-
煤矸石是煤炭开采和洗选过程中产生的一种干基灰分大于50%的岩石. 按来源可分为煤巷矸石、水洗矸石、岩巷矸石、自燃矸石、手选矸石和剥离矸石[1],故来源十分丰富,其产量约占原煤总产量的10%—25%,是煤炭工业排放量最大的固体废物,也是占地面积最大的工业固体废物之一,占全国工业固体废物的20%以上[2]. 煤矸石的排放和堆放造成了严重的资源浪费和环境污染. 露天存放的煤矸石中含有大量的有毒重金属元素,在受日晒、雨淋、风吹等自然条件的影响后,可能通过雨水渗入地表水或土壤,然后通过土壤渗入浅层地下水,这使得镉、汞等各种有毒有害元素渗入到地下,严重影响生态平衡[3 − 4]. 煤矸石相比于普通煤炭,其具有含碳量低、热值低、质地坚硬的特点,是矿山固体废弃物的一种. 其次,从化学组成来看,煤矸石主要含有无机质和有机质[5],其中无机质主要为SiO2和Al2O3,其次是Fe2O3、CaO、MgO等氧化物和单质元素. 因此,集多种有用元素于一体的特殊性质,决定了煤矸石的综合利用成为了众多学者的研究热点和重点[6].
目前,煤矸石已广泛用于有用组分回收、废水处理、建筑材料、农业生产、制备氧化铝[7 − 8]和高压电缆、发电等[9 − 12],制备煤矸石基土壤改良剂也是一种新的利用方式. 其中,煤矸石改良剂作为其资源化利用的重要方式,受到了研究者的广泛关注,然而目前煤矸石改良剂还存在一些问题,比如含硫量高、养分缺乏、重金属污染[13 − 15]等,在利用之前首先应当确定煤矸石的理化性质,通过活化改性等预处理措施,提高煤矸石与修复土壤的适配性,降低其有毒有害成分,实现煤矸石的资源化利用. 本文综述了煤矸石资源化的研究进展,对比了不同的改性方法,进一步阐述了污泥改性煤矸石在生态修复与土壤改良方面的进展,为后期煤矸石和污泥的高值化利用奠定基础.
-
煤矸石由多种岩石块体组成,成分相当复杂[16]. 从物理组成来看,煤矸石所含矿物成分比较复杂,主要矿物有黏土类矿物、碳酸盐类矿物、铝土矿、黄铁矿、石英、云母、长石、煤质和植物化石等. 就化学成分而言,主要为无机物并混合有少量有机物的混合物,其中无机物为SiO2和Al2O3,还含有不同量的Fe2O3、Cao、MgO、SO3、K2O、Na2O等无机物,以及微量稀有元素(钛、钒、钴等)[17]. 表1总结了煤矸石的组成情况,从表中可以看出煤矸石样品之间成分存在一定的差异,但是绝大多数煤矸石中所含的无机质主要为SiO2和Al2O3,其次是 Fe2O3、CaO、MgO、TiO2以及其他的氧化物等.
-
煤矸石中不具有粉煤灰和矿渣中的玻璃体等活性物质,所以一般而言未经特殊处理的煤矸石并不具有反应活性[25]. 因此,适当的活化处理措施对其反应活性的提高至关重要. 煤矸石的活化方法一般分为:热活化、化学活化、微波活化、机械活化和复合活化等[26 − 27]. 热活化是高温下煤矸石微观结构中颗粒剧烈的热运动,使煤矸石中形成大量自由端的断裂点,处于热力学不稳定状态的玻璃相结构,煤矸石经热活化后含有大量活性氧化硅以及氧化铝,从而达到活化的目的. 2012年何燕[28]研究了热活化煤矸石-水泥复合体系水化性能,结果表明煅烧温度为750 ℃,保温时间为4 h的热活化煤矸石对水泥体系的火山灰贡献率较高. 化学活化是通过引入少量的其它试剂,致使结构中共价键断裂,形成离子并进入溶液,使煤矸石中化学键不断被破坏,促使其结构解体,达到激发其活性的目的[29]. 2012年吴红等[30]利用化学方法对活化煤矸石,研究了不同激发剂对免烧砖性能的影响,实验结果表明,煤矸石基免烧砖强度在激发剂CaO和Na2SO4的激发作用下显著提高,最佳掺量为8%CaO、2%Na2SO4. 机械活化一般是指利用机械力化学原理进行活化,即通过机械能的施加使固体等物质的物理化学性质发生改变. 2011年司鹏[31]系统的研究了机械力活化过程中煤矸石的粒度、矿物结构以及反应产物活性的内在联系,发现球磨时间、方法、介质决定了煤矸石的机械力活化效果,球磨过程中煤矸石活性被充分激发. 一般情况下,上述方式单独处理时都会面临耗能大,反应不能完全进行,效率低等问题,因此出现了复合活化的方式. 有研究表明,复合活化效果通常情况下优于单一活化[32 − 33]. 2010年Li等[34]提出了一种新的复合机械-水热活化(CMHTA)技术,并以传统的机械-热激活(TMTA)技术为对比,研究结果表明,复合活化效果能显著提高粗煤矸石的活性. 2010年张晓旭等[35]采取热活化、机械活化和化学活化并用的方式将煤矸石与石灰混合活化,实验表明,当石灰和煤矸石取代水泥量的30%,其中石灰占煤矸石量的40%时,煅烧温度为675 ℃时,强度和流动性达到最佳值,与单一热活化煤矸石水泥砂浆相比强度有大幅度提高.
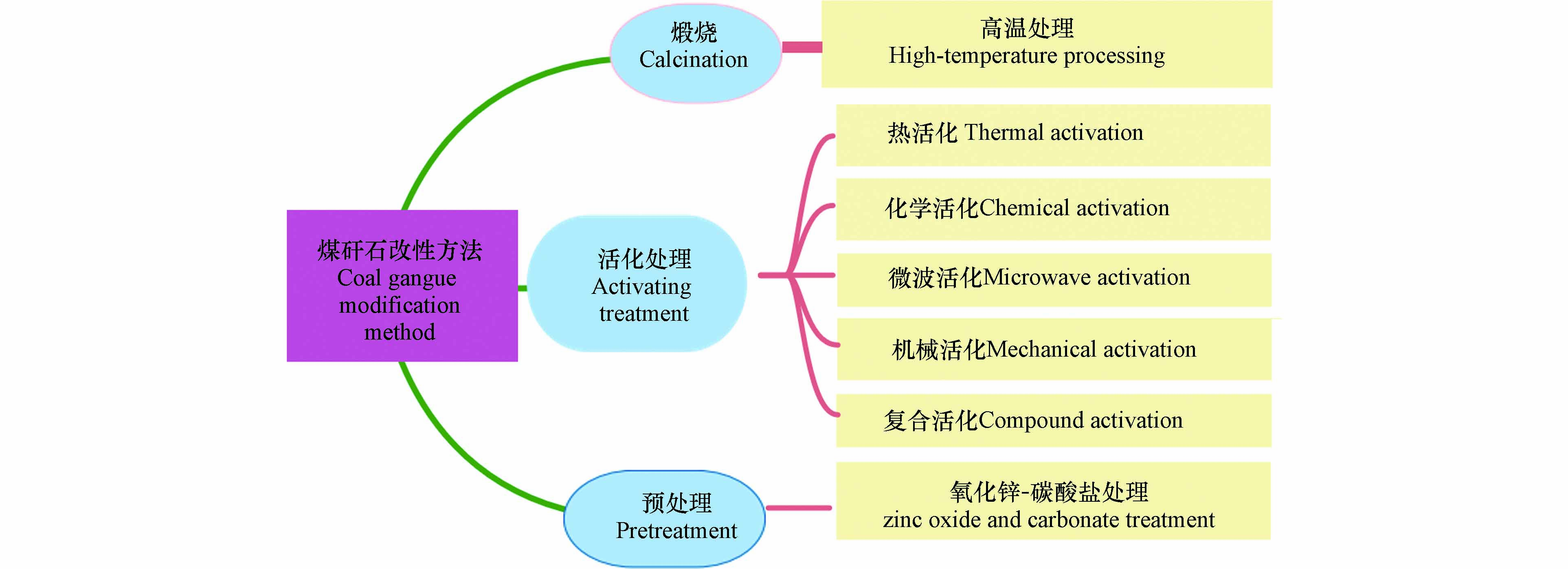
然而,由于成煤条件及环境不同导致煤矸石组分复杂且多样,活性成分含量低,其利用效率并不高,活化虽然能改变煤矸石的部分性能,但是对材料本身变化较小,达不到实际应用的特殊效果,为了提高煤矸石的活性,增加其特殊的性能,对煤矸石改性研究已经成为了热点. 改性方法如图1所示[36],其中酸改性可以使Al、Fe、Ca等金属更易溶解,改性后的煤矸石内部和表面产生的孔隙更多,使得吸附能力更强. 相比而言,碱处理不仅能溶解煤矸石中部分金属氧化物,而且能与煤矸石中存在的硅铝酸盐反应,从而合成沸石分子筛,其吸附能力比传统的沸石分子筛更强[37]. 煤矸石改性不仅降低化工产品的生产成本,而且能提高煤矸石的利用效率,并且产生更高的附加值,经济和环境效益显著,符合“低碳经济、绿色经济、循环经济”的国家政策.
-
废煤矸石综合利用是坚持走资源节约型、环境友好型发展道路的必然选择,是大势所趋. 据统计[38 − 39],12%的煤矸石用于生产建材,32%用于发电,56%用于工程及其他. 随着科学技术的发展,以及对煤矸石资源化综合利用认识的不断深入,我国众多学者已经在有用组分回收、废水处理、制备建筑材料、农业生产等方面取得了显著成绩,但并未摆脱煤矸石资源化利用率低的现状[5],下面分别从几个方面对煤矸石利用情况进行综述.
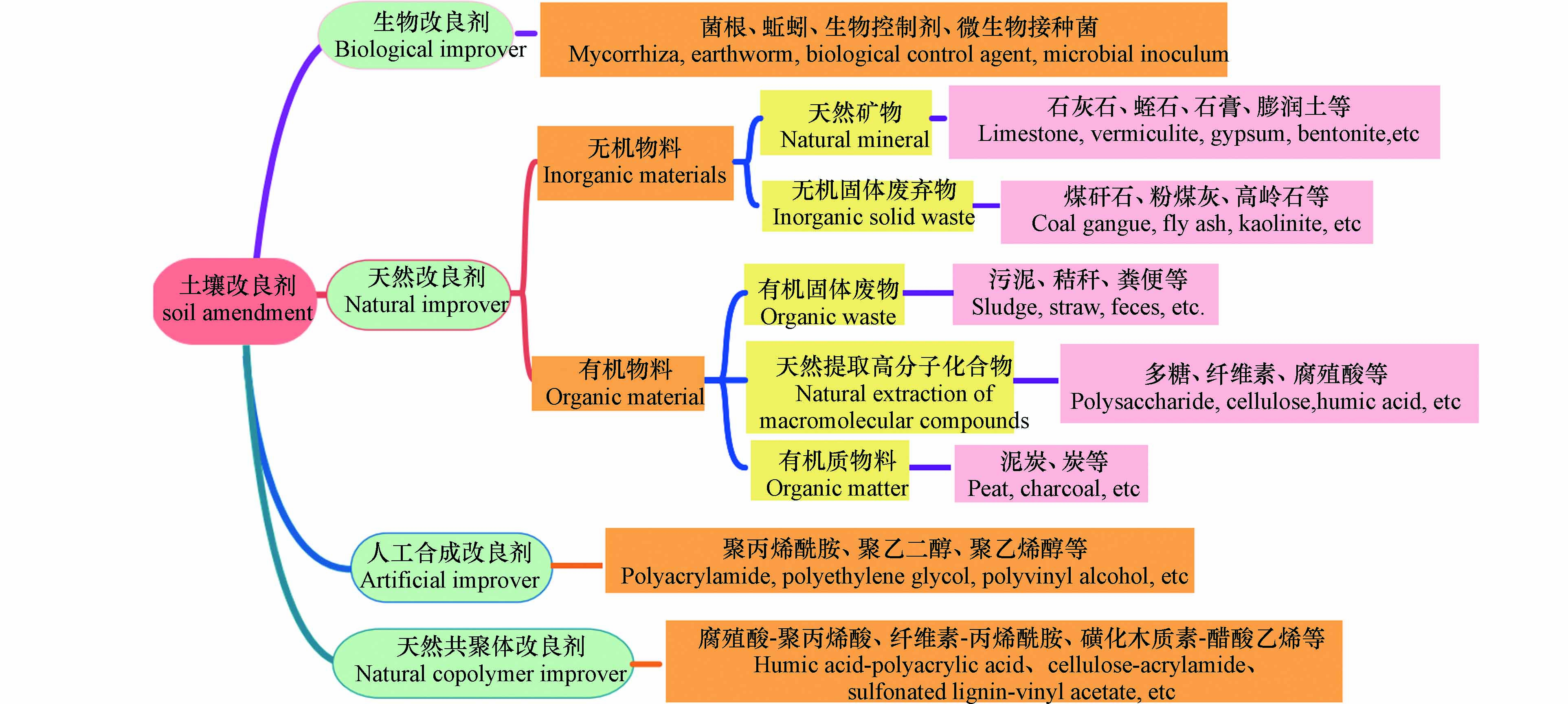
1)煤矸石作为土壤改良剂. 煤矸石中含有腐殖酸、有机质、硅、钾、铁以及多种稀有元素,能促进有益微生物的活性和植物根系的发育,因此,以煤矸石为主的土壤改良剂研究引起了学者的广泛关注. 如图2所示,目前使用的土壤改良剂,按照生产原料可以分为天然改良剂、合成改良剂、天然合成共聚物改良剂和生物改良剂[40].
煤矸石作为天然的无机固体废物,其资源十分丰富. 有研究表明,煤矸石土壤改良剂能有效治理土壤板结、沙化、盐渍化等问题,改善土壤通透性,增加土壤保水保肥能力,减少土壤水分蒸发,增加土壤耐盐碱能力,促进植物根系更好吸收微量元素[41 − 42]. 2016年王琼等[43 − 44]研究了不同的高硫煤矸石对苏打盐渍土化学性状的影响,其研究结果表明,施用高硫煤矸石对苏打盐渍土的改良有较好的效果. 2020年Li等[45]对煤矸石填筑复垦土壤重建过程进行了长达10年的研究,结果表明土壤在复垦后开始逐渐从无序状态恢复到超有序状态,为煤矸石土壤复垦技术提出了宝贵经验. 其次,煤矸石还可以作为重金属钝化剂,可以改变尾矿中锌、铅、镉、铜和铬等重金属的形态,使交换态和碳酸盐结合态转化为铁锰结合态、有机结合态和残留态,进而降低重金属的有效性[46].
2)煤矸石作为化工原料. 煤矸石中含有丰富的铝元素,是廉价易得的铝基化工原料,当煤矸石中Al2O3含量大于35%时,可利用煤矸石代替铝土矿提取和制备氧化铝、氢氧化铝和聚合氯化铝等20多种铝盐化工产品[5]. 2020年贾敏等[20]对煤矸石煅烧活化提取氧化铝技术进行研究,通过煅烧和一步酸溶工艺可以成功地生产冶金级氧化铝. 煤矸石中还含有30%—65%的氧化硅,有效回收煤矸石中的氧化硅成分可生产白炭黑、碳化硅等一系列硅系化工产品,是煤矸石高附加值利用的重要途径之一[19]. 2021年Xie等[47]研究了煤矸石中矿物的高温煅烧相变及铝硅矿物的高效分离,实验表明,煤矸石中高岭石在高温煅烧过程中发生相变,并且在相变过程中释放出活性二氧化硅矿物,可通过碱浸提将其与其他矿物分离. 煤矸石中除含有丰富的铝、硅等常见的金属外,还有少量钛、镓等元素. 通过活化煤矸石,可用来提取有价金属. 2020年辜芳等[22]通过优化pH、混合萃取剂比例、振荡时间等工艺参数,实现了混合稀土与铁、铝的有效分离. 在煤矸石的有价金属的提取过程中,还应该注重分段回收、分段磨矿,以确保有用元素的高效回收[48]. 2020年Ashfaq等[49]在低pH值下的静态和动态浸出条件下,金属离子浸出的浓度相对较高,这归因于各个金属离子配合物的溶解度积值的差异. 在目标金属离子中,金属提取率分别为30%和65%,砷和硒在静态和动态浸出测试中表现出最高的迁移率. 此外,煤矸石还可以用来制备催化剂载体[50 − 51],负载催化过硫酸盐的活性组分,制备出改性煤矸石基过硫酸盐催化剂[52 − 53],从而达到以废治废的目的.
3)煤矸石作为吸附剂. 煤矸石因其矿物成分中高岭石的存在,使得它具有一定的层间结构,同时具有优异的稳定性,通过对煤矸石进行活化和改性,或与其它吸附剂复合,可提高其比表面积和离子交换能力,制得的煤矸石基吸附材料用于去除水中氨氮、磷、有机物、重金属离子等污染物[54],也可以改善污泥中的有机物、重金属离子等具有较好的效果[5,55]. 2010年王现丽等[56]利用改性煤矸石处理味精精馏段生产废水,结果表明投加改性煤矸石对浊度、氨氮、有机污染物的去除率分别可达到70.73%,63.67%,69.81%. 2015年裴会芳等[57]以城市污泥和煤矸石为原料,进行了制备多孔陶粒的实验研究,结果表明,以煤矸石和城市污泥为原料,可以制备多孔陶粒,煤矸石和污泥中的部分重金属已溶解到硅酸盐玻璃相中,形成稳定的固溶体,不会对环境造成二次污染. 2016年Jabłońska等[58]研究了天然煤矸石和改性煤矸石的结构和表面性质,结果表明,天然煤矸石的比表面积较小,其内部主要是介孔,化学改性的煤矸石增大了总孔容和比表面积,可以用于工业废水的预处理. 2020年石凯等[59]采用两步化学活化法制得多孔煤矸石,并研究了多孔煤矸石的吸附性能,结果表明,多孔煤矸石吸附罗丹明B属于熵驱动型物理吸附. 2022年Zhang等[60]采用ZnCl2对天然煤矸石进行改性,与原煤矸石相比,改性煤矸石对含磷废水的处理能力明显提高.
4)煤矸石作为建筑材料. 煤矸石主要是碳质、泥质和砂质的混合物,在岩性上主要包含煤质、泥页岩和粉砂质泥页岩等类型[61]. 煤矸石可作为混凝土的骨料,且其矿物组成和化学成分与黏土相似,可代替黏土作为原料用于制备水泥、砖和新型墙体材料[62]. 煤矸石强度较高,经过破碎、筛分之后可以代替石子来制备混凝土. 其次,煤矸石具有良好的防腐性能,可以用作道路填料. 经检测,煤矸石的强度、抗冻性或抗裂性均满足公路技术要求,具有地基承载力高,抗滑稳定性好等优点[63]. 利用高孔隙率、强吸水性的煤矸石可生产多孔烧结砖,采用回转窑法生产煤矸石陶粒等[64]. 煤矸石是由多种矿岩组成的混合物,密实度高,荷载能力强. 同时,煤矸石具有适当的导水性、吸附特性和浸出行为,因此可将其作为充填材料用于回填复垦,不仅降低了煤矸石堆存的占地率,实现了煤矸石的就近处置,而且改善了地下采煤引起的地表沉降,具有良好的经济效益和环境效益. 2016年刘章锋等[65]通过添加煤矸石作为骨架材料,水泥作为凝胶材料,纤维作为辅助材料对污泥进行固化改性,并研究其固化机理,结果显示固化体内部黏聚力随煤矸石添加数量的增大而减小,黏聚力随煤矸石添加量的增大而增大. 2016年Hu等[66]列举了煤矸石在建筑材料、灌浆材料、空心砖等方面的应用. 砖瓦企业提供了新的发展思路和方向,是中国式的消纳污泥的重要途径,有利于行业综合利用技术水平的提升,对砖瓦行业发展低碳、环保绿色产业,加快污泥无害化、减量化、资源化综合利用有重要现实意义. 煤矸石储量大、价格低,在生产建筑材料方面有着非常好的应用前景. 但煤矸石作混凝土骨料要充分考虑其抗折强度、耐磨性、渗性和抗冻性,煤矸石制水泥要控制好煤矸石的掺入比例,煤矸石制砖要通过工或参数优化提高其可塑性,煤矸石制新型墙体材料要增加其科技投入. 同时,应当注意的是煤矸石在制备建筑材料时需要进行高温煅烧,这可能会导致煤矸石中所含有的有害微量元素以气体的形式释放到大气当中[5].
5)煤矸石作为陶瓷原料. 氧化铝和二氧化硅是陶瓷生产中常用的原料,从表1可以看出,煤矸石中的主要成分也是二氧化硅和氧化铝,而且煤矸石本身也具有大量的微孔和较高的比表面积,完全可以利用煤矸石来制备性能优异的陶瓷等材料. 然而污泥中也含有与黏土类似的硅酸盐成分,在一定条件下可以代替黏土生产陶瓷,故国内外许多学者对利用煤矸石和污泥制备多孔材料和陶粒进行了研究. 2016年支楠等[67]研究了煤矸石污泥陶粒烧结膨胀性能,结果表明,仅以污泥为原料不可能生产出合格陶粒,必须配入辅助原料,考虑到煤矸石成分等因素,故采用煤矸石为辅助原料. 2015年祁非等[68]以城市污泥和煤矸石为原料制备了陶粒,实验结果表明陶粒能有效固化城市污泥中有害重金属元素,并且不会对环境造成的二次污染. 2019年Zhou等[69]以煤矸石为原料,采用喷雾干燥烧结法制备低成本陶瓷微球吸附剂,用于水溶液中阳离子红X-5GN和阳离子蓝X-GRRL的脱除,吸附剂的吸附容量为1.044 mg·g−1和 2.170 mg·g−1,使用煤矸石陶瓷吸附剂处理有色废水可以达到以废处理废弃物的目的,煤矸石吸附剂的综合经济效益和环境效益具有广阔的应用前景. 2022年张会等[70]以煤矸石和滑石为原料,在高压使其成型,干燥后经过高温煅烧并保温,压成型法制得的试样采用XRD分析试样为堇青石,可见固体废弃物煤矸石为主要原料,可制得具有一定性能的堇青石多孔陶瓷. 同年,程冠吉等[71]利用废弃煤矸石为原料,并添加铝矾土、可溶性淀粉混合均匀成型后经烧结制成多孔莫来石陶瓷,通过测定显气孔率得到最优制作工艺.
目前,我国煤矸石综合利用方式主要有分选、采矿区充填、铺路、发电、生产空心砌块和水泥等,表2总结了煤矸石的综合利用情况. 由于废弃煤矸石中有用矿石占比较少,分选的经济成本要求较大;粒径大的煤矸石充填采矿区可能造成坍塌,粒径小的煤矸石充填又可能被雨水冲洗流失;利用煤矸石作为化工原料又会对环境造成二次污染,治理成本较高;烧制轻骨料、生产空心砌块等技术成熟,可以消纳大量煤矸石,但总体产品附加值不高. 所以急需开发一种新的方法,使得煤矸石变废为宝,提高煤矸石的可利用价值.
-
煤矸石具有一定的孔隙度、透气、保水性性能,目前已被应用于制备采煤沉陷区复垦充填基质、土壤改良剂和矿物肥料等. 通过物理、化学或生物方法将煤矸石改性,或添加其他基质共同处理等方法,可以有效改良煤矸石的理化性质,解决其生物活性差的缺陷,使其形成类似土壤性质和结构的生态基质,对于改善植物生存环境,重新建立和恢复复垦区的土壤生态体系,加速煤矸石成土化具有积极作用[72]. 煤矸石与其它物质配合,克服了其持水性差、肥力不足等缺点,同时还能调节极端pH值,同时煤矸石中的营养元素匮乏限制了其作为优质土壤改良剂的能力. 城市污泥同样作为一类产量巨大的废弃物,不仅含有大量的有机质、氮及其他养分,同时含有丰富的微生物类群,能够满足植物生长的需要. 近年来,污泥已被用于土地复垦等领域[73 − 74],既能为植物提供肥料和微量元素,又可改善土壤的理化性质,促进土壤熟化,还能增加土壤微生物的活性[75],但污泥因为病原菌和重金属的潜在危险[76],其土地施用率受到严格的限制. 针对上述两种废弃物的特性,能否找到适合的方法将二者进行处理改造,使其发挥各自优势,实现优势互补,对于两种废弃物的处置和资源化利用具有重要的意义和应用前景. 表3总结了近年来污泥和煤矸石在土壤修复利用的情况,证明了污泥耦合煤矸石治理污染土壤的可行性. 2018年包红旭等[77]公开了一种适用于无土草坪的煤矸石混合培养基质及应用,该发明是将采煤过程中产生的煤矸石、生活污水处理厂中的剩余活性污泥以及农作物秸秆作为材料配制而成. 但是,由于煤矸石和污泥中均存在一定量的重金属,作为基质应用时还是存在重金属环境风险,后续进行环境风险评估也是煤矸石和污泥作为土壤基质使用的必要条件.
煤矸石容重高于一般土壤且毛管孔隙少,将其掺入土壤可以增强土壤透气性和疏松度,具有一定的营养成分,但是难以形成土壤团聚体且缺少活性微生物;污泥农用的透气性不佳但是可提高土壤中氮磷元素、有机质的含量以及微生物,调节土壤孔隙,改善土壤的团粒结构[13]. 城市污泥直接应用于煤矸石边坡生态修复,有利于植物生长[78]. 土壤和植物的混合体系使生长基质中的有害物质逐渐减少. 对地表水环境的负影响主要是氮、磷的富营养化,但环境安全总体可控[79]. 所以将用污泥来改性煤矸石可以改善煤矸石营养元素匮乏的缺点[80],使基质具有良好的营养水平,获得理想的植物营养效果,并且在保有其良好透气性的基础上,增加保水保肥性.
-
pH是影响污泥改性煤矸石的关键影响因素之一. 在不同的pH下,污泥和煤矸石所发生的反应也存在差异. 在常温的情况下,酸性煤矸石中普遍含有较高的硫化物及其他有害金属元素,黄铁矿(FeS2)等硫化物遇降水和氧气就会氧化产生酸矿水[89](公式1、2). 煤矸石山中的有毒有害金属元素就会随酸矿水溶解排出,导致矿区周围土壤和水体的污染,并且酸矿水的排出,会影响土壤的pH,严重时会对土壤微生物以及植物造成抑制作用. 2023年卢欢等[90]研究了pH对煤矸石中重金属和SO42−释放行为的影响,初始淋溶液pH越低越有利于SO42−的释放,同时产生大量H+,体系pH降低至1.31—1.52,这是酸性矿山废水生成的根源所在. 在pH值较低的酸性环境中,溶液中有大量氢离子,吸附剂也吸附较多氢离子,造成吸附剂表面负电荷的减少,所以污泥煤矸石复合基质的材料对土壤改良的效果较好.
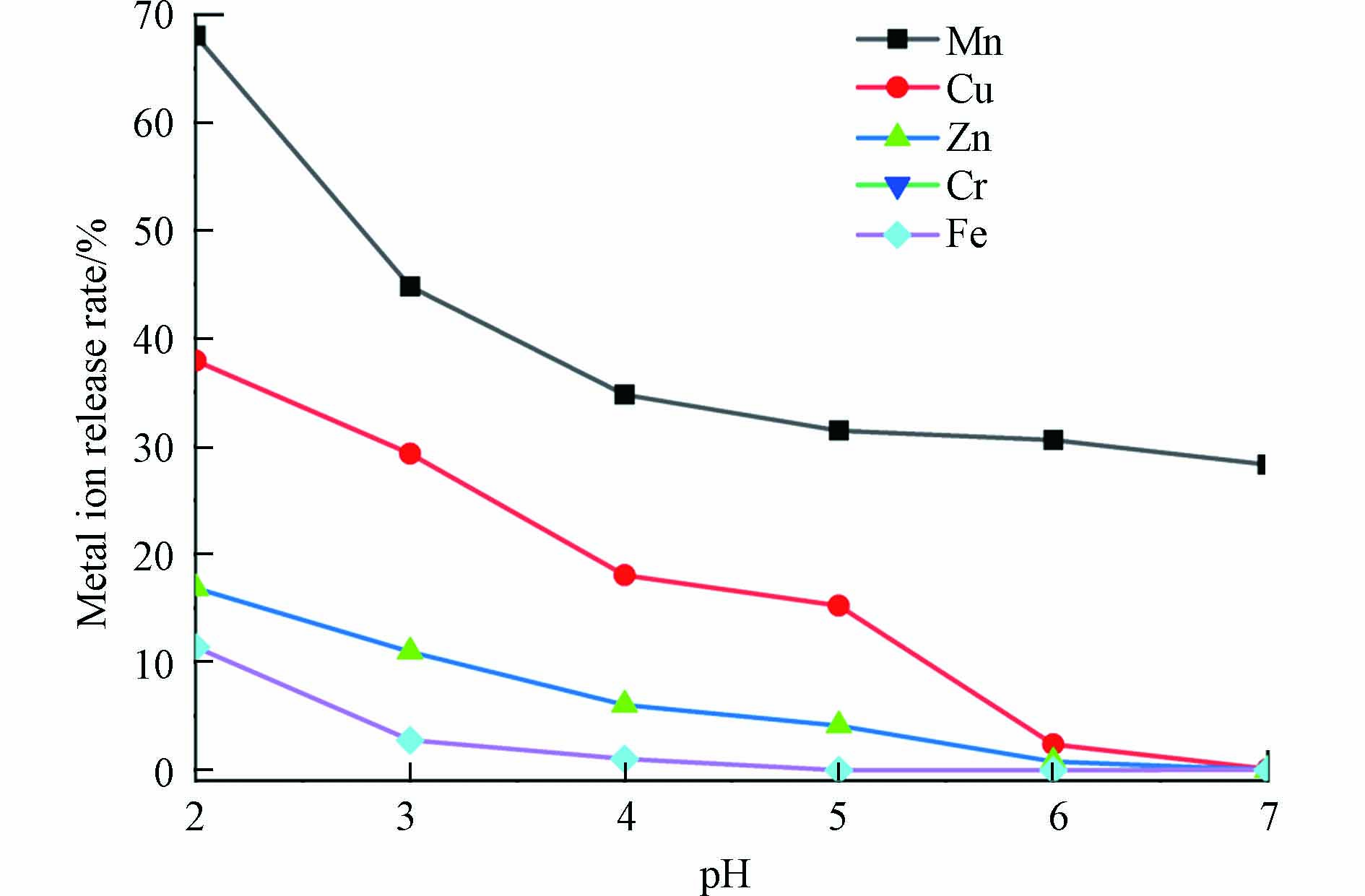
不同的污泥成分不同,pH也存在一定的差异. 2015年田卉宇等[86]研究了不同的污泥和煤矸石理化性质,结果显示pH由小到大分别为冻融污泥(pH7.08)、腐熟污泥(pH7.12)、脱水污泥(pH7.65)、煤矸石(pH8.73),并且提出污泥的添加可以有效降低煤矸石基质的pH值,有利于植物的生长. 2014年马保国等[91]利用污泥和酸性煤矸石做成淋溶柱开展柱淋溶模拟试验,从淋溶第1天至第41天,pH从2.0升至7.5并保持平衡,而单独的酸性煤矸石在淋溶模拟试验中pH迅速从2.5下降至1.5左右并保持平衡,对淋溶液进行分析后发现污泥覆盖煤矸石不仅能降低淋滤液酸性,而且能控制重金属淋溶迁移. 2022年周新华等[92]研究了pH值对碱性煤矸石碱度和重金属释放规律影响研究,如图3所示,pH值对碱性煤矸石中碱度释放具有较大影响,当pH值逐渐增大时,碱性煤矸石向水体释放的碱度随pH变大而降低,从环境污染防控角度考虑,应尽量控制碱性煤矸石堆体环境体系pH值大于6.
-
煤矸石、污泥以及其他废弃物按照不同的比例混合后,对土壤的修复效果也有所不同. 2011年Qian等[93]道报了煤矸石-粉煤灰-污泥混合物用于矿山废弃地复垦的盆栽试验研究,结果表明,煤矸石-粉煤灰-污泥比例为2:6:2是最佳的混合比例,能最大限度地减少有毒元素,提供足够的养分,3种基质的适当配比可以有效地促进植物的再生利用,增加植物对养分的吸收,为煤矸石、粉煤灰和污泥的生态利用提供参考. 2015年刘荷芳等[94]研究了生污泥、腐熟污泥和冻融污泥3种污泥在煤矸石山复垦中的应用效果,综合考虑污泥腐熟和运输的成本,最终确定煤矸石、污泥和粉煤灰的质量配比为60:30:10的混合基质可作为煤矸石山复垦的最佳选择. 2017年王迁等[87]将矿区脱水煤矸石与污泥、粉煤灰和土壤按不同质量混合,结果表明土壤中添加不同基质的混合物均不同程度地改善了土壤养分含量,满足植物生长需要,最终确定土壤、污泥、煤矸石和粉煤灰配比为60%:5%:15%:20%效果最佳. 2018年周昊等[95]以煤矿区粉煤灰、生活污泥以及煤矸石为原料,按照不同的配比添加至土壤中,最终选择污泥、煤矸石、粉煤灰和土壤质量配比为5%:15%:20%:60%为种植白三叶的最佳方案,并指出在土壤改良和植物修复过程中应着重控制其相应掺杂比,以提高改良效果及修复效率,其研究结果和王迁一致. 2018年段超等[96]发明了一种改良盐碱地的生物质废弃物土壤调理剂,其中污泥和煤矸石在调理剂中占比为75%左右,该方法成本低,能加快盐碱地改良的进展,提高改良效果. 2020年方娜[88]将污泥、煤矸石和粉煤灰按一定比例混合,用于煤矸石山复垦,结果表明,在一定程度的调整生污泥的复混比例,可以达到良好的复垦效果. 加入不同比例的煤矸石和污泥可以改善混合基质的部分性能. 煤矸石中有机质含量较污泥低,混合基质中加入煤矸石比例越高,有机质含量相对降低,速效氮、磷含量会随之降低,反之,混合基质中加入污泥比例越高,有机质含量升高,速效氮、磷含量随之升高,混合基质的性能得到改善. 污泥、煤矸石耦合过程中,配比直接影响到反应物的比例,极有可能影响整个反应.
-
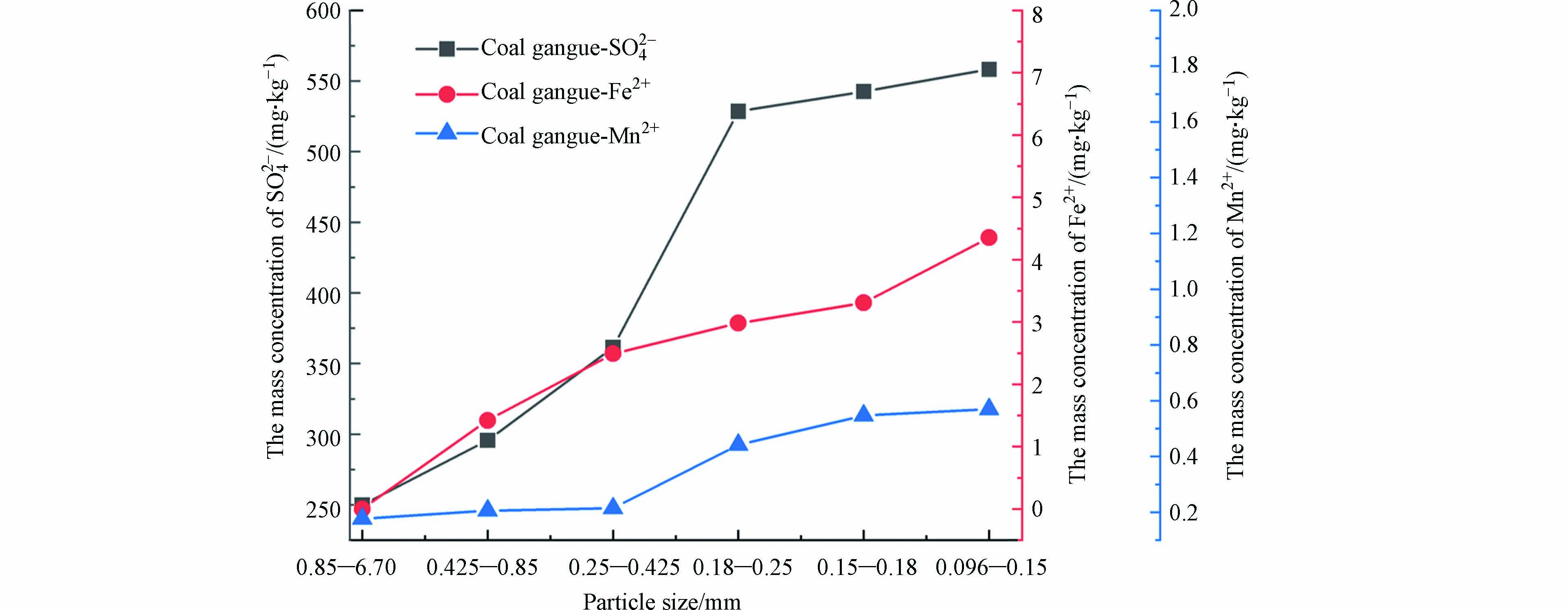
煤矸石的表面存在孔隙、附着小颗粒,且包含的赤铁矿、沸石、黄铁矿、绿泥石、高岭石和磁铁矿等矿物容易溶解. 煤矸石粒径较大,养分不足且保水性差,污泥的加入起到了填充保持作用. 煤矸石粒径越小,固液接触界面的面积越大,导致污染物溶解释放总量呈增加的趋势. 污泥粒径越小其吸附效果越好,初始离子浓度对不同重金属元素吸附效果影响有差异,吸附效果升高或降低,主要取决于活性污泥中的微生物对不同重金属元素的生物敏感性[97]. 2018年孔涛等[98]探讨了煤矸石对盐碱地绿化的改良效果及其对土壤微生物的影响,结果表明,煤矸石可以改善盐碱地的生态质量,不同粒径的煤矸石混合基质可以作为盐碱地绿化的改良剂. 2020年狄军贞等[99]研究了不同地区煤矸石污染组分溶解释放规律与粒径的关系,结果表明煤矸石粒径越小,污染物越容易溶解释放,并且建议煤矸石的粒径大于0.18—0.25 mm,如图4所示,在煤矸石粒径为0.25—6.70 mm时,SO42−、Fe2+、Mn2+的质量浓度均相对较低,可以减少煤矸石在复垦过程中离子的释放. 2021年易名儒等[100]研究了不同粒径污泥的结构稳定性,结果显示不同粒径的污泥具有不同的结构稳定性,其对污染物降解能力差异较大. 煤矸石粒径大小≤8目并与城市污泥以体积比1:1混合制成植生基质改良后的沙土理化性质有了明显改善且可以保证植物的健康生长[101]. 粒径小的颗粒基质表面能较高,同时颗粒间接触面积小,导致总表面积很大,处于较高能量状态. 2021年Han等[102]利用煤矸石覆盖矿区土壤,探究了粒径对土壤修复性能的影响,作者认为粒径小的煤矸石与空气和水接触更多,并且可以形成更窄的毛细孔,增强持水能力,最终确定覆盖用煤矸石粒径范围为0.5—2 cm效果最佳.
-
在污泥、煤矸石耦合的过程中,除了上述的温度、配比、粒径外,还有其他的因素会影响污泥改性煤矸石的性能,比如污泥和煤矸石本身的组成、水分、灰分、压力等,其中水分、灰分会随着掺杂量的改变而改变. 含水率也会影响到反应,表面含水率小于内部的含水率,产生了湿度差,由于内层相对于表层湿度较大,于是水分就从内层向表层移动. 由于污泥和煤矸石本身组成成分差异,当植物基质中的煤矸石比例逐步提高后,土壤中的磷元素会面临短缺问题,当煤矸石比例偏低时,可能出现富营养化现象,因为煤矸石与污泥的磷元素差异比有机质含量差异和氮元素含量差异要显著得多,如果煤矸石和污泥成分所造成过高的碳磷比会影响植物体内的RNA转录[103],影响植物体内的蛋白质合成,过高的氮磷比会降低植物的固氮量.
-
煤矸石的资源化利用一直是国内外学者们研究的重点,也是国家可持续发展的重大需求. 由于污泥和煤矸石的产量巨大,国家对煤矸石、污泥资源化利用给予了较大的政策支持.
(1)煤矸石、污泥资源化处理技术虽取得了快速发展,但其配套设备、技术的成熟度仍需进一步完善. 污泥和煤矸石联合后相比单类物质具有更大的优势. 尽管很多学者在煤矸石和污泥修复改良土壤方面做了大量的研究,包括煤矸石基质、土壤微生态的长期稳定性以及对植被的影响方面,但是由于煤矸石和污泥均属于固体废弃物,在资源化利用的同时,还需要考虑其对对环境的安全性.
(2)煤矸石、污泥资源化还应当关注其用量大、成本低、效益高、具有较强的针对性等特点,加强煤矸石和污泥作为土壤改良剂的产品标准和改良工程规范标准,使煤矸石、污泥土壤改良剂生产工艺、产品标准和改良过程规范化,使得煤矸石、污泥土壤改良剂能够大规模应用和推广. 因此,未来几年应加强煤矸石、污泥土壤改良剂基础理论研究及配套设备开发,进一步拓展利用途径.
(3)我国煤矸石、污泥资源化利用率虽然在逐年增加,但由于煤矸石、污泥产量巨大,资源化利用途径依然有待提高. 交叉领域的兴起为煤矸石、污泥资源化利用带来了曙光,可以加大煤矸石、污泥在其他领域的资源化应用,提倡“以废治废”的观点,解决煤矸石、污泥以及土壤带来的环境污染,实现社会经济和环境效益的协调发展.
废弃煤矸石资源化利用研究进展
Research progress on resource utilization of waste coal gangue
-
摘要: 随着社会的高速发展,工业废物堆积造成的环境问题日渐严重. 煤矸石是一种煤炭开采和洗选过程中产生的典型工业废弃物. 其大量堆积不仅占用土地资源,而且还会污染环境,引起地下水污染,造成山体滑坡、塌陷等地质灾害,严重威胁人类生存环境. 近年来,“以废治废”模式成为了工业废弃物处置的研究热点之一,也是生态修复的重要研究方向. 本文综述了煤矸石资源化利用的研究进展,进一步阐述了污泥改性煤矸石在生态修复与土壤改良方面的进展,为后期煤矸石和污泥的高值化利用奠定基础.Abstract: With the rapid development of society, the environmental problems caused by the accumulation of industrial waste are becoming more serious. Coal gangue is a typical industrial waste produced in coal mining and washing. The massive accumulation of coal gangue not only occupies land resources but also leads to the environmental pollution such as groundwater, and even geological disasters such as landslides and cave-ins, which seriously threaten human survival. In recent years, the “treating waste by waste” model has become one of the research hotspots of industrial waste disposal and also an important direction in ecological remediation research. This review sums up the progress of coal gangue resourceful utilization research, further elaborates the progress of coal gangue modified with sludge in soil improvement and ecological remediation, which lays the foundation of the long-term high-value utilization of coal gangue and sludge.
-
Key words:
- coal gangue /
- industrial waste /
- sludge /
- resource recovery /
- ecological restoration and improvement.
-

-
表 1 煤矸石组成成分表(%)
Table 1. Coal gangue composition table (%)
来源
SourceSiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO TiO2 R2O 参考文献
References掘进矸石 53.10 18.40 8.10 4.50 1.50 0.85 0.70 [17] 洗选矸石 50.50 37.90 4.15 1.80 1.07 1.60 0.65 普通煤矸石 41.10 22.90 2.40 0.73 0.34 0.86 2.00 [18] 六安市煤炭开采 37.80 21.20 2.50 2.60 0.30 0.90 1.40 [19] 内蒙古准格尔 36.90 38.98 0.33 — 0.03 1.01 0.17 [20] 于贵州盘县某矿区 37.30 17.35 18.19 6.85 1.15 4.19 — [21] 普通煤矸石 38.18 18.48 12.97 2.86 2.63 4.51 0.02 [22] 高铝煤矸石 42.17 48.41 0.07 3.77 0.94 1.35 — [23] 普通煤矸石 41.47 15.95 3.53 1.23 1.79 — 1.71 [24] 注:R2O为其他氧化物,“—”未检测到相应物质.
R2O is other oxide, and "—"indicates that the corresponding substance has not been detected.表 2 煤矸石的综合利用情况
Table 2. Comprehensive utilization of coal gangue
利用途径
Utilization ways具体方式
Specific way优点
Advantage缺点
Disadvantage分选 有用矿物 重复利用资源 有用矿石占比较少、经济成本较大 矸石 直接利用 采矿区充填 技术含量较低、操作简单、经济 充填不紧密、容易坍塌 铺路建设 耐腐蚀能力强、抗压抗剪强度大 雨水天气易打滑,存在安全隐患 生活中的应用 发电 节约能源,变废为宝 热值低,炉耗高 化工原料 硅、铝元素含量高 造成环境二次污染 建筑材料 生产水泥、砖等 节省土地和能源,变废为宝 产品受样品差异大,质量问题较多 表 3 污泥、煤矸石修复土壤利用情况
Table 3. Utilization of soil remediation by sludge and coal gangue
研究对象
Research objects研究方法
Research method结论
Conclusion参考文献
References污泥、煤矸石 混合复配,采用高羊茅盆栽试验进行验证 煤矸石粒径越小,基质黏粒含量越高;污泥堆肥能显著提高基质黏粒百分比,有利于保水保肥;植物堆肥则能提高砂粒占比,有利于透水透气 [81] 污泥、煤矸石 利用ZnCl2、盐酸对污泥、煤矸石复合基改性并对废水厌氧消化 污泥和煤矸石制备的复合基活性炭表面孔状结构发达,官能团种类增加,可改变厌氧微生物群落结构,优势菌种得到富集 [82] 优良城市污泥、煤矸石 混合复配,淋滤盆栽实验 可以有效钝化煤矸石中重金属元素,淋溶出煤矸石中的重金属含量低,且能有效提升渗滤液的pH,可以作为优良基质 [83] 城市污泥、煤矸石以及土壤 城市污泥、煤矸石土壤混合基质盆栽试验 植物-土壤系统可以逐渐降低生长介质中有害物质的浓度 [84] 污泥、煤矸石、粉煤灰以及土壤 污泥、煤矸石、粉煤灰混合后加入到土壤中进行盆栽试验 有利于植物的生长,而且复合基质中重金属污染水平处于清洁状态 [85] 污泥、煤矸石以及土壤 不同处理的污泥和煤矸石混合后加入到土壤中进行盆栽试验 能促进部分植物地下部分的生长 [86] 污泥、煤矸石、粉煤灰以及土壤 污泥、煤矸石和粉煤灰混合后加入到土壤中进行盆栽试验 土壤的有机质、全氮、有效磷及速效钾含量均达到了土壤等级的一级标准,土壤的营养成分均得到了改善 [87] 污泥、煤矸石、粉煤灰以及土壤 污泥、煤矸石和粉煤灰混合后加入到土壤中进行梯田试验 可以实现固体废弃物的资源化利用,变废为宝,同时又增加煤矸石山复垦中土壤的肥力 [88] -
[1] 贾鲁涛, 吴倩云. 煤矸石特性及其资源化综合利用现状[J]. 煤炭技术, 2019, 38(11): 37-40. JIA L T, WU Q Y. Properties and comprehensive utilization status of coal gangue resource[J]. Coal Technology, 2019, 38(11): 37-40 (in Chinese).
[2] 蔡峰, 刘泽功, 林柏泉, 等. 淮南矿区煤矸石中微量元素的研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2008, 33(8): 892-897. CAI F, LIU Z G, LIN B Q, et al. Study on trace elements in gangue in Huainan mining area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2008, 33(8): 892-897 (in Chinese).
[3] 顾霖骏, 申艳军, 王念秦, 等. 煤矸石堆积区土壤重金属潜在危害评价及污染特征[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 942-949. GU L J, SHEN Y J, WANG N Q, et al. Pollution characteristics and potential risk accessment of heavy metals in soil of coal gangue accumulation areas[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2022, 42(5): 942-949 (in Chinese).
[4] CHILIKWAZI B, ONYARI J M, WANJOHI J M. Determination of heavy metals concentrations in coal and coal gangue obtained from a mine, in Zambia[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2023, 20(2): 2053-2062. doi: 10.1007/s13762-022-04107-w [5] 李振, 雪佳, 朱张磊, 等. 煤矸石综合利用研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(6): 165-178. LI Z, XUE J, ZHU Z L, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of coal gangue[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(6): 165-178 (in Chinese).
[6] ASHFAQ M, ALI BAIG MOGHAL A, BASHA B M. The sustainable utilization of coal gangue in geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications[J]. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 2022, 26(3): 03122003. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000705 [7] 中国科学院山西煤炭化学研究所. 一种煤矸石制备纳米氧化铝的方法: CN202210828294.1[P]. 2022-09-16. Shanxi Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. A method for preparing nanometer alumina from coal gangue: CN202210828294.1[P]. September 16, 2022(in Chinese).
[8] YANG Q C, ZHANG F, DENG X J, et al. Extraction of alumina from alumina rich coal gangue by a hydro-chemical process[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2020, 7(4): 192132. doi: 10.1098/rsos.192132 [9] 韩邦华. 煤矸石在水泥行业中的综合利用[J]. 江西建材, 2019(11): 6-8. HAN B H. Comprehensive utilization of coal gangue in cement industry[J]. Jiangxi Building Materials, 2019(11): 6-8 (in Chinese).
[10] 王永刚. 固废在建材方面的资源化利用综述[J]. 广东化工, 2020, 47(21): 115-118. WANG Y G. A summary of resource utilization of solid waste in building materials[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2020, 47(21): 115-118 (in Chinese).
[11] 田莉, 于晓萌, 秦津. 煤矸石资源化利用途径研究进展[J]. 河北环境工程学院学报, 2020, 30(5): 31-36. TIAN L, YU X M, QIN J. Research progress in utilization of coal gangue resources[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 30(5): 31-36 (in Chinese).
[12] 谢娟, 夏润南, 杜红霞, 等. α-Fe2O3/煤矸石复合光催化剂的制备及其降解五氯酚性能的研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(5): 74-77. XIE J, XIA R N, DU H X, et al. Preparation of α-Fe2O3/coal gangue composite photocatalyst and its application in pentachlorophenol degradation[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(5): 74-77 (in Chinese).
[13] GAO H D, HUANG Y L, LI W, et al. Explanation of heavy metal pollution in coal mines of China from the perspective of coal gangue geochemical characteristics[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(46): 65363-65373. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14766-w [14] OUYANG S Y, HUANG Y L, GAO H D, et al. Study on the distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metal elements in coal gangue taken from 25 mining areas of China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(32): 48285-48300. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19238-3 [15] JIANG X, LU W X, ZHAO H Q, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy-metal pollution around coal gangue dump[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2014, 14(6): 1599-1610. doi: 10.5194/nhess-14-1599-2014 [16] 霍晨磊, 何亚波, 孟子浩. 煤矸石资源化利用技术综述[J]. 山西焦煤科技, 2011, 35(1): 47-49, 52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0652.2011.01.013 HUO C L, HE Y B, MENG Z H. Summary of gangue resource utilization technology[J]. Shanxi Coking Coal Science & Technology, 2011, 35(1): 47-49, 52 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0652.2011.01.013
[17] 周锦华, 胡振琪. 固体废弃物煤矸石室内击实试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2003(12): 53-55. ZHOU J H, HU Z Q. Study on indoor impaction test of coal refuse[J]. Metal Mine, 2003(12): 53-55 (in Chinese).
[18] GUO Y X, YAN K Z, CUI L, et al. Improved extraction of alumina from coal gangue by surface mechanically grinding modification[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 302: 33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.08.034 [19] GUO Y X, YAN K Z, CUI L, et al. Effect of Na2CO3 additive on the activation of coal gangue for alumina extraction[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2014, 131: 51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2014.07.001 [20] 贾敏, 杨磊. 煤矸石煅烧活化提取氧化铝技术研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2): 140-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.02.025 JIA M, YANG L. Study on technology of alumina extraction from coal gangue activated by calcination[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2): 140-144 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.02.025
[21] 刘成龙, 谢宇充, 夏举佩, 等. 煤矸石中和渣酸化提取铝、钛实验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2015, 34(4): 966-972. LIU C L, XIE Y C, XIA J P, et al. Study on extracting aluminum and titanium from neutral residues of coal gangue by acid leaching[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2015, 34(4): 966-972 (in Chinese).
[22] 辜芳, 李银, 李浩林, 等. 煤矸石酸溶液中稀土混合萃取优化实验研究[J]. 化学工程, 2020, 48(5): 31-36. GU F, LI Y, LI H L, et al. Study on optimized experiment of mixed extraction of rare earths from acid solution of coal gangue[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2020, 48(5): 31-36 (in Chinese).
[23] 范剑明. 高铝煤矸石铝硅分级提取实验研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2019, 51(11): 65-68. doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2019-0017 FAN J M. Study on sequential extraction experiment of aluminum and silicon from high-alumina coal gangue[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2019, 51(11): 65-68 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11962/1006-4990.2019-0017
[24] 罗立群, 王召, 魏金明, 等. 铁尾矿-煤矸石-污泥复合烧结砖的制备与特性[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(3): 127-131, 137. LUO L Q, WANG Z, WEI J M, et al. Preparation and characteristics of composite sintered brick by iron ore tailing, coal gangue and sewage sludge[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(3): 127-131, 137 (in Chinese).
[25] 焦亚东, 徐树全, 彭道军, 等. 煤矸石的活化方法与活化机理研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2022, 51(8): 2362-2366, 2372. JIAO Y D, XU S Q, PENG D J, et al. Research progress on activation and mechanism of coal gangue[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(8): 2362-2366, 2372 (in Chinese).
[26] ZHANG Y L, LING T C. Reactivity activation of waste coal gangue and its impact on the properties of cement-based materials–A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 234: 117424. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117424 [27] HAN R C, GUO X N, GUAN J F, et al. Activation mechanism of coal gangue and its impact on the properties of geopolymers: A review[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(18): 3861. doi: 10.3390/polym14183861 [28] 何燕. 热活化煤矸石—水泥复合体系水化性能分析[J]. 粉煤灰综合利用, 2012, 25(2): 14-17. HE Y. Research on hydration properties of blended cement based on thermal activated coal gangue[J]. Fly Ash Comprehensive Utilization, 2012, 25(2): 14-17 (in Chinese).
[29] MOGHADAM M J, AJALLOEIAN R, HAJIANNIA A. Preparation and application of alkali-activated materials based on waste glass and coal gangue: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 221: 84-98. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.071 [30] 吴红, 廖德华, 孔德顺, 等. 不同激发剂对煤矸石基免烧砖性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2012, 31(1): 221-225. WU H, LIAO D H, KONG D S, et al. Effect of different activators on properties of gangue based unfired brick[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 31(1): 221-225 (in Chinese).
[31] 司鹏. 煤矸石酸法提铝的活化技术研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2011. SI P. Activation technology for aluminum recovery from coal spoil through acid leaching route[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2011 (in Chinese).
[32] 郭丽君, 李超, 赵亮, 等. 煤矸石的机械-热复合活化研究[J]. 应用化工, 2018, 47(8): 1800-1802. GUO L J, LI C, ZHAO L, et al. Research on the mechanical and thermal activation of coal gangue[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(8): 1800-1802 (in Chinese).
[33] YANG X Y, ZHANG Y, LIN C. Microstructure analysis and effects of single and mixed activators on setting time and strength of coal gangue-based geopolymers[J]. Gels, 2022, 8(3): 195. doi: 10.3390/gels8030195 [34] LI C, WAN J H, SUN H H, et al. Investigation on the activation of coal gangue by a new compound method[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 179(1/2/3): 515-520. [35] 张晓旭, 仇玉良, 刘开平, 等. 化学激发煤矸石对水镁石纤维水泥砂浆性能影响[J]. 混凝土, 2010(11): 119-121. ZHANG X X, QIU Y L, LIU K P, et al. Research on chemical activation of coal gangue and impact on the performance of fiber brucite reinforced cement mortar[J]. Concrete, 2010(11): 119-121 (in Chinese).
[36] 王世林, 牛文静, 张攀, 等. 煤矸石的研究现状与应用[J]. 江西化工, 2019(5): 69-71. WANG S L, NIU W J, ZHANG P, et al. Research status and application of coal gangue[J]. Jiangxi Chemical Industry, 2019(5): 69-71 (in Chinese).
[37] 王丹萍, 李巧玲. 煤矸石改性的研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2014, 34(8): 50-52. WANG D P, LI Q L. Research progress in coal gangue modification[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2014, 34(8): 50-52 (in Chinese).
[38] 刘春风. CFB矸石渣资源化综合利用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016. LIU C F. Research on recycling comprehensive utilization of CFB gangue slag[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016 (in Chinese).
[39] 杨莎莎, 张贵泉. 煤矸石特性与资源化利用研究综述[C]//第四届中国国际砂石骨料大会论文集. 2017: 200-203. YANG S S, ZHANG G Q. A review on the characteristics and utilization of coal gangue as a resource [C]//Collection of papers of the 4th China International Congress on aggregate. 2017: 200-203(in Chinese).
[40] 陈义群, 董元华. 土壤改良剂的研究与应用进展[J]. 生态环境, 2008, 17(3): 1282-1289. CHEN Y Q, DONG Y H. Progress of research and utilization of soil amendments[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008, 17(3): 1282-1289 (in Chinese).
[41] ANANYEVA K, WANG W, SMUCKER A J M, et al. Can intra-aggregate pore structures affect the aggregate’s effectiveness in protecting carbon?[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2013, 57: 868-875. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.10.019 [42] BLAGODATSKAYA E, KUZYAKOV Y. Active microorganisms in soil: Critical review of estimation criteria and approaches[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2013, 67: 192-211. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.08.024 [43] 王琼, 张强, 王斌, 等. 高硫煤矸石不同细度与用量对苏打盐化土化学性状的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2016, 44(9): 1320-1324, 1363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2016.09.22 WANG Q, ZHANG Q, WANG B, et al. Effect of applying rates and fineness of high-sulfur coal gangue on chemical properties of soda-saline soil[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(9): 1320-1324, 1363 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2016.09.22
[44] 王琼, 张强, 王斌, 等. 高硫煤矸石对苏打盐化土的改良效果研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(36): 119-123. WANG Q, ZHANG Q, WANG B, et al. Improving effect of high-sulfur coal gangue on soda-saline soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(36): 119-123 (in Chinese).
[45] LI F, LI X J, HOU L, et al. A long-term study on the soil reconstruction process of reclaimed land by coal gangue filling[J]. CATENA, 2020, 195: 104874. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104874 [46] 王兴明, 王运敏, 储昭霞, 等. 煤矸石对铜尾矿中重金属(Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr和Cu)形态及生物有效性的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(10): 2688-2697. WANG X M, WANG Y M, CHU Z X, et al. Effects of coal gangue addition on the chemical fraction and bioavailability of heavy metals (Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr and Cu) in copper mine tailings[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(10): 2688-2697 (in Chinese).
[47] XIE M Z, LIU F Q, ZHAO H L, et al. Mineral phase transformation in coal gangue by high temperature calcination and high-efficiency separation of alumina and silica minerals[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 14: 2281-2288. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.129 [48] 张泽琳, 葛小冬. 煤矸石中硫铁矿工业化分选研究进展[J]. 煤炭技术, 2016, 35(10): 293-295. ZHANG Z L, GE X D. Advances in industrialization separation of iron pyrite from coal gangue[J]. Coal Technology, 2016, 35(10): 293-295 (in Chinese).
[49] ASHFAQ M, HEERA LAL M, ALI BAIG MOGHAL A. Static and dynamic leaching studies on coal gangue[M]//Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 261-270. [50] LIU F Q, XIE M Z, YU G Q, et al. Study on calcination catalysis and the desilication mechanism for coal gangue[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(30): 10318-10325. [51] 赵昱, 刘喆, 刘佳欣, 等. 煤矸石制备环境功能材料的研究进展[J]. 化学通报, 2022, 85(9): 1090-1095. ZHAO Y, LIU Z, LIU J X, et al. Research progress in environmental functional materials prepared from coal gangue[J]. Chemistry, 2022, 85(9): 1090-1095 (in Chinese).
[52] 胡浩栋. 煤矸石用于制备过硫酸盐催化剂的研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2020. HU H D. Study on the application of coal gangue for persulfate catalyst preparation[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[53] QIN L, GAO X J, SU A S, et al. Effect of carbonation curing on sulfate resistance of cement-coal gangue paste[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 278: 123897. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123897 [54] QURESHI A A, KAZI T G, BAIG J A, et al. Exposure of heavy metals in coal gangue soil, in and outside the mining area using BCR conventional and vortex assisted and single step extraction methods. Impact on orchard grass[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 255: 126960. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126960 [55] WU J X, YAN X L, LI L, et al. High-efficiency adsorption of Cr(VI) and RhB by hierarchical porous carbon prepared from coal gangue[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 275: 130008. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130008 [56] 王现丽, 牛云峰, 吴俊峰. 改性煤矸石作为废水处理吸附剂的试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2010(7): 161-162, 172. WANG X L, NIU Y F, WU J F. Experimental research on modified coal gangue as adsorbent for wastewater treatment[J]. Metal Mine, 2010(7): 161-162, 172 (in Chinese).
[57] 裴会芳, 张长森, 陈景华. 城市污泥/煤矸石制备多孔陶粒的试验研究[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2015, 51(3): 72-77. PEI H F, ZHANG C S, CHEN J H. Preparation of porous ceramsite with sludge and gangue[J]. China Ceramics, 2015, 51(3): 72-77 (in Chinese).
[58] JABŁOŃSKA B, KITYK A V, BUSCH M, et al. The structural and surface properties of natural and modified coal gangue[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 190: 80-90. [59] 石凯, 李巧玲. 多孔煤矸石吸附剂的制备及其吸附热力学研究[J]. 中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(1): 79-84, 90. SHI K, LI Q L. Preparation and adsorption thermodynamics of porous coal gangue adsorbent[J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(1): 79-84, 90 (in Chinese).
[60] ZHANG G L, ZHANG M Y, LIU Y Q, et al. Preparation of zinc-modified coal gangue and its adsorption on phosphate from wastewater[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 141-149. [61] 邓颖兰, 魏恺颉, 赵迪斐, 等. 我国煤矸石固体废弃物在建筑与环境修复领域的资源化利用[J]. 能源研究与利用, 2021(5): 33-36. DENG Y L, WEI K J, ZHAO D F, et al. Resource utilization of coal gangue solid waste in the field of building and environmental restoration in China[J]. Energy Research & Utilization, 2021(5): 33-36 (in Chinese).
[62] WU D, HOU Y B, DENG T F, et al. Thermal, hydraulic and mechanical performances of cemented coal gangue-fly ash backfill[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2017, 162: 12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2017.03.001 [63] ASHFAQ M, HEERA LAL M, ALI BAIG MOGHAL A. Utilization of Coal Gangue for Earthworks: Sustainability Perspective[C]//Advances in Sustainable Construction and Resource Management. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 203-218. [64] ZHANG Q, WANG Z J, ZHANG J X, et al. Integrated green mining technology of “coal mining-gangue washing-backfilling-strata control-system monitoring”—Taking Tangshan Mine as a case study[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(4): 5798-5811. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16083-8 [65] 刘章锋. 煤矸石污泥固化机理研究[J]. 建材与装饰, 2016(49): 175. LIU Z F. Study on solidification mechanism of coal gangue sludge[J]. Construction Materials & Decoration, 2016(49): 175 (in Chinese).
[66] HU L I . Coal gangue and its application research in building materials[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2016, 873: 96-104. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.873.96 [67] 支楠, 刘蓉, 宋方方. 煤矸石污泥陶粒烧胀性能研究[J]. 砖瓦, 2016(7): 14-17. ZHI N, LIU R, SONG F F. Study on the firing expansion of ceramsite with coal gangue added sludge[J]. Block-Brick-Tile, 2016(7): 14-17 (in Chinese).
[68] 祁非, 张长森, 陈景华. 利用城市污泥/煤矸石制备多孔陶粒的研究[J]. 陶瓷学报, 2015, 36(1): 58-63. QI F, ZHANG C S, CHEN J H. Preparation of porous ceramsite with sludge and gangue[J]. Journal of Ceramics, 2015, 36(1): 58-63 (in Chinese).
[69] ZHOU L, ZHOU H J, HU Y X, et al. Adsorption removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using ceramic adsorbents prepared from industrial waste coal gangue[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 234: 245-252. [70] 张会, 王星雨, 赵钰明, 等. 高掺量煤矸石制备堇青石多孔陶瓷的性能研究[J]. 当代化工, 2022, 51(10): 2344-2347. ZHANG H, WANG X Y, ZHAO Y M, et al. Study on the properties of porous cordierite ceramics synthesized from coal gangue with high content[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(10): 2344-2347 (in Chinese).
[71] 程冠吉, 赵维现, 邹欣伟, 等. 添加淀粉对煤矸石基多孔莫来石陶瓷的性能影响[J]. 太原科技大学学报, 2022, 43(5): 422-426. CHENG G J, ZHAO W X, ZOU X W, et al. Effect of adding starch on properties of coal gangue based porous mullite ceramics[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 2022, 43(5): 422-426 (in Chinese).
[72] 周金星, 秦琪焜, 乔浩亮, 等. 一种基于煤矸石和污泥的生态改良基质制备方法: CN111011159A[P].[2020-04-17]. ZHOU J X, QIN Q K, QIAO H L, et al. Method for preparing ecologically improved substrate based on coal gangue and sludge: CN111011159A[P]. [2020-04-17](in Chinese).
[73] OLADEJO J, SHI K Q, LUO X, et al. A review of sludge-to-energy recovery methods[J]. Energies, 2018, 12(1): 60. doi: 10.3390/en12010060 [74] RAHEEM A, SIKARWAR V S, HE J, et al. Opportunities and challenges in sustainable treatment and resource reuse of sewage sludge: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 337: 616-641. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.149 [75] 董晓芸, 柯凯恩, 胡自航, 等. 施用不同污泥堆肥对土壤理化性质及微生物活性的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(6): 70-75. DONG X Y, KE K E, HU Z H, et al. Effect of different sludge composting on soil physical and chemical properties and microbial activity[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2021, 49(6): 70-75 (in Chinese).
[76] LIN X K, LI S C, WEI Z B, et al. Indirect application of sludge for recycling in agriculture to minimize heavy metal contamination of soil[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 166: 105358. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105358 [77] 包红旭, 张欣, 苏弘治, 等. 一种适用于无土草坪的煤矸石混合培养基质及应用: CN108496749A[P]. [2018-09-07]. BAO H X, ZHANG X, SU H Z, et al. Coal gangue mixed culture medium suitable for soilless lawn and application of culture medium: CN108496749A[P]. [2018-09-07](in Chinese).
[78] LIU M J, XIA S P, WANG J, et al. Effect of agricultural application of municipal sewage sludge on plant-soil system: A review[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(12): 4134-4142. [79] YIN N N, ZHANG Z, WANG L P, et al. Variations in organic carbon, aggregation, and enzyme activities of gangue-fly ash-reconstructed soils with sludge and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi during 6-year reclamation[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(17): 17840-17849. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6941-5 [80] TANG Q, LI L Y, ZHANG S, et al. Characterization of heavy metals in coal gangue-reclaimed soils from a coal mining area[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 186: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.11.018 [81] 柯凯恩, 董晓芸, 周金星, 等. 煤矸石生态基质的制备配方及其肥力特征研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(4): 308-317. KE K E, DONG X Y, ZHOU J X, et al. Evaluation of the formula for coal gangue ecological substrate and its fertility indexes[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(4): 308-317 (in Chinese).
[82] 张明媚. 污泥-煤矸石复合基活性炭的制备及其在污水厌氧消化中的应用[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2020. ZHANG M M. Preparation of sludge-coal gangue composite activated carbon and application in anaerobic digestion of sewage[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[83] 翟全德. 城市污泥作为矿山废弃地生态修复基质的筛选与效果研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020. ZHAI Q D. Study on the selection and effect of sewage sludge used as ecological restoration matrix in mine wasteland[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[84] ZHEN C G, LENG P S, LIU L J, et al. Influences of municipal sludge applied in slope vegetation restoration on surface water environment[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(4):1321-1327. [85] 周昊, 郭姣姣, 王宇翔, 等. 基于层次分析法的山西典型矿区土壤改良效果评价[J]. 中国煤炭, 2018, 44(4): 138-143. ZHOU H, GUO J J, WANG Y X, et al. Assessment of soil improvement effects in typical mining areas in Shanxi basing upon analytic hierarchy process[J]. China Coal, 2018, 44(4): 138-143 (in Chinese).
[86] 田卉宇, 刘荷芳, 郁东宁, 等. 污泥不同处理的复混基质在矸石山复垦中的应用研究[J]. 能源环境保护, 2015, 29(3): 21-25. TIAN H Y, LIU H F, YU D N, et al. Application study of compound-mixed substrates through different sludge treatments on coal gangue reclamation[J]. Energy Environmental Protection, 2015, 29(3): 21-25 (in Chinese).
[87] 王迁, 李庆飞, 张沛沛, 等. 山西某煤矿脱水污泥及矿区固废制备土壤调节剂的试验研究[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2017(3): 71-76. WANG Q, LI Q F, ZHANG P P, et al. Experimental study on preparation of soil conditioner from dehydrated sludge of a coal mine in Shanxi Province and solid waste from mining area[J]. Coal Processing & Comprehensive Utilization, 2017(3): 71-76 (in Chinese).
[88] 方娜. 污泥、粉煤灰在大同煤矸石山复垦中的研究与应用[J]. 同煤科技, 2020(2): 11-13. FANG N. Research and application of sludge and fly ash in the reclamation of Datong Coal Gangue Dump[J]. Datong Coal Science & Technology, 2020(2): 11-13 (in Chinese).
[89] TREMBLAY R L. Controlling acid mine drainage using an organic cover: The case of the East Sullivan Mine, Abitibi Quebec[J]. American Society of Mining and Reclamation, 1994 (2): 122-127. [90] 卢欢, 董颖博, 林海. 降雨pH对煤矸石中重金属和SO42-释放行为的影响[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2023(1): 102-109. LU H, DONG Y B, LIN H. Effect of rainfall pH on the release behavior of heavy metals and SO42-in coal gangue[J]. Non-ferrous Metals(Smelting Part), 2023(1): 102-109(in Chinese).
[91] 马保国, 胡振琪. 污泥和粉煤灰覆盖煤矸石山防治污染的模拟试验研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(8): 1553-1559. MA B G, HU Z Q. Simulation experiment on control of coal gangue pollution using sewage-sludge and fly ash covering[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(8): 1553-1559 (in Chinese).
[92] 周新华, 舒悦, 周亮亮, 等. pH值对碱性煤矸石碱度和重金属释放规律影响研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(5): 2752-2758. ZHOU X H, SHU Y, ZHOU L L, et al. Study on effects of pH value on alkalinity and heavy metal release of alkaline coal gangue[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(5): 2752-2758 (in Chinese).
[93] QIAN K M, ZHANG L, WANG L P. An environmentally sound usage of both coal mining residue and sludge[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 183/184/185: 595-599. [94] 刘荷芳, 荆志林, 张克, 等. 不同污泥的复混基质性质及对牧草生长的影响[J]. 北京农学院学报, 2015, 30(3): 96-102. LIU H F, JING Z L, ZHANG K, et al. Properties of compound-mixed substrates consisted of different sludges and effects on the growth of legume forages[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 2015, 30(3): 96-102 (in Chinese).
[95] 周昊, 郭娇娇, 何绪文, 等. 煤矿区固废改良土壤对植物生长的影响[J]. 煤炭技术, 2018, 37(3): 23-25. ZHOU H, GUO J J, HE X W, et al. Research on impact of coal solid waste improved soil on plant growth[J]. Coal Technology, 2018, 37(3): 23-25 (in Chinese).
[96] 段超, 徐峰, 王金山, 等. 一种改良盐碱地的生物质废弃物土壤调理剂: CN108752127A[P]. [2018-11-06]. DUAN C, XU F, WANG J S, et al. Biomass waste soil conditioner for improving saline and alkaline land: CN108752127A[P]. [2018-11-06](in Chinese).
[97] 秦可敏. 大同矿区煤中有害微量元素的赋存特征及其环境效应[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. QIN K M. Occurrence characteristics of hazardous trace elements in coal and their environmental effects in Datong mining area[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019 (in Chinese).
[98] 孔涛, 郑爽, 张莹, 等. 煤矸石对盐碱土壤绿化和土壤微生物的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(6): 321-326. KONG T, ZHENG S, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of coal gangue on revegetation and microbial properties of an alkali-saline soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(6): 321-326 (in Chinese).
[99] 狄军贞, 鲍斯航, 杨逾, 等. 粒径对煤矸石污染物溶解释放规律影响研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(4): 178-184. DI J Z, BAO S H, YANG Y, et al. Study on effects of particle size on dissolution and release law of pollutants in gangue[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(4): 178-184 (in Chinese).
[100] 易名儒, 曾玉, 刘永, 等. 不同粒径好氧颗粒污泥的结构稳定性及污染物去除效果[J]. 环境科技, 2021, 34(5): 23-28. YI M R, ZENG Y, LIU Y, et al. Structural stability and contaminant removal efficiency of aerobic granular sludge with different particle size[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 34(5): 23-28 (in Chinese).
[101] 秦琪焜, 方健梅, 王根柱, 等. 煤矸石与城市污泥混合制备植生基质的试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(7): 304-314. QIN Q K, FANG J M, WANG G Z, et al. Experimental study of planting substrate mixed with coal gangue and municipal sludge[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(7): 304-314 (in Chinese).
[102] HAN X N, DONG Y, GENG Y Q, et al. Influence of coal gangue mulching with various thicknesses and particle sizes on soil water characteristics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79139-8 [103] 周正虎, 王传宽, 张全智. 土地利用变化对东北温带幼龄林土壤碳氮磷含量及其化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(20): 6694-6702. ZHOU Z H, WANG C K, ZHANG Q Z. The effect of land use change on soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus contents and their stoichiometry in temperate sapling stands in northeastern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(20): 6694-6702 (in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: