-
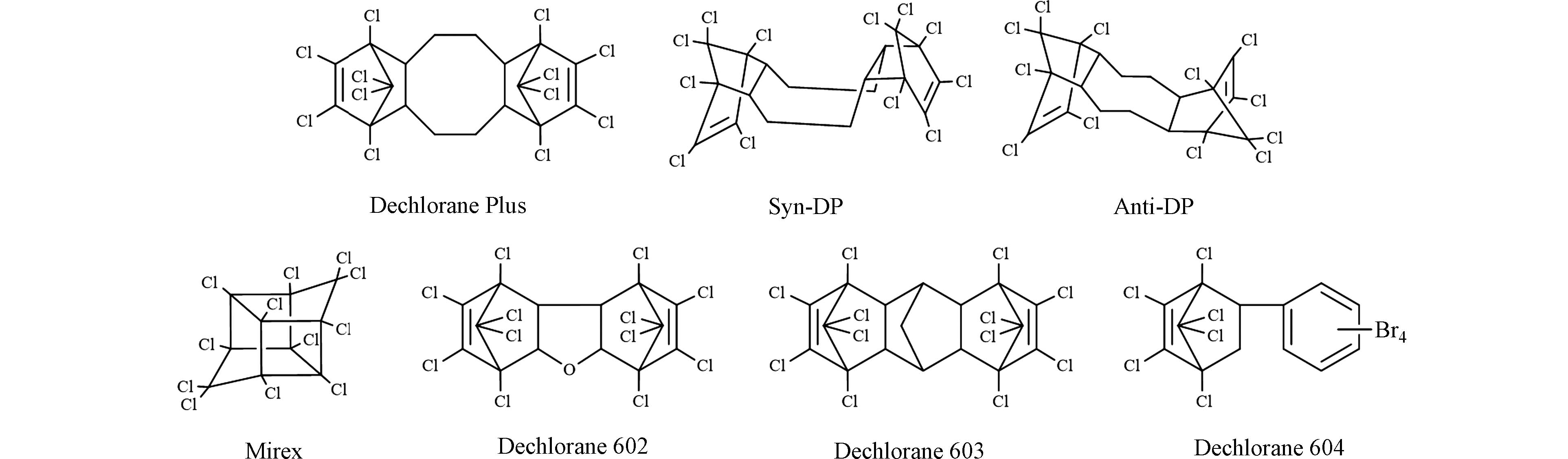
得克隆类物质(dechloranes)是一类化学性质稳定的高氯代阻燃剂,其种类包括Dechlorane 602(Dec 602)、Dechlorane 603(Dec 603)、Dechlorane 604(Dec 604)和Dechlorane Plus(DP)等,结构式如图1所示. 该类物质于20世纪60年代末被首次合成,广泛应用于电子设备、纺织品、电线电缆涂层等生产与生活用品材料中[1 − 3]. 据市场调研,DP的年产量为750—
6000 t[4]. 2006年Hoh等[5]首次在环境中检测出DP,随后人们对大气、水、土壤、生物等[6 − 11]中的得克隆类物质展开了研究,发现其在环境中普遍存在,并具有生物蓄积性[12]、长距离迁移性等与持久性有机物(persistent organic pollutants, POPs)相似的特性[13]. 此外,DP具有强疏水性(lg Kow=9.03)[4],能够通过食物链进入人体,进而危害人类生命健康. 毒理学研究表明,得克隆类物质具有神经行为毒性,能够影响胚胎发育,长期接触会对肺部、肝脏和生殖系统等造成损伤[10, 14 − 16]. 2022年,欧盟化学品管理局(European Chemicals Agency, ECHA)风险评估委员会及社会经济分析委员会联合发布了限制DP投入欧盟市场的草案,禁止生产销售DP含量超过0.1%的产品[17]. 2023年,我国将DP列入重点管控新污染物清单,自2024年1月1日起,禁止其生产、加工使用及进出口[18].得克隆类物质在实际样品中以痕量水平存在(ng·L−1或ng·kg−1—μg·kg−1),复杂基质干扰加大了对其检测的难度,需将样品前处理技术与检测方法结合,提高分析灵敏度与准确性. 样品前处理是对样品中待测组分进行提取、净化、富集的过程. 该过程耗时长、易引起误差,直接影响分析结果的准确性和可靠性[19 − 20]. 目前,液液萃取、固相萃取等被用于液体样品中得克隆类物质的分离富集,索氏提取、加速溶剂萃取等多被用于固体样品中得克隆类物质的萃取. 检测方法主要有气相色谱-质谱法、气相色谱-高分辨质谱法、气相色谱-串联质谱法以及液相色谱-串联质谱法等(见表1).
近几年关于得克隆类物质相关综述侧重报道生物体中得克隆类物质的分析方法及污染水平和来源的研究. 本文侧重总结和讨论近年来大气,水体,土壤,沉积物以及生物体中得克隆类物质的样品前处理方法和检测技术研究进展,并对该领域未来发展进行了展望.
-
液液萃取法(liquid-liquid extraction, LLE)是根据物质在两种不相溶的溶剂中溶解度的不同,使物质从一种溶剂转移到另一种溶剂中的样品前处理技术,被广泛应用于液体样品中得克隆类物质的提取. 常用的萃取剂包括二氯甲烷、正己烷等[9]. 魏葳等[22]采用液液萃取法结合气相色谱-质谱测定海水中得克隆类物质,1 L样品经50 mL二氯甲烷萃取,重复两次,硅胶固相萃取小柱净化后进行检测. 回收率为61%—91%,检出为0.01—0.08 ng·L−1. 齐虹等[23]采用二氯甲烷萃取污水中得克隆类物质,再利用硅胶层析柱净化,加标回收率为74%—122%,方法检出限为0.01—0.1 ng·L−1. 液液萃取法虽无需复杂设备,操作简单,但有机溶剂消耗量较大,易造成二次污染.
-
固相萃取(solid phase extraction, SPE)是一种利用物质在液-固两相间的分配系数或吸附能力的不同,采用选择性吸附、选择性洗脱的方式对样品进行分离、富集、净化的样品前处理技术,具有高选择性、高富集倍数且有机溶剂消耗量更少等优势[24]. 其中,吸附材料是SPE技术的核心,选择的吸附剂是否合适关系到能否实现萃取以及净化效果的好坏,决定着分析结果的准确性. Zhang等[25]建立了海水中得克隆类物质的气相色谱-串联质谱检测方法,样品经C18固相萃取圆盘提取后,用二氯甲烷洗脱,洗脱液浓缩后测定. 该方法回收率为75%—94%,检出限为0.4—0.5 pg·L−1. Huang[26] 等考察了XAD-2(苯乙烯-二乙烯基苯聚合物,孔径为9 nm,比表面积为300 m2·g−1)、XAD-4(苯乙烯-二乙烯基苯聚合物,孔径为10nm,比表面积为750 m2·g−1)、XAD-7(聚甲基丙烯酸类聚合物,比表面积为380 m2·g−1,孔径为30—40 nm)、XAD-8(聚甲基丙烯酸酯类聚合物,比表面积为140 m2·g−1,孔径为22.5 nm)4种大孔径吸附树脂对养殖海水中得克隆类物质的萃取效果. 结果表明,XAD-2对得克隆类物质富集效果最好,富集倍数可达
20000 倍. XAD-4有较高的孔隙率(>50%),能够实现水样的快速富集,因此选用XAD-2和XAD-4混合树脂作为固相萃取的吸附材料,方法检出限可达9.3—78.5 pg·L−1. 该方法能够对大体积水样(20L)中得克隆类物质进行萃取,与LLE相比,检出限可降低1—2个数量级. -
索氏提取(soxhlet extraction, SE)是从固体样品中提取目标化合物的前处理方法,该方法操作简单,重现性好,但也存在提取时间长,有机溶剂消耗量大等缺点[27]. Moller等[28]利用聚氨酯泡沫(PUF)与XAD-2树脂收集大气中的颗粒物,以二氯甲烷/正己烷(1:1, V/V)为溶剂,索氏提取16 h后检测. 该方法样品回收率在29%—85%之间,方法检出限为
0.0004 —0.07 pg·m−3. Wang等[29]建立了大气中得克隆类物质的气相色谱-质谱测定方法,利用玻璃纤维过滤器(GFF)和PUF收集大气颗粒物,样品经索氏提取方法以正己烷/丙酮(1:1, V/V)混合溶剂提取24 h后上机检测,该方法加标回收率为76%—94%,检出限为0.096—0.696 pg·m−3. 二氯甲烷-正己烷、正己烷-丙酮混合溶液是提取得克隆类物质常用的两种萃取溶液. 研究表明,得克隆类物质提取效率随丙酮比例增加而提高,但丙酮极性较强,过多会导致提取液中杂质增多,对仪器检测造成干扰,影响分析的准确性[30]. -
加速溶剂萃取(accelerated solvent extraction, ASE)是通过提高温度(50—200 ℃)和增加压力(
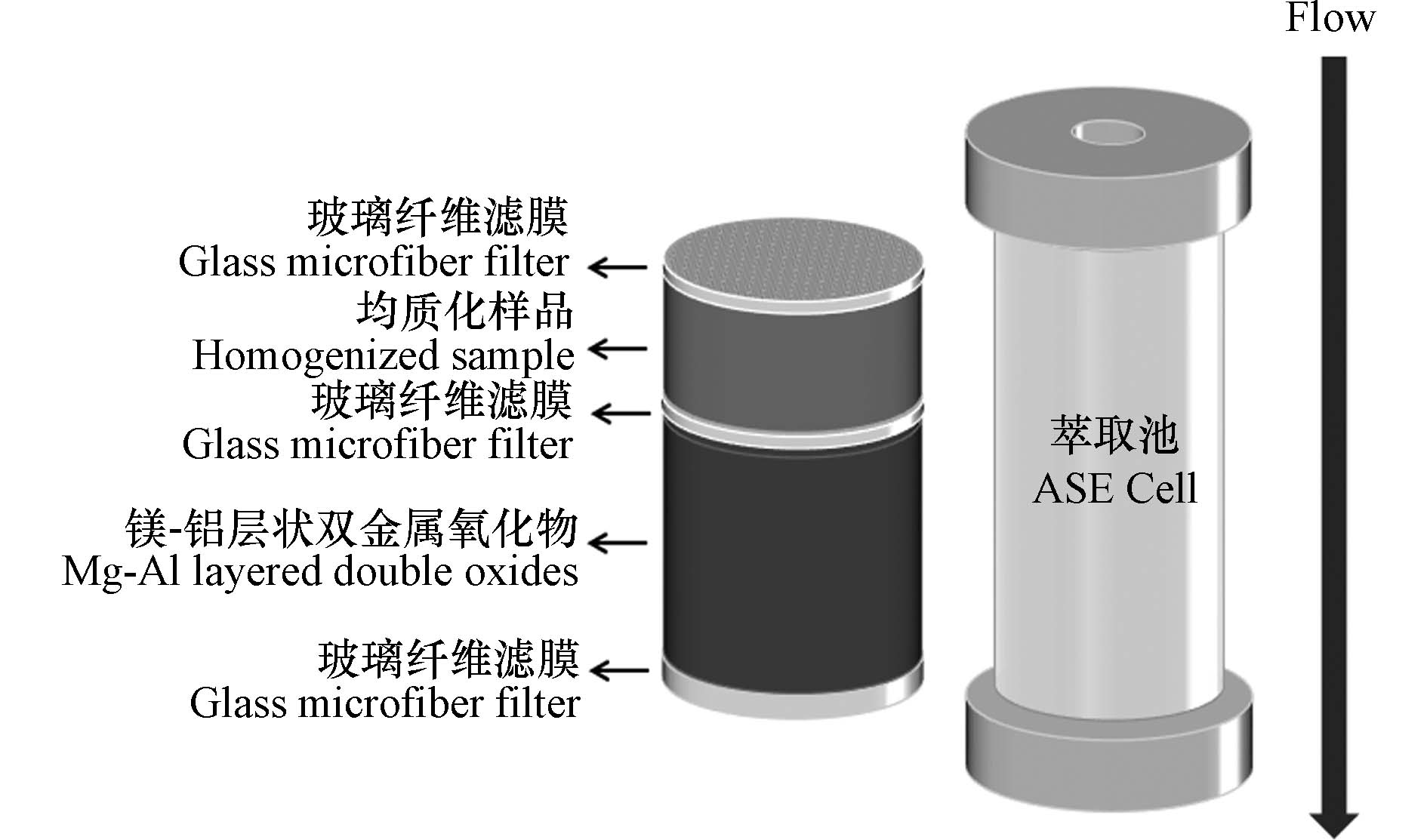
1000 —3000 psi)来对基质中的有机物进行自动萃取. 基于高温高压条件,萃取溶剂能与样品充分接触,继而改善萃取效率,减少溶剂用量,缩短提取时间[31]. 郭晓辰等[30]建立了土壤中得克隆类物质的气相色谱-串联质谱方法,土壤样品粉碎后过40目筛,在120 ℃条件下用正己烷/丙酮(1:1, V/V)混合溶剂静态提取5 min,该过程循环3次,萃取池容积22 mL,冲洗体积为60%,提取液经石墨碳黑、石墨化碳黑/乙二胺基-N-丙基(GCB/PSA)固相萃取柱净化后进行检测. 加标回收率为84.7%—108%,方法检出限为0.17—11.0 pg·g−1. 该方法灵敏度较高,可用于复杂土壤样品分析. Zhao等[32]将沉积物与硅藻土混合置于萃取池中(34 mL),以镁铝层状双金属氧化物(Mg-Al-LDO)为净化材料,萃取池内部填充如图2,样品在100 ℃和1500 psi条件下,用二氯甲烷/正己烷(1:1, V/V)萃取10 min,循环3次,采用气相色谱-质谱法进行检测,方法检出限为0.01—0.67 ng·g−1. 该方法对比了不同吸附材料的净化效果,包括C18、硅胶、弗罗里硅土(Florisil)、GCB、镁铝层状双金属氢氧化物(Mg-Al-LDH)、Mg-Al-LDO等,其中Mg-Al-LDHs具有较小的比表面积(5—20 m2·g−1),吸附容量小,孔隙率(<50%)较低,保留在Mg-Al-LDHs中的得克隆类物质洗脱困难. 此外,Mg-Al-LDHs的孔体积较小,导致得克隆类物质回收率较低. C18和硅胶脱色效果较差,对后续分析造成干扰. Mg-Al-LDHs在500 ℃条件下煅烧5 h后形成Mg-Al-LDO. Mg-Al-LDO保持层状结构的同时,比表面积增大(200—300 m2·g−1),与弗罗里硅土、GCB相比,Mg-Al-LDO净化效果较好,提取液中无残留物且脱色效果显著. 以Mg-Al-LDO为吸附材料时,得克隆类物质回收率可达95%—99%. 该方法节省了净化步骤,缩短了分析时间. 加速溶剂萃取法对固体样品的提取效率较高,全程自动化操作. 与索氏提取法相比,该方法有机溶剂消耗量少,准确度高,萃取时间短且能达到与索氏提取方法相当的回收率,常用于土壤和沉积物中得克隆类物质的提取. -
基质分散固相萃取(matrix solid-phase dispersion, MSPD)指将样品与吸附剂混合装柱,用少量溶剂清洗,把待测物洗脱下来的前处理技术. Chen等[33]利用此方法从鱼类中提取得克隆类物质,样品与硅胶混合后转移至含有0.1 g弗罗里硅土的聚丙烯固相萃取小柱中,用20 mL正己烷洗脱,洗脱液蒸发至近干,用含有内标物的丙酮溶液复溶后进行气相色谱-质谱测定. 结果表明,得克隆类化合物的回收率为73%—85%,方法检出限为3—5 pg·g−1. Roscales等[34]利用以酸性硅胶(SiO2-H2SO4, 44%)为主吸附剂的基质分散固相萃取法结合气相色谱-质谱测定野生鸟蛋中的得克隆类物质. 0.5 g样品与Na2SO4和SiO2-H2SO4混合均匀后装入含有0.5 g活性二氧化硅和2 g酸性硅胶的玻璃柱上端,用12 mL正己烷/二氯甲烷(9:1, V/V)洗脱两次,每次7 min,洗脱液浓缩至1 mL,复溶于含有内标物的壬酮后测定. 方法检出限为0.5—2 pg·g−1,样品回收率为104%—112%. MSPD集样品均化、提取、净化于一体,具有分析时间短,溶剂消耗量少,回收率高等优势,适合提取固体、半固体、高粘性食品和生物样品中的得克隆类物质.
-
固体样品基质复杂,存在脂肪、色素、有机酸等干扰,经萃取后,还需进一步净化处理,提高分析灵敏度. 净化包括固相萃取柱净化、层析柱净化及凝胶渗透色谱(GPC)3种方式. 固相萃取柱净化及层析柱净化是根据物质在固定相上的吸附力不同而进行分离,为达到净化目的,同时不吸附目标物,关键在于吸附剂的选择. 用于得克隆类物质净化的吸附材料包括硅胶、氧化铝、乙二胺基-N-丙基(PSA)、石墨化碳黑(GCB)等. 硅胶具有吸附性能好,化学性质稳定,机械强度高等特点[35 − 36],但硅胶对脂肪的容量有限,可与弗罗里硅土或氧化铝组合形成层析柱对脂肪净化. PSA含有氨基,可有效去除色素、有机酸和金属离子干扰. GCB适用于去除色素[37]. 郭晓辰等[30]采用GCB/PSA固相萃取柱对土壤中得克隆类物质的提取液进行净化,并考察了Florisil、硅胶、GCB/PSA等商品化固相萃取小柱的净化效果. 结果显示, Florisil和硅胶净化后回收率偏低,而GCB/PSA的净化效果好,最终选择GCB/PSA为净化柱,以正己烷为洗脱溶剂,得克隆类物质回收率为71.9%—112.0%. 对于生物样品,GPC可用于去除大分子的生物脂质[9]. Peng等[38]采用GPC结合填充了中性二氧化硅与酸性硅胶的层析柱对鸟类肌肉中得克隆类物质的提取液进行净化,该方法回收率可达88%—104%.
目前,根据不同的样品基质,选择合适的前处理技术十分重要. 固体样品中得克隆类物质的前处理技术以ASE和SE为主,结合固相萃取净化,达到分离目标物与杂质的目的. 对于液体样品,LLE是常用的前处理技术,但消耗有机溶剂多,操作繁琐,而SPE具有操作简便,耗时短,萃取效率高等特点,在处理液体样品时表现尤为出色,是取代LLE的技术.
-
气相色谱-质谱法(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, GC-MS)是得克隆类物质常用的检测方法之一,广泛应用于水[22 − 23, 39]、土壤[32]、生物[33, 40]和其它基质[41]中得克隆类物质的测定. 对于基质单一且得克隆类物质含量较高的样品,单四极杆质谱作为检测器即可满足检测需求. Zhen等[42]建立了索氏提取后,利用GC-MS测定河水、地表水悬浮颗粒物中得克隆类物质的方法. 水样经玻璃纤维过滤器(GFF)与XAD-2树脂过滤,收集颗粒物进行索氏提取,硅胶柱净化,采用DB-5HT色谱柱,以电子捕获负离子(ECNI)模式进行分析. 方法检出限为1.05—28.5 pg·L−1,回收率为87.7%—109%. 气相色谱/负化学电离源-质谱法灵敏度及准确度较高,但检测复杂基质样品时可能产生假阳性结果. 与气相色谱-质谱法相比,气相色谱-高分辨质谱法(GC-HRMS)具有更高的准确性及灵敏度,在分析复杂基质样品时应用广泛,但仪器价格昂贵,操作要求严格. Malak等[43]建立了加压溶剂萃取后,利用GC-HRMS测定鱼类中得克隆类物质的方法. 样品在120 ℃条件下用甲苯/丙酮(7:3, V/V)混合溶剂提取,经硅胶柱层析、凝胶渗透色谱净化,色谱柱为HT8-PCB,以电子轰击电离(EI)模式进行分析. 该方法检出限为0.1—0.5 pg·g−1,样品回收率为74%—113%. Xu等[44]建立了土壤中得克隆类物质的ASE-GC-HRMS方法. 土壤样品过60目筛,以二氯甲烷/正己烷(1:1, V/V)混合溶剂提取,经硅胶柱层析净化,采用DB-5HT色谱柱,选择离子检测(SIM)模式进行分析. 方法检出限为0.27—0.33 pg,样品回收率为88%—107%. 该方法灵敏度及准确度高,可用于土壤中痕量得克隆类物质的测定.
-
近年来,气相色谱-串联质谱法(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry, GC-MS/MS)广泛应用于环境及生物样品中得克隆类物质的测定[30, 45 − 48],与气相色谱-质谱法相比,该方法具有更高的准确性和灵敏度,可对环境中超痕量水平的得克隆类物质进行准确的定性和定量分析[30]. 刘合欢等[48]建立了土壤样品中得克隆类物质的GC-MS/MS检测方法. 样品经索氏提取方法用二氯甲烷溶剂提取48 h,提取液浓缩后经多层硅胶-氧化铝柱净化,采用DB-5HT色谱柱,选择反应检测模式(SRM)进行分析. 样品加标回收率为55%—103%,方法检出限为0.25—5 fg·g−1. 该方法选择性强,灵敏度高,可用于土壤中超痕量得克隆类物质的分析. Baron等[49]开发了一种基于ASE-GC-MS/MS测定污水处理厂污泥中得克隆类物质的方法. 样品经正己烷/二氯甲烷(1:1, V/V)混合溶剂提取,硅胶固相萃取柱净化,采用DB-5HT色谱柱,以负化学电离源(NCI),SRM模式分析. 方法检出限为1.2—2.9 pg·g−1,样品回收率为57%—76%.
-
得克隆类物质热稳定性好,具有挥发性且大部分极性较弱,气相色谱-质谱法是测定环境样品中得克隆类物质最常用的方法. 研究表明,液相色谱-串联质谱法(liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/ mass spectrometry, LC-MS/MS)也可被应用于得克隆类物质的测定. Zhou等[50]建立了地表水中得克隆类物质的LC-MS/MS方法. 水样通过GFF和XAD-4树脂过滤,采集的固体样品经丙酮/正己烷(1:1, V/V)混合溶剂提取,硅胶柱净化后,以Pinnacle DB Biphenyl色谱柱分离,大气压光电离源(APPI),多反应检测(MRM)模式检测,结果表明,得克隆类物质在0.05—25 ng·μL−1范围内呈良好线性关系,方法检出限为2—57 ng·L−1,平均回收率为74%—123%. 该方法可用于地表水中得克隆类物质的测定. Al-odaini等[51]建立了加压溶剂萃取后,利用LC-MS/MS测定海水沉积物中得克隆类物质的方法. 样品经正己烷/二氯甲烷(1:4, V/V)混合溶剂提取,硅胶柱净化后,采用ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18色谱柱分离,大气压化学电离源(APCI),MRM模式检测. 该方法检出限为0.175—0.35 ng·g−1,回收率为87%—113%.
-
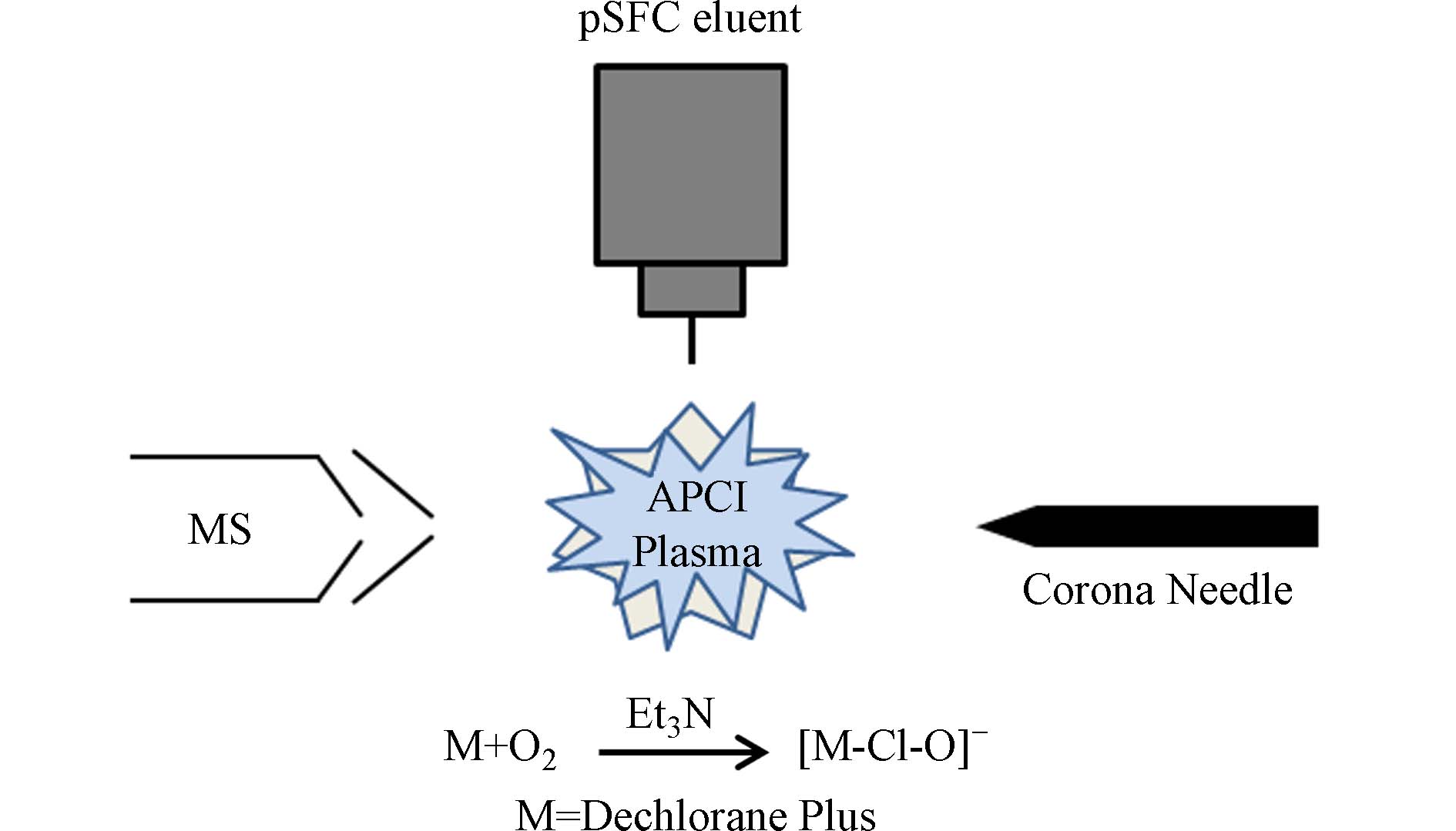
Riddell等[52]建立了一种填充柱超临界流体色谱耦合大气压化学电离源质谱(pSFC-APCI-MS)测定湖泊沉积物中得克隆类物质的方法(如图3所示). 样品经索氏提取,硅胶柱净化后测定. 当以Trefoil CEL2为色谱柱,温度70 ℃,压力13.79 MPa,乙腈/二氧化碳为流动相,流速1 mL·min−1时,分离效果最佳. 该方法测得实际环境样品中syn-DP和anti-DP浓度分别为8.2 ng·g−1和10 ng·g−1,RSD小于20%. pSFC-MS系统重现性好,分离速度快,可用于环境样品中得克隆类物质的测定.
由于得克隆类物质具有挥发性,热稳定性好,目前,气相色谱-质谱法是检测得克隆类物质常用的方法. 近年来,气相色谱-三重四极杆质谱联用测定环境样品中得克隆类物质的方法受到广泛应用,与单四极杆质谱相比,其价格更高,但灵敏度更高.
-
得克隆类物质以痕量水平广泛存在水体、大气、土壤、沉积物、以及生物体等各种环境介质中,在环境中难以降解,疏水性强,可通过食物链不断累积放大,对人体健康造成危害,因此建立得克隆类物质高灵敏、高选择性的快速分析方法对于认知和掌握其生态环境风险、环境行为、污染治理和控制都具有非常重要的现实意义. 索氏提取、液液萃取等传统的提取方法存在费时费力、有机溶剂消耗量大等缺点. 固相萃取、加速溶剂萃取等方法萃取效率高,耗时短,溶剂消耗量少,对环境友好,是目前研究得克隆类物质最常用的样品前处理方法. GC-MS或GC-MS/MS是得克隆类物质分析测定的首选方法,ECNI是最常用的电离源. 目前关于得克隆类物质分析方法的研究较少,今后应针对不同环境样品,开发吸附容量高、传质速率快和选择性强的新型吸附材料如金属有机框架材料、共价有机框架材料等,力求萃取过程更加简便快速,萃取装置微型化和现场化;发展新型检测技术,构建快速、准确、高效、自动化程度高的仪器分析方法;研发便携式快速检测仪器技术,实现得克隆类物质的现场快速分析,为其在不同环境基质中的浓度分布、转化规律提供技术支撑.
得克隆类物质检测技术及其研究进展
Research progress on detection methods of Dechloranes
-
摘要: 得克隆类物质(dechloranes)作为一类添加型氯代阻燃剂,广泛应用于电子设备、纺织品等材料的加工生产中. 随着该类阻燃剂在生产生活中的大量使用,导致其在环境中存在并不断累积,经多种介质进入人体,进而产生神经毒性,损坏肌肉细胞,对DNA产生破坏作用. 得克隆类物质具有持久性、长距离迁移性和生物蓄积性,对人体健康和环境造成严重危害,2018年被欧洲化学品管理署列入第18批高关注化合物清单. 美国国家环境保护局将得克隆划归为高产量化学品,中国也将其列入2023年重点管控新污染物清单. 因此,环境样品中得克隆类物质污染水平的准确分析和严格控制是至关重要的. 由于得克隆类物质在环境中痕量残留,且实际样品存在复杂基质干扰,需将样品前处理技术与检测方法结合以提高分析灵敏度与准确性. 本文重点围绕环境样品中得克隆类物质的样品前处理技术及仪器分析方法两方面进行综述,总结了不同样品中得克隆类物质的前处理技术(液液萃取、固相萃取、索氏提取、加速溶剂萃取、基质分散固相萃取等),详细介绍了气相色谱-质谱法、气相色谱-串联质谱法、液相色谱-串联质谱法等检测方法在得克隆类物质检测中的应用. 最后,对未来相关分析方法的发展趋势进行了展望.Abstract: Dechloranes, which are additive-type chlorine flame retardants, are widely used in the process of industrial production, such as electronic equipments and textiles. Due to extensive use and massive emissions in production and daily life, dechloranes enter the human individuals through various medium, leading to neurobehavioral toxicity, muscle injuries, and DNA damage. Dechloranes can pose a significant risk to human health and environment because of the persistent, long-distance transport and bioaccumulation. In 2018, European Chemicals Agency has added dechlorane plus of very high concern to the Candidate List. It is also subject to the United States Environmental Protection Agency’s High Production Volume challenge and in the list of Chinese New Pollutants under Key Control. It has become a great challenge to analyze dechloranes in biology and the environment because of the low level and complex matrix interference, hence, a combination of sample pretreatment methods and determination technology is imperative for enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of analysis. In this paper, various methods for sample pretreatment and instrumental analysis of dechloranes in the environment are reviewed. Sample pretreatment techniques of dechloranes are summarized, such as liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), solid phase extraction (SPE), soxhlet extraction (SE), accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) and matrix solid phase dispersive extraction (MSPD). The applications of instrument methods for dechloranes are discussed in detail, including gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Finally, the future development trends of the relevant analytical methods of dechloranes were proposed.
-
Key words:
- dechloranes /
- chlorine flame retardants /
- pretreatment /
- determination.
-

-
表 1 不同样品基质中得克隆类物质的分析方法与分析性能
Table 1. Analytical methods and performance of dechloranes in various samples
样品
Sample样品前处理
Sample
pretreatment净化
Clean-up回收率/%
Recovery仪器分析
Instrumental analysis检出限
Limit of
detection相对标准
偏差/%
RSD参考文献
Reference大气 SE 硅胶柱 76—94 GC-ECNI-MS 0.096—0.696 pg·m−3 [29] SE 硅胶柱 29—85 GC-NCI-MS 0.0004 —0.07 pg·m−3[28] 水样 LLE 硅胶柱 61—91 GC-NCI-MS 0.01—0.08 ng·L−1 <5.1 [22] LLE 硅胶柱 74—122 GC-NCI-MS 0.01—0.1 ng·L−1 <13.2 [23] LLE 硅胶柱 71—94 GC-NCI-MS 40—50 pg·L−1 <15 [53] LLE 硅胶柱 71—113 GC–NCI-MS 0.052—0.066 ng·mL−1 2—3 [54] UA-DLLME 75—92 GC-ECNI-MS 0.08—0.3 ng·L−1 <9 [39] SPE 75—94 GC-EI-MS/MS 0.4—0.5 pg·L−1 4—9 [25] 土壤及沉积物 ASE C18固相萃取柱 88.78—98.23 GC-EI-MS/MS 0.04 ng·g−1 <4.53 [47] ASE GCB/PSA固相萃取柱 84.7—108 GC-EI-MS/MS 0.17—11 pg·g−1 4.3—13 [30] ASE 活性铜 97—103 GC-ECNI-MS/MS 0.15—0.75 pg·g−1 4—5 [40] ASE 多层硅胶柱 50—90 GC-HRMS 1.6—7.8 ng·g−1 10—18 [55] ASE Florisil固相萃取柱 90.3—99.8 GC-ECNI-MS 0.01—0.67 ng·g−1 1.3—5.7 [32] ASE 硅胶柱 88—107 GC-HRMS 0.27—0.33 pg 5.2—18 [45] ASE 活性二氧化硅 61 GC-Q-TOF-HRMS 0.01—0.02 ng·g−1 <30 [56] SE 硅胶-氧化铝柱 70—85 GC-HRMS 11—2000 pg·g−1 [57] SE 多层硅胶柱 77.5—125.2 GC-MS 0.001—0.006 ng·g−1 [58] SE 硅胶-氧化铝柱 88.7—101.9 GC-ECNI-MS 0.36—110 pg·g−1 [59] SE 活性铜 78—122 GC-ECNI-MS 0.0014 —0.054 ng·g−1<14 [60] SE 硅胶柱;GPC 78—95 GC-MS/MS 5.6—79 pg·g−1 5—16 [61] SE 多层硅胶-氧化铝柱 38—128 GC-MS/MS 0.25—2.50 pg·g−1 [62] SE 氧化铝柱 93 GC-NCI-MS 17.6—27.2 ng·kg−1 11 [63] SE 硅胶-氧化铝柱 80 GC-ECNI-MS 1.3—7.6 pg·g−1 9 [64] 生物样品 MSPD 多层硅胶柱 104—112 GC-NCI-MS 0.5—2 pg·g−1 2—8 [34] MSPD Florisil固相萃取柱 73—85 GC-ECNICI-MS 3—5 pg·g−1 2—6.1 [33] MSPD 101—110 GC–NCI-MS 0.6—9 pg·g−1 1.4—4.9 [65] ASE 多层硅胶柱;GPC 74—113 GC-EI-HRMS 0.1—0.5 pg·g−1 <20 [43] ASE GPC;硅胶柱 72.4—98 GC-MS/MS 0.4—3.5 ng·g−1 [66] ASE GPC 63—121 GC-EI-HRMS 0.01—0.87 ng·g−1 2—25 [67] ASE 硅胶柱 71—91 HRGC–HRMS 0.007—0.169 pg·g−1 10 [68] SE GPC 85—121 GC-HRMS 0.04—0.99 pg·g−1 [69] SE Florisil-硅胶柱 80—121 GC–NCI-MS 0.1—0.8 pg·g−1 <20 [70] SE 活性铜;多层硅胶柱 78—121 GC-ECNI-MS 0.001— 0.0067 ng·g−1<15 [71] SE 多层硅胶柱;GPC 78—121 GC-ECNI-MS 0.02—0.68 ng·g−1 <15 [72] SE Florisil固相萃取柱 47.8—130 GC-ECNICI-MS 0.001—0.27 ng·g−1 2.9—7.1 [73] SE 多层硅胶柱 65—105 GC-ECNI-MS 33—58 pg·g−1 [74] ND. 未检出. ND. not detected -
[1] TOMY G T, PLESKACH K, ISMAIL N, et al. Isomers of dechlorane plus in Lake Winnipeg and Lake Ontario food webs[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(7): 2249-2254. [2] QIU X H, MARVIN C H, HITES R A. Dechlorane plus and other flame retardants in a sediment core from Lake Ontario[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(17): 6014-6019. [3] KAISER K L E. Pesticide Report: The rise and fall of mirex[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1978, 12(5): 520-528. [4] HANSEN K M, FAUSER P, VORKAMP K, et al. Global emissions of dechlorane plus[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 742: 140677. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140677 [5] HOH E, ZHU L Y, HITES R A. Dechlorane plus, a chlorinated flame retardant, in the great lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(4): 1184-1189. [6] ZAFAR M I, KALI S, ALI M, et al. Dechlorane Plus as an emerging environmental pollutant in Asia: A review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(34): 42369-42389. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10609-2 [7] YU Z Q, LU S Y, GAO S T, et al. Levels and isomer profiles of Dechlorane Plus in the surface soils from e-waste recycling areas and industrial areas in South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(9): 2920-2925. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.06.003 [8] YANG M, JIA H L, MA W L, et al. Levels, compositions, and gas-particle partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and dechlorane plus in air in a Chinese northeastern city[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 55: 73-79. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.03.040 [9] XIAN Q M, SIDDIQUE S, LI T, et al. Sources and environmental behavior of dechlorane plus—a review[J]. Environment International, 2011, 37(7): 1273-1284. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.04.016 [10] CHEN X P, DONG Q X, CHEN Y H, et al. Effects of Dechlorane Plus exposure on axonal growth, musculature and motor behavior in embryo-larval zebrafish[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 224: 7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.011 [11] SKOGENG L P, LUNDER HALVORSEN H, BREIVIK K, et al. Spatial distribution of Dechlorane Plus and dechlorane related compounds in European background air[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2023, 10: 1083011. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.1083011 [12] 刘红英, 罗孝俊. 生物对得克隆物种特异性立体异构体选择性富集及其潜在机理[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(1): 47-59. LIU H Y, LUO X J. Species-specific stereo-selective enrichment of DP in organisms and their possible mechanisms[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(1): 47-59 (in Chinese).
[13] GAO H, NA G S, YAO Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and source of dechloranes in soil and lichen of the fildes peninsula (Antarctica)[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(10): 2312. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15102312 [14] YANG Y, JI F N, CUI Y B, et al. Ecotoxicological effects of earthworm following long-term Dechlorane Plus exposure[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144: 2476-2481. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.023 [15] LI B H, CHEN J J, DU Q Y, et al. Toxic effects of dechlorane plus on the common carp (Cyprinus carpio) embryonic development[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 249: 126481. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126481 [16] 袁陆妗, 陆光华, 叶秋霞, 等. 环境中得克隆的蓄积及毒理学效应[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2013, 30(6): 550-553. YUAN L J, LU G H, YE Q X, et al. Accumulation in environment and ecotoxicological effects of dechlorane plus[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2013, 30(6): 550-553 (in Chinese).
[17] European Chemicals Agency. Submitted restrictions under consideration [EB/OL]. [2022-3-23]. [18] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 重点管控新污染物清单(2023年版)[EB/OL]. [2022-12-29]. [19] 严矿林, 林丽琼, 郑夏汐, 等. 样品前处理技术在气相色谱分析中的应用进展[J]. 色谱, 2013, 31(7): 634-639. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2013.05035 YAN K L, LIN L Q, ZHENG X X, et al. Progress of sample preparation techniques in gas chromatographic analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2013, 31(7): 634-639 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2013.05035
[20] 黄维妮, 林子俺. 色谱分析中样品前处理技术的发展动态[J]. 色谱, 2021, 39(1): 1-3. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.05011 HUANG W N, LIN Z A. Recent advances in sample pretreatment techniques for chromatographic analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2021, 39(1): 1-3 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.05011
[21] FEO M L, BARÓN E, ELJARRAT E, et al. Dechlorane plus and related compounds in aquatic and terrestrial biota: A review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 404(9): 2625-2637. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6161-x [22] 魏葳, 那广水, 赫春香, 等. GC-NCI/MS法分析海水中得克隆类物质[J]. 分析试验室, 2014, 33(2): 162-166. WEI W, NA G S, HE C X, et al. Determination and application of dechloranes in seawater by GC-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2014, 33(2): 162-166 (in Chinese).
[23] 齐虹, 黄俊, 沈吉敏, 等. 气相色谱-质谱联用法测定污水中得克隆阻燃剂[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2010, 42(6): 995-999. QI H, HUANG J, SHEN J M, et al. Determination of Dechloranes in waste water by GC-NCI/MS[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010, 42(6): 995-999 (in Chinese).
[24] 傅若农. 近年国内固相萃取-色谱分析的进展[J]. 分析试验室, 2007, 26(2): 100-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2007.02.026 FU R N. Advances on SPE-chromatography in China in recent two years[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2007, 26(2): 100-122 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2007.02.026
[25] ZHANG H, BAYEN S, KELLY B. Multi-residue analysis of legacy POPs and emerging organic contaminants in Singapore’s coastal waters using gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2015, 523: 219-232. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.012 [26] HUANG J J, LI R J, SHI T D, et al. Determination of multiple organic flame retardants in maricultural water using High-volume/High-throughput Solid-phase extraction followed by liquid/gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2022, 1663: 462766. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462766 [27] LUQUE de CASTRO M D, PRIEGO-CAPOTE F. Soxhlet extraction: Past and present panacea[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(16): 2383-2389. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.11.027 [28] MÖLLER A, XIE Z Y, STURM R, et al. Large-scale distribution of dechlorane plus in air and seawater from the Arctic to Antarctica[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(23): 8977-8982. [29] WANG D G, YANG M, QI H, et al. An Asia-specific source of dechlorane plus: Concentration, isomer profiles, and other related compounds[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(17): 6608-6613. [30] 郭晓辰, 饶竹, 李晓洁, 等. 加速溶剂萃取/气相色谱-三重四极杆质谱测定土壤中8种得克隆类化合物[J]. 分析测试学报, 2019, 38(2): 141-147. GUO X C, RAO Z, LI X J, et al. Determination of 8 kinds of super trace dechloranes in soil by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry with accelerated solvent extraction[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2019, 38(2): 141-147 (in Chinese).
[31] 程嘉雯, 田永, 李春欣, 等. 加速溶剂萃取技术应用于二噁英检测的研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(9): 2736-2746. CHENG J W, TIAN Y, LI C X, et al. Research progress of accelerated solvent extraction(ASE) technology in the detection of dioxins[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(9): 2736-2746 (in Chinese).
[32] ZHAO T, TANG H, CHEN D Z, et al. Rapid analysis of dechloranes in sediment and soil by selective pressurized liquid extraction using Mg-Al layered double oxides as sorbents[J]. Analytical Methods, 2017, 9(7): 1168-1176. doi: 10.1039/C7AY00009J [33] CHEN C L, TSAI D Y, DING W H. Optimisation of matrix solid-phase dispersion for the determination of Dechlorane compounds in marketed fish[J]. Food Chemistry, 2014, 164: 286-292. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.035 [34] ROSCALES J L, VICENTE A, RAMOS L, et al. Miniaturised sample preparation method for the multiresidual determination of regulated organohalogenated pollutants and related compounds in wild bird eggs[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2017, 409(20): 4905-4913. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0432-5 [35] LI Y N, ZHEN X M, LIU L, et al. Halogenated flame retardants in the sediments of the Chinese Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 234: 365-372. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.115 [36] ZHANG Z W, PEI N C, SUN Y X, et al. Halogenated organic pollutants in sediments and organisms from mangrove wetlands of the Jiulong River Estuary, South China[J]. Environmental Research, 2019, 171: 145-152. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.01.028 [37] 程嘉雯, 马继平, 李爽, 等. 六溴环十二烷的样品前处理和检测方法研究进展[J]. 色谱, 2022, 40(10): 872-881. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.03030 CHENG J W, MA J P, LI S, et al. Progress in sample pretreatment and detection methods of hexabromocyclododecanes[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2022, 40(10): 872-881 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.03030
[38] PENG Y, WU J P, LUO X J, et al. Spatial distribution and hazard of halogenated flame retardants and polychlorinated biphenyls to common kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) from a region of South China affected by electronic waste recycling[J]. Environment International, 2019, 130: 104952. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.104952 [39] HSIEH H K, CHEN C L, DING W H. Determination of Dechlorane compounds in aqueous samples using ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and gas chromatography-electron-capture negative ion-mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Methods, 2013, 5(24): 7001-7007. doi: 10.1039/c3ay41505h [40] REN G F, YU Z Q, MA S T, et al. Determination of Dechlorane Plus in serum from electronics dismantling workers in South China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(24): 9453-9457. [41] 霍炜江, 张子豪, 温信凯, 等. 气相色谱质谱法测定胶黏剂中得克隆阻燃剂[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2023, 35(3): 727-731. HUO W J, ZHANG Z H, WEN X K, et al. Determination of dechlorane plus flame retardant in adhesive by gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2023, 35(3): 727-731 (in Chinese).
[42] ZHEN X M, LI Y F, WANG X M, et al. Source, fate and budget of Dechlorane Plus (DP) in a typical semi-closed sea, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 269: 116214. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116214 [43] ABDEL MALAK I, CARIOU R, VÉNISSEAU A, et al. Occurrence of Dechlorane Plus and related compounds in catfish (Silurus spp. ) from rivers in France[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 207: 413-420. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.101 [44] XU P J, TAO B, YE Z Q, et al. Simultaneous determination of three alternative flame retardants (dechlorane plus, 1, 2-bis(2, 4, 6-tribromophenoxy) ethane, and decabromodiphenyl ethane) in soils by gas chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2015, 144: 1014-1020. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.07.031 [45] SALES C, POMA G, MALARVANNAN G, et al. Simultaneous determination of dechloranes, polybrominated diphenyl ethers and novel brominated flame retardants in food and serum[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2017, 409(19): 4507-4515. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0411-x [46] NEUGEBAUER F, DREYER A, LOHMANN N, et al. Determination of halogenated flame retardants by GC-API-MS/MS and GC-EI-MS: A multi-compound multi-matrix method[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 410(4): 1375-1387. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0784-x [47] 谢慧, 常晓云, 马钰涵, 等. 土壤和大米中得克隆检测方法的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(11): 2692-2698. XIE H, CHANG X Y, MA Y H, et al. Study on the detection method of dechlorane plus residue in soil and rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(11): 2692-2698 (in Chinese).
[48] 刘合欢, 李会茹, 张文兵, 等. 气相色谱-串联质谱法测定得克隆及其相关化合物在土壤样品中的含量[J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(3): 423-428. LIU H H, LI H R, ZHANG W B, et al. Co-analysis of dechlorane plus and related compounds in soil sample by gas chromatography coupled with triple tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(3): 423-428 (in Chinese).
[49] BARÓN E, ELJARRAT E, BARCELÓ D. Analytical method for the determination of halogenated norbornene flame retardants in environmental and biota matrices by gas chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1248: 154-160. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.05.079 [50] ZHOU S N, REINER E J, MARVIN C H, et al. Liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure photoionization tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of Dechloranes[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry:RCM, 2011, 25(3): 436-442. doi: 10.1002/rcm.4874 [51] AL-ODAINI N A, YIM U H, KIM N S, et al. Isotopic dilution determination of emerging flame retardants in marine sediments by HPLC-APCI-MS/MS[J]. Analytical Methods, 2013, 5(7): 1771-1778. doi: 10.1039/c3ay25963c [52] RIDDELL N, van BAVEL B, ERICSON JOGSTEN I, et al. Coupling of supercritical fluid chromatography to mass spectrometry for the analysis of Dechlorane Plus: Examination of relevant negative ion atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mechanisms[J]. Talanta, 2017, 171: 68-73. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.04.066 [53] QI H, LIU L Y, JIA H L, et al. Dechlorane Plus in surficial water and sediment in a northeastern Chinese River[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(7): 2305-2308. [54] WANG D P, JIA H L, HONG W J, et al. Uptake, depuration, bioaccumulation, and selective enrichment of dechlorane plus in common carp (Cyprinus carpio)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(6): 6269-6277. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07239-8 [55] ZHAO X R, CUI T T, GUO R, et al. A clean-up method for determination of multi-classes of persistent organic pollutants in sediment and biota samples with an aliquot sample[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1047: 71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.011 [56] NIPEN M, VOGT R D, BOHLIN-NIZZETTO P, et al. Spatial trends of chlorinated paraffins and dechloranes in air and soil in a tropical urban, suburban, and rural environment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 292: 118298. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118298 [57] SHEN L, JOBST K J, REINER E J, et al. Identification and occurrence of analogues of dechlorane 604 in Lake Ontario sediment and their accumulation in fish[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(19): 11170-11177. [58] HU Y X, LI Z R, XIONG J J, et al. Occurrence and ecological risks of brominated flame retardants and dechlorane plus in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary and Daya Bay, South China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 185: 114182. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114182 [59] AN Q, AAMIR M, MAO S D, et al. Current pollution status, spatial features, and health risks of legacy and emerging halogenated flame retardants in agricultural soils across China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 803: 150043. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150043 [60] XIE J L, SUN Y X, CHENG Y Y, et al. Halogenated flame retardants in surface sediments from fourteen estuaries, South China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 164: 112099. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112099 [61] QIU Y W, WANG D X, ZHANG G. Assessment of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in sediments of the Eastern Indian Ocean[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 710: 136335. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136335 [62] LI H R, SONG A M, LIU H H, et al. Occurrence of Dechlorane series flame retardants in sediments from the Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 279: 116902. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116902 [63] LI N, CHEN X W, DENG W J, et al. PBDEs and Dechlorane Plus in the environment of Guiyu, Southeast China: A historical location for E-waste recycling (2004, 2014)[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 199: 603-611. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.041 [64] QIU Y W, QIU H L, ZHANG G, et al. Bioaccumulation and cycling of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and dechlorane plus (DP) in three natural mangrove ecosystems of South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 651: 1788-1795. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.055 [65] VILLAVERDE-DE-SÁA E, VALLS-CANTENYS C, QUINTANA J B, et al. Matrix solid-phase dispersion combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of fifteen halogenated flame retardants in mollusks[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1300: 85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.05.064 [66] MARLER H, XIE J X, ADAMS D H, et al. Legacy and emerging flame retardants in sharks from the Western North Atlantic Ocean[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 829: 154330. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154330 [67] ČECHOVÁ E, SEIFERTOVÁ M, KUKUČKA P, et al. An effective clean-up technique for GC/EI-HRMS determination of developmental neurotoxicants in human breast milk[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2017, 409(5): 1311-1322. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-0059-y [68] PIZZOCHERO A C, deLa TORRE A, SANZ P, et al. Occurrence of legacy and emerging organic pollutants in whitemouth croakers from Southeastern Brazil[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 682: 719-728. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.213 [69] RJABOVA J, VIKSNA A, ZACS D. Development and optimization of gas chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry based method for the sensitive determination of Dechlorane plus and related norbornene-based flame retardants in food of animal origin[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 191: 597-606. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.095 [70] SUN R X, PAN C G, PENG F J, et al. Alternative halogenated flame retardants (AHFRs) in green mussels from the South China Sea[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 182: 109082. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.109082 [71] HU Y X, SUN Y X, PEI N C, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alternative halogenated flame retardants in mangrove plants from Futian National Nature Reserve of Shenzhen City, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 260: 114087. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114087 [72] ZHANG Z W, TONG X, XING Y, et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers, decabromodiphenyl ethane and dechlorane plus in aquatic products from the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 161(Pt A): 111733. [73] QIAO L, ZHENG X B, YAN X, et al. Brominated flame retardant (BFRs) and Dechlorane Plus (DP) in paired human serum and segmented hair[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 147: 803-808. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.047 [74] PAN H Y, LI J F T, LI X H, et al. Transfer of dechlorane plus between human breast milk and adipose tissue and comparison with legacy lipophilic compounds[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265(Pt A): 115096. -



 下载:
下载: