-
磁性纳米铁具有特殊的物理化学性质,随着纳米科学技术的快速发展,磁性纳米铁已成功应用于催化、生物技术、生物医药、磁共振成像、数据存储、生物传感器、环境污染物去除等广泛领域[1],但与此同时,此种材料所带来的潜在环境危害也有所增加[2]. 磁性纳米铁除了被用于土壤污染物去除(例如去除土壤中的重金属离子、有机污染物、无机污染物)时进入土壤,还会在生产与废弃过程中通过各种途径以“三废”的形式在土壤中积累[3].
土壤为陆生生物提供生活所必需的矿质元素和水分,是生态系统中物质与能量交换的重要场所;同时也是生态系统中生物部分和无机环境部分相互作用的产物[4]. 磁性纳米铁在土壤中的积累除了会对土壤理化性质、酶活性和温室气体排出造成影响,还会影响到土壤微生物群落的结构、功能和代谢,从而影响到整个土壤生态系统[5]. 本研究以此为出发点,总结了磁性纳米铁(以四氧化三铁磁性纳米颗粒(Fe3O4-NPs)、三氧化二铁磁性纳米颗粒(Fe2O3-NPs)和纳米零价铁(nZVI-NPs)为主)在土壤中积累所带来影响的相关研究,以期为合理利用磁性纳米铁修复土壤污染的同时尽可能减少对土壤以及微生物的危害提供理论依据.
-
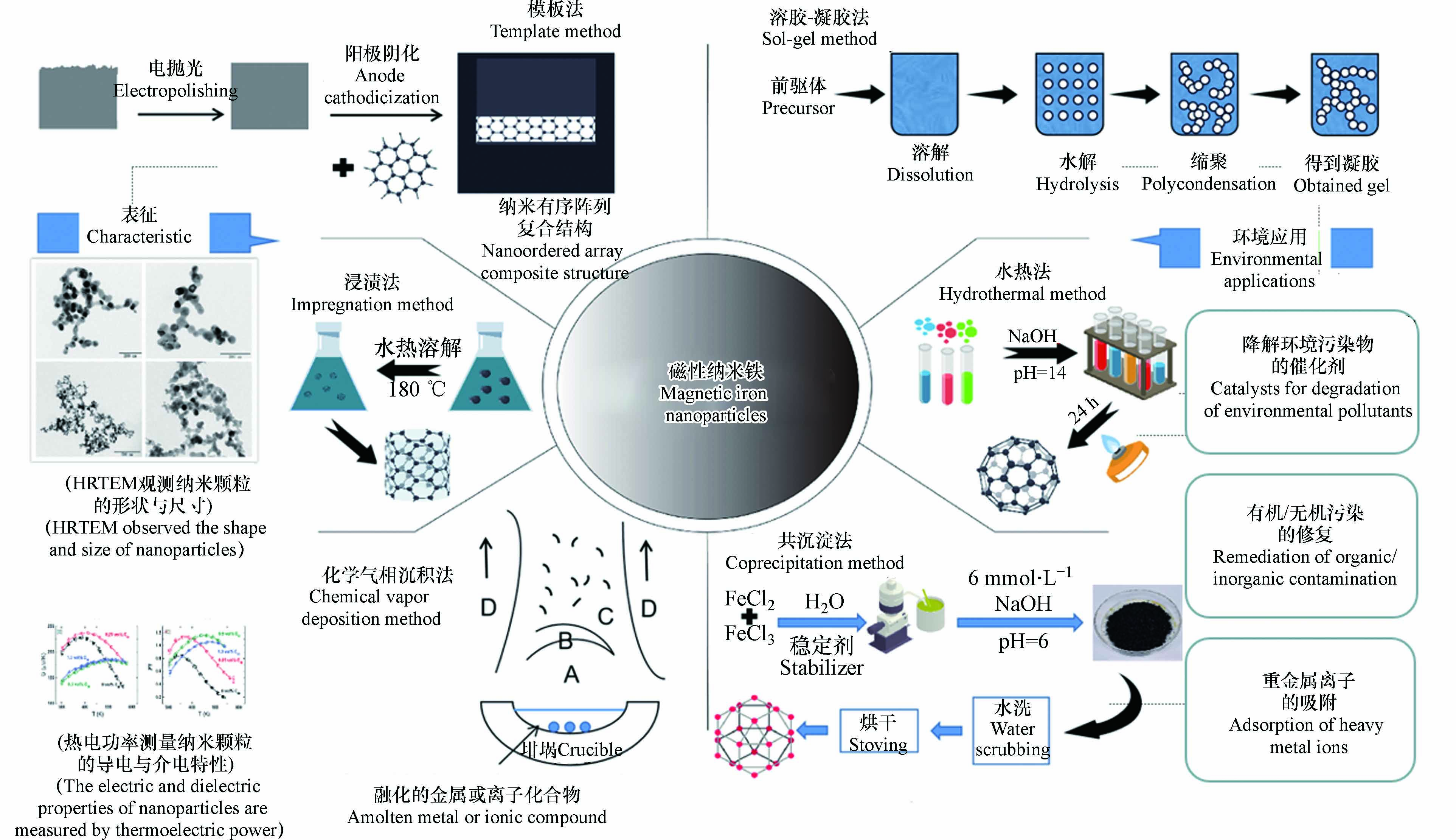
磁性纳米铁可以通过原子组装或块体材料断裂来制备,常用的制备方法有溶胶-凝胶法、水热法、共沉淀法、浸渍法、模板法、化学气相沉积法(图1)[6].
溶胶-凝胶法制备Fe3O4-NPs以亚硝酸铁为前驱体经过溶解、水解、缩聚、老化等步骤制得[7];采用水热法制备Fe2O3-NPs,样品形成的起始点是由氢氧化钠、去离子水、乙醇和油酸混合制备的溶液与七水硫酸铁水溶液混合后电磁搅拌6 h,将混合溶液在160 ℃加热24 h后,在去离子水和乙醇中洗涤6次,在75 ℃温度下干燥12 h后得到[8];采用化学共沉淀法合成Fe3O4-NPs的材料有: 六水合氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)、四水合氯化铁(FeCl2·4H2O)、水溶液混合后得到混合溶液,向混合溶液中添加NaOH将混合溶液pH调整至6后共沉淀生成Fe3O4-NPs;用浸渍法制备Fe2O3-NPs时,首先是将制备好的水凝胶与铁盐浸渍,然后在180 ℃温度下煅烧,合成分散在硅干凝胶中不同含量的Fe2O3-NPs样品[9];在绿色合成战略中,对环境无害的溶剂、无毒化学品和可再生材料的利用是要考虑的一些关键问题,例如利用纤维素薄膜作为辅助材料,通过电抛光、阳极阴化等步骤合成了单分散磁性Fe2O3-NPs[10];化学气相沉积是一种用于生产高质量、高性能固体材料的化学过程. 在利用化学气相沉积法合成Fe2O3-NPs、Fe3O4-NPs的过程中,水(基材)暴露在一种或多种挥发性前驱体中,这些前驱体在基材表面发生反应和分解,以产生所需的沉积[11].
nZVI-NPs的合成可以通过铣削、蚀刻和机加工等机械和化学过程将大尺寸材料转化为nZVI-NPs;或是通过化学合成、自组装、位置组装等方法逐个将原子或分子组装为nZVI-NPs,具体可分为氯化铁合成法、硫酸亚铁合成法以及自上而下法合成nZVI-NPs[12].
-
为了研究不同合成技术制备的磁性纳米铁的性能,目前已有多种技术用于磁性纳米铁的表征,例如采用X射线衍射(XRD)、场发射散射电子显微镜(FESEM)、高分辨透射电子显微镜(HRTEM)、原子力显微镜(AFM)、光子相关光谱(PCS)、动态光散射(DLS)、凝聚粒子计数器(CPC)等设备获得所制备样品的尺寸和形状,通过扫描电子显微镜、透射电子显微镜等设备观察纳米粒子的表面形貌以及长度和直径[13 − 14].
介电损耗切线、电阻率、电导率等是研究者通常观察到的磁性纳米铁的性质. 热电功率(TEP)测量和红外光谱证实,激光辐照纳米颗粒后,随着温度的升高,纳米颗粒的电导率增加,电阻率降低[15]. 磁性纳米铁的光电导性质,无论正负,都可以通过对光电导研究来证实,同时在对磁性纳米铁光学性质的表征上,目前已有一系列模型来确定纳米颗粒的光学性质,但其中最流行的模型是Tauc模型[16]. Tauc模型目前已经被用来观察铁酸镁(MgFe2O4)纳米材料的能量带隙等光学性质[17].
-
磁性纳米铁作为一种新型的纳米材料,因其独特的性质,如纳米效应、磁性、热/pH敏感性、生物相容性和稳定性等而备受关注[18]. 因此,磁性纳米铁应用越来越广泛,特别是在环境保护领域,例如作为环境污染物的催化剂、有机/无机污染物的环境修复治理等. 本节讨论了铁基磁性纳米材料用于环境应用的最新进展[19].
-
磁性纳米铁可以作为催化剂将污染物分子分解或转化为毒性较小的代谢物. 浸渍氧化-沉淀法合成的Fe3O4-NPs是降解泮托拉唑的非均相催化剂,在最佳条件下降解效率达到98.0%[20]. 另一种采用先进的反向共沉淀法制备的Fe3O4-NPs在超声辐照和活化H2O2作用下,60 min内可以降解约90%的罗丹明B[21]. 此外,Fe3O4-NPs还被用作非均相催化剂载体,以获得易于分散在普通溶剂中、高比表面积和可重复利用性的生物制品[22]. 例如,制备氨基功能化的Fe3O4-NPs并将其与戊二醛偶联(粒径范围为10—100 nm),可催化多种生物转化反应,包括乙酸乙酯合成和植物油酯交换制备生物柴油[23].
-
近年来,nZVI-NPs因其卓越的环境修复能力而受到极大关注. 它们的修复机制取决于nZVI-NPs的吸附和还原性能以及污染物的性质[24]. 实验研究表明,nZVI-NPs可以有效转化各种环境有机污染物,包括有机污染物,如卤代烃(如三氯乙烯)和有机染料(如甲基橙、紫红),采用nZVI-NPs对三氯乙烯进行脱氯,三氯乙烯去除率大于99%[25]. nZVI-NPs还可以有效转化多种环境无机污染物,包括重金属离子(如镍、汞、砷、铬)、放射性元素(如铀)和类金属(如硝酸盐或磷酸盐)[26].
-
利用Fe3O4-NPs修饰酵母细胞制成的纳米复合材料是去除铬的良好生物吸附剂[27]. Fe3O4-NPs修饰后的酵母细胞的吸附能力比未修饰的酵母细胞提高了3倍. 改性吸附剂对1000 mg·g−1铬溶液在最佳条件下的吸附量为186.32 mg·g−1,而未改性吸附剂的吸附量为137.31 mg·g−1[28]. 此外,表1归纳了部分通过各种方法合成的磁性纳米铁去除重金属应用的相关研究.
-
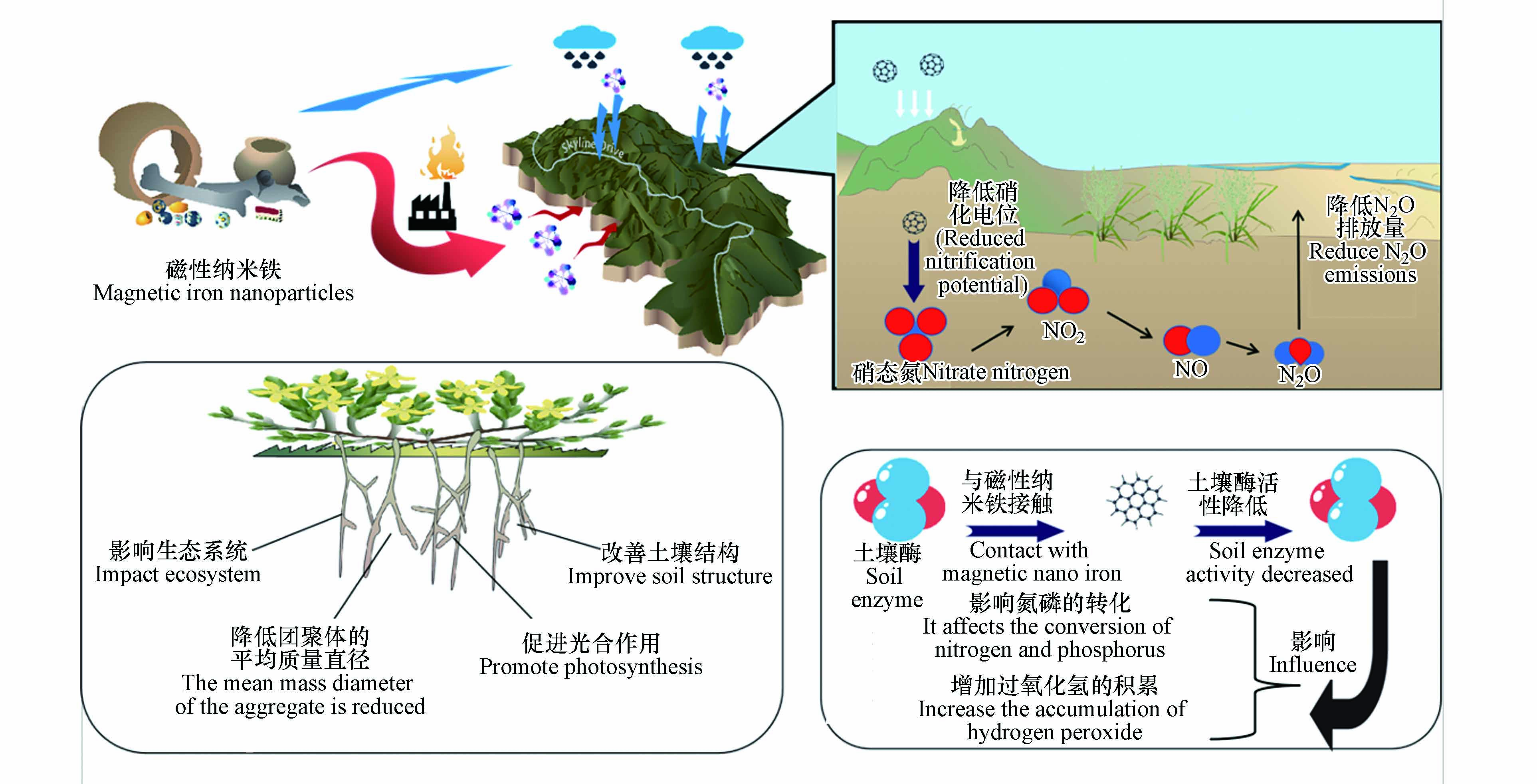
一些向环境释放大量磁性纳米铁的产品包括涂料、颜料、油漆、电子仪器,在生产阶段,大约有0.1%—2%的磁性纳米铁会到达环境中[35]. 其中进入土壤的磁性纳米铁占进入环境总量的10%—25%[36],磁性纳米铁不仅通过农业中的直接土地应用进入土壤(例如以磁性纳米铁为原料制成的具有成本效益、生物相容性和生物降解性的功能纳米材料被人为释放到土壤中以增加作物产量和有针对性地输送农药和营养物质,增强植物对各种胁迫因素的抵抗力,并作为纳米传感器检测各种污染物、植物疾病和植物营养不足)[37],还可通过垃圾焚烧进入大气沉积、降水和农业灌溉从大气和水环境中进入土壤[38],之后对土壤生态系统、团聚体的平均质量直径、光合作用和土壤结构等方面产生影响[39].
-
磁性纳米铁通过废物处理、空中沉积或污水处理厂等直接或间接处理方法进入土壤,因此需要了解磁性纳米铁与土壤之间的相互作用以及对土壤理化性质的影响[40],天然纳米颗粒如铁氧化物、黏土、有机质和其他矿物,是陆地生态系统进行生化过程的重要组成部分[41 − 42]. 磁性纳米铁的进入可能通过改变天然纳米颗粒的分布而影响土壤的发育或行为,从而影响生态系统[43]. 此外,磁性纳米铁的存在也会改变土壤性质,Sun等将Fe3O4-NPs应用于低钙寒农田,结果表明,Fe3O4-NPs降低了团聚体的平均质量直径,并且增加了土壤容重和土壤体积含水量. 此外,增加Fe3O4-NPs含量也会增加土壤的渗透阻力,从而使土壤的渗透阻力增大,减少根系生长,同时降低土壤饱和导水率,影响植物吸水[44 − 45]. 此外Fe3O4-NPs的积累会增加土壤中三价铁的浓度,从而使土壤pH值升高,pH的升高同样会影响植物生长. 另一方面,当土壤的水饱和时,三价铁可以转化为亚铁,亚铁参与其中叶绿素的合成,在光合作用中起着重要的作用[46].
此外,根据Yan等的研究,向土壤中释放Fe3O4-NPs会提高玉米的抗氧化能力,促进玉米的生长,其原因是Fe3O4-NPs造成土壤中叶绿素、糖、蛋白质和营养元素含量的增加以及丙二醛含量的降低,对土壤中的有机质含量产生了影响[47].
-
土壤酶是土壤中最活跃的有机成分之一[48],磁性纳米铁与土壤酶接触后,会降低部分土壤酶的活性,并最终会影响氮磷的转化、增加过氧化氢的积累、造成土壤肥力降低和对微生物产生不良影响. 此部分总结了磁性纳米铁对转化酶、脲酶、磷酸酶和过氧化氢酶等酶活性的影响,以评估磁性纳米铁对土壤酶活性的影响[49]. You等[50]用3种纳米材料(纳米氧化锌、纳米氧化铈、纳米氧化钛)与Fe3O4-NPs对土壤酶活性的影响进行比较,结果表明两种土壤微生物群落在纳米氧化锌处理后均表现出过氧化氢酶活性降低、脲酶活性升高的趋势. 此外,与对照相比,黑土中含纳米氧化锌的土壤转化酶活性显著提高,盐碱地土壤转化酶活性呈下降趋势,而在在黑土中,只有纳米氧化锌处理后显著降低了磷酸酶活性[50]. 因此,在上述几类磁性纳米铁中,纳米氧化锌对4种酶活性的影响均强于其他材料. 与含纳米氧化锌的土壤相比,含纳米氧化铈的土壤过氧化氢酶和磷酸酶活性与对照差异不显著,含纳米氧化铈的土壤的脲酶活性显著低于对照组. 纳米氧化钛和Fe3O4-NPs处理的过氧化氢酶和转化酶活性在盐碱地显著降低,而在黑土中不显著. 在不同浓度的磁性纳米铁处理下,黑土和盐碱土土壤酶活性变化一致[51].
此外,Fe2O3-NPs和Fe3O4-NPs增加土壤中转化酶和脲酶的数量,促进土壤中碳、氮的周转[52]. 然而,只有某些特定的细菌受益于这种变化,而不是整个土壤微生物种群,这是由于土壤微生物的脱氢酶没有得到增强[53].
-
通过各种途径释放到土壤中的磁性纳米铁不仅影响土壤养分循环,还影响CO2、CH4和N2O等温室气体的排放[54],并影响全球气候变化,N2O是全球变暖的重要温室气体之一[55],在100年时间尺度上其全球变暖趋势是CO2的298倍,生态系统过程在N2O排放中起着重要作用,农业系统每年排放N2O约为2.7亿t[56]. 不同类型的纳米颗粒直接影响土壤硝化和反硝化过程,并影响N2O的排放,例如磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒可显著影响土壤的硝化电位,从而降低土壤中N2O的排放量,硝化菌和反硝化菌对纳米颗粒的响应随纳米颗粒类型和土壤类型的不同而不同[57](如图2所示).
Fe2O3-NPs由于其所具有的磁性从而对土壤呼吸产生影响,在Fe2O3-NPs磁性的辐射作用下,土壤微生物增强对土壤有机碳的分解能力,增强了土壤的呼吸作用,最终导致土壤排放量增加[58],并且会通过影响土壤中的电子迁移过程来抑制CH4的排放,此外,Fe2O3-NPs的磁性会对土壤微生物的活性有激活作用,并且对土壤呼吸产生影响,最终导致土壤中CO2的排放量增加[59].
YANG等[60]的研究发现,Fe3O4-NPs会促进土壤中一种高度富集的丁酸盐氧化联合体的富集转移过程,在Fe3O4-NPs的作用下会持续增强丁酸盐氧化和CH4的生成,添加碳纳米管替代Fe3O4-NPs也产生了类似的刺激效果,而Fe3O4-NPs表面的二氧化硅涂层则完全消除了这种刺激作用,说明Fe3O4-NPs的导电性在促进共氧化过程释放CH4中起着关键作用[60].
-
微生物在地球化学循环中发挥着重要作用,对土壤功能,特别是有机质分解和养分循环至关重要;因此,它们在调节植物生产力、群落动态和土壤形成中都很重要[61]. 微生物通过其代谢活性参与土壤无机组分的转化、移动和固定化,一个表面为1 Ha、度为30 cm的土壤可能总共含有10 mg的细菌和10 mg的真菌[62],这种微生物群落在维持土壤功能和陆地生态系统方面发挥着重要作用[63]. 它们也是污染物降解过程中的主要参与者,如有机质矿化,促进生态系统中的养分循环,从而促进土壤肥力[64]. 微生物之间以及微生物与高等生物之间也保持着关键的共生和致病关系[65],由于其关键而广泛的作用,土壤微生物的代谢活动已被用作评估土壤中人为活动释放的污染物(如金属和农药)的影响的测量端点. 这些测量值通常被用于生态风险评估[66].
-
Fe2O3-NPs和Fe3O4-NPs对细菌群落的影响可能归因于纳米颗粒的两种特性及其对微生物代谢的促进作用[67],由于其微小的尺寸和稳定性,Fe2O3-NPs和Fe3O4-NPs极容易运输到土壤中[68],提高了土壤表面积与体积之比,因此相对于块状材料,纳米颗粒更容易部分分解和释放离子[69]. 此外,纳米颗粒具有最活跃的表面位点(主要是Fe2O3-NPs上的Fe-OH位点,能够与天然有机化合物结合)[70]. 例如,在土壤中的有机化合物,如腐殖酸和黄腐酸的辅助下,磁性纳米铁的添加可以增强铁对土壤细菌的生物有效性. 腐植酸是动植物残基在理化和微生物降解过程中形成的,在自然系统中含量丰富,它具有由烷基和芳香族单元组成的骨架,与羧酸、酚羟基和醌官能团结合,可与磁性纳米铁表面产生很强的亲和力[71]. 腐殖酸对磁性纳米铁的吸收通常通过空间和静电效应的结合提高其稳定性. 此外,由于腐殖酸与氧化铁表面位之间的配体交换反应,溶解的三价铁离子从磁性纳米铁表面进入水相. 因此,土壤中的生物有效铁离子增加,进而刺激土壤中某些微生物的生长[72].
并且Fe2O3-NPs对土壤细菌群落的影响更有利,Zeng等的研究指出,大部分磁性纳米铁由于产生活性氧(ROS)而具有毒性,而化学稳定的Fe2O3-NPs没有明显的细胞毒性,含有Fe2+的纳米颗粒会导致大肠杆菌存活率的剂量依赖性下降,主要是由于氧化应激,纳米颗粒由完全氧化的晶体组成,因此在环境中高度稳定,产生氧化应激的能力较低[73]. 相比之下,Fe3O4-NPs由于其结构内电子迁移率高和Fe2+的扩散而不稳定,因此,部分磁性纳米铁的不良影响可以通过Fe3O4-NPs释放Fe2+来抵消,导致细菌群落丰富度的增强较弱,细菌群落组成的变化较小[74].
-
nZVI-NPs可以潜在地刺激细菌生长,从而可能发生土壤细菌群落结构的一些变化[75 − 76]. 采用荧光原位杂交(FISH)、变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)和磷脂脂肪酸分析(PLFA)研究nZVI-NPs对微生物多样性的影响[77]. 施用nZVI-NPs 72 h后,Fajardo等观察到土壤微生物群落结构和系统发育组成发生了显著变化[78]. 荧光原位杂交分析表明,当nZVI-NPs对微生物群落施加选择性压力时,微生物多样性发生了变化,促进了某些微生物类群(古菌、α-变形菌和低G + C革兰氏阳性菌)的优势,而其他微生物类群(β-变形菌和γ-变形菌及其亚纲)的减少,添加10 g·kg−1 nZVI-NPs 28 d后的性梯度凝胶电泳图谱也表明细菌群落组成发生了显著变化. Pawlett等人的报告提到,nZVI-NPs导致所有测试的土壤质地中的磷脂脂肪酸分析剖面发生改变,但这些影响取决于土壤中的有机质含量[79]. 这些研究表明,nZVI-NPs可在短期内(4个月)显著改变土壤微生物群落结构,影响细菌、古菌和真菌的种群数量[80].
Liu等将不同浓度nZVI-NPs暴露后,观测土壤生态系统的响应,结果表明长期暴露nZVI-NPs对土壤微生物群落特征无显著影响,但可以促进蚯蚓的生长,从而进一步提高了土壤营养元素的生物有效性,为nZVI-NPs应用于污染修复与治理的环境安全性评估提供了科学依据[81].
Kasem等[82]的研究结果表明,注射羧甲基纤维素稳定的nZVI-NPs通过促进厌氧菌和脱氯菌的生长,对污染修复产生了积极的影响. 此外,这种影响是非常持久的,可能是由于羧甲基纤维素的缓慢发酵和生物质的缓慢腐烂[82]. 根据Kocur等观察到的含氯挥发性有机物降解产物,在使用注射羧甲基纤维素稳定的nZVI-NPs后,呼吸有机卤化物的微生物会得到增强[83],在两年的监测期间,含氯挥发性有机污染物在处理区域持续降解. Ahmad等的实验结果表明,nZVI-NPs会降低抑瘤性化合物和氯仿等生物可降解化合物的浓度,从而降低对微生物活性的抑制作用,由此产生的条件促进了有机卤化物呼吸微生物的丰度的增加[84]. 随着纳米技术产业的不断发展,以及其对环境所具有的潜在污染性质,纳米颗粒对自然系统的影响正成为一个日益活跃的研究领域,实验结果表明施用注射羧甲基纤维素稳定的nZVI-NPs后,微生物种群数量显著增加,其中包括负责含氯挥发性有机物降解的脱卤菌. 由于观察到这种显著的含氯挥发性有机物降解是由于两种电子供体(nZVI-NPs和羧甲基纤维素)的结合,因此需要做更多的工作来进一步评估纳米颗粒和纳米技术对环境的影响[85].
-
单一碳源利用(SCSU)系统基于对土壤微生物群落代谢特性的广泛调查,检测土壤微生物种群的功能能力,所得数据可以使用多元技术进行分析,以比较群落的代谢能力[86]. 然而,由于土壤微生物群落是由快速生长和缓慢生长的有机体组成的,因此生长缓慢的有机体可能不包括在本分析中[87]. SCSU的优势包括其区分微生物群落的能力强、操作简便、可重复性和大量描述群落代谢特征数据的生成[88].
微量热法是通过微量热仪对代谢过程的热效应进行实时、高频、精确的监测、绘制微量热曲线,展示土壤微生物稳定期及对数生长期的热散逸[89],再通过模型拟合,可分析获得微生物生物量,微生物群落的潜在最大代谢活性、响应时间、比生长速率、周转速率,活性微生物比例等参数,用于表征微生物群落的代谢特征[90 − 91].
-
磁性纳米铁会直接作用或通过废水排放等间接方式作用于土壤微生物群落,许多磁性纳米铁对微生物具有杀伤特性,从而进一步抑制土壤微生物群落的代谢活动,如固氮、氨化、反硝化、溶磷和其他促进微生物生长的活动[92]. 但是某些磁性纳米铁在低浓度下会促进某些微生物代谢过程,从而促进微生物生长,对土壤微生物群落的数量及丰富度产生影响[93]. 例如,Rajput等过研究对纳米银和Fe2O3-NPs对土壤微生物硝化作用的影响,发现Fe2O3-NPs能促进土壤微生物的硝化作用,而纳米银则抑制微生物硝化作用,且存在剂量效应[94 − 95]. 当浓度增大时,氨氮不易转化,氨氧化较弱,而后通过实时定量PCR发现,纳米银降低了对土壤中微生物数量的影响,而Fe2O3-NPs的影响不显著,然后通过分析土壤中氨氧化细菌和古菌,发现随着纳米银浓度的增加,土壤中氨氧化细菌和古菌数量显著减少[96 − 97],Fe2O3-NPs增加了土壤中氨氧化细菌的数量[98]. 通过微热仪表征土壤微生物的代谢特征,发现纳米氧化银对土壤微生物的代谢活动有负作用,且表现为剂量效应,即随着纳米银浓度的增加,负作用越大. 相反,Fe2O3-NPs对微生物代谢有正向作用,且随着浓度的增加而增加[99],此外土壤中有机卤化物呼吸微生物在Fe2O3-NPs的刺激下,在提高对含氯挥发性有机污染物降解的同时,微生物丰富度也会发生变化(如图3).
-
环境中的各种因素(如天然有机物(NOM)、酸碱度(pH)、离子(IONS)和背景离子)可以改变磁性纳米铁和测试生物的表面性质,从而改变磁性纳米铁对土壤微生物代谢的影响. 溶液pH和IS在磁性纳米铁和藻类细胞的异质团聚中发挥重要作用,这有助于稀释纳米颗粒的细胞毒性[100]. Ranmadugala等报道了Ca2+在影响nZVI-NPs对大肠杆菌的毒性方面的双重作用. 一方面,Ca2+的存在可以通过增强nZVI-NPs的聚集和沉淀来抑制nZVI-NPs的杀菌作用;另一方面,Ca2+可能作为桥梁促进nZVI-NPs对细菌的粘附,从而造成更严重的影响[101]. 相对高浓度的Ca2+(40 mg·L−1)甚至可以将带负电荷的nZVI-NPs转化为带正电荷的nZVI-NPs,使颗粒更有利于吸附带负电荷的大肠杆菌. 每种生物都有特定的适宜温度,光的进入对某些生物,特别是藻类和植物的生长至关重要. 环境中营养物质的可获得性也是一个决定性因素,一般来说,充足的营养物质的供应可以提高生物体对磁性纳米铁的耐受性. 基质类型(水、土壤或沉积物)是控制纳米颗粒毒性的重要因素. 组分尤其是有机质和黏土会强烈影响磁性纳米铁的流动性和有效性,导致磁性纳米铁在土壤或沉积物中的毒性低于水体. 在现实环境中,生物接触到的是转化后的磁性纳米铁,因此,在环境相关的测试条件下,磁性纳米铁对微生物代谢影响的研究备受关注,这使我们能够更好地了解其生态危害,尽可能减轻其对土壤微生物群落的不良影响[102].
-
随着磁性纳米铁应用的日益广泛,人们对其在环境中发展潜力和潜在影响进行了研究,磁性纳米铁通过多种方式释放到土壤中后,与土壤中的生物化学成分及微生物相互作用,最终对土壤理化性质以及微生物群落自身及代谢产生影响. 磁性纳米铁进入土壤后,会对土壤容重、土壤体积含水量、渗透阻力以及有机物质含量等产生影响,且在不同类型的土壤中,磁性纳米铁对土壤酶活的影响不同. 此外,磁性纳米铁通过改变土壤的硝化电位、微生物对有机碳的分解能力及电子迁移来改变土壤温室气体排放量. 磁性纳米铁对微生物群落的影响则体现在刺激土壤微生物的生长、改变微生物群落的结构与数量以及对微生物代谢的影响. 未来的研究方向可从以下几个方面开展:
(1)磁性纳米铁在环境领域和农业上的应用使得它通过主动或被动的方式进入土壤环境,在最大限度地减少或消除废物的产生和减少污染的同时,自身在土壤中的积累也会对土壤理化性质以及微生物群落的结构、功能以及代谢产生负面效应;因此今后除了加强农业及环境领域应用的同时,还需要考虑自身积聚所带来的负面生态效应,寻求用最适合的用量来达到最优的效果.
(2)重金属等有害有毒污染物(如铅、镉、汞等)和有机化合物(如苯、二甲苯、甲苯溶剂和农药)农药是环境中的整治目标,通过共价键、马来酰亚胺、配体交换,在磁性纳米铁表面设计并引入功能和活性位点,可提高磁性纳米铁的反应性和与重金属等污染物的反应程度,应用前景广阔,因为通过这些途径功能化的磁性纳米铁吸附剂用于污染物去除的研究十分匮乏.
(3)在研究磁性纳米铁对土壤组成结构及微生物群落代谢特征的影响的同时,以微生物为基础合成磁性纳米铁的研究取得了重大进展,然而,磁性纳米铁生物合成过程的改进和应用还需要进行大量的研究. 与物理和化学方法相比,微生物合成纳米颗粒的过程相对较慢,在合成中不建议使用病原微生物,因为它可能限制所产生的磁性纳米铁在涉及人类或动物接触的应用中使用,制备的磁性纳米铁应对生物和环境无毒,因此对利用微生物合成磁性纳米铁进行毒性研究至关重要,对能够产生稳定磁性纳米铁的微生物的研究有助于开发可靠的生产工艺,促进磁性纳米铁的发展.
磁性纳米铁对土壤理化性质及微生物群落和代谢的影响研究进展
Effects of magnetic nano - iron on soil physicochemical properties and microbial community and metabolism
-
摘要: 近年来,磁性纳米铁因其独特性能在生物医学、农业、工业、生命科学及环境保护领域广泛应用. 随着磁性纳米铁的大范围应用,其对环境和人体健康将带来的潜在影响,已经引起科学界的广泛关注. 本文系统总结了近年来磁性纳米铁的相关文献资料,探讨了磁性纳米铁的合成方法、表征及环境应用;我们重点强调了磁性纳米铁对土壤理化性质及微生物群落和代谢的潜在影响. 最后展望了磁性纳米铁在未来的环境应用、发展及纳米毒理学亟待研究的重要问题. 本文旨在更加全面地揭示磁性纳米铁的环境可持续性,为其安全使用和环境功能化应用提供一定的参考.Abstract: In recent years, magnetic nano-iron has been widely used in biomedicine, agriculture, industry, life science and environmental protection due to its unique properties. With the wide application of magnetic nano-iron, their potential impact on the environment and human health has attracted wide attention from the scientific community. In this paper, we systematically summarized the relevant literature of magnetic nano- iron in recent years, and also discussed the synthesis method, characterization and environmental application of magnetic iron nanoparticles. We highlight the potential effects of magnetic nano-iron on the soil physicochemical properties, microbial communities and metabolism. Finally, we prospect the important problems about the environmental application, development and nanotoxicology of magnetic nano-iron in the future . This paper aims to comprehensively reveal the environmental sustainability of magnetic nano-iron, and provide some references for its safe use and environmental functional applications.
-
Key words:
- smagnetic-nano iron /
- soil /
- environmental implication /
- microbiological population /
- metabolism.
-

-
表 1 绿色合成的磁性纳米铁去除重金属的应用
Table 1. Application of green synthetic magnetic iron nanoparticles for removal of heavy metals
磁性纳米铁种类
Magnetic nano iron species去除金属种类
Removing metal type去除效率
Removal efficiency参考文献
References纳米零价铁 六价铬 90 min 99.45% Huang et al. (2017)[29] 四氧化三铁纳米颗粒 钙和镉 120 min 钙55%, 镉40% Sebastian et al.(2018)[30] 铁纳米颗粒 六价铬 90 min 99.29% Wei et al. (2017)[31] 纳米零价铁、 氧化铁纳米颗粒 六价铬 35 min 98.9% Jin et al. (2017)[32] 氧化铁纳米颗粒 镉 90 min 90.0% Ehrampoush et al.(2015)[33] 纳米零价铁 六价铬 90 min 89.9% Qiu et al. (2017)[34] -
[1] AJINKYA N, YU X F, KAITHAL P, et al. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (IONP) synthesis to applications: Present andfuture[J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 13(20): 4644. doi: 10.3390/ma13204644 [2] ANDRADE R G D, VELOSO S R S, CASTANHEIRA E M S. Shape anisotropic iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis and biomedical applications[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(7): 2455. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072455 [3] FATIMA H, LEE D W, YUN H J, et al. Shape-controlled synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different iron precursors and capping agents[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(41): 22917-22923. doi: 10.1039/C8RA02909A [4] JACINTO M J, SILVA V C, VALLADÃO D S, et al. Biosynthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: A review[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2021, 43(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10529-020-03047-0 [5] DOLORES MÁRQUEZ-MEDINA M, RODRÍGUEZ-PADRÓN D, BALU A M, et al. Mechanochemically synthesized supported magnetic Fe-nanoparticles as catalysts for efficient vanillin production[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(3): 290. doi: 10.3390/catal9030290 [6] NAYEEM J, ALIM AL-BARI M A, MAHIUDDIN M, et al. Silica coating of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles by reverse microemulsion method and their functionalization with cationic polymer P(NIPAm-co-AMPTMA) for antibacterial vancomycin immobilization[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 611: 125857. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125857 [7] TAKAI Z I, MUSTAFA M, ASMAN S, et al. Preparation and characterization of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles by sol-gel method[J]. Int J Nanoelectron Mater, 2019, 12: 37-46. [8] TADIC M, PANJAN M, DAMNJANOVIC V, et al. Magnetic properties of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal synthesis method[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 320: 183-187. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.193 [9] MAHARJAN A, DIKSHIT P K, GUPTA A, et al. Catalytic activity of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for hydrogen peroxide decomposition: Optimization and characterization[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2020, 95(9): 2495-2508. [10] LIU S L, TAO D D, ZHANG L N. Cellulose scaffold: A green template for the controlling synthesis of magnetic inorganic nanoparticles[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 217: 502-509. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2011.11.010 [11] RANE A V, KANNY K, ABITHA V K, et al. Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites[M]//Synthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 121-139. [12] MUKHERJEE R, KUMAR R, SINHA A, et al. A review on synthesis, characterization, and applications of nano zero valent iron (nZVI) for environmental remediation[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 46(5): 443-466. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2015.1103832 [13] SAMROT A V, SAHITHYA C S, SELVARANI A J, et al. A review on synthesis, characterization and potential biological applications of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles[J]. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2021, 4: 100042. doi: 10.1016/j.crgsc.2020.100042 [14] SARWAR A, WANG J, KHAN M S, et al. Iron oxide (Fe3O4)-supported SiO2 magnetic nanocomposites for efficient adsorption of fluoride from drinking water: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption isotherm analysis[J]. Water, 2021, 13(11): 1514. doi: 10.3390/w13111514 [15] SHUKLA S, KHAN R, DAVEREY A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles, and their applications in wastewater treatment: A review[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 24: 101924. [16] SMALLMAN R E, NGAN A H W. Characterization and analysis[M]//Modern Physical Metallurgy. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 159-250. [17] YOSHIDA T, NAKAMURA T, HIGASHI O, et al. Magnetic fractionation and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic particle imaging[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 57(8): 080302. doi: 10.7567/JJAP.57.080302 [18] BHALERAO T S. Magnetic nanostructures: environmental and agricultural applications[M]//Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 213-224. [19] BHATERIA R, SINGH R. A review on nanotechnological application of magnetic iron oxides for heavy metal removal[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2019, 31: 100845. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100845 [20] HE Y Z, WANG Z W, WANG H, et al. Metal-organic framework-derived nanomaterials in environment related fields: Fundamentals, properties and applications[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2021, 429: 213618. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213618 [21] SAHARAN P, CHAUDHARY G R, MEHTA S K, et al. Removal of water contaminants by iron oxide nanomaterials[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2014, 14(1): 627-643. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2014.9053 [22] LI W L, FORTNER J D. (Super)paramagnetic nanoparticles as platform materials for environmental applications: From synthesis to demonstration[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2020, 14(5): 1-9. [23] KOLLURU S S, AGARWAL S, SIREESHA S, et al. Heavy metal removal from wastewater using nanomaterials-process and engineering aspects[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 150: 323-355. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.04.025 [24] MOHAMMED L, GOMAA H G, RAGAB D, et al. Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: A review[J]. Particuology, 2017, 30: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2016.06.001 [25] NGUYEN M D, TRAN H V, XU S J, et al. Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Structures, synthesis, magnetic properties, surface functionalization, and emerging applications[J]. Applied Sciences (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 11(23): 11301. [26] REHMAN A U, NAZIR S, IRSHAD R, et al. Toxicity of heavy metals in plants and animals and their uptake by magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 321: 114455. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114455 [27] SOHAIL M I, WARIS A A, AYUB M A, et al. Environmental application of nanomaterials: A promise to sustainable future[M]//Engineered Nanomaterials and Phytonanotechnology: Challenges for Plant Sustainability. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 1-54. [28] ZHOU Q X, LI J, WANG M Y, et al. Iron-based magnetic nanomaterials and their environmental applications[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 46(8): 783-826. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2016.1160815 [29] HUANG X Y, WANG W, LING L, et al. Heavy metal-nZVI reactions: The core-shell structure and applications for heavy metal treatment[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2017, 75(6): 529. doi: 10.6023/A17020051 [30] SEBASTIAN A, NANGIA A, PRASAD M N V. A green synthetic route to phenolics fabricated magnetite nanoparticles from coconut husk extract: Implications to treat metal contaminated water and heavy metal stress in Oryza sativa L[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 174: 355-366. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.343 [31] WEI Y F, FANG Z Q, ZHENG L C, et al. Biosynthesized iron nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Eichhornia crassipes and its mechanism in the hexavalent chromium removal[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 399: 322-329. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.090 [32] JIN S Y, PARK B C, HAM W S, et al. Effect of the magnetic core size of amino-functionalized Fe3O4-mesoporous SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles on the removal of heavy metal ions[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2017, 531: 133-140. [33] EHRAMPOUSH M H, MIRIA M, SALMANI M H, et al. Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by green synthesis iron oxide nanoparticles with tangerine peel extract[J]. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 2015, 13(1): 84. doi: 10.1186/s40201-015-0237-4 [34] QIU Y, ZHANG Q, GAO B, et al. Removal mechanisms of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by biochar supported nanosized zero-valent iron: Synergy of adsorption, reduction and transformation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 115018. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115018 [35] HAN X, WANG F, Zhao Y, et al. Recycling of iron ore tailings into magnetic nanoparticles and nanoporous materials for the remediation of water, air and soil: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2022: 1-24. [36] CHUANG P Y, CHIA Y, LIOU Y H, et al. Characterization of preferential flow paths between boreholes in fractured rock using a nanoscale zero-valent iron tracer test[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(7): 1651-1662. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1426-7 [37] BANIJAMALI S, FEIZIAN M, BIDABADI A A, et al. Evaluation uptake and translocation of iron oxide nanoparticles and its effect on photosynthetic pigmentation of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium) ‘Salvador’[J]. Journal of Ornamental Plants, 2019, 9(4): 245-258. [38] AHMED B, RIZVI A, ALI K, et al. Nanoparticles in the soil–plant system: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2021, 19(2): 1545-1609. doi: 10.1007/s10311-020-01138-y [39] MEDINA-PÉREZ G, FERNÁNDEZ-LUQUEÑO F, VAZQUEZ-NUÑEZ E, et al. Remediating polluted soils using nanotechnologies: Environmental benefits and risks[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2019, 28(3): 1013-1030. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/87099 [40] RAFFI M M, HUSEN A. Impact of fabricated nanoparticles on the rhizospheric microorganisms and soil environment[M]//Nanomaterials and Plant Potential. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 529-552. [41] RAWAT S, PULLAGURALA V L R, ADISA I O, et al. Factors affecting fate and transport of engineered nanomaterials in terrestrial environments[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 2018, 6: 47-53. [42] XU Z X, LONG X, JIA Y, et al. Occurrence, transport, and toxicity of nanomaterials in soil ecosystems: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2022, 20(6): 3943-3969. doi: 10.1007/s10311-022-01507-9 [43] 张旭升. 不同植被修复模式下土壤真菌的研究及纳米材料对土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2021. ZHANG X S. Study on soil fungi under different vegetation restoration patterns and the effect of nanomaterials on soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[44] SUN P, SUN Y Y, LUO Y H, et al. The application progress of nano materials for remediation in contaminated soil[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 692(3): 032035. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/692/3/032035 [45] XIN X P, ZHAO F L, ZHAO H M, et al. Comparative assessment of polymeric and other nanoparticles impacts on soil microbial and biochemical properties[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 367: 114278. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114278 [46] JAIN A, SINGH N, KHAN S. Nanomaterials for soil reclamation[M]//Advances in Environmental Engineering and Green Technologies. IGI Global, 2021: 530-541. [47] YAN L, LI P Y, ZHAO X P, et al. Physiological and metabolic responses of maize (Zea mays) plants to Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 718: 137400. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137400 [48] GALAKTIONOVA L, GAVRISH I, LEBEDEV S. Bioeffects of Zn and Cu nanoparticles in soil systems[J]. Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences, 2019, 11(4): 259-270. doi: 10.1007/s13530-019-0413-5 [49] ASADISHAD B, CHAHAL S, AKBARI A, et al. Amendment of agricultural soil with metal nanoparticles: Effects on soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(4): 1908-1918. [50] YOU T T, LIU D D, CHEN J, et al. Effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities in two different soil types[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2018, 18(1): 211-221. doi: 10.1007/s11368-017-1716-2 [51] SUN W, DOU F, Li C, et al. Impacts of metallic nanoparticles and transformed products on soil health[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 51(10): 973-1002. YANG H Y, ZHANG X, DANG D, et al. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on CH4 and N2O emissions and microbial communities in two typical paddy soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2021, 27(3): 725-733 (in Chinese). [52] ELHAMBAKHSH A, GHANAATIAN A, KESHAVARZ P. Glutamine functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for high-performance carbon dioxide absorption[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 94: 104081. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2021.104081 [53] DIMKPA C O. Can nanotechnology deliver the promised benefits without negatively impacting soil microbial life?[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2014, 54(9): 889-904. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201400298 [54] PEREA VELEZ Y S, CARRILLO-GONZALEZ R, GONZÁLEZ-CHÁVEZ M. Interaction of metal nanoparticles–plants–microorganisms in agriculture and soil remediation[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2021, 23(9): 1-48. [55] HU L F, FENG Z Y, YU Y X, et al. Effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on nitrous oxide emissions in agriculture soil[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(6): 770. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12060770 [56] RAJA M A, HUSEN A. Role of nanomaterials in soil and water quality management[M]//Nanomaterials for Agriculture and Forestry Applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020: 491-503. [57] PUSPITASARI P, YAZIRIN C, BACHTIAR L A, et al. Application of nanocatalyst iron oxide (Fe2O3) to reduce exhaust emissions (CO and HC)[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 432: 012004. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/432/1/012004 [58] 吴江利, 罗学刚, 李宝强, 等. 微生物菌肥作用下荒漠土壤微生物群落结构和功能研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(9) 216-223. WU J L, LUO X G, LI B Q, et al. Researches on microbial community structure and function in desert soil under microbial fertilizer[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(9): 216-223 (in Chinese).
[59] FU L, SONG T Z, ZHANG W, et al. Stimulatory effect of magnetite nanoparticles on a highly enriched butyrate-oxidizing consortium[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1480. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01480 [60] 杨浩宇, 张潇, 党迪, 等. 纳米氧化铁对水稻土CH4和N2O排放及微生物的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2021, 27(3): 725-733. YANG H Y, ZHANG X, DANG D, et al. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on CH4 and N2O emissions and microbial communities in two typical paddy soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2021, 27(3): 725-733 (in Chinese).
[61] CHEN Q L, DING J, ZHU Y G, et al. Soil bacterial taxonomic diversity is critical to maintaining the plant productivity[J]. Environment International, 2020, 140: 105766. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105766 [62] JIA Y, WHALEN J K. A new perspective on functional redundancy and phylogenetic niche conservatism in soil microbial communities[J]. Pedosphere, 2020, 30(1): 18-24. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(19)60826-X [63] ZHONG Y, YAN W M, WANG R W, et al. Decreased occurrence of carbon cycle functions in microbial communities along with long-term secondary succession[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 123: 207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.05.017 [64] van der BOM F, NUNES I, RAYMOND N S, et al. Long-term fertilisation form, level and duration affect the diversity, structure and functioning of soil microbial communities in the field[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 122: 91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.04.003 [65] ZHENG Q, HU Y T, ZHANG S S, et al. Soil multifunctionality is affected by the soil environment and by microbial community composition and diversity[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 136: 107521. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107521 [66] 尹雪梅, 王晓凤. 纳米Fe3O4对玉米叶面积和根际微生物群落功能多样性的影响[C]//中国土壤学会土壤环境专业委员会第十九次会议暨“农田土壤污染与修复研讨会”第二届山东省土壤污染防控与修复技术研讨会摘要集. 济南, 2017: 139. YIN X M, WANG X F. Effects of nano Fe3O4 on leaf area and rhizosphere microbial community functional diversity in maize[C]//. The 19th Conference of Soil Environment Committee of Soil Society of China and the 2nd Workshop on Soil Pollution Control and Remediation in Shandong Province Abstract Collection. Jinan, 2017: 139(in Chinese).
[67] HE S Y, FENG Y Z, REN H X, et al. The impact of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles on the soil bacterial community[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2011, 11(8): 1408-1417. doi: 10.1007/s11368-011-0415-7 [68] KUMAR P, BURMAN U, KAUL R K. Ecological risks of nanoparticles[M]//Nanomaterials in Plants, Algae, and Microorganisms. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 429-452. [69] REN X M, GUO L, CHEN Y, et al. Effect of magnet powder (Fe3O4) on aerobic granular sludge (AGS) formation and microbial community structure characteristics[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(8): 9707-9715. [70] SAIF S, TAHIR A, CHEN Y S. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their environmental applications and implications[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 2016, 6(11): 209. doi: 10.3390/nano6110209 [71] SHEN Y X, JIANG B, XING Y. Recent advances in the application of magnetic Fe3O4 nanomaterials for the removal of emerging contaminants[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(7): 7599-7620. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11877-8 [72] MAI T, HILT J Z. Magnetic nanoparticles: reactive oxygen species generation and potential therapeutic applications[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2017, 19(7): 1-10. [73] ZENG Q Z, XU J, HOU Y, et al. Effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles exposure on the treatment efficiency of phenol wastewater and community shifts in SBR system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 407: 124828. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124828 [74] LEFEVRE E, BOSSA N, WIESNER M R, et al. A review of the environmental implications of in situ remediation by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI): Behavior, transport and impacts on microbial communities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 565: 889-901. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.003 [75] FAJARDO C, GARCÍA-CANTALEJO J, BOTÍAS P, et al. New insights into the impact of nZVI on soil microbial biodiversity and functionality[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 2019, 54(3): 157-167. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2018.1535159 [76] ANZA M, SALAZAR O, EPELDE L, et al. The application of nanoscale zero-valent iron promotes soil remediation while negatively affecting soil microbial biomass and activity[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2019, 7: 19. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2019.00019 [77] FAJARDO C, ORTÍZ L T, RODRÍGUEZ-MEMBIBRE M L, et al. Assessing the impact of zero-valent iron (ZVI) nanotechnology on soil microbial structure and functionality: A molecular approach[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 86(8): 802-808. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.041 [78] PAWLETT M, RITZ K, DOREY R A, et al. The impact of zero-valent iron nanoparticles upon soil microbial communities is context dependent[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20(2): 1041-1049. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-1196-2 [79] YE W F, LU J, YE J F, et al. The effects and mechanisms of zero-valent iron on anaerobic digestion of solid waste: A mini-review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 278: 123567. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123567 [80] KOCUR C M D, LOMHEIM L, MOLENDA O, et al. Long-term field study of microbial community and dechlorinating activity following carboxymethyl cellulose-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron injection[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(14): 7658-7670. [81] LIU C E, YUE M H, TAN H L, et al. Effects of nano-zero-valent iron(nZVI) on earthworm-bacteria-soil systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(10): 1722-1732. [82] KASEM K K, MOSTAFA M, ABD-ELSALAM K A. Iron-based nanomaterials: Effect on soil microbes and soil health[M]//Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 261-285. [83] AHMAD S, LIU X M, TANG J C, et al. Biochar-supported nanosized zero-valent iron (nZVI/BC) composites for removal of nitro and chlorinated contaminants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133187. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133187 [84] PENG D H, WU B, TAN H, et al. Effect of multiple iron-based nanoparticles on availability of lead and iron, and micro-ecology in lead contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 228: 44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.106 [85] ADHIKARI K, HARTEMINK A E. Linking soils to ecosystem services—a global review[J]. Geoderma, 2016, 262: 101-111. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.08.009 [86] LI L, XU M G, EYAKUB ALI M, et al. Factors affecting soil microbial biomass and functional diversity with the application of organic amendments in three contrasting cropland soils during a field experiment[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(9): e0203812. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203812 [87] MOSCATELLI M C, SECONDI L, MARABOTTINI R, et al. Assessment of soil microbial functional diversity: Land use and soil properties affect CLPP-MicroResp and enzymes responses[J]. Pedobiologia, 2018, 66: 36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.pedobi.2018.01.001 [88] NKONGOLO K K, NARENDRULA-KOTHA R. Advances in monitoring soil microbial community dynamic and function[J]. Journal of Applied Genetics, 2020, 61(2): 249-263. doi: 10.1007/s13353-020-00549-5 [89] GHOSH S, JOSHI K, WEBSTER T J. Removal of heavy metals by microbial communities[M]//Wastewater Treatment Reactors. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2021: 537-566. [90] FAKRUDDIN M, BIN MANNAN K S. Methods for analyzing diversity of microbial communities in natural environments[J]. Ceylon Journal of Science (Biological Sciences), 2013, 42(1): 19. doi: 10.4038/cjsbs.v42i1.5896 [91] KHAN S T. Interaction of engineered nanomaterials with soil microbiome and plants: Their impact on plant and soil health[M]//Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 41. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 181-199. [92] QIAN H F, KE M J, QU Q, et al. Ecological effects of single-walled carbon nanotubes on soil microbial communities and soil fertility[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2018, 101(4): 536-542. doi: 10.1007/s00128-018-2437-y [93] 曹鑫磊, 姜浩, 杨宝山, 等. 纳米银对小麦秸秆还田土壤中酶活性及微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 山东科学, 2021, 34(3): 80-89. CAO X L, JIANG H, YANG B S, et al. Effects of nano-silver on enzyme activity and microbial community functional diversity in wheat straw returning soil[J]. Shandong Science, 2021, 34(3): 80-89.(in Chinese).
[94] RAJPUT V D, MINKINA T M, BEHAL A, et al. Effects of zinc-oxide nanoparticles on soil, plants, animals and soil organisms A review[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2018, 9: 76-84. [95] SHI X D, WEI W, WU L, et al. Zero-valent iron mediated biological wastewater and sludge treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 130821. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130821 [96] TIAN L Y, SHEN J P, SUN G X, et al. Foliar application of SiO2 nanoparticles alters soil metabolite profiles and microbial community composition in the pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L. ) rhizosphere grown in contaminated mine soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(20): 13137-13146. [97] VANZETTO G V, THOMÉ A. Bibliometric study of the toxicology of nanoescale zero valent iron used in soil remediation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.092 [98] ZHU X W, BLANCO E, BHATTI M, et al. Impact of metallic nanoparticles on anaerobic digestion: A systematic review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 757: 143747. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143747 [99] LEI C, SUN Y Q, TSANG D C W, et al. Environmental transformations and ecological effects of iron-based nanoparticles[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 232: 10-30. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.052 [100] MAHANTY B, JESUDAS S, PADMAPRABHA A. Toxicity of surface functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles toward pure suspension culture and soil microcosm[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2019, 12: 100235. [101] RANMADUGALA D, EBRAHIMINEZHAD A, MANLEY-HARRIS M, et al. Magnetic immobilization of bacteria using iron oxide nanoparticles[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2018, 40(2): 237-248. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2477-0 [102] SEIFAN M, EBRAHIMINEZHAD A, GHASEMI Y, et al. The role of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the bacterially induced calcium carbonate precipitation[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(8): 3595-3606. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8860-5 -



 下载:
下载: