMA穿过血脑屏障,而其他毒性较高的砷形态则被阻隔在外. 为了研究这种慢性食物相暴露后, 小鼠脑组织代谢组学和脂质组学的变化与肠道微生物的相关性,上述研究者在此实验基础上测定小鼠粪便各砷形态及含量,发现此种亚慢性砷暴露下的脑代谢和脂质均受到了显著干扰,因此,大脑中的代谢紊乱可能与由砷引起的肠道微生物代谢紊乱有关[17]. 这种代谢紊乱的发生可能会干扰肠道微生物群,导致肠道菌群功能失调,造成宿主功能障碍,导致免疫毒性,并可能与神经退行性等疾病有关,从而对生物体健康造成危害. 国内外研究者对小鼠/大鼠进行了大量的亚慢性砷暴露实验研究,某种程度上为人类流行病学和毒理学研究奠定了坚实的基础.
-
随着水产养殖技术、人类消费水平的不断提高、水产市场的规模化,以及水产品本身味道鲜美、富含蛋白质、低热量、高吸收效率,为人类优质动物蛋白的重要来源[79]. 人类对水产品的摄入逐年增加,如前文所述,砷易累积在水生生物中,经由食物链传递至人体内,导致人类暴露于砷隐患中,因此,对人类水产品膳食摄入砷或者从环境中吸收砷后人体对砷代谢的情况受到了研究者们的广泛关注(图3). 慢性砷暴露导致的疾病如外周动脉疾病、高血压、皮肤癌、膀胱癌等,不仅与砷暴露的剂量有关还与个体甲基化能力和代谢模式有关[80]. 经人体摄入的砷在肝脏中经氧化还原和甲基化代谢后,绝大部分的砷以As(Ⅲ)、As(Ⅴ)、DMA和MMA的形式经尿液排出[81]. 另外,有研究表明,从外环境中进入人体的无机砷有80%—90%经胃肠道吸收后,主要在肝脏内进行甲基化的转化过程,先经砷甲基转移酶催化产生MMA,随后经酶促作用产生DMA,以尿液形式排出体外,并在此过程中产生活性中间体[82 − 83].
了解人类接触砷的情况可以根据血液、头发、指甲和尿液中的砷水平浓度来估计,毛发和指甲是砷的富集靶组织[84],通过测定头发和指甲中的砷浓度可以反映人类长期接触砷的情况,血液和尿液则反映最近接触砷的情况[85]. 为了解新疆奎屯垦区居民对砷的接触情况,袁雪花等[84]对当地居民的指甲和头发进行总砷和As(Ⅲ)的测定,发现超过一半的头发样品中总砷质量比超过卫生部标准,接近20%的人群头发总砷高于中国头发总砷上限建议值. 不同的人群对砷的耐受程度不同,人体对砷也具有一定的耐受机制,在对妇女及儿童尿中的砷形态研究时发现儿童比成人对砷敏感,其对砷甲基化的能力高于成人[86],在相同浓度砷暴露下,发现女性对砷的甲基化能力可能高于男性[87]. 因此,在人体内,有毒和致癌的无机砷进行生物转化,以致癌物DMA和MMA的形式通过尿液排出,在此过程中产生活性中间体,而不同的哺乳动物、种群群体和个体之间砷的代谢具有显著的差异性,砷的甲基化在个体间有巨大差异,而导致这些巨大差异的原因需要进一步研究.
-
进入人体内的砷经胃肠道吸收、肝脏代谢转化等作用后,降低了砷对人体的毒性,然而砷对人体的毒性仍然不能小觑. 人类慢性砷暴露会干扰人体内氨基酸代谢,影响生物体的结构和功能[88],体内谷胱甘肽(GSH)作为细胞内重要的抗氧化剂,缺乏可使机体产生氧化应激,砷引起毒性的部分原因是氧化应激的发生,从而产生活性氧(ROS)、超氧阴离子、羟基自由基、有机超氧化物和耗尽机体内的抗氧化剂,从而损害蛋白质、脂质和DNA,导致癌症、神经退行性等疾病的发生[89 − 90]. 另外,γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)作为人体主要的抑制神经递质在受到外源性损害及应激条件下会升高,以减少体内ROS的累积[91],因此,机体为保护自身身体机能的正常运行,在遭受外源性物质损害时,可通过增加GABA的含量帮助机体维持体内氧化水平,这与杜航等[92]对慢性砷中毒患者头发中的砷代谢产物与氧化应激的关系研究一致.
在砷对人体毒性的研究中发现男性和女性受到的砷毒性有所差异,男性似乎比女性更易受到砷相关皮肤效应和肝脏的影响[93],女性更易受到肺部,膀胱和糖尿病的影响[94]. 砷的甲基化产物MMAⅢ、DMAⅢ毒性大于无机砷,在经长期砷暴露的人体尿液中砷形态的研究发现,受试者尿液MMAV升高则砷的甲基化效率下降,这可能是MMAⅢ浓度增加所致,人类流行病学研究表明,尿液中的MMAV水平升高或砷甲基化效率降低与由砷引起的相关疾病存在显著相关性,如膀胱癌、皮肤癌、高血压或者其他皮肤病变等[95]. 因此,砷的代谢与其毒性密切相关,且高度依赖于代谢物的甲基化效率,而这种甲基化效率可能也与性别相关,由此导致男性和女性经相同浓度的砷暴露后产生不同的砷毒性效应.
-
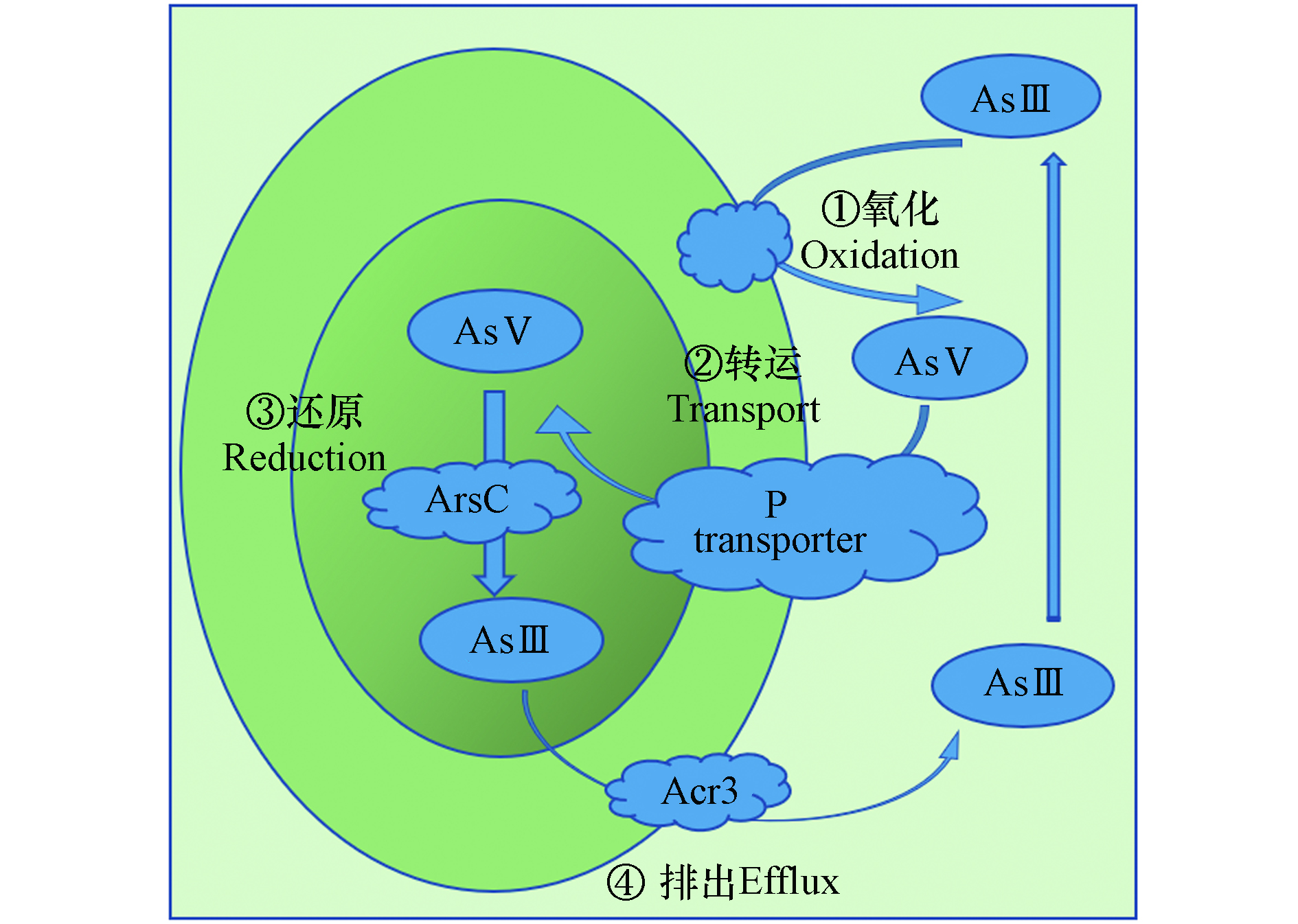
尽管砷对藻类微生物具有毒性,但许多蓝藻细菌对环境中高水平浓度的砷具有耐受性,同时由于藻类细胞壁含有各种可以吸附重金属的官能团[96],因此,许多藻类可以从水介质中吸收砷达到修复环境砷污染的目的,并且藻类对环境中的砷具有高效的去除效果且对砷的吸收具有环境友好型的特点,是一种极具潜力能修复环境重金属污染的物种. 许多藻类微生物介导的砷的生物转化在砷循环中起着重要作用[97],而微生物氧化As(Ⅲ)是全球砷循环的关键环节,人类已经能从各种水生和土壤环境中分离出多种As(Ⅲ)氧化微生物[98]. 为此,了解藻类微生物对砷的氧化还原代谢具有重要意义,因此众多学者对此展开了大量研究. 例如,Zhang等[98]研究发现蓝藻介导的砷氧化还原受PO43-调节,发现随着P浓度的升高,As(Ⅲ)更容易被聚囊藻氧化,机体对As(Ⅴ)的吸收可能通过P转运系统或竞争性地结合到As(Ⅴ)还原酶(ArsC)的活性位点,通过减少As(Ⅴ)的摄取从而减少As(Ⅴ)的还原. Wang等[99]研究了淡水铜绿微囊藻假单胞菌(Synechocystis)时发现其对As(Ⅲ)有一定的敏感性,对As(Ⅴ)有较高的耐受性,对As(Ⅲ)的吸收比对As(Ⅴ)的吸收更为明显,As(Ⅲ)氧化为As(Ⅴ)是该菌的主要转化过程,此外,Inskeep等[100]在对微藻砷的氧化还原代谢中首次报道了类似As(Ⅲ)氧化酶的成功扩增,表明需氧的As(Ⅲ)氧化基因广泛分布于细菌领域以及存在于含砷的水土系统中,并在砷的全球循环中起着关键作用.
微生物对藻类的吸收代谢修复了环境中的砷污染,许多对藻类微生物砷代谢的研究发现机体对砷的氧化还原是一个动态循环过程,例如聚囊藻对砷的氧化还原动态过程如下(图4),在P限制条件下,As(Ⅲ)先在聚囊藻表面氧化为As(Ⅴ),随后As(Ⅴ)通过P转运体进入细胞内,细胞内通过As(Ⅴ)还原酶(ArsC)将As(Ⅴ)还原为As(Ⅲ),最后As(Ⅲ)经As(Ⅲ)外排蛋白(Acr3)转运出细胞[98]. 微藻对砷的解毒过程则是通过细胞表面吸附、细胞内As(Ⅲ)氧化、As(Ⅴ)还原和硫醇络合以及隔离到液泡中,经过甲基化的砷形态可以转化为毒性较低的有机砷,如AsS和AsL,进而从细胞中排出[96]. 众多研究都表明藻类微生物对砷的高效吸收与转化,显著促进了环境中砷的迁移转化,利于降低环境中的重金属污染,因此,未来可继续深入研究藻类微生物与砷的生物修复关系,势必可以有效改进全球水生环境中的重金属污染问题.
-
除藻类微生物外,环境中的其他细菌也同时修复环境中的砷污染,在对细菌砷代谢的研究中发现,原核生物大肠杆菌中有两个磷酸盐转运体:磷酸盐无机转运体(Pit)和磷酸盐特异性转运体(Pst),这两者都催化吸收As(Ⅴ),同样,真核生物酿酒酵母中存在一些磷酸盐转运体吸收转运As(Ⅴ)[66]. As(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅲ)分别通过磷酸盐转运体、糖摄取系统和甘油蛋白进入细胞,一些研究表明砷干扰这些蛋白质或其各自在原核生物中转录的累积[101],影响PO43-的运输,在砷氧化杆菌的实验中,研究者利用转录组学的方法发现在非特异性无机磷酸盐转运体存在下,As(Ⅲ)pit的表达被诱导[102],在高As(Ⅴ)浓度下,这些磷酸盐结合蛋白的高选择性使得这些生物体能吸收足够多的磷酸盐,以确保这些微生物的生存.
人类已经能从不同的环境(碱湖、温泉、酸性矿水系统)中分离出耐砷及能进行砷代谢的原核生物,这些微生物具有不同的碳和能量需求以及不同的砷耐受水平[103]. 为了抵消砷的毒性,一些微生物已经发展出了耐受和利用砷进行呼吸代谢的作用机制[2],包括吸附、沉淀、氧化还原和甲基化转化[104],例如,原核生物能抵抗和代谢砷,其已经进化出能抵抗和代谢这些化学毒性的代谢系统[1],经细胞质砷酸还原酶将As(Ⅴ)还原为As(Ⅲ),并将As(Ⅲ)通过膜As(Ⅲ)外排泵从细胞质中排出[105]. 将As(Ⅴ)还原为As(Ⅲ)可能是微生物的对砷的一种解毒机制,因为As(Ⅲ)更容易从细胞中排出. 如果微生物可以将无机砷转化为毒性较低的五价甲基物质(例如MMAV和DMAV),那么无机砷的生物甲基化也可以是一种解毒机制[58]. 而有研究报道微生物的生物甲基化过程中产生的甲基化产物(MMAⅢ、DMAⅢ)毒性大于无机砷[17],这表明需要继续研究微生物的生物甲基化与砷解毒的过程.
-
砷作为全球生态系统的重要污染物,一直备受关注,国内外对砷在水生生物中经累积、转化,随食物链传递至人体产生毒性作用的研究颇为丰富,其不同赋存形态对生物体产生的细胞毒性、基因毒性受到广泛研究,大量研究表明砷在不同水生生物体内的生物累积、转化代谢、毒性作用存在显著差异,与生物体自身对砷的累积特性及所处的环境情况密切相关,因此国内外对砷限量值的设定有所差异,由于鱼类、甲壳类、双壳类、藻类生存环境中不同化学介质及不同砷浓度水平等因素,导致砷在这些水生生物体内产生毒性差异,而造成这些差异的原因仍需进一步研究.
上述关于砷在水生生物中的生物累积、转化、毒性作用的研究已取得大量成果,但在这些研究过程中发现的甲基化产物的毒性机制、未知砷形态的识别等研究仍值得继续探索,未来的研究可从以下几个方面进行:①环境中的微生物对砷的吸收转化极大程度上降低了环境中的砷浓度,修复了受砷污染的水体,因此,未来应当继续深入研究微生物对砷的生物修复作用;②砷甲基化过程中产生的甲基化产物(MMAⅢ、DMAⅢ)毒性高于无机砷,这些甲基化产物不稳定,能迅速氧化为五价无机砷,在许多动物实验中很难区分这些甲基化产物和五价无机砷,同时,在这些动物实验中发现含有大量未知砷,而这些未知砷是否是这些甲基化产物的进一步代谢产物有待验证,因此,今后需要进一步研究这些甲基化产物以及这些未知砷;③不同的哺乳动物、种群群体和个体之间砷的代谢及甲基化具有显著的差异性,导致这些巨大差异的原因需要进一步研究;④如前文所述,在一些对砷解毒的研究过程中发现,加入外源性物质有助于砷的甲基化率,因此未来可以更加深入探讨外源性物质与砷共同作用的解毒过程与砷代谢组学的关系.
砷在水生生物中的生物累积、转化及在其他生物体内的代谢毒理学研究进展
Research progress on arsenic's bioaccumulation and biotransformation in aquatic organisms, and its metabolism and toxicology in other organisms
-
摘要: 砷作为全球水生生态系统的重要污染物,普遍存在于淡水和海洋环境中,具有一定的生物累积性与生物毒性. 水生生物作为生态系统的重要组成部分,砷在全球生物化学循环的过程中通过迁移、累积、转化、富集在水生生物体内,产生毒性作用,而砷对水生生物的毒性与其在水生生物中的赋存形态有关. 目前关于砷在水生生物中的生物累积、生物转化及其代谢毒理的基础科学研究受到国内外研究者的广泛关注,而少有对该领域内的研究进展、研究热点、趋势方向的系统整合,本文针对这一领域文献进行梳理,系统阐述了砷在水生生物中的生物累积和生物转化情况;概述了砷在水生生物、小鼠/大鼠、人体、微生物等生物中的毒性作用及代谢机制;并提出了未来有关砷研究可关注的重点及方向. 本文可为进一步阐明砷在水生生物中的生物累积转化规律及砷的代谢毒性作用,为研究者进一步深入探索该领域内科学问题提供参考资料,同时对水产品安全、环境生态、医学等相关领域的研究具有一定的借鉴意义.Abstract: Arsenic is a bioaccumulative and biotoxic pollutant in global aquatic ecosystems and can be ubiquitously found in freshwater and marine environments. In the global biochemical cycle process, Arsenic can migrate, bioaccumulate, transform, and accumulate in aquatic organisms, resulting in toxic effects. The toxicity of Arsenic is related to its valences. Various studies have focused on preliminary research of Arsenic's behaviors and metabolic toxicology in aquatic environments. Still, a systematic review is not yet performed on the research progress, highlights, and trend. This paper summarized published reports and detailed the bioaccumulation and biotransformation processes of Arsenic in aquatic environments. It also addressed its toxic effects and metabolic mechanisms in aquatic biota, mice/rat, human, microorganisms, and other organisms. Also, we proposed the emphasis and direction of future work on Arsenic. This paper could serve as reference material for researchers exploring scientific issues in this and other close research fields, such as aquatic product safety, environmental ecology, and medicine.
-
Key words:
- arsenic /
- aquatic organisms /
- bioaccumulation /
- biotransformation /
- toxic effects /
- metabolic mechanisms.
-

-
表 1 国内外部分地区水产品含砷情况
Table 1. The concentration of Arsenic in aquatic products around the world
采样年份
Year地区
Region检测项目
Detection projects水产品种类
Aquatic products category含量/(mg·kg−1)
Concentration参考文献
Reference2010—2013 茂名市(中国) 无机砷
Inorganic Arsenic鱼类Fish ND—0.071 [43] 甲壳类Crustaceans ND—0.073 双壳类Bivalves ND—0.040 无壳类 Shellless ND—0.120 2012 巴伦支海
Barents sea总砷
Total Arsenic红帝王蟹
Paralithodes camtschaticus10.000±5.000 [44] 2015 韩国
Korea总砷
Total Arsenic头足类动物Cephalopods 2.620—13.100 [45] 2015 绍兴市(中国) 总砷
Total Arsenic淡水甲壳类
Freshwater crustaceansND—0.710 [46] 淡水鱼类
Freshwater fishND—0.740 海水甲壳类
Marine crustaceans0.042—7.300 海水双壳类
Marine bivalvesND—1.510 海水头足类
Marine cephalopodsND—4.260 海水鱼类Marine fish 0.028—3.900 2016—2017 浙江省(中国) 无机砷
Inorganic Arsenic贝类Bivalves <0.100 [47] 虾类Shrimp <0.100 鱼类Fish <0.100 头足类Cephalopods <0.100 2017 保定市(中国) 总砷
Total Arsenic淡水鱼Freshwater fish 0.024—0.250 [48] 河虾River shrimp 0.180—0.525 河蟹River crab 0.660—2.680 2017 德比湖(波兰)
Lake Dabie (Poland)总砷
Total Arsenic中华绒螯蟹
Eriocheir sinensis0.031—0.191 [49] 2018 上海市(中国) 总砷
Total Arsenic淡水鱼类Freshwater fish 0.005—0.474 [50] 海水鱼类Marine fish 0.035—13.000 淡水甲壳类
Freshwater crustaceans0.052—0.905 海水甲壳类
Marine crustaceans0.010—6.580 头足类Cephalopods 0.021—0.475 双壳类Bivalves 0.020—0.472 2018 孟加拉国
Bangladesh总砷
Total Arsenic滇西低线鱲Barilius barila 0.083±0.023 [51] 剑鲑口波鱼Salmostoma acinaces 0.021±0.001 印度小鳞鲥Gudusia chapra 0.278±0.074 露斯塔野鲮Labeo rohita <0.020 印度细齿鲱Corica soborna 0.161±0.037 剑鳠Sperata aor <0.020 2018 图苏库缇
(南印度)
Thoothukudi, (South India)总砷
Total Arsenic甲壳类 Crustaceans 3.190—16.500 [52] 头足类Cephalopods 1.100—9.190 2017—2020 广西省(中国) 无机砷
Inorganic Arsenic鱼类 Fish ND—0.276 [53] 虾 Shrimp ND—1.141 螺 Screw ND—0.150 蟹 Crab ND—1.513 贝类Bivalves ND—0.138 ND:Not Detected. 表 2 部分组织或国家砷限量比较
Table 2. The comparison of arsenic limited value in some organizations or countries
组织或国家
Organizations or countries水产品类别
Aquatic products category限量值/(mg·kg−1)
Limited value参考文献
Reference总砷*
Total Arsenic无机砷**
Inorganic Arsenic孟加拉国
Bangladesh— — — [51] CAC
Codex Alimentarius Commission— — — [54] 欧盟
European Union— — — 日本
Japan— — — 韩国
Korea— — — 澳大利亚
Australia鱼类Fish — 2.000 甲壳类Crustaceans — 2.000 软体动物Mollusk — 1.000 中国
China水产动物及其制品
Aquatic animals and their products— 0.500 [55] 鱼类及其制品
Fish and fish products— 0.100 印度尼西亚
Indonesia海藻Seaweed 1.000 — [56] 鱼类制品Fish products 2.000 — 美国
the United States of America甲壳类Crustaceans 76.000 — [57] 贝类Bivalves 86.000 — 注:“—”表示该国家或组织未对水产品中总砷及无机砷进行限量规定;*以总砷计,**先测定总砷,若总砷含量水平超过无机砷限量值则需测定无机砷. Note:"-" indicates that the countries or organizations do not set the limited value of total Arsenic and inorganic Arsenic in aquatic products; *measured as total Arsenic, ** measured total Arsenic first, if the total Arsenic content level exceeds the limited value of inorganic Arsenic, then measured inorganic Arsenic. -
[1] ANDRES J, BERTIN P N. The microbial genomics of arsenic[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2016, 40(2): 299-322. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv050 [2] CROGNALE S, ZECCHIN S, AMALFITANO S, et al. Phylogenetic structure and metabolic properties of microbial communities in arsenic-rich waters of geothermal origin[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 2468. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02468 [3] BISSEN M, FRIMMEL F H. Arsenic—a review. part Ⅰ: Occurrence, toxicity, speciation, mobility[J]. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 2003, 31(1): 9-18. doi: 10.1002/aheh.200390025 [4] 陈朋, 晏磊, 王雄, 等. 砷的生物转化与代谢机制研究进展[J]. 生命科学研究, 2013, 17(6): 554-560. CHEN P, YAN L, WANG X, et al. Progresses on biotransformation and metabolic mechanism of arsenic[J]. Life Science Research, 2013, 17(6): 554-560(in Chinese).
[5] NAUJOKAS M F, ANDERSON B, AHSAN H, et al. The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: Update on a worldwide public health problem[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2013, 121(3): 295-302. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1205875 [6] SHARMA V K, SOHN M. Aquatic arsenic: Toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation[J]. Environment International, 2009, 35(4): 743-759. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2009.01.005 [7] NIEGEL C, MATYSIK F M. Analytical methods for the determination of arsenosugars—A review of recent trends and developments[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2010, 657(2): 83-99. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.10.041 [8] 刘香丽, 汪倩, 宋超, 等. 不同砷形态在水产品中的毒理及转化研究进展[J]. 农学学报, 2019, 9(12): 33-38. doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas20190500026 LIU X L, WANG Q, SONG C, et al. Arsenic forms in aquatic products: Progress research on toxicology and transformation[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2019, 9(12): 33-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas20190500026
[9] 於海燕. 铁对砷代谢及毒性效应影响的体外胃肠模拟研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2016. YU H Y. Arsenic metabolism and toxicity influenced by ferric iron in simulated gastrointestinal tract[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2016. (in Chinese).
[10] DOPP E, HARTMANN L M, von RECKLINGHAUSEN U, et al. Forced uptake of trivalent and pentavalent methylated and inorganic arsenic and its cyto-/ genotoxicity in fibroblasts and hepatoma cells[J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2005, 87(1): 46-56. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi218 [11] BYEON E, KANG H M, YOON C, et al. Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic compounds in aquatic organisms[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2021, 237: 105901. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105901 [12] ESETLILI M T, ESETLILI B C, OZEN F, et al. Determination of the arsenic pollution due to geothermal sources in the agricultural lands of alangulluaydin region[J]. Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology, 2014, 15(4): 1555-1563. [13] BAE H S, KANG I G, LEE S G, et al. Arsenic exposure and seafood intake in Korean adults[J]. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 2017, 36(5): 451-460. [14] NG J C, WANG J P, SHRAIM A. A global health problem caused by arsenic from natural sources[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 52(9): 1353-1359. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00470-3 [15] NIÑO S A, MORALES-MARTÍNEZ A, CHI-AHUMADA E, et al. Arsenic exposure contributes to the bioenergetic damage in an Alzheimer's disease model[J]. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 2019, 10(1): 323-336. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00278 [16] 王琛绯, 石明, 王佳婷, 等. 食物慢性砷暴露对小鼠脑组织中砷形态的影响[J]. 现代食品科技, 2020, 36(7): 289-297. WANG C F, SHI M, WANG J T, et al. Arsenic species analyses of mice brain under chronic arsenic exposure through food[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2020, 36(7): 289-297(in Chinese).
[17] WANG C F, DENG H Y, WANG D B, et al. Changes in metabolomics and lipidomics in brain tissue and their correlations with the gut microbiome after chronic food-derived arsenic exposure in mice[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 228: 112935. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112935 [18] LIN C, PING M L, ZHANG X, et al. In vitro bio-accessibility and distribution characteristic of each arsenic species in different fishes and shellfishes/shrimps collected from Fujian of China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 420: 126660. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126660 [19] CHEN L Z, ZHANG W, GUO Z Q, et al. Effects of acclimation on arsenic bioaccumulation and biotransformation in freshwater medaka Oryzias mekongensis after chronic arsenic exposure[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 238: 17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.011 [20] CUI D, ZHANG P, LI H P, et al. The dynamic effects of different inorganic arsenic species in crucian carp ( Carassius auratus) liver during chronic dietborne exposure: Bioaccumulation, biotransformation and oxidative stress[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 727: 138737. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138737 [21] CUI D, ZHANG P, LI H P, et al. The dynamic changes of arsenic biotransformation and bioaccumulation in muscle of freshwater food fish crucian carp during chronic dietborne exposure[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 100: 74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.07.005 [22] KIM J H, KANG J C. The arsenic accumulation and its effect on oxidative stress responses in juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, exposed to waterborne arsenic (As3+)[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2015, 39(2): 668-676. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.01.012 [23] KUMAR R, BANERJEE T K. Analysis of arsenic bioaccumulation in different organs of the nutritionally important catfish, Clarias batrachus (L. ) exposed to the trivalent arsenic salt, sodium arsenite[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2012, 89(3): 445-449. doi: 10.1007/s00128-012-0714-8 [24] JUNCOS R, ARCAGNI M, SQUADRONE S, et al. Interspecific differences in the bioaccumulation of arsenic of three Patagonian top predator fish: Organ distribution and arsenic speciation[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 168: 431-442. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.077 [25] JUMA H, BATTAH A, SALIM M, et al. Arsenic and cadmium levels in imported fresh and frozen fish in Jordan[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2002, 68(1): 132-137. doi: 10.1007/s00128-001-0229-1 [26] NAIR M, JAYALAKSHMY K V, BALACHANDRAN K K, et al. Bioaccumulation of toxic metals by fish in a semi-enclosed tropical ecosystem[J]. Environmental Forensics, 2006, 7(3): 197-206. doi: 10.1080/15275920600840438 [27] 杜森, 张黎. 砷在海洋食物链中的生物放大潜力及发生机制探讨[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(1): 54-66. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20181112002 DU S, ZHANG L. Biomagnification potential and the mechanisms of arsenic in marine food chains[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(1): 54-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20181112002
[28] 宋梦萍, 杨常亮, 张璟, 等. 食物相暴露条件下尼罗罗非鱼对砷的累积与转化[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(6): 1897-1904. SONG M P, YANG C L, ZHANG J, et al. Accumulation and transformation of arsenic in Oreochromis niloticus under food phase exposure[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(6): 1897-1904(in Chinese).
[29] HONG S, KHIM J S, PARK J, et al. Species- and tissue-specific bioaccumulation of arsenicals in various aquatic organisms from a highly industrialized area in the Pohang City, Korea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 192: 27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.05.004 [30] ZHANG W, WANG W X, ZHANG L. Arsenic speciation and spatial and inter species differences of metal concentrations in mollusks and crustaceans from a South China Estuary[J]. Ecotoxicology, 2013, 22((4): ): 671-682. doi: 10.1007/s10646-013-1059-8 [31] DEVESA V, SÚÑER M A, LAI V W M, et al. Distribution of arsenic species in the freshwater crustacean Procambarus clarkii[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2002, 16(12): 692-700. doi: 10.1002/aoc.374 [32] LIAO Z H, CHUANG H C, HUANG H T, et al. Bioaccumulation of arsenic and immunotoxic effect in white shrimp ( Penaeus vannamei) exposed to trivalent arsenic[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2022, 122: 376-385. [33] YAMAGUCHI S, CELINO F T, ITO A, et al. Effects of arsenic on gonadal development in freshwater crab, Somanniathelphusa pax, in Vietnam and Geothelphusa dehaani in Japan[J]. Ecotoxicology (London, England), 2008, 17(8): 772-780. doi: 10.1007/s10646-008-0228-7 [34] RADKE B, DEMBSKA G, PAZIKOWSKA-SAPOTA G, et al. Many faces of arsenic[J]. Oceanological and Hydrobiological Studies, 2019, 48(1): 90-104. doi: 10.1515/ohs-2019-0010 [35] JEON C, PARK J Y, YOO Y J. Characteristics of metal removal using carboxylated alginic acid[J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(7): 1814-1824. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00389-X [36] WOLFE-SIMON F, SWITZER BLUM J, KULP T R, et al. A bacterium that can grow by using arsenic instead of phosphorus[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6034): 1163-1166. doi: 10.1126/science.1197258 [37] LIN Y B, HUANG Z X, WU L, et al. Influence of phosphorus on the uptake and biotransformation of arsenic in Porphyra haitanensis at environmental relevant concentrations[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 800: 149534. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149534 [38] ELIAS M, WELLNER A, GOLDIN-AZULAY K, et al. The molecular basis of phosphate discrimination in arsenate-rich environments[J]. Nature, 2012, 491(7422): 134-137. doi: 10.1038/nature11517 [39] BAHAR M M, MEGHARAJ M, NAIDU R. Influence of phosphate on toxicity and bioaccumulation of arsenic in a soil isolate of microalga Chlorella sp[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(3): 2663-2668. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5510-7 [40] RODRIGUEZ CASTRO M C, URREA G, GUASCH H. Influence of the interaction between phosphate and arsenate on periphyton's growth and its nutrient uptake capacity[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 503/504: 122-132. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.094 [41] ZHANG S, DENG R, LIN D H, et al. Distinct toxic interactions of TiO2 nanoparticles with four coexisting organochlorine contaminants on algae[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2017, 11(9/10): 1115-1126. [42] LUO Z X, WANG Z H, YAN Y M, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles enhance inorganic arsenic bioavailability and methylation in two freshwater algae species[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 238: 631-637. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.070 [43] 李海丽, 王丽, 古雪香, 等. 茂名市主要水产品中无机砷含量分析及其健康风险评价[J]. 食品工业, 2020, 41(10): 337-340. LI H L, WANG L, GU X X, et al. Analysis of inorganic arsenic content and health risk assessment in main aquatic products in Maoming[J]. The Food Industry, 2020, 41(10): 337-340(in Chinese).
[44] JULSHAMN K, VALDERSNES S, DUINKER A, et al. Heavy metals and POPs in red king crab from the Barents Sea[J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 167: 409-417. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.003 [45] NHO E Y, KHAN N, CHOI J Y, et al. Determination of toxic metals in cephalopods from south Korea[J]. Analytical Letters, 2016, 49(10): 1578-1588. doi: 10.1080/00032719.2015.1107082 [46] 樊伟, 王晶, 王若燕, 等. 绍兴市水产品中6种重金属调查[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2017, 34(6): 536-538. doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2017.06.017 FAN W, WANG J, WANG R Y, et al. Investigation of 6 heavy metals in aquatic products of Shaoxing City[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2017, 34(6): 536-538(in Chinese). doi: 10.16241/j.cnki.1001-5914.2017.06.017
[47] 梅光明, 严国, 常家琪, 等. 浙江沿海海产品无机砷污染调查及食用风险分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(12): 218-223, 229. MEI G M, YAN G, CHANG J Q, et al. Investigation on inorganic arsenic pollution of seafood in Zhejiang coast and potential dietary health risk assessment[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(12): 218-223, 229(in Chinese).
[48] 杨磊, 崔建超. 保定地区食品中有害元素污染状况调查[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2017, 27(22): 3307-3309. YANG L, CUI J C. Investigation on harmful elements contamination in food in Baoding[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2017, 27(22): 3307-3309(in Chinese).
[49] NĘDZAREK A, CZERNIEJEWSKI P, DROST A, et al. The distribution of elements in the body of invasive Chinese mitten crabs ( Eriocheir sinensis H. Milne-Edwards, 1853) from Lake Dąbie, Poland[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2017, 60: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2017.03.003 [50] 蔡华, 罗宝章, 熊丽蓓, 等. 上海市水产品中重金属污染情况[J]. 卫生研究, 2018, 47(5): 740-743. CAI H, LUO B Z, XIONG L B, et al. Heavy metal pollution in aquatic products in Shanghai[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2018, 47(5): 740-743(in Chinese).
[51] SHORNA S, SHAWKAT S, HOSSAIN A, et al. Accumulation of trace metals in indigenous fish species from the old Brahmaputra River in Bangladesh and human health risk implications[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2021, 199(9): 3478-3488. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02450-y [52] SHALINI R, JEYASEKARAN G, SHAKILA R J, et al. Concentrations of trace elements in the organs of commercially exploited crustaceans and cephalopods caught in the waters of Thoothukudi, South India[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 154: 111045. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111045 [53] 陈清德, 黄艳桃, 唐琼, 等. 2017—2020年广西市售水产品重金属污染评价及健康风险评估[J]. 职业与健康, 2021, 37(17): 2332-2335. CHEN Q D, HUANG Y T, TANG Q, et al. Evaluation on heavy metals pollution and assessment on health risk of commercial aquatic products in Guangxi Province from 2017-2020[J]. Occupation and Health, 2021, 37(17): 2332-2335(in Chinese).
[54] 陈丽辉. 中国与主要国际组织、发达国家水产品中重金属限量比对分析研究[J]. 渔业研究, 2020, 42(4): 394-403. CHEN L H. Comparative analysis of the limited quantity of heavy metals in aquatic products of China with major international organizations and developed countries[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2020, 42(4): 394-403(in Chinese).
[55] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量: GB 2762—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. National Food Safety Standard Limited of Contaminana in Food: GB 2762—2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017(in Chinese).
[56] Indonesian Food and Drug Administration. G/SPS/N/IDN/142, Draft Regulation of Indonesian Food and Drug Authority of The Republic of Indonesia on Heavy Metals Contaminants Requirements in Processed Food[EB/OL]. Indonesia, 2022: 8-11 (2022-2-3), [2022-6-11]. [57] 乔艺飘, 张龙飞, 顾润润, 等. 高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定水产品中砷形态的研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1084-1097. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019122003 QIAO Y P, ZHANG L F, GU R R, et al. Determination of arsenic species in aquatic products by high performance liquid chromatography inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1084-1097(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019122003
[58] RAHMAN M A, HASSLER C. Is arsenic biotransformation a detoxification mechanism for microorganisms?[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2014, 146: 212-219. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.11.009 [59] JAISHANKAR M, TSETEN T, ANBALAGAN N, et al. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals[J]. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 2014, 7(2): 60-72. doi: 10.2478/intox-2014-0009 [60] SINGH N, KUMAR D, SAHU A P. Arsenic in the environment: Effects on human health and possible prevention[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2007, 28(2 Suppl): 359-365. [61] ZHANG W, GUO Z Q, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Biotransformation and detoxification of inorganic arsenic in Bombay oyster Saccostrea cucullata[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2015, 158: 33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.10.021 [62] ZHANG W, MIAO A J, WANG N X, et al. Arsenic bioaccumulation and biotransformation in aquatic organisms[J]. Environment International, 2022, 163: 107221. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107221 [63] MEHMOOD M A, QADRI H, BHAT R A, et al. Heavy metal contamination in two commercial fish species of a trans-Himalayan freshwater ecosystem[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2019, 191(2): 104. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7245-2 [64] RAHMAN M A, HOGAN B, DUNCAN E, et al. Toxicity of arsenic species to three freshwater organisms and biotransformation of inorganic arsenic by freshwater phytoplankton ( Chlorella sp. CE-35)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 106: 126-135. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.03.004 [65] HE Q, QU R J, WANG X H, et al. Toxicity of arsenic to Photobacterium phosphoreum, Daphnia magna, and Danio rerio at different pH levels[J]. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 2016, 44(1): 72-77. doi: 10.1002/clen.201400124 [66] ROSEN B P. Biochemistry of arsenic detoxification[J]. FEBS Letters, 2002, 529(1): 86-92. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03186-1 [67] 王旭, 董燕, 耿安静, 等. 4种形态砷在大鼠体内的药物动力学及亚急性毒性比较研究[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2017, 29(4): 400-406. WANG X, DONG Y, GENG A J, et al. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and subacute toxicity for four arsenic species in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2017, 29(4): 400-406(in Chinese).
[68] 赵梦醒, 刘淇, 曹荣, 等. 海带中砷在大鼠体内代谢过程中的形态变化[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(8): 54-60. ZHAO M X, LIU Q, CAO R, et al. Changes of species of arsenic in kelp during metabolism in rats[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(8): 54-60(in Chinese).
[69] 于霄云, 钟媛, 牛玉红, 等. 谷胱甘肽与亚硒酸钠对饮水砷暴露小鼠体内砷代谢的影响[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2008, 42(9): 636-639. YU X Y, ZHONG Y, NIU Y H, et al. Effect of glutathione and sodium selenite on the metabolism of arsenic in mice exposed to arsenic through drinking water[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2008, 42(9): 636-639 (in Chinese).
[70] 代华, 夏茵茵, Ting-Li Han, 等. 慢性砷暴露对小鼠脑和血清代谢组学的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(9): 1192-1197. DAI H, XIA Y Y, TING-LI H, et al. Effect of chronic arsenic exposure on mouse brain tissue and serum metabolomics[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(9): 1192-1197(in Chinese).
[71] HE Z X, XU Y D, MA Q L, et al. SOX2 modulated astrocytic process plasticity is involved in arsenic-induced metabolic disorders[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 435: 128942. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128942 [72] ZHONG G L, WAN F, WU S F, et al. Arsenic or/and antimony induced mitophagy and apoptosis associated with metabolic abnormalities and oxidative stress in the liver of mice[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 777: 146082. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146082 [73] 王艳艳, 姜红梅, 安玉, 等. 三氧化二砷对小鼠大脑组织神经递质代谢酶基因及其受体基因表达谱的影响[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2012, 29(11): 671-673. WANG Y Y, JIANG H M, AN Y, et al. Influence of arsenic trioxide on gene expression profiles of metabolic enzymes and receptors for neurotransmitters in Cerebrum of mice[J]. Journal of Environmental & Occupational Medicine, 2012, 29(11): 671-673(in Chinese).
[74] 王健龄, 苏伟, 凌志, 等. 慢性饮水砷暴露小鼠无机砷代谢产物的蓄积与分布[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2019, 36(10): 912-917. WANG J L, SU W, LING Z, et al. Accumulation and distributions of inorganic arsenic metabolites in tissue of mice chronically exposed to arsenic in drinking water[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2019, 36(10): 912-917(in Chinese).
[75] 杨慧, 戴守辉, 王富华, 等. 海产品中的砷形态及其毒理代谢研究[J]. 农产品质量与安全, 2017(1): 21-26, 32. YANG H, DAI S H, WANG F H, et al. Overview on arsenic speciation, its metabolism and toxicity in seafood[J]. Quality and Safety of Agro-Products, 2017(1): 21-26, 32(in Chinese).
[76] KENYON E M, HUGHES M F. A concise review of the toxicity and carcinogenicity of dimethylarsinic acid[J]. Toxicology, 2001, 160(1/2/3): 227-236. [77] 汤施展, 陈中祥, 黄晓丽, 等. 水产品中砷形态分析研究进展[J]. 水产学杂志, 2019, 32(2): 55-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2019.02.009 TANG S Z, CHEN Z X, HUANG X L, et al. Progress in analysis of arsenic speciation in fishery products[J]. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2019, 32(2): 55-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2019.02.009
[78] 李晗君, 林婧, 李玉锋, 等. 亚慢性砷暴露小鼠体内不同形态砷的分布及对DNA的损伤作用[J]. 卫生研究, 2013, 42(5): 764-769, 776. doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2013.05.010 LI H J, LIN J, LI Y F, et al. Distribution of arsenic species and its DNA damage in subchronic arsenite-exposed mice[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2013, 42(5): 764-769, 776(in Chinese). doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2013.05.010
[79] FABINYI M, LIU N, SONG Q Y, et al. Aquatic product consumption patterns and perceptions among the Chinese middle class[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2016, 7: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2016.01.013 [80] TSENG C H. A review on environmental factors regulating arsenic methylation in humans[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2009, 235(3): 338-350. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.12.016 [81] THOMAS D J, STYBLO M, LIN S. The cellular metabolism and systemic toxicity of arsenic[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2001, 176(2): 127-144. doi: 10.1006/taap.2001.9258 [82] SCHLÄWICKE ENGSTRÖM K, BROBERG K, CONCHA G, et al. Genetic polymorphisms influencing arsenic metabolism: Evidence from Argentina[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2007, 115(4): 599-605. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9734 [83] MOLIN M, ULVEN S M, MELTZER H M, et al. Arsenic in the human food chain, biotransformation and toxicology - Review focusing on seafood arsenic[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2015, 31: 249-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2015.01.010 [84] 袁雪花, 苏玉红. 奎屯高砷地下水灌溉区居民头发和指甲中砷含量研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(4): 1519-1523. YUAN X H, SU Y H. On the arsenic content rate in the hair and nail of the residents due to the high arsenic groundwater pollution in Kuitun irrigated area, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(4): 1519-1523(in Chinese).
[85] ORLOFF K, MISTRY K, METCALF S. Biomonitoring for environmental exposures to arsenic[J]. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. Part B, Critical Reviews, 2009, 12(7): 509-524. doi: 10.1080/10937400903358934 [86] 李昕, 徐苑苑, 李冰, 等. 砷暴露母子砷代谢特点及DNA损伤差异[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2006, 22(9): 1099-1100. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0580.2006.09.042 LI X, XU Y Y, LI B, et al. Study on characteristics of arsenic metabolism and DNA damage between mother and child under arsenic exposure[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2006, 22(9): 1099-1100(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0580.2006.09.042
[87] TSENG C H, HUANG Y K, HUANG Y L, et al. Arsenic exposure, urinary arsenic speciation, and peripheral vascular disease in Blackfoot disease-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2005, 206(3): 299-308. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2004.11.022 [88] WANG X X, MU X L, ZHANG J, et al. Serum metabolomics reveals that arsenic exposure disrupted lipid and amino acid metabolism in rats: A step forward in understanding chronic arsenic toxicity[J]. Metallomics, 2015, 7(3): 544-552. doi: 10.1039/C5MT00002E [89] WU G Y, FANG Y Z, YANG S, et al. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health[J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2004, 134(3): 489-492. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.3.489 [90] FLORA S J S. Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2011, 51(2): 257-281. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.008 [91] SHI H L, SHI X L, LIU K J. Oxidative mechanism of arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2004, 255(1/2): 67-78. doi: 10.1023/B:MCBI.0000007262.26044.e8 [92] 杜航, 龚进, 代华, 等. 慢性砷中毒患者头发代谢物特征的代谢组学研究[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2018, 35(2): 163-167. DU H, GONG J, DAI H, et al. Metabonomics study on metabolic profile of hair samples from chronic arsenic poisoning patients[J]. Journal of Environmental & Occupational Medicine, 2018, 35(2): 163-167(in Chinese).
[93] MEZA M, GANDOLFI A J, KLIMECKI W T. Developmental and genetic modulation of arsenic biotransformation: A gene by environment interaction?[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2007, 222(3): 381-387. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.12.018 [94] VAHTER M, AKESSON A, LIDÉN C, et al. Gender differences in the disposition and toxicity of metals[J]. Environmental Research, 2007, 104(1): 85-95. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2006.08.003 [95] HUANG Y K, TSENG C H, HUANG Y L, et al. Arsenic methylation capability and hypertension risk in subjects living in arseniasis-hyperendemic areas in southwestern Taiwan[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2007, 218(2): 135-142. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.10.022 [96] WANG Y, WANG S, XU P P, et al. Review of arsenic speciation, toxicity and metabolism in microalgae[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2015, 14(3): 427-451. doi: 10.1007/s11157-015-9371-9 [97] WANG H T, LIANG Z Z, DING J, et al. Arsenic bioaccumulation in the soil fauna alters its gut microbiome and microbial arsenic biotransformation capacity[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 417: 126018. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126018 [98] ZHANG S Y, RENSING C, ZHU Y G. Cyanobacteria-mediated arsenic redox dynamics is regulated by phosphate in aquatic environments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(2): 994-1000. [99] WANG Z H, LUO Z X, YAN C Z. Accumulation, transformation, and release of inorganic arsenic by the freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2013, 20(10): 7286-7295. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1741-7 [100] INSKEEP W P, MACUR R E, HAMAMURA N, et al. Detection, diversity and expression of aerobic bacterial arsenite oxidase genes[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 9(4): 934-943. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01215.x [101] ROSEN B P, LIU Z J. Transport pathways for arsenic and selenium: A minireview[J]. Environment International, 2009, 35(3): 512-515. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2008.07.023 [102] CLEISS-ARNOLD J, KOECHLER S, PROUX C, et al. Temporal transcriptomic response during arsenic stress in Herminiimonas arsenicoxydans[J]. BMC Genomics, 2010, 11: 709. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-709 [103] OREMLAND R S, STOLZ J F. The ecology of arsenic[J]. Science, 2003, 300(5621): 939-944. doi: 10.1126/science.1081903 [104] HUANG J H. Impact of microorganisms on arsenic biogeochemistry: A review[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2014, 225(2): 1-25. [105] SILVER S, PHUNG L T. Genes and enzymes involved in bacterial oxidation and reduction of inorganic arsenic[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(2): 599-608. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.2.599-608.2005 -



 下载:
下载: