-
随着社会工业经济的发展,空气污染问题日益严重,其中代表性的污染物氮氧化物(NOx)因其酸性性质及臭氧生成前驱体的身份而受到广泛关注。氮氧化物的人为源来自化石/生物质的燃烧、机动车尾气及化工行业的排放。氮氧化物在对流层的化学环境中起着重要作用,其不仅会形成硝酸盐改变其他颗粒的物理化学性质,还能与硫酸盐协同作用产生二次污染物有机气溶胶,进而引发酸沉降、温室效应、光化学烟雾及雾霾等环境问题,损害生态环境并对人类健康造成威胁[1-3]。根据国家统计局2011—2019年统计年鉴显示,氮氧化物的减排速度相比于硫氧化物来说较为缓慢[4]。目前“十四五”大气污染防治专项规划已在编制中,生态环境部表示依旧将改善空气质量与促进污染物减排量作为主要目标,着重针对臭氧前驱体物NOx和VOCs设计减排目标,表明氮氧化物控制减排仍是我国大气污染防治工作的重点。
目前对于氮氧化物的消除以烟气净化技术居多,其中选择性催化还原法SCR(Selective Catalytic Reduction)因其高脱硝效率成为研究热点技术。催化剂是保证脱硝性能的关键因素之一,研究者们已经陆续制备出多种高效催化剂,但由于实际应用环境中的烟气含有碱(土)金属会致使催化剂中毒失活,使其脱硝性能及使用寿命大幅降低,造成材料的浪费以及经济的损失。因此迫切需要研究者们开发出有良好碱(土)金属耐受性且温度适应性好的高效脱硝催化剂。
研究者们致力于通过表面改性获得稳定抗碱(土)金属中毒、更具实际应用能力的SCR催化剂。基于此,本文总结了提高催化剂对碱(土)金属耐受性的改性方法研究进展,阐述了SCR催化剂碱(土)金属中毒机理、不同方法提高耐受性的抗中毒机制、中毒催化剂不同再生方法及量子化学计算在材料领域的应用,为SCR催化剂开发应用及抗中毒性能研究提供研究思路和参考。
-
碱(土)金属化合物是造成SCR催化剂强烈中毒失活的因素之一,随着推行可再生能源如生物质能逐渐取代化石燃料能源,烟气中会出现更多碱(土)金属化合物[5]。烟气中常见的碱金属K、Na和碱土金属Ca、Mg主要通过物理钝化与化学失活作用使催化剂性能损失。
-
碱(土)金属氧化物及盐类或与酸性气体反应后形成难溶性颗粒物,沉积在SCR催化剂表面及孔道内,阻碍活性位点发挥氧化还原作用。Zhu等[6]利用铜基小孔沸石Cu-SSZ-39催化剂负载Na、K、Ca、Mg的4种碱(土)金属进行抗中毒实验研究,发现催化剂的氮氧化物转化率从未负载的95%分别下降至40%、15%、26%、19%。通过N2O物理吸附试验得出中毒后,催化剂表面积和孔体积明显减小,归结于碱(土)金属颗粒堵塞微孔。
-
碱(土)金属存在会促进催化剂生成稳定无活性的硝酸盐物种,覆盖活性位点[7]。Zhou等[8]通过研究预吸附NO+O2和NH3在V2O5/CeO2催化剂上的瞬态反应,发现碱金属催化剂上的硝酸盐物种在NH3引入后不能被消耗,硝酸根在碱金属中毒后的催化剂上反应性变得不活跃。
-
碱(土)金属与催化剂酸性位点发生反应,削弱催化剂表面酸性位点的数量及强度。以SCR工业催化剂V2O5-TiO2为例,碱(土)金属占据Brönsted酸位点后,抑制了NH3的吸附,造成催化剂活性下降[9],催化剂碱金属中毒机理如下[10]。

-
催化剂碱(土)金属中毒会削弱活性组分性能,抑制氧化还原反应的发生。Su等[11]研究了Mn-Ce/AC(活性炭)催化剂负载CaO的中毒机理,Ca/Mn物质的量比=0.5的中毒条件下催化剂在75℃时NO转化率从新鲜催化剂的69.5%下降到中毒后的38.2%,表征发现催化剂通过SCR反应中的关键步骤MnO2→Mn2O3+Oα提供化学吸附氧,而CaO负载后催化剂表面MnO2转化为Mn2O3,Mn3+氧化还原能力较弱抑制了中间产物−NH2的生成,减小了NO2的生成速率。
-
针对SCR催化剂对碱(土)金属中毒机理,目前改良SCR催化剂抗碱(土)金属中毒性能的方法集中在利用酸位点多的金属改性以提高催化剂表面酸性、酸化催化剂提供额外酸性位点、分隔催化剂活性位点与碱(土)金属中毒位点等。
-
Ce具有成本低、储存与释放氧能力强、良好氧化还原性能等优点,且已被证实可以有效提高催化剂SCR性能[12]。Ce添加产生Ce3+/Ce4+间电子转移效应有利于催化剂形成表面活性氧,并可增加酸性位含量。
Yan等[13]利用超小纳米沸石EMT为前驱体制备沸石型催化剂Si5Al2OX,Ce改性后催化剂获得良好碱金属耐受性。采用典型浸渍法在催化剂上负载1%wt K后,催化剂H2-TPR实验结果显示其还原性能明显下降。然而,NH3-TPD表征结果显示改性后的Ce-Si5Al2OX催化剂拥有最高吸附容量,提供了更多酸性位点,尤其是Lewis酸性位点。但CeO2-Si5Al2OX由于Ce在铝硅酸盐表面形成不规则氧化铈聚集体导致催化剂活性很差。这种现象同样出现在Cao等[14]制备的Ce-Zr共负载钒钨钛催化剂中,实验表明浸渍法会导致Ce烧结形成CeO2晶体,对于脱硝性能及抗中毒能力产生负面影响。随即作者使用共沉淀法制备了Ce/Zr物质的量比为2∶1的V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂有最佳抗K中毒性能,Ce、Zr结合到TiO2中形成均匀的TiO2-CeO2-ZrO2固溶体,获得更多表面酸性及氧化还原能力。作者认为Ce/Zr共负载的VWTi催化剂抗碱金属中毒机制可能是由于Ce4+与K的结合导致形成Ce-O-K物种,而同时Zr4+能提高其热稳定性,允许更多的Ce4+与K结合,从而保护活性中心V5+物种[15]。
Wang等[16]制备了5%wt Ce改性的H-SAPO-34酸性分子筛负载铜基催化剂,在K、Ca分别负载1%wt的共中毒条件下,催化剂在210—330 ℃仍表现出NO转化率>90%的优异性能。Ce添加剂使Cu2+物种溢出迁移至催化剂表面并促进其电子转移效应,改善氧化还原循环,Ce促进了酸性载体捕获碱(土)金属,自身也表现出与碱金属结合的能力。Peng等[17]利用Ce改性MnOx/TiO2催化剂以提高其抗碱性能,MnXCe1-XO2固溶体的形成使[O-Ce-O-Mn-O]单元在TiO2表面构建,由于Mn4+(0.067 nm)与Ce4+(0.101nm)离子半径与价电子的不同,K被拉离Ce且只与Mn结合,保留了充足的Lewis酸性位点捕获NH3。
Hu等[18]发现在V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂中掺杂Ce后,Ce3+的存在会引起氧空位及电荷不平衡现象,提高催化剂表面化学吸附氧含量,促进V4++Ce4+
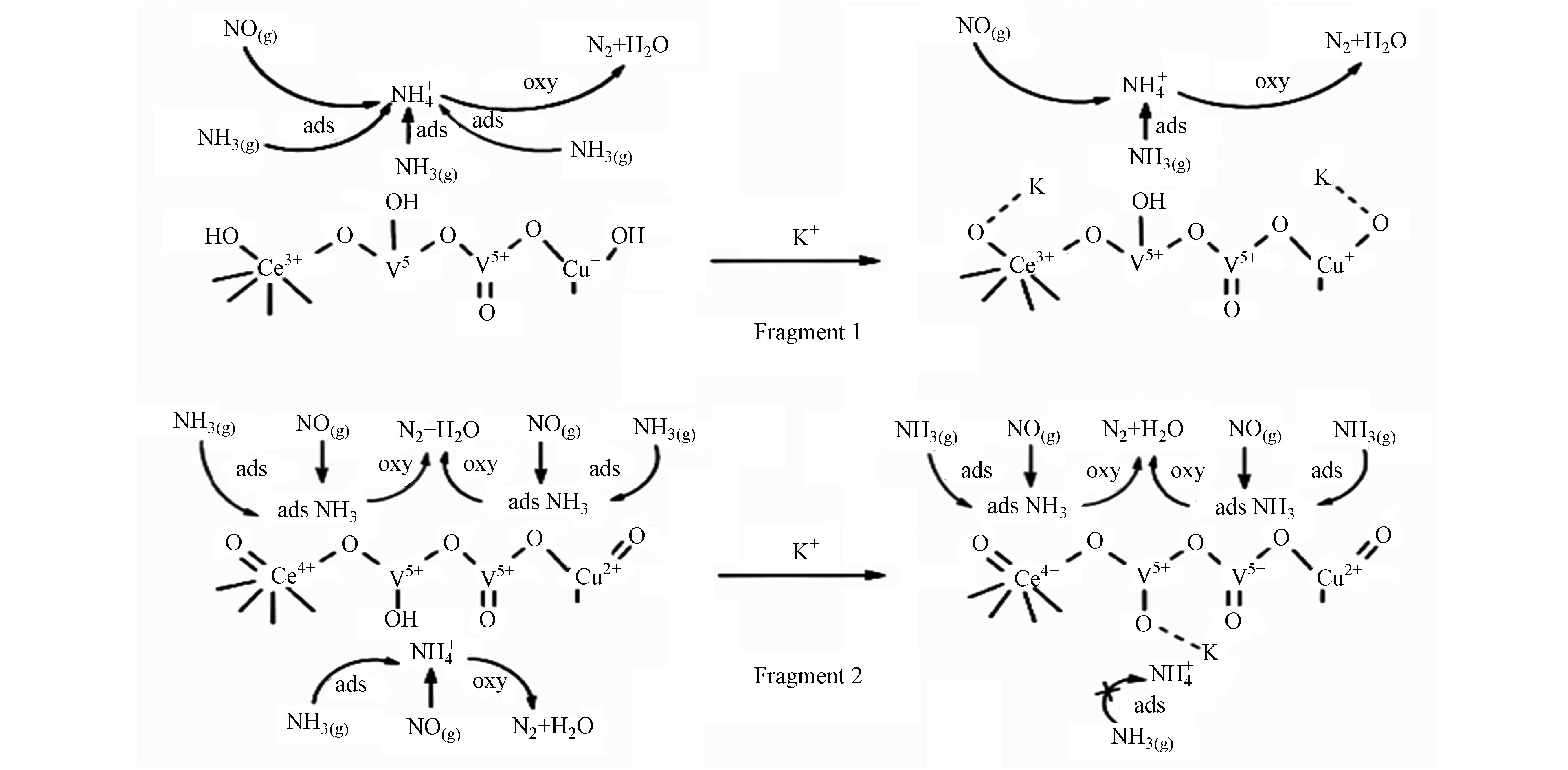
$\leftrightarrows $ V5++Ce3+氧化还原循环,诱导新B酸位点生成。Li等[19]利用0. 30%Ce和0.05%Cu改性的V2O5-WO3/TiO2催化剂在0.2%wt K中毒后仍保持89%的脱硝效率,而未改性催化剂中毒后脱硝效率只能维持在50%,VWCeCuTi催化剂抗碱金属中毒机理如图1所示,K破坏Brönsted酸位形成V5+—O—K导致NH3吸附量减少,而改性后催化剂仍遵循Eley-Rideal机理,Ce与Cu的协同作用使表面活性氧数量增加,并提供了额外的酸位点保持NH3吸附量。Yan等[20]模拟K/V物质的量比为4的中毒条件,传统钒钨钛催化剂几乎完全失活,而Ce-VWTi在350 ℃时仍可达到90%的氮氧化物转化率,这种现象也同样发生在Ca、Mg中毒情况下。XPS显示Ce添加使催化剂中毒后仍保留一定比例的Ce3+/Ce4+以维持Oα的含量,Ce作为活性中心参与到反应中,促进表面氧空位的产生以提高催化还原活性。Chen等[21]将10%wt Ce(SO4)2加入V2O5-TiO2催化剂后发现其在Na/V=1的中毒条件下仍有良好脱硝效率,350 ℃时氮氧化物转化率比同等条件下的市售VWTi催化剂高43.2%,Ce(SO4)2显著增强了催化剂表面酸性和氧化还原能力,SO42-更是促进了催化剂表面固体酸的形成,有利于NH3的吸附。Hu等[22]通过与市售V-W/Ti催化剂相比发现,V-Ce(SO4)2/Ti总酸度增加30%,在其上观察到由Ce引入而产生的更高比例表面活性氧和快速还原能力。Nie等[23]发现K+通过吸附在催化剂表面形成固体颗粒使其中毒,作者利用Ce(SO4)2取代传统钒钨钛催化剂中的WO3,由于铈离子优异的氧化还原性能和SO42−产生的酸性使得催化剂有良好抗碱金属中毒能力。
有趣的是,Wang等[24]发现适量碱金属也可在一定程度上促进SCR反应,作者将CeO2负载到硫酸化的ZrO2上进行1%wt K沉积中毒模拟,发现KCeSZ催化剂反而表现出更强催化还原活性,高SCR性能要求足够的表面酸度,但表面碱性的增加可加强对NO的吸附与氧化。Li等[25]也得出相同的结论,XRD与拉曼光谱显示CeO2-WO3催化剂在负载Ca后,原本分散良好的WOX转变为结晶的CaWO4物种。Ca中毒虽影响了催化剂结构、还原性及表面酸度,但其存在显著提高表面化学吸附氧和Ce4+含量及对NO2的吸附能力,增强Lewis酸数量与热稳定性,促进了L酸位上NO2和活性NHX的反应,以上现象可抵消中毒后催化剂酸位减少带来的部分不利影响。
-
研究表明将Ti引入催化剂可增强其氧化还原能力并提高催化剂表面总酸量。Xu等[26]利用Ti改性层间柱撑法合成的铁基蒙脱石催化剂Fe-Ti-MMT,该物质在24 h稳定性实验中SCR性能及抗中毒耐受性表现良好。引入Ti后提高了铁钛间电子转移能力,使铁倾向于转化为更易还原的低价态,通过Py-IR发现Ti修饰使催化剂形成更多Lewis酸中心,改变了碱金属结合位点以保护活性Fe位点免受中毒。Yan等[27]开发出TiO2修饰的酸化MnOX八面体分子筛催化剂OMS-5(H)@TiO2,在Ti/Mn物质的量比为0.4时催化剂有最好耐碱金属性能。OMS-5具有丰富的酸中心,引入Ti后发生相互作用使Ti失去电子从而增加Lewis酸中心的强度,同时导致Mn4+及表面吸附氧含量增加以提高催化活性。
-
MoO3是SCR催化剂重要添加剂,在反应中总是充当结构或化学促进剂[28]。Zhang等[29]将MoO3作为安全缓冲剂添加到Fe2O3/TiO2催化剂中,在Na+为500 μmol·g−1的毒性负载下,最优配比30%wt Fe2O3/15%wt MoO3/TiO2催化剂在整个实验温度范围内活性为新鲜催化剂的95%,表征结果表明Na+扩散进入MoO3层状结构中被固定以保护活性位点。Wang等[28]利用Mo改性钒-钛酸纳米管研究了对碱金属与磷中毒的双抗性效果,XPS显示Mo的添加使V4+物种和氧缺陷均随之增加,确保了表面上丰富的NO吸附及活化。Wu等[30]制作了Mo、Sb共掺杂的V0.04W0.03/TiO2催化剂有良好抗碱金属腐蚀能力,表征发现Mo的加入使催化剂增大比表面积且丰富了V4+和Oβ含量,TPR、TPD表征发现催化剂表面酸性和氧化还原能力的增强在抗碱金属中毒中起着关键作用。
-
Zr能提高催化剂表面化学吸附氧含量以增强催化剂氧化还原能力。Xue等[31]制备了Zr改性Cu/ZSM-5催化剂,XPS结果表明Ca负载使催化剂表面Cu原子量明显减少,而0.1%wt Zr掺杂增强了Cu表面分散性,是催化剂抗Ca中毒最主要的原因,同时Zr的引入削弱了CaO与CuO间相互作用,进一步促进了CuO的还原作用。Liu等[32]发现Zr掺杂能显著提高Ce/TiO2催化剂抗K中毒活性,并在Ti∶Zr =1∶1达到最佳效果,H2-TPR显示Zr加入后,Ce/TiO2还原峰在较低温度下出现,意味着催化剂表面氧迁移率增加,同时O2-TPD表明Zr可促进Ce/TiO2表面NO的氧化。Xu等[33]也在Zr负载的CeTiOX催化剂上发现被保留的Ce3+和氧缺陷,使其表现出更高氧化还原能力和表面酸性。Kang等[34]选择Fe3+与Zr4+共掺杂改性CeTiOX催化剂以提高其抗碱能力,Fe与Zr优先与K结合形成Fe-O-K与Zr-O-K物种保护了Ce-O-Ti,改性后催化剂得以保留还原性能促进NH3活化和NO氧化,Zr促进了Fe-O物种在催化剂表面的均匀分布,继而提供额外酸性位点。
-
利用酸位点较多的金属铌(Nb)改性催化剂也是提高碱金属耐受性的有效方法之一,Nb4+存在总是伴随着氧缺陷出现,可促进催化剂表面化学吸附氧的产生。Wang等[35]合成了以CeO2纳米管作为壳材料,掺杂Nb作为核相的新型催化剂。K中毒后Nb-CeNTs仍保持78%的NOX转化性能。H2-TPR和NH3-FTIR表征发现掺杂Nb有助于维持Nb5+/Nb4+和Ce4+/Ce3+氧化还原循环平衡,提高CeNTs氧化还原能力并在碱金属中毒后产生丰富Brönsted酸性位点来缓解中毒情况。黄力等[36]制备的Nb改性V-Mo/Ti催化剂也发现Nb可显著提高催化剂表面酸性和化学吸附氧数量,有效缓解碱金属对催化剂的毒害作用。Wang等[37]发现Nb掺杂的CuNbTi催化剂在2% K2O条件下仍可保持80%的NOX转化率和高达98%的N2选择性,而传统VWTi催化剂在K负载后表面活性相颗粒发生团聚导致完全失活。Jiang等[38]对比不同方法制备的Ce-Nb-Ti催化剂对K的耐受性,发现浸渍法使催化剂表面获得更多Ce3+及化学吸附氧含量,其表面强大还原能力和可观数量的Lewis酸性位点对碱金属有良好抗性。Ma等[39]以草酸铌为前驱体通过溶胶凝胶法制备的Nb-Ce/WOX-TiO2催化剂对抗碱金属K中毒有良好效果,催化剂表征发现NbCe/WTi上形成了与聚合NbOX物种相关的酸性位点,且由于Nb-O-Ce中Nb5+与Ce4+间电荷不平衡现象导致催化剂表面活性氧含量明显增加。
-
提高耐碱性的一个可行方法是采用强酸性载体,该载体提供足够的酸性位点与碱性离子相互作用,从而保护活性位点[40]。
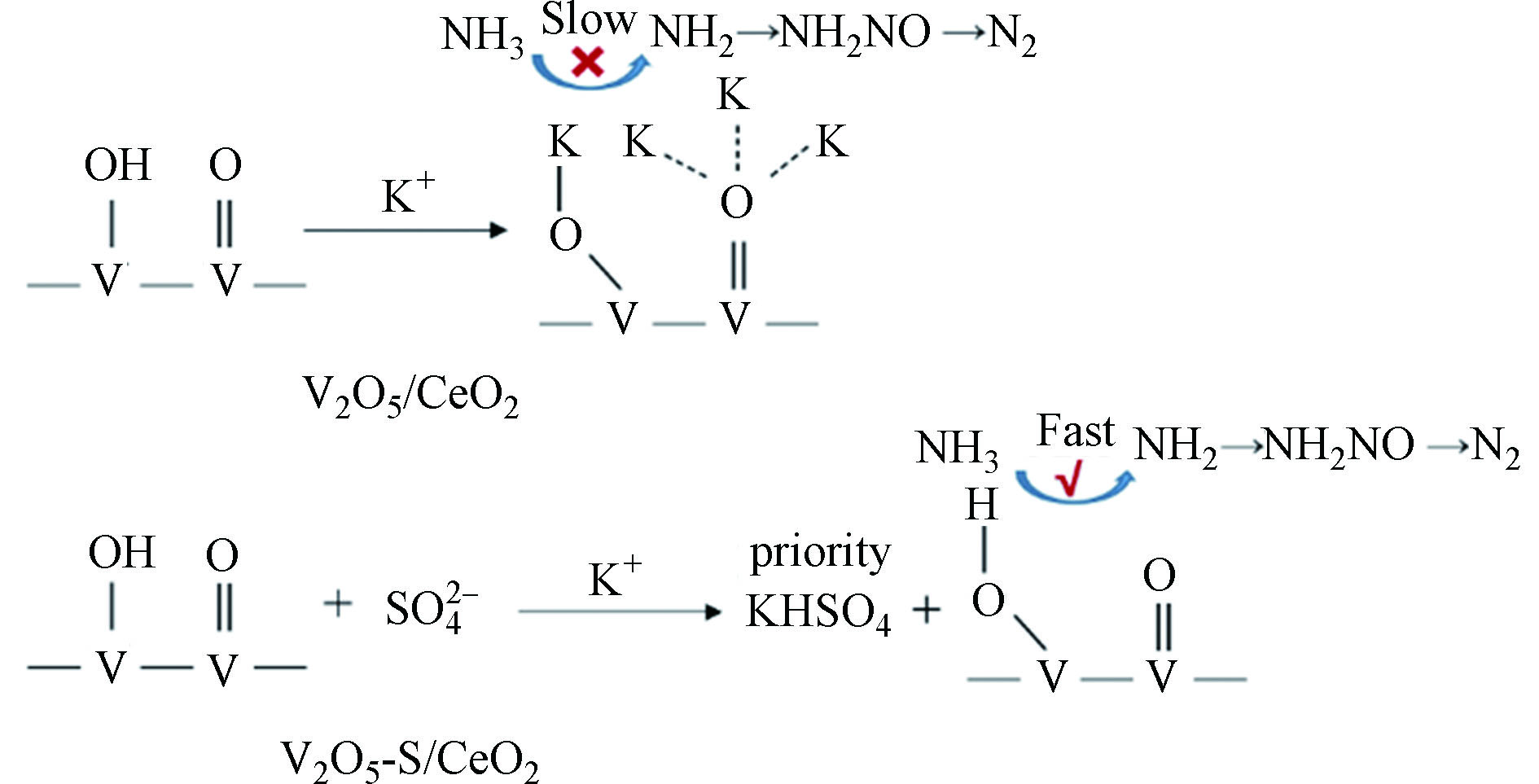
Zhou等[8]利用VOSO4代替NH4VO3作为V2O5制备前驱体合成V2O5-S/CeO2催化剂,并用浸渍法负载1%wt K2O模拟中毒实验,含有SO42−的催化剂在260—370 ℃的温度范围内显示出90%以上的NO转化率和良好的N2选择性,而反观没有SO42−的V2O5/CeO2催化剂NO转化率下降到80%以下且在高温区出现N2选择性下降现象。V2O5-S/CeO2在240 ℃的长期稳定性实验中也保持了良好性能,24 h内NO转化率几乎不变。作者通过原位拉曼光谱揭示催化剂抗中毒机理如图2所示,催化剂在100℃暴露于1000×10−6的NH3时,K中毒处理的催化剂在原位拉曼光谱中出现KHSO4,表明碱金属在中毒过程中更愿意与SO42−结合形成硫酸盐从而保护V=O物种,而在V2O5/CeO2催化剂中K取代NH3与V=O物种作用导致NH3几乎不吸附。Du等[41]制备了Cu、Fe硫酸盐改性的铈钛混合氧化物,催化剂负载1.2%wt K2O中毒后在300—350 ℃范围内NO转化率保持在80%以上,硫酸盐改性的催化剂具有“双位点效应”,K+将Cu—SO4断键并与SO42-结合,同时释放Cu形成新的CuOX活性位点。
Song等[42]发现硫酸化的FeSTi固体超强酸催化剂利用部分硫位点捕获碱(土)金属形成相应硫酸盐,其余硫作为活性位点增强催化剂Lewis酸强度,负载1%wt K2O和2%wt CaO的催化剂在特定温度范围内NOX转化率均达90%以上。Zhou等[43]对CeO2催化剂进行硫酸化处理,发现吸附在K/CeO2-S和CeO2-S上NH3物种强度相似,原位红外研究表明硫酸化导致了催化剂明显改善Brönsted酸位点。Yao等[44]同样发现硫酸处理可提高CeO2-TiO2/P25催化剂表面酸性,促进NH3物种吸附。Gao等[45]利用硫酸化处理载体合成的CeO2/SO42−-ZrO2固体超强酸催化剂因显著增强的催化剂表面酸性而获得优异碱金属抗性,K/Ce物质的量比为0.4的中毒条件下,催化剂在380 ℃、GHSV=180000 h−进行了长达168 h的脱硝效率测试,其一直保持高于85%的NO转化率且随时间延长并未有下降的趋势。
-
SCR催化剂最为有效的抗中毒方法是彻底分离活性位点和碱金属毒化位点,并可为后续毒化位点定向去除或原位再生技术提供研究基础。
Du等[46]利用具有微孔结构的硅铝酸盐矿物HY作为载体与缓冲区保护催化剂活性Fe2O3物种,在Na+为1000 μmol·g−1中毒条件下仍保持对NH3-SCR反应100%原始催化活性。吡啶红外光谱和H2-TPR显示Fe2O3/HY中毒前后催化剂酸性位点及还原性几乎无变化。HY优异的阳离子交换能力使碱(土)金属交换嵌入到沸石微孔中并固定在内部,减少外部沉积覆盖活性位点的现象发生。Zha等[47]开发出hollandite型结构的Mn-Ti氧化物与Cu-SAPO-34复合的催化剂(HMT@Cu-S),碱金属K中毒后在260—350 ℃仍然保持80%以上的NO转化率。其特殊结构的锰钛氧化物因离子交换机制形成抗中毒的有效保护层,原位漫反射红外光谱显示,催化剂碱金属中毒后拥有更高的NH3、NOX吸附量,且物种不稳定易于参与SCR反应。Zha等[48]设计了Fe掺杂的氧化锰八面体分子筛催化剂OMS-2,其载体孔道内位点可通过离子交换机制而捕获碱金属,使催化剂中毒后仍保留大量酸性位点以供吸附氮氧化物。Hu等[49]提出锰钡矿HMO孔道捕获碱金属离子交换配位机制,结合DFT计算发现,碱金属离子先通过离子交换机制与HMO中Brönsted酸位点质子发生反应,后经过配位机制固定在HMO孔道内尺寸合适的空穴中。Liu等[50]发现V5+改性六方MoO3合成的V-HMO因其强酸性和大量孔道结构而作为拥有碱金属捕获位点的催化剂载体。利用V-HMO载体复合V2O5活性组分后在抗碱金属中毒方面表现出优异效果,200—350 ℃测试温区内脱硝效率均有上升,甚至在300 ℃时效率提高80%以上。
Huang等[51]发现,六方结构HWO因其强酸性可提供丰富的高特异性碱(土)金属捕获位点,即使在高浓度SO2存在条件下依然可以精准捕获碱金属。传统钒钨钛催化剂在低负载毒性115 μmol·g−1cat耐碱性也很差,并在4 h后完全失活,利用HWO作为催化剂载体在高毒性负载350 μmol·g−1cat和GHSV=200000 h−1条件下催化活性迅速达到高效稳定状态,NO转化率保持在92%。作者通过DFT计算得出,相比于表面结合,K+固定在HWO孔道内节约了2.31 eV的能量,且与孔道壁内氧原子形成稳定配位构型,从而有效保护活性组分V2O5免受中毒。Zheng等[52]研究V2O5/HWO也得出相似的结论,HWO拥有空间分离的催化活性位点和碱金属捕获位点,K+与捕获位点上的O间电子转移作用是抗中毒机制的驱动力。Huang[53]等同样认为HWO的高抗碱性来自于活性位点结合的K+自发向催化剂内部孔道迁移的保护机制。
Liu等[54]制作合成的核壳催化剂在抗碱金属方面有不俗表现,以负载FeOX纳米粒子的小颗粒状Beta分子筛为核,介孔CeO2薄膜为壳,合成Fe/Beta@Meso-CeO2纳米结构核壳型NH3-SCR催化剂,K-Fe/Beta@Meso-CeO2在<600 ℃的温度范围内比没有CeO2薄膜包覆的催化剂显示出更优异的催化性能,甚至高于新鲜Fe/Beta。NO+O2共吸附原位红外揭示介孔CeO2层壳形成有效保护层防止K+与Brönsted酸位上孤立的Fe3+交换形成非活性寡核FeXOY团簇。Huang等[55]发现与普通负载相比,核壳结构的MnFeOX@TiO2催化剂表现出优异耐钾性,钛壳一方面通过捕获碱金属保护壳内活性成分,另一方面促进NOX和NH3的吸附加强NH3-SCR反应。
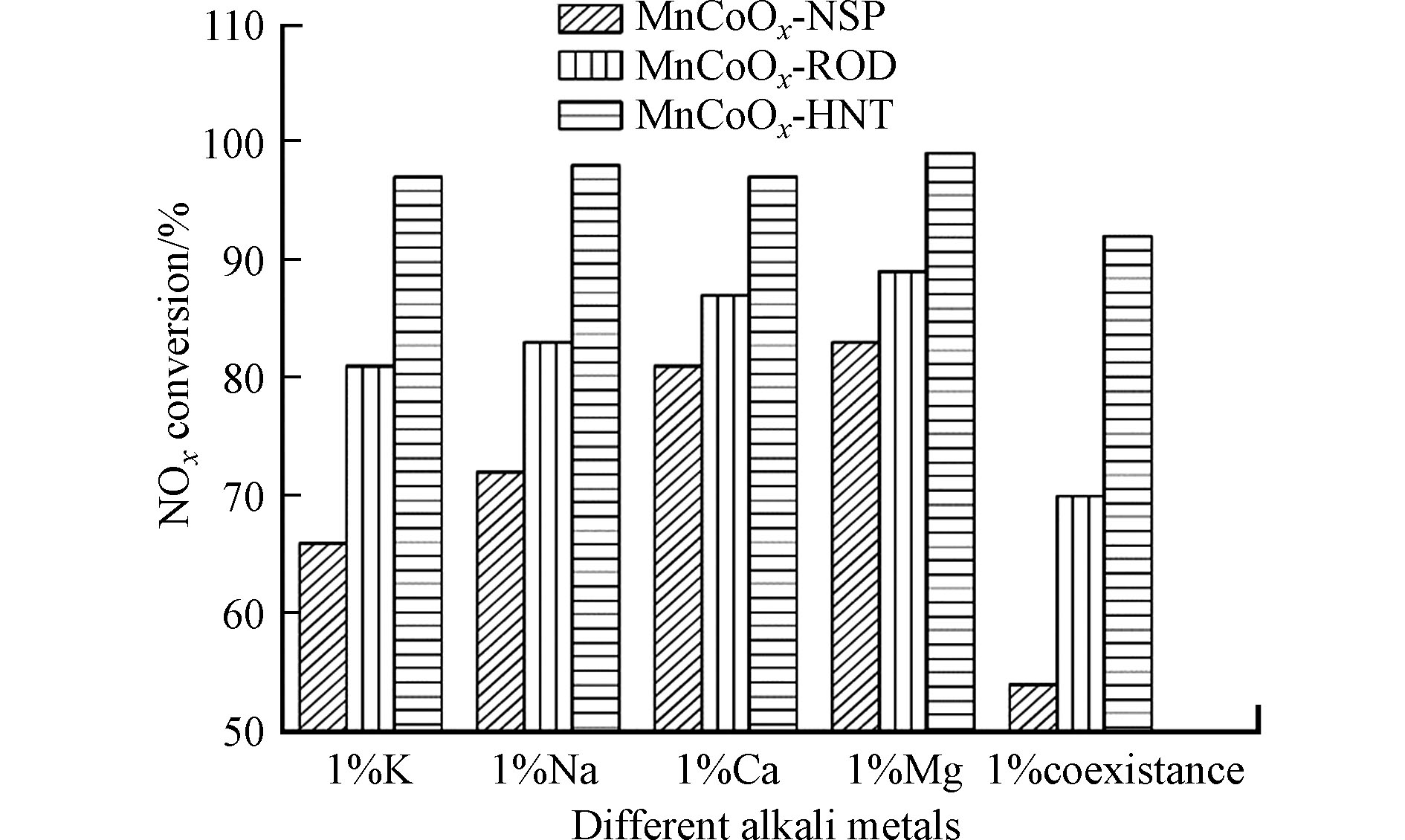
Chen等[56]制备了CeO2纳米颗粒沉积的钛酸盐纳米管(TNTs)催化剂因其壳层保护机制而免受严重的碱金属中毒,夹层中H2Ti12O25孔道内质子可与Na+进行离子交换将其锁定为NaXH2-XTi12O25。Wang等[57]以乙醇洗涤的钛酸盐纳米管为载体负载铈基催化剂,添加Na+、K+、Ca2+后NO转化率高达97%、88%、95%。其显著的抗碱(土)金属中毒能力主要源于改性纳米管中结构性可离子交换羟基的增加,这种变化极大的增强了催化剂表面酸性,且一定程度上在CeO2上保持了较大比例的Ce3+和氧空位含量。Shi等[58]利用乙酰丙酮金属盐为前驱体制备的MnCoOX-HNT中空纳米管催化剂可提供大量酸位点,MnCoOX-HNT在不同中毒条件下NOX转化率如图3所示,Na、K、Ca、Mg分别0.25wt%共存时,其NOX转化率仍保持92.2%的高效水平,显示了在多物种混合环境下的应用潜力。MnCoOX-HNT突出的抗中毒能力归因于中空纳米管独特的结构可有效保护催化剂内表面活性位点,其表面丰富的羟基作为牺牲位点固定碱(土)金属。
-
目前废弃催化剂处理成为一大难题,SCR催化剂因中毒或自身活性组分的生物毒性而填埋受限,再生以最大限度的恢复其结构和理化性质成为良好发展趋势[59]。再生技术作为一种循环思想,是实现延续SCR催化剂使用寿命,减缓失效催化剂处理压力的重要手段,催化剂再生取代更换新鲜催化剂可降低SCR运行成本[60]。
-
水洗法是恢复失活催化剂活性成本较小、易于实现的再生方法。Peng等[61]发现利用水洗法可恢复碱金属中毒CeO2-WO3催化剂活性,再生催化剂在160 ℃以下氮氧化物转化率甚至超越新鲜催化剂,通过DFT理论计算推测这种现象可能是表面羟基的促进作用所导致,H2O在催化剂表面解离为H+和OH−,H+与表面氧原子紧密结合并形成新的Brönsted酸位。Cimino等[62]取用城市垃圾焚烧炉尾气处理的SCR装置中运行18000 h的商用VWTi催化剂进行水洗再生,发现水洗法可有效恢复催化剂比表面积,且对溶解度较低的硫酸钙小颗粒有浸出作用。Shen等[63]分别对比水洗法和酸洗法处理的Na、K中毒Mn-CeO2/Zr分层粘土催化剂的失活恢复效果,结果表明水洗法可有效去除中毒催化剂中钠盐与钾盐,其优势在于很大程度上减少了锰铈活性组分的流失。
-
稀硫酸再生是SCR催化剂碱金属中毒后常用的有效再生方法,但其强酸性会降低催化剂机械稳定性,并同时浸渍出大量活性组分使其流失,需后续增加活化液浸渍环节以保证催化剂高效脱硝率。Liu等[64]利用H2SO4溶液再生钾中毒催化剂有良好效果,但强烈的酸溶液同时也造成催化剂表面部分活性组分的流失,作者随即将CeO2掺杂到催化剂中以补充流失的活性组分。Li等[65]发现利用乙酸酸洗碱金属中毒催化剂可获得优异再生效果,而活性组分几乎不受影响,与传统硫酸酸洗法相比省去活化液浸泡步骤。Wang等[66]利用草酸和硅钨酸再生K2O中毒的CuNbTi催化剂,在300—350 ℃范围内两种酸再生的催化剂均显示90%以上的NOX转化率,XRD、XPS等表征发现再生并未破环纳米管的结构,还使表面酸位、化学吸附氧及Cu+比例明显提升。Wang等[60]开发的酸洗再生法可以达到去除毒物并原位增强催化剂进一步的抗碱能力,最具效益的酸液组合0.10 mol·L−1 H2SO4和0.10 mol·L−1 (NH4)2S2O8可使再生催化剂在240—410 ℃的较宽温度范围内NOX转化率高于80%,较温和的酸洗方法使再生过程中只有8%V和12%W流失,S2O82−基团的引入在活化过程中提高了催化剂表面酸性。
-
利用表面活性剂去除催化剂中碱土金属有成本低、效率高及活性成分损失少等优点,有良好工业应用前景。Li等[59]利用烷基酚聚氧乙烯(10)醚(OP-10)实现了Ca毒性78%的去除,使催化剂在300—500 ℃内有80%以上NOX转化率,表征发现再生使其恢复大量Brönsted酸位点和羟基位点,保留了大部分钒和钨,无需额外活性成分补充。Li等[67]利用羟基亚乙基二膦酸(HEDP)在弱酸环境下提高碱土金属溶解性能并定向络合Ca2+,1%wt HEDP对中毒催化剂进行再活化,350 ℃时NOX转化率可恢复至96%,对活性组分钒损失35%。
-
随着量子化学技术的进步,密度泛函理论(density functional theory,DFT)逐渐应用于各研究领域,DFT致力于用简单电子密度取代复杂多电子波函数作为研究基本量,基于此的第一性原理计算可以在分子水平上揭示碱金属对SCR催化剂的中毒效应机理及探索提高SCR催化剂对碱金属的耐受性机制。
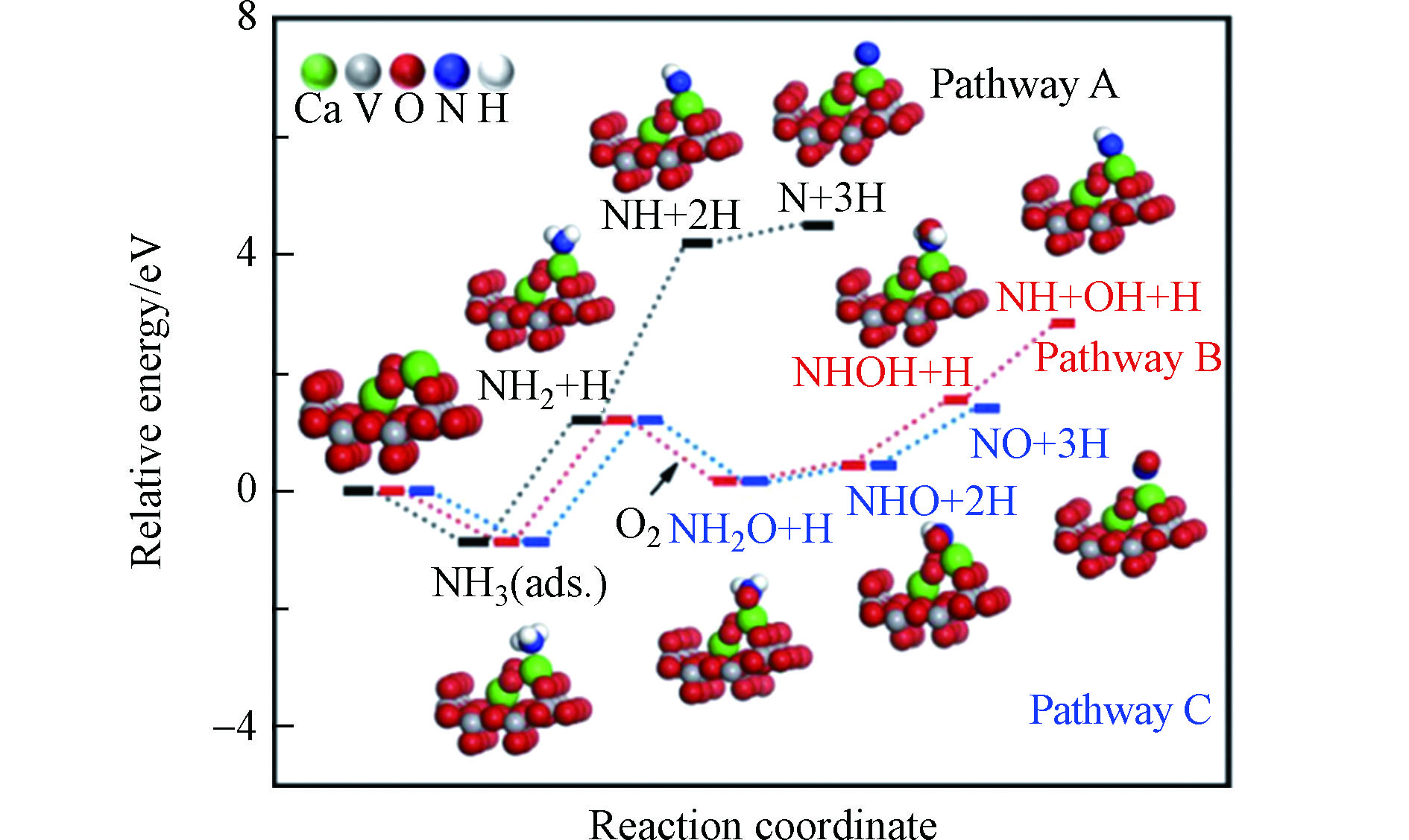
Zheng等[68]利用DFT理论计算模拟Ca对钒基催化剂的毒化作用,通过比较不同反应路径(如图4)发现NH3吸附在CaO位点上发生氧化反应遵循:NH3(ads.)→NH2→NH2O→NHO→NO的过程,揭示了碱土金属中毒后NH3-SCR和NH3氧化反应间的竞争机制。Lyu等[69]研究了Na、K对Brönsted酸位点的影响,发现相比于新鲜α-Fe2O3催化剂中N-H距离0.169 nm来说,Na、K中毒后N-H距离增大到0.286 nm和0.298 nm,表明NH3分子在中毒后远离了Brönsted酸位点并削弱与之相互作用的能力,导致催化剂脱硝效率下降。
Wang等[37]利用广义梯度近似(GGA)法进行了密度泛函理论计算,将K原子作为探针与CuNbTi催化剂上4个功能位点结合,其结合能遵循Ti-OH>Nb-OH>Nb=O>Ti=O顺序,分别为−1.08 eV、−2.33 eV、−2.83 eV、−3.44 eV,基于铜钛催化剂合成过程,Cu与H优先消耗Ti=O,而K则与Nb-OH、Nb=O结合生成KNbO3以保护活性铜物种。Cai等[70]开发出CeO2-SnO2@ SO42−/TiO2超强酸催化剂,在GHSV=100000 h−1下表现出良好抗碱金属(K)和碱土金属(Ca)中毒性能,DFT计算活性位点与K结合能表明K首先倾向于和TiO2/SO42−结合,当表面硫酸根被消耗完后,催化剂本相中SO42−会被K诱导迁移至表面继续反应,为XPS显示中毒后催化剂表面硫含量增加提供合理解释。
-
SCR技术是目前最成熟有效的控制NOX排放的方法之一,但SCR催化剂对烟气中毒性物质抵抗力较弱,极大的限制了催化剂使用效果及寿命,因此对碱(土)金属毒化催化剂机理的探究可帮助研发更具碱(土)金属耐受性的高效催化剂,目前研究集中在单一物种中毒情况下中毒机理及改性再生的探究,在未来发展中应更注重以下几点:
(1)多数催化剂利用简单浸渍法负载毒物以模拟中毒实验,与实际应用中碱金属中毒过程差异较大,在今后研究中应向实际中毒过程靠拢,研究开发更具实际应用性能的抗中毒SCR催化剂。
(2)烟气中含有多种导致SCR催化剂中毒失活的成分:碱(土)金属、重金属、SO2及水蒸气等,单一毒物作用情况在现实应用中基本不可能存在,需要更多研究多物种联合中毒条件下SCR催化剂的抗中毒能力,提出多抗策略。
(3)既有多物种共中毒情况,应考虑在多重毒物联合条件下开发再生方法以追求理想再生效果。
(4)量子化学理论计算可从微观角度辅助阐述实验反应机理,是催化剂研究领域的有利方法之一,但目前应用有限。应在今后研究中将理论计算与实验紧密结合,开发出绿色无害、稳定高效的脱硝催化剂。
SCR催化剂抗碱(土)金属中毒及再生研究进展
Research progress on resistance to alkali (alkaline earth) metal poisoning and regeneration of SCR catalysts
-
摘要: 控制氮氧化物排放技术中,选择性催化还原(SCR)法因脱硝效率高且技术成熟稳定成为目前广泛应用的技术,烟气中碱(土)金属导致催化剂活性中心的失活现象是目前工业烟气SCR脱硝催化剂应用的一个瓶颈。基于此,开发有良好碱(土)金属耐受性的低温高效SCR催化剂是当务之急。本文整理和归纳了SCR催化剂碱(土)金属中毒机理,探讨了提高催化剂抗碱(土)金属中毒的改性方法及作用机制、中毒催化剂的再生方法及量子化学计算的应用,最后对SCR催化剂的未来研究发展方向进行了展望。Abstract: Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) method has attracted much attention in nitrogen oxide emission controlling technology because of excellent denitrification performance and stable application. The deactivation of catalyst active sites caused by alkali (earth) metals in flue gas is one of the bottlenecks which limits the industrial application of catalysts. In this paper, the mechanism of the poisoning effect of alkali (earth) metals on SCR catalysts was summarized in detail. The modification methods and mechanism of improving the catalyst resistance to alkali (earth) metal poisoning were discussed. The regeneration methods of poisoned catalyst and the application of quantum chemical calculation were explored. Finally, the future research direction of SCR catalysts was prospected, which is helpful to provide references for the development of efficient and stable SCR catalysts.
-
Key words:
- SCR catalyst /
- resistance to alkali (earth) metal poisoning /
- regeneration /
- DFT
-

-
-
[1] 李国亮. 氮氧化物对环境的危害及污染控制技术 [J]. 山西化工, 2019, 39(5): 123-124,135. doi: 10.16525/j.cnki.cn14-1109/tq.2019.05.44 LI G L. Hazards of nitrogen oxides to the environment and pollution control technology [J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(5): 123-124,135(in Chinese). doi: 10.16525/j.cnki.cn14-1109/tq.2019.05.44
[2] WALTERS W W, THARP B D, FANG H, et al. Nitrogen isotope composition of thermally produced NOx from various fossil-fuel combustion sources [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(19): 11363-11371. [3] CHU B W, MA Q X, LIU J, et al. Air pollutant correlations in China: Secondary air pollutant responses to NOx and SO2 control [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2020, 7(10): 695-700. [4] 王军霞, 李曼, 敬红, 等. 我国氮氧化物排放治理状况分析及建议 [J]. 环境保护, 2020, 48(18): 24-27. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2020.18.004 WANG J X, LI M, JING H, et al. Analysis and suggestions on nitrogen oxide emission control in China [J]. Environmental Protection, 2020, 48(18): 24-27(in Chinese). doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2020.18.004
[5] XIONG S C, WENG J X, LIAO Y, et al. Alkali metal deactivation on the low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over MnOx-CeO2: A mechanism study [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(28): 15299-15309. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b05175 [6] ZHU N, SHAN W P, SHAN Y L, et al. Effects of alkali and alkaline earth metals on Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124250. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124250 [7] 周学荣, 张晓鹏. SCR催化剂碱(土)金属中毒的研究进展 [J]. 化学通报, 2015, 78(7): 590-596. doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2015.07.002 ZHOU X R, ZHANG X P. Research progress in alkali metal poisoning of selective catalytic reduction catalysts [J]. Chemistry, 2015, 78(7): 590-596(in Chinese). doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2015.07.002
[8] ZHOU G Y, MAITARAD P, WANG P L, et al. Alkali-resistant NOx reduction over SCR catalysts via boosting NH3 adsorption rates by in situ constructing the sacrificed sites [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(20): 13314-13321. [9] SZYMASZEK A, SAMOJEDEN B, MOTAK M. The deactivation of industrial SCR catalysts—A short review [J]. Energies, 2020, 13(15): 3870. doi: 10.3390/en13153870 [10] 袁玲, 邱兆富, 杨骥, 等. SCR催化剂碱(土)金属中毒及其改性再生研究进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(4): 117-121. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201804024 YUAN L, QIU Z F, YANG J, et al. Research progress of alkali (alkaline earth) metal poisoning and modified regeneration of scr catalyst [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(4): 117-121(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201804024
[11] SU Z H, REN S, CHEN Z C, et al. Deactivation effect of CaO on Mn-Ce/AC catalyst for SCR of NO with NH3 at low temperature [J]. Catalysts, 2020, 10(8): 873. doi: 10.3390/catal10080873 [12] ZHOU J, GUO R T, ZHANG X F, et al. Cerium oxide-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: A review [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(4): 2981-2998. [13] YAN L J, JI Y Y, WANG P L, et al. Alkali and phosphorus resistant zeolite-like catalysts for NOx reduction by NH3 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(14): 9132-9141. [14] CAO J, YAO X J, CHEN L, et al. Effects of different introduction methods of Ce4+ and Zr4+ on denitration performance and anti-K poisoning performance of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(11): 1207-1214. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2019.11.005 [15] CAO J, YAO X J, YANG F M, et al. Improving the denitration performance and K-poisoning resistance of the V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst by Ce4+ and Zr4+ co-doping [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 40(1): 95-104. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(18)63184-5 [16] WANG P L, YAN L J, GU Y D, et al. Poisoning-resistant NOx reduction in the presence of alkaline and heavy metals over H-SAPO-34-supported Ce-promoted Cu-based catalysts [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(10): 6396-6405. [17] PENG Y, LI J H, SI W Z, et al. Ceria promotion on the potassium resistance of MnOx/TiO2 SCR catalysts: An experimental and DFT study [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 269: 44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.052 [18] HU G, YANG J, TIAN Y M, et al. Effect of Ce doping on the resistance of Na over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2018, 104: 112-118. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.04.009 [19] LI H R, MIAO J F, SU Q F, et al. Improvement in alkali metal resistance of commercial V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts modified by Ce and Cu [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(24): 14707-14719. doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-03919-5 [20] YAN Z D, SHI X Y, YU Y B, et al. Alkali resistance promotion of Ce-doped vanadium-titanic-based NH3-SCR catalysts [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 73: 155-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.01.024 [21] CHEN Y R, WANG M X, DU X S, et al. High resistance to Na poisoning of the V2O5-Ce(SO4)2/TiO2 catalyst for the NO SCR reaction [J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2018, 18(12): 2948-2955. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2017.11.0521 [22] HU W S, ZHANG Y H, LIU S J, et al. Improvement in activity and alkali resistance of a novel V-Ce(SO4)2/Ti catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 206: 449-460. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.036 [23] NIE H, LI W, WU Q R, et al. The poisoning of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 and V2O5-Ce(SO4)2/TiO2 SCR catalysts by KCl and the partial regeneration by SO2 [J]. Catalysts, 2020, 10(2): 207. doi: 10.3390/catal10020207 [24] WANG H Q, GAO S, YU F X, et al. Effective way to control the performance of a ceria-based DeNOx catalyst with improved alkali resistance: Acid–base adjusting [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(27): 15077-15084. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b00793 [25] LI X, LI X S, LI J H, et al. High calcium resistance of CeO2-WO3 SCR catalysts: Structure investigation and deactivation analysis [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 317: 70-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.027 [26] XU D, WU W H, WANG P L, et al. Boosting the alkali/heavy metal poisoning resistance for NO removal by using iron-titanium pillared montmorillonite catalysts [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 399: 122947. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122947 [27] YAN L J, GU Y D, HAN L P, et al. Dual promotional effects of TiO2-decorated acid-treated MnOx octahedral molecular sieve catalysts for alkali-resistant reduction of NOx [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(12): 11507-11517. [28] WANG P L, GAO S, WANG H Q, et al. Enhanced dual resistance to alkali metal and phosphate poisoning: Mo modifying vanadium-titanate nanotubes SCR catalyst [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2018, 561: 68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2018.05.023 [29] ZHANG J, HUANG Z W, DU Y Y, et al. Alkali-poisoning-resistant Fe2O3/MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for the selective reduction of NO by NH3: The role of the MoO3 safety buffer in protecting surface active sites [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(1): 595-603. [30] WU P, SHEN K, LIU Y L, et al. Enhanced activity and alkali metal resistance in vanadium SCR catalyst via co-modification with Mo and Sb [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, 11(12): 4115-4132. [31] XUE H Y, MENG T, LIU F F, et al. Enhanced resistance to calcium poisoning on Zr-modified Cu/ZSM-5 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(66): 38477-38485. doi: 10.1039/C9RA07722G [32] LIU S W, GUO R T, SUN X, et al. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx over Ce/TiZrOx catalyst: The promoted K resistance by TiZrOx support [J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2019, 462: 19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.015 [33] XU B Q, XU H D, LIN T, et al. Promotional effects of Zr on K+-poisoning resistance of CeTiOx catalyst for selective catalytic reductionof NOx with NH3 [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(8): 1354-1361. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)61102-0 [34] KANG K K, YAO X J, HUANG Y K, et al. Insights into the co-doping effect of Fe3+ and Zr4+ on the anti-K performance of CeTiOx catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 125821. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125821 [35] WANG P L, CHEN S, GAO S, et al. Niobium oxide confined by ceria nanotubes as a novel SCR catalyst with excellent resistance to potassium, phosphorus, and lead [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 231: 299-309. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.024 [36] 黄力, 王虎, 纵宇浩, 等. Nb改性V-Mo/Ti脱硝催化剂的抗Na中毒性能研究 [J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2020, 48(5): 34-37,83. HUANG L, WANG H, ZONG Y H, et al. Study on the anti-Na poisoning performance of Nb modified V-Mo/Ti denitration catalyst [J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2020, 48(5): 34-37,83(in Chinese).
[37] WANG X X, CONG Q L, CHEN L, et al. The alkali resistance of CuNbTi catalyst for selective reduction of NO by NH3: A comparative investigation with VWTi catalyst [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 246: 166-179. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.049 [38] JIANG Y, GAO W Q, BAO C Z, et al. Comparative study of Ce-Nb-Ti oxide catalysts prepared by different methods for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2020, 496: 111161. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2020.111161 [39] MA Z R, WENG D, WU X D, et al. A novel Nb-Ce/WOx-TiO2 catalyst with high NH3-SCR activity and stability [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2012, 27: 97-100. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2012.07.006 [40] KHAN M N, HAN L P, WANG P L, et al. Tailored alkali resistance of DeNOx catalysts by improving redox properties and activating adsorbed reactive species [J]. iScience, 2020, 23(6): 101173. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101173 [41] DU X S, WANG X M, CHEN Y R, et al. Supported metal sulfates on Ce-TiOx as catalysts for NH3-SCR of NO: High resistances to SO2 and potassium [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2016, 36: 271-278. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2016.02.013 [42] SONG L, YUE H R, MA K, et al. FeSTi superacid catalyst for NH3-SCR with superior resistance to metal poisons in flue gas [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(45): 16878-16888. [43] ZHOU Z Z, LAN J M, LIU L Y, et al. Enhanced alkali resistance of sulfated CeO2 catalyst for the reduction of NOx from biomass fired flue gas [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2021, 149: 106230. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2020.106230 [44] YAO X J, KANG K K, CAO J, et al. Enhancing the denitration performance and anti-K poisoning ability of CeO2-TiO2/P25 catalyst by H2SO4 pretreatment: Structure-activity relationship and mechanism study [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 269: 118808. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118808 [45] GAO S, WANG P L, CHEN X B, et al. Enhanced alkali resistance of CeO2/SO42––ZrO2 catalyst in selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2014, 43: 223-226. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.10.017 [46] DU Y Y, HUANG Z W, ZHANG J, et al. Fe2O3/HY catalyst: A microporous material with zeolite-type framework achieving highly improved alkali poisoning-resistant performance for selective reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(12): 7078-7087. [47] ZHA K W, KANG L, FENG C, et al. Improved NOx reduction in the presence of alkali metals by using hollandite Mn–Ti oxide promoted Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2018, 5(6): 1408-1419. doi: 10.1039/C8EN00226F [48] ZHA K W, FENG C, HAN L P, et al. Promotional effects of Fe on manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves for alkali-resistant catalytic reduction of NOx: XAFS and in situ DRIFTs study [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122764. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122764 [49] HU P P, HUANG Z W, GU X, et al. Alkali-resistant mechanism of a hollandite DeNOx catalyst [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(11): 7042-7047. [50] LIU X N, GAO J Y, CHEN Y X, et al. Rational design of alkali-resistant NO reduction catalysts using a stable hexagonal V-doped MoO3 support for alkali trapping [J]. ChemCatChem, 2018, 10(18): 3999-4003. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201800818 [51] HUANG Z W, LI H, GAO J Y, et al. Alkali- and sulfur-resistant tungsten-based catalysts for NOx emissions control [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(24): 14460-14465. [52] ZHENG L, ZHOU M J, HUANG Z W, et al. Self-protection mechanism of hexagonal WO3-based DeNOx catalysts against alkali poisoning [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(21): 11951-11956. [53] HUANG Z W, GU X, WEN W, et al. A “smart” hollandite DeNO(x) catalyst: Self-protection against alkali poisoning [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2013, 52(2): 660-664. doi: 10.1002/anie.201205808 [54] LIU J X, LIU J, ZHAO Z, et al. Fe/Beta@Meso-CeO2 nanostructure core-shell catalyst: Remarkable enhancement of potassium poisoning resistance [J]. Catalysis Surveys from Asia, 2018, 22(4): 181-194. doi: 10.1007/s10563-018-9251-8 [55] HUANG C Y, GUO R T, PAN W G, et al. SCR of NOx by NH3 over MnFeOx@TiO2 catalyst with a core-shell structure: The improved K resistance [J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2019, 92(5): 1364-1378. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2018.09.005 [56] CHEN X B, WANG H Q, WU Z B, et al. Novel H2Ti12O25-confined CeO2 catalyst with remarkable resistance to alkali poisoning based on the “shell protection effect” [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(35): 17479-17484. doi: 10.1021/jp205069w [57] WANG P L, WANG H Q, CHEN X B, et al. Novel SCR catalyst with superior alkaline resistance performance: Enhanced self-protection originated from modifying protonated titanate nanotubes [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(2): 680-690. doi: 10.1039/C4TA03519D [58] SHI Y R, YI H H, GAO F Y, et al. Facile synthesis of hollow nanotube MnCoOx catalyst with superior resistance to SO2 and alkali metal poisons for NH3-SCR removal of NOx [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 265: 118517. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118517 [59] LI X S, LIU C D, LI X, et al. A neutral and coordination regeneration method of Ca-poisoned V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2017, 100: 112-116. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2017.06.034 [60] WANG Y J, GE D J, CHEN M X, et al. A dual-functional way for regenerating NH3-SCR catalysts while enhancing their poisoning resistance [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2018, 117: 69-73. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.08.028 [61] PENG Y, LI J H, CHEN L, et al. Alkali metal poisoning of a CeO2-WO3 catalyst used in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: An experimental and theoretical study [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(5): 2864-2869. [62] CIMINO S, FERONE C, CIOFFI R, et al. A case study for the deactivation and regeneration of a V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst in a tail-end SCR unit of a municipal waste incineration plant [J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(5): 464. doi: 10.3390/catal9050464 [63] SHEN B X, YAO Y, CHEN J H, et al. Alkali metal deactivation of Mn-CeOx/Zr-delaminated-clay for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 180: 262-269. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.07.004 [64] LIU S J, JI P D, YE D, et al. Regeneration of potassium poisoned catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2019, 19(3): 649-656. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2018.07.0273 [65] LI J X, ZHANG P, CHEN L, et al. Regeneration of selective catalyst reduction catalysts deactivated by pb, as, and alkali metals [J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(23): 13886-13893. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01283 [66] WANG X X, MA H Y, SHI Y, et al. Regeneration of alkali poisoned TiO2-based catalyst by various acids in NO selective catalytic reduction with NH3 [J]. Fuel, 2021, 285: 119069. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119069 [67] LI X, LI X S, CHEN J J, et al. An efficient novel regeneration method for Ca-poisoning V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst [J]. Catalysis Communications, 2016, 87: 45-48. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.06.017 [68] ZHENG Y, GUO Y Y, WANG J, et al. Ca doping effect on the competition of NH3-SCR and NH3 oxidation reactions over vanadium-based catalysts [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(11): 6128-6136. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c00677 [69] LYU Z K, NIU S L, HAN K H, et al. Theoretical insights into the poisoning effect of Na and K on α-Fe2O3 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2021, 610: 117968. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117968 [70] CAI S X, XU T Y, WANG P L, et al. Self-protected CeO2–SnO2@SO42–/TiO2 catalysts with extraordinary resistance to alkali and heavy metals for NOx reduction [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(19): 12752-12760. -



 下载:
下载: