-
渤海是我国唯一的半封闭性内海,具有优越的地理位置和丰富的自然资源,在我国经济、军事、社会发展等方面都具有重要的战略地位. 进入21世纪以来,环渤海区域社会经济持续高速发展,污染物排海总量居高不下,使渤海水质不断恶化,亟需对生态环境进行综合治理,重金属污染治理是对渤海生态环境治理的重要一环.
目前,对于渤海湾地区的重金属污染中,研究较多的重金属有铜、镉、铅、锌等,其中锌的浓度显著高于其它重金属,曾有研究者检测到渤海湾地区沉积物中锌的平均浓度是铜的3倍、铅的4倍左右[1]. 虽然锌是生物体生长发育所必需的一种微量元素,但是当其在环境中的浓度过高时,就会对环境中的生物体产生毒性,对生态系统的健康产生威胁[2-3],因此锌也是一种很常见的重金属污染物. 然而对于渤海湾地区锌污染的研究目前主要集中于沉积物环境[4-5],对于海水中的重金属污染以及锌的海水水生生物水质基准的研究较少.
水质基准对于水体污染状况的有效评价具有重要意义,是水环境质量管理和污染控制的一项基础性工作[6]. 自上世纪60年代以来,美国、加拿大、澳大利亚、欧盟等已经对水质基准进行了大量的研究,形成了完整的水质基准指定体系,并颁布了自己的环境水质基准文件,其中规定了一些典型污染物的淡水、海水水质基准值[7]. 由美国建立的双值基准体系已经得到全世界的广泛应用. 印度[8]、韩国[9]等国家则起步较晚,近年来有学者推导了其砷、镉、铅等重金属的水质基准值. 我国在1997年公布了国家标准海水水质标准,不同于海水水生生物水质基准,它将海域分为4类水并分别规定了锌浓度限值[10],直到2017年才颁布了淡水水生生物水质基准制定技术指南[11]. 目前已有的水质基准研究较多是针对淡水环境,对于海水环境的研究较少. 我国已有的海水水质基准研究比较零散,包括重金属镉[12]、汞[13]、铅[14]等,有机污染物硝基苯[15]、三氯生[16]以及一些营养盐[17]的海水水质基准值. 水质基准值也会受到环境因素的影响,有研究推导了锌的淡水水质基准并发现其随水体硬度的升高而降低[18],但是对锌的海水水质基准还没有具体研究. 本研究参考已有的水质基准推导方法,根据收集到的对渤海湾本地物种的毒性数据,推导了适用于渤海湾地区的锌长期和短期海水水质基准,并对渤海湾地区的锌潜在生态风险进行了评价,填补了我国海水水质基准研究领域的部分空白,为渤海湾及其邻近海域的区域化精细管理提供了理论依据.
-
本研究用于基准推导的数据主要来自两部分,一部分为渤海湾本地物种实测数据,一部分为资料检索数据. 资料检索数据来自生态毒理学知识库(ECOTOX,http://cfpub.epa.gov/ecotox),以及文献数据库中国知网(CNKI)、Web of Science(WOS,http://www.isiknowledge.com). 在进行毒性数据筛选时,受试生物应反映渤海湾海水生物区系特征,优先选择栖息或分布于渤海海洋环境的代表性海洋生物. 只纳入试验用水为海水的毒性数据,优先采用流水式试验获得的毒性数据,剔除试验设计不完善的数据. 急性毒性试验的暴露时间不大于96 h,以LC50、EC50为毒性终点;对于慢性毒性试验,暴露时间需至少涵盖1个敏感生命阶段,毒性终点为NOEC、LOEC等. 用于水质基准推导的毒性数据需要至少涵盖3个营养级,并且满足“3门8科”要求[19].
-
根据筛选的毒理数据,在实验室内补充了7种渤海湾存在物种的急性毒性试验. 所有生物均在室内驯养1周,选择活力良好的个体使用灭菌的人工海水进行毒性试验,在试验前24 h内不投喂. 正式试验前均进行了预试验确定浓度范围,每一个急性毒性试验都设置了5个浓度梯度,1个空白对照,每个浓度梯度设置3个平行,包括空白对照,利用软件SPSS 25.0和GraphPad Prism 8计算和绘制水生生物的LC50和EC50. 试验条件以及物种来源等详细信息如表1所示.
-
本论文使用物种敏感度分布法推导水质基准(参考OECD基准推导体系[20]及我国淡水水质基准推导指南[11]). 推导方法如下:
式中,SMAVi为物种i的种平均急性值;SMCVi为物种i的种平均慢性值;ATV为急性毒性值;CTV为慢性毒性值;
对数据进行正态分布检验,符合正态分布的数据方能进行物种敏感度分布(SSD)模型拟合.
将急性/慢性毒性值取对数并分别从小到大进行排序,确定其毒性秩次R,依据公式3分别计算物种的累积频率P,进行SSD模型拟合.
式中,N为物种的个数.
本研究采用EPA SSD-Toolbox软件进行SSD模型拟合,并利用MATLAB 软件计算相关参数. 依据SSD-Toolbox软件输出参数以及模型拟合的R2、RMSE、SSE,确定最优拟合模型. 根据确定的最优拟合模型拟合的SSD曲线,确定累积频率5%所对应的SMAVi/SMCVi,即为急性/慢性5%物种危害浓度HC5.
由于缺乏足够的慢性毒性数据,长期水质基准(LWQC)使用最终急性慢性比(FACR)从急性数据外推到慢性数据. 本研究中有效毒性数据的数量大于15并涵盖足够的营养级生物,评估因子取值为2. 计算公式如下:
式中,AF为评估因子;SWQC为短期水生生物水质基准;LWQC为长期水生生物水质基准;FACR为最终急慢性比.
-
生态风险评价可以评价由于受体暴露在单个或多个胁迫因子下而可能发生或正在发生的负生态效应的可能性. 本文采用熵值法对渤海湾及临近海域的锌污染状况进行量化表达. 锌的浓度数据为2020年夏季和秋季在渤海湾及临近海域实地监测. 其中夏季采样站点39个,秋季采样站点41个. 通常来说,熵值法是将渤海湾地区锌暴露浓度(EC)除以基准连续浓度(CCC)得到的风险熵[21],其中基准连续浓度(CCC)与长期水质基准(LWQC)的含义相同. 也有研究者利用急性和慢性基准值分别计算短期和长期风险[22],具体方法如下[23]:
HQ的具体范围分别为HQ<0.1、0.1≤HQ<1、1≤HQ<10、HQ≥10,分别代表评估区域不存在明显风险、低风险、中等风险和高风险.
-
研究共收集到毒性数据91条,其中动物急性毒性数据62条,涉及水生动物23种,隶属于6门18科21属;水生植物急性毒性数据10条,涉及5种水生植物,隶属于2门5科5属;动物慢性毒性数据16条,涉及水生动物8种,隶属于5门8科8属;植物慢性毒性数据2条,涉及水生植物2种,隶属于2门2科2属. 生物富集数据28条,涉及渤海生物中的2门6科6属中的6种水生动物.
-
针对于本土物种开展的急性毒性试验共涉及试验数据13条,涉及4门6科6属6种水生动物,1种水生植物. 各物种的平均急性毒性值见表2.
-
(1)锌的短期水质基准
收集到渤海物种的急性数据共94条,其中试验得到数据13条,共涉及8门27科30属32种. 急性数据满足 “3门8科”最低要求.
对急性和慢性毒性值分别进行正态分布检验(D'Agostino-Pearson检验),发现P<0.05不符合正态分布. 对急性和慢性毒性值进行对数转换后符合正态分布,可以进行物种敏感度分布(SSD)模型拟合. 各物种的种平均急性值SMAVi及累积频率如表3所示.
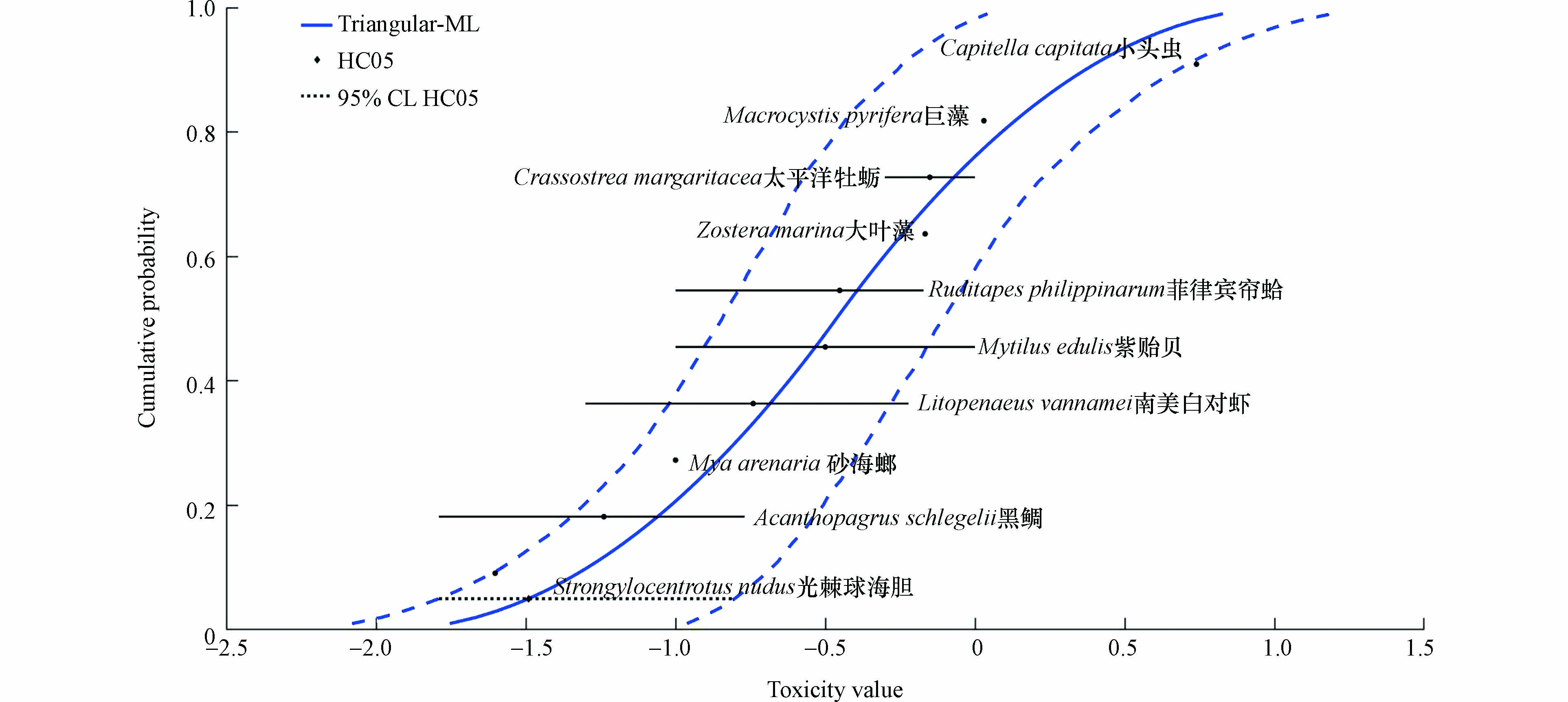
将筛选后的数据库检索急性毒性数据和试验数据利用SSD-Toolbox分别进行基于ML方法和MH方法的normal分布、logistic分布、triangular分布、gumbel分布和weibull分布的拟合. 锌短期水质基准模型拟合曲线如图1所示,拟合结果见表4.经检验,基于MH(metropolis Hastings)方法的gumbel分布为最优拟合模型拟合的SSD曲线,对应HC5=224.8 μg∙L−1. 除以评估因子值2后,即锌海水水生生物短期水质基准SWQC=112.40 μg∙L−1.
(2)锌的长期水质基准
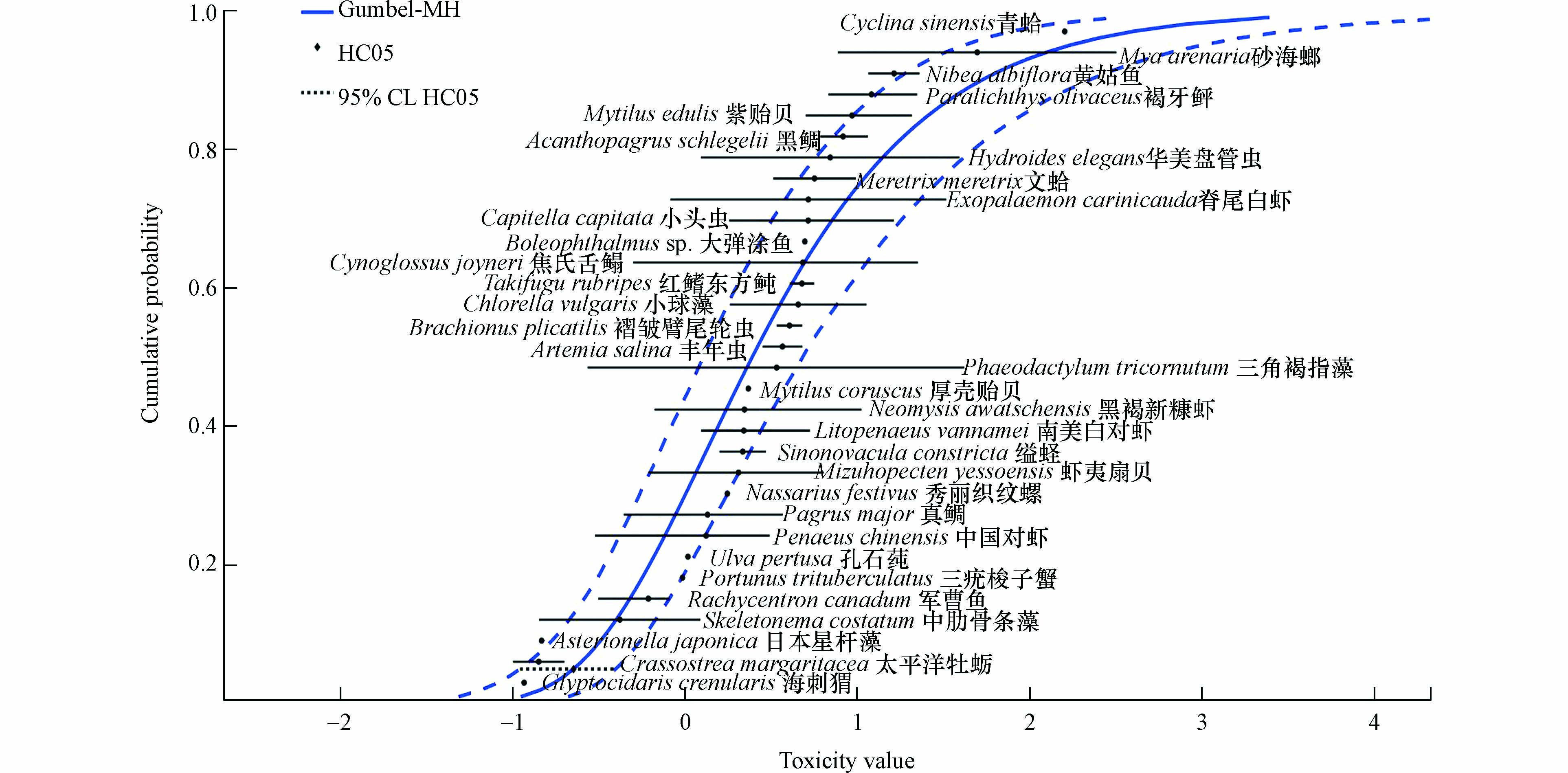
收集到慢性毒性数据18条,涉及7门10科10属10种. 各物种的对数种平均慢性值lg(SMCVi)及累积频率如表5所示.慢性数据不满足 “3门8科”最低要求,但参考OECD水质基准指南,认为急、慢性数据均符合“至少10种物种”的要求,因此直接采用SSD法进行水质基准的推导.
利用SSD-Toolbox分别进行基于ML方法和MH方法的6种分布的拟合. 锌长期水质基准模型拟合曲线如图2所示,拟合结果见表6.
经检验,基于ML(maximum Likelihood)方法的triangular分布为最优拟合模型拟合的SSD曲线,对应HC5=32.3 μg∙L−1. 评估因子取值为2. 除以评估因子值2后,即为锌海水水生生物长期水质基准LWQC=16.15 μg∙L−1.
-
目前我国海水水质标准Ⅰ类海水规定锌浓度为20 μg·L−1, Ⅲ类海水锌的浓度为100 μg·L−1,与本次研究推导出的LWQC和SWQC水平相当,说明现行Zn的水质标准订制较为合理. 比较分析该研究与其他国家或地区推导的锌水质基准值发现,美国[72]基于毒性百分数法制定的短期水质基准值为 120 μg∙L−1,该研究中的短期基准值( 112.40 μg∙L−1) 相对较低. 加拿大[73]基于评价因子法制定的长期基准值为 30 μg∙L−1,澳大利亚[74]基于物种敏感度分布法制定的长期基准值为8 μg∙L−1,该研究长期基准值(16.15 μg∙L−1) 低于加拿大的基准值,高于澳大利亚的基准值. 产生差异的主要原因是:①不同国家在进行水质基准推导时各国的生物区系不尽相同;②不同的生物区系中存在不同的敏感物种;③使用方法、受试生物和水化学条件不同. 除此之外,由于毒性数据收集量的限制,该研究没有考虑硬度、温度、pH等环境因素对水质基准的影响,在不同的试验环境条件下,得出的结果也会有所不同,后续应当结合渤海地区的具体环境条件得出更精确的锌水质基准.
-
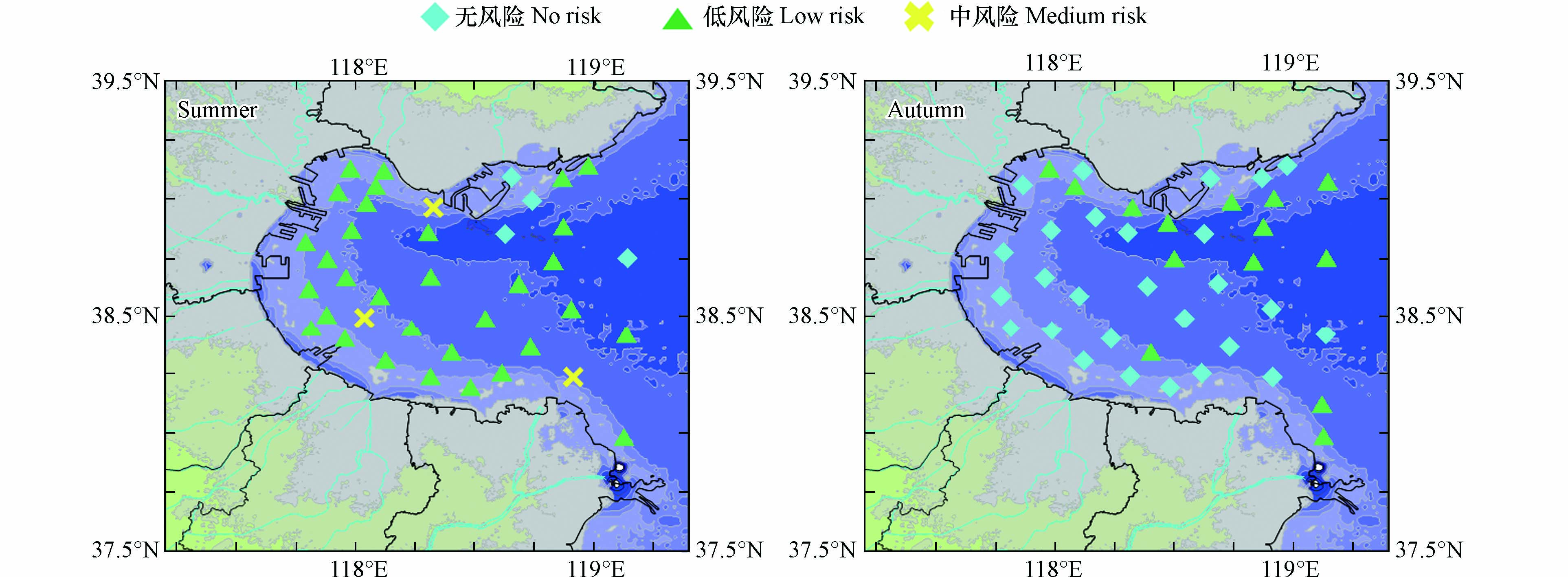
利用推导得到的短期水质基准以及2020年夏季和秋季采集的渤海湾表层水样的水质数据,对渤海湾锌的潜在生态风险进行评价,结果如图3所示. 夏季39个有效监测站点中,无风险站点4个,占比10.26%;低风险站点32个,占比82.05%;中风险站点3个,占比7.69%. HQ值最低为0.0038,最高为2.8365,整体呈现低风险. 秋季41个有效监测站点中,无风险站点28个,占比71.79%;低风险站点13个,占比33.33%. HQ值最低为0.0080,最高为0.3941,整体以无风险为主,风险较低. 从以上结果可以看出,2020年渤海湾锌的短期潜在生态风险较低.
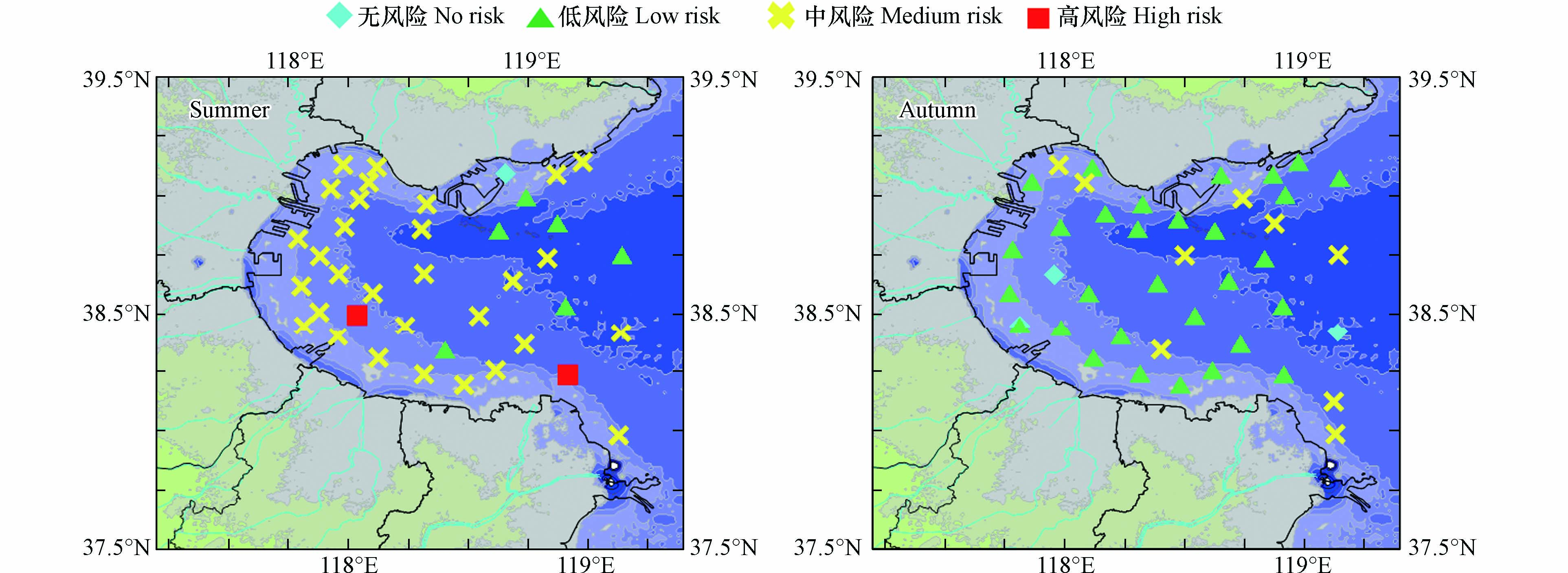
利用同种方法对锌的长期潜在生态风险进行了评价,结果如图4所示. 在夏季采样的39个有效监测站点中,无风险站点1个,占比2.56%;低风险站点6个,占比15.38%;中风险站点30个,占比76.92%;高风险站点2个,占比5.13%. HQ值最低为0.0273,最高为19.7414,整体呈现中风险. 在秋季采样的41个有效监测站点中,无风险站点3个,占比7.69%;低风险站点30个,占比76.92%;中风险站点8个,占比20.51%. HQ值最低为0.0566,最高为2.7429,整体呈现低风险. 从以上结果可以看出,2020年渤海湾具有一定的长期潜在生态风险,部分近岸海域具有高风险,应引起足够的重视.
-
使用收集筛选的毒性数据集和水生生物毒理试验相结合,基于物种敏感度分布法推导出渤海湾海水锌的短期水质基准为112.40 μg∙L−1,长期水质基准为16.15 μg∙L−1. 目前我国海水水质标准Ⅰ类海水规定锌的浓度为20 μg·L−1, Ⅲ类为100 μg·L−1,与本次研究得出的LWQC和SWQC水平相当,说明现行Zn的水质标准订制较为合理,对于防控锌的长期和短期潜在生态风险有一定积极作用. 利用推导的水质基准和渤海湾2020年的水质监测数据,基于熵值法分析了渤海湾海水锌的潜在生态风险,结果表明, 渤海湾水体锌的短期潜在生态风险较低,但具有长期潜在生态风险,并具有季节差异,夏季风险高于秋季风险.
渤海湾锌海水水质基准推导及潜在生态风险评价
Derivation of seawater quality criteria and potential ecological risk assessment of zinc in Bohai Bay
-
摘要: 渤海湾地处我国经济最发达的地区之一,由于流域污染负荷排放超过环境承载力,水生态系统和功能受到不同程度的破坏. 海水水质基准是制定海洋水质标准与科学保护海洋环境的基础,但目前我国海水水质基准的研究较为匮乏. 本研究采用物种敏感度分布曲线法,利用甄选获得的文献数据和毒理试验获得的试验数据,推导了渤海湾重金属锌的海水水质基准. 其中短期水质基准为112.40 μg∙L−1,长期水质基准为16.15 μg∙L−1. 同时,在2020年夏季和秋季分别对渤海湾及其临近海域的水体锌污染状况进行了监测,基于熵值法对渤海湾及其临近海域进行了锌的潜在生态风险评价. 评价结果表明,2020年渤海湾及其临近海域水体中锌的短期潜在生态风险较低,但存在长期风险. 高风险区域主要分布在近岸海域,并且夏季高于秋季.Abstract: Bohai Bay is located in one of the most economically developed areas in China. As the pollution load exceeds the environmental capacity, the aquatic ecosystem and functions of the Bohai Bay have been damaged to a certain extent. Seawater quality criteria are the basis for the establishment of seawater quality standards and rational protection of marine environment, but currently there are few studies on seawater quality criteria in China. This study derived the seawater quality criteria for zinc in Bohai Bay by species sensitivity distribution curve method. The derived short-term and long-term water quality criteria were 112.4 μg∙L−1 and 16.15 μg∙L−1, respectively. In the summer and autumn of 2020, the distribution of zinc in the Bohai Bay and its adjacent waters were monitored respectively. Ecological risks of zinc were assessed based on entropy method. The results showed that the short-term ecological risk of zinc in Bohai Bay and its adjacent waters in 2020 was low, but there was a long-term risk. The high-risk areas were mainly distributed in the coastal areas. In addition, the potential ecological risk for zinc in Bohai Bay has a seasonal variation, and it was higher in summer than in autumn.
-

-
表 1 急性毒性试验条件
Table 1. Experimental conditions for toxicity test
试验物种
Experimental species温度/℃
Temperature年龄
Age通气
Ventilate光照
Illumination体长
Body length暴露时间
Exposure time来源
Source丰年虫
Artemia salina26 成体 否 24 h光照 2 mm 24 h, 48 h 购自华霖 红鳍东方鲀
Takifugu rubripes20 — 持续通气 12 h光照
12 h黑暗8 mm 72 h, 96 h 购自唐山瑞辉水产 南美白对虾
Litopenaeus vannamei23 — 持续通气 12 h光照
12 h黑暗2 cm 24 h, 48 h, 72 h 购自黄骅泰阳种业 褶皱臂尾轮虫
Brachionus plicatilis25 — 持续通气 12 h光照
12 h黑暗170 μm 24 h 购自熙霖水族 小球藻
Chlorella vulgaris25 — 持续通气 12 h光照
12 h黑暗6—8 μm 24 h 分离纯化于渤海 文蛤
Meretrix meretrix12 成体 持续通气 12 h光照
12 h黑暗4.5 cm 48 h, 72 h 捕捞自滨海新区鲤鱼门 缢蛏
Sinonovacula constricta24 蛏苗 持续通气 12 h光照
12 h黑暗1 cm 24 h, 48 h 天津农学院 表 2 锌对渤海物种的急性试验数据
Table 2. Acute experimental data of zinc on species in Bohai Sea
门
Phylum科
Family属
Genus种
Species急性毒性/(μg∙L−1)
Acute toxicity脊索动物门 鲀科 东方鲀属 红鳍东方鲀 4770 软体动物门
软体动物门帘蛤科 文蛤属 文蛤 5650 竹蛏科 缢蛏属 缢蛏 2160 轮虫动物门 臂尾轮虫科 臂尾轮虫属 褶皱臂尾轮虫 4800 节肢动物门 盐水丰年虫科 丰年虫属 丰年虫 3680 节肢动物门 对虾科 滨对虾属 南美白对虾 2190 绿藻门 小球藻科 小球藻属 普通小球藻 1820 表 3 种平均急性值及累积频率
Table 3. Average acute value and cumulative frequency of species
拉丁学名
Binomial nomenclature物种i
Species参考文献
References种平均急性值/ (μg∙L−1)
SMAVi种平均急性值对数
lg(SMAVi, μg∙L−1)毒性秩次
R累积频率
PGlyptocidaris crenularis 海刺猬 [24] 120 2.07 1 0.0303 Crassostrea margaritacea 太平洋牡蛎 [25-26] 140 2.15 2 0.0606 Asterionella japonica 日本星杆藻 [27] 147 2.17 3 0.0909 Skeletonema costatum 中肋骨条藻 [28-29] 417.9 2.62 4 0.1212 Rachycentron canadum 军曹鱼 [30] 610 2.79 5 0.1515 Ulva pertusa 孔石莼 [31] 966 2.98 6 0.1818 Portunus trituberculatus 三疣梭子蟹 [32] 1040 3.02 7 0.2121 Penaeus chinensis 中国对虾 [33] 1320 3.12 8 0.2424 Pagrus major 真鲷 [34] 1350 3.13 9 0.2727 Nassarius festivus 秀丽织纹螺 [35] 1760 3.25 10 0.3030 Mizuhopecten yessoensis 虾夷扇贝 [36] 2040 3.31 11 0.3333 Sinonovacula constricta 缢蛏 试验 2160 3.33 12 0.3636 Litopenaeus vannamei 南美白对虾 [37] 2200 3.34 13 0.3939 Neomysis awatschensis 黑褐新糠虾 [38] 2211.3 3.34 14 0.4242 Mytilus coruscus 厚壳贻贝 [39] 2330 3.37 15 0.4545 Phaeodactylum tricornutum 三角褐指藻 [40-41] 3404.1 3.53 16 0.4848 Artemia salina 丰年虫 试验 3676.6 3.57 17 0.5152 Brachionus plicatilis 褶皱臂尾轮虫 [42] 4040 3.61 18 0.5455 Chlorella vulgaris 普通小球藻 [43] 4539.7 3.66 19 0.5758 Takifugu rubripes 红鳍东方鲀 试验 4770 3.68 20 0.6061 Cynoglossus joyneri 焦氏舌鳎 [44] 4830 3.68 21 0.6364 Boleophthalmus sp. 大弹涂鱼 [45] 4960 3.7 22 0.6667 Capitella capitata 小头虫 [46-49] 5150 3.71 23 0.6970 Exopalaemon carinicauda 脊尾白虾 [50-51] 5190 3.72 24 0.7273 Meretrix meretrix 文蛤 试验 5650 3.75 25 0.7576 Hydroides elegans 华美盘管虫 [52] 6960 3.84 26 0.7879 Acanthopagrus schlegelii 黑鲷 [53] 8270 3.92 27 0.8182 Mytilus edulis 紫贻贝 [54-56] 9330 3.97 28 0.8485 Paralichthys olivaceus 褐牙鲆 [57] 12090 4.08 29 0.8788 Nibea albiflora 黄姑鱼 [58] 16350 4.21 30 0.9091 Mya arenaria 砂海螂 [59] 49640 4.7 31 0.9394 Cyclina sinensis 青蛤 [60] 160000 5.2 32 0.9697 表 4 锌短期水质基准模型拟合结果
Table 4. Fitting result of zinc short-term water quality criteria
分布
Distribution方法
Method5%物种危害浓度/
(μg∙L−1)
HC5P值
P贝叶斯信息量准则
BIC赤池信息量准则
AIC标准误差
SE变异系数
CV1 normal ML 0.2356 0.2218 — 188.6254 0.1124 0.4772 2 logistic ML 0.2690 0.3836 — 187.0556 0.1354 0.5033 3 triangular ML 0.2115 0.0919 — 189.7002 0.1172 0.5539 4 gumbel ML 0.2474 0.0040 — 194.3988 0.0889 0.3592 5 weibull ML 0.0524 0.0170 — 195.9028 0.0610 1.1649 6 burr ML 0.2289 0.4466 — 189.1945 0.1734 0.7576 7 normal MH 0.2039 0.3894 191.3393 — 0.0942 0.4208 8 logistic MH 0.2253 0.2820 189.7914 — 0.1136 0.4532 9 triangular MH 0.1581 0.7142 193.3590 — 0.0678 0.3925 10 gumbel MH 0.2248 0.5770 197.1874 — 0.0739 0.3123 11 weibull MH 0.0613 0.4892 198.6593 — 0.0477 0.6934 12 burr MH 0.2785 0.5014 193.2010 — 0.1274 0.5040 注:ML(maximum likelihood)最大似然法;MH(metropolis Hastings) 蒙特卡罗方法;AIC(Akaike Information Criterion)赤池信息量准则;BIC(Bayesian Information Criterion)贝叶斯信息量准则;CV(Coefficient of Variation)变异系数;SE(standard error)标准误差. 表 5 种平均慢性值及累积频率
Table 5. Average chronic value and cumulative frequency of species
拉丁学名
Binomial nomenclature物种i
Species参考文献
References种平均慢性值/(μg∙L−1)
SMCVi种平均慢性值对数
lg(SMCVi/(μg∙L−1))毒性秩次
R累积频率
PStrongylocentrotus nudus 光棘球海胆 [61] 25.0 1.40 1 0.0909 Acanthopagrus schlegelii 黑鲷 [62] 57.7 1.76 2 0.1818 Mya arenaria 砂海螂 [63] 100.0 2 3 0.2727 Litopenaeus vannamei 南美白对虾 [64] 181.7 2.26 4 0.3636 Mytilus edulis 紫贻贝 [65-66] 316.2 2.5 5 0.4545 Ruditapes philippinarum 菲律宾帘蛤 [67-68] 353.4 2.55 6 0.5455 Zostera marina 大叶藻 [69] 681.4 2.83 7 0.6364 Crassostrea margaritacea 太平洋牡蛎 [65,70] 707.1 2.85 8 0.7273 Macrocystis pyrifera 巨藻 [71] 1071 3.03 9 0.8182 Capitella capitata 小头虫 [46] 5490 3.74 10 0.9091 表 6 锌长期水质基准模型拟合结果
Table 6. Fitting result of zinc long-term water quality criteria
分布
Distribution方法
Method5%物种危害浓度/
(μg∙L−1)
HC5P值
P贝叶斯信息量准则
BIC赤池信息量准则
AIC标准误差
SE变异系数
CV1 normal ML 0.0273 0.9840 — 17.7111 0.0290 1.0622 2 logistic ML 0.0250 0.9181 — 18.5087 0.0302 1.2069 3 triangular ML 0.0323 0.9880 — 18.8520 0.0383 1.1853 4 gumbel ML 0.0335 0.8581 — 19.2264 0.0255 0.7622 5 weibull ML 0.0085 0.9600 — 20.1572 0.0293 3.4534 6 burr ML 0.0281 0.8901 — 23.1102 0.0372 1.3234 1 normal MH 0.0148 0.0076 18.2863 — 0.0186 0.8349 2 logistic MH 0.0126 0.0078 18.5469 — 0.0191 0.9154 3 triangular MH 0.0127 0.0188 18.8871 — 0.0145 0.7565 4 gumbel MH 0.0219 0.0646 19.1847 — 0.0166 0.6037 5 weibull MH 0.0169 0.4582 20.7388 — 0.0213 1.0890 6 burr MH 0.0445 0.5232 21.7195 — 0.0245 0.9756 注:ML(maximum likelihood)最大似然法;MH(metropolis Hastings) 蒙特卡罗方法;AIC(Akaike Information Criterion)赤池信息量准则;BIC(Bayesian Information Criterion)贝叶斯信息量准则;CV(Coefficient of Variation)变异系数;SE(standard error)标准误差. -
[1] 王丽平, 雷坤, 乔艳珍. 天津渤海湾近岸海域沉积物中4种常见重金属的分布及其风险分析 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2017, 36(5): 693-698. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2017.05.009 WANG L P, LEI K, QIAO Y Z. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of four common metals in coastal sediment of Bohai Bay along Tianjin City, China [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2017, 36(5): 693-698(in Chinese). doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2017.05.009
[2] TOMILINA I I, GREMYACHIKH V A, GREBENYUK L P, et al. The effect of zinc oxide nano- and microparticles and zinc ions on freshwater organisms of different trophic levels [J]. Inland Water Biology, 2014, 7(1): 88-96. doi: 10.1134/S1995082914010155 [3] COOPER N L, BIDWELL J R, KUMAR A. Toxicity of copper, lead, and zinc mixtures to Ceriodaphnia dubia and Daphnia carinata [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2009, 72(5): 1523-1528. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.03.002 [4] 许艳, 王秋璐, 曾容, 等. 渤海湾表层沉积物重金属污染状况及年际变化分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(9): 4255-4263. XU Y, WANG Q L, ZENG R, et al. Pollution status and interannual variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Bohai Bay[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 42(9): 4255-4263.
[5] 陈秀, 李爽兆, 袁德奎, 等. 渤海湾沉积物重金属的分布特征及影响因素 [J]. 海洋科学进展, 2017, 35(3): 382-391. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2017.03.008 CHEN X, LI S Z, YUAN D K, et al. Distribution characteristics of sediment heavy metals in Bohai Bay and its effect factors [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2017, 35(3): 382-391(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2017.03.008
[6] 孙雪华, 孙成, 刘红玲. 考虑物种权重校验保护太湖水生生物的铅基准 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(6): 1578-1589. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020021203 SUN X H, SUN C, LIU H L. Weighted species sensitivity distribution method to derive site-specific quality criteria of lead for protection of aquatic life in Tai Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(6): 1578-1589(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020021203
[7] 刘俐, 李亚兵, 刘红玲. 太湖保护水生生物2, 4-二氯苯酚基准研究 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(7): 1774-1787. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019050502 LIU L, LI Y B, LIU H L. Derivation of water quality criteria of 2, 4-dichlorophenol for protection of aquatic life in Tai Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(7): 1774-1787(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019050502
[8] KARTHIKEYAN P, MARIGOUDAR S R, MOHAN D, et al. Prescribing sea water quality criteria for arsenic, cadmium and lead through species sensitivity distribution [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208: 111612. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111612 [9] LEE M S, LEE J H, AN Y J, et al. Development of water quality criteria for arsenic to protect aquatic life based on species sensitivity distribution [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 189: 109933. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109933 [10] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 中华人民共和国国家标准海水水质基准[S]. 2017. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. National Standard of the People's Republic of China for seawater quality reference[S]. 2017 (in Chinese).
[11] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 淡水水生生物水质基准制定技术指南: HJ 831—2017[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2017. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. Technical guideline for deriving water quality criteria for the protection of freshwater aquatic organisms: HJ 831—2017[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2017 (in Chinese).
[12] 陈莉, 蔡文倩, 韩雪萌, 等. 镉对渤海本地种的急性毒性效应及其海水水质基准推导 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(9): 93-102. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20200284 CHEN L, CAI W Q, HAN X M, et al. Acute effect of cadmium on native species and seawater quality criteria derivation in the Bohai Sea [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(9): 93-102(in Chinese). doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20200284
[13] 康凯莉, 管博, 李正炎. 中国近海环境中汞的水质基准与生态风险 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(1): 102-114. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20170377 KANG K L, GUAN B, LI Z Y. Marine water quality criteria derivation and ecological risk assessment for mercury in coastal waters in China [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(1): 102-114(in Chinese). doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20170377
[14] 洪鸣, 王菊英, 张志锋, 等. 海水中金属铅水质基准定值研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(2): 626-633. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.02.044 HONG M, WANG J Y, ZHANG Z F, et al. Study on seawater quality criteria for lead [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(2): 626-633(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.02.044
[15] 王莹, 穆景利, 王菊英. 我国硝基苯的海水水质基准及生态风险评估研究 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(1): 160-168. WANG Y, MU J L, WANG J Y. Derivation of marine water quality criteria and assessment of ecological risk of nitrobenzene in China [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(1): 160-168(in Chinese).
[16] 牛志广, 张玉彬, 吕志伟, 等. 三氯生的水质基准推导及其对渤海湾近岸海域的生态风险 [J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2019, 52(7): 754-762. NIU Z G, ZHANG Y B, LÜ Z W, et al. Derivation of water quality criteria for triclosan concentration and its ecological risk to the coastal waters of Bohai Bay [J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2019, 52(7): 754-762(in Chinese).
[17] 朱韻洁, 朱晓艳, 林英姿, 等. 辽东湾营养盐基准值的研究与确定 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2021, 11(6): 1131-1136. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210065 ZHU Y J, ZHU X Y, LIN Y Z, et al. Study and determination of nutrient criteria in Liaodong Bay [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2021, 11(6): 1131-1136(in Chinese). doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210065
[18] LI L, HE Y J, SONG K, et al. Derivation of water quality criteria of zinc to protect aquatic life in Taihu Lake and the associated risk assessment [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 296: 113175. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113175 [19] US EPA. Guidelines for Deriving Numerical National Water Quality Criteria for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Their Uses[S]. Washington DC: Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency, 1985. [20] European C. Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment Part II[S]. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substances, and Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the placing of biocidal products on the market, 2003. [21] LIU Q, XU X Q, ZENG J N, et al. Development of marine water quality criteria for inorganic mercury in China based on the retrievable toxicity data and a comparison with relevant criteria or guidelines [J]. Ecotoxicology (London, England), 2019, 28(4): 412-421. doi: 10.1007/s10646-019-02032-2 [22] WEN J J, CUI X Y, GIBSON M, et al. Water quality criteria derivation and ecological risk assessment for triphenyltin in China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 161: 397-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.012 [23] LIU X Y, TU M C, WANG S P, et al. Research on freshwater water quality criteria, sediment quality criteria and ecological risk assessment of triclosan in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 816: 151616. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151616 [24] XU X, WANG X, LI Y, et al. Acute toxicity and synergism of binary mixtures of antifouling biocides with heavy metals to embryos of sea urchin Glyptocidaris crenularis [J]. Human & Experimental Toxicology, 2011, 30(8): 1009-1021. [25] WATLING H R. Comparative study of the effects of zinc, cadmium, and copper on the larval growth of three oyster species [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1982, 28(2): 195-201. doi: 10.1007/BF01608575 [26] CHAPMAN P M, MCPHERSON C. Comparative zinc and lead toxicity tests with Arctic marine invertebrates and implications for toxicant discharges [J]. Polar Record, 1993, 29(168): 45-54. doi: 10.1017/S0032247400023202 [27] FISHER N S, JONES G J. Heavy metals and marine phytoplankton: Correlation of toxicity and sulfhydryl-binding [J]. Journal of Phycology, 1981, 17(1): 108-111. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.1981.tb00827.x [28] WALSH G E, MCLAUGHLIN L L, YODER M J, et al. Minutocellus polymorphus: A new marine diatom for use in algal toxicity tests [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1988, 7(11): 925-929. [29] WONG S W Y, LEUNG P T Y, DJURISIĆ A B, et al. Toxicities of nano zinc oxide to five marine organisms: Influences of aggregate size and ion solubility [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2010, 396(2): 609-618. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-3249-z [30] Acute toxicity test to determine the effects of copper, zinc and cyanide on cobia (Rachycentron canadum) resources in north Vietnam[J]. Australasian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2005, 11(3): 163-166 [31] HAN Y S, BROWN M T, PARK G S, et al. Evaluating aquatic toxicity by visual inspection of thallus color in the green macroalga Ulva: Testing a novel bioassay [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(10): 3667-3671. [32] 包坚敏, 王志铮, 杨阳, 等. 4种重金属离子对三疣梭子蟹大眼幼体的急性毒性 [J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(4): 395-398. BAO J M, WANG Z Z, YANG Y, et al. Acute toxicity of four heavy metals on megalopa larvaes of Portunus trituberculatus [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2007, 26(4): 395-398(in Chinese).
[33] 吴彰宽, 陈国江. 二十三种有害物质对对虾的急性致毒试验 [J]. 海洋科学, 1988, 12(4): 36-40. WU Z K, CHEN G J. Studies of acuie intoxication by some harmful substances on Penaeus orientalis K [J]. Marine Sciences, 1988, 12(4): 36-40(in Chinese).
[34] 蓝伟光, 陈霓. Hg, Cu, Cd, Zn 对真鲷仔鱼的急性毒性研究 [J]. 海洋科学, 1991, 15(5): 56-60. LAN W G, CHEN N. Acute toxicity of Hg, Cu, Cd, Zn to larvae of red sea bream, chrysophrys major [J]. Marine Sciences, 1991, 15(5): 56-60(in Chinese).
[35] CHEUNG S G, TAI K K, LEUNG C K, et al. Effects of heavy metals on the survival and feeding behaviour of the sandy shore scavenging gastropod Nassarius festivus (Powys) [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2002, 45: 107-113. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00324-1 [36] 朱丽岩, 唐学玺, 徐怀恕, 等. 锌对虾夷扇贝和刺参幼体的毒性效应 [J]. 海洋通报, 1999, 18(4): 34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.1999.04.005 ZHU L Y, TANG X X, XU H S, et al. Toxic effect of zinc on the larval Patinopecten yessoensis and Apostichopu sjaponnicus [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1999, 18(4): 34-37(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.1999.04.005
[37] WU J P, CHEN H C. Effects of cadmium and zinc on oxygen consumption, ammonium excretion, and osmoregulation of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 57(11): 1591-1598. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.07.033 [38] 窦亚卿, 成永旭, 唐伯平, 等. Cu2+、Zn2+对黑褐新糠虾(Neomysis awatschensis)的毒性作用 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2008, 27(1): 33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2008.01.009 DOU Y Q, CHENG Y X, TANG B P, et al. Toxic effects of Cu2+, Zn2+ on Neomysis awatschensis [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2008, 27(1): 33-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2008.01.009
[39] 周光锋, 王志铮, 杨阳, 等. 4种重金属离子对厚壳贻贝幼贝的急性毒性 [J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(4): 391-394. ZHOU G F, WANG Z Z, YANG Y, et al. Acute toxic effects of four heavy metalson juveniles of Mytilus coruscus Gould [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2007, 26(4): 391-394(in Chinese).
[40] ROSKO J J, RACHLIN J W. The effect of copper, zinc, cobalt and manganese on the growth of the marine diatom Nitzschia closterium [J]. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club, 1975, 102(3): 100. doi: 10.2307/2484731 [41] HORVATIĆ J, PERSIĆ V. The effect of Ni2+, Co2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ on the growth rate of marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin: Microplate growth inhibition test [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2007, 79(5): 494-498. doi: 10.1007/s00128-007-9291-7 [42] 金解敏, 杨家新, 陈立侨. 铜锌离子对褶皱臂尾轮虫的急性毒性试验 [J]. 水产科技情报, 1999, 26(3): 121-123,126. doi: 10.16446/j.cnki.1001-1994.1999.03.007 JIN J M, YANG J X, CHEN L Q. The toxic effect of copper and zinc on rotifer Brachionus plicatilis [J]. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 1999, 26(3): 121-123,126(in Chinese). doi: 10.16446/j.cnki.1001-1994.1999.03.007
[43] 胡冰, 王华, 张冬冬, 等. 纳米TiO2和Cu(Ⅱ)、Zn(Ⅱ)对小球藻和新月菱形藻的毒性研究 [J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2015, 30(5): 489-493. HU B, WANG H, ZHANG D D, et al. Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles, Cu(Ⅱ) and Zn(Ⅱ) to Chlorella sp. and Nitzschia closterium [J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2015, 30(5): 489-493(in Chinese).
[44] 崔可铎, 刘玉梅, 侯兰英. 汞等六种重金属对鱼卵孵化和仔鱼成活的影响 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1987, 18(2): 138-144. CUI K D, LIU Y M, HOU L Y. Effects of six heavy metals on hatching eggs and survival of larval of marine fish [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1987, 18(2): 138-144(in Chinese).
[45] KIDWAI S, AHMED M. Heavy metal bioassays on selected fauna from the Karachi coast (Northwest Arabian Sea) [J]. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 1999, 31(2): 147-157. [46] REISH D J, GERLINGER T V, PHILLIPS C A, et al. Toxicity of formulated mine tailings on marine Polychaete [J]. Marine Biological Consultants, Coasta Mesa, 1977, CA: 133. [47] REISH D J, LEMAY J A. Toxicity and bioconcentration of metals and organic compounds by Polychaeta [J]. Ophelia, 1991, 5: 653-660. [48] REISH D J. The effects of heavy metals on polychaetous annelids[J]. Review International Oceanography Mediterranean. 1978, 49(3): 99-104 [49] REISH D J, MARTIN J M, PILTZ F M, et al. The effect of heavy metals on laboratory populations of two polychaetes with comparisons to the water quality conditions and standards in Southern California marine waters [J]. Water Research, 1976, 10(4): 299-302. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(76)90170-6 [50] 张彩明, 陈应华. Cr6+、Mn7+和Zn2+对脊尾白虾幼虾的单一毒性和联合毒性 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2013, 32(2): 235-238. ZHANG C M, CHEN Y H. Acute toxicity and joint toxicity of Cr6+, Mn7+ and Zn2+ on Palaemon carincauda juvenile [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2013, 32(2): 235-238(in Chinese).
[51] 郑琰晶, 魏社林, 吴进孝, 等. Cu2+、Zn2+、SDS、DBS对脊尾白虾的毒性试验 [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2006, 25(5): 87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2006.05.015 ZHENG Y J, WEI S L, WU J X, et al. Toxicity effect of Cu2+, Zn2+, SDS and DBS on Palaemon carincauda [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2006, 25(5): 87-90(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2006.05.015
[52] GOPALAKRISHNAN S, THILAGAM H, RAJA P V. Comparison of heavy metal toxicity in life stages (spermiotoxicity, egg toxicity, embryotoxicity and larval toxicity) of Hydroides elegans [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 71(3): 515-528. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.09.062 [53] 吕敢堂, 王志铮, 邵国洱, 等. 4种重金属离子对黑鲷幼鱼的急性毒性研究 [J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2010, 29(3): 206-210. LV G T, WANG Z Z, SHAO G E, et al. Acute toxicity of four kinds of heavy metal on juveniles Sparus Macrocephalus [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2010, 29(3): 206-210(in Chinese).
[54] HIETANEN B, SUNILA I, KRISTOFFERSSON R. Toxic effects of zinc on the common mussel Mytilus edulis l. Bivalvia in brackish water i. physiological and histopathological studies [J]. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 1988, 25: 341-347. [55] AMIARD-TRIQUET C, BERTHET B, METAYER C, et al. Contribution to the ecotoxicological study of cadmium, copper and zinc in the mussel Mytilus edulis [J]. Marine Biology, 1986, 92(1): 7-13. doi: 10.1007/BF00392739 [56] ABEL P D. Effect of some pollutants on the filtration rate of Mytilus [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1976, 7(12): 228-231. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(76)90267-8 [57] 黄伟. 汞、铅、锌对褐牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)早期发育过程毒理作用的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2010. HUANG W. Toxic effects of mercury, lead and zinc on early life stages of flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010(in Chinese).
[58] 王志铮, 刘祖毅, 吕敢堂, 等. Hg2+、Zn2+、Cr6+对黄姑鱼幼鱼的急性致毒效应 [J]. 中国水产科学, 2005, 12(6): 745-750. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2005.06.013 WANG Z Z, LIU Z Y, LU G T, et al. Acute toxic effects of Hg2+, Zn2+ and Cr6+ on Nibea albiflora juvenile [J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2005, 12(6): 745-750(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2005.06.013
[59] EISLER R, HENNEKEY R J. Acute toxicities of Cd2+, Cr^+6, Hg2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ to estuarine macrofauna [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1977, 6(1): 315-323. doi: 10.1007/BF02097772 [60] 周凯, 么宗利, 来琦芳, 等. 重金属Zn2+、Cd2+对青蛤幼贝的致毒效应 [J]. 海洋渔业, 2007, 29(1): 63-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2007.01.012 ZHOU K, YAO Z L, LAI Q F, et al. Acute toxicity effects of Zn2+ and Cd2+ on juveniles of clam (Cyclina sinensis) [J]. Marine Fisheries, 2007, 29(1): 63-67(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2007.01.012
[61] DURKINA V B. Morphofunctional changes in development of Sea Urchin Offspring as a Result of adult exposure to copper and zinc[J]. Russian Journal of Marine Biology. 1995, 21(6): 351-355 (in Chinese). [62] ZHANG L, WANG W X. Effects of Zn pre-exposure on Cd and Zn bioaccumulation and metallothionein levels in two species of marine fish [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2005, 73(4): 353-369. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.04.001 [63] PARISEAU J, SAINT-LOUIS R, DELAPORTE M, et al. Potential link between exposure to fungicides chlorothalonil and mancozeb and haemic neoplasia development in the soft-shell clam Mya arenaria: A laboratory experiment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 58(4): 503-514. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.12.011 [64] WU J P, CHEN H C. Effects of cadmium and zinc on the growth, food consumption, and nutritional conditions of the white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2005, 74(2): 234-241. doi: 10.1007/s00128-004-0575-x [65] GÉRET F, JOUAN A, TURPIN V, et al. Influence of metal exposure on metallothionein synthesis and lipid peroxidation in two bivalve mollusks: The oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and the mussel (Mytilus edulis) [J]. Aquatic Living Resources, 2002, 15(1): 61-66. doi: 10.1016/S0990-7440(01)01147-0 [66] NAYLOR G P L. The responses of Cockles to heavy metal pollution and their use in the study of metal to metal uptake interactions[D]. UK: University of Manchester, 1987: 169. [67] MARTÍN-DÍAZ M L, BLASCO J, GONZÁLEZ de CANALES M, et al. Bioaccumulation and toxicity of dissolved heavy metals from the Guadalquivir Estuary after the Aznalcóllar mining spill using Ruditapes philippinarum [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2005, 48(2): 233-241. doi: 10.1007/s00244-003-9202-9 [68] NG T, WANG W X. Detoxification and effects of Ag, Cd, and Zn pre-exposure on metal uptake kinetics in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum [J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2004, 268: 161-172. doi: 10.3354/meps268161 [69] ZOSTERA M. The uptake of heavy metals in eelgrass zostera marina and their effect on growth[J]. Ecological Bulletion. 1984, 36: 81-89. [70] WATLING H. The effects of metals on mollusc filtering rates [J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of South Africa, 1981, 44(3): 441-451. doi: 10.1080/00359198109520587 [71] ANDERSON B S, HUNT J W, MARTIN M, et al. Marine Bioassay Project. 3rd Report. Protocol Development: Reference Toxicant and Initial Complex Effluent Testing. Div. of Water Qual. Rep. No. 88-7WQ, State Water Resources[R]. Control Board, State of California, Sacramento, CA, 1988: 154 . [72] US EPA. Ambient water quality criteria for zinc[S]. New York: Office of Water, US Environmental Protection Agency, 1980. [73] CCME. Canadian environmental quality guidelines[S]. Winnipeg: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, 2010. [74] ANZEC C, ARMCAN Z. Australian and new zealand guidelines forfresh and marinewater quality[S]. Canberra: Australian and NewZealand Environment and Conservation Council and Agricultureand Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand, 2000. -



 下载:
下载: