-
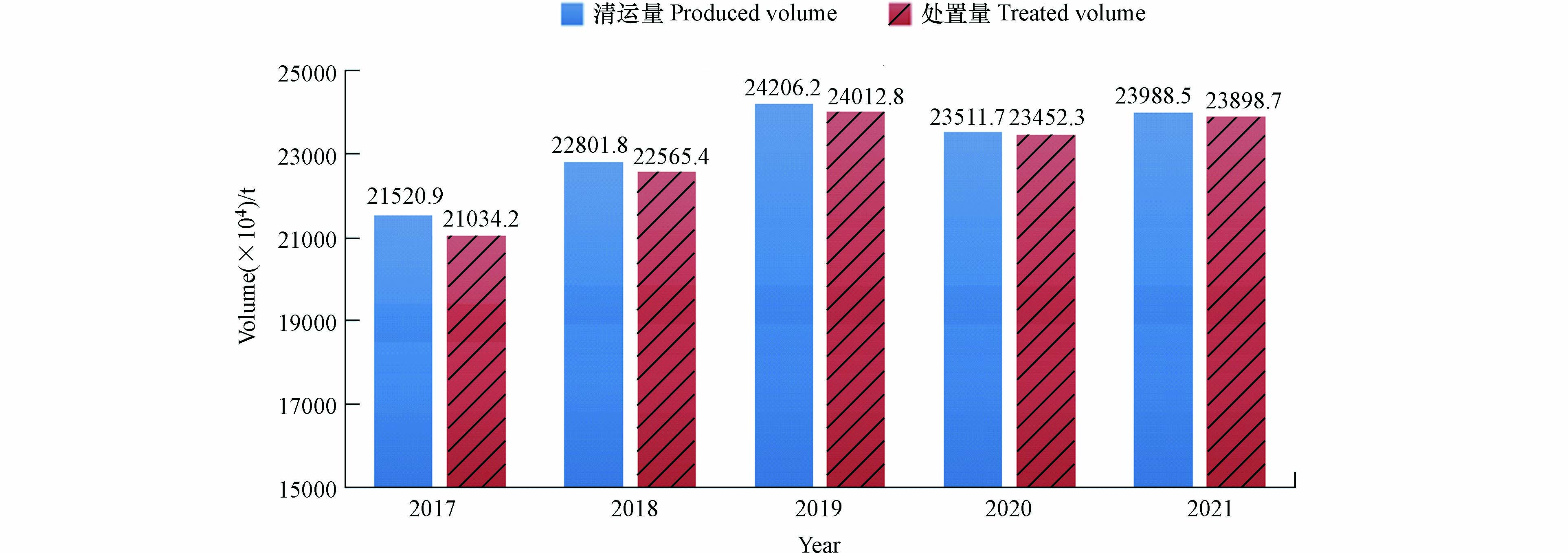
进入21世纪以来,全球经济呈现爆发式增长,GDP总量翻了接近3倍,尤其是发展中国家的进步尤为迅速,大量农村人口涌入大城市,城市化的快速发展必然导致生活垃圾的快速增加. 城市生活垃圾种类繁多,主要包括食物垃圾、纸张、塑料、木材、纺织品等[1]. 国家统计局在《中国统计年鉴2021》中记录:我国2020年的城市生活垃圾清运总量为23511.7万吨,无害化处理量23452.3万吨(如图1所示),生活垃圾无害化处理率达到99.7%,基本实现了闭环处置.
垃圾填埋和焚烧是世界上两种主要的垃圾处理方式[2]. 相比于焚烧技术,填埋法更为简单便捷,早年是主流的垃圾处置方式. 然而垃圾填埋需占用大量土地,在土地资源日益稀缺的今天,并不适合未来的可持续发展需求. 更为严重的问题是垃圾填埋后随着雨水的渗透和时间的推移,垃圾降解会产生大量的垃圾渗滤液,逐渐污染周围的土壤并随着地下水系统蔓延至江河湖海中. 因此,焚烧法近年来得到广泛应用,规模占比逐渐增长到垃圾无害化处理量的50%以上[3]. 生活垃圾经过焚烧处理后,体积、质量均可显著减少,有机物质完全焚烧产生的热量可用于供暖发电,真正实现废物的资源化利用,间接减少了碳排放[4]. 在发改委2014年发布的《国家重点推广的低碳技术目录(第一批)》中,垃圾焚烧也被作为低碳技术进行了广泛推广. 2020年国家发改委等多个部门联合发布了《城镇生活垃圾分类和处理设施补短板强弱项实施方案》,方案中提出要全面推进焚烧处理能力建设,鼓励发展以焚烧为主的垃圾处理方式,2023年在垃圾日产量超过300 t的地区基本实现原生垃圾“零填埋”.
城市垃圾焚烧主要有两种颗粒副产物,即焚烧炉底灰和垃圾焚烧飞灰(以下简称“飞灰”)[5]. 其中,焚烧炉底灰指的是垃圾经焚烧之后残留在炉床上的固体废物,而飞灰主要是在垃圾焚烧烟气净化系统中收集到的细颗粒粉末物质. 由于污染物浓度低,城市垃圾焚烧底灰被广泛用作建筑施工领域的二级原材料[6]. 然而飞灰因为其含有较高的有毒元素(铅、镉、汞、钼、镍、硒等)和其它污染物(二噁英、呋喃、硫酸盐和氯化物等),《国家危险废物名录》规定为危险废物,编号HW18. 飞灰的收集、储存、运输、安全处置会对环境和人类健康产生严重影响,因此必须谨慎处理.
目前飞灰的处置方式主要有两种:(1)稳定化/固化后填埋;(2)资源化利用生产建材[7]. 稳定化/固化法是将危险废物与黏结剂混合,通过物理和化学手段降低污染物的浸出性,然后将危险废物转化为符合填埋处理要求的一般废弃物[8]. 经过成型处理的飞灰混合物料具有低毒性、低溶解性、低迁移性,能在较为安全的条件下运输与处置[9]. 水泥由于价格低廉、固化效率高,被广泛用于危险材料的稳定化/固化和污染场地修复. 但水泥对重金属的固化效果并不稳定,且水泥固化会使飞灰显著增容,导致填埋量增加,因此药剂稳定化后填埋近年来成为主流[10]. 常用药剂分为无机和有机两种,此类技术工艺简单、固化效果好、投资费用低,且处理后飞灰基本不增容[11]. 然而,正如垃圾填埋的问题一样,飞灰填埋也开始面临土地资源紧缺的问题,并且飞灰属于危险废弃物,填埋的隐患更大,场地建设费用也远高于一般填埋场. 2020年8月中国发布了首个飞灰污染治理技术规范(HJ 1134—2020),文件中明确处置后的飞灰如果符合国家标准的具体要求,可被列为一般废物,甚至可作为资源进一步利用. 因此如何实现飞灰的绿色循环越来越受到重视,本文将综合阐述飞灰的各类资源化处理技术及相应资源化产品.
-
飞灰的理化特征差别较大,主要是由垃圾组分、锅炉类型和烟气净化系统的具体情况决定的[12]. 目前主流的机械炉排炉飞灰产生量较少,约为入炉垃圾量的1.5%—4%;对比之下,流化床焚烧炉的飞灰产生量较多,约为入炉垃圾量的10%—20%[13]. 飞灰外观一般均为浅灰色粉末,内部结构比较复杂,不同炉型飞灰的形貌有较大区别,流化床飞灰的颗粒尺寸较大且杂乱无章,而炉排炉飞灰颗粒粒径较小且呈球形[13].
飞灰的化学组成主要为钙、氯、钠、钾等氧化物或盐类,其中钙离子的存在多源于烟气处理系统中脱酸投加的石灰,而氯、钠、钾等离子多源于垃圾自身的化学组成[14]. 氯离子多以可溶性氯化物或氯酸盐的形式存在,含量一般为10%—30%,最高也可达40%左右[14]. 可溶性氯盐是飞灰无害化、资源化处置的难点,不仅会增加重金属的浸出毒性和迁移风险,还会降低资源化产品的强度和稳定性[15]. 在高温熔融/烧结的过程中,飞灰内可溶盐会挥发至烟气中,造成设备堵塞、腐蚀、结皮等问题. 而在水泥窑协同处置时,大量氯盐的存在会对水泥窑设备造成不可逆的伤害,生产的水泥产品达不到GB 175—2007《通用硅酸盐水泥》标准中的指标要求[16]. 因此,水洗预处理逐渐成为飞灰资源化处置不可或缺的一环,并且可以从水洗液中进一步回收高价值的氯化钾[17].
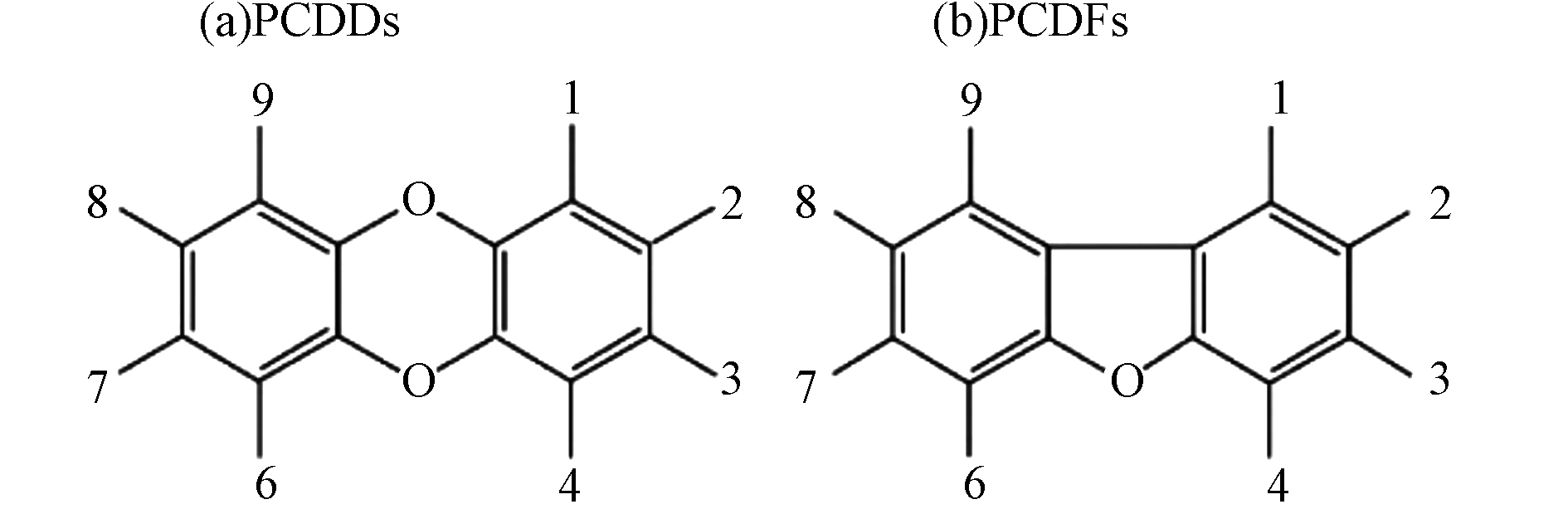
垃圾焚烧过程中会产生剧毒的二噁英,在烟气处置系统内气相中的二噁英转移到灰相中,通过一系列措施可以降低烟气中二噁英浓度(包括燃烧装置升级、烟气快速降温以及烟道清灰等),有效控制飞灰中的二噁英含量,但无法实现彻底清除[18]. 二噁英属氯代含氧三环芳烃类化合物,成分较为复杂,具体包括多氯代二苯并二噁英(PCDDs)和多氯代二苯并呋喃(PCDFs)两大类[18]. 二噁英的存在使得飞灰无法简单地被直接资源化利用,其降解被认为是飞灰无害化处置的必要条件[19]. 二噁英结构如下:
除二噁英外,重金属也是飞灰中的主要有毒成分,重金属含量与垃圾焚烧工艺、垃圾给料成分等有关,使飞灰具有一定浸出毒性[20]. 由于国内垃圾分类尚处于起步阶段,塑料类、织物类、灰土、纸品类垃圾中不可避免地混杂一些金属元素物质. 垃圾焚烧过程中熔点较低的部分重金属在高温下挥发进入烟气中,后在烟气处理系统内降温凝结富集到飞灰中,Hg、Pb、Cu、Cd、Cr、Zn、Ni是飞灰中常见的几种重金属[20]. 谷忠伟[21]对比流化床和机械炉排炉两种垃圾焚烧炉型产生的飞灰,发现炉排炉飞灰的重金属含量普遍高于流化床飞灰,其中流化床/炉排炉飞灰中Pb和Cd平均含量分别为1022.28/2458.48 mg·kg−1和68.08/180.84 mg·kg−1.
-
飞灰的特殊性质决定了其资源化处置难度较大[14],为此国家和地方政府也出台了一系列技术规范进行指导(表1). 其中,HJ 1134—2020《生活垃圾焚烧飞灰污染控制技术规范(试行)》的发布具有重要历史意义,对利用飞灰资源化制备水泥熟料、水泥混合材、免烧砖、混凝土掺和料、烧结陶粒、玻璃体等建材产品的工艺路线提出了明确的污染控制要求,规范了相应的产品指标和检测方法,为推动行业的发展起到积极的标准引导作用.
在水泥窑协同处置生产水泥熟料方面,HJ 1134标准中要求处置过程中的污染防治措施应遵循GB 30485《水泥窑协同处置固体废物污染控制标准》及HJ 662《水泥窑协同处置固体废物环境保护技术规范》,制得水泥熟料产品的指标应满足GB 30760《水泥窑协同处置固体废物技术规范》的要求,重金属含量限值/可浸出浓度如表2所示. 此外,HJ 1134标准中提到飞灰可以通过高温熔融/烧结处理得到玻璃体、轻骨料(陶粒)等资源化产品,但不得用于烧结砖生产;高温资源化产物只能用于生产建筑材料,不得用于其它用途,其重金属浸出浓度不得超过GB/T 14848《地下水质量标准》中Ⅲ类水的浓度限值(检测方法为HJ/T 299《固体废物浸出毒性浸出方法硫酸硝酸法》). 2021新发布的GB/T 41015《固体废物玻璃化处理产物技术要求》也适用于飞灰熔融处置后产物的玻璃化判定及质量管理.
考虑到高温资源化技术的处置成本较高[14],HJ 1134标准对非高温重金属固化技术也给出路线指引,明确飞灰可以作为部分替代原料,生产水泥混合材、混凝土掺和料、免烧砖等建筑材料,产品的重金属浸出浓度参考GB 30760《水泥窑协同处置固体废物技术规范》的要求. 但HJ 1134标准要求此类技术必须配套二噁英预解毒设施,飞灰中二噁英的分解去除率应达到99%以上,处理后产物中二噁英残留含量应低于50 ng-TEQ·kg−1. 飞灰资源化利用时,二噁英的去除要求明显严于GB 16889—2008《生活垃圾填埋场污染控制标准》中二噁英含量(或等效毒性量)低于3 μg·kg−1的规定限值. 此外,HJ 1134标准中明确要求飞灰作为替代原料生产建筑材料时,无论采用何种资源化工艺,还应保证氯含量满足建筑材料生产原料和工艺的控制要求. 由此可见,二噁英、重金属和氯盐的控制是飞灰资源化技术的关键.
除行业标准外,部分地区近年来也出台了一些地方标准来规范飞灰的资源化利用,如天津的地方标准DB12《高温烧结处置生活垃圾焚烧飞灰制陶粒技术规范》,规定陶粒产品参照GB 34330的规定,按照相应的产品进行管理;江苏出台了DB32∕T 3558—2019《生活垃圾焚烧飞灰熔融处理技术规范》,明确规定了熔融固化体在用作各类产品时参考的产品质量标准(细骨料参照GB/T 14684;粗骨料参照GB/T 14685;矿渣棉参照GB/T 11835;泡沫玻璃参照JC/T 647).
同时,为了进一步规范飞灰资源化的某些特殊产品,一些团体标准近年来也在紧锣密鼓的编制中,如中国再生资源回收利用协会批准发布的《表面处理污泥、生活垃圾焚烧飞灰烧结制备衍生轻集料》(发布编号:T/ZGZS 0301—2020),标准规定了表面处理污泥、生活垃圾焚烧飞灰烧结制备衍生轻集料的产品质量和污染物控制要求等.
-
飞灰的物理化学性质启发了研究人员寻找其新的处置和资源回收技术,各类技术规范也为飞灰资源化途径指明了方向. 其中,HJ 1134标准系统性地对水泥窑协同、高温烧结/熔融、非高温生产建材3类资源化技术提出了明确的污染控制技术要求,结合目前学界广泛研究的飞灰中高价值金属提取技术[7],本节将按以下技术分类展开详细讨论:(1)飞灰与水泥生料混合燃烧制备水泥熟料;(2)高温烧结/熔融制备建材;(3)非高温重金属固化技术;(4)资源化提取高价值金属(图2).
-
水泥和混凝土是世界上使用最广泛的建筑材料,而普通硅酸盐水泥是最常用的水泥类型. 水泥生产工艺成熟,但熟料烧制的过程也存在一些环境问题:(1)石灰石在煅烧过程中分解造成大量的二氧化碳排放;(2)生产过程中需要消耗大量的黏土和石灰石原料,造成能源和自然资源的密集消耗;(3)黏土等原料在煅烧过程中分解产生酸性气体(如SO2和NOx),对环境造成污染[22]. 飞灰富含硅、钙、铝、铁和硫,其化学成分与生产水泥用的原料非常相似,研究发现可以与水泥原料一起混合燃烧制备水泥熟料[23]. 与单独使用石灰石相比,碳含量较低的飞灰在水泥窑中共燃有助于减少二氧化碳排放. 与此同时,由于混合燃烧过程中的高温(超过1450℃)和碱性环境,飞灰中的一些潜在有毒元素(如Pb、Zn和Cu)和大多数有机污染物(如二噁英和呋喃)可以被化学固定或完全摧毁[24]. 鉴于上述优点,水泥窑协同处置技术成为了飞灰资源化处置领域的主流选择,在2018年的《国家先进污染防治技术目录(固体废物处理处置领域)》中被作为推荐技术进行推广. 目前,我国水泥窑协同处置飞灰的工艺已较为成熟(图3),达到工业化应用水平,各省也陆续建设了水泥窑协同处置飞灰项目.
-
在水泥原材料中加入飞灰来生产普通硅酸盐水泥是可行的,但氯、碱含量严重限制了飞灰的掺入量. 飞灰中大量含氯化合物的存在会导致水泥窑的腐蚀和堵塞,以及烧制成的水泥存在抗压强度低和耐久性问题[15]. 同时,飞灰中碱金属含量过高,会导致水泥和混凝土的孔隙结构和强度损失[26]. 根据美国混凝土协会ACI 318技术规范,仅从矿物学成分来看,最高允许掺入67.8%的飞灰生产水泥熟料,但要求限制熟料中碱含量时,飞灰的活性掺入量降至3.7%,当氯化物和碱含量都受到限制时,比例进一步下降到0.3%. 因此,必须进行预处理,以尽量减少氯盐和碱金属含量对飞灰基水泥熟料质量的影响.
水洗预处理可有效去除飞灰中的氯化物和部分可溶性有毒元素,合适的工艺选择很重要,并且洗涤液需循环使用,以减少水资源消耗[27]. 水洗过程中可以通过向洗涤液中添加无机酸或化学沉淀剂来调节pH值,提高水体中钙盐溶解度,从而抑制有毒元素的浸出[15]. 除无机酸外,在洗涤过程中鼓泡CO2气体也可以降低溶液的pH值,并使重金属元素及钙离子共沉淀[28]. 例如,Wang等[29]开发了一种绿色循环的飞灰资源化路线:将从水泥窑富含二氧化碳的尾气吹入洗液中进行飞灰预处理,然后将干燥后的飞灰与石灰石、黏土一起进行研磨、均质,送入回转窑,在1400 ℃下煅烧制成水泥熟料.
尽管水洗预处理能够提高飞灰基水泥熟料的质量,但是清洗后的飞灰掺入仍会对水泥水合物的形成有不利影响,延缓砂浆/混凝土早期强度的形成[26]. Bogush等[26]制备了飞灰掺入量为35%的普通硅酸盐水泥熟料,发现洗涤后的飞灰抑制了3CaO·SiO2 (C3S)和3CaO·Al2O3 (C3A)的形成,导致砂浆抗压强度较低. Pan等[30]在水泥原料中掺入预处理后的飞灰(1.75%)和底灰(3.50%)生产普通硅酸盐水泥,发现混凝土凝结时间显著延长. 此外,社会面有大量的富钙固废需要掺入生产水泥熟料,这也限制了飞灰作为原料用于普通硅酸盐水泥生产.
-
低能耗水泥一般指烧制温度低于1200 ℃的水泥产品. Alinite水泥是低能耗水泥中的代表类型,通过在硅酸盐水泥生料中掺入CaCl2煅烧而制得,被普遍认为是环保水泥,Ca11(Si, Al)4O18Cl是其主要矿物相[31]. 由于煅烧温度较低(约1100 ℃),生产Alinite水泥的能耗比普通硅酸盐水泥低30%左右[32],因此研究人员开始探索用飞灰部分替代普通原料生产Alinite水泥,例如同济大学施惠生教授带领的团队已经成功地掺入少量的飞灰烧制成Alinite水泥的熟料[33]. Wu等[34]以30%飞灰为原料,在1200 ℃煅烧2 h,制得质量优良的Alinite水泥,与普通硅酸盐水泥的抗压强度相比,掺入飞灰制备的Alinite水泥具有较高的早期强度. 另外,当石膏掺入量为3%—5%时,掺入飞灰制备的Alinite水泥具有较高的抗压强度(40—120 MPa)和良好的抗碳化性能、透水性、抗氧化性能,并且能够抵抗硫酸盐的侵蚀[35].
硫铝酸钙水泥也是一种低能耗水泥,传统上由石灰石、铝土矿和石膏作为原料生产制得,以硫铝酸钙为主要矿物相[36]. 在实验室规模的研究中,Wu等[37]用飞灰部分替代原材料生产硫铝酸钙水泥,在1250 ℃下焙烧2 h,飞灰的掺入量达到30%,掺入飞灰制备的硫铝酸钙水泥样品第3天抗压强度为83.9 MPa,约为第28天抗压强度(92.8 MPa)的90%,表现出较好的早期抗压强度. 掺入飞灰制备的硫铝酸钙水泥除具有良好的抗压强度外,还具有较好的透水性、抗干缩和碳化性能,以及较高的抗硫酸盐腐蚀性能[38]. 经洗涤预处理后,飞灰在混合料中的掺入比例可进一步达到35%,利用洗涤后的飞灰(35%)、烟气脱硫石膏(37.5%)和铝灰(27.5%),在1250 ℃焙烧30 min后可形成固体废物基硫铝酸盐水泥[39],实现不同工业副产物的优势互补,从而促进飞灰和其它副产物的综合利用.
此外,从物理性能角度看,完全以飞灰和底灰为原料合成生态水泥理论上是可行的,适当的化学添加剂配合CO2活化可促进生态水泥的反应活性. 例如Ghouleh等[40]采用85%的烟气处理废弃物和15%的添加剂(熟石灰和硅砂)为原料,1000 ℃烧结30 min可合成生态水泥. 值得一提的是,这种以废弃物资源化生产的生态水泥在2 h的碳化活化后表现出与普通硅酸盐水泥相似的结合能力,抗压强度达到53 MPa,CO2的固定量为6.7%. 类似地,一种完全以垃圾焚烧残渣(30%飞灰、25%底灰、45%石灰渣)为原料,在2 h CO2活化后制成的新型生态水泥,其第28天强度约为55 MPa,与普通硅酸盐水泥相当[41]. 这类利用垃圾焚烧废渣生产低能耗生态水泥的工艺,废物利用率极高,为飞灰循环利用提供了一种新的技术选择,但产品稳定性和潜在环境影响(如废气处置、有毒元素迁移)仍需进一步研究.
-
水泥窑协同处置技术虽然成熟度较高,但产能有限且受地域约束较大,并不能覆盖全国各城市飞灰的资源化处置. 高温烧结/熔融处理对飞灰的减容、重金属固化、二噁英降解效果极其显著,被认为是实现飞灰无害化的有效选择之一[42]. 飞灰经熔融无害化处置后形成的玻璃态熔渣传统方法是将其进行填埋处置,也可高温预处理后作为胶凝剂或掺合料制备建材,但能耗较大,产品价值不高[43]. 为此,不少科研人员开始研究如何将飞灰高温烧结/熔融制备微晶玻璃、泡沫玻璃、轻骨料和陶瓷砖等建筑材料.
-
微晶玻璃又称微晶玉石或陶瓷玻璃,是通过晶化热处理在基础玻璃内均匀地析出大量的微小晶体而形成的多相复合体,因其优异的综合性能可作为一种新型的建筑材料. 飞灰与微晶玻璃生产原料的化学组分类似,理论上可以利用飞灰作为原料制备出附加值较高的微晶玻璃[44]. Fan等[45]以飞灰为主要原料,在高温下成功制得密度为3.42 g·cm−3、维氏硬度为6.91 GPa、浸出毒性符合US EPA浸出标准要求的微晶玻璃,并对工艺参数,包括添加剂成分、热处理温度和反应时间进行了研究和优化.
在此基础上,为了进一步降低处置成本,不少研究证明飞灰可以与其它废弃物共融制备微晶玻璃. 例如,Vu等[46]以80%底灰和20%飞灰的混合物为原料,通过控制反应条件制得主要晶相为铝长石Ca2Al2SiO7、Ca2MgSiO7和CaSiO3的微晶玻璃,产品的耐化学性和重金属浸出毒性均满足工程和建筑应用的需求. Zhao等[47]以飞灰、酸洗污泥和废玻璃为原料,先在1450 °C下保温熔融得到基础玻璃熔融,再在850 °C结晶制备微晶玻璃,同时还研究了酸洗污泥(10%—26%)和废玻璃(34%—50%)添加量对形核、晶化温度的影响. 李志川等[48]以飞灰为主原料,通过优势配伍粉煤灰和废玻璃,制备了全废物基微晶玻璃,所制得的产品中重金属浸出浓度远低于GB 5085.3—2007《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》中的浸出浓度阈值,抗压强度在总体上随烧结温度和碱度的升高而升高.
-
泡沫微晶玻璃是由碎玻璃、发泡剂、发泡促进剂和改性添加剂等原料,细磨混合后经过高温熔化、发泡、退火而制成的无机非金属玻璃材料,因其具有优良的吸声性、绝缘性和力学性能,在建筑和功能材料领域具有广阔的应用前景,附加值较高[49]. Liu等[50]以飞灰和底灰粉末为原料,添加少量碳酸钙为发泡剂,磷酸钠为泡沫稳定剂,制备了密度为0.67 g·cm−3、抗压强度为10.56 MPa、浸出毒性低于US EPA危险废物浸出阈值的泡沫微晶玻璃,并研究了原料组成、发泡温度和发泡时间对其性能的影响. 类似的,张晗等[51]以飞灰和废玻璃作为原料,通过添加少量发泡剂CaCO3、助熔剂H3BO3,制备多孔陶瓷玻璃,分析表明产物中主要生成了CaSiO3玻璃晶相,烧结温度超过900 ℃时重金属浸出浓度低于GB 5085.3《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》中的阈值要求.
以熔融飞灰为原料烧制泡沫微晶玻璃需要对发泡剂、熔体黏度进行优选和控制,而熔体黏度和表面张力是控制发泡过程的关键因素[52]. 研究发现通过碱激发玻璃悬浮液预制泡沫玻璃坯体可有效减少熔体黏度对发泡过程的影响,然后再利用烧结工艺强化,制得的泡沫微晶玻璃力学性能更优[53]. 张俊杰[49]以各50% wt的飞灰与底灰经玻璃化后在NaOH溶液中进行碱激发,固液比为55:45,形成无机凝胶体之后加入二次铝灰渣发泡剂在模具中75 ℃养护24 h后形成强度较低(<0.1 MPa)的多孔坯体,最后经过1150 °C高温析晶强化后形成泡沫微晶玻璃,产物的孔隙率、体积密度和抗压强度分别为79.66%、0.75 g·cm−3和5.55 MPa.
-
轻骨料是用轻粗骨料、轻细骨料或普通细骨料、水泥、水、外加剂和掺和料配制而成的,可作为混凝土,其表观密度一般不大于1.95 g·cm−3,具有导热系数低、隔音、防火等优点. 前期研究已经论证了将固体废物(如冶金渣、沉积物、煤飞灰、城市垃圾焚烧残留物和各种灰烬)回收为人工轻质骨料的可行性[54]. 烧结作为主要的热处理方法,用于将飞灰回收成轻质骨料,以固定有毒金属元素,减少飞灰的体积[5]. Wei等[55]认为,较高的烧结温度和较长的烧结时间可以提高飞灰中有毒元素的固化效率. 陶粒是应用最多的一种轻骨料,魏国侠等[56]开展了河流污染底泥与飞灰混合后烧制陶粒的实验研究,发现污泥与飞灰的合适配比为4:1,焙烧温度宜控制在1150 ℃左右,在最佳条件下烧制陶粒的筒压强度为4.56 MPa,通过高温烧结处置后重金属和二噁英都能得到有效控制. 吴玉杰等[57]以废玻璃、污泥、飞灰、盐渍土等为原料(含量分别为10%、6%、70%、8%)烧制陶粒,制备的高强度陶粒其有毒污染物浸出浓度均满足GB/T 5085.3《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》的要求. 此外轻质骨料还可以固定二氧化碳(颗粒质量的3.5%—11.1% wt的二氧化碳),具有更高的环境优势和低碳足迹. CO2固化处理可进一步提高轻质骨料的性能,体现为降低吸水率、快速发展早期强度[58]. 在未来的研究中,需要研究飞灰的前处理、掺入量、固化条件(如固化时间和复合条件)和成球参数,以获得稳定的飞灰衍生的轻骨料产品.
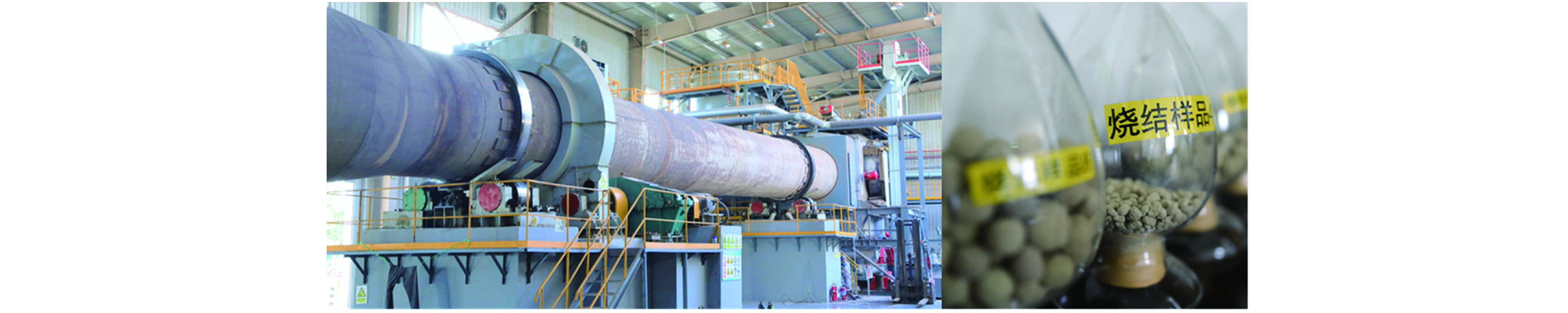
目前,天津壹鸣环境污染治理有限公司已完成了此类技术的工业化验证,年处理飞灰10万吨,涵盖天津市大部分和北京市部分飞灰的安全处置,年产陶粒建筑材料25万吨(图4).
-
建筑陶瓷除了在性能上追求高强度、高耐磨、多功能等,如何降低生产成本也是提高产品竞争力的有效方式. 因此在生产过程中合理地掺入各类工业废弃物既可以减少部分原料的使用,同时可实现协同处置的目的[59]. 飞灰主要矿物成分是硅酸盐及铝硅酸盐,玻璃相含量高达50%以上,理论上作为一部分原料烧制陶瓷砖是可行的[60]. 张海英等[61]以飞灰、黄陶土、文石、缸砂为原料(用量分别为25%、55%、10%、10%)烧制陶瓷砖,950 ℃煅烧后成品抗压强度达到MU 15级,Zn、Hg、As、Pb、Cd、Ni、Cr、Cu等重金属得到有效固化. 然而,相比于烧制水泥熟料和熔融等技术,飞灰烧制陶瓷砖的研究较少,仍需进一步优化工艺.
-
高温处置技术能同步实现飞灰中二噁英、重金属等有毒元素的去除或固化,然而综合处置成本较高,并且高温下的安全风险及重金属气化带来的环境风险不可忽视[14]. 因此,非高温重金属固化技术的发展也备受关注,主要可利用飞灰制备混凝土、免烧砖、地聚合物、沸石、沥青胶浆、可控性低强度材料等. 需要注意的是根据HJ 1134—2020标准的要求,飞灰作为替代原料生产非高温建筑材料前,应预先对飞灰进行二噁英解毒处理(可选用高温熔融或低温热解技术),并不鼓励飞灰低温处理后直接应用于建材行业. 飞灰二噁英高温降解技术已初步得到应用,但是能耗过高,安全风险大,非高温的降解技术目前处于中试验证阶段[19]. 此外,飞灰处置后用作土壤改良剂和污泥调节剂等领域也有研究[62],但是由于涉及土地和农作物安全,政策上并不鼓励.
-
研究发现飞灰的化学成分类似于粉煤灰、高炉矿渣等辅助性胶凝材料,可用于部分替代水泥制备混凝土[63]. 粒径在1—50 μm之间的辅助胶凝材料为首选,当粒径超过100 μm时,火山灰活性显著降低[27]. 飞灰颗粒细小,粒径通常小于100 μm,含有丰富的Ca、Al和Si元素,这使其成为了辅助胶凝材料的可选替代材料[63]. 宁博等[64]开展了单掺飞灰和复掺矿物掺合料的混凝土试验,发现单掺10%飞灰的混凝土抗压强度优于空白组和复掺矿物掺合料组,证明飞灰作为混凝土掺合料是可行的. 常威等[65]开展了循环流化床焚烧炉飞灰制备混凝土免烧砖的性能研究,结果表明当水泥用量为30%时,用飞灰和水泥混合制备免烧砖强度可达到12.8 MPa,重金属的浸出毒性在养护时间内均低于GB16889—2008的规定;砖体强度随着水泥掺量的增加显著提升,当水泥用量比例提升至35%时,其抗压强度则达到国标建筑用砖的MU 15级. 姚挺[66]为探究飞灰制备混凝土实心砖资源化利用的可行性,以水洗脱氯飞灰为掺料制备了混凝土实心砖,结果表明掺加8.3%水洗飞灰的混凝土实心砖,其抗压强度满足GB/T 21144《混凝土实心砖》的MU 15级,重金属浸出毒性远低于GB 5085.3《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》的标准限值. 虽然洗涤前处理可以降低飞灰中的氯化物和硫酸盐,但洗涤过程会导致飞灰的火山灰活性下降,机械力化学处理(如干法或湿法研磨工艺)被提出以改善飞灰的特性,减轻火山灰活性的损失[67]. 此外,因飞灰具有固定CO2的能力,Viet等[68]提出了一种新工艺,将飞灰同时用作矿物碳化的二氧化碳固定剂和生产绿色建筑材料的辅助胶凝材料.
然而根据HJ 1134—2020标准的要求,飞灰作为替代原料生产非高温建筑材料前,应预先选用高温熔融或低温热解技术对飞灰进行二噁英解毒处理. Lin等[43]预先将飞灰在1400 ℃下进行玻璃化处置,然后在普通硅酸盐水泥中掺入10%—40%的玻璃化渣制备混凝土,水化实验结果表明掺入玻璃渣后的产品强度较普通水泥更高. 宾灯辉等[69]采用低温热解技术预先降解掉飞灰中95%以上的二噁英,然后将解毒后的飞灰与水泥、矿料等混合制备混凝土路基材料,实验结果表明飞灰路基试块中Cr、Cd、Ni、Mn、Zn、Pb的浸出浓度均低于GB 5085.3—2007《危险废物鉴别标准 浸出毒性鉴别》的标准限值.
-
地聚合物是一种无定形到半晶态的非金属材料,是由固体铝硅酸盐材料与碱激发剂混合制成的一种无机铝硅酸盐聚合物,具体优良的耐酸碱、耐高温、吸附和催化性能,在建筑和功能材料领域受到广泛关注. 飞灰富含硅铝酸盐类物质,具有非晶态硅铝酸盐的特点,在合适的制备条件下可以作为原料资源化制备飞灰基地聚合物. 图5为飞灰基地聚合物制备工艺流程[70]. 李春林[71]将飞灰与碱激发剂混合制备出具有优异力学性能的地聚合物,当飞灰占比为60%时,产物具有最佳的抗压强度,可用作建筑材料. Xu等[72]比较了两种类型的飞灰(炉排炉飞灰和流化床飞灰)对地聚合的影响,飞灰中钙化合物和氯盐含量的不同导致了制备的地聚合物力学性能的变化. 为满足实心混凝土砌块的强度要求(>12 MPa, GB/T 21144—2007),炉排炉飞灰和流化床飞灰的最高掺入比例分别为30%和40%. 洗涤预处理可以去除部分飞灰中的氯化物和硫酸盐,从而提高飞灰基地聚合物的性能[73]. 易龙生等[74]以水洗飞灰和粉煤灰为原料(比例为1:1),在地聚合反应过程中添加油酸钠为稳泡剂、双氧水为发泡剂,利用双氧水在碱性条件下分解产生气体的方法制备多孔保温材料,材料抗压强度和导热系数分别为0.48 MPa和0.091 W·(m·K)−1,满足保温材料的行业要求.
地聚合反应过程中所采用的碱激发剂一般为NaOH或KOH等氢氧化物与Na2SiO3或K2SiO3等硅酸盐的混合物[70]. 赵剑[75]研究发现,单掺NaOH时Pb2+的固化效果最好,复掺NaOH/Na2SiO3(1:1)时Cu2+、Zn2+和Cd2+的固化效果最好. 然而,Phair等[76]研究发现,采用NaOH/Na2SiO3固化Pb2+的效果比单独使用NaOH或者Na2SiO3作为碱激发剂时更好. 由此可见,不同地区、不同季节、不同批次的飞灰组分均有所区别,而不同成分的飞灰很难用同样配比的碱激发剂实现最佳的地聚合固化效果,这也是限制这一技术应用的重要影响因素. 此外,地聚合反应中并未涉及飞灰中二噁英的处置,需配置二噁英前处理技术.
-
飞灰与碱激发剂按照一定比例充分混合均匀后,在高温高压的环境中发生水热反应可合成稳定的硅铝酸盐产物,如钠菱沸石、斜方钙沸石、X沸石、方沸石等,各类沸石材料具有不同的功能和应用方向,实现飞灰无害化处理[77]. 与地聚合反应类似,水热法也需要添加碱性物质参与反应,但水热法的反应条件要求更高,研究表明水热固化处理后飞灰中的重金属浸出毒性大幅降低,同时可以降解一部分二噁英等有机污染物[78]. 为了进一步提高反应效率,邱琪丽[79]研究使用微波加热的方式替代常规传导加热,结果发现微波水热法固化飞灰中重金属的效果更加稳定,且降解飞灰中二噁英的效率也更高. 刘林林[80]尝试在水热反应过程中鼓入氧气以提升溶液的氧化活性,飞灰中二噁英的降解率显著提升,相同降解率要求下可降低了水热反应温度,降低处置成本. 陈钱[81]通过添加含硅试剂、采用微波加热方式、碱熔融预处理等方法,提高了对飞灰中的Si、Al资源的利用效率,最终制得NaP1沸石、方沸石、方钠石等新型沸石材料,并验证了水热产物在吸附、催化降解污染物方面的应用潜力. 冯文丽[82]以飞灰为原料制备成沸石载体,进而合成了高价值的Ni型和Ni/NiO型催化剂,性能与商用载体负载镍制备催化剂的性能相当,但反应条件较为复杂,工业化难度较大.
水热法能耗较低(相比于高温处理工艺),对重金属的固化效果好(相比于地聚合反应),兼备二噁英降解的能力,副产的沸石材料附加值较高,具有很好的发展前景. 但该技术对处理设备要求高,投资和占地较大,产生的废液需要二次处理,二噁英的去除效率距离资源化产品的要求仍有一定差距,需要不断的研究优化.
-
沥青胶浆通常由沥青和填料组成,具有填充和胶结作用,填料通常使用矿粉. 飞灰的化学组成与矿粉类似,适合作为一种新型填料制备沥青胶浆,而沥青具有柔性包裹颗粒物的天然特性,可以固化/稳定化飞灰中的有害物质,为飞灰的资源化利用新增一条途径[83].
谭巍等[84]发现,将沥青混合料中掺入飞灰后可改善产品的水稳定性和耐高温性能,浸出毒性检测结果显示飞灰在沥青路面中的应用对其重金属浸出具有较好的抑制作用. 颜可珍等[85]在研究中同样发现,相比矿粉,使用飞灰作为填料后沥青胶浆的高温稳定性有一定的增强作用. 李菁若等[86]发现,飞灰掺量超过2%时沥青混合料的冻融劈裂抗拉强度比(TSR)不满足JTG F40—2004《公路沥青路面施工技术规范》的要求,飞灰水洗预处理后再掺入沥青混合料中,产品的抗拉强度可显著提升. 在掺有飞灰的沥青混合料中添加聚酯纤维或者高黏沥青可进一步提升产品的自身强度,使TSR稳定满足JTG F40—2004的要求[87]. Sawada等[88]发现,在沥青混合料中掺入飞灰的同时加入适量的硫粉和氢氧化钠,可以提高飞灰中重金属的固化效果,但产物的高温稳定性有所下降.
2015年,中国铁建十九局三公司将飞灰作为细集料掺配到沥青混合料中,于承建的黔高速公路大修工程中开展了中试研究[89]. 然而使用飞灰制备沥青胶浆的工艺并未涉及飞灰中二噁英的处置,存在较大的环境风险,建议需配置二噁英前处理技术. 重庆三峰环境集团股份有限公司与中国环境研究院合作正在开展利用低温热解预处理后飞灰作为沥青掺合料的中试研究.
-
可控性低强度材料是一种自流平、自压实、胶结充填材料,主要应用于沟槽充填、结构充填、路面基层、矿山充填等. 在前期的研究中,疏浚底泥、明矾泥、造纸污泥、采石场粉尘、粉煤灰和城市垃圾焚烧底灰都成功地作为原料用于生产可控低强度材料[90]. 飞灰只要对有害物质有效地进行了防浸出处理,制备可控性低强度材料理论上也是可行的[91]. Li等[92]将含量10%的飞灰和铁尾矿混合制备成可控低强度材料,满足充填体的使用要求. 杨恒等[93]将飞灰与钢渣微粉、矿渣粉、脱硫石膏、尾砂等混合,通过选择最佳的原料比制备充填材料进行了砂浆试验,测试结果显示:料浆流动度满足自流型胶结充填的流动性需求,充填料试块28 d的抗压强度满足矿山充填要求,各重金属离子浸出浓度低于饮用水标准. 然而相比于具有防渗措施的正规填埋场,简单的填充处理对飞灰中污染物的稳定化效果和长期浸出毒性提出了更高要求,利用飞灰等固体废弃物通过简单的物理混合制备可控性低强度材料的风险较大.
-
如前所述,飞灰资源化处置的技术路线多为水洗除氯盐、降解二噁英、固化重金属后生产建筑材料. 其中,氯盐水洗废液资源化制备工业盐(氯化钠、氯化钾)的技术已经基本成熟,并在水泥窑协同处置的前处理工段得到广泛应用[17]. 然而,飞灰中的金属元素却仅是被固化后保留在建筑材料中,不仅增加了后期的浸出风险,更是资源浪费. 飞灰颗粒中富含Zn、Pb、Cu、Cd等有毒金属元素,同时这些元素也是高价值的二次资源. 近年来人们不断研究飞灰中金属资源回收技术,以解决环境问题和提供矿产资源[94]. 3种主要的回收技术包括热分离、湿法冶金(即化学萃取、生物浸出)和电化学修复工艺[95].
-
热分离技术是利用目标元素在高温下的挥发性,回收气态金属冷却生成浓缩金属材料,作为冶金原料重复使用[96]. Jacob等[97-98]研究发现,各种金属在不同气氛下的挥发性差别较大,实验样品中Pb、Cd、Cu在1100 °C空气气氛下大部分会挥发,而Zn挥发率较低,原因是高温下生成Zn2SiO4及ZnAl2O4;对比之下,Pb、Cd和Zn在氩气气氛下大部分会挥发,而Cu的挥发性只有10%. 氯化剂(HCl、CaCl2和MgCl2等)的加入有利于提高飞灰中金属氯化物的挥发性[99]. Chan等[100]在1050 °C下探讨添加氯化物对重金属挥发特性的影响,结果表明添加氯化剂后,Zn的挥发率显著增加至90%左右,而在参照组中,未添加时对应的数值只有40%. 但是由于热分离工艺温度较高,所以能耗高,成本高,很难得到工业化应用,且尾渣的处置问题也依旧存在.
-
湿法冶金技术主要包括化学浸出和生物浸出. 化学浸出使用的药剂一般为酸碱和络合剂的组合,Tang等[101]通过盐酸浸出飞灰中的重金属离子,然后分别使用LIX 860N-I和Cyanex 572萃取铜和锌,铜的回收率可达95%以上,锌的回收率为61%. 瑞士Schlumberg[102]也成功利用湿法冶金技术从飞灰中回收锌,回收的锌纯度非常高(99.9%). Loginova等[103]发现,乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)和葡萄糖酸盐的组合能够提高化学浸出后金属的回收率. 与化学浸出原理不同,生物浸出是利用微生物菌种从废水中提取金属. 研究发现用氧化亚铁硫杆菌和氧化硫硫杆菌混合培养的微生物浸出飞灰和底灰,可回收90%以上的Zn和Cu[104]. 然而,生物浸出是一个耗时的过程,有效的菌株很难培养. 因此,从飞灰中回收有价值元素的生物浸出技术仍处于发展阶段,未来需要重点研究浸出机理、关键因素、菌种培养条件和工艺优化,以提高生产效率.
-
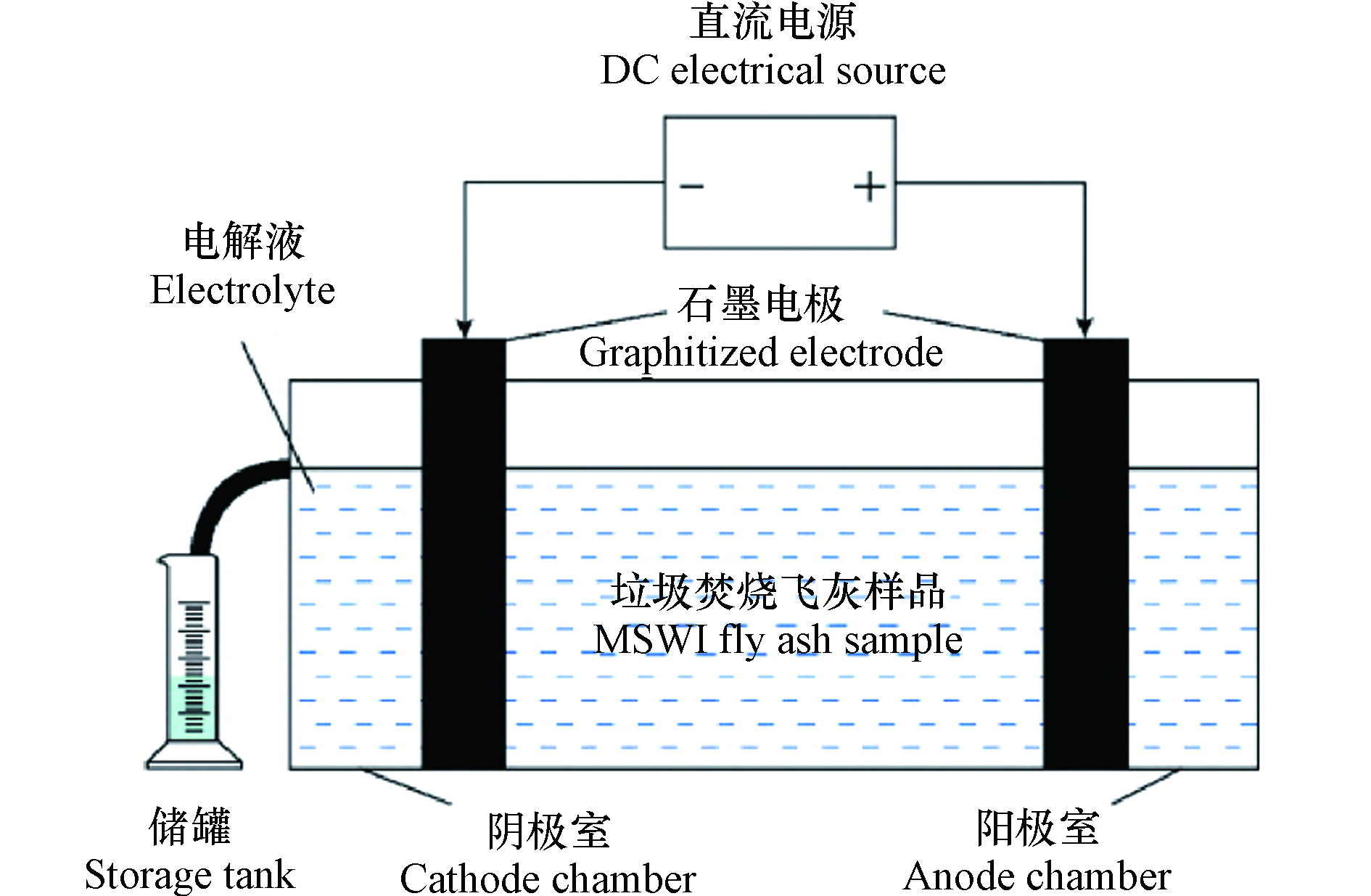
电化学修复技术的原理是在待处置样品区建立直流电场,通过电解触发氧化还原反应在样品区形成阶梯式pH分布,使金属离子在电场中迁移,以达到去除污染物并回收有价值元素的目的(图6)[105]. 最早电化学修复技术在环保领域主要应用于受重金属污染土壤的修复,也用于矿山尾矿和污水污泥等,后来逐步有研究用于处置飞灰[106]. Jensen等[107]使用电化学修复技术处理飞灰后发现目标元素(如Mn、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb)的浸出显著减少.
氯离子在电化学过程中会迁移氧化形成氯气,降低电化学修复效率并增加污染物. Ferreira等[108]通过水洗预处理除去飞灰中的氯盐,然后在飞灰样品中添加葡萄糖酸盐作为增溶剂进行电化学修复去除金属离子,结果显示飞灰中重金属含量明显降低,电解效率显著提升. 与传统的二维电解槽相比,三维电极可显著提高了飞灰中金属元素的去除效率,Zn、Pb、Cd和Cu的回收率分别提高了44%、41%、17%和46%[109],酸化和超声预处理可进一步提高元素的回收率[110].
电化学修复技术可以从飞灰中直接回收有价值元素,而不需要消耗化学物质,属于绿色环保工艺. 然而,电化学过程能耗较高,电解装备的投资也较大,重金属去除率较低,处置后产物难以满足建材化的要求,目前还处于实验室研究阶段.
-
目前,飞灰资源化技术的研究较多,但因各种限制得到工业化应用的技术较少. 表3对各条资源化路线及其产品进行了汇总和比较,可以看出,各类技术均有各自的优缺点,项目实施前需结合实际情况选用合适的技术.
综合而言,水泥窑协同处置、高温烧结/熔融技术的高温环境可以高效降解二噁英和固化重金属,其中烧制普通硅酸盐水泥可以通过改造现有水泥窑来实现,投资相对较低,目前已得到成熟的工业化应用[10]. 高温烧结技术在制备轻骨料方面也已经在局部地区实现了工业化应用,但重金属固化效果不及水泥窑协同及熔融技术,且工程投资较大,需考虑与其它固废的协同处置以降低成本[56]. 而飞灰熔融技术虽然脱毒效果较好,但需要1500 ℃左右的高温环境,同时高价值资源化产品的生产工艺较为复杂,设备投资和运行成本均居高不下,目前仍处于试验阶段[49].
相比之下,非高温重金属固化技术的能耗、安全风险较低,可以生产混凝土/免烧砖、地聚合物、沸石、沥青胶浆等各类建材或功能性材料,但产品中二噁英含量难以满足资源化的要求[7],建议配置低温热解或其它非高温二噁英预处理设备,污染物处置的效果和稳定性还有待长期研究. 目前,利用飞灰资源化制备混凝土/免烧砖[65-66]和沥青胶浆[89]正处于工业化试验阶段.
与上述飞灰处置工艺不同,重金属资源化提取技术可以直接回收高价值的金属化合物用于冶金,实现金属的全产业链循环,处置金属含量较高的飞灰时具有较好的经济价值[111]. 具体工艺包括热分离技术、湿法冶金技术(化学浸出、生物浸出)和电化学修复技术等,其中生物浸出技术处置成本较低但效率也低、耗时较长,难以满足工业化运行的要求;而其它金属提取工艺的综合处置成本较高,且资源化残渣存在二次处置的问题,目前仅停留在实验室研究阶段[111].
-
本文根据飞灰的处置现状及已有的研究进展,综述了当前已具有规模化应用及潜力的飞灰资源化技术及相应的副产物,包括(1)飞灰与水泥生料混合燃烧制备水泥熟料;(2)高温烧结/熔融制备建材;(3)非高温重金属固化技术;(4)资源化提取高价值金属. 这4类工艺理论上均能实现飞灰无害化、资源化的应用,但都存在一些限制的瓶颈. 其中,水泥窑协同处置飞灰的技术相对比较成熟,是未来一段时间内飞灰资源化利用的主力,但受限于水泥生产企业的地域分布、协同处置设施技术要求和入炉固体废物特性要求等限制,该技术无法彻底解决飞灰资源化的问题. 高温烧结/熔融技术不受地域限制,但项目投资和运行成本较高,无法单独大规模推广,需考虑与其它固废的协同处置以降低成本. 对比之下,非高温飞灰资源化技术的处置成本较为合理,产品种类选择性也较多,近年来得到广泛研究,与烧结/熔融技术形成直接竞争关系. 此外,飞灰中重金属资源化提取技术不仅处置成本较高,且资源化残渣存在二次处置的问题,仅停留在实验室研究阶段.
综上所述,环境友好、成本可控、因地制宜的飞灰资源化处置技术仍需进行长期研究,可以重点关注以下方面:
(1)飞灰资源化处置面临的主要问题是成本过高(相比于填埋法)和产品长期安全性难以保证,因此降低处置成本、减少产品中污染物的浸出毒性始终是技术研究的关键. 目前工业化应用关注的重点是控制飞灰处置过程的能耗,通过合理地降低反应温度、减少水洗除氯的液固比、优化药剂用量和配方、缩短工艺流程等措施可以直接降低处置成本. 此外,提高飞灰资源化产品的附加值也可以作为间接降低处置成本的一种有效手段,密度低、抗压强度高、浸出毒性稳定达标的高端建材产品是未来的发展方向,相关的工业化探索仍需加强.
(2)在飞灰资源回收领域,相比于水泥窑协同处置、高温烧结/熔融技术,非高温重金属固化技术的工业化应用尚处于探索阶段,除HJ1134外相关的指导性文件较少,资源化后的产品指标也可能不适合套用建材或其它产品的现行标准,随着各类试验性研究的开展,后期需出台更多细分技术的指导性文件作为理论支撑和设计依据.
(3)未来土地资源日益紧张,对于前期已经填埋的大量固化/稳定化飞灰,如何将其作为原料实现资源化利用的研究尚处于起步阶段.
城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰资源化处置技术及产品概述
Overview of resources reuse technologies and corresponding products for municipal solid waste incineration fly ash
-
摘要: 城市垃圾焚烧飞灰由于其聚集着大量的重金属、二噁英、可溶盐等有害成分,被定义为一种危险废物. 现有处置方法是对其进行安全化填埋或资源化利用,前者是目前的主流工艺. 然而,随着土地资源的日益紧缺和人们环保意识的提高,更符合可持续发展的飞灰资源化技术近年来得到了广泛的关注. 随着人们的持续开发与研究,已形成了多种各具特色的飞灰资源化技术,但总体而言,其仍多处于研究阶段,仅少数技术完成了工业化应用. 本文根据最新有关飞灰资源化处理的研究报道,结合相关的行业标准及技术规范,对飞灰资源化处理的技术路线、产品、原理以及其各自存在的优缺点等进行了综述及评述,以期为飞灰资源化处理技术的实际工业化应用提供理论依据和技术参考.Abstract: Municipal waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash is defined as a kind of hazardous waste due to large amounts of leachable heavy metals, dioxins, soluble salts and other harmful components contained. The main disposal methods of MSWI fly ash are safe landfill and resource reuse, in which the former is currently the dominant process. However, with the increasing shortage of land resources and rising awareness of environmental protection, recycling technologies more in line with the sustainable development have attracted widespread attention in recent years. A variety of recycling technologies for MSWI fly ash have been thus developed and reported. However, most of these technologies are still in the laboratory stage, and only a few of them have achieved industrial applications. This paper mainly reviews the technical routes, products of MSWI fly ash resource recovery, operation principles and the advantages and disadvantages of these technologies on the basis of the latest reports, relevant industry standards and technical specifications. This work can serve as a theoretical basis and technical guidance for the practical industrial applications of the resource reuse technologies for MSWI fly ash.
-

-
表 1 飞灰资源化处置技术规范
Table 1. Recycling technical standards of MSWI fly ash
标准号
Standard number名称
Title技术类型
TechniquesHJ 1134—2020 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰污染控制技术规范(试行) 全门类飞灰处置、资源化利用技术 GB 30485—2013 水泥窑协同处置固体废物污染控制标准 水泥窑协同处置技术 HJ 662—2013 水泥窑协同处置固体废物环境保护技术规范 水泥窑协同处置技术 GB/T 30760—2014 水泥窑协同处置固体废物技术规范 水泥窑协同处置技术 GB/T 41015—2021 固体废物玻璃化处理产物技术要求 高温熔融处置技术 DB32/T 3558—2019 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰熔融处理技术规范 高温熔融处置技术 DB12/T 779—2018 高温烧结处置生活垃圾焚烧飞灰制陶粒技术规范 高温烧结处置技术 T/ZGZS 0301—2020 表面处理污泥、生活垃圾焚烧飞灰烧结制备衍生轻集料 高温烧结处置技术 表 2 水泥熟料中重金属含量限值/可浸出质量浓度限值
Table 2. Limit/ Leachable mass concentration limit standards of heavy metals in cement clinker
As Pb Cd Cr Cu Ni Zn Mn 含量限值/(mg·kg−1) 40 100 1.5 150 100 100 500 600 可浸出质量浓度限值/(mg·kg−1) 0.10 0.30 0.03 0.20 1.00 0.20 1.00 1.00 表 3 各类飞灰资源化技术对比
Table 3. Comparison of resource recovery technologies for MSWI fly ash
工艺
Technique处置原理
Principle产品
Product产品价值/
(元·t−1)
Value of
product处置成本/
(元·t−1)
Cost of
disposal工业化应用
Industrial
application优点
Advantage缺点
Disadvantage混合燃烧制备水泥熟料 利用水泥窑的高温和碱性环境,降解水洗飞灰中的二噁英,同时将重金属固化在水泥熟料中 普通硅酸盐水泥 300—500 900—1500[10] 工业化 技术成熟,无需新增烧结设备,水泥需求大 全国水泥窑分布不均,飞灰的掺入对设备有一定的损伤. 低能耗水泥 200—800 800—1300[33] 理论阶段 烧制温度较低,能耗省 产品市场小,重金属有长期浸出风险. 高温烧结/熔融制备建材 利用1400 ℃以上的高温环境降解飞灰中的二噁英,同时将重金属固化在熔融玻璃体中 微晶玻璃 >800 2000—3000[10] 理论阶段 污染物控制效果稳定,产品附加值较高 设备投资较大,能耗高,烟气中夹带重金属,存在二次飞灰问题 泡沫微晶玻璃 >800 2500—3500[112] 理论阶段 污染物控制效果稳定,产品附加值高 设备投资大,工艺复杂,处置成本高,烟气中夹带重金属,存在二次飞灰问题 利用1000 ℃左右的高温环境降解飞灰中的二噁英,同时将重金属固化在烧结体中 轻骨料 300—800 1000—1500[112] 工业化 可协调处置污泥等废弃物,产品需求较大,已有工业化案例 重金属固化效果不如熔融技术,设备投资较大,能耗高,烟气中夹带重金属,存在二次飞灰问题. 陶瓷砖 >800 1000—1500[61] 理论阶段 烧制温度较低,能耗省,产品附加值较高 重金属固化效果难以稳定达到资源化产品的要求,烟气中夹带重金属,存在二次飞灰问题. 非高温重金属固化技术 利用水泥固化、药剂稳定化、沥青固化、碱激发固化、水热处理等非高温工艺实现飞灰中重金属稳定化/固化处置,一般需配套二噁英预处理设备 混凝土/免烧砖 200—400 800—1200[69] 试验阶段 处置成本不高,产品需求大 需配置二噁英、氯离子预处理设备,投资较大. 地聚合物 100—300 500—800[70] 理论阶段 处置成本不高,工艺较为简单 重金属固化条件不稳定,需配置二噁英、氯离子预处理设备,投资较大,产品需求小. 非高温重金属固化技术 利用水泥固化、药剂稳定化、沥青固化、碱激发固化、水热处理等非高温工艺实现飞灰中重金属稳定化/固化处置,一般需配套二噁英预处理设备 沸石材料 >800 1200—1500[112] 理论阶段 可同步实现二噁英及重金属的控制,工艺相对简单 反应条件苛刻,设备结构复杂,难以规模化生产,二噁英去除效率较低,废水需二次处理. 沥青胶浆 200—500 800—1200[84] 试验阶段 处置成本不高,产品需求大 需配置二噁英、氯离子预处理设备,投资较大. 可控低强度材料 <100 400—500[21] 理论阶段 工艺简单,处置成本低 污染物迁移风险大,政策并不鼓励. 土壤改良剂/污泥调节剂 <100 400—600[10] 理论阶段 工艺简单,处置成本低 污染物迁移风险大,政策并不鼓励. 资源化提取高价值金属 采用特定的工艺分离、提取飞灰中的重金属,残渣需二次处置 金属化合物 >800 1000—3000[111] 理论阶段 产品附加值高 资源提取后残渣的二次处置问题依然存在. -
[1] BRUNNER P H, RECHBERGER H. Waste to energy - key element for sustainable waste management [J]. Waste Management, 2015, 37: 3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.02.003 [2] TRINDADE A B, PALACIO J C E, GONZÁLEZ A M, et al. Advanced exergy analysis and environmental assesment of the steam cycle of an incineration system of municipal solid waste with energy recovery [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 157: 195-214. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.11.083 [3] MA W C, CHEN D M, PAN M H, et al. Performance of chemical chelating agent stabilization and cement solidification on heavy metals in MSWI fly ash: A comparative study [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 247: 169-177. [4] 龙吉生, 杜海亮, 邹昕, 等. 关于城市生活垃圾处理碳减排的系统研究 [J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(8): 1143-1153. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.20220325001 LONG J S, DU H L, ZOU X, et al. Systematic study on carbon emission reduction of municipal solid waste treatment [J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 37(8): 1143-1153(in Chinese). doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.20220325001
[5] QUINA M J, BORDADO J M, QUINTA-FERREIRA R M. Recycling of air pollution control residues from municipal solid waste incineration into lightweight aggregates [J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34(2): 430-438. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.10.029 [6] VALLE-ZERMEÑO R D, GÓMEZ-MANRIQUE J, GIRO-PALOMA J, et al. Material characterization of the MSWI bottom ash as a function of particle size. Effects of glass recycling over time [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 581/582: 897-905. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.047 [7] 蒋旭光, 常威. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰的处置及应用概况 [J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2015, 43(1): 7-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4303.2015.01.002 JIANG X G, CHANG W. Review for treatment and application of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2015, 43(1): 7-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4303.2015.01.002
[8] 林昌梅. 适用GB16889—2008的垃圾焚烧厂飞灰处理成本分析 [J]. 环境卫生工程, 2010, 18(6): 50-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8206.2010.06.019 LIN C M. Cost analysis of fly ash treatment in waste incineration plants to meet GB 16889—2008 [J]. Environmental Sanitation Engineering, 2010, 18(6): 50-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8206.2010.06.019
[9] QUINA M J, BORDADO J C M, QUINTA-FERREIRA R M. Stabilisation/solidification of APC residues from MSW incineration with hydraulic binders and chemical additives [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 264: 107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.014 [10] 吴昊, 刘宏博, 田书磊, 等. 城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰利用处置现状及环境管理 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2021, 11(5): 1034-1040. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210083 WU H, LIU H B, TIAN S L, et al. Current situation for utilization and disposal and environmental management of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2021, 11(5): 1034-1040(in Chinese). doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210083
[11] 杨彦, 孔昭健. 螯合剂处理生活垃圾焚烧飞灰的稳定化技术研究与实践 [J]. 有色冶金节能, 2019, 35(4): 55-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5122.2019.04.014 YANG Y, KONG Z J. Study and practice on stabilization technology of the treatment of fly ash from MSW incineration by chelating agent [J]. Energy Saving of Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2019, 35(4): 55-59(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5122.2019.04.014
[12] 蒋旭光, 陈钱, 赵晓利, 等. 水热法稳定垃圾焚烧飞灰中重金属研究进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(8): 4473-4485. JIANG X G, CHEN Q, ZHAO X L, et al. A review on hydrothermal treatment for stabilization of heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(8): 4473-4485(in Chinese).
[13] 章骅, 于思源, 邵立明, 等. 烟气净化工艺和焚烧炉类型对生活垃圾焚烧飞灰性质的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(1): 467-476. ZHANG H, YU S Y, SHAO L M, et al. Influence of air pollution control(APC) systems and furnace type on the characteristics of APC residues from municipal solid waste incinerators [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(1): 467-476(in Chinese).
[14] 马懿, 郑仁栋, 周志昊, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰处置技术与应用瓶颈 [J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(5): 237-243. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202205033 MA Y, ZHENG R D, ZHOU Z H, et al. Bottleneck of application of disposal technologies for fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2022, 40(5): 237-243(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202205033
[15] 马保国, 苏华伟, 李相国, 等. 城市垃圾焚烧飞灰预处理技术研究 [J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2013, 35(4): 22-26. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2013.04.005 MA B G, SU H W, LI X G, et al. Research on pretreatment technology of municipal solid wastes incineration fly ash [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2013, 35(4): 22-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2013.04.005
[16] DONTRIROS S, LIKITLERSUANG S, JANJAROEN D. Mechanisms of chloride and sulfate removal from municipal-solid-waste-incineration fly ash (MSWI FA): Effect of acid-base solutions [J]. Waste Management, 2020, 101: 44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.09.033 [17] 范庆玲, 郭小甫, 袁俊生. 垃圾焚烧飞灰水洗液纯化及无机盐分离 [J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(3): 67-71,76. FAN Q L, GUO X F, YUAN J S. Purification and inorganic salts separation of waste incineration fly ash water washing solution [J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(3): 67-71,76(in Chinese).
[18] 杨虎城, 陈柏杭, 牟靖芳, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧厂烟气中二噁英的分布及净化特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(10): 2256-2265. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112608 YANG H C, CHEN B H, MU J F, et al. Distribution characteristics of PCDD/Fs in flue gas from municipal solid waste incineration plant [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(10): 2256-2265(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112608
[19] 王肇嘉, 秦玉, 顾军, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰二噁英控制技术研究进展 [J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(10): 116-123. WANG Z J, QIN Y, GU J, et al. Research progress of dioxin control technologies in fly ash from domestic waste incineration [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(10): 116-123(in Chinese).
[20] 何品晶, 吴长淋, 章骅, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰及其稳定化产物的长期浸出行为 [J]. 环境化学, 2008, 27(6): 786-790. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2008.06.018 HE P J, WU C L, ZHANG H, et al. The long-term leaching behavior of air pollution control residues and its treatment products [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2008, 27(6): 786-790(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2008.06.018
[21] 谷忠伟. 稳定剂对垃圾焚烧飞灰中重金属的稳定化效果研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020. GU Z W. Research of stabilization effect of stabilizers on heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020(in Chinese).
[22] CHEN Z L, ZHANG S, LIN X Q, et al. Decomposition and reformation pathways of PCDD/Fs during thermal treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 394: 122526. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122526 [23] NIDHEESH P V, KUMAR M S. An overview of environmental sustainability in cement and steel production [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 231: 856-871. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.251 [24] HUBER F, BLASENBAUER D, MALLOW O, et al. Thermal co-treatment of combustible hazardous waste and waste incineration fly ash in a rotary kiln [J]. Waste Management, 2016, 58: 181-190. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2016.09.013 [25] LIU G R, ZHAN J Y, ZHENG M H, et al. Field pilot study on emissions, formations and distributions of PCDD/Fs from cement kiln co-processing fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerations [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 299: 471-478. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.052 [26] BOGUSH A A, STEGEMANN J A, ZHOU Q Z, et al. Co-processing of raw and washed air pollution control residues from energy-from-waste facilities in the cement kiln [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 254: 119924. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119924 [27] JOSEPH A M, SNELLINGS R, van den HEEDE P, et al. The use of municipal solid waste incineration ash in various building materials: A Belgian point of view [J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2018, 11(1): 141. doi: 10.3390/ma11010141 [28] DILIBERTO C, MEUX E, DILIBERTO S, et al. A zero-waste process for the management of MSWI fly ashes: Production of ordinary Portland cement [J]. Environmental Technology, 2020, 41(9): 1199-1208. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2018.1525434 [29] WANG L, JIN Y Y, NIE Y F, et al. Recycling of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for ordinary Portland cement production: A real-scale test [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2010, 54(12): 1428-1435. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.06.006 [30] PAN J R, HUANG C, KUO J J, et al. Recycling MSWI bottom and fly ash as raw materials for Portland cement [J]. Waste Management, 2008, 28(7): 1113-1118. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2007.04.009 [31] KIM Y M, HONG S H, KIM H. Synthesis and hydration characteristics of alinite cement [J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2002, 85(8): 1941-1946. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.2002.tb00385.x [32] KESIM A G, TOKYAY M, YAMAN I O, et al. Properties of alinite cement produced by using soda sludge [J]. Advances in Cement Research, 2013, 25(2): 104-111. doi: 10.1680/adcr.11.00040 [33] 施惠生, 吴凯, 邓恺, 等. 利用城市垃圾焚烧飞灰研制阿利尼特水泥熟料 [J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2009, 37(7): 1092-1096. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.07.006 SHI H S, WU K, DENG K, et al. Preparation of alinite cement clinker from municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2009, 37(7): 1092-1096(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.07.006
[34] WU K, SHI H S, de SCHUTTER G, et al. Preparation of alinite cement from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2012, 34(3): 322-327. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.11.016 [35] GUO X L, SHI H S, WU K, et al. Performance and risk assessment of alinite cement-based materials from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA) [J]. Materials and Structures, 2016, 49(6): 2383-2391. doi: 10.1617/s11527-015-0655-x [36] TELESCA A, MARROCCOLI M, PACE M L, et al. A hydration study of various calcium sulfoaluminate cements [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2014, 53: 224-232. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.07.002 [37] WU K, SHI H S, GUO X L. Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for sulfoaluminate cement clinker production [J]. Waste Management, 2011, 31(9/10): 2001-2008. [38] GUO X L, SHI H S, HU W P, et al. Durability and microstructure of CSA cement-based materials from MSWI fly ash [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2014, 46: 26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2013.10.015 [39] MAO Y P, WU H, WANG W L, et al. Pretreatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and preparation of solid waste source sulphoaluminate cementitious material [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 385: 121580. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121580 [40] GHOULEH Z, SHAO Y X. Turning municipal solid waste incineration into a cleaner cement production [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 195: 268-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.209 [41] ASHRAF M S, GHOULEH Z, SHAO Y X. Production of eco-cement exclusively from municipal solid waste incineration residues [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2019, 149: 332-342. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.06.018 [42] 竹涛, 种旭阳, 王若男, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰处理技术研究进展 [J]. 洁净煤技术, 2022, 28(7): 189-201. doi: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.21080202 ZHU T, CHONG X Y, WANG R N, et al. Research progress on the treatment technology of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2022, 28(7): 189-201(in Chinese). doi: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.21080202
[43] LIN K L, WANG K S, TZENG B Y, et al. The hydration characteristics and utilization of slag obtained by the vitrification of MSWI fly ash [J]. Waste Management, 2004, 24(2): 199-205. doi: 10.1016/S0956-053X(03)00131-4 [44] 范文迪. 垃圾焚烧飞灰微晶玻璃化及Cr固化机理[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2018. FAN W D. Manufacture of glass-ceramic made from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and the solidification mechanism of Cr[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018(in Chinese).
[45] FAN W D, LIU B, LUO X, et al. Production of glass–ceramics using Municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Rare Metals, 2019, 38(3): 245-251. doi: 10.1007/s12598-017-0976-8 [46] VU D H, WANG K S, CHEN J H, et al. Glass-ceramic from mixtures of bottom ash and fly ash [J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(12): 2306-2314. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.05.040 [47] ZHAO S Z, LIU B, DING Y J, et al. Study on glass-ceramics made from MSWI fly ash, pickling sludge and waste glass by one-step process [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 271: 122674. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122674 [48] 李志川, 杨一博, 马蒸钊, 等. 利用生活垃圾焚烧飞灰制备全废物基微晶玻璃 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(6): 1925-1932. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202112151 LI Z C, YANG Y B, MA Z Z, et al. Preparation of entirely waste-based glass-ceramics from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2022, 16(6): 1925-1932(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202112151
[49] 张俊杰. 垃圾焚烧灰渣制备泡沫微晶玻璃工艺及其机理[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2021. ZHANG J J. Preparation and mechanism of glass-ceramic foams based on municipal solid waste incineration ash[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2021(in Chinese).
[50] LIU B, YANG Q W, ZHANG S G. Integrated utilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and bottom ash for preparation of foam glass–ceramics [J]. Rare Metals, 2019, 38(10): 914-921. doi: 10.1007/s12598-019-01314-2 [51] 张晗, 林晓亮, 余阳. 垃圾焚烧飞灰掺杂废玻璃烧结制备多孔陶瓷 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(8): 4534-4538. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201503140 ZHANG H, LIN X L, YU Y. Preparation of sintered porous ceramic from vitrified MSW fly ash and waste glass [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(8): 4534-4538(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201503140
[52] HAN J S, LI G H, GAO H N, et al. Foaming mechanisms of different foaming agents and their effects on the microstructures of porous magnesia ceramics [J]. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 2020, 56(3): 1005-1011. doi: 10.1007/s41779-019-00443-2 [53] ZHANG J J, LIU B, ZHANG X Y, et al. A novel approach for preparing glass ceramic foams from MSWI fly ash: Foaming characteristics and hierarchical pore formation mechanism [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 18: 731-744. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.02.090 [54] VALLE-ZERMEÑO R D, FORMOSA J, CHIMENOS J M, et al. Aggregate material formulated with MSWI bottom ash and APC fly ash for use as secondary building material [J]. Waste Management, 2013, 33(3): 621-627. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.09.015 [55] WEI N. Leachability of heavy metals from lightweight aggregates made with sewage sludge and municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2015, 12(5): 4992-5005. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120504992 [56] 魏国侠, 王承智, 孙磊, 等. 污染底泥与焚烧飞灰混烧陶粒实验研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(2): 134-138. WEI G X, WANG C Z, SUN L, et al. Production of ceramics from pollution sediment and incinerator fly ash [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(2): 134-138(in Chinese).
[57] 吴玉杰, 王渊, 曲烈. 垃圾焚烧飞灰高强陶粒的制备及微观研究 [J]. 混凝土, 2016(6): 63-65,69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2016.06.017 WU Y J, WANG Y, QU L. Preparation and microstructure of ceramsite made from w aste incineration fly ash [J]. Concrete, 2016(6): 63-65,69(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2016.06.017
[58] GUNNING P, HILLS C D, CAREY P, et al. Carbonation of MSWI APCr for reuse as a light-weight aggregate [J]. Materials Science, 2012, 44: 1-7. [59] 杨陈, 张银亮, 陈欢, 等. 利用废旧电池回收产生固废协同建筑弃土制备陶瓷砖的试验研究 [J]. 中国陶瓷, 2020, 56(5): 47-51. doi: 10.16521/j.cnki.issn.1001-9642.2020.05.008 YANG C, ZHANG Y L, CHEN H, et al. Experimental study on preparation of ceramic bricks by solid waste from recycling waste batteries and building waste soil [J]. China Ceramics, 2020, 56(5): 47-51(in Chinese). doi: 10.16521/j.cnki.issn.1001-9642.2020.05.008
[60] DENG Y, GONG B, CHAO Y, et al. Sustainable utilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for ceramic bricks with eco-friendly biosafety [J]. Materials Today Sustainability, 2018, 1/2: 32-38. doi: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2018.11.002 [61] 张海英, 赵由才, 祈景玉. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰制陶瓷砖 [J]. 环境工程, 2009, 27(6): 90-93. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.2009.06.001 ZHANG H Y, ZHAO Y C, QI J Y. Study on utilization of mswi fly ash in ceramic brick [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2009, 27(6): 90-93(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.2009.06.001
[62] 王旭. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰资源化利用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. WANG X. Study on the recycling of MSWI fly ash[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017(in Chinese).
[63] LOTHENBACH B, SCRIVENER K, HOOTON R D. Supplementary cementitious materials [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2011, 41(12): 1244-1256. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2010.12.001 [64] 宁博, 欧阳东, 徐畏婷, 等. 垃圾焚烧飞灰混凝土试验研究 [J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2011(9): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2011.09.005 NING B, OUYANG D, XU W T, et al. Experimental research of concrete with municipal solid waste incineration(MSWI) fly ash [J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2011(9): 16-19(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2011.09.005
[65] 常威, 蒋旭光, 邱琪丽, 等. 全烧垃圾流化床炉飞灰制备免烧砖的性能研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(7): 2224-2232. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0995 CHANG W, JIANG X G, QIU Q L, et al. Performance of non-fired brick making from fly ash in a purely burning municipal solid waste circulating fluidized bed incinerator [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(7): 2224-2232(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0995
[66] 姚挺. 水洗脱氯飞灰掺加制备混凝土实心砖的资源化利用研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2022, 47(4): 164-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2022.04.037 YAO T. Investigation on resource utilization of water-washed fly ash incorporated into solid concrete brick [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2022, 47(4): 164-168(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2022.04.037
[67] ZACCO A, BORGESE L, GIANONCELLI A, et al. Review of fly ash inertisation treatments and recycling [J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2014, 12(1): 153-175. doi: 10.1007/s10311-014-0454-6 [68] BUI VIET D, CHAN W P, PHUA Z H, et al. The use of fly ashes from waste-to-energy processes as mineral CO2 sequesters and supplementary cementitious materials [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 398: 122906. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122906 [69] 宾灯辉, 周炼川, 李洪刚, 等. 掺加解毒飞灰的路基材料重金属浸出特征与潜在风险 [J]. 环境卫生工程, 2021, 29(2): 63-70. doi: 10.19841/j.cnki.hjwsgc.2021.02.009 BIN D H, ZHOU L C, LI H G, et al. Heavy metal leaching characteristics and potential risk from subgrade materials mixed with detoxification fly ash [J]. Environmental Sanitation Engineering, 2021, 29(2): 63-70(in Chinese). doi: 10.19841/j.cnki.hjwsgc.2021.02.009
[70] 金漫彤. 地聚合物固化生活垃圾焚烧飞灰中重金属的研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2011. JIN M T. Immobilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash with geopolymer[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2011(in Chinese).
[71] 李春林. 基于地聚合反应的生活垃圾焚烧飞灰资源化利用实验研究 [J]. 工业安全与环保, 2021, 47(2): 97-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2021.02.021 LI C L. Experimental study on resource utilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash based on geopolymerization [J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 47(2): 97-100(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2021.02.021
[72] XU P, ZHAO Q L, QIU W, et al. Microstructure and strength of alkali-activated bricks containing municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash developed as construction materials [J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(5): 1283. doi: 10.3390/su11051283 [73] FERRARO A, FARINA I, RACE M, et al. Pre-treatments of MSWI fly-ashes: A comprehensive review to determine optimal conditions for their reuse and/or environmentally sustainable disposal [J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2019, 18(3): 453-471. doi: 10.1007/s11157-019-09504-1 [74] 易龙生, 刘涛, 吴倩, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰-粉煤灰基多孔保温材料的制备 [J]. 矿冶工程, 2021, 41(1): 124-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.01.029 YI L S, LIU T, WU Q, et al. Preparation of porous thermal insulation material with MSWI fly ash and coal ash [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2021, 41(1): 124-127(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.01.029
[75] 赵剑. 城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰胶凝活性及其固化/稳定化技术研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2017. ZHAO J. Study on cementitious activity and solidification/stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2017(in Chinese).
[76] PHAIR J W, van DEVENTER J S J. Characterization of fly-ash-based geopolymeric binders activated with sodium aluminate [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(17): 4242-4251. [77] 綦懿, 李天如, 王宝民, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰固化稳定化安全处置及建材资源化利用进展 [J]. 建材技术与应用, 2021(1): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9441.2021.01.006 QI Y, LI T R, WANG B M, et al. Progress in solidification and stabilization of MSWI fly ash for safe disposal and resource utilization of building materials [J]. Research & Application of Building Materials, 2021(1): 16-22(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9441.2021.01.006
[78] JING Z Z, MATSUOKA N, JIN F M, et al. Municipal incineration bottom ash treatment using hydrothermal solidification [J]. Waste Management, 2007, 27(2): 287-293. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.01.015 [79] 邱琪丽. 垃圾焚烧飞灰的微波水热法无害化处置及产物吸附性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. QIU Q L. Study on microwave-assisted hydrothermal disposal and product adsorption property of MSWI fly ash[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019(in Chinese).
[80] 刘林林. 城市垃圾焚烧飞灰中二噁英水热降解规律研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. LIU L L. Study on hydrothermal degradation law of dioxins in municipal waste incineration fly ash[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[81] 陈钱. 改进水热法处理垃圾焚烧飞灰合成沸石机理研究及其产物应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2022. CHEN Q. Zeolite fabrication from MSWI fly ash by modified hydrothermal methods, and the applications[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022(in Chinese).
[82] 冯文丽. 垃圾焚烧飞灰高值化利用制备类沸石基加氢催化剂[D]. 拉萨: 西藏大学, 2022. FENG W L. High-value utilization of waste incineration fly ash to prepare zeolite-like hydrogenation catalyst[D]. Lasa: Tibet University, 2022(in Chinese).
[83] 吴书君, 唐军, 吴艳玲. 飞灰替代矿粉对沥青胶浆性能的影响 [J]. 山东交通学院学报, 2022, 30(3): 115-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0032.2022.03.016 WU S J, TANG J, WU Y L. The influence of fly ash replacement of mineral powder on performance of asphalt mortar [J]. Journal of Shandong Jiaotong University, 2022, 30(3): 115-122(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0032.2022.03.016
[84] 谭巍, 李菁若, 季炜, 等. 城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰在沥青混合料中的应用 [J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(4): 14-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.04.003 TAN W, LI J R, JI W, et al. Application of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash in asphalt mixture [J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(4): 14-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.04.003
[85] 颜可珍, 郑凯高, 胡迎斌. 城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰在沥青胶浆中的应用 [J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2018, 15(10): 2509-2517. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.2018.10.008 YAN K Z, ZHENG K G, HU Y B. Application of municipal solid waste incinerator ash in asphalt mortar [J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(10): 2509-2517(in Chinese). doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.2018.10.008
[86] 李菁若, 谭巍. 城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰对沥青混合料TSR的影响分析 [J]. 中外公路, 2016, 36(1): 250-253. doi: 10.14048/j.issn.1671-2579.2016.01.054 LI J R, TAN W. Influence analysis of MWSI fly ash on TSR in asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2016, 36(1): 250-253(in Chinese). doi: 10.14048/j.issn.1671-2579.2016.01.054
[87] 李菁若, 丁金西, 刘瑞全, 等. 生活垃圾焚烧飞灰造粒颗粒在沥青混合料中的应用研究 [J]. 公路交通技术, 2020, 36(6): 42-48. LI J R, DING J X, LIU R Q, et al. Study on application of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash granulated particles in asphalt mixture [J]. Technology of Highway and Transport, 2020, 36(6): 42-48(in Chinese).
[88] SAWADA K, MATSUDA H, MIZUTANI M. Immobilizatoin of lead compounds in fly ash by mixing with asphalt, sulfur and sodium hydroxide [J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2001, 34(7): 878-883. doi: 10.1252/jcej.34.878 [89] 陈毅国. 焚烧飞灰在沥青路面中的应用 [J]. 交通世界, 2017(9): 129-131. CHEN Y G. Application of MWSI fly ash in asphalt pavement [J]. TranspoWorld, 2017(9): 129-131(in Chinese).
[90] WANG L, ZOU F L, FANG X L, et al. A novel type of controlled low strength material derived from alum sludge and green materials [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 165: 792-800. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.01.078 [91] CHEN L, WANG L, CHO D W, et al. Sustainable stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by incorporation of green materials [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 222: 335-343. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.057 [92] LI J, ZHANG S Q, WANG Q, et al. Feasibility of using fly ash-slag-based binder for mine backfilling and its associated leaching risks [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 400: 123191. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123191 [93] 杨恒, 倪文, 马旭明, 等. 胶结充填采矿协同资源化利用垃圾焚烧飞灰固化机理研究 [J]. 金属矿山, 2018(3): 196-200. YANG H, NI W, MA X M, et al. Study on the mechanism of synergistic utilization of fly ash from solid waste incineration by cemented filling mining [J]. Metal Mine, 2018(3): 196-200(in Chinese).
[94] FUNARI V, BRAGA R, BOKHARI S N H, et al. Solid residues from Italian municipal solid waste incinerators: A source for “critical” raw materials [J]. Waste Management, 2015, 45: 206-216. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.11.005 [95] GENG C, LIU J G, WU S C, et al. Novel method for comprehensive utilization of MSWI fly ash through co-reduction with red mud to prepare crude alloy and cleaned slag [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121315. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121315 [96] KURASHIMA K, MATSUDA K, KUMAGAI S, et al. A combined kinetic and thermodynamic approach for interpreting the complex interactions during chloride volatilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste fly ash [J]. Waste Management, 2019, 87: 204-217. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.02.007 [97] JAKOB A, STUCKI S, KUHN P. Evaporation of heavy metals during the heat treatment of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1995, 29(9): 2429-2436. [98] JAKOB A, STUCKI S, STRUIS R P W J. Complete heavy metal removal from fly ash by heat treatment: Influence of chlorides on evaporation rates [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1996, 30(11): 3275-3283. [99] YU J, SUN L S, MA C, et al. Mechanism on heavy metals vaporization from municipal solid waste fly ash by MgCl2·6H2O [J]. Waste Management, 2016, 49: 124-130. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.12.015 [100] CHAN C, JIA C Q, GRAYDON J W, et al. The behaviour of selected heavy metals in MSW incineration electrostatic precipitator ash during roasting with chlorination agents [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1996, 50(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1016/0304-3894(96)01774-8 [101] TANG J F, SU M H, WEI L Z, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the effectiveness on metals recovery and decontamination from MSWI fly ash by an integrating hydrometallurgical process in Guangzhou [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 728: 138809. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138809 [102] SCHLUMBERGER S, SCHUSTER M, RINGMANN S, et al. Recovery of high purity zinc from filter ash produced during the thermal treatment of waste and inerting of residual materials [J]. Waste Management & Research:the Journal of the International Solid Wastes and Public Cleansing Association, ISWA, 2007, 25(6): 547-555. [103] LOGINOVA E, PROSKURNIN M, BROUWERS H J H. Municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash composition analysis: A case study of combined chelatant-based washing treatment efficiency [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 235: 480-488. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.096 [104] FUNARI V, GOMES H I, CAPPELLETTI M, et al. Optimization routes for the bioleaching of MSWI fly and bottom ashes using microorganisms collected from a natural system [J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2019, 10(12): 3833-3842. doi: 10.1007/s12649-019-00688-9 [105] 黄涛. 城市生活垃圾焚烧飞灰残留重金属电动去除强化技术研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2017. HUANG T. Research on the residual heavy metal removal from the MSWI fly ash by electrokinetic remediation enhancement technology[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2017(in Chinese).
[106] 魏国侠, 刘汉桥, 武振华, 等. 电渗析法分离医疗垃圾焚烧飞灰浸出液中重金属 [J]. 过程工程学报, 2014, 14(5): 776-781. WEI G X, LIU H Q, WU Z H, et al. Separation of heavy metals from leaching solution of hospital waste incinerator fly ash by electrodialysis [J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2014, 14(5): 776-781(in Chinese).
[107] JENSEN P E, KIRKELUND G M, PEDERSEN K B, et al. Electrodialytic upgrading of three different municipal solid waste incineration residue types with focus on Cr, Pb, Zn, Mn, Mo, Sb, Se, V, Cl and SO4 [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 181: 167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.06.012 [108] FERREIRA C D, JENSEN P, OTTOSEN L, et al. Preliminary treatment of MSW fly ash as a way of improving electrodialytic remediation [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 2008, 43(8): 837-843. [109] ZHANG Y W, HUANG T, HUANG X, et al. Study on electro-kinetic remediation of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with a three-dimensional electrode [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(45): 27846-27852. doi: 10.1039/C7RA01327B [110] HUANG T, ZHOU L L, LIU L F, et al. Ultrasound-enhanced electrokinetic remediation for removal of Zn, Pb, Cu and Cd in municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes [J]. Waste Management, 2018, 75: 226-235. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.029 [111] WANG H, ZHU F, LIU X, et al. A mini-review of heavy metal recycling technologies for municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Waste Management & Research, 2021, 39(9): 1135-1148. [112] 邱琪丽, 蒋旭光. 垃圾焚烧飞灰在污染物控制领域中的应用探讨 [J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(7): 3855-3864. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2021-1673 QIU Q L, JIANG X G. Application of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash in the field of pollutant control [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(7): 3855-3864(in Chinese). doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2021-1673
-



 下载:
下载: