-
苯硫酚(thiophenol, PhSH)是一种有用的有机合成中间体,广泛应用于制药、农用化学品和各种工业产品的制备[1]. 它们也是具有剧毒和污染的化学物质,被美国环境保护署列为优先处理的污染物之一[2]. 长时间接触PhSH会导致严重的健康问题,包括中枢神经系统损伤、呼吸困难、呕吐、甚至死亡. 此外,PhSH不仅毒性大,还具有强烈的刺激性和挥发性,接触时间不能超过15 min[3-4]. 然而,即使在浓度很低的溶液中,PhSH也有一种可怕的气味,长时间接触会导致恶心和头痛,应尽量缩短与PhSH的接触时间[5-6]. 因此,构建可快速、高选择性识别PhSH的荧光探针在环境科学和生物科学领域都具有重要的意义.
近年来,硫醇类荧光探针的开发引起了人们的极大兴趣[7-14]. Wang课题组报道了首个基于分子内光诱导电荷转移(photoinduced charge transfer, PET)机理的PhSH探针,该探针以4-氨基-7-硝基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑(NBD)作为荧光团,2,4-二硝基苯磺酰胺(2, 4-dinitrobenzene sulfonamide, DNBS)为识别基团,具有良好的水溶性和选择性,但由亲核取代释放的荧光团的荧光量子产率较低(Φ = 0.02),且反应时间太长[15]. 随后,科研工作者以DNBS为识别基团,构建了多种能够区分脂肪族硫醇和PhSH类化合物的荧光探针,然而它们有的显示相对较弱的荧光强度,一些需要有机化合物作为助溶剂,有些则受需要使用高pH值的影响,有的选择性较差,有的检测过程耗时较长(孵育时间长达1 h),只有少数几种方法可以应用于实际检测[4, 16-18]. 因此,一种反应速度快、适用于实际环境和生物样品中PhSH检测的荧光探针还有待开发.
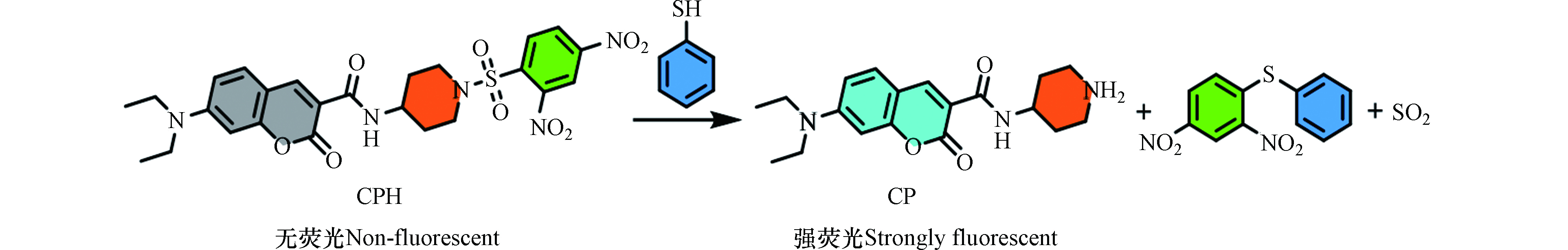
香豆素染料具有高的荧光强度、良好的溶解性、高效的细胞渗透等优点,是荧光探针的理想荧光团[19-21]. 本文以香豆素衍生物CP为荧光团、强吸电子基团DNBS为识别基团,成功构建了荧光增强型香豆素类荧光探针CPH. 由于CP和DNBS之间的PET过程,探针CPH自身没有荧光. 向探针溶液中加入PhSH后,由于PhSH介导的裂解反应,荧光团CP被释放,探针CPH溶液的荧光恢复,从而实现水溶液中PhSH的检测(图1). 探针CPH的荧光强度随PhSH浓度的增加而增加,线性范围为0—16 μmol·L−1. 该方法对PhSH的检测具有响应速度快(荧光强度在5 min时可达到平台期)、选择性好(不受生物硫醇的干扰)且灵敏度较高(检出限为0.13 μmol·L−1)的特点. 此外,CPH可用于HeLa细胞和环境水样中PhSH的定量测定.
-
2-(7-偶氮苯并三氮唑)-N,N,N',N'-四甲基脲六氟磷酸酯(HATU)、N,N-二异丙基乙胺(DIPEA)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)、三氟乙酸、2, 4-二硝基苯磺酰氯、半胱氨酸(cysteine, Cys)、高半胱氨酸(homocysteine, Hcy)、谷胱甘肽(glutathione, GSH)、抗坏血酸(ascorbic acid, AA),分析纯,上海阿拉丁生化技术有限公司. 柱层析硅胶(200—300目),青岛海洋化工有限公司. 除非另有说明,其他所有化学试剂均可在市场上获得并使用前经过标准方法处理. 溶剂用常规方法干燥后再蒸馏.
400 MHz核磁共振波谱仪(NMR),美国瓦里安公司;布鲁克micrOTOF-QⅡ型质谱仪(HRMS),德国布鲁克公司;日立FL-4600荧光分光光度计,日本日立公司;岛津UV-2600紫外分光光度计,日本岛津公司;Zeiss LSM880激光共聚焦显微镜,德国蔡司公司;Sartorius PB-10 pH计,德国赛多利斯公司;硅胶柱规格为内径26 mm,有效长度305 mm,北京欣维尔玻璃仪器有限公司.
-
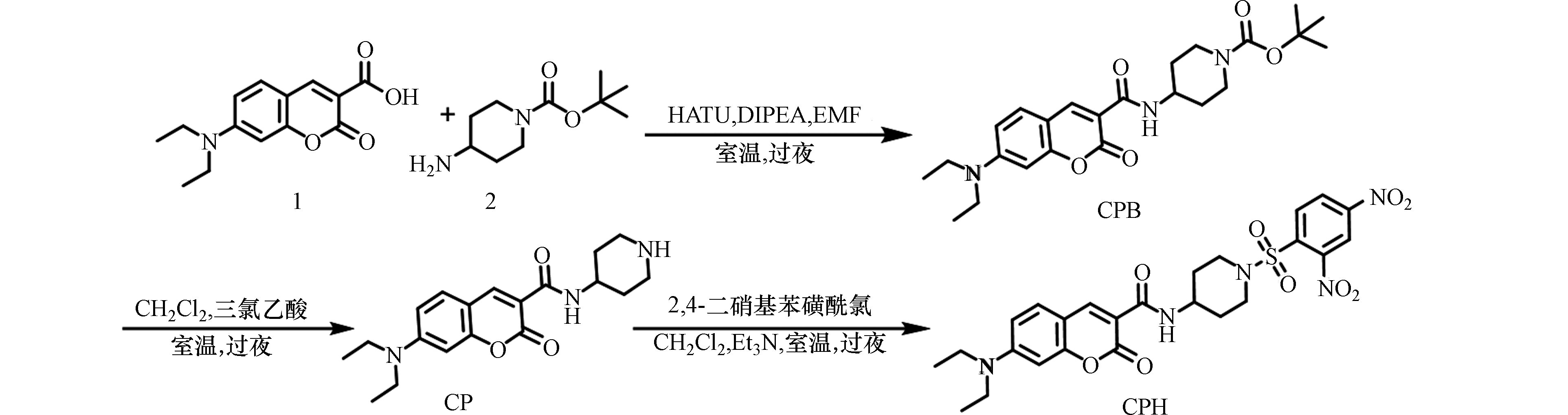
将7-二乙基氨基香豆素-3-羧酸(1)(65.3 mg, 0.25 mmol)、2(50.0 mg, 0.25 mmol)、HATU(70 μL, 0.4 mmol)和DIPEA(57.8 mg, 0.38 mmol)混合物在无水DMF(5 mL)和氩气的保护下,室温搅拌一夜. 将混合物倒入盐水中,所得沉淀经硅胶柱层析(体积比为CH2Cl2/CH3OH = 10/1,400 mL)过滤提纯,得到化合物CPB(83 mg,产率为75%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm): 8.81 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 8.70 (s, 1H), 7.45 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 6.55 (s, 1H), 4.18—4.06 (m, 1H), 4.01 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, 2H), 3.46 (dt, J = 13.9, 6.8 Hz, 4H), 2.97 (dd, J = 15.1, 8.3 Hz, 2H), 1.98 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 2H), 1.57—1.48 (m, 1H), 1.46 (s, 9H), 1.32—1.27 (m, 1H), 1.24 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H). HRMS (ESI) m/z: C24H33N3O5 [M+H]计算值为466.2318;实测值为466.2309.
-
将化合物CPB(44.3 mg, 0.1 mmol)溶于CH2Cl2(2 mL)中,再加入三氟乙酸(2 mL). 混合物溶液在室温下搅拌一夜,蒸发除去溶剂,所得产物经硅胶柱层析(体积比为CH2Cl2/CH3OH = 20/1,600 mL)净化得到化合物CP(33 mg,产率为95%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ (ppm):9.40 (s, 1H), 8.65 (s, 1H), 8.64—8.58 (m, 1H), 7.69 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.81 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.62 (s, 1H), 4.10 —3.97 (m, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 3.47 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 4H), 3.22 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, 2H), 2.99 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 2.03 (d, J = 11.5 Hz, 2H), 1.75 (q, J = 10.4 Hz, 2H), 1.12 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 6H). HRMS (ESI) m/z: C19H25N3O3 [M+H]计算值为344.1974;实测值为344.1974.
-
将化合物CP(34.3 mg, 0.1 mmol)与3 mL CH2Cl2和Et3N(3倍当量)混合. 然后,在0 °C下,将2, 4-二硝基苯磺酰氯(26.6 mg, 0.1 mmol)的CH2Cl2(3 mL)溶液滴加到上述溶液中. 10 min后,移去冰浴,在室温下搅拌混合物6 h. 反应混合物用CH2Cl2稀释、水洗(10 mL×3)后,用Na2SO4干燥,然后蒸发溶剂,进一步硅胶柱层析(体积比为CH2Cl2/ CH3CN = 20/1,700 mL)得到白色固体CPH(52.2 mg,产率为90%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm):8.85 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 8.66 (s, 1H), 8.54—8.46 (m, J = 11.9, 3.3 Hz, 2H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 6.71— 6.64 (m, 1H), 6.51 (s, 1H), 4.18—4.06 (m, 1H), 3.82 (d, J = 13.1 Hz, 2H), 3.45 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H), 3.13 (t, J = 11.0 Hz, 2H), 2.15—2.05 (m, 2H), 1.76—1.62 (m, 2H), 1.23 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm):162.88, 162.70, 157.75, 152.72, 149.82, 148.28, 137.89, 132.58, 131.30, 126.22, 119.92, 110.29, 109.87, 108.53, 96.79, 45.53, 45.29, 45.12, 31.59, 12.50. HRMS (ESI) m/z: C25H27N5O9S [M+Na]计算值为596.1427;实测值为596.1395.
合成路线见图2.
-
探针CPH(1 mmol·L−1)的储备液是用分析级DMSO配制的. 其他分析物包括Cys、Hcy、GSH等均溶解在去离子水(10 mL)中,得到浓度为10 mmol·L−1水溶液.
-
将探针CPH溶液(40 μL, 1 mg·mL−1)、约4 mL 磷酸盐缓冲溶液(phosphate buffer solution, PBS)和不同体积的PhSH原液(1 mmol·L−1)加入到10 mL比色管中,最后用PBS稀释至5 mL. 混合后,记录荧光和紫外-可见吸收光谱. λex/λem = 415/480 nm,激发和发射光的狭缝宽度均为5 nm.
-
实验之前,将Hela细胞接种在包含无菌盖玻片的6孔培养皿中,贴壁24 h. 然后移除介质,37 °C下在RPMI介质中将细胞与探针CPH溶液(8 μmol·L−1)共同孵化30 min后,用PBS清洗细胞3次,移除未反应的探针后,37 °C下让细胞进一步与PhSH(2 μmol·L−1和10 μmol·L−1)培养30 min. 随后,再用PBS清洗细胞3次,在Olympus FV1200共聚焦激光扫描显微镜上进行细胞成像实验. CPH的激发波长为405 nm,发射强度收集范围为430—550 nm.
为了研究细胞毒性,将Hela细胞接种在24孔板中,在处理前培养24 h,然后暴露于不同浓度(2—10 μmol·L−1)的探针CPH中24 h. 然后,将MTT溶液(20 μL,5.0 mg·mL−1)加入到每个孔中,37 °C下培养4 h后,除去上清液. 向每个孔中加入150 μL的DMSO,溶解形成甲赞晶体,振荡10 min后,用酶标仪(WD-2102A自动酶标仪,北京市六一仪器厂)读取430 nm处的吸光度. 所有的MTT试验均重复4次. 通过探针处理过的样品与对照样品的吸光度比值来评估探针的细胞毒性.
-
考虑到其他组分的干扰,采用标准添加法测定真实水样中PhSH的含量. 以本实验室自来水和汉江汉中段的河水为研究对象,分别采集了2个50 mL的样品. 水样在试验前利用孔径为0.22 μm的水相微孔滤膜进行过滤,用20 mmol·L−1, pH 7.4的PBS调节水样的pH值. 将探针CPH(8 μmol·L−1)和不同浓度(0、2、6、10 μmol·L−1)的PhSH原液加入等分水样中,室温孵育5 min,记录溶液的荧光强度. λex/λem = 415/480 nm,激发和发射光的狭缝宽度均为5 nm.
-
由于PhSH和生物硫醇结构中均含有巯基,开发可区分PhSH和生物硫醇的荧光探针极具挑战性. 然而,PhSH的pKa值比生物硫醇的pKa要低很多(PhSH是6.5,Cys是8.44,GSH是8.6)[15]. 因此,在生理pH下,PhSH大部分以具有亲核能力的硫醇盐形式存在(Ar-S−)[22],而生物硫醇则主要以活性较弱的中性形式存在(R-SH),这为可选择性的检测PhSH提供了一个突破口. 此外,在生理pH下,磺酰胺很容易被PhSH裂解,但不容易被脂肪族硫醇裂解. 因此,我们选择CP为荧光团,DNBS为识别基团,构建荧光探针CPH用于PhSH的高选择性检测.
-
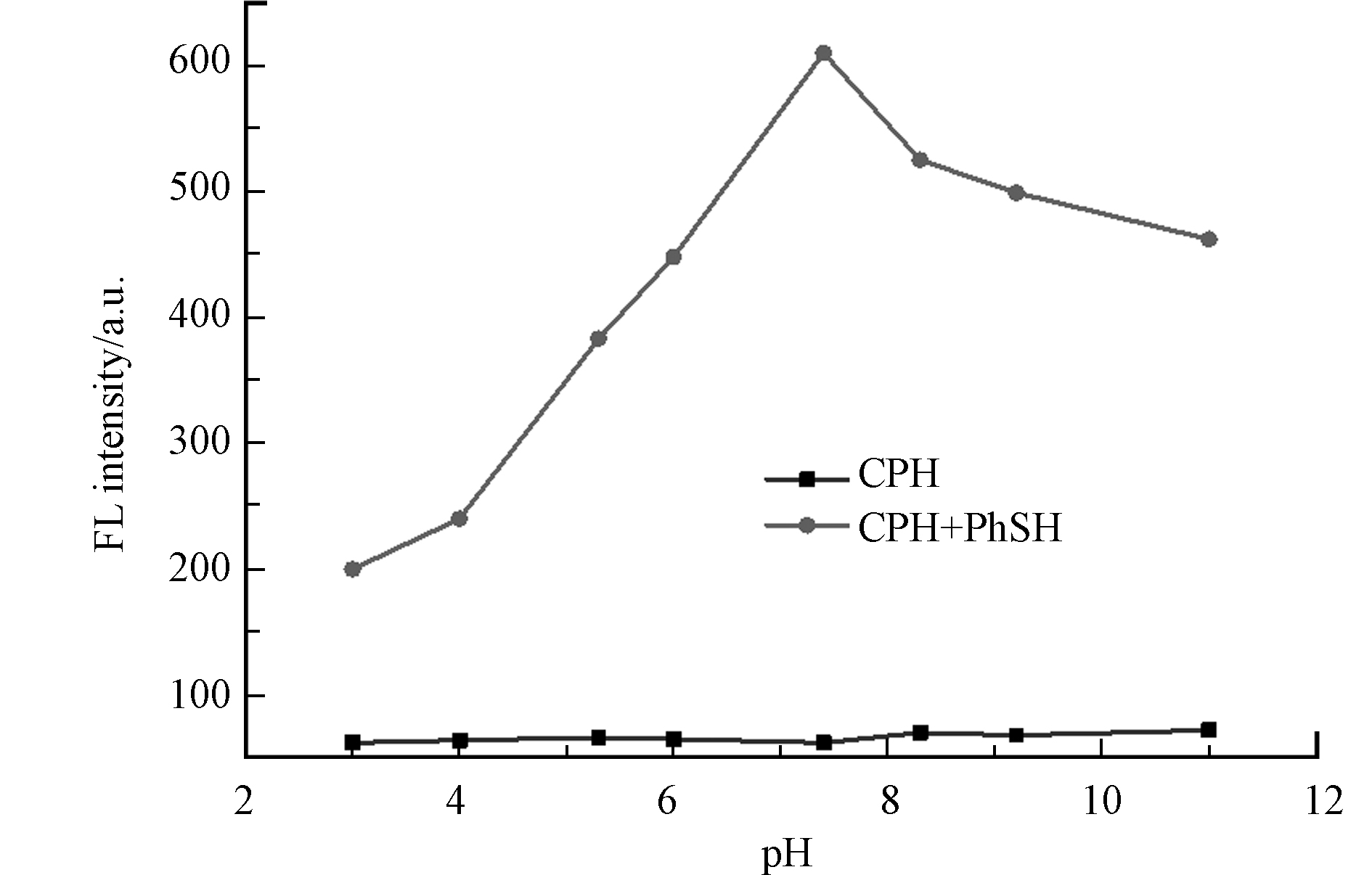
由于pH值会影响探针和PhSH的响应行为,首先研究了pH值对其荧光性质的影响. 如图3所示,在20 mmol·L−1PBS缓冲溶液中,探针CPH的荧光性能不随溶液pH值的变化而变化,这意味着该探针CPH在pH 3.0—11.0范围内的化学结构和荧光性质都相对稳定. 加入PhSH溶液后,混合液的荧光强度随pH的增加而增加,在pH 7.4时达到最大值. 因此,测试的最佳pH值设置为7.4.
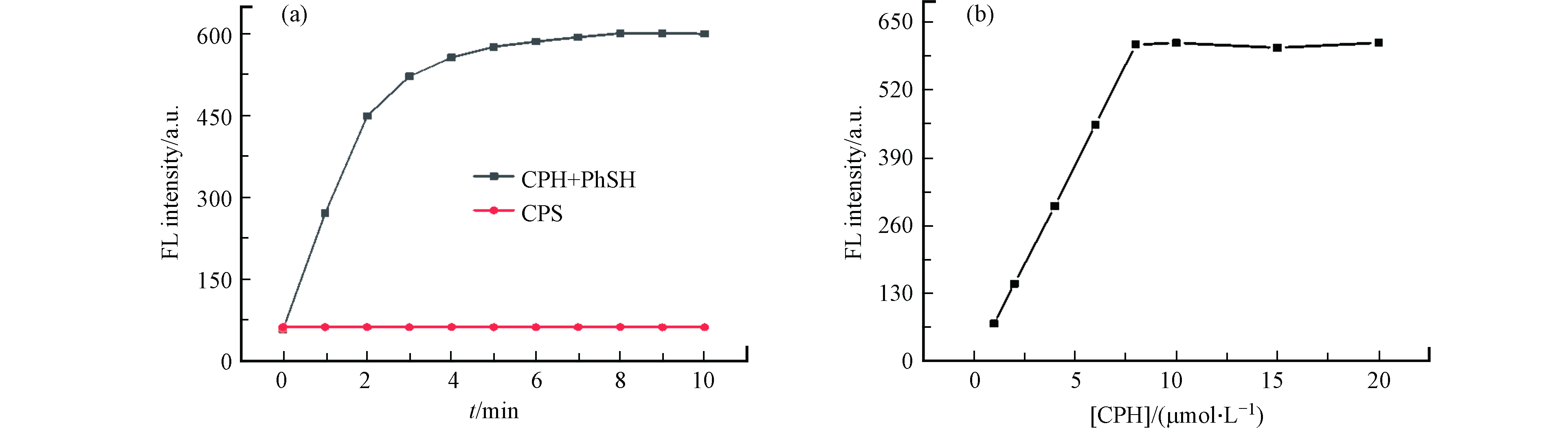
随后,研究了加入PhSH(60 μmol·L−1)后,探针CPH缓冲溶液(pH 7.4,20 mmol·L−1PBS)的荧光强度随时间的变化,以评价探针CPH对PhSH的传感能力. 值得注意地是,探针CPH对PhSH反应迅速,在5 min内基本完成反应(如图4所示),且荧光强度在10 min内变化不大. 因此,所有测量的检测时间设置为5 min. 此外,我们研究了加入60 μmol·L−1的PhSH后,CPH浓度对检测体系荧光强度的影响(图4). 实验结果表明,随着CPH溶液浓度从1 μmol·L−1增加到20 μmol·L−1,体系的荧光强度逐渐增加,并在8 μmol·L−1时达到最大值. 因此,CPH溶液的浓度选择为8 μmol·L−1.
-
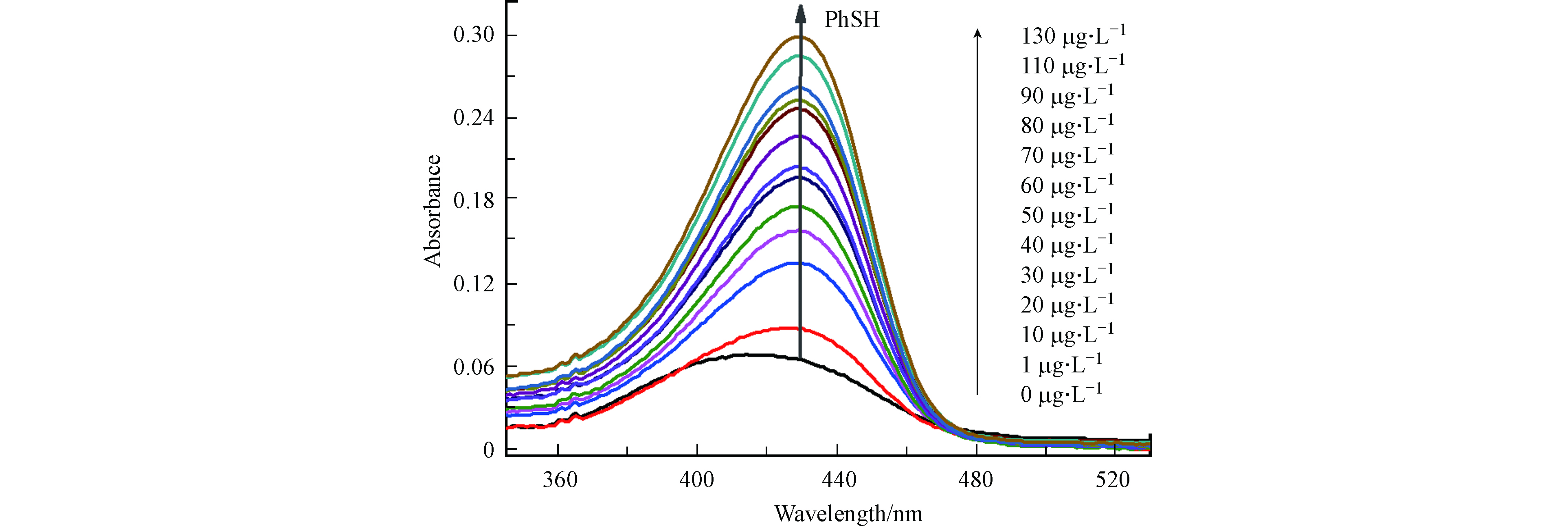
在pH 7.4、反应时间5 min及CPH浓度为8 μmol·L−1的条件下,测定了探针CPH缓冲溶液(pH 7.4,20 mmol·L−1PBS)与不同浓度的PhSH反应后的紫外-可见吸收光谱. 如所示图5,CPH在430 nm处的吸光度随PhSH浓度增加而增加,且最大吸收波长从410 nm红移到430 nm处,证明了探针CPH“裸眼”探测PhSH的可能性.
在PBS缓冲溶液中(pH 7.4,20 mmol·L−1),测定了探针与不同浓度的PhSH反应后的荧光光谱图. 如图6a所示,CPH与PhSH反应后,检测体系的最大发射波长从470 nm红移到480 nm处,是由于生成了香豆素衍生物CP,荧光强度随着PhSH浓度的增加而逐渐增加,且与PhSH浓度之间呈良好的线性关系,线性范围为0—16 μmol·L−1(图6b内嵌图). 线性回归方程为:Y = 22.22X+ 62.51,相关系数r=0.9917,Y为CPH的荧光强度,X为PhSH的浓度(μmol·L−1). 检出限(LOD)为0.13 μmol·L−1(3σ/k). 这些结果表明,CPH可在一定浓度范围内实现水溶液中PhSH含量的定量检测.
-
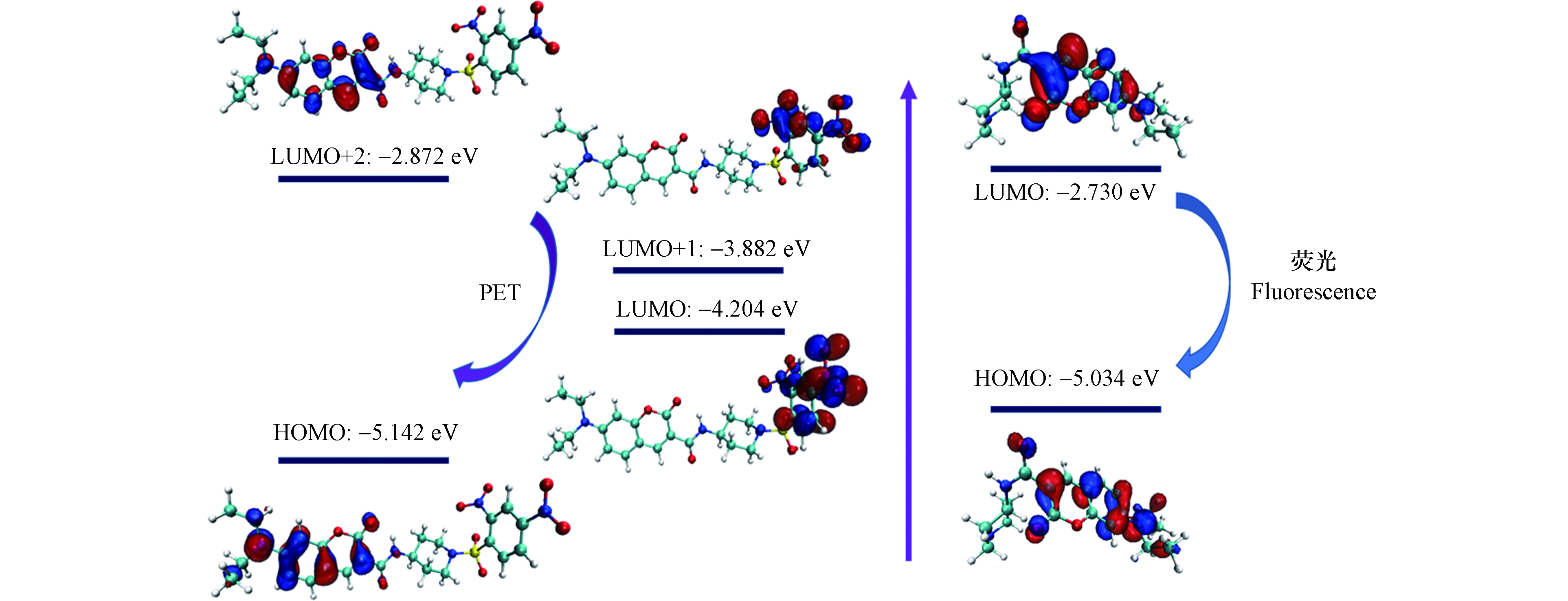
为了解释探针CPH对PhSH的传感机制,进行了DFT计算(图7). 前沿轨道图表明,CPH的LUMO(‒4.204 eV)和LUMO+1(‒3.882 eV)轨道的能量位于CPH的HOMO(‒5.142 eV)和LUMO+2(‒2.872 eV)轨道的能量之间,这意味着CPH分子内部存在PET过程,且由于PET过程的有效抑制,探针CPH基本上是非荧光的. 然而,探针CPH与PhSH反应后,由于DNBS基团的去除,产物CP的LUMO(‒2.730 eV)和HOMO(‒5.034 eV)轨道的能量差变小,荧光恢复.
-
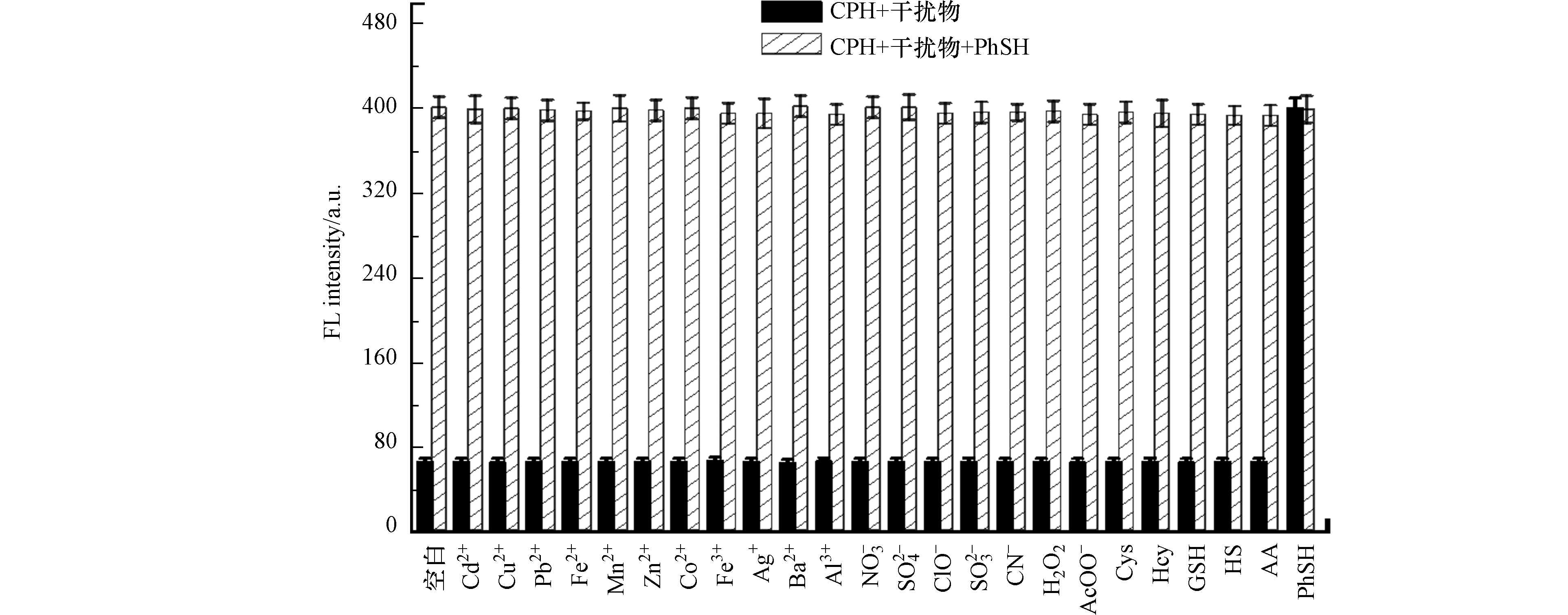
为了探索探针CPH的选择性,研究了其他分析物对PhSH检测的干扰,如相关的生物硫醇(500 μmol·L−1 Cys、500 μmol·L−1 Hcy和1 mmol·L−1 GSH)、常见的亲核试剂(100 μmol·L−1 HS−、500 μmol·L−1 AA、1 mmol·L−1 SCN‒)以及其他可能的干扰物质(Cd2+、Cu2+、Pb2+、Fe2+、Mn2+、Zn2+、Co2+、Fe3+、Ag+、Ba2+、Al3+、NO3−、SO42−、ClO−、SO32‒、H2O2、AcOO−,浓度均为1 mmol·L−1)(图8). 然而,即使在高浓度下,被测物种均未引起荧光强度的明显变化. 只有加入16 μmol·L−1PhSH时,探针缓冲溶液(8.0 μmol·L−1,pH 7.4,20 mmol·L−1PBS)的荧光强度才显著增强,表明探针CPH对PhSH具有特别的选择性,不受任何干扰物的影响.
此外,在其他干扰物存在下,向探针CPH的溶液中加入PhSH进行竞争实验. 当探针CPH的溶液加入PhSH时,可以观察到较强的荧光,且不受其他测试物的干扰. 结果表明,在其他各种分析物存在的情况下,探针CPH对PhSH的检测仍然非常有效.
-
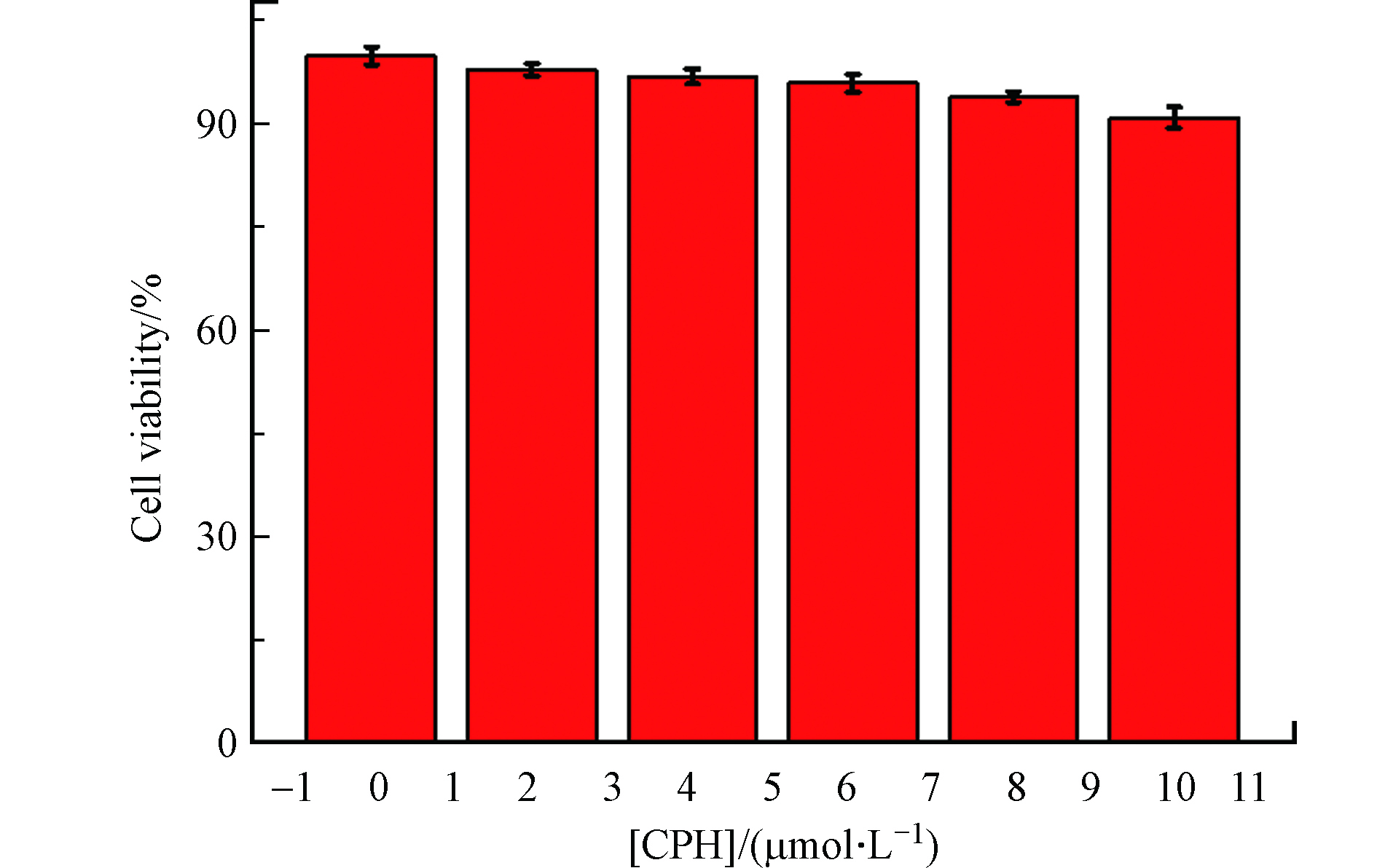
在细胞成像实验前,用MTT法检测探针CPH的细胞毒性(0、2、4、6、8、10 μmol·L−1). 如图9所示,孵育后细胞存活率保持在91%以上,表明探针CPH较低细胞毒性.
在HeLa细胞中对探针CPH检测PhSH的能力进行了初步研究,并用荧光共聚焦显微镜观察实验结果. HeLa细胞与CPH(8 μmol·L−1)共同培养30 min后,进一步与不同浓度的PhSH(2、10 μmol·L−1)一起孵育20 min,记录荧光图像. 图10显示了2 μmol·L−1 PhSH处理HeLa细胞后可观察到清晰的细胞轮廓和可见的蓝色荧光,经10 μmol·L−1PhSH处理后,蓝色荧光变得更加明亮. 因此,探针CPH可成功应用于细胞中PhSH的高选择性检测.
-
为了验证该方法在环境科学中的实用性,采用标准添加法利用探针CPH测定了汉江水样和实验室自来水样中PhSH的含量[23]. 将探针CPH直接加入水样中,未观察到明显的荧光增强. 在水样中添加不同浓度(0、2、6、10 μmol·L−1)的PhSH后,用上述方法测定时,PhSH的回收率均不低于95%(表1),表明该探针可实现水样中PhSH的定量检测,回收率良好. 实验结果表明, 该探针可作为一种有效的荧光工具检测环境水样品中PhSH的含量.
-
以香豆素为荧光团,DNBS为识别单元,成功设计了基于PET机理的荧光增强型探针CPH. 它具有细胞渗透性好、毒性低、响应快、灵敏度好、对常见干扰物具有较高的选择性的特点. 探针CPH具有良好的定量检测PhSH的能力,线性响应范围为0—16 μmol·L−1. 此外,CPH可以用于HeLa细胞中PhSH的荧光成像和水样中PhSH的检测. 综上所述,实验结果表明探针CPH在生物样品和环境样品中PhSH的高效定量分析中具有很大的应用前景.
一种快速识别苯硫酚的荧光探针的构建及其在细胞和环境样品中的应用
Construction of a fluorescent probe for rapid recognition of thiophenol and its application in living cells and environmental samples
-
摘要: 由于苯硫酚(thiophenol, PhSH)在环境及生物体系中的剧毒性,开发可特异性识别PhSH的探针具有重要意义。本研究以香豆素为荧光团,2, 4 - 二硝基苯磺酰胺为识别单元,基于分子内光诱导电荷转移机制,开发了一种新型的荧光增强型探针CPH,实现PhSH的检测。该探针能高选择性、高灵敏度地区分生物硫醇和PhSH,具有细胞渗透性好、毒性低、响应快的特点。值得注意地是,探针CPH可对不同浓度的PhSH迅速做出反应,具有良好的定量检测PhSH的能力,线性响应范围为0—16 μmol·L−1,检出限为0.13 μmol·L−1。此外,新型探针可成功检测HeLa细胞中的PhSH,且可定量测定水样中PhSH的含量,回收率可达95%以上。实验结果表明探针在环境科学和生物科学领域具有广阔的应用前景。Abstract: Due to the extreme toxicity of thiophenol in environmental and biological systems, it is of great significance to develop a probe for the specific recognition of thiophenol. In this study, a novel off-on fluorescent probe CPH was developed using coumarin as the fluorophore and 2, 4-dinitrobenzene sulfonate as the recognition unit based on intramolecular photo-induced charge transfer mechanism. This probe exhibiting good cell permeability, low toxicity and fast response can distinguish thiophenol from biothiols with high selectivity and sensitivity. It is noteworthy that the probe CPH can quickly respond to different concentrations of thiophenol, and a good linear relationship between the fluorescence intensity of CPH and thiophenol concentration (0—16 μmol·L−1) was performed, displaying a limit of detection of 0.13 μmol·L−1. In addition, the new probe has been successfully used for determining thiophenol in HeLa cells and environmental water samples with a recovery of more than 95%, indicating that the probe CPH has a broad application prospect in environmental science and biological science.
-
Key words:
- fluorescent probe /
- thiophenol /
- high selectivity /
- cell imaging /
- environmental water samples
-

-
表 1 CPH检测环境水样中的PhSH(n = 3)
Table 1. CPH detection of PhSH in environmental water samples (n = 3)
样品
Sample加入量/(μmol·L−1)
Adding amount测得量a± SDb/(μmol·L−1)
Determinations回收率/%
Recovery rateRSD/% 自来水 0.0 0.0±0.1 — — 2.0 1.9±0.1 95.0 3.0 6.0 5.9±0.1 98.3 1.2 10.0 10.4±0.2 104.0 1.5 汉江水 0.0 0.0±0.1 — — 2.0 1.9±0.1 95.0 3.3 6.0 6.1±0.2 101.7 2.8 10.0 10.3±0.3 103.0 2.7 a3次测量平均值. aMean of three determinations。b标准偏差. bStandard deviation -
[1] HAO Y Q, YIN Q Y, ZHANG Y T, et al. Recent progress in the development of fluorescent probes for thiophenol [J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(20): 3716. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203716 [2] WU Q Q, WANG J B, LIANG W L. A red-to-near-infrared fluorescent probe for the detection of thiophenol based on a novel hydroxylflavone-quinoline-amino molecular system with large Stokes shift [J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2021, 190: 109289. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2021.109289 [3] 张改清, 阴彩霞. 基于二氰基异佛尔酮的荧光探针在检测苯硫酚中的应用 [J]. 无机化学学报, 2021, 37(7): 1245-1250. doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2021.161 ZHANG G Q, YIN C X. Application of fluorescent probe based on dicyanoisophorone in detection of thiophenol [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 37(7): 1245-1250(in Chinese). doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2021.161
[4] WANG Z, HAN D M, JIA W P, et al. Reaction-based fluorescent probe for selective discrimination of thiophenols over aliphaticthiols and its application in water samples [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(11): 4915-4920. doi: 10.1021/ac300512b [5] XU T, ZHAO S J, WU X L, et al. Β-cyclodextrin-promoted colorimetric and fluorescence turn-on probe for discriminating highly toxic thiophenol from biothiols [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(16): 6413-6421. [6] GHAMALI M, CHTITA S, OUSAA A, et al. QSAR analysis of the toxicity of phenols and thiophenols using MLR and ANN [J]. Journal of Taibah University for Science, 2017, 11(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jtusci.2016.03.002 [7] LI J, ZHANG C F, YANG S H, et al. A coumarin-based fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of thiophenols and its application [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(6): 3037-3042. doi: 10.1021/ac403885n [8] 葛文奇, 圣迎迎, 乔亚东, 等. 苯硫酚荧光探针研究进展 [J]. 化学传感器, 2017, 37(1): 9-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2298.2017.01.003 GE W Q, SHENG Y Y, QIAO Y D, et al. Research progress of thiophenol fluorescence probe [J]. Chemical Sensors, 2017, 37(1): 9-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2298.2017.01.003
[9] DUAN N, WANG H, LI Y N, et al. The research progress of organic fluorescent probe applied in food and drinking water detection [J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2021, 427: 213557. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213557 [10] CHEN X Q, ZHOU Y, PENG X J, et al. Fluorescent and colorimetric probes for detection of thiols [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(6): 2120-2135. doi: 10.1039/b925092a [11] WANG H, WU X M, YANG S X, et al. A rapid and visible colorimetric fluorescent probe for benzenethiol flavor detection [J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 286: 322-328. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.033 [12] LI F, YAO W, TIAN C H, et al. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for selective detection of thiophenol derivatives [J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2022, 271: 120870. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2022.120870 [13] LI Y Q, SU W, ZHOU Z L, et al. A dual-response near-infrared fluorescent probe for rapid detecting thiophenol and its application in water samples and bio-imaging [J]. Talanta, 2019, 199: 355-360. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.02.022 [14] WU Y Q, SHI A P, LIU H Y, et al. A novel near-infrared xanthene-based fluorescent probe for detection of thiophenol in vitro and in vivo [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(40): 17360-17367. doi: 10.1039/D0NJ03370G [15] JIANG W, FU Q Q, FAN H Y, et al. A highly selective fluorescent probe for thiophenols [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2007, 46(44): 8445-8448. doi: 10.1002/anie.200702271 [16] WANG X B, ZHOU J H, ZHANG D T, et al. A very fast 3-hydroxy-coumarin-based fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of thiophenols and its application in water samples [J]. Analytical Methods, 2016, 8(38): 6916-6922. doi: 10.1039/C6AY02037B [17] WU J J, SU D D, QIN C Q, et al. A fast responsive chromogenic and near-infrared fluorescence lighting-up probe for visual detection of toxic thiophenol in environmental water and living cells [J]. Talanta, 2019, 201: 111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.113 [18] LIN V S, CHEN W, XIAN M, et al. Chemical probes for molecular imaging and detection of hydrogen sulfide and reactive sulfur species in biological systems [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(14): 4596-4618. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00298A [19] KATERINOPOULOS H E. The coumarin moiety as chromophore of fluorescent ion indicators in biological systems [J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2004, 10(30): 3835-3852. doi: 10.2174/1381612043382666 [20] 赵慧君, 吴通, 孙玥, 等. 基于香豆素的比率型荧光探针对溶液及气相中三氟化硼的检测 [J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2422-2427. ZHAO H J, WU T, SUN Y, et al. A coumarin-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for BF3 detection in solution and air [J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2422-2427(in Chinese).
[21] 刘忠诚, 杜美利, 韩翔, 等. 香豆素类荧光探针对硫化氢检测的研究进展 [J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2021, 11(6): 27-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2021.06.006 LIU Z C, DU M L, HAN X, et al. Research progress of coumarin fluorescent probes for hydrogen sulfide detection [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 11(6): 27-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2021.06.006
[22] KOWADA T, MAEDA H, KIKUCHI K. BODIPY-based probes for the fluorescence imaging of biomolecules in living cells [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(14): 4953-4972. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00030K [23] ZHANG S R, WANG Q, WU F F, et al. Merocyanine-based turn-on fluorescent probe for the sensitive and selective determination of thiophenols via a pKa shift mechanism [J]. Talanta, 2020, 216: 120965. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120965 -



 下载:
下载: