-
随着现代工业化和城镇化进程的加快,人类高强度的活动导致重金属被排放到环境中,造成了严峻的大气、土壤和水环境重金属污染问题[1-2]. 环境中的重金属污染具有蓄积性、持久性和不可逆性,其不仅会改变环境的组成和功能,还会影响农作物的生长,造成农产品的产量和品质的下降,甚至可能影响人体健康,因而越来越受到人们的重视[3]. 重金属污染已成为我国乃至全球重点关注的污染之一[4]. 其中,重金属铅和类金属砷均是毒性较大的重金属污染物[5-6]. 基于对铅和砷的生物学效应和人体健康损害的认识,美国环境保护署(USEPA)已将铅和砷列为毒性效应最强的重金属[7],同时国际癌症研究机构(IARC)也将砷列为I类人类致癌物,铅列为很可能的人类致癌物质(2A类)[8].
为了保护生态环境和人群健康,依据重金属的单一毒性效应,世界各国或组织颁布了不同介质中重金属的浓度限量值[9]. 然而很多研究表明,低于浓度限量值的重金属混合物仍会对生物体产生毒性效应,造成一定的损伤[10]. 重金属的复合污染已成为环境科学研究的热点之一. 砷和铅很容易受到人类活动的影响,共存于环境中,造成复合污染[11-12]. 共存的砷和铅很可能会发生相互作用,从而影响各自在动植物中的生物可利用性及其毒性效应[13]. 然而,目前针对砷和铅的复合毒性效应研究较少,已有的研究主要集中于砷或者铅单一毒性或者与其他污染物的复合毒性,而且铅对砷的毒性效应的影响研究缺乏[14-15]. 为此,本研究拟研究铅对砷毒性效应的影响,探讨砷和铅的复合毒性效应.
此外,毒代动力学过程可以反映重金属从生物体外到生物体内的浓度,决定了重金属在生物体内的残留量,关系到该重金属对生物体的毒性效应. 毒代动力学已被广泛应用于重金属毒性效应的研究. Gao等[16]采用毒代动力学方法阐释预暴露对重金属毒性效应的影响并将毒代动力学用于斑马鱼幼鱼和成鱼毒性敏感性差异的研究[17]. Huang等[18]也采用毒代动力学方法阐释了野生蚯蚓对镉具有更强耐受力的原因. 此外,暴露环境的物理(如温度)和化学(如盐度、pH)因素对重金属毒性效应的改变也与毒代动力学过程的变化密切相关[19]. 而环境中共存的重金属之间也可能会发生相互作用,改变生物体对重金属的吸收、转化、代谢和积累等毒代动力学过程,导致毒性效应的变化[20]. 因此,毒代动力学分析可成为重金属复合毒性效应形成机制研究的有力工具之一[21]. 据此,本研究将结合毒代动力学过程阐释铅对砷毒性效应影响形成的可能原因.
本研究将开展砷和铅对斑马鱼的复合毒性效应研究,重点关注铅对砷的斑马鱼毒性效应的影响,探讨砷和铅对斑马鱼的复合毒性效应,并利用毒代动力学过程分析方法阐释铅对砷的毒性效应影响的可能原因.
-
供试生物:实验用雌性斑马鱼(Danio rerio)为4月龄野生型AB品系,购买自国家斑马鱼资源中心.
实验试剂:醋酸铅((CH3COO)2Pb·3H2O,≥99.5%)和浓硝酸(HNO3,65.0%—68.0%)(国药上海化学试剂公司)、亚砷酸钠(NaAsO2,99%)(北京伊诺凯科技有限公司)、铅和砷标准溶液(浓度均为1000 μg·mL−1)(国家标准物质资源平台).
实验设备:Ymnl-48组织均研磨器(南京以马内利仪器设备公司)、MARS6微波消解系统(美国CEM公司)、Agilent 7700电感耦合等离子体串联质谱仪(ICP-MS,安捷伦科技有限公司)
-
野生成年斑马鱼购买后置于28 °C的流通式系统中养殖,光暗周期为14 h:10 h. 在开展暴露实验前,斑马鱼在一个装有15 L曝气水的玻璃水箱中驯化. 所有斑马鱼每天喂食2次新鲜孵化的丰年虫. 斑马鱼暴露实验开始前,分别开展铅和砷的96 h预暴露实验以确定暴露实验水溶液中重金属的浓度. 铅和砷预暴露实验结果表明,铅的96 h 10%致死浓度(LC10)为1.44 mg·L−1,砷的96 h 半数致死浓度(LC50)为32 mg·L−1. 本文主要研究铅对砷的毒性效应的影响,因此铅的浓度设为对斑马鱼无明显致死效应的水平(1.44 mg·L−1),而砷的浓度设为对斑马鱼产生一定致死效应的水平(20 mg·L−1). 斑马鱼暴露实验分为动力学吸收阶段实验和动力学消除阶段实验. 使用超纯水配制重金属铅、砷暴露母液,浓度分别为0.6 g·L−1和4 g·L−1,现用现配. 实验时用曝气水分别配制成1.44 mg·L−1铅和/或20 mg·L−1砷的暴露水溶液. 动力学吸收阶段实验设置3种暴露情形,即对照组、20 mg·L−1砷单独暴露组和1.44 mg·L−1铅+20 mg·L−1砷共同暴露组. 每种暴露情形共设置30个鱼缸,每个鱼缸中放入5条斑马鱼. 动力学吸收阶段实验的暴露时间为96 h,暴露开始后的8、24、48、72、96 h分别取样并记录斑马鱼死亡情况,每个时间点取3个平行样(即3个鱼缸). 动力学吸收阶段实验结束后,立即将3种暴露情形剩余的斑马鱼转移至对应不含砷的暴露水溶液中,即3种暴露情形变为对照、曝气水暴露和1.44 mg·L−1铅暴露,开始动力学消除阶段实验. 动力学消除阶段暴露开始后的1、2、3、5、7 d分别取样并记录斑马鱼死亡情况,每个时间点取3个平行样. 每天更换新鲜暴露水溶液,以维持暴露水溶液重金属浓度的稳定性.
-
重金属铅和砷的含量分析参照已报道的研究方法开展[22-23]. 暴露结束后对斑马鱼进行冰冻处死,将斑马鱼体表擦干后称重并收集在离心管中,全鱼样品磨碎后放入消解管中,加入10 mL浓硝酸并盖紧瓶盖后放入微波消解系统中消解2 h直至溶液清澈透明,然后用超纯水定容至10 mL. 消解后的全鱼样品以及暴露水溶液都经Whatman GF-C滤纸(0.22 μm孔径)过滤到离心管中. 铅和砷在暴露水溶液和斑马鱼体内的浓度通过ICP-MS在KED模式下测定,仪器的相对标准偏差控制在5%以内. 水溶液和斑马鱼体内重金属的含量分别以mg·L−1和mg·kg−1表示.
-
为模拟毒代动力学相关参数,吸收和消除速率常数ku和ke,本研究采用一级一室动力学模型对重金属的毒代动力学过程进行模拟. 使用Scientist® (Micromath, USA)软件包根据式(1)对实验数据进行拟合.
式中,Cb表示斑马鱼体内砷的浓度(mg·kg−1),Cw表示暴露水溶液中砷的浓度(mg·L−1),ku表示吸收速率常数(L·kg−1·d−1),ke表示消除速率常数(d−1).
评价砷在斑马鱼体内发生生物积累能力的指标——生物浓缩因子(bioconcentration factor, BCF)根据式(2)计算得到. 砷在斑马鱼体内的半衰期(t1/2)根据式(3)计算得到.
本研究中采用t-test方法对不同暴露实验组获得的吸收速率常数ku和消除速率常数ke进行统计分析比较. 使用单因素方差分析法(one-way ANOVA)对不同暴露实验组斑马鱼致死率进行统计分析比较. 所有的统计分析均使用Sigmaplot 12.3(Systat Software Incorporation, San Jose, CA, USA)进行.
-
通过对暴露实验开始和结束阶段水中砷和铅的化学分析可以发现,暴露水溶液更换前后水中砷和铅的浓度为各自理论加标浓度的89%、96%和85%、93%,表明暴露过程中水溶液的砷和铅的浓度均保持稳定,并且与各自理论加标浓度相接近. 一方面暴露实验过程中每天会更新加标水溶液,另一方面重金属性质稳定,短时间内不易发生代谢转化,因此,水中砷和铅的浓度与各自理论加标浓度接近. 在污染物毒代动力学的研究中,控制和维持暴露介质中污染物浓度的稳定性十分重要[24-25]. 其他许多关于污染物动力学的研究也均采用了换水或者被动加标的方法维持暴露实验过程中污染物浓度的稳定性,以便于毒代动力学研究的开展[26-28].
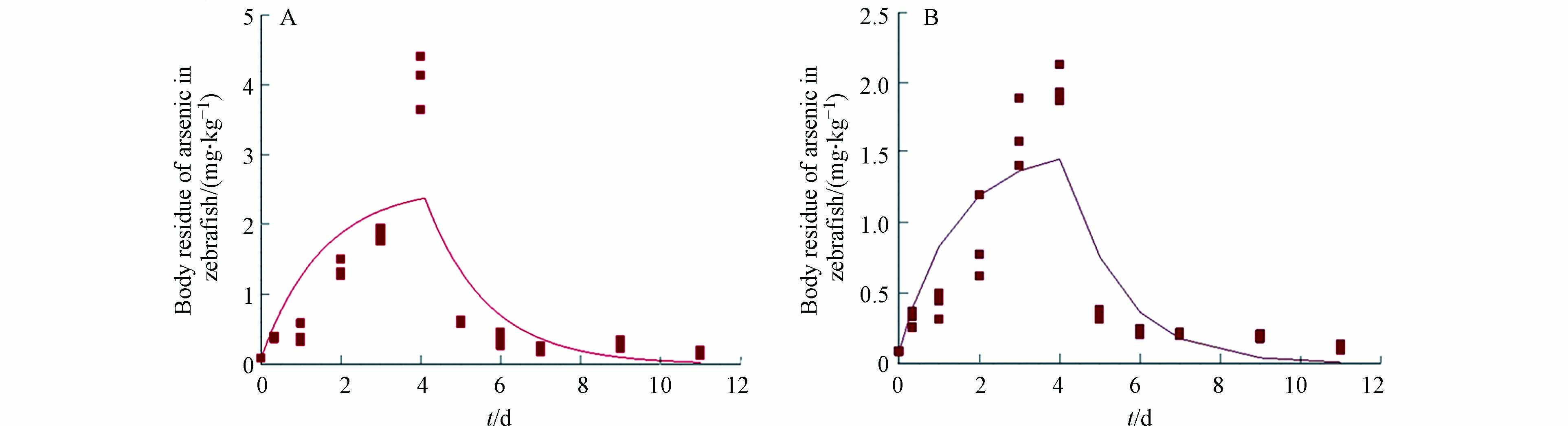
分析两种暴露实验情形下不同采样时间点的斑马鱼体内的重金属残留量可以发现,吸收阶段(0 d至4 d)斑马鱼体内的砷浓度均随着暴露时间的延长而显著升高,且砷在斑马鱼体内的积累呈现出先快后慢的现象;消除阶段(4 d至11 d)斑马鱼体内的砷浓度均逐步降低,且砷在斑马鱼体内的消除也呈现出先快后慢的现象(图1). 本研究结果与Chen等[29]报道的砷在青鳉鱼(Oryzias melastigma)吸收和消除现象类似. 斑马鱼暴露8 h后体内的砷浓度便发生显著性升高,说明斑马鱼在本研究条件下易于吸收和富集砷.
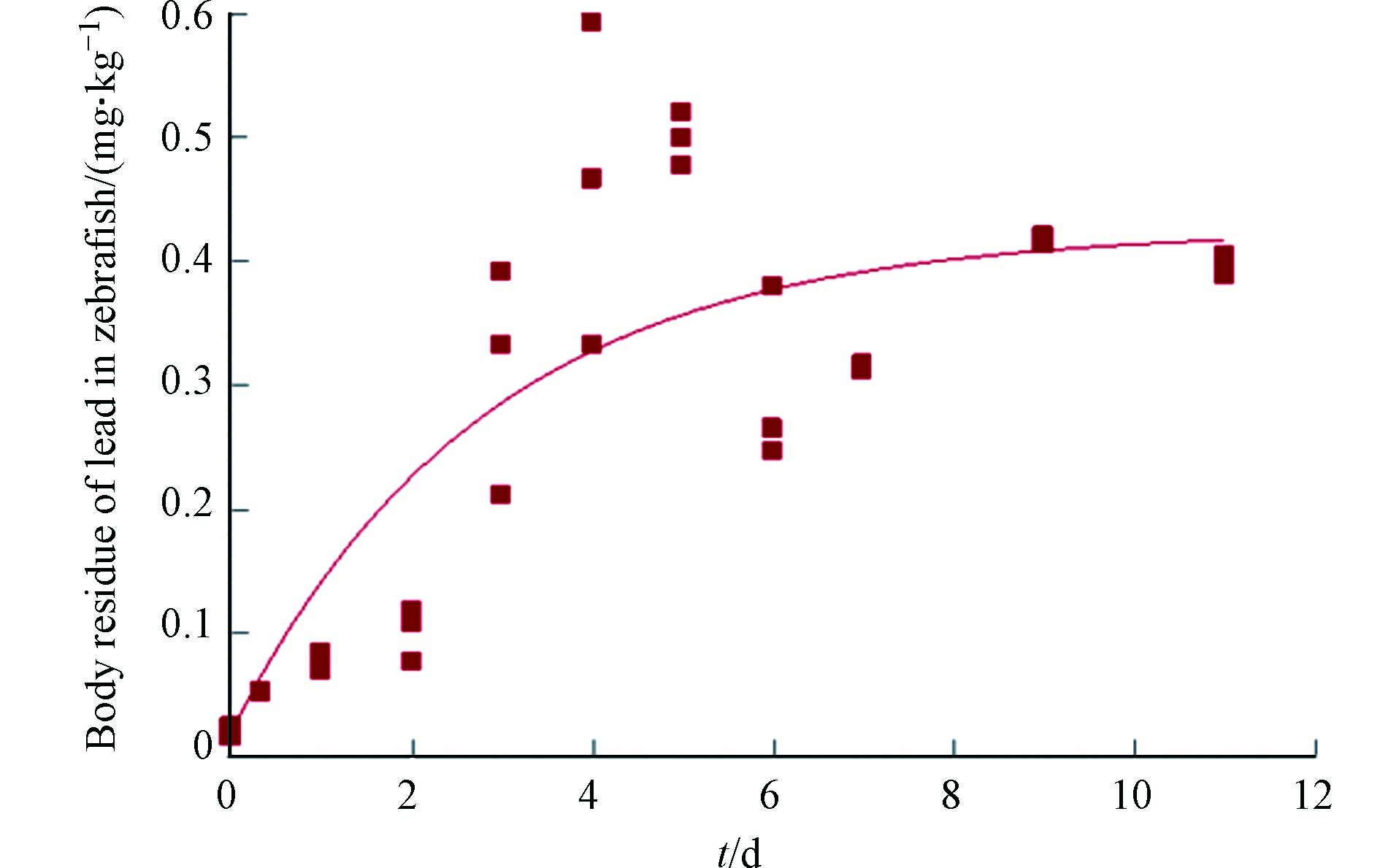
此外,在砷和铅共同暴露情形下,吸收阶段和消除阶段的暴露水溶液中均含有铅,因此,斑马鱼体内的铅的浓度随着暴露时间(包含吸收和消除暴露时间)的延长逐步升高直至基本维持稳定(图2). 与砷一样,铅在斑马鱼体内的富集也呈现出先快后慢的现象,而且暴露8 d左右斑马鱼体内的铅基本可以达到稳态,且稳态浓度约为0.4 mg·kg−1. 本研究关于铅在斑马鱼体内的动力学现象与Gao等[30]和Zhang等[31]的研究结果类似.
-
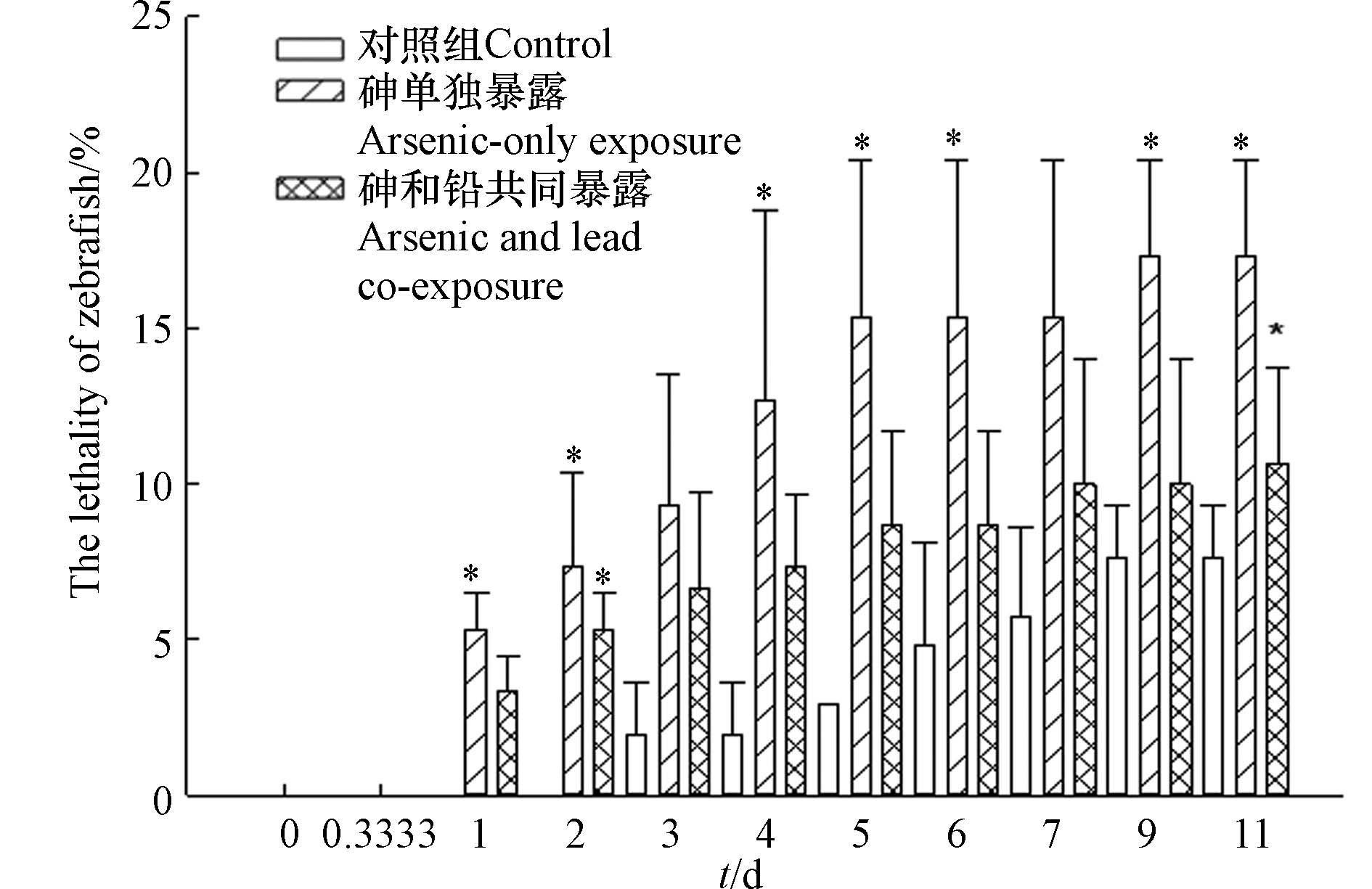
如图3所示,对照组中斑马鱼的致死率最高为7.6%,并且不同暴露时间的斑马鱼致死率并无显著性差异,满足毒性实验的质控要求. 砷单独暴露实验情形下,在吸收暴露阶段(0 d至4 d),斑马鱼的平均致死率升至12.7%,显著高于对照组(1.9%);在消除暴露阶段(4 d至11 d),斑马鱼平均致死率升至17.3%,但是不同时间点的致死率并无显著性差异. 吸收暴露实验阶段,斑马鱼暴露于含砷的水溶液中,导致斑马鱼致死率逐步提高,而将斑马鱼转移到清水中开展消除暴露实验后,斑马鱼不再受砷的污染胁迫,几乎不再发生死亡. 砷单独暴露时,斑马鱼暴露4 d的致死率为12.7%±6.1%,符合预先的动力学实验设计. 本研究中获得砷对斑马鱼的96 h-LC50为32 mg·L−1,与Liu等[32]报道的砷对斑马鱼的96 h-LC50(56 mg·L−1)以及Sarkar等[33]报道的三氧化二砷对斑马鱼的96 h-LC50(17.5 mg·L−1)的研究结果相接近. 砷和铅共同暴露实验情形下,在吸收暴露阶段,斑马鱼的平均致死率逐步升至7.3%;在消除暴露阶段,斑马鱼的平均致死率升至10.7%,但并未产生显著性变化. 吸收暴露阶段,斑马鱼暴露于含砷和铅的水中,导致斑马鱼致死率逐步升高. 然而,斑马鱼转移至只含铅的水中开展消除暴露实验后,斑马鱼的致死率变化不明显. 从消除暴露实验结果可见,铅的存在对斑马鱼并未造成明显的致死效应. 结果符合本研究中暴露实验设计,即铅不产生明显致死效应,探究铅对砷的毒性效应和毒代动力学的影响.
对比分析两种暴露情形斑马鱼的致死率可以发现,在同一暴露时间下(如暴露96 h时),砷单独暴露组的斑马鱼致死率(12.7%±6.1%)要显著高于对照组斑马鱼的致死率(1.9%±1.7%),略高于砷和铅共同暴露组斑马鱼的致死率(7.3%±2.3%),而砷和铅共同暴露组斑马鱼的致死率大多略高于对照组斑马鱼的致死率但并无显著性差异. 由此可见,本研究条件下,砷会对斑马鱼产生明显的致死效应,铅并未对斑马鱼造成明显的致死效应,但是铅与砷共存时斑马鱼的致死效应被减弱,说明铅的共存显著降低了砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应. 关于重金属间的复合毒性效应作用类型及形成机制的研究有很多,已报道的复合毒性作用类型既包括协同作用,也有拮抗作用,并且形成机制也各有差异. 氧化压力是重金属产生毒性效应的重要致毒机制之一[34-35],而低浓度的铅可能会激发生物体的抗氧化保护机制,如抗氧化酶活性的升高,减轻氧化压力[36],从而抑制砷的毒性效应. 有研究发现不同毒性单位配比的铅与镉以及铅与铬对斑马鱼胚胎的致死率和孵化率的复合毒性均表现为拮抗效应[37],这可能与铅激发了生物体的保护机制(抗氧化机制)相关,也与重金属之间可能存在的竞争相关. 重金属需要通过细胞膜进入细胞,而多种重金属共存时可能会在跨细胞膜转运时产生竞争,也可能改变细胞膜的通透性,从而影响重金属进入生物体过程. 镉与铬对斑马鱼胚胎的致死率和孵化率的协同毒性效应可能是由于镉与细胞表面膜蛋白的巯基、羰基、氨基等作用,改变细胞膜结构和稳定性,增强细胞膜通透性,导致重金属更加容易进入细胞[37]. 本研究中铅是否影响砷进入生物体的过程,从而减弱砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应,可以通过毒代动力学研究进一步明晰.
此外,有研究发现砷和镉共同暴露对钩虾的致死性呈现拮抗效应[38]. 该研究发现,与单一重金属暴露相比,砷和镉混合暴露会导致钩虾生物富集性下降,生物体内的重金属量降低,从而导致毒性效应降低. Vellinger等[39]进一步研究发现砷和镉混合暴露导致钩虾体内γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸连接酶活性升高、谷胱甘肽(GSH)和金属硫蛋白(MT)含量增加,加快了重金属被排除生物体外的速率,增强了重金属代谢解毒过程. 本研究中铅是否加快了砷的消除速率以及降低了砷的生物富集性,从而降低了砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应,也可以通过毒代动力学研究进一步解释. 综合上述相关研究结果,开展重金属的毒代动力学过程研究可以进一步阐述本研究中铅减弱砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应的相关机制.
-
污染物在生物体内的毒代动力学过程直接影响着该污染物对生物体的毒性效应. 当生物体暴露于混合污染物中,其中一种污染物可能会影响其他污染物的吸收、生物转化、分配和消除,这些导致了污染物间的相互作用,很有可能改变污染物的毒性效应[40-42]. 因此,毒代动力学过程的研究能够在一定程度上解释复合毒性产生原因. 本研究采用一级一室动力学模型分别对两种暴露情形中砷的毒代动力学过程进行拟合,斑马鱼体内砷的毒代动力学拟合曲线如图1所示. 两组暴露情形拟合曲线的决定系数(R2)分别为0.66和0.77(表1),表明两组毒代动力学暴露实验中获得的砷的残留量数据均能够较好地进行一级动力学模拟[31].
Cui等[14]关于砷在鲫鱼肌肉中的动态变化的研究发现亚砷酸盐的吸收速率常数为0.041 g·g−1·d−1、消除速率常数为0.708 d−1,该结果与本研究中砷单独暴露实验组的结果类似. 对比两组暴露情形中砷的吸收速率常数和消除速率常数(表1)可以发现,铅的存在显著降低了斑马鱼对砷的吸收速率并加快了斑马鱼对砷的消除速率,因此导致砷和铅共同暴露组斑马鱼体内砷的残留量低于砷单独暴露组斑马鱼体内砷的残留量. 该结果正好验证了前述毒理实验结果,即铅的存在显著降低了砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应,砷和铅产生拮抗效应. 与此同时,砷单独暴露时斑马鱼对砷的生物浓缩因子也显著高于砷和铅共同暴露时斑马鱼对砷的生物浓缩因子. 该结果也进一步说明铅的存在降低了砷在斑马鱼体内富集的能力,削弱了砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应. 前期有许多研究也表明生物体中一种污染物会影响另一种污染物的毒代动力学过程,进而影响另一种污染物对该生物体的毒性效应. Broerse等[43]研究发现,镉的共存影响了芘在土壤中生活的弹尾目生物Folsomia candida体内的毒代动力学过程. 镉的存在降低了芘的吸收和消除速率,同时加快了芘发生生物转化为其羟基代谢产物,但是减慢了其羟基化代谢产物进一步的代谢. 可以看出,重金属镉的存在显著地影响了污染物芘的生物积累和代谢. Steevens和Benson[44]发现,甲基汞的吸收和消除速率明显受到共暴露的另一种污染物——毒死蜱的影响. 当底栖生物钩虾(Hyalella azteca)同时暴露于甲基汞和毒死蜱时,毒死蜱加速了生物体对甲基汞的吸收,但是减缓甲基汞的消除,使得更多的甲基汞被生物体积累,导致两种污染物间产生相互作用. 砷的化学性质与细胞内多种物质(磷酸酯、葡萄糖和甘油等)类似,导致砷可以通过多种运输通道进入细胞,如水通道蛋白(AQP)和己糖转运蛋白(HXT)[45]. 而ABC转运蛋白和多药耐药相关蛋白(MRP)是砷排出细胞的重要蛋白[45-46],其中ABC转运蛋白被认为是水生生物应对环境污染物的第一道防御机制[47]. 铅的存在可能会与AQP和HXT等运输通道发生相互作用,降低相关基因表达水平,阻碍斑马鱼对砷的吸收. 此外,低浓度铅的存在可能激活生物体防御机制,如增强ABC转运蛋白和MRP相关基因表达水平,加速斑马鱼对污染物的排出. 然而,铅是否是通过作用砷的转运通道来降低砷的吸收速率以及加快砷的消除速率还需深入展开研究.
-
本研究选用斑马鱼作为模式生物开展了铅和砷的复合毒性效应评价,发现本研究中铅单独暴露对斑马鱼未产生明显致死效应,而共同暴露时铅能够显著降低砷对斑马鱼的致死效应. 本研究进一步通过毒代动力学研究发现铅的存在既降低了斑马鱼对砷的吸收速率,又加快了斑马鱼对砷的消除速率,导致斑马鱼降低对砷的富集能力,从而削弱了砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应. 毒代动力学研究有力阐释了砷和铅对斑马鱼形成拮抗效应的原因. 本研究揭示了砷和铅的复合毒性及形成原因,充实了重金属的复合毒性基础数据.
铅对砷的毒性效应及毒代动力学过程的影响
The influence of lead on toxic effect of arsenic and its toxicokinetic process
-
摘要: 为探究铅对砷的毒性效应的影响及其原因,本研究选用斑马鱼作为模式生物开展了毒理实验,以评价砷和铅的复合毒性效应,分析斑马鱼体内重金属残留量,并采用一级一室动力学模型模拟了砷的毒代动力学过程. 毒理实验结果表明,铅对斑马鱼未产生明显致死效应,砷对斑马鱼的致死效应随暴露时间增长显著增强,而铅的共存能够显著降低砷对斑马鱼的致死性,砷和铅对斑马鱼的致死性呈现出拮抗效应. 毒代动力学结果表明,铅的存在显著加快了斑马鱼对砷的消除速率并减弱了吸收速率,可降低斑马鱼对砷的富集能力,从而削弱了砷对斑马鱼的毒性效应. 本研究揭示了砷和铅对斑马鱼的拮抗效应并从污染物毒代动力学的角度解释了复合毒性形成原因,充实了重金属的复合毒性效应基础数据,可提高重金属风险评估的准确性.Abstract: To explore the influence of lead on arsenic toxicity and its formation mechanism, zebrafish was selected as model organism to conduct toxicology test in this study. Joint toxicity of arsenic and lead was evaluated. Body residue of metals in zebrafish was analyzed and toxicokinetic process of arsenic was simulated by first order one compartment toxicokinetic model. The toxicology test results indicated lead did not generate lethal effect for zebrafish, but lethal effect caused by arsenic increased significantly with the increase of exposure time. However, the coexistence of lead can significantly reduce the lethality of arsenic to zebrafish. Arsenic and lead showed antagonistic effects on zebrafish lethality. The toxicokinetic results showed the presence of lead significantly accelerated the elimination rate and reduced the uptake rate of arsenic in zebrafish. Thus, the bioconcentration ability of arsenic in zebrafish was weakened and the toxic effect of arsenic on zebrafish was mitigated. This study revealed the antagonistic effect of arsenic and lead on zebrafish and explained the mechanism of joint toxicity from the perspective of toxicokinetic. It provides basic data of joint toxicity for metals and improved the accuracy of risk assessment of metals.
-
Key words:
- arsenic /
- lead /
- toxic effect /
- toxicokinetic /
- zebrafish.
-

-
表 1 砷单独暴露以及砷和铅共同暴露时斑马鱼体内砷的毒代动力学参数(n=3)
Table 1. Toxicokinetic parameters of arsenic in zebrafish in arsenic-only exposure and arsenic and lead co-exposure (n=3)
毒代动力学参数
Toxicokinetic parameter砷单独暴露
Arsenic-only exposure砷和铅共同暴露
Arsenic and lead co-exposureku/(L·kg−1·d−1) 0.0825±0.0170 0.0560±0.0089 ke/d−1 0.645±0.153 0.729±0.131 t1/2/d 8.4 12.4 BCF/(L·kg−1) 0.128 0.0768 R2 0.66 0.77 -
[1] 余涛, 蒋天宇, 刘旭, 等. 土壤重金属污染现状及检测分析技术研究进展 [J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(2): 460-476. YU T, JIANG T Y, LIU X, et al. Research progress in current status of soil heavy metal pollution and analysis technology [J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(2): 460-476(in Chinese).
[2] WU Y F, LI X, YU L, et al. Review of soil heavy metal pollution in China: Spatial distribution, primary sources, and remediation alternatives [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 181: 106261. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106261 [3] 黎森, 王敦球, 于焕云. 铅-砷交互作用影响小白菜生长及铅砷积累的效应研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(1): 170-180. LI S, WANG D Q, YU H Y. Effect of Pb and As interaction on the growth and As and Pb accumulation of Brassica campestris L. [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(1): 170-180(in Chinese).
[4] QIN Y H, TAO Y Q. Pollution status of heavy metals and metalloids in Chinese lakes: Distribution, bioaccumulation and risk assessment [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 248: 114293. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114293 [5] FATOKI J O, BADMUS J A. Arsenic as an environmental and human health antagonist: A review of its toxicity and disease initiation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 2022, 5: 100052. doi: 10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100052 [6] FLORA G, GUPTA D, TIWARI A. Toxicity of lead: A review with recent updates [J]. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 2012, 5(2): 47-58. doi: 10.2478/v10102-012-0009-2 [7] JONES E A, WRIGHT J M, RICE G, et al. Metal exposures in an inner-city neonatal population [J]. Environment International, 2010, 36(7): 649-654. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2010.04.007 [8] World Health Organization. Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–132[EB/OL]. [2022-09-23]. [9] 汤亚云, 管凡荀, 高鹏飞, 等. 不同国家或组织动物源性食品中重金属限量标准的比较研究 [J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2022(14): 8-13+21. doi: 10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2021.04.0346 TANG Y Y, GUAN F X, GAO P F, et al. Comparative study on heavy metal limit standards of animal derived food in different countries or organizations [J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2022(14): 8-13+21(in Chinese). doi: 10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2021.04.0346
[10] FOWLER B A, WHITTAKER M H, LIPSKY M, et al. Oxidative stress induced by lead, cadmium and arsenic mixtures: 30-day, 90-day, and 180-day drinking water studies in rats: An overview [J]. Biometals, 2004, 17(5): 567-568. doi: 10.1023/B:BIOM.0000045740.52182.9d [11] 钱学诗, 李勇, 钱壮壮, 等. 北亚热带东部次生阔叶林降水过程中的镉、铅、砷含量变化 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 979-989. QIAN X S, LI Y, QIAN Z Z, et al. Changes of cadmium, lead and arsenic contents during precipitation in the secondary broad-leaved forest in the eastern area of north subtropics, China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(5): 979-989(in Chinese).
[12] 曲良, 谭海涛, 刘涛, 等. 北部湾铁山港附近海域水体和沉积物重金属分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(3): 757-768. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022102606 QU L, TAN H T, LIU T, et al. Distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the seawater and sediment of Tieshan Port, Beibu Gulf [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(3): 757-768(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2022102606
[13] 杨小俊, 次仁德吉, 吴雪莲, 等. 铅—砷交互作用对青稞苗期生长及铅砷吸收积累的影响 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(9): 2189-2196. YANG X J, CIRENDEJI, WU X L, et al. Effect of Pb-As interaction on highland barley growth and Pb-As uptake and accumulation at seedling stage [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(9): 2189-2196(in Chinese).
[14] CUI D, ZHANG P, LI H P, et al. The dynamic changes of arsenic biotransformation and bioaccumulation in muscle of freshwater food fish crucian carp during chronic dietborne exposure [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 100: 74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.07.005 [15] LIU X S, WANG J M, HUANG Y W. Quantifying the effect of nano-TiO2 on the toxicity of lead on C. dubia using a two-compartment modeling approach [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 127958. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127958 [16] GAO Y F, XIE Z C, ZHU J X, et al. Understanding the effects of metal pre-exposure on the sensitivity of zebrafish larvae to metal toxicity: A toxicokinetics–toxicodynamics approach [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 209: 111788. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111788 [17] GAO Y F, ZHANG Y, FENG J F, et al. Toxicokinetic−toxicodynamic modeling of cadmium and lead toxicity to larvae and adult zebrafish [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 251: 221-229. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.003 [18] HUANG C D, GE Y, SHEN Z Q, et al. Reveal the metal handling and resistance of earthworm Metaphire californica with different exposure history through toxicokinetic modeling [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 289: 117954. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117954 [19] WANG W X, TAN Q G. Applications of dynamic models in predicting the bioaccumulation, transport and toxicity of trace metals in aquatic organisms [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 1561-1573. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.043 [20] OLLSON C J, SMITH E, HERDE P, et al. Influence of co-contaminant exposure on the absorption of arsenic, cadmium and lead [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 168: 658-666. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.010 [21] 冯剑丰, 高永飞, 朱景雪, 等. 毒代-毒效动力学模型及其在金属水生态风险评估中的应用研究进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(11): 10-18,124. FENG J F, GAO Y F, ZHU J X, et al. Application of toxicokinetic-toxicodynamic models in aquatic ecological risk assessment for metals [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(11): 10-18,124(in Chinese).
[22] 甘露菁, 荣菡, 杨丹, 等. 斑马鱼对铜、铅和镍的生物富集动力学研究 [J]. 中国食物与营养, 2019, 25(11): 25-29. GAN L J, RONG H, YANG D, et al. Bioaccumulation kinetics of Brachydanio rerio on copper, lead and nickel [J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2019, 25(11): 25-29(in Chinese).
[23] 李欢, 张静丽, 张诗雨, 等. 四环素和砷对斑马鱼的联合毒性及机制 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(7): 3371-3380. LI H, ZHANG J L, ZHANG S Y, et al. Combined toxicity and underlying mechanism of tetracycline and arsenic on zebrafish [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(7): 3371-3380(in Chinese).
[24] ADOLFSSON-ERICI M, ÅKERMAN G, JAHNKE A, et al. A flow-through passive dosing system for continuously supplying aqueous solutions of hydrophobic chemicals to bioconcentration and aquatic toxicity tests [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 86(6): 593-599. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.10.024 [25] OECD. Test No. 417: Toxicokinetics, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4[M]. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2010. [26] CHEN X, LI H Z, ZHANG J J, et al. Does cadmium affect the toxicokinetics of permethrin in Chironomus dilutus at sublethal level? Evidence of enzymatic activity and gene expression [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 218: 1005-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.051 [27] 祁红学, 李慧珍, 游静. 被动加标在水生生态风险评价中的应用——以多氯联苯分配系数的测定为例 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(2): 45-55. QI H X, LI H Z, YOU J. Application of passive dosing in aquatic ecological risk assessment: A case study of measuring partition coefficients of polychlorinated biphenyls [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(2): 45-55(in Chinese).
[28] LI H Z, YOU J, WANG W X. Multi-compartmental toxicokinetic modeling of fipronil in tilapia: Accumulation, biotransformation and elimination [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 360: 420-427. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.085 [29] CHEN L Z, SONG D D, ZHANG W, et al. The dynamic changes of arsenic bioaccumulation and antioxidant responses in the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma during chronic exposure [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2019, 212: 110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.05.001 [30] GAO Y F, KANG L L, ZHANG Y, et al. Toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic (TK-TD) modeling to study oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of heavy metals in zebrafish [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 220: 774-782. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.197 [31] ZHANG Y, FENG J F, GAO Y F, et al. Physiologically based toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic (PBTK-TD) modelling of Cd and Pb exposure in adult zebrafish Danio rerio: Accumulation and toxicity [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 249: 959-968. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.115 [32] LIU F J, GENTLES A, THEODORAKIS C W. Arsenate and perchlorate toxicity, growth effects, and thyroid histopathology in hypothyroid zebrafish Danio rerio [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 71(7): 1369-1376. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.036 [33] SARKAR S, MUKHERJEE S, CHATTOPADHYAY A, et al. Low dose of arsenic trioxide triggers oxidative stress in zebrafish brain: Expression of antioxidant genes [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 107: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.05.012 [34] BYEON E, KANG H M, YOON C, et al. Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic compounds in aquatic organisms [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2021, 237: 105901. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105901 [35] 李梓萌, 李肖乾, 张文慧, 等. 重金属复合污染对生物影响的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11): 3331-3343. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021033107 LI Z M, LI X Q, ZHANG W H, et al. Research progress on the effects of heavy metal compound pollution on organisms [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(11): 3331-3343(in Chinese). doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021033107
[36] MUTHUSAMY S, PENG C, NG J C. Effects of binary mixtures of benzo[a]pyrene, arsenic, cadmium, and lead on oxidative stress and toxicity in HepG2 cells [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 165: 41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.137 [37] 邢胜男. 斑马鱼胚胎发育毒性试验评价重金属联合生物毒性[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2016. XING S N. Evaluation of combined biotoxicity of heavy metals by zebrafish embryo development toxicity test[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2016 (in Chinese).
[38] VELLINGER C, PARANT M, ROUSSELLE P, et al. Antagonistic toxicity of arsenate and cadmium in a freshwater amphipod (Gammarus pulex) [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2012, 21(7): 1817-1827. doi: 10.1007/s10646-012-0916-1 [39] VELLINGER C, GISMONDI E, FELTEN V, et al. Single and combined effects of cadmium and arsenate in Gammarus pulex (Crustacea, Amphipoda): Understanding the links between physiological and behavioural responses [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2013, 140/141: 106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.05.010 [40] MEHLER W T, DU J, LYDY M J, et al. Joint toxicity of a pyrethroid insecticide, cypermethrin, and a heavy metal, lead, to the benthic invertebrate Chironomus dilutus [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2011, 30(12): 2838-2845. doi: 10.1002/etc.689 [41] LI X X, CUI X W, ZHANG X, et al. Combined toxicity and detoxification of lead, cadmium and arsenic in Solanum nigrum L. [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 121874. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121874 [42] LIU X S, WANG J M, HUANG Y W. Understanding the role of nano-TiO2 on the toxicity of Pb on C. dubia through modeling—Is it additive or synergistic? [J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2022, 16(5): 59. [43] BROERSE M, OORSPRONG H, van GESTEL C A M. Cadmium affects toxicokinetics of pyrene in the collembolan Folsomia candida [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2012, 21(3): 795-802. doi: 10.1007/s10646-011-0839-2 [44] STEEVENS J A, BENSON W H. Toxicokinetic interactions and survival of Hyalella azteca exposed to binary mixtures of chlorpyrifos, dieldrin, and methyl mercury [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2001, 51(4): 377-388. doi: 10.1016/S0166-445X(00)00127-2 [45] GARBINSKI L D, ROSEN B P, CHEN J. Pathways of arsenic uptake and efflux [J]. Environment International, 2019, 126: 585-597. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.058 [46] MILLER D S, SHAW J R, STANTON C R, et al. MRP2 and acquired tolerance to inorganic arsenic in the kidney of killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) [J]. Toxicological Sciences, 2007, 97(1): 103-110. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfm030 [47] JEONG C B, KIM H S, KANG H M, et al. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) proteins in aquatic invertebrates: Evolutionary significance and application in marine ecotoxicology [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2017, 185: 29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.01.013 -



 下载:
下载: