-
地下水作为水资源重要组成部分,不仅是居民生活用水和工农业生产用水的主要来源,也是推动社会经济可持续发展和维持区域生态环境稳定的重要保障[1]. 在自然条件下,地下水化学组分主要受水文、气候和地质等因素控制;但随着人类活动的加剧,地下水化学组分也受到工农业生产和地下水超采等因素影响[2-3]. 开展地下水化学特征及控制因素研究,有助于揭示地下水演化过程.
目前,研究地下水化学特征及控制因素的传统方法主要有水化学类型法、图解法和离子比例关系等[4-5]. 近年来,受人类活动影响,地下水水化学组分来源趋于复杂化,仅采用传统方法难以区分自然因素和人为因素对地下水的控制作用[6]. 因此,多元统计分析、水文地球化学模拟和同位素技术等方法逐渐被应用到地下水化学特征及控制因素的研究[7-10].
重庆市万州区地处三峡库区腹心地带,是“成渝地区双城经济圈建设”在渝东北地区的经济主战场. 该区是以山地农业和农村经济为主的农业大区,浅层地下水是该区居民生活用水和工农业生产用水的主要来源. 以往关于重庆市浅层地下水的研究多集中在污染风险评价、污染源解析与环境影响因素识别等方面[11-12],而对于浅层地下水化学特征及控制因素的研究相对缺乏. 因此,本文综合运用数理统计、Piper三线图、Gibbs图、离子比例关系、Pearson相关性分析、因子分析和水文地球化学模拟等方法,对重庆市万州区浅层地下水进行系统分析,阐明该区浅层地下水化学特征及控制因素,以期为区内地下水资源的合理开发利用、生态环境保护及经济圈的建设提供科学依据.
-
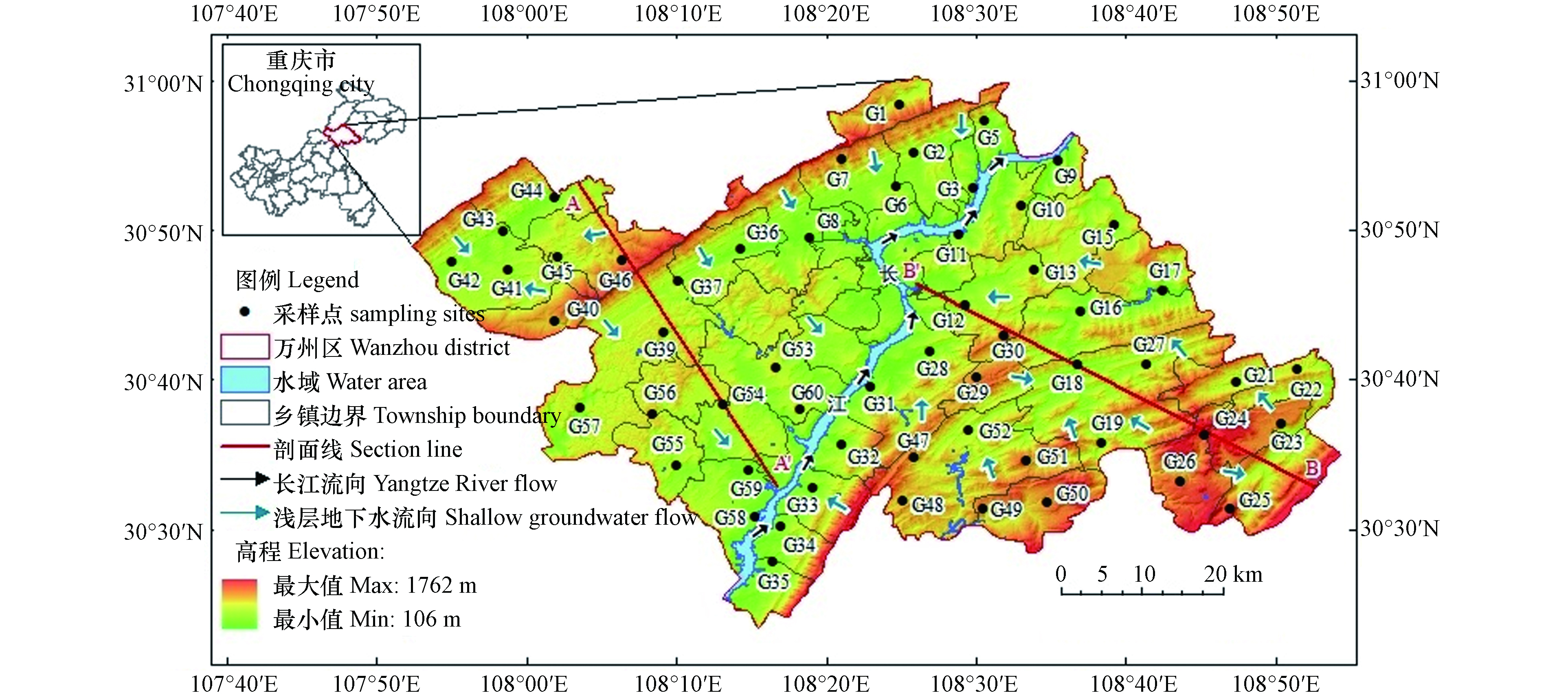
重庆市万州区位于107°52′22″—108°53′25″ E,30°24′25″—31°14′58″ N,地处长江中上游结合部,海拔约106—1762 m,总面积为3456.38 km²(图1). 区内地质构造由东北部大巴山褶皱带、东南部川鄂湘黔隆起褶皱带和中西部川东褶皱带组成;出露地层以侏罗纪为主,三叠纪次之,局部地区分布古生代二叠纪,并有新生代第四纪地层;该区地处扬子陆块,长江自西南—东北走向贯穿全区,长江以西地势北高南低,长江以东地势北低南高,区内山脉多呈东北—西南走向且平行延伸;境内地形较为破碎,低山、丘陵、低中山和山间平地约占全区面积的1/2,零星分布有平坝和台地. 该区属亚热带湿润季风气候,天气温和,雨量充沛,无霜期长;多年平均气温为17.7 ℃,多年平均降雨量为1243 mm,多年平均蒸发量为620 mm.
区内浅层地下水以侏罗系地层中的风化带裂隙水为主,埋深一般为2—6 m,丘坡和丘顶埋深可达17—18 m;主要补给来源为降雨入渗、水库渗漏、河流侧向入渗和农田灌溉回归入渗等;主要排泄方式为人工开采、泉水溢出和向下游侧向径流等;整体上,西部浅层地下水自西北向东南方向径流,东部浅层地下水自东南向西北方向径流.
-
2021年10月,对研究区浅层地下水进行系统采集,水样均采自民用井,共采集浅层地下水样56组,其中西部25组、东部31组(图1). 取样采用500 mL聚乙烯塑料水样瓶,采样前用去离子水清洗采样瓶3次,然后再用待取水样润洗3次,所有水样用0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤;用于阴离子测试的样品过滤后直接密封保存,用于阳离子测试的样品,添加高纯硝酸酸化至pH≤2.采样完成后用GPS记录采样点经纬度和高程.
采用pH检测计(pH818)、笔试电导率/溶解性总固体(TDS)计(AR8011)和氧化还原电位计(AZ8552)现场测定水样pH值、温度、电导率、TDS和氧化还原电位,测试精度分别为0.01、0.1 ℃、1 μS·cm−1、1 mg·L−1和1 mV.离子测定由国土资源部地下水矿泉水及环境检测中心完成,其中K+、Na+、Ca2+和Mg2+使用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(iCAP6300)进行测定;Cl-、SO42-和NO3-使用离子色谱仪(ICS1100)进行测定;HCO3-采用酸碱滴定法进行测定,各离子检出限为0.01 mg·L−1.
为检验数据可靠性,采用公式(1)进行检验:
式中,
$ E $ 为相对误差;$ Z $ 为离子电荷数;$ {m}_{\mathrm{a}}\mathrm{、}{m}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 为阴阳离子摩尔浓度,单位为mol·L-1. 经计算,所有水样阴阳离子电荷平衡误差均在±5%以内. -
研究区浅层地下水阴阳离子浓度关系分别为
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ >${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ >Cl−,Ca2+>Na++K+>Mg2+(图2),其中${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Cl-和${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 浓度变化范围分别为11.98—353.90 mg·L−1、2.16—35.13 mg·L−1和2.38—88.88 mg·L−1;Na++K+、Ca2+和Mg2+浓度变化范围分别为0.30—37.04 mg·L−1、4.00—104.80 mg·L−1和0.12—23.17 mg·L−1. 浅层地下水阴离子以${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 为主,占总阴离子浓度的84.0%,阳离子以Ca2+为主,占总阳离子浓度的72.0%.研究区西部浅层地下水各离子浓度普遍高于东部(图2),其中
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 和Ca2+空间分布规律相似,${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 和Ca2+含量较高的浅层地下水主要分布在西部和东北部,沿地下水流向均呈增大趋势;Cl−、Na++K+和Mg2+空间分布规律相似,Cl−、Na++K+和Mg2+含量较高的浅层地下水主要分布在西部、东部和南部,在西部沿地下水流向均呈增大趋势,而在东部沿地下水流向无明显规律性;${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 含量较高的浅层地下水主要分布在东部,自北向南呈递减趋势. 东部浅层地下水pH值普遍高于西部,沿地下水流向无明显规律性;TH和TDS空间分布规律基本一致,较高TH和TDS浅层地下水主要分布在东部和北部,沿浅层地下水流向均呈增大趋势. 研究区浅层地下水绝大部为淡软水,且呈弱碱性. -
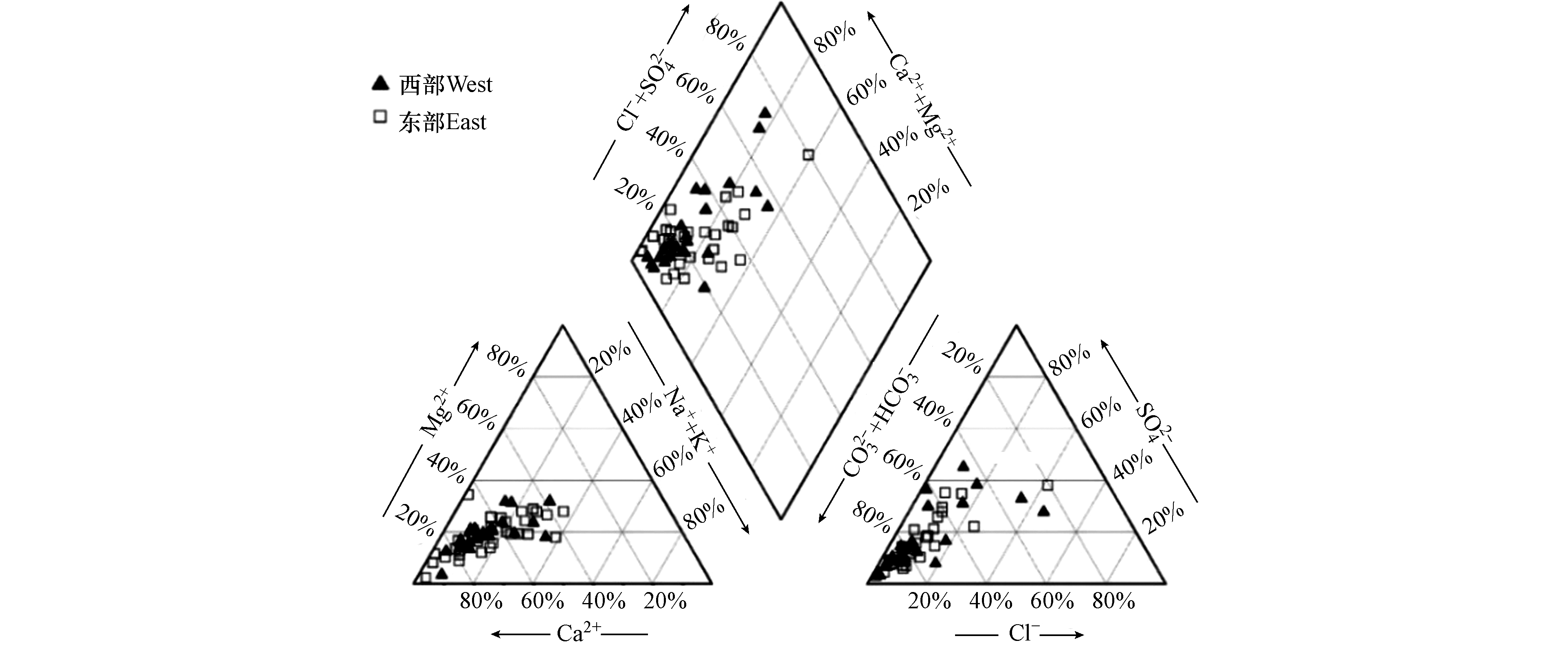
Piper三线图可以直观地反映各离子的相对含量[13-14]. 研究区绝大部分水样点的阳离子趋向于Ca2+端元,阴离子趋向于HCO3-端元(图3),说明浅层地下水以HCO3-Ca型为主.
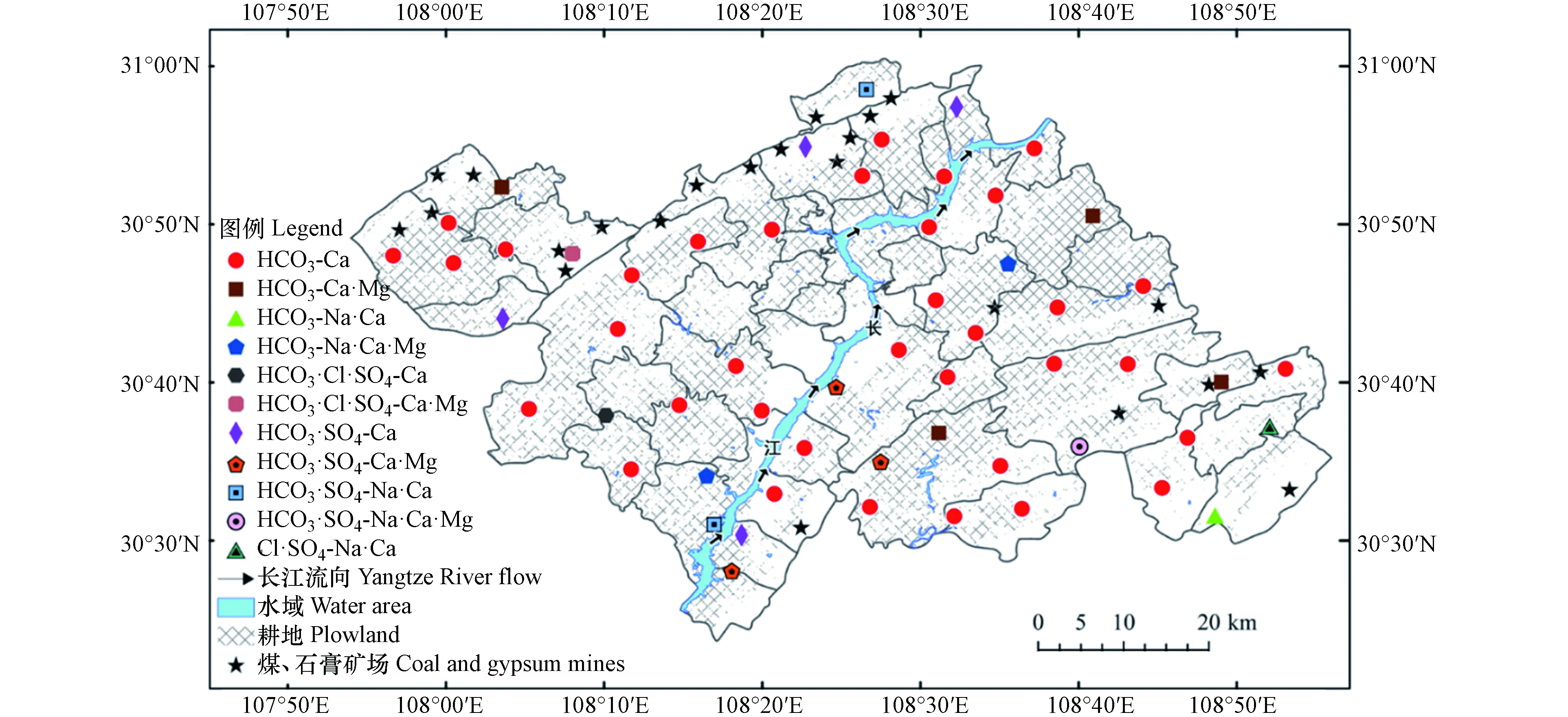
为更直观地分析研究区西部与东部浅层地下水水化学类型差异,按照舒卡列夫分类法对地下水进行分类[15],并绘制水化学类型空间分布图(图4). 西部浅层地下水类型有HCO3、HCO3·SO4和HCO3·Cl·SO4型,分别占西部总水样数的72%、20%和8%;东部浅层地下水类型有HCO3、HCO3·SO4和Cl·SO4型,分别占东部总水样数的80.7%、16.1%和3.2%,说明西部浅层地下水水化学类型受SO42-影响较大.
由研究区中部至边缘地区,地下水阴离子类型由HCO3型向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl·SO4和Cl·SO4型演变;阳离子类型由Ca型向Ca·Mg、Na·Ca和Na·Ca·Mg型演变. 经调查,研究区边缘地区分布有煤、石膏矿场以及耕地,说明浅层地下水化学演化过程可能受到人类活动影响[16].
-
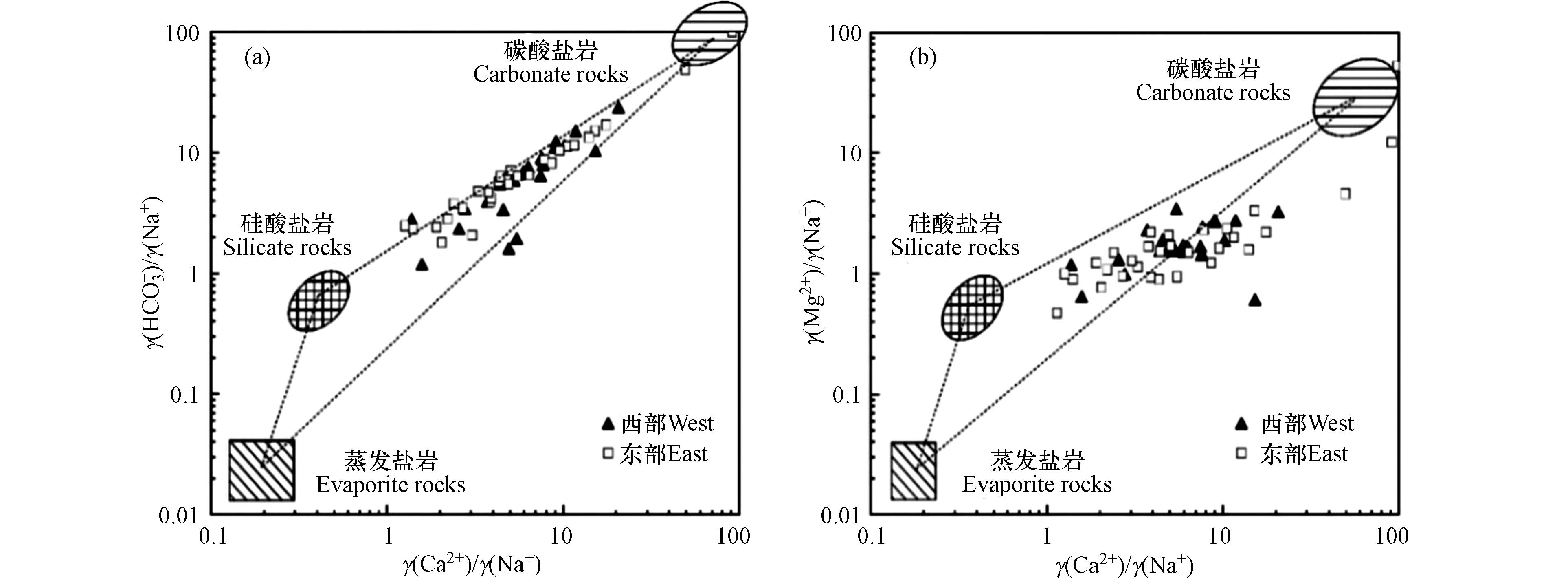
利用离子比例关系对研究区浅层地下水离子来源进行分析[17]. 当γ(Na++K+)与γ(Cl−)比值大于1时,地下水化学组分除了受岩盐溶滤作用影响外,还可能受到硅酸盐岩溶滤、蒸发盐岩溶滤和阳离子交换等作用影响;当比值小于1时,地下水化学组分可能受到人类活动影响[18]. 由研究区浅层地下水γ(Na++K+)与γ(Cl−)关系可知(图5a),绝大部分水样点分布在y=x上方,说明浅层地下水中Na++K+除了来源于岩盐的溶滤外,还可能来源于硅酸盐岩溶滤、蒸发盐岩溶滤以及正向阳离子交换等.
当γ(Ca2++ Mg2+)与γ(
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )比值大于1时,地下水中Ca2+和Mg2+除了来源于碳酸盐岩溶滤外,还存在其它含Ca2+、Mg2+矿物的溶滤;当比值小于1时,Ca2+和Mg2+可能来源于蒸发盐岩溶滤[19]. 由研究浅层地下水γ(Ca2++Mg2+)与γ(${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )关系可知(图5b),绝大部分水样点分布在y=x上方,说明浅层地下水中Ca2+和Mg2+除了来源于碳酸盐岩溶滤外,还存在其它来源.当γ(Ca2+)与γ(Mg2+)比值大于2时,地下水中Ca2+和Mg2+来源于碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩溶滤;当比值介于1与2之间时,Ca2+来源以方解石溶滤为主;当比值等于1时,Ca2+和Mg2+来源以白云石溶滤为主;当比值小于1时,地下水中可能存在蒸发盐岩溶滤[20]. 由研究区浅层地下水γ(Ca2+)与γ(Mg2+)关系可知(图5c),所有水样点分布在y=x与y=2x之间以及y=2x上方,说明浅层地下水中Ca2+、Mg2+来源于碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩溶滤,其中碳酸盐岩以方解石和白云石为主. 研究区所有水样点分布在γ(Ca2+)/γ(
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )=1线上方(图5d),且无显著线性关系,说明地下水中Ca2+来源受蒸发盐岩溶滤影响不大.利用γ(
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )与γ(${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ +Cl−)关系可以判断碳酸盐岩、硅酸盐岩和蒸发盐岩溶滤对地下水化学组分的贡献程度[21]. 由研究区浅层地下水γ(${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )与γ(${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ +Cl−)关系可知(图5e),所有水样分布在y=x上方,进一步说明地下水离子来源受蒸发盐岩溶滤影响较小.当γ(Ca2++Mg2+)与γ(
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ +${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )比值大于1时,地下水中Ca2+和Mg2+来源于碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩溶滤;当比值等于1时,水化学组分同时存在碳酸盐岩和蒸发盐岩溶滤;当比值小于1时,地下水中Ca2+和Mg2+来源于蒸发盐岩溶滤[22]. 结合图5b—图5f分析可知,研究区浅层地下水中${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 主要来源于人类活动[23]. -
Pearson相关性分析可以揭示各化学组分来源的相似性和差异性[24]. 研究区浅层地下水Na++K+与Mg2+、Cl−、
${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 存在较强相关性(表1),说明Na++K+来源受硅酸盐岩溶滤、岩盐溶滤和农业活动影响,其中以硅酸盐岩和岩盐溶滤为主;Cl−与Na++K+和Mg2+存在较强相关性,说明Cl−主要来源于岩盐溶滤;Ca2+、Mg2+与${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 存在较强相关性,说明Ca2+、Mg2+和${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 主要来源于碳酸盐岩溶滤;${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 与各离子都不存在显著相关性,进一步说明了浅层地下水中${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 来源主要受人类活动影响. -
Gibbs图最初被用于判断地表水受到的蒸发浓缩、岩石溶滤和大气降雨控制作用[25-26]. 由于地下水在含水层中滞留时间长,受水岩相互作用影响明显,若将Gibbs图用于分析地下水化学演化过程,应适当增大“岩石溶滤控制”区域范围[27].
研究区绝大部分水样点分布在“岩石溶滤控制”区域(图6),说明浅层地下水化学组分主要受岩石溶滤作用控制,同时部分水样点有向“大气降雨控制”区域移动的趋势,说明浅层地下水化学组分除了受岩石溶滤作用控制外,还受到一定的大气降雨影响. 其中西部水样点相对于东部水样点在“岩石溶滤控制”区域分布更集中,这是由于西部大部分区域地势平缓(图1),浅层地下水在含水层中的运移速度较慢,有助于水岩相互作用的进行,而东部大部分区域地势较陡,浅层地下水在含水层中的运移速度较快,水岩相互作用相对于西部较弱[28].
地下水化学组分一般来源于蒸发盐岩、硅酸盐岩和碳酸盐岩溶滤,通过离子端元图可分析地下水受到的岩石溶滤作用[29-30]. 由研究区浅层地下水γHCO3-/γNa+与γCa2+/γNa+端元图可知(图7a),水样点均分布在硅酸盐岩和碳酸盐岩端元之间,而在蒸发盐岩端元附近无水样点分布,说明浅层地下水化学组分主要受硅酸盐岩和碳酸盐岩溶滤控制,并且西部与东部水样点在端元图中的分布规律无明显差异,说明西部与东部含水层岩性相似.
在γMg2+/γNa+与γCa2+/γNa+端元图中(图7b),水样点有偏离碳酸盐岩端元的趋势,可能与浅层地下水阳离子交换作用有关.
-
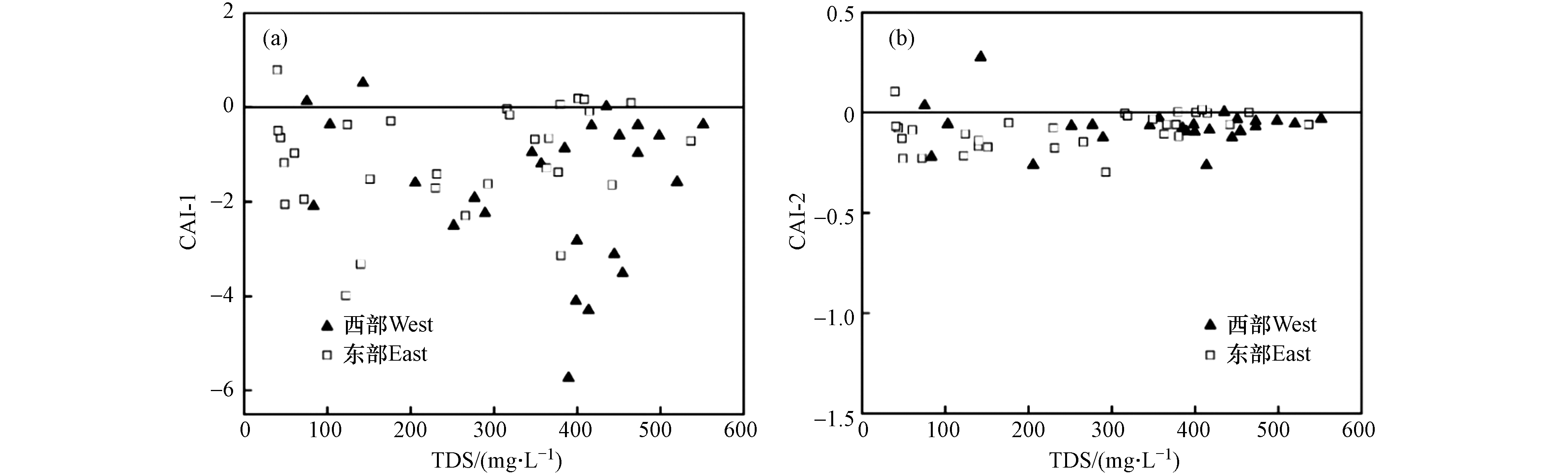
通过γ(Ca2++Mg2+-
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ -${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )与γ(Na+-Cl−)关系可以判断地下水是否发生阳离子交换作用,若两者比值接近−1,说明存在阳离子交换作用[31]. 由研究区浅层地下水γ(Ca2++Mg2+-${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ -${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )与γ(Na+-Cl−)关系图可知(图8),西部水样点分布在y=−1.14x+0.37附近,并且存在较强的相关性(R2=0.91),说明西部浅层地下水发生了较强的阳离子交换作用;而东部水样点分布在y=−0.73x+0.02附近,相关性较弱(R2=0.60),说明阳离子交换作用相对弱于西部.利用氯碱指数(CAI-1和CAI-2)可进一步判断地下水阳离子交换作用进行的方向[32]. 若CAI-1和CAI-2为负值时,发生正向阳离子交换作用;若CAI-1和CAI-2为正值时,发生逆向阳离子交换作用[33]. 研究区绝大部分水样点的CAI-1和CAI-2为负值(图9),说明浅层地下水以正向阳离子交换作用为主,即水中Ca2+和Mg2+与含水层岩石吸附的Na+和K+发生交换.
-
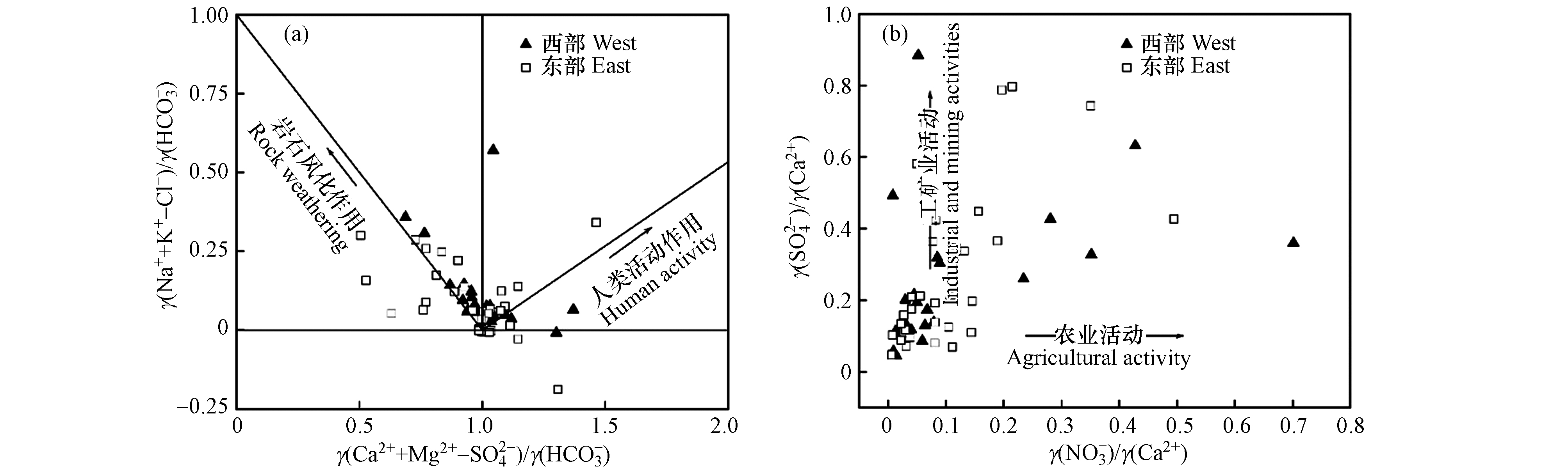
利用γ(Na++K+-Cl-)/γ(
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )与γ(Ca2++Mg2+-${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/γ(${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )关系可以判断岩石风化作用和人类活动作用对地下水化学组分的贡献程度[34]. 研究区浅层地下水样点在“岩石风化作用”和“人类活动作用”区域均有分布(图10a),说明浅层地下水化学组分同时受岩石风化作用和人类活动作用影响,但以岩石风化作用为主.利用γ(
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/γ(Ca2+)与γ(${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ )/γ(Ca2+)关系,可以进一步判断工矿业活动和农业活动对地下水化学组分的贡献程度[35]. 由研究区浅层地下水γ(${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/γ(Ca2+)与γ(${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ )/γ(Ca2+)关系可知(图10b),水样点明显趋向于“工矿业活动”,说明工矿业活动在人类活动作用中占主导地位.因子分析能在损失较少信息的基础上对水化学参数进行综合分析,提取影响地下水化学组分的主要因子[36-37]. 通过对研究区浅层地下水TDS、TH、Na++K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Cl−、${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 和${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 进行因子分析,得到旋转成分矩阵(表2).西部共提取3个主因子,东部共提取2个主因子. 其中西部与东部第一主因子F1中TDS、TH、Ca2+、Mg2+和HCO3-载荷较高,主要反映碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩溶滤对地下水化学组分的影响;西部与东部第二主因子F2中Na++K+和Cl-载荷较高,主要反映岩盐溶滤对地下水化学组分的影响;西部第三主因子F3与东部第二主因子F2中SO42-和NO3-载荷较高,主要反映工矿业活动和农业活动对地下水化学组分的影响.
整体上,研究区浅层地下水化学组分主要受碳酸盐岩溶滤控制,其次为硅酸盐岩和岩盐溶滤;除矿物溶滤载荷外,西部SO42-载荷最大,NO3-载荷次之,而东部NO3-载荷最大,SO42-载荷次之,说明工矿业活动和农业活动对研究区浅层地下水均有较大影响,但西部工矿业活动较强,东部农业活动较强.
-
PHREEQC软件可定量模拟地下水受到的水岩相互作用[38]. 沿浅层地下水流向A—A'和B—B'(图1),分别在研究区西部与东部选择一条路径进行水文地球化学模拟,路径1:G45→G39→G60;路径2:G24→G18→G12. 根据前文分析结果,选取岩盐、方解石、白云石、CO2(g)和阳离子交换(NaX、CaX2)作为“可能矿物相”.
模拟结果表明(表3),路径1上岩盐、方解石和白云石均发生溶解作用,随着方解石和白云石的溶解,浅层地下水Ca2+浓度增加,使方解石首先沉淀,对比路径G46→G39→G54上Na+浓度2.39 mg·L−1→4.21 mg·L−1→18.99 mg·L−1,Ca2+浓度11.35 mg·L−1→75.82 mg·L−1→87.74 mg·L−1,Mg2+浓度4.20 mg·L−1→7.00 mg·L−1→15.67 mg·L−1,符合实际. 路径2上岩盐、方解石和白云石均发生溶解作用,随着岩盐、方解石和白云石的溶解,浅层地下水Na+、Ca2+和Mg2+浓度会逐渐增加,对比路径G24→G18→G12上Na+浓度2.42 mg·L−1→7.06 mg·L−1→9.94 mg·L−1,Ca2+浓度9.12 mg·L−1→20.26 mg·L−1→67.57 mg·L−1,Mg2+浓度1.14 mg·L−1→4.22 mg·L−1→12.15 mg·L−1,符合实际. 且路径1上阳离子交换摩尔转移量大于路径2,说明研究区西部浅层地下水发生的阳离子交换作用强于东部,与前文分析结果一致.
-
(1)研究区浅层地下水主要为淡软水,且呈弱碱性;地下水阴阳离子分别以
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Ca2+为主;水化学类型以HCO3-Ca型为主. 由研究区中部至边缘地区,地下水阴离子类型由HCO3型向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl·SO4和Cl·SO4型演变;阳离子类型由Ca型向Ca·Mg、Na·Ca和Na·Ca·Mg型演变.(2)研究区浅层地下水中Na++K+主要来源于硅酸盐岩和岩盐溶滤,其次还受到一定农业活动影响;Ca2+和Mg2+主要来源于碳酸盐岩溶滤,且以方解石和白云石溶滤为主,其次为硅酸盐岩溶滤;
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 主要来源于碳酸盐岩溶滤;Cl−主要来源于岩盐溶滤;${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 主要来源于工矿业活动.(3)研究区浅层地下水化学组分受岩石溶滤作用、正向阳离子交换作用和人类活动作用控制. 其中,岩石溶滤作用以碳酸盐岩溶滤为主,其次为硅酸盐岩和岩盐溶滤;在阳离子交换作用中,西部地下水的阳离子交换作用强于东部;在人类活动对地下水的影响作用中,西部工矿业活动作用较强,东部农业活动作用较强.
(4)研究区浅层地下水水文地球化学模拟结果表明,沿地下水流向,地下水离子浓度呈递增趋势,岩盐、方解石和白云石均发生溶解.
重庆市万州区浅层地下水化学特征及控制因素
Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of shallow groundwater in Wanzhou District, Chongqing
-
摘要: 浅层地下水作为重庆市万州区居民生活用水和工农业生产用水的主要来源,是推动该区社会经济可持续发展和维持区域生态环境稳定的重要保障. 为研究重庆市万州区浅层地下水化学特征及控制因素,于2021年10月采集浅层地下水样品56组. 综合运用数理统计、Piper三线图、Gibbs图、离子比例关系、Pearson相关性分析、因子分析和水文地球化学模拟等方法,对万州区浅层地下水化学特征、离子来源和控制因素进行分析. 结果表明,研究区浅层地下水以淡软水为主,且呈弱碱性,阴阳离子以
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 、Ca2+为主,浅层地下水类型以HCO3-Ca为主;由研究区中部至边缘地区,阴离子类型由HCO3型向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl·SO4和Cl·SO4型演变,阳离子类型由Ca型向Ca·Mg、Na·Ca和Na·Ca·Mg型演变;浅层地下水离子主要来源于碳酸盐岩、硅酸盐岩和岩盐溶滤;浅层地下水化学组分受岩石溶滤作用、正向阳离子交换作用和人类活动作用控制;水文地球化学模拟结果表明,沿浅层地下水流向,浅层地下水离子浓度呈递增趋势,岩盐、方解石和白云石均发生溶解,西部浅层地下水的阳离子交换作用强于东部. 研究结果可为重庆市万州区浅层地下水资源的合理开发利用、生态环境保护和经济圈的建设提供科学依据.Abstract: Shallow groundwater, as the main source of domestic water and industrial and agricultural production water for residents in Wanzhou District, Chongqing, is an important guarantee for promoting the sustainable socio-economic development of the area and maintaining the stability of the regional eco-environment. In order to study the hydrochemical characteristics and control factors of shallow groundwater in Wanzhou District, Chongqing, 56 sets of shallow groundwater samples were collected in October 2021. Comprehensive use of mathematical statistics, Ternry diagram, Gibbs diagram, ion proportional relationship, Pearson correlation analysis, factor analysis methods and hydrogeochemical simulation are used to analyze the hydrochemical characteristics, ion sources and control factors of shallow groundwater in Wanzhou. The results showed that: The shallow groundwater in the study area are dominated by fresh and soft water, and it was weakly alkaline, the anions and anions are dominated by${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ and Ca2+, and the type of shallow groundwater is dominated by HCO3-Ca; From the middle to the edge of the study area, the types of anions evolve from HCO3 to HCO3·SO4, HCO3·Cl·SO4 and Cl·SO4, and the types of cations evolve from Ca to Ca·Mg, Na·Ca and Na·Ca·Mg; The ions of shallow groundwater are mainly originated from filtration of carbonate rocks, silicate rocks and halite; The chemical components of shallow groundwater are controlled by rock dissolution, positive cation exchange and human activities; The results of hydrogeochemical simulation showed that along the flow direction of shallow groundwater, the ion concentration in shallow groundwater was increasing, halite, calcite and dolomite were dissolved, the cation exchange effect of shallow groundwater in the west was stronger than in the east. The research results can provide a scientific basis for the rational development and utilization of shallow groundwater resources, eco-environmental protection and the construction of economic circles in Wanzhou District, Chongqing. -

-
图 10 重庆市万州区浅层地下水γ(Na++K+-Cl−)/γ(
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ )与γ(Ca2++ Mg2+-${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ) /γ(HCO3-)、γ(${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/γ(Ca2+)与γ(${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ )/γ(Ca2+)关系Figure 10. Relationship between γ(Na++K+-Cl-)/γ(
${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ ) and γ(Ca2++ Mg2+-${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/γ(HCO3-), and γ(${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ )/γ(Ca2+) and γ(${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ )/γ(Ca2+) of shallow groundwater in Wanzhou District, Chongqing表 1 重庆市万州区浅层地下水离子间相关系数
Table 1. Correlation coefficients between ions of shallow groundwater in Wanzhou District, Chongqing
Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ Cl− ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ Na++K+ 1 Ca2+ 0.245 1 Mg2+ 0.616** 0.577* 1 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 0.265* 0.937* 0.691** 1 Cl− 0.652** 0.284* 0.520** 0.201 1 ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 0.448** 0.471** 0.369** 0.294* 0.325* 1 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ 0.534** 0.035 0.184 −0.141 0.474** 0.266* 1 注:** 表示在0.01水平上线性相关,* 表示在0.05水平上线性相关.
Note: ** P<0.01; * P<0.05.表 2 重庆市万州区浅层地下水旋转成分矩阵
Table 2. Rotational component matrix of shallow groundwater in Wanzhou District, Chongqing
水化学组分
Hydrochemical compositions西部 West 东部 East F1 F2 F3 F1 F2 TDS 0.970 0.213 0.086 0.907 0.159 TH 0.972 0.133 0.134 0.984 0.138 Na++K+ 0.336 0.769 −0.073 0.120 0.943 Ca2+ 0.951 −0.064 0.203 0.968 0.056 Mg2+ 0.584 0.684 −0.143 0.736 0.376 ${\rm{HCO}}_3^{-} $ 0.975 0.053 −0.192 0.985 −0.105 Cl− 0.041 0.868 0.185 0.343 0.816 SO42- 0.325 0.020 0.828 0.460 0.628 ${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $ −0.219 0.581 0.635 −0.028 0.880 贡献率/% 48.320 24.674 13.905 50.939 32.488 累计贡献率/% 48.320 72.994 86.889 50.939 83.427 表 3 重庆市万州区浅层地下水路径反向模拟结果
Table 3. Reverse simulation results of routes of shallow groundwater in Wanzhou District, Chongqing
矿物相
Mineral phase化学式
Chemical formula路径1 / (mmol·L−1)
Routes1路径2/ (mmol·L−1)
Routes2G46→G39 G39→G54 G24→G18 G18→G12 岩盐 NaCl 2.010×10−4 5.478×10−4 2.146×10−5 1.129×10−4 方解石 CaCO3 1.696×10−3 −1.049×10−4 2.352×10−4 8.438×10−4 白云石 CaMg(CO3) 2 1.809×10−4 3.568×10−4 1.220×10−4 3.263×10−4 CO2 CO2 2.818×10−3 2.504×10−4 5.880×10−4 2.001×10−3 阳离子交换 NaX 3.195×10−4 9.546×10−4 1.699×10−4 1.249×10−5 CaX2 −1.597×10−4 −4.773×10−4 −8.494×10−5 −6.246×10−6 注:表内数值为摩尔转移量,正值表示溶解,负值表示沉淀.
Note: The values in the table are molar transfer amount, positive value indicates dissolution, and negative value indicates precipitation. -
[1] LUKAČ REBERSKI J, RUBINIĆ J, TERZIĆ J, et al. Climate change impacts on groundwater resources in the coastal karstic adriatic area: A case study from the dinaric Karst [J]. Natural Resources Research, 2020, 29(3): 1975-1988. doi: 10.1007/s11053-019-09558-6 [2] XING L N, GUO H M, ZHAN Y H. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 70/71: 250-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.017 [3] SUNKARI E D, ABU M, BAYOWOBIE P S, et al. Hydrogeochemical appraisal of groundwater quality in the Ga west municipality, Ghana: Implication for domestic and irrigation purposes [J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2019, 8: 501-511. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2019.02.002 [4] 王珺瑜, 王家乐, 靳孟贵. 济南泉域岩溶水水化学特征及其成因 [J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 821-831. WANG J Y, WANG J L, JIN M G. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of Karst water in Jinan spring catchment [J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(5): 821-831(in Chinese).
[5] LOVE D, HALLBAUER D, AMOS A, et al. Factor analysis as a tool in groundwater quality management: Two southern African case studies [J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 2004, 29(15/16/17/18): 1135-1143. [6] RAYNE T W, BRADBURY K R, KRAUSE J J. Impacts of a rural subdivision on groundwater quality: Results of long-term monitoring [J]. Ground Water, 2019, 57(2): 279-291. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12666 [7] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 等. 毕节市北部岩溶地下水水化学特征及影响因素的多元统计分析 [J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4): 1446-1456. YUAN J F, DENG G S, XU F, et al. The multivariate statistical analysis of chemical characteristics and influencing factors of Karst groundwater in the northern part of Bijie City, Guizhou Province [J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(4): 1446-1456(in Chinese).
[8] XIAO Q, JIANG Y J, SHEN L C, et al. Origin of calcium sulfate-type water in the Triassic carbonate thermal water system in Chongqing, China: A chemical and isotopic reconnaissance [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 89: 49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.11.011 [9] BUSICO G, CUOCO E, KAZAKIS N, et al. Multivariate statistical analysis to characterize/discriminate between anthropogenic and geogenic trace elements occurrence in the Campania Plain, Southern Italy [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 234: 260-269. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.053 [10] van GELDERN R, SCHULTE P, MADER M, et al. Insights into agricultural influences and weathering processes from major ion patterns [J]. Hydrological Processes, 2018, 32(7): 891-903. doi: 10.1002/hyp.11461 [11] 张虹, 张代钧, 卢培利. 重庆市页岩气开采的浅层地下水污染风险评价 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(4): 2016-2024. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201510208 ZHANG H, ZHANG D J, LU P L. Primary assessment of shallow ground water pollution risk for shale gas exploitation in Chongqing [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(4): 2016-2024(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201510208
[12] 张虹, 魏兴萍, 彭名涛. 重庆市浅层地下水污染源解析与环境影响因素识别 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(12): 2896-2906. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.08.10 ZHANG H, WEI X P, PENG M T. Analysis of pollution sources and identification of environmental influencing factors of shallow groundwater in Chongqing, China [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(12): 2896-2906(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.08.10
[13] 姜体胜, 曲辞晓, 王明玉, 等. 北京平谷平原区浅层地下水化学特征及成因分析 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(11): 122-127. JIANG T S, QU C X, WANG M Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater and the origin in the Pinggu Plain, Beijing [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(11): 122-127(in Chinese).
[14] 冯建国, 赫明浩, 李贵恒, 等. 泰莱盆地孔隙水水化学特征及其控制因素分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2594-2600. FENG J G, HE M H, LI G H, et al. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of porewater in the Tailai Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2594-2600(in Chinese).
[15] 陈晨, 高宗军, 李伟, 等. 泰莱盆地地下水化学特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6): 1339-1347. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090504 CHEN C, GAO Z J, LI W, et al. Characteristics and possible factors of hydrochemistry in the groundwater in Tailai Basin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(6): 1339-1347(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090504
[16] 刘鑫, 向伟, 马小军, 等. 黄土高原中部浅层地下水化学特征及影响因素 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(11): 5201-5209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.11.028 LIU X, XIANG W, MA X J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of shallow groundwater in the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(11): 5201-5209(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.11.028
[17] 林聪业, 孙占学, 高柏, 等. 拉萨地区地下水水化学特征及形成机制研究 [J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(5): 49-58. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.2.2 LIN C Y, SUN Z X, GAO B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Lhasa area, China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(5): 49-58(in Chinese). doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.2.2
[18] LEHN G O, JACOBSON A D, DOUGLAS T A, et al. Constraining seasonal active layer dynamics and chemical weathering reactions occurring in North Slope Alaskan watersheds with major ion and isotope (δ34SSO4, δ13CDIC, 87Sr/86Sr, δ44/40Ca, and δ44/42Ca) measurements [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 217: 399-420. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.07.042 [19] 魏世博, 王哲, 李飞, 等. 内蒙古额济纳平原地下水氢氧同位素和水化学特征及其演化规律[J/OL]. 中国地质: 1-14. WEI S B, WANG Z, LI F, et al. Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotope and hydrochemistry in the Ejina plain groundwater and its hydrochemical evolution[J/OL]. Geology in China: 1-14(in Chinese).
[20] 孔晓乐, 杨永辉, 曹博, 等. 永定河上游地表水-地下水水化学特征及其成因分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9): 4202-4210. KONG X L, YANG Y H, CAO B, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and factors of surface water and groundwater in the upper Yongding River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(9): 4202-4210(in Chinese).
[21] 钱程, 武雄. 盐池内流区地下水水化学特征及其形成作用 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(3): 169-175. QIAN C, WU X. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in the inner flow area in Yanchi [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(3): 169-175(in Chinese).
[22] 曾小仙, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 石河子市浅层地下水化学特征及其成因分析 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(1): 68-75. doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.01.08 ZENG X X, ZENG Y Y, ZHOU J L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and cause analysis of the shallow groundwater in Shihezi City [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(1): 68-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.01.08
[23] 孟舒然, 吕敦玉, 王翠玲, 等. 郑州市中牟县地下水水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(3): 977-986. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010802 MENG S R, LV D Y, WANG C L, et al. Research of groundwater chemical characteristics and controlling factors in Zhongmu County, Zhengzhou City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(3): 977-986(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010802
[24] 房丽晶, 高瑞忠, 贾德彬, 等. 草原流域地下水化学时空特征及环境驱动因素: 以内蒙古巴拉格尔河流域为例 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(5): 2161-2169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.05.020 FANG L J, GAO R Z, JIA D B, et al. Spatial-temporal characteristics of groundwater quality and its environmental driving factors of Steppe Basin—taken Balaguer River Basin of Inner Mongolia for instance [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(5): 2161-2169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.05.020
[25] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry [J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [26] MARANDI A, SHAND P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs diagram [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 97: 209-212. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.07.009 [27] 魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水化学特征及演化规律 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201901211 WEI X, ZHOU J L, NAI W H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Kashgar delta area in Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(9): 4042-4051(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201901211
[28] 寇永朝, 华琨, 李洲, 等. 泾河支流地表水地下水的水化学特征及其控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(7): 3142-3149. KOU Y C, HUA K, LI Z, et al. Major ionic features and their possible controls in the surface water and groundwater of the Jinghe River [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(7): 3142-3149(in Chinese).
[29] 成思, 温瑶, 许畅畅, 等. 崇明岛浅层地下水化学特征及其影响机制 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(5): 1120-1128. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.09.13 CHENG S, WEN Y, XU C C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and impact mechanism of shallow groundwater in Chongming Island, China [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(5): 1120-1128(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.09.13
[30] GAILLARDET J, DUPRÉ B, LOUVAT P, et al. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 159(1/2/3/4): 3-30. [31] XIAO J, JIN Z D, WANG J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics, controlling factors and solute sources of groundwater within the Tarim River Basin in the extreme arid region, NW Tibetan Plateau [J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 380/381: 237-246. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.01.021 [32] SINGH N, SINGH R P, KAMAL V, et al. Assessment of hydrogeochemistry and the quality of groundwater in 24-Parganas districts, West Bengal [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(1): 375-386. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3431-2 [33] NEMATOLLAHI M J, CLARK M J R, EBRAHIMI P, et al. Preliminary assessment of groundwater hydrogeochemistry within Gilan, a northern Province of Iran [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2018, 190(4): 242. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-6543-4 [34] 何锦, 张幼宽, 赵雨晴, 等. 鲜水河断裂带虾拉沱盆地断面地下水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(3): 1236-1244. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201808117 HE J, ZHANG Y K, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of groundwater in the xialatuo basin section of the Xianshui River [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(3): 1236-1244(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201808117
[35] 张涛, 何锦, 李敬杰, 等. 蛤蟆通河流域地下水化学特征及控制因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(11): 4981-4990. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201804070 ZHANG T, HE J, LI J J, et al. Major ionic features and possible controls in the groundwater in the hamatong river basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(11): 4981-4990(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201804070
[36] MOSTAZA-COLADO D, CARREÑO-CONDE F, RASINES-LADERO R, et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization of a shallow alluvial aquifer: 1 baseline for groundwater quality assessment and resource management [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639: 1110-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.236 [37] PAZAND K, KHOSRAVI D, GHADERI M R, et al. Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of groundwater in a semi-arid region using major ion chemistry: A case study of Ardestan Basin in Central Iran [J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2018, 6: 245-254. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2018.01.008 [38] BARZEGAR R, ASGHARI MOGHADDAM A, NAZEMI A H, et al. Evidence for the occurrence of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater of Khoy plain, northwestern Iran, using ionic ratios and geochemical modeling [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(16): 597. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7782-y -





 下载:
下载: