-
土壤质量是农业生产中粮食安全的重要保障[1]. 随着工业的发展,土壤污染日益严重,其中重金属污染已成为社会广泛关注的土壤污染问题之一[2]. 工业三废的排放、矿产资源的开发以及农业生产中化肥、农药的过量施用是土地中重金属污染的主要来源[3]. 据资料显示我国农业耕地受重金属污染面积近20万km2,约占耕地总面积的20%[4]. 进入土壤的重金属会通过扬尘、饮水或食物链传递等途径在人体富集,进而损害人体器官、影响神经系统甚至会引发癌症[5].
矿产资源开发、金属冶炼与加工等过程中产生含重金属的“三废”以堆砌、沉降等形式进入土壤,是造成矿区及其影响区土壤重金属污染的主要来源之一,严重威胁生态系统和人体健康[6]. 内蒙古自治区矿产资源十分丰富,储量大、种类多、分布较为集中,据资料显示2015年全自治区已发现144种矿种,亚矿种有164种,占全国已发现矿种的83.72%,其中有43种矿产资源储量高居全国前三[7]. 据统计自治区现存有色金属采选业企业数量约140余家,包含多种矿物采选,其中铅锌矿采选企业数量最多. 从地域看自治区有色金属采选业企业主要分布于内蒙古东部地区,主要集中于赤峰市、锡林郭勒盟、呼伦贝尔市3个盟市,占全区企业数量的80%以上[8]. 矿产资源的开发、冶炼和加工造成矿区及其影响区土壤重金属污染. Hu等[9]研究发现,内蒙古赤峰市某典型有色金属矿区As、Cd、Cu、Pb和Zn的含量都超过了当地土壤背景值,潜在生态风险评价结果表明,矿区以及周边地带都处于中等风险水平. 郭伟等[10]研究发现,包头尾矿库区周边土壤都受到了重金属Pb、Cu、Zn、和Mn不同程度的污染,影响了周边的生态环境安全. 杨勇等[11]研究发现,锡林郭勒盟胜利煤田露天矿区土壤中重金属元素Cu含量高于内蒙古背景值. 周妍姿等[12]学者测定了内蒙古土壤剖面样品Ni、Mn、Cr、Cu、Zn、As和Pb重金属的浓度,结果表明,所有重金属类型变异性均较高,意味着影响土壤重金属含量的自然和人为因素的区域分异极为强烈.
虽然近些年关于内蒙古地区土壤重金属污染及生态风险评估的研究取得了一些进展,但大部分都是围绕有色金属矿区或矿区周边农田土壤展开的研究[13 − 15],而对于内蒙古草原地区土壤重金属来源途径、分布特征及生态风险评估相关的研究则鲜有报道. 内蒙古自治区拥有全国面积最大的草原,总面积为74.9185万km2[16]. 草原土壤的健康对于维持草原生产力和筑牢我国北方生态安全屏障至关重要. 内蒙古中东部地区主要的植被类型分为森林、典型草原、草甸草原和荒漠草原,几乎涵盖内蒙古地区的所有植被类型;而且内蒙古中东部地区人口相对密集,人类活动、资源开采等行为都会对土壤环境和理化性质产生一定影响. 因此开展内蒙古地区草原土壤中重金属元素污染特征和生态风险评估的研究具有重要的科学与实际意义. 本研究以内蒙古中东部草原土壤作为研究对象,按植被类型进行样带划分并进行采样,分析土壤中6种重金属元素(Cd、Cr、As、Zn、Pb和Cu)的含量及其空间分布特征,采用地累积污染指数法、潜在生态风险指数法和风险评估指数法对土壤中重金属的生态风险进行评价. 本文旨在揭示内蒙古地区草原土壤的重金属污染状况,为内蒙古地区生态环境保护和土壤污染防治提供科学依据.
-
研究区域位于内蒙古自治区中东部地区,由东向西分别为鄂温克族自治旗(EWK)、新巴尔虎左旗(XZQ)、西乌旗(XWQ)、锡林浩特(XLHT)、商都(SD)、苏尼特右旗(SNTYQ)、四子王旗(SZWQ),面积分别为0.43、2.20、2.25、1.47、0.43、2.23、2.55万km2. 研究区自东向西包括的主要土壤类型为黑土、黑钙土和栗钙土,植被类型分别为森林、草甸草原、典型草原和荒漠草原. 研究区属温带季风气候,冬季漫长严寒,夏季温热短促,年均降水量为190—442 mm. 全年多盛行西风及北偏西风,年平均风速在3 m·s−1以上,最大风速可达20 m·s−1以上.
-
样品采集于2019年夏季(7月中下旬). 根据植被类型不同在研究区内划分16个采样带,详细信息如表1所示,每条样带设置若干采样点. 采集表层土 0—20 cm 的混合土样. 合计采集土壤样品共104件.
将采集的土样带回实验室并及时风干,风干后挑出枯枝落叶、植物根、砾石等,然后分别过20目和100目筛备用. 土壤重金属元素(Cd、Cr、As、Zn、Pb和Cu)的全量采用HNO3-HCl-HClO4法消解[17],有效态含量用DTPA浸提法提取[18],用电感耦合等离子发射光谱仪(赛默飞,ICP-MS)进行含量测定[19]. 研究区全量重金属分布格局采用反距离权重法(inverse distance weighted, IDW)进行分析[20]. 其原理是假设未知点处属性值是在局部领域内中所有数据点的距离加权平均值. 该方法综合了泰森多边形的邻近点方法和趋势面分析的渐变方法的长处,因此经常被用在各种GIS分析中[21].
-
地累积污染指数法同时考虑了人为活动和自然条件下成土母质对周边环境的影响[22]. 该方法可以反映重金属元素的自然分布特征. 其计算公式为:
式中, Igeo为地累积污染指数;Cn(mg·kg−1)为土壤样品中重金属n的实际测量值;C0(mg·kg−1)为背景值,本文采用内蒙古自治区土壤背景值[23];K为引起背景值变动的修正系数,本文取值1.5. 地累积指数法将污染程度总共划分为7个等级,分别为无污染(Igeo<0)、无污染-中污染(0≤Igeo<1)、中污染(1≤Igeo<2)、中污染-强污染(2≤Igeo<3)、强污染(3≤Igeo<4)、强污染-极强污染(4≤Igeo<5)、极强污染(Igeo≥5).
-
潜在生态风险指数评价法因其综合考虑了重金属含量、毒性水平和环境对重金属污染的敏感性等因素而被广泛应用于评估土壤环境中的潜在生态风险[24]. 其计算公式为:
式中,RI为重金属综合潜在生态危害风险指数;Eir为单种重金属潜在生态危害系数;i为第i种重金属;Ps(mg·kg−1)为重金属质量浓度实测值;Pn(mg·kg−1)为参考值,以内蒙古地区土壤背景值为参比[23];Tr为毒性响应系数,Zn、Cr、Cu、As、Cd、Pb的毒性响应系数分别为1、2、5、10、30、5[25]. 单项潜在生态危害指数将污染程度划分为5个等级,分别为低生态危害(Eir<40)、中等生态危害(40≤Eir<80)、较重生态危害(80≤Eir<160)、重生态危害(160≤Eir<320)和严重生态危害(Eir≥320). 综合潜在生态危害指数将污染程度划分为4个等级,分别为低生态危害(RI<150)、中等生态危害(150≤RI<300)、重生态危害(300≤RI<600)和严重生态危害(RI≥600).
-
风险评估指数法是依据重金属弱酸提取态的质量分数将风险评估指数划分为若干个等级[26]. 计算方法为:
式中,
$ {C}_{i} $ (mg·kg−1)为样品中重金属弱酸提取态的浓度,$ {C}_{0} $ (mg·kg−1)为重金属的全量浓度. 当RAC<1%时,重金属的生物可利用性程度极低,对环境无风险; 当1%<RAC<10% 时,生物可利用性程度低,对环境低风险; 当10%<RAC<30% 时,生物可利用性程度中等,对环境中等风险; 当30%<RAC<50%时,生物可利用性程度高,对环境为高风险;当RAC>50%时,为极高风险. -
由表2可知,研究区土壤各重金属元素Zn、Cr、Cu、As、Cd、Pb的总含量平均值分别为116.87、27.14、12.79、11.51、0.19、11.50 mg·kg−1, Cr、Cu和Pb元素浓度均低于内蒙古土壤背景值,Zn、As、Cd的平均浓度分别是其背景值的1.98倍、1.53倍和3.58倍. Pb处于中等变异程度,其余元素均处于高等变异. 表明Zn、Cr、Cu、As和Cd在不同区域的重金属累积程度差异较大,各种元素在空间分布上存在分布不均匀的现象,而且具有局部富集的趋势. 其中,Cd的平均浓度值/背景值明显高于其它元素,说明研究区土壤中Cd是主要的污染物.
-
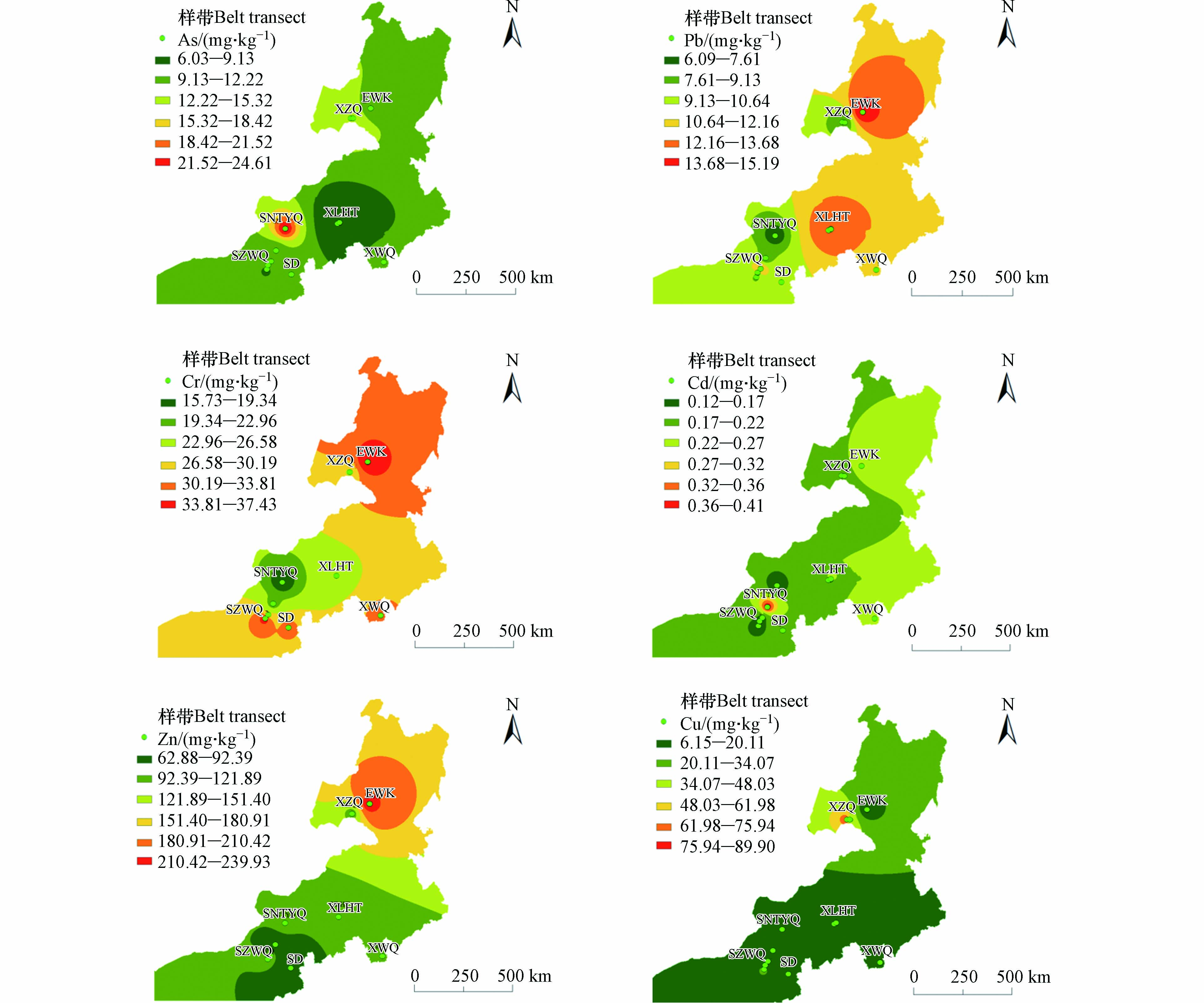
为揭示各重金属元素在空间上的分布特征,运用反距离权重法对土壤重金属进行插值[20]. 如图1所示,Cr在鄂温克族自治旗、西乌旗、商都、四子王旗土壤中的含量要高于其它研究区;Cu元素在新巴尔虎左旗土壤中的含量相对较高;Pb元素则在鄂温克族自治旗和锡林浩特土壤中具有相对较高的累积;Zn元素在鄂温克族自治旗地区土壤中含量较高,平均含量为188.24 mg·kg−1,是背景值的3倍. As元素在新巴尔虎左旗和苏尼特右旗具土壤中有较高的累积,分别是背景值的2.00倍和2.91倍;Cd元素在鄂温克族自治旗、西乌旗、锡林浩特和苏尼特右旗土壤中的含量相对较高,平均含量分别是背景值的3.19、4.73、4.12、3.31倍. 以上研究结果说明,不同地区土壤中重金属元素污的染程度不同.
-
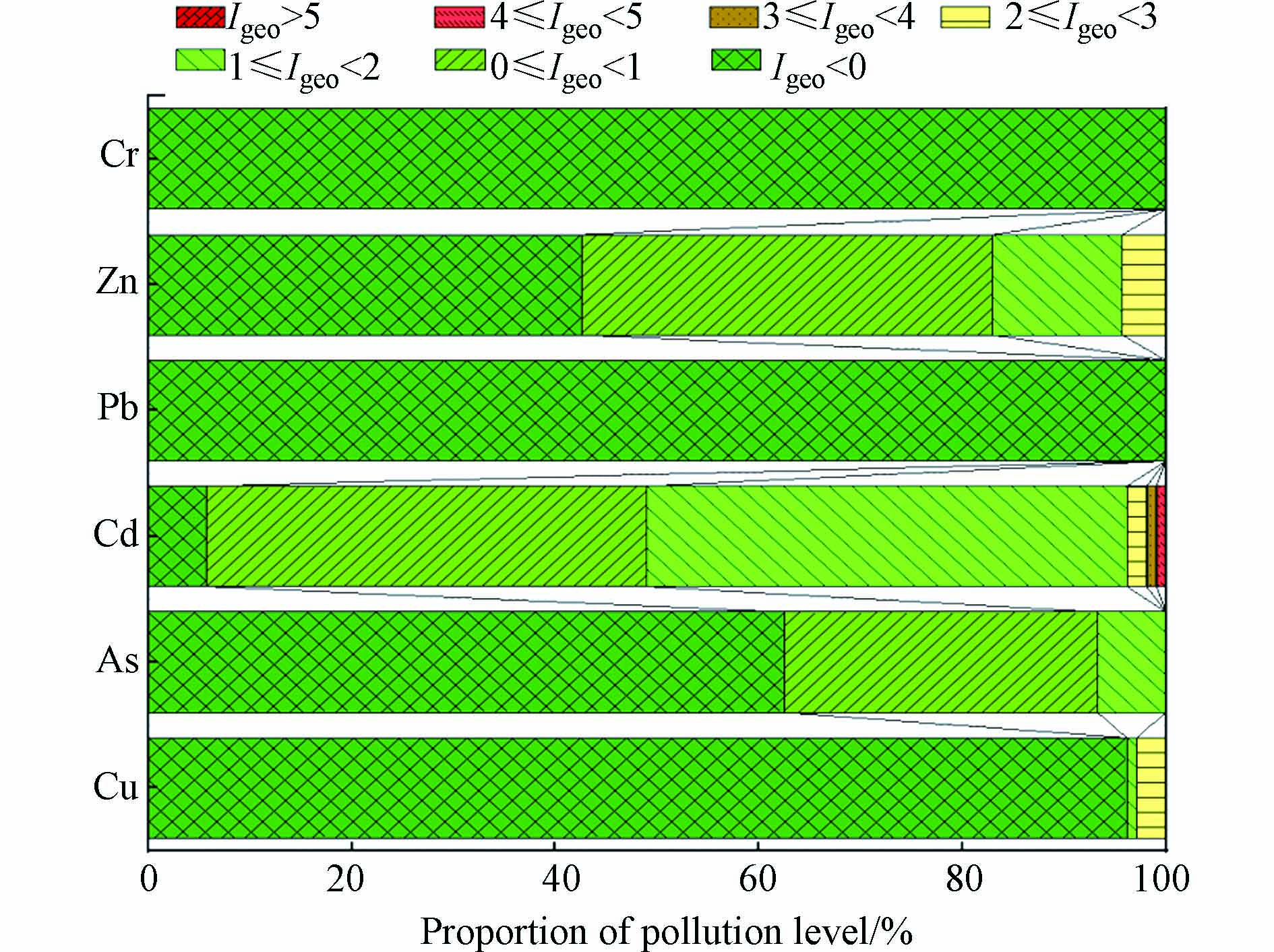
地累积指数评价结果如图2所示,研究区土壤未受Cr和Pb元素污染. Zn元素有40%的样点属于无污染-中污染,13%的样点属于中污染,4%的样点属于中污染-强污染. As元素有31%的样点属于无污染-中污染,7%的样点属于中污染. Cu元素污染相对较轻,只有4%的样点处于中污染、中污染-强污染. Cd污染相对于其它元素较为严重,有43%的样点属于无污染-中污染,47%的样点属于中污染,且在个别样点呈现中等或较强污染. 从整体看,Cd元素是研究区的主要污染物,有51%的样点呈现中度及以上污染,其次为Zn元素,有17%的样点呈现中度及以上污染,As元素的污染相对较轻. 说明研究区土壤中重金属存在一定程度的潜在生态危害.
-
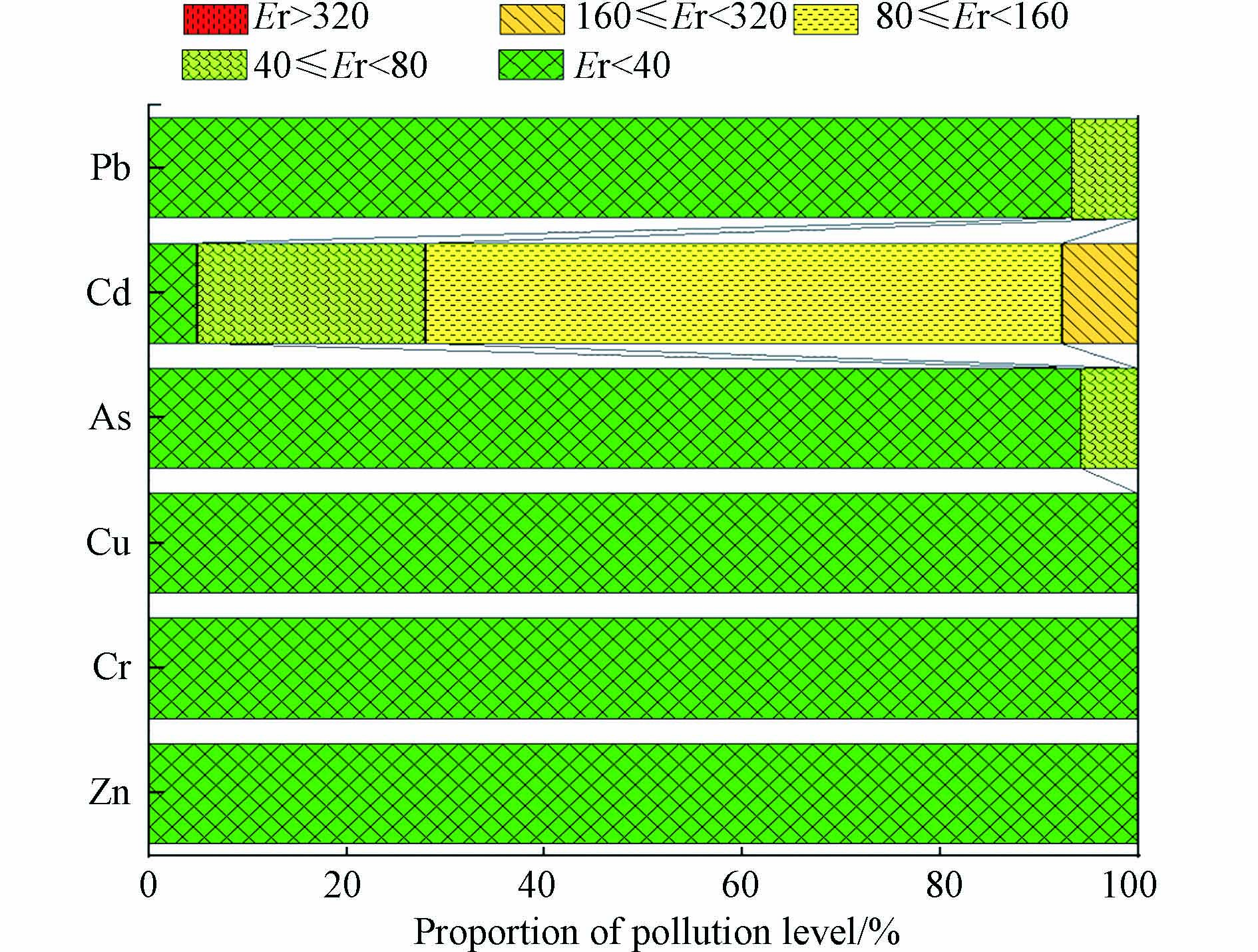
由图3可以看出,研究区土壤中全量重金属元素Cd是单项潜在生态危害较高的元素,其中Cd元素在64%的样点属于较重生态危害,在8%的样点属于重生态危害,中等生态危害以下的样点占28%. 其余元素的生态危害都相对较低. 整体而言研究区单项潜在生态危害普遍较低,只有Cd元素相比于其他元素具有一定的潜在危害.
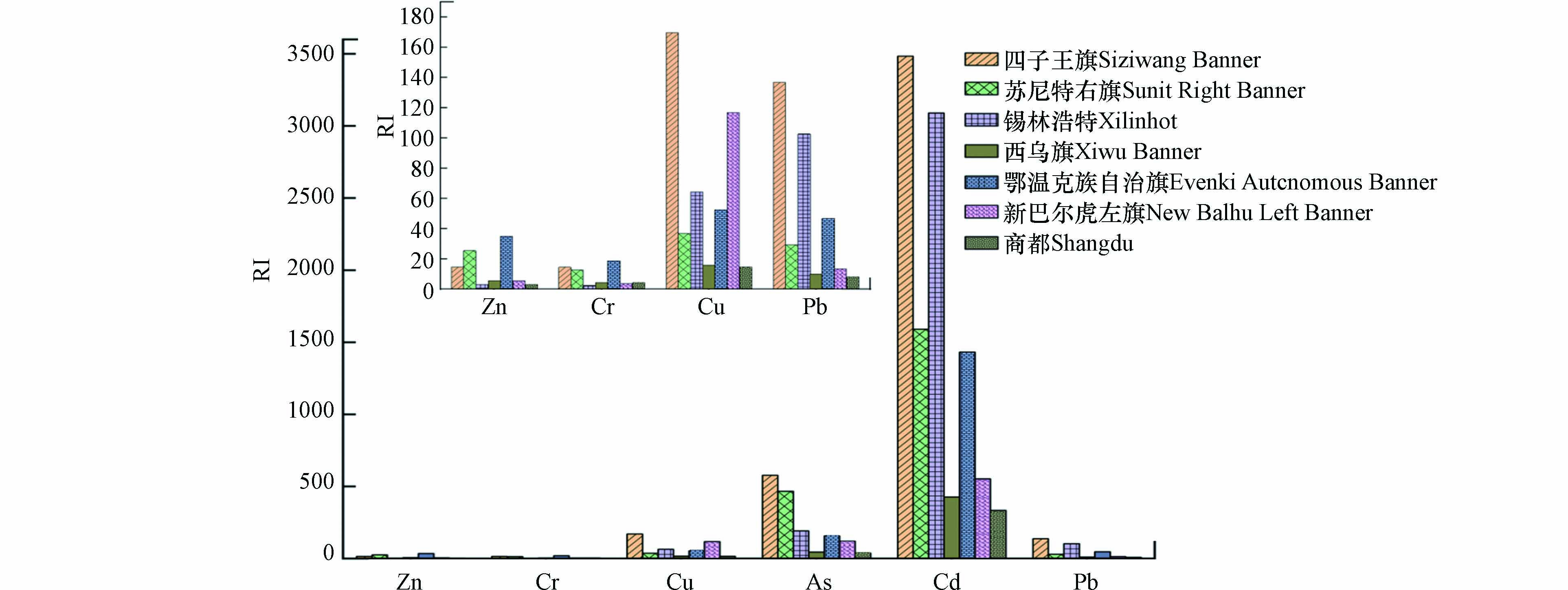
如图4所示,不同地区采样点土壤全量重金属潜在生态危害综合指数 (RI)计算结果显示,Zn、Cr和Pb元素在所有研究区土壤中均处于低生态危害. Cu元素在四子王旗土壤中处于中等生态危害,As元素在四子王旗和苏尼特右旗土壤中处于重度生态危害,在锡林浩特土壤中处于中等生态危害,其余研究区均处于低生态危害. 研究区土壤受Cd污染较为严重,四子王旗、苏尼特右旗、锡林浩特和鄂温克族自治旗土壤中Cd均处于严重生态危害,西乌旗、新巴尔虎左旗和商都土壤中则处于重度生态危害. 从整体看,大多数重金属对于环境的生态危害相对较低,但研究区土壤中Cd元素对生态环境的潜在风险不容忽视.
-
重金属在土壤环境中有多种赋存形态,根据BCR连续浸提法[27]可以将其分为酸提取态、可还原态(铁锰氧化物结合态)、可氧化态(有机结合态)和残渣态. 酸提取态是指可被植物吸收利用的一类金属,因此对重金属的形态进行分析比全量更为重要. 为了进一步准确评估土壤中重金属的生态风险,对土壤中各金属元素的有效态含量进行了检测. 从表3中可以看出,土壤中各有效态的重金属占全量的质量分数都相对较低. 有效态占全量重金属的比例(1.06%—7.07%)较低,根据Perin等[26]基于重金属不同赋存形态的结合力强弱而提出的风险评估指数法(RAC),研究区RAC的范围在1%—10%,说明研究区土壤中重金属生物可利用性低,对环境构成的风险也比较低.
-
内蒙古自治区地域辽阔,矿产资源丰富. 全区的有色矿产资源集中分布在内蒙古中东部地区,例如呼伦贝尔市北部、赤峰市北部和锡林郭勒盟东北部[28]. 通过Cd元素、As元素和Zn元素的空间分布图可以发现,苏尼特右旗地区土壤中的Cd和As以及鄂温克族自治旗的Zn含量具有较高的累积. 苏尼特右旗已发现的矿藏资源有34种,其中具有开发价值的矿产有20种,鄂温克族自治旗伊敏矿区是我国最早开发的五大露天煤矿之一,除此之外伊敏煤电公司从成立到2011年,坑口电厂总装机容量达340万千瓦,为亚洲最大的坑口电厂[29 − 30]. 因此矿产资源的开发可能是导致研究区重金属污染的原因之一. 一方面矿产资源的开发可能将深埋于土壤中的金属暴露在露天环境中,有色金属尾矿的扬尘颗粒含有大量的金属元素,通过大气沉降进行长距离迁移. 苏尼特右旗气候类型属中温带半干旱大陆性气候,春季干旱多风,夏季干燥,四季温差较大;常年盛行偏西风,一般风力为3— 5级,最大可达9—10级,平均风速可达5.5 m·s-1[31]. 苏尼特右旗属荒漠草原,其地表植被稀疏,防风固沙能力较弱,因此重金属可能通过风蚀作用进行长距离迁移. 另一方面在矿产资源开采的过程中会产生大量的酸性废水,这些废水中含有离子态的重金属元素,通过排水或降水的方式进入到水体或者土壤中进而影响周边生态环境[32]. 鄂温克族自治旗在进行矿产资源的开采过程中必然会产生一些矿山地质环境问题,矿山开发会破坏地下水含水层结构,矿坑疏干排水会将废水中的重金属离子释放到周边环境中,进而造成土壤重金属污染[33]. 除采矿活动外,其他人类活动也可能是引起内蒙古地区重金属污染的原因之一,已有的调查表明,在交通运输过程中,汽车尾气排放、轮胎或路面的磨耗和交通物品泄漏等都会有重金属暴露的风险;通过道路径流、路面喷洒等方式对周围土壤、水体、植物产生一定的影响[34]. 除此之外过度放牧和开垦等行为也会使当地的草原生态受到威胁,如景观结构变化、生物量降低、物种多样性降低等[35]. 人类活动对植被的间接影响最终导致植物对重金属的吸附能力下降,环境中的重金属元素累积越来越多.
在进行土壤重金属风险评估时仅以全量重金属作为评估土壤质量的唯一标准是相对片面的,实际对人类健康构成威胁的主要是有效态重金属. 根据风险评估指数法(RAC)评估结果显示研究区重金属生物可利用性低,但是Cu元素和As元素的风险评估指数偏高,其主要原因在于大多数Cu元素在碱性条件下以沉淀的形式存在于土壤环境中,但也有一部分会被土壤胶体所吸附,土壤内蒙古地区土壤类型大部分为黑钙土、栗钙土 ,因此被土壤胶体所吸附的Cu2+可能会被Ca2+置换下来,从而使得土壤环境中有效态Cu含量偏高[36]. As在土壤中的赋存形态与环境的pH有关,有研究指出当pH在2—7的范围内,土壤对As的吸附能力较强,当pH > 10或 < 1时,土壤对As的吸附能力最弱[37]. 内蒙古地区土壤pH普遍大于7,因此土壤环境中有效态As的含量会相对偏高. 从总体看研究区有效态重金属对环境构成的风险较低. 这可能与研究区土壤理化性质也有一定的关系. 据资料显示内蒙古自治区草原总面积为74.9185万km2是耕地面积的8倍[16]. 草原土壤有机质含量相对较高,草类植被生命周期短,每年死亡大量的地上茎叶和地下根系,为土壤提供了大量的有机质,内蒙古地区秋季昼夜温差较大,导致微生物分解有机质的速率受到影响,有机质积累较多[38]. 有机质在腐殖化过程中会产生高分子有机物,进而强化对重金属离子的固定[39]. 除此之外内蒙古地区土壤pH普遍大于7. 在碱性条件下,离子态的重金属会转化成沉淀,被固定在土壤环境中. 所以从重金属赋存形态来看,重金属对于生态环境的危害相对较低.
根据地累积指数法和潜在综合污染指数法的评价结果可以认定内蒙古中东部地区草原土壤可能存在Cd污染问题,为加强土壤污染防治,建设北疆亮丽风景线,根据本研究结果提出如下几点防治建议:①开展大尺度的土壤重金属污染调查研究和风险评价工作,划定风险等级和区域,根据不同风险等级区域提出合理的防治措施;②明确草原土壤中重金属的污染来源及污染贡献率,以便于更精准的从源头防控;③分析土壤中重金属的赋存形态,研究其在土壤-牧草系统中的迁移规律,从而采取有效的防治措施,降低重金属对土壤-牧草生态系统的破坏.
-
(1)研究区土壤中重金属元素Zn、As和Cd元素平均含量高于内蒙古土壤背景值,分别是背景值的1.98倍、1.53倍和3.58倍,其他元素含量均低于背景值.
(2)研究区不同地区土壤中重金属元素污染程度不同,Zn元素在鄂温克族自治旗地区含量较高;As元素在新巴尔虎左旗和苏尼特右旗具有较高的累积;Cd元素在鄂温克族自治旗、西乌旗、锡林浩特的含量相对较高.
(3)风险评估指数法评价结果显示,研究区重金属生物可利用性较低,对环境构成的风险也相对较低.
(4)地累积指数和潜在生态危害综合指数评价结果显示,研究区土壤中Cd是对生态环境构成潜在危害较大,其他元素从整体看都属于低生态危害. 需要有关环保部门引起高度重视,加强动态监测,做好防治工作,减少重金属污染对草原生态系统的破坏.
内蒙古中东部地区草原土壤中重金属分布特征及生态风险评价
Distribution characteristics and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in grassland soils in the east-central region of Inner Mongolia
-
摘要: 为探究内蒙古中东部地区草原土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险状况,采集四子王旗、苏尼特右旗、商都、锡林浩特、西乌旗、新巴尔虎左旗、鄂温克族自治旗等地区土壤,对其中重金属元素(Cd、Cr、As、Zn、Pb和Cu)的全量和有效态含量进行测定,运用空间插值法分析内蒙古草原土壤中重金属含量的空间分异特征;同时采用地累积指数法、潜在生态风险指数法和风险评估指数法对重金属元素的生态风险进行了评价. 结果表明,内蒙古中东部地区草原土壤全量重金属元素Cr、Cu、Pb的平均含量相对较低,而Cd、As和Zn全量的均值分别是背景值的3.58倍、1.53倍和1.98倍. 地累积指数评价结果显示Cd的污染程度最高,其它元素污染程度相对较低. 潜在生态风险指数评价结果显示Cd为研究区土壤中最主要的潜在生态危害因子,其次是As,其它元素则处于低生态危害. 风险评估指数法结果显示,研究区土壤中有效态重金属占重金属总量的百分含量不到10%,说明研究区土壤中重金属元素的生物可利用性较低,对环境构成的风险也相对较低. 综合来看,研究区土壤中Cd元素存在一定的潜在风险,需引起有关部门高度重视,加大监测力度.Abstract: To investigate the characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metal pollution in grassland soils in the east-central region of Inner Mongolia, soils were collected from Siziwang Banner, Sunit Right Banner, Shangdu, Xilinhot, Xiwuqi, Xinbahuzuo Banner and Ewenke Autonomous Banner. The total and available content of heavy metals (Cd, Cr, As, Zn, Pb and Cu) in soils were determined, the spatial variation characteristics of heavy metal contents in grassland soils of Inner Mongolia were analyzed using spatial interpolation method. The ecological risks of heavy metals were also evaluated using the geological accumulation index, the potential ecological risk index and the risk assessment index. The results showed that the average total contents of Cr, Cu and Pb in the grassland soil of the east-central region of Inner Mongolia were relatively low, while the average total contents of Cd, As and Zn were 3.58, 1.53 and 1.98 times of the background values respectively. The results of the evaluation of the ground accumulation index show that the pollution level of Cd is the highest, while those of other elements is relatively low. The evaluation results of potential ecological risk index showed that Cd was the most important potential ecological hazard factor in the soils of the study area, followed by As, and the other elements were in low ecological hazard. The results of risk assessment index method showed that the available heavy metals in the soils of the study area accounted for less than 10% of the total heavy metals content, indicating that the bioavailability of heavy metal elements in the soils of the study area is low and the risk posed to the environment is relatively low. In general, there is a certain potential risk of Cd in the soil in the study area, which needs to be highly valued by relevant departments and strengthened monitoring.
-
Key words:
- inner Mongolia /
- grassland soil /
- heavy metal pollution /
- risk assessment.
-

-
表 1 土壤采样信息表
Table 1. Soil sampling information table
编号
Number样带编号
Sample number纬度
Latitude经度
Longitude海拔/m
Altitude采样点数
Number of sampling points草原类型
Grassland type1 四子王旗样带1 111.9014 41.7850 1454.30 3 荒漠草原 2 四子王旗样带2 111.9933 41.9729 1498.20 6 荒漠草原 3 四子王旗样带3 111.9972 41.9778 1503.00 18 荒漠草原 4 四子王旗样带4 112.1908 42.1355 1347.76 18 荒漠草原 5 苏尼特右旗样带1 112.5493 42.6040 1163.06 3 荒漠草原 6 苏尼特右旗样带2 113.2477 43.5407 983.21 13 荒漠草原 7 锡林浩特样带1 116.6773 43.5634 1227.04 2 典型草原 8 锡林浩特样带2 116.5593 43.5432 1182.20 19 典型草原 9 锡林浩特样带3 116.6979 43.5844 1212.34 3 典型草原 10 锡林浩特样带4 116.6972 43.5824 1240.35 1 典型草原 11 西乌旗样带 119.1073 41.5543 990.95 3 典型草原 12 鄂温克族自治旗样带1 119.7077 48.5129 720.30 3 草甸草原 13 鄂温克族自治旗样带2 119.7132 48.5197 717.58 8 草甸草原 14 新巴尔虎左旗样带1 118.2716 48.1963 613.10 3 草甸草原 15 新巴尔虎左旗样带2 118.4293 48.1735 670.00 3 草甸草原 16 商都样带 113.3901 41.4881 1391.00 3 荒漠草原 表 2 研究区土壤中不同重金属元素总含量统计表(mg·kg−1)
Table 2. Total contents of different heavy metals in soil of the study area(mg·kg−1)
元素
Element最大值
Maximum最小值
Minimum平均值Average 背景值
Background标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Coefficient of variation平均值/背景值
Average/Background valueZn 411.07 34.21 116.87 59.10 82.53 70.62% 1.98 Cr 60.84 8.49 27.14 41.40 10.22 37.67% 0.66 Cu 110.38 2.90 12.79 14.10 15.94 124.57% 0.91 As 44.41 4.21 11.51 7.50 44.18 71.76% 1.53 Cd 1.10 0.03 0.19 0.053 0.11 60.98% 3.58 Pb 18.04 3.84 11.50 17.20 3.60 31.32% 0.67 表 3 研究区土壤中不同重金属元素有效态含量统计表(mg·kg−1)
Table 3. Statistical table of available state contents of different heavy metal elements in soil of the study area(mg·kg−1)
元素
Element平均值
Average最大值
Maximum最小值
Minimum标准差
Standard deviation变异系数
Coefficient of variationRAC/% Zn 2.63 6.89 1.40 0.02 44.05 2.25 Cr 0.94 1.32 0.68 0.00 10.43 3.46 Cu 1.84 8.53 0.84 0.08 60.19 7.07 As 3.21 3.63 2.41 0.05 9.55 6.22 Cd 0.03 0.05 0.02 0.24 32.41 1.06 Pb 0.99 2.30 0.54 0.03 42.63 2.93 -
[1] WU Y F, LI X, YU L, et al. Review of soil heavy metal pollution in China: Spatial distribution, primary sources, and remediation alternatives[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 181: 106261. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106261 [2] LI P, LI X J, BAI J K, et al. Effects of land use on the heavy metal pollution in mangrove sediments: Study on a whole island scale in Hainan, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 824: 153856. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153856 [3] THANGAVELU L, VEERARAGAVAN G R, MALLINENI S K, et al. Role of nanoparticles in environmental remediation: An insight into heavy metal pollution from dentistry[J]. Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications, 2022: 1946724. [4] 陈能场, 郑煜基, 何晓峰, 等. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692. CHEN N C, ZHENG Y J, HE X F, et al. Analysis of the Report on the national general survey of soil contamination[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(9): 1689-1692 (in Chinese).
[5] MIAO F F, ZHANG Y M, LI Y, et al. Implementation of an integrated health risk assessment coupled with spatial interpolation and source contribution: A case study of soil heavy metals from an abandoned industrial area in Suzhou, China[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2022, 36(9): 2633-2647. doi: 10.1007/s00477-021-02146-2 [6] LUO G F, HAN Z W, XIONG J, et al. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of tailings in the Qinglong Dachang antimony mine, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(25): 33491-33504. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12987-7 [7] 内蒙古自治区人民政府办公厅关于印发自治区矿产资源总体规划(2016—2020年)的通知[J]. 内蒙古自治区人民政府公报, 2017(23): 6. [8] 米敬, 赵鹏, 马婷, 等. 内蒙古自治区有色金属采选业重金属排放现状及环保问题的思考与建议[J]. 环境与发展, 2022, 34(5): 81-85. MI J, ZHAO P, MA T, et al. Consideration and suggestion on heavy metals emission status and environmental protection problems in nonferrous metal mining and dressing industry in Inner Mongolia[J]. Environment and Development, 2022, 34(5): 81-85 (in Chinese).
[9] HU Z G, WANG C S, LI K Q, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of soil heavy metals over a typical nonferrous metal mine area in Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(18): 638. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7771-1 [10] 郭伟, 赵仁鑫, 张君, 等. 内蒙古包头铁矿区土壤重金属污染特征及其评价[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(10): 3099-3105. GUO W, ZHAO R X, ZHANG J, et al. Distribution characteristic and assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in the iron mining of Baotou in Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(10): 3099-3105 (in Chinese).
[11] 杨勇, 刘爱军, 朝鲁孟其其格, 等. 锡林郭勒露天煤矿矿区草原土壤重金属分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(5): 885-892. YANG Y, LIU A J, CHAO L, et al. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metals of opencut coal mining in Inner Mongolia Xilingol typical steppe[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(5): 885-892 (in Chinese).
[12] 周妍姿, 王钧, 曾辉, 等. 内蒙古土壤重金属的空间异质性及污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(8): 1381-1387. ZHOU Y Z, WANG J, ZENG H, et al. Spatial characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(8): 1381-1387 (in Chinese).
[13] 郭祥义, 王永康, 张必敏, 等. 内蒙古半干旱草原某铅锌矿区土壤性质及重金属污染生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37((4): ): 851-859. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017080903 GUO X Y, WANG Y K, ZHANG B M, et al. Soil properties and pollution assessment of heavy metals in a lead-zinc mining area of semiarid grassland in Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37((4): ): 851-859 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017080903
[14] 朱荟, 郑春丽, 白晶晶, 等. 内蒙古某尾矿废弃地周边土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2022, 34(6): 55-62. ZHU H, ZHENG C L, BAI J J, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution assessment for a tailings disposal area periphery in Inner Mongolia[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(6): 55-62 (in Chinese).
[15] RONG Y, RUI S, HONG Z. Evaluation on heavy metal contamination and its potential ecological risk in soil: A case study of nonferrous metal smelting zone in Wulatehouqi[J]. Soils, 2016, 48(2): 314-321. [16] 宝祥, 王晶杰. 内蒙古草原现状与动态研究[J]. 内蒙古草业, 2005, 17(4): 9-10, 22. BAO X, WANG J J. Study on the present situation and dynamics of grassland in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Prataculture, 2005, 17(4): 9-10, 22 (in Chinese).
[17] ZHANG W, LONG J H, ZHANG X R, et al. Pollution and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the soil and sediment around the HTM tailings pond, northeastern China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(19): 7072. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17197072 [18] CAO F F, KONG L H, YANG L Y, et al. Geochemical fractions and risk assessment of trace elements in soils around Jiaojia gold mine in Shandong Province, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(17): 13496-13505. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4618-0 [19] LI Y L, LI P Y, LIU L N. Source identification and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the topsoil of the Weining plain (northwest China)[J]. Exposure and Health, 2022, 14(2): 281-294. doi: 10.1007/s12403-021-00438-0 [20] 李娇, 滕彦国, 吴劲, 等. 基于PMF模型及地统计法的乐安河中上游地区土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(6): 984-992. LI J, TENG Y G, WU J, et al. Source apportionment of soil heavy metal in the middle and upper reaches of le’an river based on PMF model and geostatistics[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(6): 984-992 (in Chinese).
[21] 闫文帅. 基于高斯过程的地理时空数据插值模型及其应用[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2022. YAN W S. Geographic spatiotemporal data interpolation model based on Gaussian process and its application[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2022 (in Chinese).
[22] MULLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2: 108-118. [23] 王妍. 呼和浩特市保护地苔藓植物对土壤性质及重金属的影响研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2020. WANG Y. Effects of bryophytes on soil properties and heavy metals in protected areas of Hohhot city[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[24] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [25] 李富, 刘赢男, 郭殿凡, 等. 哈尔滨松江湿地重金属空间分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(11): 1869-1878. LI F, LIU Y N, GUO D F, et al. Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of the Songjiang wetland in Harbin city[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(11): 1869-1878 (in Chinese).
[26] PERIN G, CRABOLEDDA L, LUCCHESE M, et al. Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of northern adriatic sea: A new approach for environmental toxicity determination[J]. Heavy Metals in the Environment, 1985, 2(1): 454-456. [27] URE A M, QUEVAUVILLER P, MUNTAU H, et al. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. an account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the commission of the European communities[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1993, 51(1/2/3/4): 135-151. [28] 辛江. 内蒙古东南部多金属成矿系列与找矿模型[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. XIN J. The polymetallic metallogenic series and exploration model in the southeast of Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2013 (in Chinese).
[29] 牡丹. 苏尼特右旗县域经济发展中政府职能研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2013. MU D. Study on Sonid Right Banner County economic development of the function of the government[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University, 2013 (in Chinese).
[30] 许蕊. 呼伦贝尔能源矿产集中开采区矿山地质环境调查与研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. XU R. Hulun Buir energy minerals concentrated investigation and research on the mine geological environment in mining area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014 (in Chinese).
[31] 岳征文, 张瑞强, 王健, 等. 苏尼特右旗草原矿区土壤重金属污染特征与生态恢复[J]. 林业资源管理, 2017(6): 124-130. YUE Z W, ZHANG R Q, WANG J, et al. Research on the characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution and ecological restoration in grassland mining area of sunite County[J]. Forest Resources Management, 2017(6): 124-130 (in Chinese).
[32] YOUNG G, CHEN Y Q, YANG M. Concentrations, distribution, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the iron tailings of Yeshan National Mine Park in Nanjing, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 271: 129546. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129546 [33] 何身焱, 刘波, 王水华, 等. 长江中游南岸某工业园区土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2022, 36(6): 787-794. HE S Y, LIU B, WANG S H, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil of an industrial park on the south bank of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2022, 36(6): 787-794 (in Chinese).
[34] 任志建, 余爱华, 徐贝贝. 路域环境中土壤重金属污染的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2022, 51(3): 787-792. REN Z J, YU A H, XU B B. Research progress in heavy metal pollution of roadside soil[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(3): 787-792 (in Chinese).
[35] 米红胤. 荒漠草原综合生态风险评价: 以内蒙古四子王旗为例[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2016. MI H Y. Integrated ecological risk assessment on desert steppe— in Siziwang County, Inner Mongolia, for example[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2016 (in Chinese).
[36] 刘冠男, 刘新会. 土壤胶体对重金属运移行为的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32((7): ): 1308-1317. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.07.026 LIU G N, LIU X H. A review on the impact of soil colloids on heavy metal transport[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32((7): ): 1308-1317 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.07.026
[37] 尹带霞. 稻田土壤中砷迁移转化及其机制的原位研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2020. YIN D X. The mechanism of arsenic mobility and transformation in paddy soils with in-situ sensor techniques[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[38] 秦瑞杰. 草本植物生长发育对土壤团聚体和养分动态变化的影响研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2011. QIN R J. Effects of herbage growth on dynamic changes of soil aggregation and nutrients[D]. Yangling: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University, 2011 (in Chinese).
[39] 李璐, 王震宇, 林道辉, 等. 天然有机质与重金属相互作用的分析方法进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(2): 182-189. LI L, WANG Z Y, LIN D H, et al. Advances in analytical methods for investigating the interaction between natural organic matters and heavy metals[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(2): 182-189 (in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: