-
抗生素自被发现以来,就已被广泛应用于各行业中。抗生素是一种在较低浓度就能抑制影响其他生物机能的化学物质,拥有良好的治疗效果和促进生物生长的能力[1]。抗生素的出现帮助人类解决了许多人体和动植物病害等方面的问题,在各领域特别是动物饲料及医药品的生产中发挥了巨大的作用[2]。随着科技的发展,抗生素越来越难以从人类社会中剥离出来。但通常情况下,人和动物对抗生素的消化吸收能力很差,进入人或动物体内的抗生素中超过60%会通过粪便和尿液被排放到环境中[3]。此外,大量来源于医院、农场、养殖场和工厂等地的抗生素也会经过雨水和污水排放而流入水环境中[4],而进入环境介质的中的抗生素由于其复杂的结构和较强的抑制杀菌能力导致其难以被生物降解。这些流入环境中的抗生素可能会诱导耐药菌株的生成,而若致病菌或条件致病菌从中获得了抗药因子,则将对生态环境与社会安全产生严重的潜在威胁[5]。早在2015年,中国患者的抗生素使用率就已超过80%[6],远高于同年的欧美国家,而全球各地也早已出现了关于水体抗生素污染问题的报道[7-8],其中中国的抗生素污染问题则较为突出,如对上海黄浦江的调查中发现了高浓度的磺胺类以及四环素类抗生素[9],而2014年京杭大运河则被检出其抗生素浓度超过自然水体的10000倍[10]。随着抗生素对水环境造成的威胁不断扩大,越来越多的研究者开始聚焦于水环境中抗生素污染的修复和去除工作[11]。
目前常用于去除水体中抗生素的方法主要包括吸附、光化学降解、微生物降解、超声降解、膜处理工艺、人工湿地等,部分方法存在成本高、稳定性差、工艺复杂等问题[11-12]。吸附作为一种常用有效且成本低廉的技术,常被应用于水体中抗生素的去除[13],而生物炭相较于活性炭、碳纳米管、黏土矿物、离子交换树脂等其他几种常用吸附剂,拥有成本低廉、制备简单、原材料来源广泛和环境友好等优点[14]。生物炭是一种在限氧或无氧环境下高温热解生物质产生的一种芳香程度高且具有多孔径结构和大量表面活性官能团的富碳固体物质[15]。研究表明部分生物炭对水体中特定的抗生素具有一定的吸附去除效果[7,16],但由于生物炭本身带负电,很多情况下对抗生素吸附能力表现并不佳,而通过在制备过程中或之后对生物炭表面进行修饰或者使用化学试剂处理可以定向改变其部分理化性质,这种改性通常可显著提高生物炭对目标污染物的吸附能力[17],因此对生物炭进行改性已成为当下生物炭研究领域的必然趋势[18]。
目前改性生物炭已广泛运用于许多水体污染物的去除研究,例如重金属、营养物质及有机污染物[19-20]。目前,对生物炭比较常用的改性方法可以大致分为化学、物理以及生物改性方法,其中化学方法是较常用的改性方法[21]。现如今对生物炭进行改性的方法繁多,同时用于吸附的抗生素种类不同也会造成吸附效果和机理出现较大的差异。目前虽出现了很多关于改性生物炭对水体中抗生素的吸附研究报道,但部分研究中对抗生素吸附机理方面的解释还不够清晰。同时,由于生物炭理化性质受生物质类型和碳化条件的影响较大,不同生物炭对不同污染物的吸附效果及过程也不同。因此有必要对现有的研究进行归纳总结。本文对改性生物炭的制备及其理化性质表征、吸附污染物的影响因素以及对水体抗生素的吸附机理和吸附效果等方面进行综述。
-
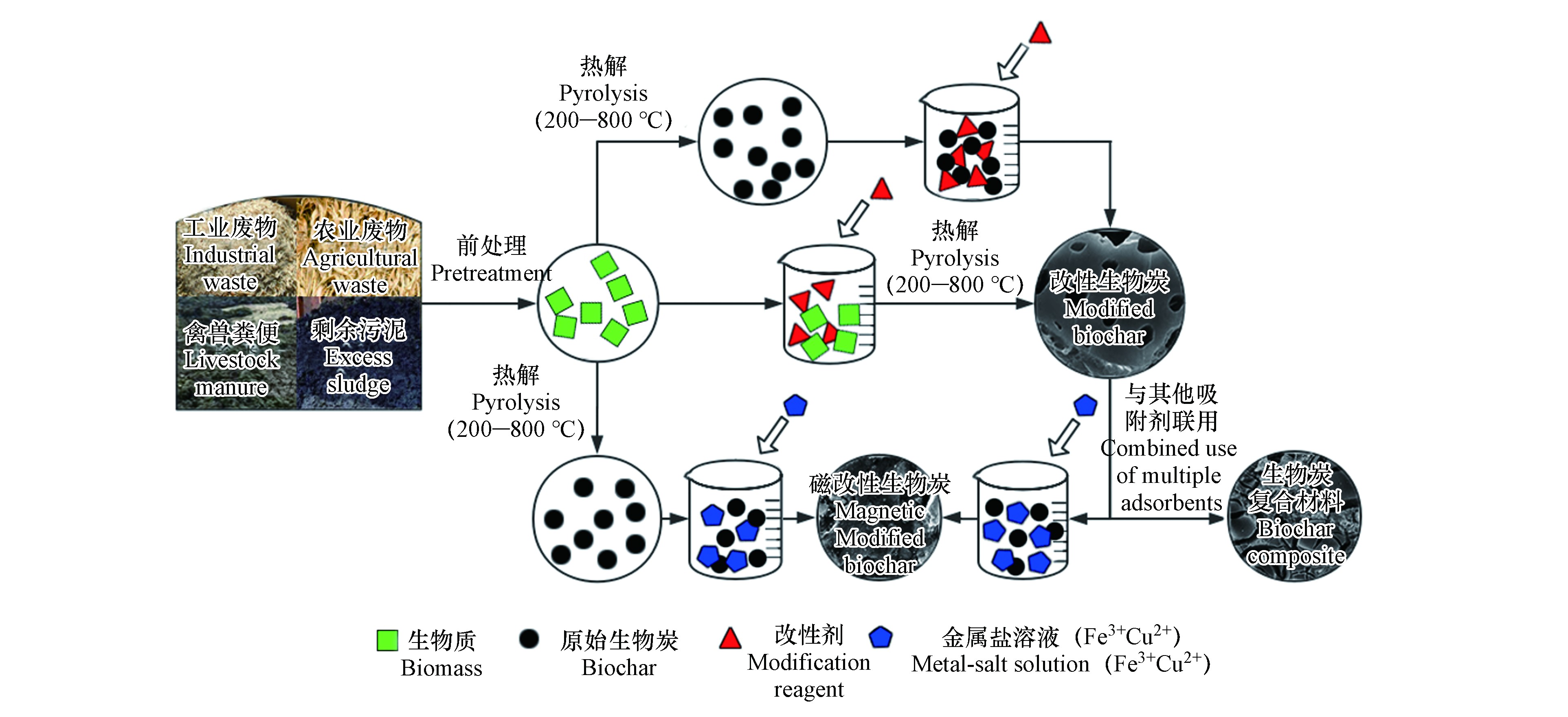
生物炭制备的原材料来源广泛且价格低廉,按照制备原料的不同,生物炭可以大体分成:木质生物炭、粪便炭、植物秸秆炭、稻壳炭、污泥生物炭等类型[22-23]。这些生物炭通常稳定性较高且不易被氧化[24],利用工、农、林业废物制成的生物炭作为吸附剂来修复水体抗生素污染不仅为废物的重复利用提供了方案,也有利于水体抗生素污染的修复工作[25]。
但在许多情况下,直接热解制成的生物炭对部分抗生素的吸附效果存在较大的局限性,这种局限性主要是因为单纯控制碳化条件难以改变生物炭孔隙、比表面积大小以及表面含氧官能团等影响吸附性能的因素[25]。部分制备的原始生物炭对抗生素体现出的吸附效果不佳。如在赵涛[26]的研究中,700 ℃下制备的花生壳、皇竹草、玉米秸秆对磺胺嘧啶的最大吸附量分别为1.89、5.29、5.79 mg·g−1。研究者在600 ℃下制备的木屑生物炭对左氧氟沙星的最大吸附量为7.72 mg·g−1[27]。Wang等[28]的研究结果显示,最适温度下的稻草生物炭对水体中四环素(TC)的最大吸附量为13.85 mg·g−1。其他的研究中发现马铃薯茎叶生物炭对诺氟沙星的吸附量也低于10 mg·g−1[29]。而在改性生物炭对四环素的吸附实验中,通过将KOH溶液与杨木生物炭进行混合后制备出的改性生物炭对四环素的吸附量从4.30 mg·g−1提升到了21.17 mg·g-1[30]。因此,对生物炭进行改性将有助于解决生物炭对抗生素吸附性能不佳的问题。
-
制备改性生物炭的方法大体可以分为对生物炭原材料进行预处理或对制备完成后的原始生物炭进行改性处理,即通过在生物炭的制备过程中或之后对其表面进行修饰或者使用化学试剂处理从而得到部分理化性质被改变的生物炭,通过改性改变生物炭的比表面积、孔径大小、表面官能团及表面化学结构等因素使改性后的生物炭更加适合对目标物的吸附[31]。改性生物炭常规的制备流程如图1所示。许多研究证明通过对生物炭进行特定的改性后,生物炭对目标物的吸附能力显著提高[17],且改性可能使生物炭的制备成本降低或者定向改变生物炭作为吸附剂时的部分缺点,例如分离回收困难等[32]。目前对用于水体中抗生素吸附的生物炭进行改性常用的方法可以大致分为化学、物理以及生物改性方法,其中化学方法是最常用且有效的改性方法[21]。
化学改性通常是指在生物炭制备前,向生物炭原材料中添加酸、碱、还原剂、氧化剂等化学试剂从而在生物炭热解过程中改变生物炭的物理化学性质[33],或在生物炭制备完成后加入化学试剂直接处理生物炭从而修饰生物炭的表面性质及令官能团发生改变。例如将在350 ℃下热解成的松木屑生物炭与磷酸溶液混合并二次热解后制备出来的磷酸改性生物炭表面结构发生了明显的变化,改性后生物炭的比表面积提高幅度较大,这使磷酸改性生物炭对氧氟沙星(OFL)和诺氟沙星(NOR)的吸附能力得到了显著的提升[34]。使用酸、碱试剂改性能对生物炭的理化性质带来显著的改变,酸改性后的生物炭中氧的含量显著增加并产生更多的酸性官能团。有研究表明使用硫酸改性的小麦秸秆生物炭比表面积扩大,且酚羟基类酸性官能团含量显著增加[35],但相比于碱改性,酸改性生物炭的比表面积增量通常较低,且碱改性给生物炭带来的碱性物质如OH−离子或NH2基团可以与生物炭表面的官能团发生反应,可增强生物炭对带负电荷物质和水中有机污染物的吸附能力[18,36]。化学改性通常能较好的增加生物炭比表面积大小和表面官能团含量从而提升吸附性能,但由于使用酸、碱、氧化剂等化学试剂作为改性剂,在实际运用中有产生二次污染的风险[31]。
物理改性常用的手段是在制备完成后对生物炭进行二次煅烧来进一步清除生物炭表面孔隙中的杂质进而改变生物炭孔隙结构,增加其比表面积,从而提高生物炭的吸附性能[37],将生物炭加热到800—900 ℃保持1—2 h后通入氢气、氩气或空气可使生物炭表面形成新的官能团[38]。或通过微波处理对生物炭进行改性,如对玉米秸秆生物炭进行微波改性后,其对Cd的吸附量达到了26.90 mg·g−1,但在同一研究中,使用NaOH溶液改性的生物炭对Cd的吸附能力几乎都大于微波改性生物炭[39]。
而用生物方法改性的研究则相对较少,这可能是由于生物方法改性的过程较为繁琐且对环境条件的要求较高。在使用硝化菌改性的稻壳生物炭去除水体氨氮的研究中,固定了硝化菌的生物炭在保留原吸附能力的同时发挥出了微生物的高效降解作用[40]。研究显示使用有效微生物群菌 ( effective microorganisms,EM) 和聚磷菌改性后的秸秆生物炭对水体氮、磷的去除效果相较于未改性生物炭高,对氮源和磷源需求量较高的菌生存条件可能是产生这一现象的原因[37]。
此外还有例如将生物炭与金属盐溶液混合制备的磁改性生物炭,生物炭的磁改性即对生物炭原材料进行共沉淀使其负载铁化合物再进行高温热解制备成磁改性生物炭,或在原始生物炭制备完成时加入磁性物质例如Fe3O4使两者充分反应混合后再次高温煅烧增加其稳定性[41]。在生物炭表面负载铁氧化物后,SEM能谱仪中显示出了明显的Fe峰,说明负载的Fe成功在生物炭表面生成氧化物等化合物[42]。黄芪草药生物炭的比表面积大小经过磁改性后得到了十分显著的提升[43]。也有研究证明通过紫外辐射对生物炭进行改性也会增强生物炭对污染物的吸附能力[44]。改性生物炭的制备方法众多,使用多种方法联用制备的复合改性生物炭可能会产生更好的效果[45],不同的改性方法对生物炭产生的影响差异较大,而在选择改性方法时除了考虑吸附能力还需注意经济效益。
-
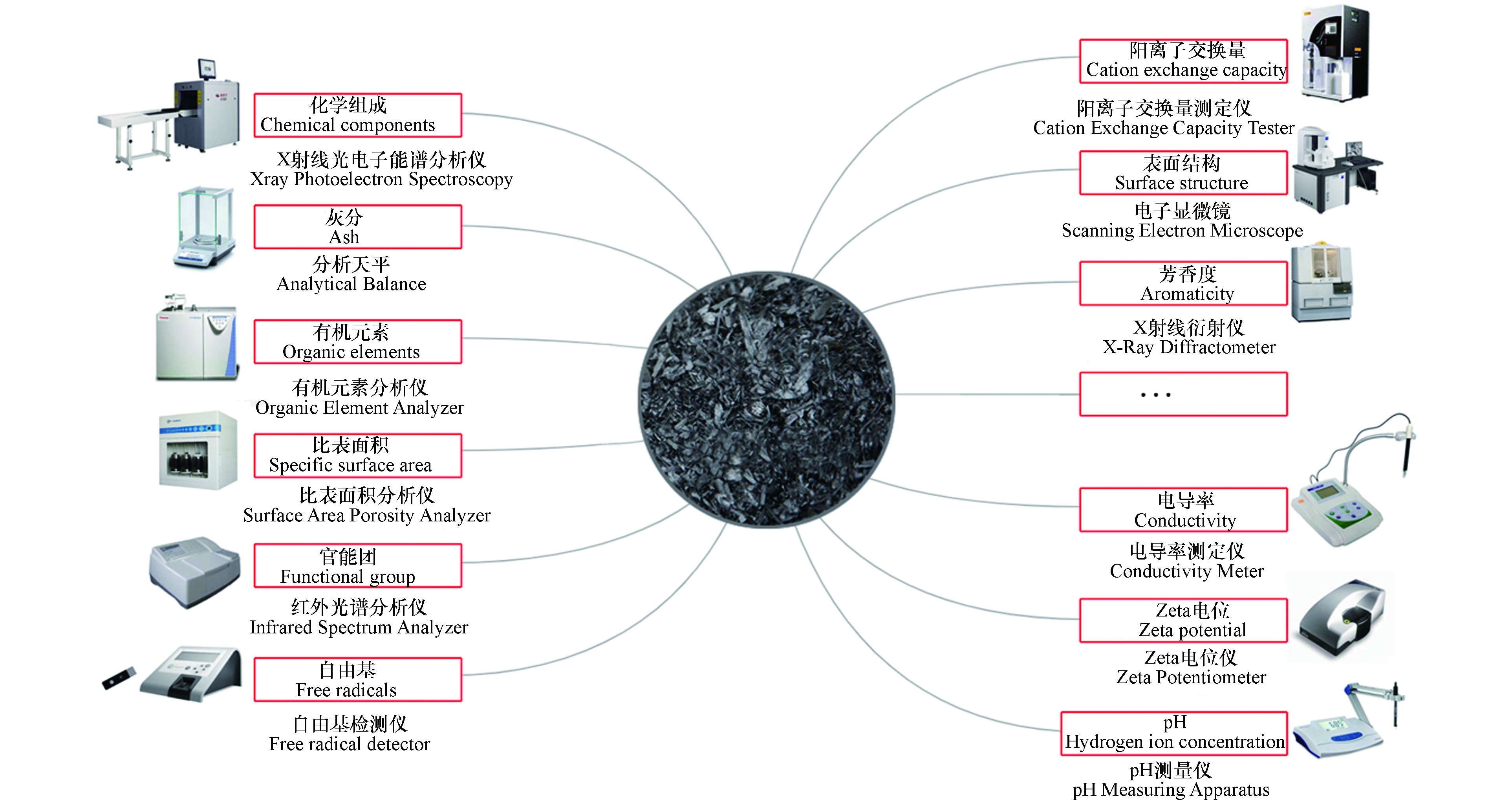
对改性生物炭理化性质的表征有助于对吸附行为和机理的解释。改性生物炭的理化性质在很大程度上决定了吸附的过程及效率,而生物炭的理化性质受生物炭制备时间、热解温度、原材料选取和改性方法等因素的影响而发生改变[14],对改性生物炭理化性质的测定主要包括pH值、形貌特征、表面官能团等(图2)。
生物炭的灰分主要由生物炭原材料决定,高灰分含量可能会导致生物炭表面孔隙堵塞从而降低吸附能力,因此对灰分的测量可作为解释生物炭吸附能力的依据,研究表明部分改性方法可以减少生物炭灰分从而使更多的孔隙暴露出来[46]。测量生物炭的阳离子交换量和Zeta电位有助于初步预测该生物炭对目标污染物的吸附能力,如较低的Zeta电位绝对值和较低的阳离子交换量均不利于对阳离子的吸附[47]。生物炭的pH值主要由制备原材料和热解温度决定,研究显示在250—650 ℃的热解温度间,4种生物炭(稻草、玉米秸秆、木屑、鸡粪)的pH值随热解温度的升高而升高,且随热解温度的升高pH值的提升速率逐渐放缓[48]。不同温度下制备的生物炭表面特征以及元素组成存在差异,对生物炭进行改性会改变原生物炭的元素组成,可以通过元素分析仪清晰的看出改性前后生物炭内部元素的变化从而判断发生的结构变化,如在探究几种改性方法对生物炭理化性质的影响研究中[18],对生物炭进行酸改性后,H/C和O/C较未改性有所增加,这意味着酸改性后生物炭的芳香度减小、极性增加且疏水性降低,碱改性后生物炭的N/C增加,则表明在改性的生物炭表面上存在更多的负责基本性质的含氮基团。比表面积是预测生物炭吸附能力的一个重要参数,它可以非常直观地显示出吸附材料表面的吸附面积,为了提升生物炭的吸附性能,改性后生物炭比表面积与孔隙结构大小的改变都应有利于生物炭的吸附过程,如磁改性后的柚子皮生物炭比表面积明显增加,平均孔径略有减小,这说明生物炭的表面孔隙从少而大转变为多而密集的结构,这样的结构将更有利于粒径较小的污染物的附着[41]。生物炭的表面官能团受到改性方法的影响较大,表面官能团种类和数量的不同将影响生物炭对目标物的吸附能力,可以通过FTIR分析来鉴定改性前后生物炭表面官能团的变化,如在采用铁、酸碱联合以及铁氧化改性生物炭对氨氮吸附影响的研究中[49],通过FTIR分析发现铁氧化改性生物炭出现了更多的—OH、C=O以及C—O官能团,其他几种吸附了氨氮的改性生物炭FTIR图谱中也均出现了明显的C—O官能团,因此这几类改性生物炭对氨氮的吸附量增加的主要原因可能是改性后C—O官能团的增加。
不同改性方法会使生物炭的理化性质及表征产生较大的区别,因此应根据不同污染物的属性和实际需求,有针对性地选择改性方法,从而提高生物炭的吸附能力。而全面分析测量改性生物炭的各理化性质将有助于对生物炭吸附能力的强弱进行科学的解释,其中比表面积、孔隙结构和表面官能团是生物炭吸附抗生素等有机污染物的最主要影响因素[50-51],如在程扬等[52]的研究中,三桠苦药渣生物炭对四环素(TC)的吸附能力大于同温度下制备的玉米秸秆生物炭,这是由于前者拥有更大的比表面积、更规整的孔隙结构和更丰富的表面官能团。
-
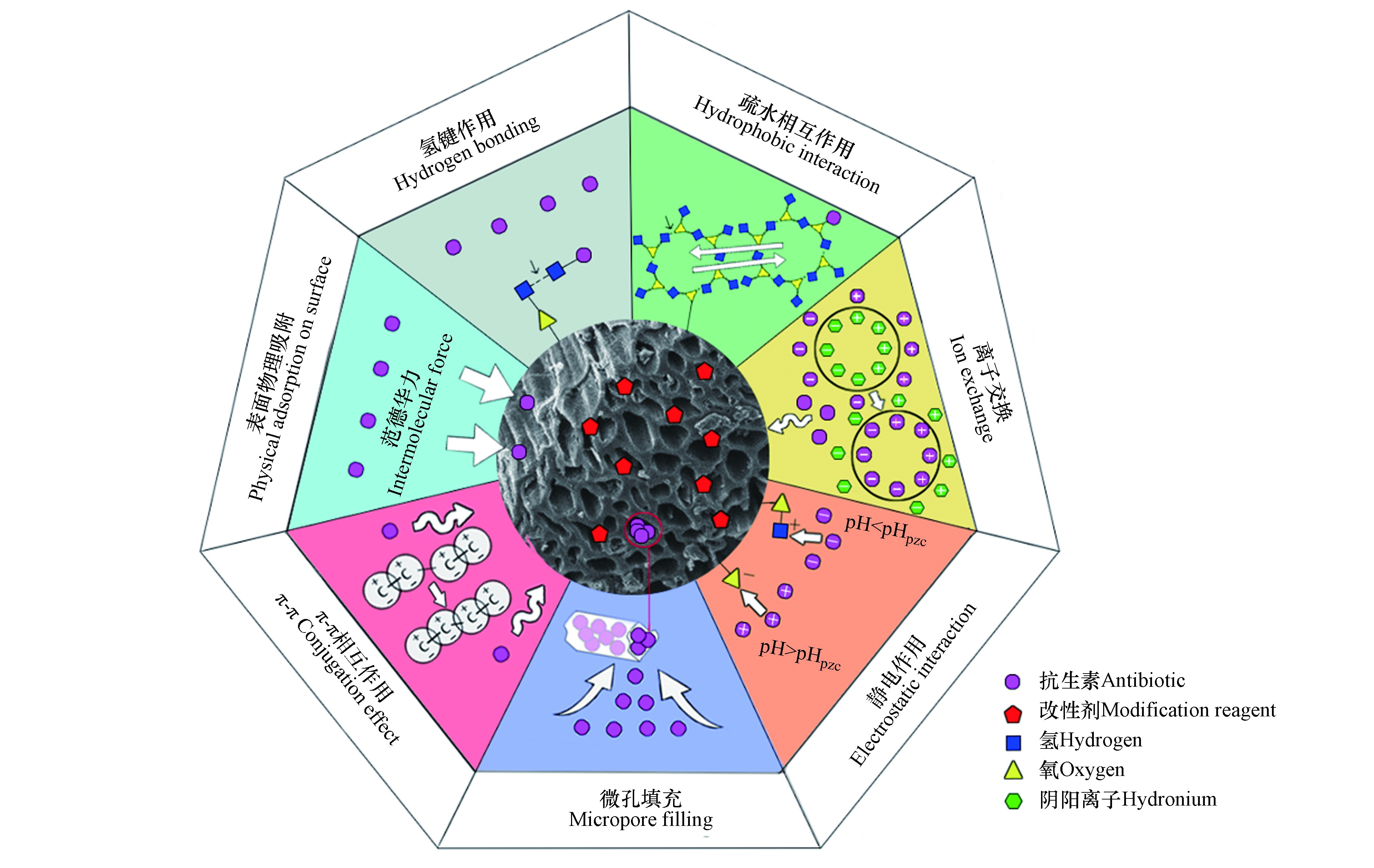
改性生物炭对水体污染修复的研究主要集中于对水体重金属、阴离子污染物、营养物质和抗生素等有机污染物的吸附去除。随着水体中抗生素污染的日益严重,使用改性生物炭修复抗生素污染水的研究也逐渐增加。排入水体环境的抗生素从来源可以大致分为医用抗生素、农用抗生素和工业生产残留抗生素。其中水体中残留浓度较高且常用于生物炭吸附研究的抗生素主要有磺胺类(SA)、喹诺酮类(FQ)、大环内酯类(MA)、四环素类(TC)、氯霉素类抗生素(CP)等。生物炭对水中抗生素的主要吸附机制有微孔填充、表面物理吸附、氢键作用、π-π相互作用、静电作用、离子交换以及疏水相互作用等(图3),这些吸附作用共同影响生物炭的吸附过程及吸附效率[53]。
-
水体中典型的磺胺类抗生素有磺胺二甲嘧啶(SMZ)、磺胺嘧啶(SD)、磺胺乙酰胺(SCT)、磺胺吡啶(SPD)、磺胺甲异恶唑(SMX)、磺胺噻唑(ST)、醋酸铵甲恶唑(ASMZ)、磺胺二甲异恶唑(SIZ)、磺胺氯哒嗪(SCP)、磺胺对甲氧嘧啶(SM)、磺胺多辛(SDO)、磺胺甲嘧啶(SMR)、磺胺间甲氧嘧啶(SMM)等。磺胺类抗生素是全球使用量最大的畜禽用药之一,产量与排放量较大,贵阳市南明河中40种典型抗生素中有34种被检测出来,其中磺胺类抗生素被发现为主要污染物[54]。
Tian等[55]在其配制的SMX 溶液中分别单独添加生物炭粉和KMnO4等待反应30 min,结果显示生物炭和KMnO4对SMX的去除率均低于10%,而当把KMnO4和生物炭混合后加入SMX溶液后反应30 min后,SMX的去除率达到了97%,几乎可以将其完全去除,一级动力学模型可以更好地拟合该反应过程。氧化剂改性后生物炭比表面积、总孔体积和含氧基团的增加使生物炭吸附能力大大提高,且KMnO4氧化剂改性后的生物炭表面出现的Mn化合物能更容易的将SMX氧化为分子量较大的含氧有机物,它们会很容易的被负载锰的生物炭通过物理吸附和氢键作用所捕捉从而提高吸附效果。部分氧化剂被证明可以用来改善生物炭的孔隙性质并增加含氧官能团,从而可以增强生物炭与污染物之间的相互作用提高吸附性能,可见使用强氧化剂作为生物炭的改性材料以去除水体抗生素是十分有效的手段。
李蕊宁等[17]用500 ℃下制备的马铃薯茎叶生物炭分别与200 mL浓度为10%的H2SO4和3 mol·L−1 KOH溶液混合搅拌,以制得酸改性生物炭和碱改性生物炭,探究了原始生物炭和酸、碱改性等3种生物炭对水中ST的吸附性能。研究中发现碱改性生物炭和酸改性生物炭的比表面积、总孔体积和微孔体积均有减少,这是因为酸碱具有氧化性,在改性过程中部分生物炭被氧化,使孔壁塌缩,生物炭的孔道结构重新调整。且氧化生成的表面含氧官能团也会对孔道结构形成一定的堵塞,致使孔道体积减小。其吸附实验结果显示酸改性后的生物炭平衡吸附量7.69 mg·g−1为原始生物炭3.20 mg·g−1的2.4倍,而碱改性生物炭的吸附性能提升较不明显。该酸、碱改性生物炭对ST的吸附存在化学吸附并主要以物理吸附为主,其中氢键起重要作用。
在实际运用生物炭修复水体污染时,小颗粒状的生物炭往往面临从水中分离回收困难的问题,靠后续处理分离又将增加整个工艺流程从而造成成本的提升,因此生物炭的回收问题也应纳入考虑。研究证明通过对生物炭进行负磁改性不仅能显著提升生物炭的吸附性能,且在吸附结束后可以通过外加磁场使磁改性生物炭从水中分离[56],磁改性后的生物炭表现出了良好的回收利用能力[57]。Reguyal等[58]将制备好的松木屑生物炭与FeCl2溶液混合搅拌之后添加KOH和KNO3溶液继续反应,干燥后获得了磁改性松木屑生物炭(MPSB),研究了MPSB对SMX的吸附性能及机理。通过表征后发现,MPSB的比表面积比原始生物炭低,其吸附能力也较未改性生物炭弱,这可能是由于纳米级的Fe3O4 进入孔道堵塞了生物炭表面的孔隙从而减少了吸附位点所致[59]。即不是所有情况下改性都能针对性的增加生物炭对目标抗生素的吸附亲和力。研究了MPSB与SMX的吸附机理与性能后,发现π-π相互作用以及疏水相互作用在吸附中起了重要作用,且当pH值为2—3时MPSB对SMX表现出最佳的亲和力,但同时发现在这样的低pH值条件下有Fe从MPSB中析出。由于磁改性后生物炭表面产生高强度的磁性,吸附完成后MPSB被轻松的从溶液中分离出来。
相较于未改性生物炭,使用氧化剂或酸对生物炭进行改性后,其对磺胺类抗生素的吸附能力展现出了较大的提升,在考虑经济效益的基础上对改性生物炭再进行负磁更有利于提高生物炭的吸附率以及重复利用率。由于磺胺类抗生素是离子型抗生素,除了微孔填充等物理吸附作用外,静电作用和离子交换作用也是重要的吸附机理之一[51],且磺胺类抗生素的苯环结构能较轻易的与类石墨化结构的生物炭发生π-π相互作用,因此疏水相互作用和π-π相互作用也可能为改性生物炭对磺胺类抗生素的主要吸附机理。
-
常见的喹诺酮类抗生素有马波沙星(MAR)、氟罗沙星(FLE)、甲磺酸培氟沙星(PEF)、诺氟沙星(NOR)、环丙沙星(CIP)、甲磺酸达诺沙星(DAN)、氧氟沙星(OFL)、恩诺沙星(ENR)等,其中CIP和NOR在各河流中的检测浓度检测率较高[60]。
Kong等[43]在700 ℃下热解制备了黄芪草药废渣生物炭,加入Fe2+/Fe3+混合溶液搅拌、洗涤、冷却后制备出了磁改性生物炭(M-BC),以利用M-BC吸附溶液中的CIP。尽管M-BC的某些孔被氧化铁颗粒阻塞,改性后的生物炭比表面积仍从4.40 m2·g−1提升到203.70 m2·g−1,这为目标抗生素提供了更多的吸附位点。吸附实验进行12 h后M-BC对CIP的吸附量达到饱和(既(68.90±3.23)mg·g−1)。另外有研究指出磁性生物炭与MnOx的复合材料具有大量的官能团和高比表面积,且易于集成与分离。Li等[45]制备了以KMnO4作为改性剂的磁性马铃薯茎叶生物炭基锰氧化物的复合物,通过SEM仪器分析后发现改性后生物炭表面更加粗糙,这可能是由于生物炭表面氧化物的堆积,元素分析后证实了这一猜测,即氧化铁和锰氧化物成功在生物炭表面生成。生物炭表面的氧化物提升了生物炭的吸附能力,该改性生物炭对NOR、CIP和ENR的吸附性能较未改性生物炭分别提高了1.2、1.5、1.6倍,且通过外加磁场可轻松的将该生物炭从水中分离出来。Wang等[50]发现ENR在pH 5时以阳离子形态存在,阳离子交换在吸附中起了重要作用,表面带负电荷的生物炭经过酸碱改性后产生大量酸性和碱性基团,这大大促进了化学吸附的进行。
生物炭对喹诺酮类抗生素的吸附能力在经过酸、碱、氧化剂及磁改性后均显示出了不同程度的提升,适当的磁改性可以在不破坏生物炭表面吸附结构的同时大幅增加生物炭比表面积,这有助于生物炭的物理吸附。除了改变生物炭表面结构而增强的微孔填充与表面沉淀作用,Hu等[61]的研究中发现阳离子交换、静电作用和π - π相互作用在复合磁改性生物炭对CIP的吸附中也起着重要作用。
-
四环素类抗生素包含金霉素、土霉素、TC、强力霉素以及二甲胺基四环素等。此类抗生素是保健产品和动物饲料生产中最常用的抗生素之一[21],中国2013年内四环素类抗生素的使用量几乎为英国总抗生素使用量的6倍[62]。加入饲料中的四环素会随着动物粪便进入土壤随之渗进水体环境,相比于常用的光催化等技术去除水体中的四环素类抗生素,使用生物炭的吸附方法更加实用且环保。
杨奇亮等[21]以 NaHCO3和三聚氰胺为改性剂制备了玉米秸秆改性多孔生物炭,改性后生物炭的比表面积、亲水性、极性、芳香性都明显提高,且生物炭表面官能团更加丰富,孔隙结构也发生了明显的改变,这使得该生物炭对四环素的吸附能力得到了大幅度的提升,这其中静电作用、π-π相互作用以及氢键作用为重要吸附机理。Chen等[63]发现溶液pH值从5增加到9磷酸改性的猪粪生物炭吸附能力较未改性生物炭明显增强并逐渐提升,但其吸附能力在同种条件下略低于稻草类生物炭,这是因为尽管化学吸附在该吸附过程中占主导地位,但稻草类生物炭相比于猪粪生物炭的表面特征更加适合对抗生素的吸附。Jing等[64]制备了甲醇改性稻壳生物炭以研究对四环素的吸附效果,用甲醇在酸性条件下对生物炭进行修饰,发生的酯化反应和生物炭与甲醇之间的羰基反应改变了生物炭的理化性质。由于生物炭表面的杂质被去除,改性后生物炭的比表面积从51.86 m2·g-1提升到65.97 m2·g−1。FTIR分析发现改性显著的改变了生物炭表面的官能团和含氧基团。吸附实验发现用甲醇进行简单的改性也能将稻壳生物炭对TC的吸附效率提升近乎两倍,官能团和含氧基团性质的变更可能在提高生物炭对TC的吸附能力中起重要作用,拟二级动力学能更好的模拟该吸附过程。
改性生物炭对TC的吸附通常都不是以简单的物理吸附为主,而是物理化学复合吸附的过程。有研究指出氢键作用、静电作用以及π-π相互作用在改性生物炭对TC的吸附过程中至关重要[30,63,65]。
-
医疗上常用的大环内酯类抗生素主要有红霉素、罗红霉素、阿奇霉素、克拉霉素、地红霉素、氟红莓素、泰利霉素和泰乐菌素(TYL)等。大环内酯类抗生素具有良好的抗菌作用和广泛的药理作用,在医疗领域、畜牧养殖和水产养殖的广泛应用也导致各地出现了水体MCs超标的报道。朱琳等[66]发现北京市清河水体中的藻类和水生植物受到各类抗生素污染产生了环境风险,其中MCs为影响该水体的主要污染物质之一。水环境中过量的MCs将带来急性或慢性毒作用从而影响水体微生物并对环境产生破坏[67]。
Guo等[59]用600 ℃下热解成的棕榈生物炭并与Fe(NO3)3·9H2O混合搅拌改性制备出针铁矿改性生物炭,发现改性后针铁矿颗粒紧密的嵌入了生物炭表面的同时生物炭比表面积明显减少,这可能是由于针铁矿堵塞了生物炭表面的孔隙结构。但吸附实验发现针铁矿改性后生物炭对TYL的最大吸附量增加约36%,说明该生物炭对TYL的吸附不是单一的物理吸附,TYL表面的带电官能团可能与生物炭表面的芳香结构发生相互作用。进一步分析发现阳离子交换、静电、氢键、疏水及供-受体相互作用均作用于该吸附过程。但目前使用改性生物炭对大环内酯类抗生素吸附相关的研究较少,未来的研究应加强对该类抗生素的关注。
-
氯霉素类抗生素是高效的广谱抗生素,它包括氯霉素(CP)、甲砜霉素及无味氯霉素等。氯霉素在畜牧业中有着广泛的应用,环境中的氯霉素流入人体会导致人体肠道的菌群失调从而导致多种疾病的产生。
吴智威[68]研究了使用乙醇和NaOH制备的改性竹炭生物炭对CP的吸附过程,并对改性生物炭用Fe和Cu进行了负磁,负载于生物炭的Fe发生氧化以提供电子来加速对CP的降解,即该磁改性生物炭对CP的去除过程由吸附和降解同时进行,其中吸附以化学吸附为主导。该生物炭在4—6的pH范围内不仅对CP的去除率有了较大的提升,且去除速度也提升明显,但生物炭表面上的Fe、Cu的颗粒间存在磁性作用,容易发生团聚现象,反而可能会影响吸附的过程。另外有研究将纳米级零价铁固定在了功能化生物炭上制备出磁性生物炭复合材料[69],发现该复合材料拥有较好的固液分离能力和较高的重复利用性,对CP的去除同时存在还原和吸附作用,且相比于未负磁的功能化生物炭,对CP的吸附能力提高了约57%。CP在pH值低于5.5时会形成电荷辅助氢键,可以促进较低pH环境下的吸附过程,Langmuir等温方程与该吸附过程的拟合度更高。而由于铁对氯霉素的阳离子交换能力较生物炭表面的羧基高,在pH为4.0—4.5的范围内时该生物炭对CP的吸附主要以氢键、静电作用以及生物炭表面的含铁官能团与氯霉素表面的硝、羟基官能团的快速相互作用所决定。另外也有研究指出电子给体-供体和氢键作用在改性生物炭吸附CP的过程中起了重要作用[7]。
改性生物炭的原材料、改性剂、改性方法、目标抗生素的种类都在很大程度上影响着生物炭对抗生素的吸附性能及机理。由于较明显的多孔结构和较大的剩余量,农作物秸秆及茎叶成为了生物炭制备中最常用的原材料之一,而由于较好的改性效果,改性材料以酸、碱、氧化剂等化学试剂为主,同时采用磁改性来提升生物炭吸附和重复利用能力的研究也逐渐增加。但现有许多研究未将生物炭的制备成本纳入考虑,部分复杂的改性方法拥有较好效果的同时可能存在成本过高的问题。
表1列出了改性与未改性生物炭的部分表征和对水体中不同抗生素的吸附能力。可以看出在改性方法、生物炭原材料和目标抗生素都不一样的情况下,改性后的生物炭大多表现出了强于原始生物炭的吸附能力,且不同生物炭及条件下最大吸附量出现较大的差距。其中在不考虑成本的情况下,添加酸、碱和氧化剂并联用磁改性的生物炭表现出了良好的吸附效果。少部分改性后吸附能力反而降低的生物炭可能是由于改性剂与生物炭附着不牢固或是改性剂破坏了生物炭原本的表面结构导致[58],因此某种改性方法对不同生物炭吸附能力的影响不能一概而论。
-
改性生物炭吸附水体抗生素的效率在很大程度上受制备原材料种类的影响,这种影响主要是由于生物炭内的有机碳含量、孔隙大小及结构、比表面积、官能团数量及种类的差异所产生[51]。几种类型的生物炭比表面积从大到小依次为稻壳类生物炭、粪便类生物炭、植物秸秆生物炭、木质生物炭、污泥生物炭[51]。生物炭的pH值取决于制备原材料以及制备的工艺过程,其通常呈中性或碱性[75]。研究表明,在600 ℃下制备的稻草、猪粪[76]、玉米秸秆生物炭和三桠苦药渣生物炭,对水体中四环素的吸附效率差距较大[52]。而同样使用玉米秸秆生物炭作为吸附剂,其对磺胺嘧啶、磺胺氯哒嗪、磺胺甲恶唑3种磺胺类抗生素的吸附效率也产生出较大的差异,玉米秸秆生物炭对磺胺甲恶唑的吸附效率远大于磺胺嘧啶和磺胺氯哒嗪[26,77],可见同种生物炭对不同抗生素的吸附性能也有着较大的差异。
不同改性方法和改性试剂对生物炭理化性质及吸附能力的影响存在较大差异,各改性方法通常都能使生物炭表面官能团的数量与丰富度增加,同时改变原有孔隙结构,大多能正面影响生物炭的吸附能力[46,78-79]。但也有研究发现对生物炭进行磁改性后虽然解决了生物炭回收困难的问题,但改性后生物炭的比表面积减少,对抗生素的吸附能力没有增强甚至出现了降低[58],这可能是由于改性材料堵塞了生物炭表面的吸附位点或破坏了生物炭原本的吸附结构。生物炭和改性试剂间产生的反应也可能对吸附能力产生负面影响,如KMnO4与生物炭混合时间超过12、24、36、48 h后该改性生物炭对SMX的去除效率从97%分别降低至89%、83%、69%和53%,这是由于KMnO4是强氧化剂,在生物炭和KMnO4的混合过程中,生物炭消耗了KMnO4的氧化能力[55]。
原始生物炭的制备温度也在很大程度上影响改性生物炭的吸附能力,这是因为不同温度制成的生物炭表面结构区别较大,而比表面积和孔隙结构等是影响生物炭物理吸附最主要的因素。如800 ℃下制备的玉米秸秆生物炭对SMX的吸附性能明显大于600 ℃和400 ℃制备出的生物炭[52],改性玉米秸秆生物炭对CP的吸附能力也显示出随热解温度上升而提高的趋势,在热解温度超过800 ℃后吸附性能提升不明显,考虑到经济效益,以800 ℃为最适热解温度[21]。Lian等[80]在250、400、600、800 ℃热解温度下制备了丹参生物炭,生物炭的比表面积、灰分和pH值都随温度提升,而产率从91.9%快速掉到了29.1%,吸附的强度也随之降低。同样在350 ℃温度下制备的磷酸改性生物炭对OFL和NOR的吸附效率明显大于200、500、650 ℃温度下制备的同类生物炭[34]。即通常越高温度制备的生物炭吸附能力越强,但过高的热解温度又有可能破坏生物炭原有的结构或表面官能团造成吸附能力的降低[51],因此最适热解温度应从包括经济效益在内的多方面进行考虑。
改性生物炭对抗生素的吸附效率随着生物炭的投加量逐渐增加并到一定程度后趋于平缓,而投加量的选择则需综合考虑吸附效果与经济性。反应时间的影响也与此类似,反应开始后一段时间内水体中的抗生素被迅速去除,并在一定时间后达到吸附饱和,Reguyal等[58]制备的磁改性松木屑生物炭对水体中SMX的吸附在反应30 min时就达到了平衡,之后吸附能力逐渐趋于平缓,此时的吸附能力为最大吸附量。但过长的反应时间有可能会导致生物炭表面的改性材料与生物炭发生反应从而使吸附能力降低[55]。另外离子强度也会影响吸附过程中的静电作用,从而影响生物炭对污染物的吸附和解吸过程[81]
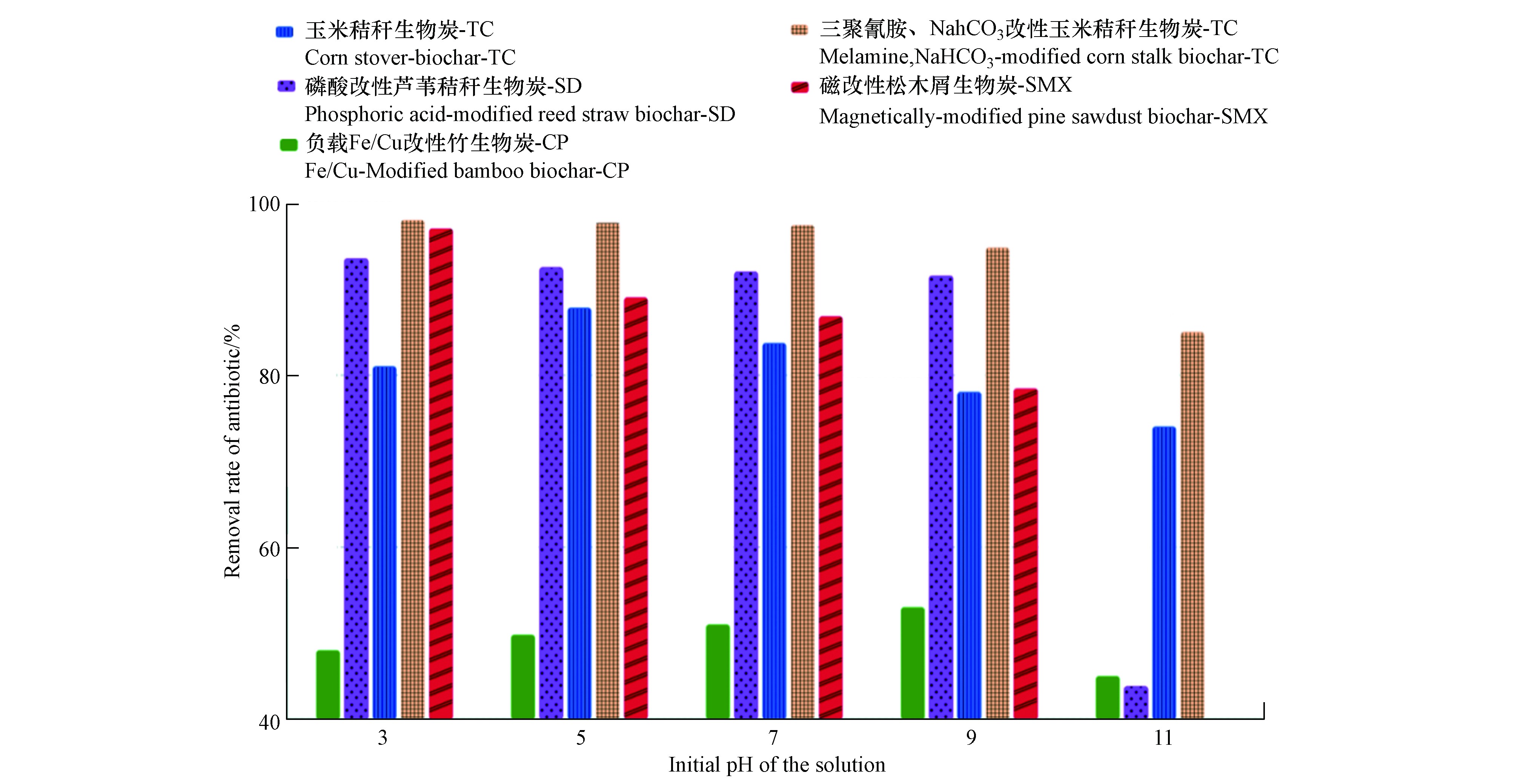
吸附时背景溶液的pH值直接影响改性生物炭的吸附效率及过程,这种影响同时作用于改性生物炭和目标抗生素。图4为几种生物炭及改性生物炭对不同抗生素的吸附量或去除率随pH变化过程,可看出不同生物炭吸附能力随pH值变化的敏感度差距较大,这可能是因为不同改性生物炭对溶液的缓冲能力不一致,但总体来说在较高的pH值条件下,均显示出了对抗生素吸附性能不同程度的下降。这是因为改性生物炭所处溶液的pH值低于零点电荷(pHpzc)时带正电,此时生物炭对阴离子态较多且带负电的抗生素静电排斥力较低,而pH值升高的过程中生物炭负电性增强,导致了其与抗生素的亲和力降低,吸附能力开始减弱[82-83]。
溶液pH值会改变生物炭表面的电荷及抗生素的存在形式从而影响吸附效率及吸附过程,研究证明以pH 5.5为分界点时,土霉素(OTC)分别主要以OTC+与OTC±(pH<5.5)和以 OTC +、OTC±、OTC−(pH>5.5)的形态存在[51],磺胺类抗生素在低pH值条件下主要以阳离子形态存在,而当pH值>7时磺胺类抗生素主要以阴离子形态存在,这使低pH值下π-π相互作用成为主导的吸附机制,而高pH值背景下这些阴离子可以通过氢键与生物炭表面的羧基进行结合[84],主要吸附机制的变更导致了吸附性能出现差异。NaHCO3和三聚氰胺改性玉米秸秆生物炭对TC的吸附性能就随着pH值从3提升到11而逐渐降低,这是因为pH>7.7时,TC主要以阴离子形式存在,而该改性生物炭表面带负电荷,即生物炭和TC之间发生了强静电排斥现象从而影响了吸附效率[21]。pH值还会影响附着于生物炭的改性材料,在对生物炭进行磁改性并负载Fe/Cu的研究中[68],发现该改性生物炭在弱酸条件下对CP的吸附能力较好,在碱性环境中,OH−与Fe3+和Fe2+反应生成的氢氧化物会附着在Fe/Cu表面上来阻断反应的正常进行。而在强酸性环境中,过量H+导致的Fe快速腐蚀将会减缓主反应的进行从而降低原本的吸附效率。
改性生物炭对抗生素的吸附过程及效率受到有机碳含量、孔隙大小及结构、改性方法及材料、比表面积、官能团、pH值、热解温度、离子强度、投加量等多种内外因素的影响,部分影响条件同时作用于生物炭、抗生素与改性材料,而改性生物炭对抗生素的吸附是一个复杂的多种机制共同作用的过程,因此在研究生物炭对抗生素的吸附实验或制备生物炭的过程中应当全面综合考虑各个因素的影响。
-
对生物炭进行改性以增强其对水体中抗生素的吸附性能已成为生物炭领域研究的热点。但改性方法与改性材料的多样化也对相关研究带来一些问题。因此,在今后的研究过程中应该注意以下几个方面:
(1)将改性生物炭作为吸附剂时,应结合实际生产中的能耗,综合多方面考虑生物炭热解温度、投加量及原材料种类等影响因素,寻求吸附效果和经济效益的平衡点。
(2)目前的改性方法大多集中于将生物炭与化学试剂进行混合改性,该方法虽取得较好的效果,但制备成本较高,因此未来研究中改性材料的选取应向低成本和可回收利用废物方向发展,回归生物炭以废治废的优势。
(3)许多改性方法和材料的选择仍处于实验阶段,在大规模生产和运用中存在改性材料成本高、方法复杂、时间要求严格、实际水体中污染物复杂等多方面的限制,因此研究中应尽量考虑改性生物炭作为吸附剂大规模生产和应用的适用性。
(4)部分稳定性不高的改性材料可能随着时间的推移从生物炭表面分离出来,这会导致新的水体残留物生成从而造成二次污染,因此实验中应尽量考虑改性材料可能对水体造成的影响。
改性生物炭对水体中抗生素的去除研究进展
Research progress on the removal of antibiotics in water by modified biochar
-
摘要: 随着社会经济的不断发展,抗生素造成的水体环境污染问题已不容忽视。利用生物炭去除水体中的抗生素是解决这一问题的有效手段之一。然而,原始生物炭对水体中抗生素等有机污染物的去除存在一定局限性,因此对生物炭进行改性以提升其吸附能力尤为必要。生物炭的吸附性能受生物质类型、碳化条件和改性方法等因素影响较大,导致目前虽然开展了许多相关研究,但结论不一,尤其是在不同改性生物炭对不同抗生素吸附机理的解释方面还不是很清楚,因此有必要对现有研究进行系统地归纳和总结。本文首先对用于抗生素吸附的改性生物炭制备方法及理化性质表征方法进行了介绍,综述了改性生物炭对不同种类抗生素(磺胺类、喹诺酮类、四环素类、大环内酯类、氯霉素类)的吸附效果、吸附机理及其影响因素(如溶液pH值、热解温度、改性材料等),对比分析了生物炭改性前后吸附效果的差异,对目前改性生物炭用于去除水体中抗生素存在的问题进行了分析和总结,在此基础上,对今后该领域的研究和发展方向进行了展望,以期为将来开展相关的研究工作提供一定的参考。Abstract: With the constant development of the social economy, the water pollution caused by antibiotics have already become serious. Removing antibiotics from water through the biochar is an effective solution to the problem. However, there are some limitations about the removal of antibiotics and other organic pollutants by the pristine biochar, so it is necessary to modify the biochar so as to improve its adsorption capacity. The adsorption capacity of the biochar is greatly related to biomass types, carbonization conditions and modification methods. As a result, although a lot of related research have been carried out, there are different conclusions, especially the obscure explanation of the adsorption mechanisms on various antibiotics by different modified biochar. Therefore, it is necessary to systematically summarize the current research results. Firstly, the preparation and physicochemical characterization methods of the modified biochar for antibiotic adsorption are introduced. The adsorption effects, adsorption mechanisms and influencing factors (such as solution pH value, pyrolysis temperature and modified material) of different kinds of antibiotics (sulfonamides, quinolones, tetracyclines, macrolides and chloramphenicols) are reviewed. The difference of the adsorption effect before and after biochar modification is analyzed and summarized. On this basis, suggestions and future perspectives are proposed, providing a reference for future research.
-
Key words:
- modified biochar /
- antibiotic /
- adsorption mechanism /
- wastewater treatment
-

-
表 1 改性(未改性)生物炭表征及对典型抗生素的吸附能力
Table 1. Characterization of modified (unmodified) biochar and its adsorption capacity for typical antibiotics
生物质
Biomass改性方法及试剂
Methods and reagents of
modification抗生素类型
Types of
antibiotics最大吸
附量/
(mg·g−1)
Maximum
adsorption
capacity热解温度/℃
Pyrolysis
temperature溶液pH 比表面积/
(m2·g−1)
Specific
surface
area平均
孔径/nm
Average
pore size来源
文献
Reference马铃薯茎叶 原生物炭与H2SO4溶液混合,
酸改性磺胺噻唑 7.69
(3.20)500 5.30 92.85(99.43) 2.79
(3.12)[17] 芦苇秸秆 原生物体与磷酸溶液浸渍并负载TiO2制得复合材料 磺胺嘧啶 5.50
(—)500 6.46 — — [70] 农产品 原生物炭与KMnO4混合 磺胺甲恶唑 — — 5.00 86.30(114.10) — [55] 松木屑 原生物炭与Fecl2混合,磁改性 磺胺甲恶唑 13.83
(17.49)650 4.00 125.80(297.80) 9.60
(3.67)[58] 竹子 使用球磨技术处理原生物炭 磺胺吡啶 57.90
(—)450 6.00 — — [71] 黄芪草药 原生物炭与Fe2+/Fe3+溶液混合,
磁改性环丙沙星 68.90
(—)700 6.00 203.70(4.40) — [43] 马铃薯茎叶 磁改性生物炭与KMnO4混合,磁性生物炭基锰氧化物的复合物 环丙沙星 8.37
(5.58)500 3.00 252.00(99.43) 2.56
(3.12)[45] 樟树叶 原生物炭负载纳米氧化锌与Fe盐溶液混合改性 环丙沙星 449.40
(—)650 4.00 915.00(19.00) — [61] 酒糟 原生物炭与氯化铁、硫酸锰溶液混合改性 左氧氟沙星 181.00
(—)800 5.00 93.40(—) — [72] 马铃薯茎叶 磁改性生物炭与KMnO4混合,磁性生物炭基锰氧化物的复合物 诺氟沙星 6.94
(5.78)500 3.00 252.00(99.43) 2.56
(3.12)[45] 松木屑 原生物炭与磷酸溶液浸渍后再次
热解诺氟沙星 337.60
(1.96)350 5.57 1148.32(9.15) 2.18(12.41) [34] 马铃薯茎叶 磁改性生物炭与KMnO4混合,磁性生物炭基锰氧化物的复合物 恩诺沙星 7.19
(4.49)500 3.00 252.00(99.43) 2.56
(3.12)[45] 玉米秸秆 原生物炭与磷酸溶液混合改性 恩诺沙星 41.91
(38.07)500 5.00 14.17(3.01) 0.73
(1.29)[50] 玉米秸秆 原生物炭与KOH溶液混合改性 恩诺沙星 58.29
(38.07)500 5.00 22.69(3.01) 0.64
(1.29)[50] 鸡骨 原生物炭与Fe2+/Fe3+溶液混合,
磁改性四环素 98.89
(9.83*)500 8.00 328.06(316.05) — [73] 玉米秸秆 生物炭原材料与NaHCO3、三聚氰胺混合后热解 四环素 347.00
(9.83*)800 4.00—7.00
(3.00—9.00*)1401.00
(356.28*)3.46(2.62*) [21,52] 稻壳 生物炭原材料与甲醇溶液混合改性 四环素 18.53
(10.25)383—412 2.00 65.97(51.86) — [64] 杨木 原生物炭与KOH溶液混合改性 四环素 21.17
(4.30)300 5.00 1.61(—) — [30] 猪粪 原生物炭与磷酸溶液混合改性 四环素 160.30
(—)700 9.00 319.04(227.56) — [63] 稻草 原生物炭与磷酸溶液混合改性 四环素 167.50
(—)700 9.00 372.21(369.26) — [63] 污泥 与壳聚糖与Fe/S混合制备复合改性吸附材料 四环素 183.01
(51.78)500 5.00 — — [74] 竹子 负载Fe/Cu的乙醇改性生物炭复合材料 氯霉素 5.20
(0.077)450 5.00 — — [68] 棕榈 原生物炭与针铁矿混合改性 泰乐菌素 — 600 9.00 230.50(120.50) 38.00(38.00) [59] 注:“()”内为未改性生物炭的相关数据;“ — ”表示原文未提及;“ * ”表示该数据出自不同文献
Note: “()” means the corresponding data of unmodified biochar; “ — ”means there is no record in the original documents"; “ * ” means the data comes from different documents. -
[1] ZHANG J S, WANG S. Trace for the motivations of the coalminers' off-site behaviors based on the evolutionary game theory [J]. Journal of Safety & Environment, 2018, 18(2): 657-663. [2] TANG Y Q, YE Q, ZHENG W Y. Research status and development of antibiotics [J]. World Notes on Antibiotics, 2019, 40(4): 295-300. [3] ZHANG H Q, JIA Y Y, KHANAL S K, et al. Understanding the role of extracellular polymeric substances on ciprofloxacin adsorption in aerobic sludge, anaerobic sludge, and sulfate-reducing bacteria sludge systems [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(11): 6476-6486. [4] LIEN L T, LAN P T, CHUC N T, et al. Antibiotic resistance and antibiotic resistance genes in escherichia coli Isolates from hospital wastewater in vietnam [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(7): 699-710. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14070699 [5] CHAUDHARY A S. A review of global initiatives to fight antibiotic resistance and recent antibiotics׳ discovery [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2016, 6(6): 552-556. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2016.06.004 [6] 胡譞予. 水环境中抗生素对健康的危害 [J]. 食品与药品, 2015, 17(3): 215-219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2015.03.022 HU X Y. Harm of antibiotics in aquatic environment on health [J]. Food and Drug, 2015, 17(3): 215-219(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2015.03.022
[7] AHMED M B, ZHOU J L, NGO H H, et al. Chloramphenicol interaction with functionalized biochar in water: sorptive mechanism, molecular imprinting effect and repeatable application [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 885-895. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.239 [8] WALIA S K, MURLEEDHARN C, BAND J, et al. Quantitation of antibiotic resistance genes pollution in hospital waste water effluent and Urban Clinton River Water, Michigan, USA [J]. Current Medicine Research and Practice, 2016, 6(4): 149-151. doi: 10.1016/j.cmrp.2016.07.005 [9] 章强, 辛琦, 朱静敏, 等. 中国主要水域抗生素污染现状及其生态环境效应研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(7): 1075-1083. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.07.001 ZHANG Q, XIN Q, ZHU J M, et al. The antibiotic contaminations in the main water bodies in China and the associated environmental and human health impacts [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(7): 1075-1083(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.07.001
[10] 曾冠军, 柳娴, 马满英. 水体中抗生素污染研究进展 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(3): 72-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.03.025 ZENG G J, LIU X, MA M Y. Research progress of antibiotic pollution in water [J]. Journal of Anhui Agr, 2017, 45(3): 72-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.03.025
[11] 耿冲冲, 王亚军. 污水中抗生素生化去除研究进展 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2019, 31(3): 12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2019.03.004 GENG C C, WANG Y J. Research progress of biochemical treatment on antibiotics removal from wastewater [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2019, 31(3): 12-16(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2019.03.004
[12] AHMED M B, ZHOU J L, NGO H H, et al. Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from water and wastewater: Progress and challenges [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 532: 112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.130 [13] 程宪伟, 梁银秀, 于翔霏, 等. 水体中抗生素污染及其处理技术研究进展 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(s1): 125-132. CHENG X W, LIANG Y X, YU X F, et al. The contamination and treatment technologies for antibiotics in water: a review [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(s1): 125-132(in Chinese).
[14] LI X N, SONG Y, JIA M Y, et al. A review of researches on biochar adsorbing organic contaminants and its mechanism [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54: 1313-1325. [15] ALLER M F. Biochar properties: Transport, fate, and impact [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 46(14/15): 1183-1296. [16] SUN B B, LIAN F, BAO Q L, et al. Impact of low molecular weight organic acids (LMWOAs) on biochar micropores and sorption properties for sulfamethoxazole [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 214: 142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.017 [17] 李蕊宁, 王兆炜, 郭家磊, 等. 酸碱改性生物炭对水中磺胺噻唑的吸附性能研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(11): 4119-4128. LI R N, WANG Z W, GUO J L, et al. Adsorption characteristics of sulfathiazole in aqueous solution by acid /alkali modified biochars [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(11): 4119-4128(in Chinese).
[18] AHMED M B, ZHOU J L, NGO H H, et al. Progress in the preparation and application of modified biochar for improved contaminant removal from water and wastewater [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 214: 836-851. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.057 [19] LIAN G Q, WANG B, LEE X Q, et al. Enhanced removal of hexavalent chromium by engineered biochar composite fabricated from phosphogypsum and distillers grains [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 697: 134119. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134119 [20] ZHENG Y L, WANG B, WESTER A E, et al. Reclaiming phosphorus from secondary treated municipal wastewater with engineered biochar [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 362: 460-468. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.036 [21] 杨奇亮, 吴平霄. 改性多孔生物炭的制备及其对水中四环素的吸附性能研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(12): 3973-3984. YANG Q L, WU P X. Preparation of modified porous biochar and its adsorption properties for tetracycline in water [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(12): 3973-3984(in Chinese).
[22] 陈坦, 周泽宇, 孟瑞红, 等. 改性污泥基生物炭的性质与重金属吸附效果 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(4): 1842-1848. CHEN T, ZHOU Z Y, MENG R H, et al. Characteristics and heavy metal adsorption performance of sewage sludgederived biochar from co-pyrolysis with transition metals [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(4): 1842-1848(in Chinese).
[23] 王彤彤, 王晓琳, 任志胜, 等. 不同原料制备的生物炭形貌结构及表面特性研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(1): 42-48. WANG T T, WANG X L, REN Z S, et al. Microscopic morphology and surface features of biochars derived from different raw materials [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(1): 42-48(in Chinese).
[24] ZHU L, LEI H W, WANG L, et al. Biochar of corn stover: Microwave-assisted pyrolysis condition induced changes in surface functional groups and characteristics [J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2015, 115: 149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2015.07.012 [25] JANG H M, KAN E. Engineered biochar from agricultural waste for removal of tetracycline in water [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 284: 437-447. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.131 [26] 赵涛. 不同生物炭对水中磺胺类抗生素的吸附及机理研究 [D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016: 31-51. ZHAO T. Absorption characteristics and mechanisms of sulfonamides in aquatic solutions by biochars derived from different biomass materials [D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2016: 31-51 (in Chinese).
[27] YI S Z, GAO B, SUN Y Y, et al. Removal of levofloxacin from aqueous solution using rice-husk and wood-chip biochars [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 150: 694-701. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.112 [28] WANG H, CHU Y X, HUANG F, et al. Sorption of tetracycline on biochar derived from rice straw under different temperatures [J]. Plos One, 2017, 12(8): 1-14. [29] LI Y, WANG Z W, XIE X Y, et al. Removal of norfloxacin from aqueous solution by clay-biochar composite prepared from potato stem and natural attapulgite [J]. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2017, 514: 126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.11.064 [30] HUANG H, TANG J C, GAO K, et al. Characterization of KOH modified biochars from different pyrolysis temperatures and enhanced adsorption of antibiotics [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(24): 14640-14648. doi: 10.1039/C6RA27881G [31] WANG B, GAO B, FANG J. Recent advances in engineered biochar productions and applications [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 47(22): 2158-2207. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2017.1418580 [32] JIN H, CAPAREDA S C, CHANG Z, et al. Biochar pyrolytically produced from municipal solid wastes for aqueous As(Ⅴ) removal: Adsorption property and its improvement with KOH activation [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 169: 622-629. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.06.103 [33] KARIMNEZHAD L, HAGHIGHI M, FATEHIFAR E, et al. Adsorption of benzene and toluene from waste gas using activated carbon activated by ZnCl2 [J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2014, 8(6): 835-844. [34] 储刚, 赵婧, 刘洋, 等. 氧氟沙星和诺氟沙星在磷酸改性生物炭上的等温吸附行为 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 462-470. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017090403 CHU G, ZHAO J, LIU Y, et al. Sorption of ofloxacin and norfloxacin on modified biochars using phosphoric acid treatment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 462-470(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017090403
[35] 左昊, 徐康宁, 孟萍萍, 等. 硫酸改性小麦秸秆生物炭对氨氮吸附特性研究 [J]. 应用化工, 2017, 46(7): 1237-1242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.07.001 ZUO H, XU K N, MENG P P, et al. Adsorption characteristics of ammonium nitrogen in aqueous solution for biochar modified with sulfuric acid [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(7): 1237-1242(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.07.001
[36] VITHANAGE M, RAJAPAKSHA A U, ZHANG M, et al. Acid-activated biochar increased sulfamethazine retention in soils [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(3): 2175-2186. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3434-2 [37] 计海洋, 汪玉瑛, 刘玉学, 等. 生物炭及改性生物炭的制备与应用研究进展 [J]. 核农学报, 2018, 32(11): 207-213. JI H Y, WANG Y Y, LIU Y X. et al. Advance in preparation and application of biochar and modified biochar research [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(11): 207-213(in Chinese).
[38] LI Y C, SHAO J G, WANG X H, et al. Characterization of modified biochars derived from bamboo pyrolysis and their utilization for target component (furfural) adsorption [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(8): 5119-5127. [39] WANG R F, ZHOU Y N, MENG H B, et al. Adsorption of Cd in solution by different modified biochar [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(6): 103-111. [40] 赏国锋, 张涵, 沈逸菲, 等. 生物炭固定化硝化菌去除水样中氨氮的研究 [J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2014, 32(5): 44-47. SHANG G F, ZHANG H, SHEN Y F, et al. Removal of ammonia nitrogen in aqueous samples by biochar immobilized nitrifying bacteria [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Agricultural Science), 2014, 32(5): 44-47(in Chinese).
[41] 郭晓慧, 康康, 于秀男, 等. 磁改性柚子皮与杏仁壳生物炭的理化性质研究 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(z1): 164-171. GUO X H, KANG K, YU X N, et al. Study on physicochemical properties of magnetic modified biochar derived from pyrolysis of pomelo peel and apricot kernel shell [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(z1): 164-171(in Chinese).
[42] 郑晓青, 韦安磊, 张一璇, 等. 铁锰氧化物/生物炭复合材料对水中硝酸根的吸附特性 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(3): 1220-1232. ZHENG X Q, WEI A L, ZHANG Y X, et al. Characteristic of nitrate adsorption in aqueous solution by iron and manganese oxide /biochar composites [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(3): 1220-1232(in Chinese).
[43] KONG X R, LIU Y X, PI J C, et al. Low-cost magnetic herbal biochar: characterization and application for antibiotic removal [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(7): 6679-6687. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8376-z [44] 李桥, 高屿涛, 姜蔚, 等. 紫外辐照改性生物炭对土壤中Cd的稳定化效果 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(10): 5708-5714. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201611090 LI Q, GAO Y T, JIANG W, et al. Stabilization of Cd contaminated soil by ultraviolet irradiation modified biocha [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(10): 5708-5714(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201611090
[45] LI R N, WANG Z W, ZHAO X T, et al. Magnetic biochar-based manganese oxide composite for enhanced fluoroquinolone antibiotic removal from water [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(31): 31136-31148. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3064-1 [46] 王瑞峰, 周亚男, 孟海波, 等. 不同改性生物炭对溶液中Cd的吸附研究 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2016, 18(6): 103-111. WANG R F, ZHOU Y N, MENG H B, et al. Adsorption of Cd in solution by different modified biochar [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(6): 103-111(in Chinese).
[47] 鲁小娟, 田小平, 王磊. 不同原料生物炭对NH4+-N, PO43−-P吸附性能的差异性及其成因分析 [J]. 化工环保, 2019, 39(2): 196-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.02.015 LU X J, TIAN X P, WANG L. Different absorption abilities of biochars from different raw materials to NH4+-N and PO43−-P and their mechanisms [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(2): 196-201(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.02.015
[48] ZHOU Q, HUANG D K, LANG Y U, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperature, time and biochar mass ratio on pH value determination for four biochar solutions [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2015, 6(3): 195-200. [49] 王思源, 申健, 李盟军, 等. 不同改性生物炭功能结构特征及其对铵氮吸附的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(5): 1037-1045. WANG S Y, SHEN J, LI M J, et al. Functional and structural characteristics of different modified biochar and its impacts on ammonium nitrogen adsorption [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(5): 1037-1045(in Chinese).
[50] WANG W, MA X L, SUN J, et al. Adsorption of enrofloxacin on acid/alkali-modified corn stalk biochar [J]. Spectroscopy Letters, 2019, 52(7): 367-375. doi: 10.1080/00387010.2019.1648296 [51] 钟金魁, 李柳, 钟志为, 等. 生物炭对抗生素环境行为的影响研究进展 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2018, 18(2): 657-663. ZHONG J K, LI L, ZHONG Z W, et al. Advances on the research of the effect of biochar on the environmental behavior of antibiotics [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2018, 18(2): 657-663(in Chinese).
[52] 程扬, 沈启斌, 刘子丹, 等. 两种生物炭的制备及其对水溶液中四环素去除的影响因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(3): 1328-1336. CHENG Y, SHEN Q B, LIU Z D, et al. Preparation of two kinds of biochar and the factors influencing tetracycline removal from aqueous solution [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(3): 1328-1336(in Chinese).
[53] PEIRIS C, GUNATILAKE S R, MLSNA T E, et al. Biochar based removal of antibiotic sulfonamides and tetracyclines in aquatic environments: A critical review [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 246: 150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.150 [54] 王娅南, 彭洁, 黄合田, 等. 贵阳市城市河流典型抗生素的分布特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(9): 160-169. WANG Y N, PENG J, HUANG H T, et al. Distribution characteristics of typical antibiotics in Urban Rivers of Guiyang City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(9): 160-169(in Chinese).
[55] TIAN S Q, WANG L, LIU Y L, et al. Enhanced permanganate oxidation of sulfamethoxazole and removal of dissolved organics with biochar: Formation of highly oxidative manganese intermediate species and in-situ activation of biochar [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(9): 5282-5291. [56] ZHANG H, XUE G, CHEN H, et al. Magnetic biochar catalyst derived from biological sludge and ferric sludge using hydrothermal carbonization: Preparation, characterization and its circulation in Fenton process for dyeing wastewater treatment [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 191: 64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.026 [57] 杜文琪, 曹玮, 周航, 等. 磁性生物炭对重金属污染废水处理条件优化及机理 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(2): 492-500. DU W Q, CAO W, ZHOU H, et al. Optimization and the mechanismin treatment of heavy metals wastewater with magnetic biochar [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(2): 492-500(in Chinese).
[58] REGUYAL F, SARMAH A K, GAO W. Synthesis of magnetic biochar from pine sawdust via oxidative hydrolysis of FeCl2 for the removal sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 321: 868-878. [59] GUO X, DONG H, YANG C, et al. Application of goethite modified biochar for tylosin removal from aqueous solution [J]. Colloids Surfaces A:Physicochemical Engineering Aspects, 2016, 502: 81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.05.015 [60] FU H, LI X B, WANG J, et al. Activated carbon adsorption of quinolone antibiotics in water: Performance, mechanism, and modeling [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 29(6): 145-152. [61] HU Y, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. An efficient adsorbent: Simultaneous activated and magnetic ZnO doped biochar derived from camphor leaves for ciprofloxacin adsorption [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 288: 121511. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121511 [62] 张杏艳, 陈中华, 龚胜, 等. 畜禽粪便残留四环素类抗生素的水体污染状况及生态毒理效应 [J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2016, 37(5): 30-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5190.2016.05.011 ZHANG X Y, CHEN Z H, GONG S, et al. Current situation of water pollution caused by tetracycline antibiotics in animal manure and its ecotoxicological effect [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2016, 37(5): 30-33(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5190.2016.05.011
[63] CHEN T W, LUO L, DENG S H, et al. Sorption of tetracycline on H3PO4 modified biochar derived from rice straw and swine manure [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 267: 431-437. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.074 [64] JING X R, WANG Y Y, LIU W J, et al. Enhanced adsorption performance of tetracycline in aqueous solutions by methanol-modified biochar [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 248: 168-174. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.006 [65] ZHOU Y Y, HE Y Z, LIU X C, et al. Analyses of tetracycline adsorption on alkali-acid modified magnetic biochar: Site energy distribution consideration [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 2260-2266. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.393 [66] 朱琳, 张远, 渠晓东, 等. 北京清河水体及水生生物体内抗生素污染特征 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(2): 139-146. ZHU L, ZHANG Y, QU X D, et al. Occurrence of antibiotics in aquatic plants and organisms from qing river, Beijing [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(2): 139-146(in Chinese).
[67] GUO X T, ZHANG J, GE J H, et al. Sorption and photodegradation of tylosin and sulfamethazine by humic acid-coated goethite [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(122): 100464-100471. doi: 10.1039/C5RA17587A [68] 吴智威. 改性竹炭负载Fe/Cu对废水中氯霉素去除研究 [D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2012. 17-58. WU Z W. Modified bamboo charcoal loading Fe/Cu to remove chloramphenicol in wastewater [J]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2012. 17-58 (in Chinese).
[69] AHMED M B, ZHOU J L, NGO H H, et al. Nano-Fe0 immobilized onto functionalized biochar gaining excellent stability during sorption and reduction of chloramphenicol via transforming to reusable magnetic composite [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 322: 571-581. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.063 [70] 朱青. 改性生物炭对水中磺胺嘧啶的去除试验研究 [D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2018. 13-38. ZHU Q. Modified biochar to remove sulfadiazinel in wastewater [D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2018. 13-38 (in Chinese).
[71] HUANG J S, ZIMMERMAN A R, CHEN H, et al. Ball milled biochar effectively removes sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics from water and wastewater [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 258: 113809. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113809 [72] XIANG Y J, XU Z Y, ZHOU Y Y, et al. A sustainable ferromanganese biochar adsorbent for effective levofloxacin removal from aqueous medium [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 237: 124464. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124464 [73] OLADIPO A A, IFEBAJO A O. Highly efficient magnetic chicken bone biochar for removal of tetracycline and fluorescent dye from wastewater: Two-stage adsorber analysis [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 209: 9-16. [74] LIU J L, ZHOU B Q, ZHANG H, et al. A novel biochar modified by chitosan-Fe/S for tetracycline adsorption and studies on site energy distribution [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 294: 122152. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122152 [75] AHMAD M, RAJAPAKSHA A U, LIM J E, et al. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 99(3): 19-33. [76] WANG H, FANG C R, WANG Q, et al. Sorption of tetracycline on biochar derived from rice straw and swine manure [J]. Rsc Advances, 2018, 8(29): 16260-16268. doi: 10.1039/C8RA01454J [77] LIAN F, SUN B B, CHEN X, et al. Effect of humic acid (HA) on sulfonamide sorption by biochars [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 204: 306-312. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.05.030 [78] WANG W, ZHANG J, CHEN T, et al. Preparation of TiO2-modified biochar and its characteristics of photo-catalysis degradation for enrofloxacin [J]. Entific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 6588. [79] ZENG S, KAN E. Chemical activation of forage grass-derived biochar for treatment of aqueous antibiotic sulfamethoxazole [J]. Acs Omega, 2020, 5(23): 13793-13801. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00983 [80] LIAN F, SUN B B, SONG Z G, et al. Physicochemical properties of herb-residue biochar and its sorption to ionizable antibiotic sulfamethoxazole [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 248: 128-134. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.021 [81] 郎印海, 刘犇, 何淑雯, 等. 诺氟沙星在壳聚糖-生物炭复合材料上的解吸行为研究 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2018, 48(11): 22-28. LANG Y H, LIU B, HE S W, et al. Desorption of norfloxacin sorbed on chitosan-biochar composite [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(11): 22-28(in Chinese).
[82] HAMEED B H, SALMAN J M, AHMAD A L. Adsorption isotherm and kinetic modeling of 2, 4-D pesticide on activated carbon derived from date stones [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 163(1): 121-126. [83] ZHOU Y Y, LIU X C, XIANG Y J, et al. Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: Adsorption mechanism and modelling [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 266-273. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.178 [84] AHMED M B, ZHOU J L, NGO H H, et al. Single and competitive sorption properties and mechanism of functionalized biochar for removing sulfonamide antibiotics from water [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 311: 348-358. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.106 -



 下载:
下载: