-
随着工业化进程的推进,土壤重金属污染问题日益严重,对粮食生产安全、农业发展可持续性、土壤生态环境构成了严重威胁[1-2]. 镉、铅作为最常见的土壤重金属污染物,因具有生物毒性大,污染强度高的特点而备受研究者关注[3-4]. 重金属在土壤中隐蔽性强、不能被微生物降解,并可通过地下水、植物等媒介危及人类健康,因此采取措施对重金属污染土壤进行修复显得尤为必要. 对土壤重金属的化学钝化修复是指向土壤中加入钝化剂,以物理吸附、离子交换、氧化还原或与重金属形成络合物、螯合物、沉淀等作用方式使重金属转变为在土壤中不易溶出的形态,降低污染物的生物毒性和迁移性,从而达到安全修复污染土壤的目的[5-7]. 该法具有操作简便、修复迅速、投入小、效果好、不改变土壤条件等优点,在重金属污染土壤修复中有着较为广阔的应用前景[8].
传统的钝化材料主要有石灰类物质[9]、有机物料[10]、黏土矿物等[11],能够降低土壤溶液中的重金属离子的活性,但存在钝化效率低、对土壤扰动大等不足. 近些年来,纳米材料因具有大的比表面积、高的反应活性、强的吸附和螯合性能[12],已成为目前污染土壤修复研究的热点[13]. 有研究者将纳米羟基磷灰石、纳米二氧化钛、纳米黑炭等[14-16]应用于土壤污染治理,相关材料表现出极高的重金属钝化效率,但由于材料本身价格昂贵、稳定性差等缺点,限制了其在土壤修复中的应用. 因此,开发出一种钝化性能良好、经济环保的新型钝化材料具有极其重要的理论和现实意义.
纳米二氧化硅材料可以缓解土壤中重金属对植物的毒害,降低重金属的移动性[17-18],且成本低廉、无毒无污染,是极具应用潜力的钝化材料之一. 然而二氧化硅钝化重金属产物结合力较弱,在长期土壤环境中存在解吸的风险. 为了提高二氧化硅材料对重金属的吸附效率和结合力,人们用巯基、氨基硅烷偶联剂[19-20]等对其表面进行修饰,可以明显提升材料对重金属Cd、Pb的钝化效果. 但是二氧化硅粒径小、表面能高,极易发生微粒间的团聚,降低了可与重金属发生反应的有机修饰剂的利用率. 改善纳米微粒的聚集状态,构建多孔、大孔结构的纳米二氧化硅材料可以充分发挥表面钝化基团的作用,提升其对土壤污染物的钝化性能.
本文以硅酸钠为二氧化硅前驱体,分别制备表面带有氨基和环氧基团的纳米二氧化硅,同时采用含巯基的硅烷偶联剂对其表面修饰,通过氨基和环氧基的架桥作用来支撑纳米二氧化硅的部分二次堆积孔结构,阻止由于二氧化硅表面羟基发生缩聚而造成的颗粒团聚,研究了二次堆积孔结构对有效基团巯基与重金属结合效率的影响.
-
硅酸钠(河南省纳米材料工程技术研究中心)、三乙醇胺(分析纯,成都市科龙化工试剂厂)、二乙三胺五乙酸(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司)、结晶氯化钙(分析纯,天津市光复精细化工研究所)、无水乙醇(分析纯,国药集团试剂有限公司)、电导率为18.2MΩ cm的去离子水(自制)、γ-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES,工业级,南京创世化工助剂有限公司)、γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧)丙基三甲氧基硅烷(GLYMO,工业级,南京品宁偶联剂有限公司)、γ-巯丙基三甲氧基硅烷(MPTS,工业级,南京品宁偶联剂有限公司).
DF-101S型集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器,郑州长城科工贸有限公司;JJ-1型定时电动搅拌器,郑州长城科工贸有限公司;SHB-Ⅲ型循环水式多用真空泵,郑州国瑞仪器有限公司;GZX-9023MBE型数显不锈钢鼓风干燥箱,上海博讯实业有限公司;YP5002型电子天平,余姚市金诺天平仪器有限公司;AE-200型分析天平,梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;CHA-AB型空气恒温振荡器,金坛市精达仪器制造厂;TD5M-WS型离心机,湖南赛特湘仪器;VERTEX 70Ⅱ型傅立叶变换红外光谱仪,德国布鲁克光谱仪器公司;Besorp-Max II型比表面积和孔径分析仪,北京精微高博科学技术有限公司;Zetasizer Nano系列纳米粒度电位仪,英国马尔文仪器公司;JEM-2010plus型透射电子显微镜,日本JEOL公司;Agilent 5100型电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES),美国Agilent公司.
-
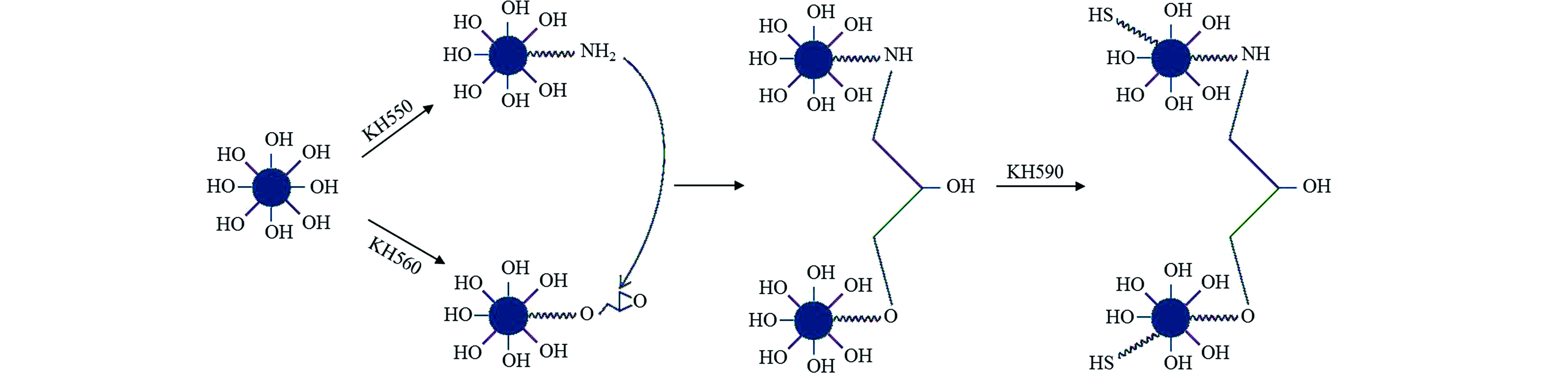
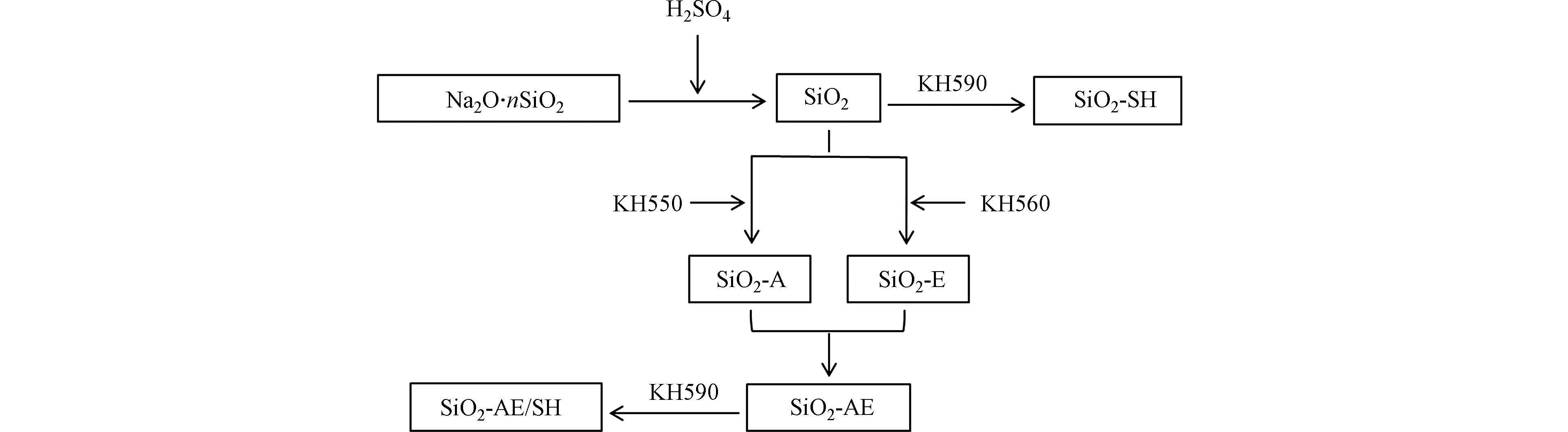
改性纳米二氧化硅钝化材料的制备过程如图1所示.
(1) 将100 g硅酸钠水溶液均匀分散在220 mL去离子水中,水浴升温至40℃,向反应体系中加入稀硫酸调节体系pH值至3—4;70℃恒温1 h,80℃恒温1 h,得到纳米二氧化硅乳液. 用布氏漏斗过滤,产物用去离子水洗涤3次,120℃干燥5 h,得到纳米SiO2(SiO2).
(2) 步骤(1)制备的纳米二氧化硅滤饼分散在150 mL去离子水中,搅拌均匀,取1.71 mmol·g−1 γ-巯丙基三甲氧基硅烷与等质量无水乙醇混合后逐滴加入反应体系;50℃恒温1 h,70℃恒温1 h,80℃恒温1 h. 抽滤,120℃干燥5 h,得到巯基修饰的纳米二氧化硅修复剂(SiO2-SH).
(3) 步骤(1)制备的纳米二氧化硅分为两等份,分别分散于75 mL去离子水中,搅拌均匀,升温至50℃,分别将0.58 mmol·g−1 γ-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷和0.48 mmol·g−1 γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧)丙基三甲氧基硅烷与等质量无水乙醇混合后,逐滴加入反应体系;50℃恒温1 h,70℃恒温1 h,80℃恒温1 h,分别得到氨基和环氧基修饰的二氧化硅乳液,将两种乳液混合均匀,调节pH值为8—9,65℃下恒温反应3 h,抽滤,120℃干燥5 h,得到具有较大孔结构的纳米二氧化硅修复剂(SiO2-AE).
(4) 步骤(3)制备的纳米二氧化硅混合乳液降温至50℃,将一定量γ-巯丙基三甲氧基硅烷(分别设定为0.77、0.87、1.10、1.40、1.71 mmol·g−1)逐滴加入反应体系;50℃恒温1 h,70℃恒温1 h,80℃恒温1 h;抽滤,120℃干燥5 h,得到巯基修饰的具有较大孔结构的纳米二氧化硅修复剂(SiO2-AE/SH).
-
TEM: 取少量的干燥完全的样品粉末分散于无水乙醇中,浓度约为1‰,超声分散均匀;取2—3滴悬浊液于铜网上,待乙醇挥发完全后,用透射电子显微镜对样品的微观形貌进行测试.
FTIR:取少量的样品与溴化钾混合(约为1∶100),研磨均匀后压片,采用红外光谱仪进行测试,波长范围为400—4000 cm−1.
Zeta电位分析:配置一定浓度的样品-水分散液,超声使其分散均匀,用于 ZETA 电位分析.
比表面积及孔径分析:利用低温氮气吸附BET多点法对样品进行比表面积及孔容孔径的测量.
-
污染土壤采自河南省济源市重金属污染农田,采样深度为表层 0—20 cm,自然风干,过20目筛,混合均匀后室温储存. 土壤中铅、镉的总量分别为2510.00 mg·kg−1和23.84 mg·kg−1,DTPA提取态铅、镉的含量分别为1335.00 mg·kg−1和12.58 mg·kg−1.
称取污染土壤25.00 g于250 mL 离心瓶中,添加不同质量比例的修复剂,加入50 mL DTPA 提取剂(成分为0.005 mol·L−1DTPA,0.1 mol·L−1TEA,0.01 mol·L−1CaCl2);25℃下恒温振荡2 h ((180±20) r·min−1),离心3 min(4000 r·min−1),定性滤纸过滤. 用ICP-OES光谱仪测试上清液中重金属元素的含量.
在前期研究工作[21-23]的基础上,依据《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166-2004)对污染土壤中DTPA溶液提取的重金属Pb、Cd离子进行测试分析.
实验结果测定及误差分析:土壤样品分析过程中采用国家有色金属及电子材料分析测试中心多元素标准溶液 GNM-M181182-2013进行分析质量控制,标样测定结果均在参比物质环境标准样品GSBZ 50009-88铜、铅、锌、镉、镍与铬200930允许误差范围内.
实验数据处理:采用Excel 2010和Origin 2019b进行数据处理分析及绘图. 通过计算土壤中DTPA提取态镉、铅的钝化率(Ei)来评估修复剂的钝化效果. 计算公式如(1)所示. 其中,C0为未添加修复剂时DTPA提取原始土壤中污染物的浓度(mg·L−1),Ci为添加修复剂后DTPA提取土壤中污染物的浓度(mg·L−1).
-
(1)巯基修饰大孔道结构纳米二氧化硅的结构设计
氨基、环氧基、巯基等硅烷偶联剂修饰的纳米二氧化硅的结构设计如图2所示. 首先,以硅酸钠为硅源,硫酸为沉淀剂合成表面含有丰富活性羟基的纳米二氧化硅;分别以硅烷偶联剂APTES、GLYMO作为修饰剂,通过硅烷偶联剂表面的烷氧基水解形成的硅羟基与二氧化硅表面的羟基发生缩合反应形成Si—O—Si键,将含活性官能团的有机碳链负载在二氧化硅表面,获得氨基、环氧基修饰的纳米二氧化硅. 氨基在碱性条件下会使环氧基开环,通过活泼氢发生的加成反应使两种二氧化硅达到桥接的目的. 由于颗粒间的空间位阻,可以调控二氧化硅的孔道结构,使其具备多孔特性;最后,以硅烷偶联剂MPTS作为修饰剂在氨基、环氧基桥接后的多孔二氧化硅表面负载巯基,获得具有大孔道结构以及重金属反应活性的改性纳米二氧化硅.
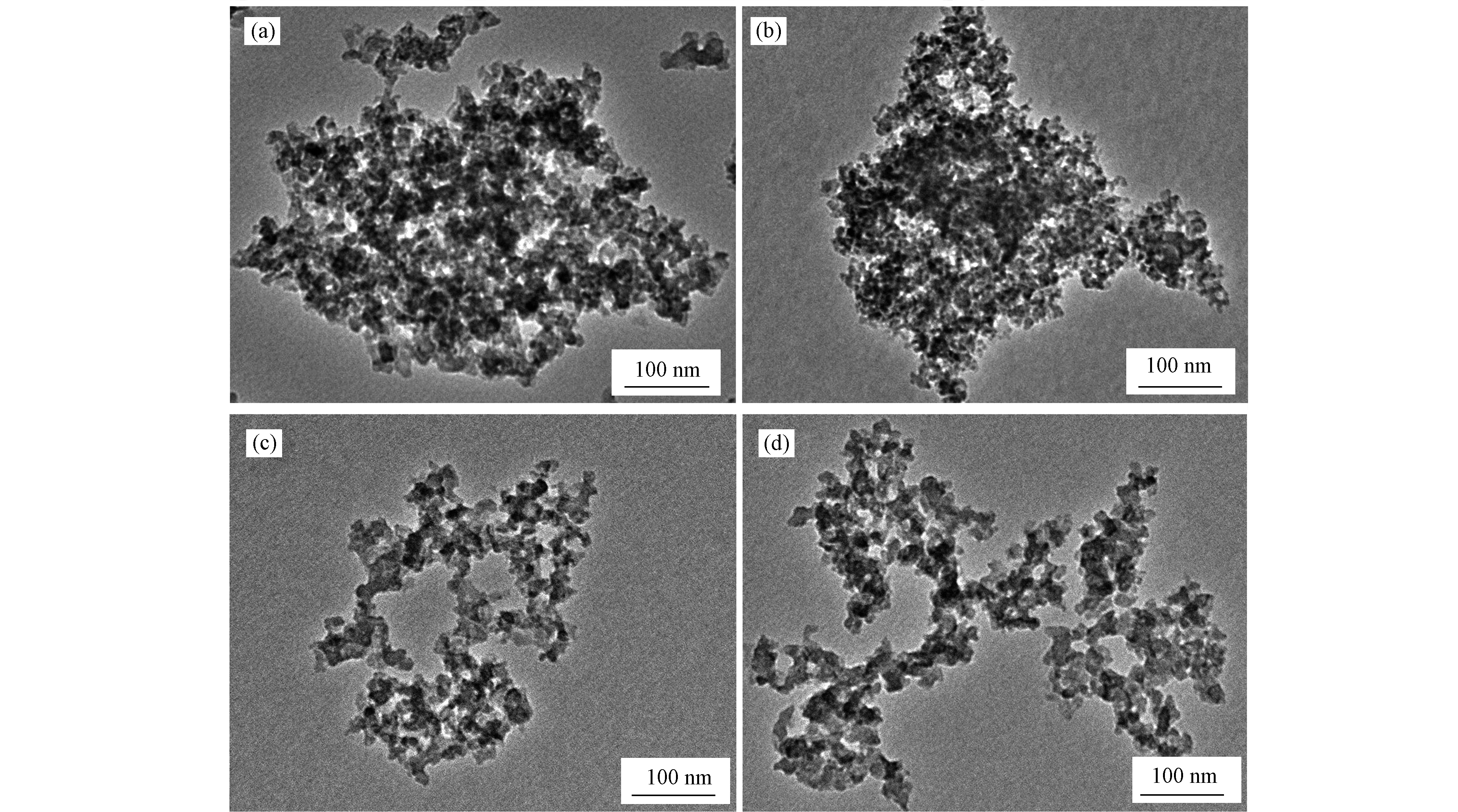
(2)透射电镜分析
图3为制备材料的透射电镜图. 图3a为未修饰的纳米二氧化硅(SiO2),图3b为巯基修饰的纳米二氧化硅(SiO2-SH),图3c为氨基、环氧基桥接的大孔道结构的纳米二氧化硅(SiO2-AE),图3d为巯基修饰的氨基、环氧基桥接的纳米二氧化硅(SiO2-AE/SH). 从图3可以看出,所有纳米二氧化硅一次粒径为10—50 nm. 未经修饰的二氧化硅颗粒团聚严重(图3a),二次堆积的颗粒孔结构不发达,这是由于其表面存在大量亲水性较强的硅羟基,干燥过程中易发生脱水反应,造成孔的塌陷;巯基修饰后(图3b)纳米二氧化硅粒径未发生变化,团聚情况稍有改善,是由于表面有机基团的存在降低了表面能,减轻了孔的塌陷;相比SiO2和SiO2-SH,SiO2-AE(图3c)由于氨基、环氧基的架桥作用和表面有机化支撑了内部孔道结构,使得团聚和塌陷作用进一步减弱,形成了明显的堆积孔;继续修饰巯基后的纳米SiO2-AE/SH(图3d),表面能进一步降低,材料内部呈现明显的网络结构,具有丰富的孔结构.
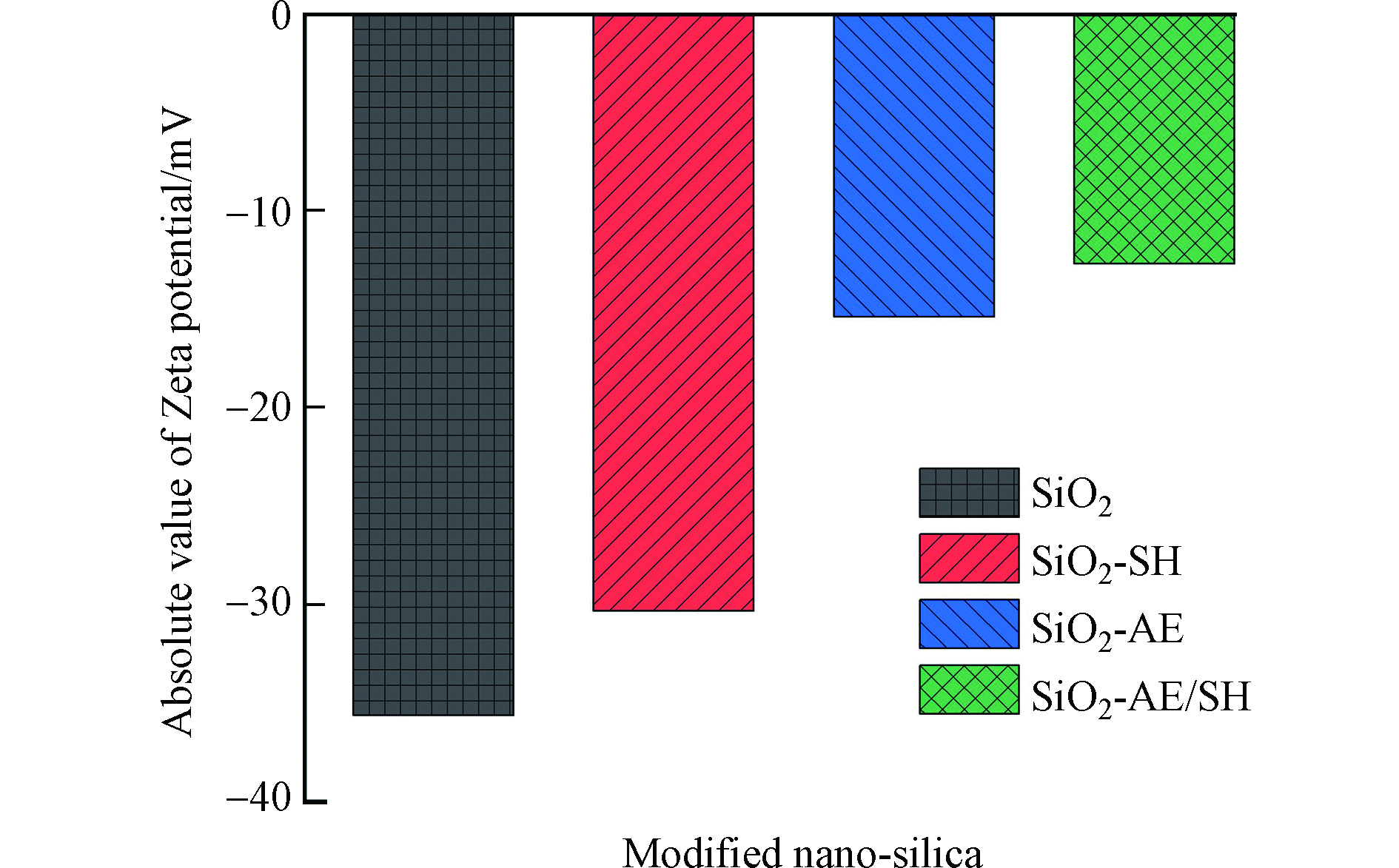
(3)Zeta电位分析
图4为改性SiO2在介质水中的Zeta电位分析结果. 由图4可知,未修饰的纳米SiO2表面存在有丰富的硅羟基,使其携带大量的负电荷,Zeta电位值为−35.6 mV,在水溶液中呈现较强的负电性.
采用硅烷偶联剂对其表面进行改性,偶联剂一端与SiO2发生脱水缩合反应,使SiO2表面的硅羟基减少,电负性降低[24]. 降低程度与表面硅烷偶联剂的用量多少相对应. 巯基修饰纳米SiO2(SiO2- SH)的Zeta电位值为−30.3 mV;氨基、环氧基桥接的纳米SiO2(SiO2-AE)的Zeta电位值为−15.4 mV;氨基、环氧基、巯基的3种硅烷偶联剂修饰的SiO2(SiO2-AE/SH)的Zeta电位值为−12.7 mV. Zeta电位值向正电位方向移动可以证明,改性后SiO2表面的硅羟基数量逐渐减少,使得团聚情况有所改善.
(4)比表面积及孔径分析
图5(a)分别为未修饰的二氧化硅(SiO2)、巯基修饰的二氧化硅(SiO2-SH)、巯基修饰的大孔径二氧化硅(SiO2-AE/SH)的N2吸脱附曲线. 从图5可以看出,3条曲线都属于Ⅳ型N2吸脱附曲线,且存在有H2型滞后环,说明合成的二氧化硅是颗粒的二次堆积形成的多孔结构. SiO2、SiO2-SH、SiO2-AE/SH曲线出现滞后环的相对压力分别为0.4、0.5、0.6,逐渐增大,说明修饰后的二氧化硅孔道增大;且相比于SiO2-SH,SiO2-AE/SH曲线在高相对压力区上升的比较快,说明SiO2-AE/SH中的孔比较多,SiO2-AE/SH 曲线在相对压力为0.9时对N2的吸附量最高,说明SiO2-AE/SH的孔最大. 因此桥接作用和表面有机化对增大二氧化硅的孔径起到了一定的作用,孔结构的大小顺序为SiO2-AE/SH > SiO2-SH > SiO2.
图5(b)为改性二氧化硅的孔容-孔径微分(log)分布曲线. 由图5可以看出,改性前后的二氧化硅孔径分布较宽,改性后的二氧化硅孔径明显增大,未修饰的二氧化硅(SiO2)、巯基修饰的二氧化硅(SiO2-SH)、巯基修饰的大孔径二氧化硅(SiO2-AE/SH)的最可几孔径分别为3.2、6.6、17.4 nm.
表1列出了改性二氧化硅的比表面积及平均孔径数据. 从表1可以看出,相比未修饰的二氧化硅(SiO2),修饰后的二氧化硅比表面积有所降低,巯基修饰纳米SiO2(SiO2- SH)的比表面积为562.5 m2·g−1,氨基、环氧基、巯基修饰的SiO2(SiO2-AE/SH)的比表面积为376.9 m2·g−1. 这可能是由于表面修饰剂的存在降低了纳米二氧化硅的表面极性,使比表面积呈现下降的趋势. 但修饰后二氧化硅的孔径有所增加,且SiO2-AE/SH的孔径(10.6 nm)较SiO2-SH(6.8 nm)大. 这是由于二氧化硅表面修饰的氨基和环氧基反应后,一方面通过桥接作用固定了颗粒的相对位置,另一方面较多的有机碳链对二氧化硅表面活性羟基的缩聚产生了位阻效应,降低了二氧化硅粒子之间的团聚,起到了支撑二氧化硅聚集体孔结构的作用,与TEM结果相一致.
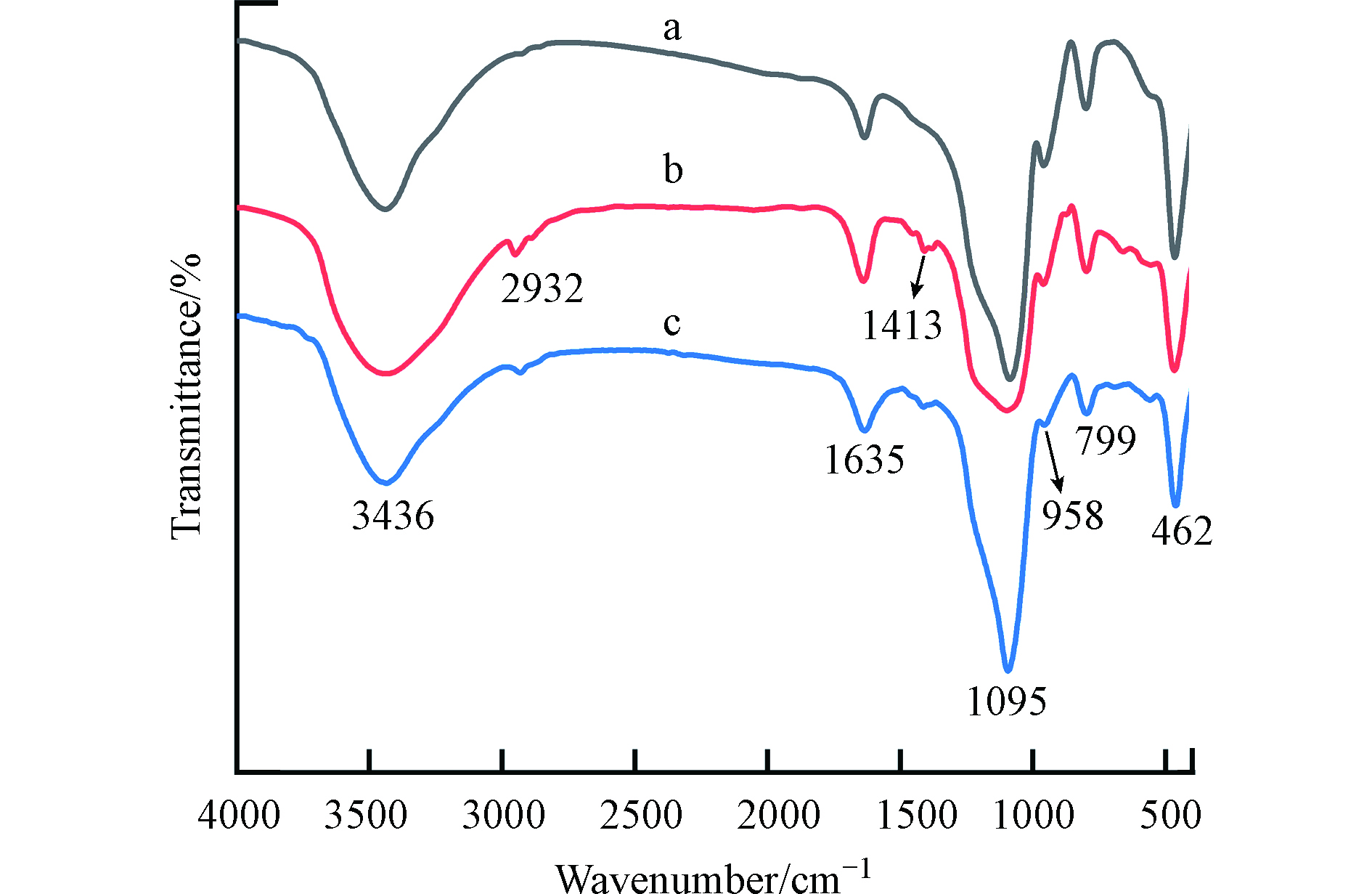
(5)红外光谱分析
图6为改性二氧化硅的红外光谱图. 图6a、b、c分别为未修饰的二氧化硅(SiO2)、氨基、环氧基桥接的大孔道结构的二氧化硅(SiO2-AE)、巯基修饰的氨基、环氧基桥接的二氧化硅(SiO2-AE/SH)的红外光谱曲线. 其中,a、b、c曲线在1095、799、462 cm−1处分别出现了Si—O—Si的反对称伸缩振动峰、对称伸缩振动峰与弯曲振动峰,958 cm−1处是Si-OH的伸缩振动和弯曲振动峰. 1635 cm−1、3436 cm−1是O—H的伸缩振动峰和H—O—H的弯曲振动峰.
与a曲线相比,b、c曲线均在1413 cm−1、2932 cm−1处出现了两个吸收峰,分别是—CH3的变形振动峰和—CH2—的不对称伸缩振动峰,说明功能性基团的有机碳链负载在二氧化硅表面. 与b曲线相比,c曲线在 958cm−1处Si—OH峰的下降,这是由于引入巯基硅烷偶联剂后MPTS与纳米二氧化硅表面羟基发生反应,消耗了部分羟基.
-
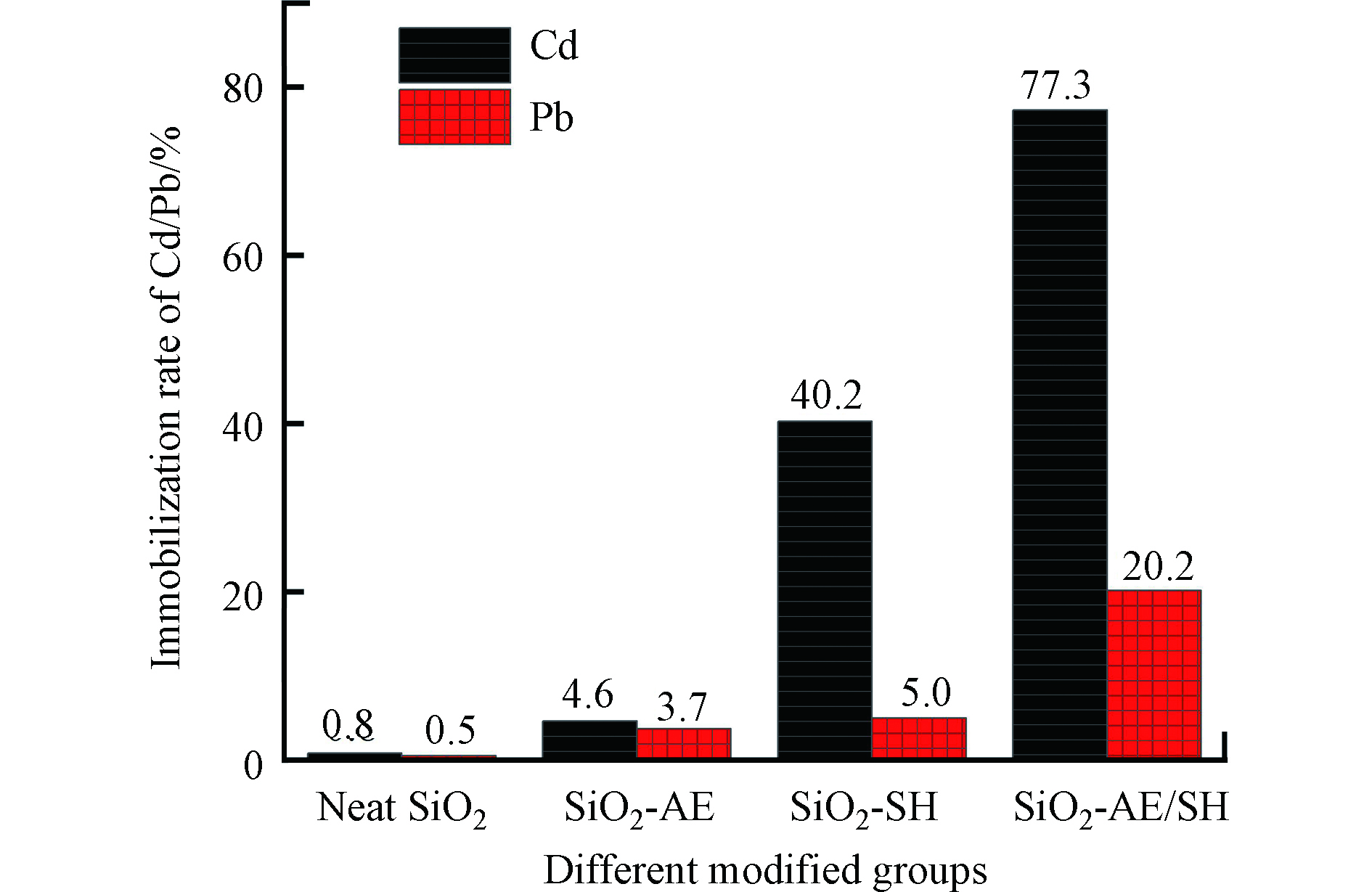
图7为添加4%的质量比例后,不同类型的改性纳米二氧化硅对土壤中DTPA提取态Cd、Pb的钝化率. 从图7可见,未修饰的二氧化硅(SiO2)对重金属Cd、Pb的钝化率都较低,这是因为未修饰的二氧化硅孔结构不发达,与活性重金接触概率较低,且主要以物理吸附作用于活性重金属,钝化能力较弱.
SiO2-AE对Cd、Pb的钝化率较SiO2稍有提高,分别为4.6%和3.7%,这一方面可能是由于含氨基和环氧基的有机碳链的修饰降低了二氧化硅之间的团聚作用,使其表面孔结构更加丰富,吸附能力提高,另一方面可能是由于表面修饰的残余氨基与重金属发生络合反应,钝化了一部分重金属,使得钝化率有所提高. 在相同修饰剂量下,SiO2-SH对Cd、Pb的钝化率远高于SiO2-AE,分别为40.2%和5.0%,表明巯基可能与重金属离子形成稳定的巯基金属配合物,有效的钝化了土壤中的Cd、Pb污染物;而SiO2-AE/SH对Cd、Pb的钝化率远高于SiO2-SH与SiO2-AE之和,分别为77.3%和20.2%,一方面可能是由于残余氨基和巯基的协同作用增强了SiO2-AE/SH对重金属的螯合能力,另一方面是由于氨基和环氧基的桥接使SiO2-AE/SH的孔结构增大,后修饰的巯基附着在孔道或颗粒表面,土壤中的重金属离子更容易进入孔道,与表面有效基团巯基发生作用的概率明显增大.
负载巯基的改性二氧化硅(SiO2-SH,SiO2-AE/SH)对重金属Cd的钝化率要高于重金属Pb,出现这种现象的可能原因是:一是土壤中的Cd主要以活性高的可交换态存在,容易与修复剂结合;二是土壤中DTPA提取态Cd的含量远远低于Pb,被钝化时变化比例较大.
-
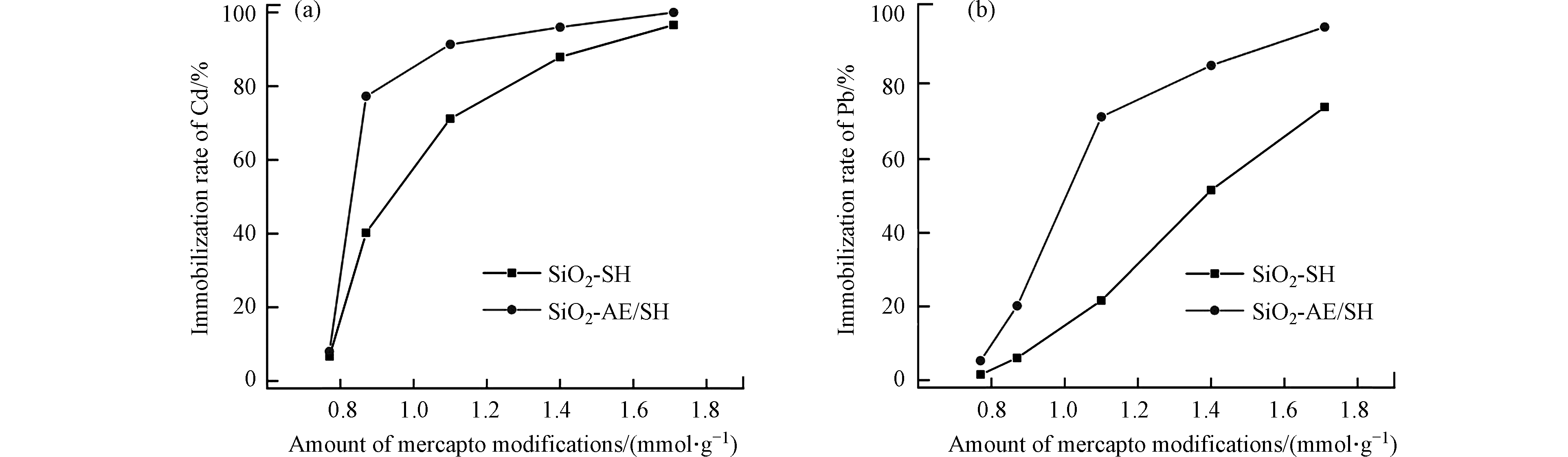
为了进一步研究构建二次孔结构对材料钝化性能的影响,对比了SiO2-SH和SiO2-AE/SH两种修复剂的钝化性能. 考察了修复剂添加比例为4%时,不同巯基修饰量下SiO2-SH和SiO2-AE/SH修复剂对土壤中DTPA提取态Cd、Pb含量的影响,结果如图8.
从图8可见,在巯基修饰量为0.77 mmol·g−1时,两种类型的二氧化硅对Cd、Pb的钝化率相差不大,均在10%以下. 随着巯基修饰量的增加,SiO2-SH和SiO2-AE/SH对Cd、Pb的钝化率都增加,且SiO2-AE/SH的钝化效率明显高于SiO2-SH. 进一步增大巯基修饰量,两种修复剂间的钝化性能差距降低. 在巯基修饰量较少的情况下,巯基在二氧化硅表面负载比较稀疏,修饰密度较低,对重金属的钝化率本身就低,故两种二氧化硅对重金属的钝化率测试结果相差不大;当巯基负载量增大时,差别明显加大,主要是纳米二氧化硅干燥形成二次聚集体颗粒时,使一定量的巯基被包埋于内部,SiO2-SH孔径相对较小,降低了巯基与水溶性重金属离子的接触概率,导致巯基的有效利用率下降. SiO2-AE/SH由于具有一定的大孔道结构,通过毛细作用可使重金属与巯基的接触概率增加,提高了巯基的利用效率,也在一定程度上增大了巯基基团的有效含量. 因此,在巯基修饰量相同的情况下,SiO2-AE/SH对重金属的钝化率要高于SiO2-SH. 当修饰剂为1.10 mmol·g−1时,SiO2-AE/SH对铅离子的钝化效率是SiO2-SH的1.28倍,SiO2-AE/SH对镉离子的钝化效率是SiO2-SH的3.31倍.
随着巯基含量的进一步增加,两种材料的钝化效率差异逐渐降低. 在巯基修饰量为1.71 mmol·g−1时,SiO2-SH和SiO2-AE/SH对重金属Cd已基本完全钝化,而对重金属Pb的钝化率分别为74.1%和95.8%. 这可能是由于过量的巯基修饰剂使得二氧化硅表面具有足够数量的-SH,因此孔结构对其影响不再十分明显. 因此,在巯基含量相同时,具有较大孔结构的SiO2-AE/SH材料,提高了功能化官能团巯基的利用率,对重金属Cd、Pb的钝化率高于SiO2-SH.
-
本文通过氨基/环氧基的架桥作用制备了一种孔结构丰富的纳米二氧化硅,在其表面进一步修饰巯基得到一种高效的重金属污染土壤纳米修复剂. 结果表明,有机碳链的支撑作用降低了二氧化硅粒子之间的团聚,使得所制备的纳米二氧化硅具有较大的二次堆积孔结构,提高了功能性基团巯基的利用率. 在添加比例为4%、巯基修饰量为1.71 mmol·g−1时,所制备的大孔结构纳米二氧化硅修复剂可使土壤中DTPA提取态Cd、Pb的含量分别由12.58 mg·kg−1和1335.00 mg·kg−1降低至0.01 mg·kg−1和55.94 mg·kg−1,钝化效率分别达到99.9%和95.8%.
巯基功能化大孔二氧化硅的制备及其对土壤中二乙三胺五乙酸(DTPA)提取态Cd、Pb的钝化性能
Preparation of thiol groups modified macroporous structured nano-silica and its immobilization of Cd and Pb in contaminated soils
-
摘要: 以硅酸钠为前驱体,分别制备表面带有氨基和环氧基团的纳米二氧化硅,利用氨基和环氧基团的桥接反应构建具有大孔结构的纳米二氧化硅,进一步在其表面负载具有重金属反应性的巯基基团,最终得到一种具有重金属高效反应性的纳米材料,并将其用于对土壤重金属的钝化修复.红外光谱、透射电镜、比表面积等分析显示,氨基和环氧基有机基团的修饰降低了纳米二氧化硅颗粒之间的团聚,两种基团之间的架桥反应,构建了具有较大孔径的二氧化硅聚集结构.通过研究改性二氧化硅对污染土壤中DTPA提取态Cd、Pb的钝化作用,发现巯基修饰的大孔径纳米二氧化硅(SiO2-AE/SH)大幅提高了对重金属的钝化率;在添加比例为4%,修饰剂量为1.10 mmol·g−1时,SiO2-AE/SH对Cd的钝化效率是巯基修饰纳米二氧化硅(SiO2-SH)的1.28倍,对Pb的钝化效率是SiO2-SH的3.31倍.此研究为构建高效、大孔结构重金属钝化材料提供了一种方法,此材料也有望发展成为多孔硅过滤介质,应用于重金属废水处理.Abstract: Sodium silicate is used as the precursor to prepare nano-SiO2 with amine and epoxy groups on the surface. Two kinds of SiO2 are bridged through the reaction between amino and epoxy groups to build nano-SiO2 with macroporous structure. Thiol groups with heavy metal reactivity were further loaded on its surface to afford a type of highly reactive SiO2 nanomaterial for immobilization of heavy metals in soils. FTIR, TEM, and specific surface area analysis show that the modification of amino and epoxy organic groups reduces the agglomeration between nano-SiO2 particles, and the bridging reaction between amino and epoxy groups help construct a macroporous aggregated SiO2 structure. By studying the immobilization effect of modified SiO2 on the effective states of Cd and Pb in contaminated soils, the thiol-modified macroporous nano-SiO2 greatly can improve the immobilization rate of heavy metals. When the addition ratio is 4% and the modification dosage is 1.10 mmol·g−1, the immobilization efficiency of SiO2-AE/SH to cadmium ions and lead ions is 1.28 times and 3.31 times than that of SiO2-SH, respectively. This research provides a method for constructing high-efficiency, large-pore structure nanomaterials for heavy metal passivation, and this material is also expected to play roles in the treatment of heavy metal wastewater as porous silicon filter.
-
Key words:
- surface modification /
- nano-silica /
- contaminated soils /
- immobilization /
- cadmium/lead
-

-
表 1 改性纳米二氧化硅的表面性质
Table 1. Surface properties of modified nano-silica
改性二氧化硅Modified nano-silica 比表面积SBET/(m2·g−1) 平均孔径Daverage/nm SiO2 690.8 3.3 SiO2−SH 562.5 6.8 SiO2−AE/SH 376.9 10.6 -
[1] 龚海明, 马瑞峻, 汪昭军, 等. 农田土壤重金属污染监测技术发展趋势 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(2): 140-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2013.02.025 GONG H M, MA R J, WANG Z J, et al. Development of technologies for monitoring agricultural soil heavy metal pollution [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(2): 140-147(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2013.02.025
[2] 安婧, 宫晓双, 魏树和. 重金属污染土壤超积累植物修复关键技术的发展 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(11): 3261-3270. AN J, GONG X S, WEI S H, et al. Research progress on technologies of phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(11): 3261-3270(in Chinese).
[3] 胡雪芳, 田志清, 梁亮, 等. 不同改良剂对铅镉污染农田水稻重金属积累和产量影响的比较分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(7): 3409-3417. HU X F, TIAN Z Q, LIANG L, et al. Comparative analysis of different soil amendment treatments on rice heavy metal accumulation and yield effect in Pb and Cd contaminated farmland [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(7): 3409-3417(in Chinese).
[4] XU C, CHEN H X, XIANG Q, et al. Effect of peanut shell and wheat straw biochar on the availability of Cd and Pb in a soil–rice (Oryza sativa L. ) system [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 25(2): 1147-1156. [5] KOMAREK M, VANEK A, ETTLER V. Chemical stabilization of metals and arsenic in contaminated soils using oxides - a review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 172: 9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.07.045 [6] 曹心德, 魏晓欣, 代革联, 等. 土壤重金属复合污染及其化学钝化修复技术研究进展 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(7): 1141-1453. CAO X D, WEI X X, DAI G L, et al. Combined pollution of multiple heavy metals and their chemical immobilization in contaminated soils: a review [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 5(7): 1141-1453(in Chinese).
[7] 邹雪艳, 李小红, 赵彦保, 等. 化学钝化法修复重金属污染土壤研究进展 [J]. 化学研究, 2018, 29(6): 14-23. ZOU X Y, LI X H, ZHAO Y B, et al. Research progress for chemical immobilization in heavy metal contaminated soils [J]. Chemical Research, 2018, 29(6): 14-23(in Chinese).
[8] 李剑睿, 徐应明, 林大松, 等. 农田重金属污染原位钝化修复研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(4): 721-728. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.04.029 LI J R, XU Y M, LIN D S, et al. In situ immobilization remediation of heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(4): 721-728(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.04.029
[9] GARAU G, CASTALDI P, SANTONA L, et al. Influence of red mud, zeolite and lime on heavy metal immobilization, culturable heterotrophic microbial populations and enzyme activities in a contaminated soil [J]. Geoderma, 2007, 142(1/2): 47-57. [10] JIANG J P, YUAN X B, YE L L, et al. Characteristics of straw biochar and its influence on the forms of arsenic in heavy metal polluted soil [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 409/410: 133-138. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.409-410.133 [11] LIANG X F, HAN J, XU Y M, et al. In situ field-scale remediation of Cd polluted paddy soil using sepiolite and palygorskite [J]. Geoderma, 2014, 235/236(4): 9-18. [12] 王萌, 陈世宝, 李娜, 等. 纳米材料在污染土壤修复及污水净化中应用前景探讨 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 29(2): 140-147. WANG M, CHEN S B, LI N, et al. Development of technologies for monitoring agricultural soil heavy metal pollution [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(2): 140-147(in Chinese).
[13] 刘蕊, 周启星, 马奇英. 纳米材料在污染水体和土壤修复中的应用 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(9): 1852-1859. LIU R, ZHOU Q X, MA Q Y, et al. Applications of nanomaterials in remediation of contaminated water and soil: A review [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(9): 1852-1859(in Chinese).
[14] JIN Y, LIU W, LI X L, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite immobilized lead and enhanced plant growth of ryegrass in a contaminated soil [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 95: 25-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.071 [15] 丁园, 刘燕红, 郝双龙, 等. 化学改良剂对红壤中铜、镉吸附行为的影响 [J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2010, 32(4): 824-828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2010.04.035 DING Y, LIU Y H, HAO S L, et al. Effect of adjustments on Cu and Cd sorption in red soil [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2010, 32(4): 824-828(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2010.04.035
[16] CHENS J M, LIU Y Z, WANG H W. Effects of surface-modified nano-scale carbon black on Cu and Zn fractionations in contaminated soil [J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2014, 16(1): 86-94. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2012.759530 [17] RIZWAN M, MEUNIER J D, MICHE H, et al. Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W. ) grown in a soil with aged contamination [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 209/210: 326-334. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.033 [18] 宁东峰. 土壤重金属原位钝化修复技术研究进展 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(23): 72-80. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16010119 NING D F. A review of in situ passivation repairing technology of heavy metals in soil [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(23): 72-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16010119
[19] BAO S Y, LI K, NING P, et al. Highly effective removal of mercury and lead ions from wastewater by mercaptoamine-functionalised silica-coated magnetic nano-adsorbents: Behaviours and mechanisms [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 393: 457-466. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.098 [20] 任小明, 赵辉, 朱妍娇, 等. 纳米二氧化硅粒子的改性研究 [J]. 湖北大学学报∶自然科学版, 2016, 38(6): 522-526. REN X M, ZHAO H, ZHU Y J, et al. Modification of nano silicon dioxide particles [J]. Journal of Hubei University (Natural Science), 2016, 38(6): 522-526(in Chinese).
[21] 王帝伟, 刘祎丹, 易春辉, 等. 改性纳米二氧化硅对Cd污染农田土壤的钝化修复 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1106-1112. WANG D W, LIU Y D, YI C H, et al. Stabilization of Cd-contaminated agricultural soils by modified nano-silica [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5): 1106-1112(in Chinese).
[22] CAO P L, QIU K Y, ZOU X Y, et al. Mercapto propyltrimethoxysilane- and ferrous sulfate-modified nano-silica for immobilization of lead and cadmium as well as arsenic in heavy metal-contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266(Pt 3):115152. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115152. [23] LIAN M M, FENG Q Q, WANG L F, et al. Highly effective immobilization of Pb and Cd in severely contaminated soils by environment-compatible, mercapto-functionalized reactive nanosilica [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 235: 583-589. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.015 [24] KOSAK A, BAUMAN M, PADEZNIK GOMILSEK J, et al. Lead (II) complexation with 3-mercaptopropyl- groups in the surface layer of silica nanoparticles: sorption, kinetics and EXAFS/XANES study [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 229: 371-379. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.11.115 -



 下载:
下载: