-
城市地表径流对城市水环境质量的影响不容忽视,被称为影响水环境质量的第二大污染源[1],屋面是城市最典型的不透水下垫面,直接影响着城市面源污染。报道显示,城市不透水面积中屋面面积高达40%~50%[2],有些地区竟高达75%[3]。城市屋面雨水径流便于集蓄且水质相对较好,对其加以开发利用必将成为趋势[4-5]。若能利用这部分雨水资源,将在很大程度上缓解城市水资源短缺问题。西安是一座水源性和水质性双重缺水的城市[6-7],开发利用屋面雨水径流将成为缓解西安市水资源短缺的重要方法[6, 8]。但一般屋面径流初期雨水污染严重[9-10],且国内外尚未对初期雨水有统一的界定,多采用“负荷”和“浓度”[11-12]2种方法界定,即将多少毫米降水深度或次降雨前多少分钟的雨水定义为初期雨水。侯立柱等[13]根据径流污染物浓度随径流时间趋于稳定将降雨15~20 min的雨水定义为初期雨水;陆怡诚等[4]根据径流污染物浓度随径流时间趋于稳定将大雨降雨30 min,中雨及中小雨降雨50 min的雨水定义为初期雨水;胡龙辉等[14]将雨水水质指标浓度达到稳定时的6 mm降雨量定义为初期雨水;HAGEMANN等[15]将2 mm的降雨量定义为初期雨水;刘鹏等[16]将降雨前期4 mm降水深度的径流定义为初期雨水。屋面径流污染具有随机性和多变性,这主要是因为受地理区域、降雨特征、气候状况、前期晴天时间、屋面材质等因素影响[17-20],所以,初期雨水的判定应根据各地区具体情况合理确定。本研究通过监测西安市3场典型、高频次的屋面雨水径流,根据“浓度”即污染指标浓度随径流时间变化来定义初期雨水,监测的污染指标有SS、COD、TN、NH3-N、TP、浊度、Pb、Zn、Cu、Cd、Ni、Cr等。针对西安市屋面初期雨水水质进行研究,可以明确径流水质污染程度,进而对其加以治理防控,使雨水资源化切实可行。这对解决西安市水资源问题,尤其对西安市屋面初期雨水径流重金属的研究至关重要。本研究监测西安市最主要的屋面类型—沥青油毡屋面初期雨水径流重金属指标,旨在研究初期雨水径流重金属的污染程度和变化特征,给出屋面初期雨水径流重金属浓度范围,为后续研究西安市此类屋面初期雨水径流重金属的予以参考价值。
目前,我国关于屋面径流的研究主要集中在水质情况的监测分析,鲜有污染控制方面的报道。1990年,美国提出从源头对径流污染进行削减的低影响开发(low impact development,LID)策略——径流污染源头治理[21-22]。本研究旨在确定西安屋面初期径流并根据初期径流水质、水量特征及雨水斗构造,结合LID技术设计截污装置,研究该截污装置的透水性能、工作状态、截污效果、清洗更换周期及有效过滤区高度,利用该截污装置对屋面径流污染进行源头治理,以期为治理西安市屋面径流污染提供参考,缓解用水紧张问题。其他地区可参考本研究方法和结果设计、开发或选用合适的装置。
全文HTML
-
1)采样地点。本研究采样地点选择在南二环长安大学桥梁结构安全技术国家工程实验室。屋面类型为沥青油毡屋面,该屋面从未清扫维护卫生,汇流面积108 m2。雨水径流通过屋面雨水落水管处采集。
2)采样方法。雨期使用棕色玻璃瓶按照人工时间间隔采样法采集径流水样。采样原则:产流30 min内,每5 min采样1次;30~60 min,每10 min采样1次;60~120 min,每20 min采样1次;120~180 min,每30 min采样1次;此后每1 h采样1次直至径流结束[23]。采样频次随雨强、径流量适当调整,如雨强增大,径流量增加,可加大采样频次。
3)监测方法。雨期降雨特征使用JDZ01-1型数字雨量计进行同步监测,西安市典型高频次的3场降雨的特征见表1。雨停后,将采集的径流水样立即在实验室中检测,采用文献中的方法[24]进行测定,检测指标有SS、COD、TN、NH3-N、TP、浊度、Pb、Zn、Cu、Cd、Ni、Cr。
-
通常,为避免截污网袋堵塞导致路面积水会在截污挂篮上部设置若干溢流孔,且为了便于清洁、更换网袋和取出外框会使截污挂篮长宽尺寸小于雨水口20~100 mm[21-22],借鉴这些已有雨水口截污挂篮实践经验以此设计西安市屋面雨水斗截污装置。西安市屋面一般采用87型DN100铸铁雨水斗,单斗的服务面积约为450~600 m2。87型DN100铸铁雨水斗能够满足西安市不同降雨重现期雨水径流排放,但初算采用87型DN100铸铁雨水斗设计截污装置,其短管设计高度太高,不适用。为了能够在源头截污净化屋面径流,遂在87型DN100铸铁雨水斗短管底部连接DN200长度为1 000 mm的铸铁管,进行截污装置设计。拟定截污装置分上、下2个部分,这2部分总高为800 mm,上部为溢流区,直径180 mm,高200 mm,侧壁开若干溢流孔;下部为过滤区,直径160 mm,高600 mm,紧贴其内部设相同大小的截污网袋,外部为透水的多孔滤网。截污净化装置如图1所示。
截污装置实验材料为排水、过滤、防护、隔离性能很好的土工布。土工布又称土工织物,它是一种透水性合成材料,是由合成纤维通过编织或针刺而成。本实验中土工布的各项性能指标[22, 25]见表2。截污净化实验包括以下3种。
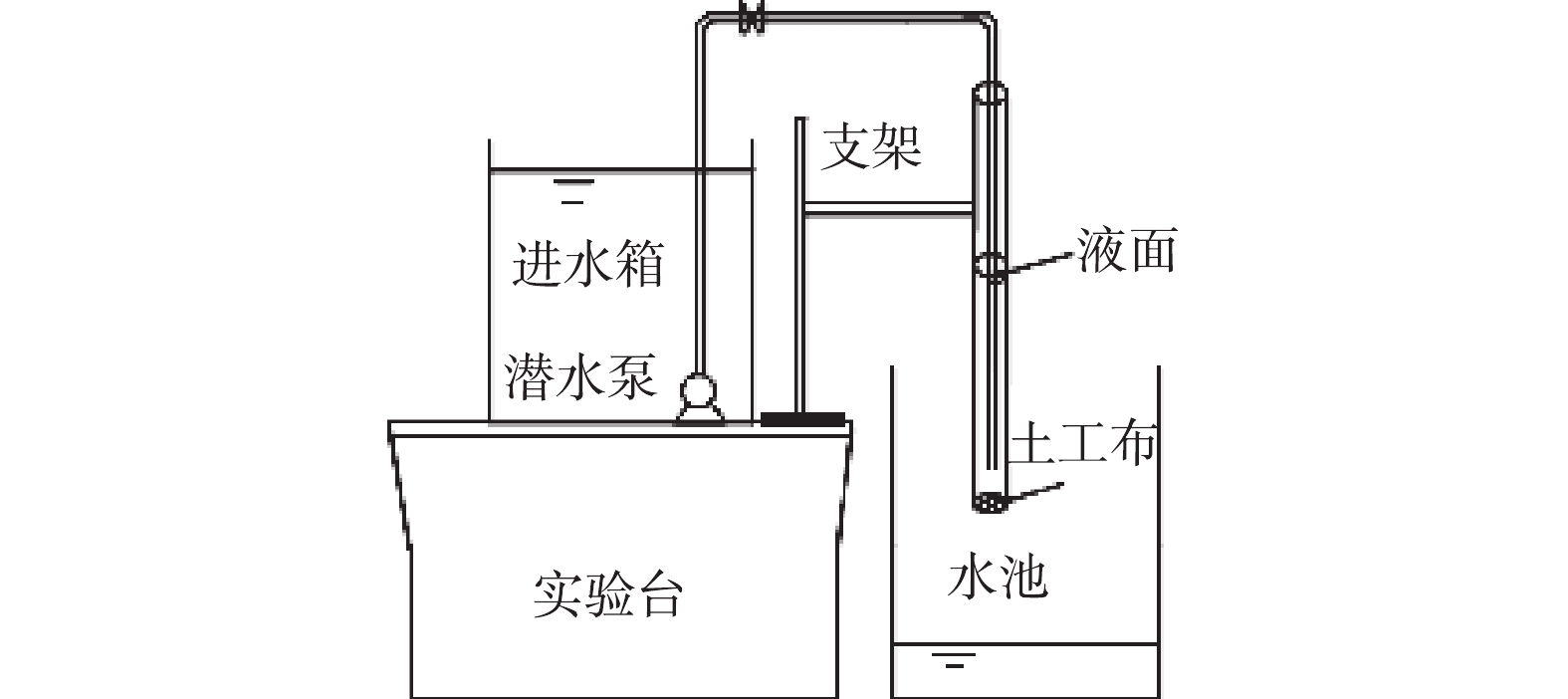
1)透水性能实验。实验装置:采用管底分别为5种不同规格的土工布封闭的有机玻璃管进行透水性能实验,该管长500 mm、内径17 mm且管壁上带有刻度。实验装置如图2所示。 实验方法:实验开始,开启潜水泵使进水箱中的自来水流入有机玻璃管中,通过阀门控制进水流量;分别测试5种不同规格土工布过滤时的过滤压力与过滤速度之间的关系。
2)工作状态实验。实验装置:采用一有机玻璃管进行工作状态实验,该管长500 mm、内径17 mm且管壁上带有刻度。实验装置如图2所示。实验方法:用2 mm的标准土壤分离筛筛分去除晴天屋面收集的沉积物中大的颗粒杂物,选取单位面积质量为350 g·m−2土工布,称取不同质量的筛分后的沉积物与水混合,让其均匀沉积于土工布上;实验开始,开启潜水泵使进水箱中的自来水流入有机玻璃管中,通过阀门控制进水流量,观测在不同的截污量下,土工布过滤压力与过滤速度之间的关系,明确截污装置的工作状态。
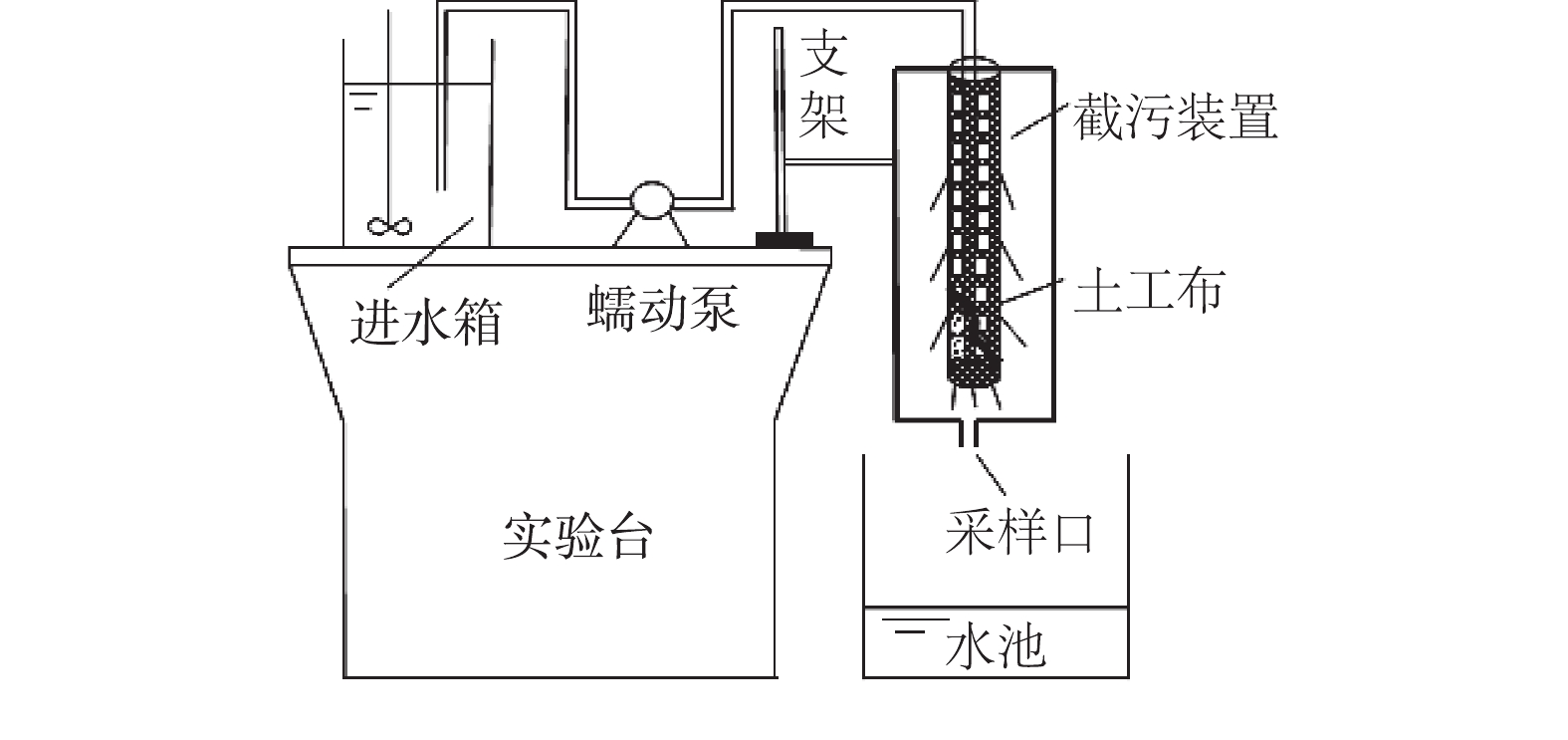
3)截污效果实验。实验装置:用5种不同规格土工布制作直径40 mm、高500 mm的网袋,分别固定在圆柱型金属框内做成截污装置,在装置底部设取样口,外设固定于支架上的集水罩,进水箱中装有配制的屋面径流和机械搅拌装置,实验时启动机械搅拌装置和蠕动泵,将进水箱中的污水引入截污装置中。实验装置如图3所示。实验方法:参考西安市文教区屋面初期雨水水质监测结果,称取适量经2 mm标准土壤分离筛筛分去除较大颗粒物的晴天清扫的屋面沉积物配置径流污水。实验进水水质SS 142.67 mg·L−1、浊度53.07 NTU、TP 0.33 mg·L−1、TN 24.19 mg·L−1、NH3-N 19.84 mg·L−1、COD 180.61 mg·L−1。在确保截污装置不发生溢流的条件下,连续进水6 h,进水流量大小采用蠕动泵进行调节控制,在出水口采样处每30 min取样一次。由于《生活杂用水水质标准》(GB/T 18920-2002)未作对重金属要求且有研究[26-28]发现重金属与颗粒物之间存在相关性,即去除颗粒物的同时也去除了一部分重金属,因此本实验过滤出水只监测SS、COD、TN、NH3-N、TP、浊度浓度。
1.1. 屋面初期雨水径流水质研究
1.2. 截污净化装置
-
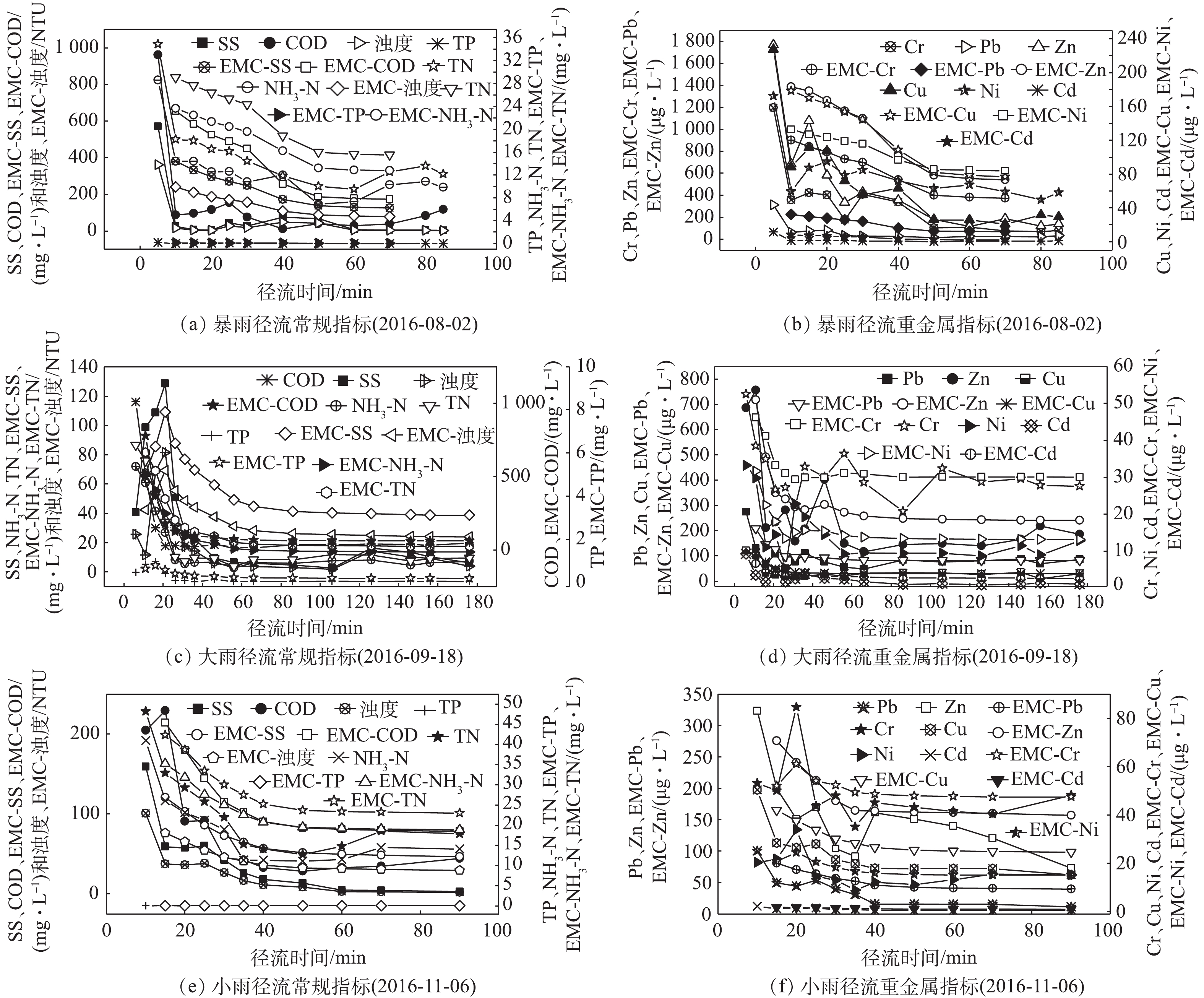
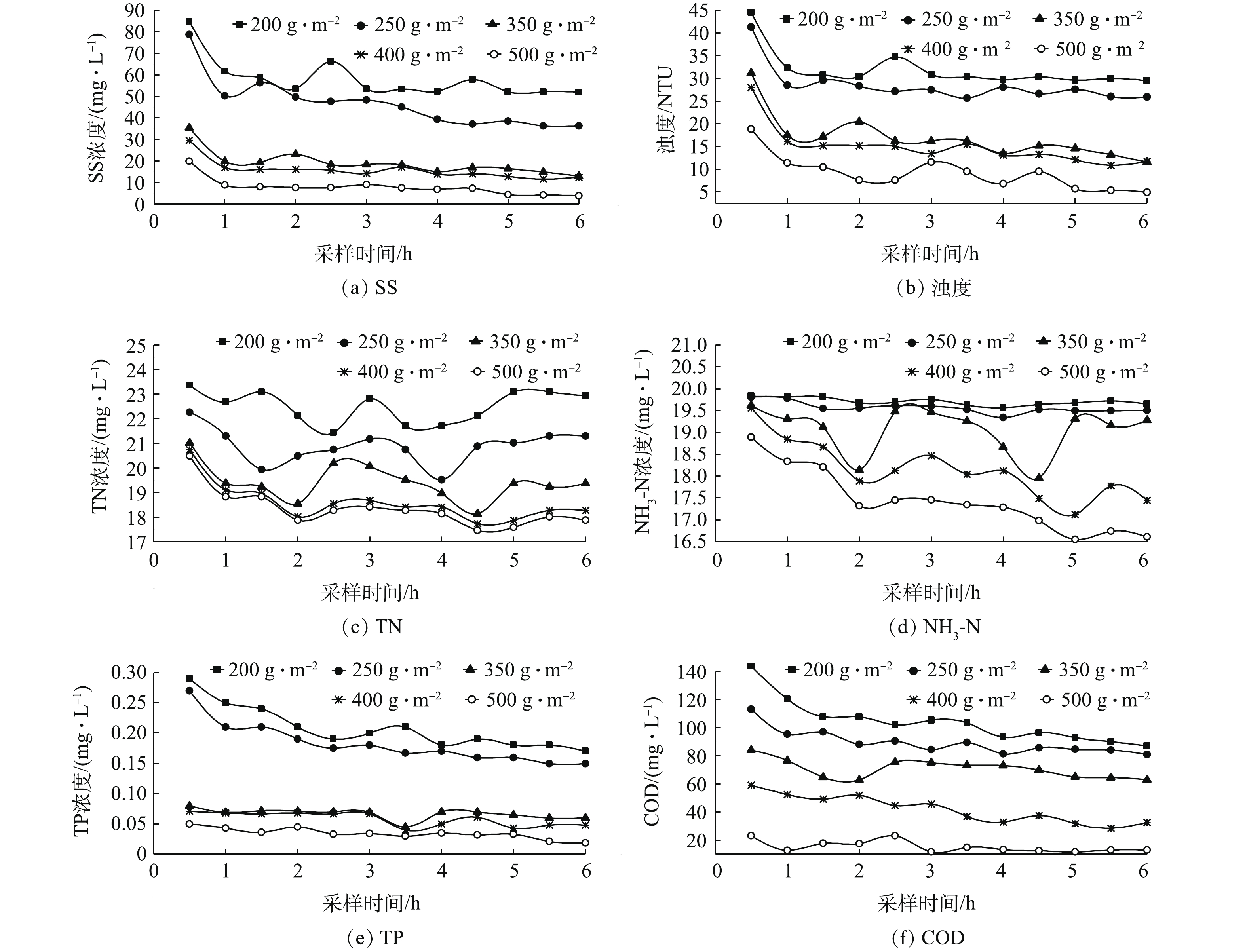
3场典型屋面径流水质随径流时间的变化及初期雨水的径流时间浓度均值(EMC)见图4。由监测结果可见,3场屋面径流污染物SS、COD、浊度、TP、NH3-N、TN、Cr、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni、Cd的浓度均随径流时间发生锯齿状波动并最终趋于稳定。这表明,同一类型的下垫面的径流污染物浓度随径流时间的变化具有相似的变化规律。暴雨,该降雨类型降雨强度大,对屋面冲刷能力强,降雨初期径流污染物浓度大,随着径流时间的延长,污染物浓度急剧减小并在产流30~40 min趋于稳定。大雨,该降雨类型随着降雨强度的增大,其对屋面冲刷能力增强,屋面污染物大多被冲刷掉,径流污染物浓度增大;随着降雨强度的减小,径流污染物浓度显著减小并在产流40~50 min趋于稳定。小雨,该降雨类型全程降雨强度小,水质波动小,径流污染物浓度逐渐下降并在产流40~50 min趋于稳定。本研究结合前人研究[4, 13-14],根据屋面径流污染物浓度随径流时间趋于稳定的时间来确定初期径流。将西安市暴雨次降雨前30~40 min的雨水定义为初期雨水,大雨和小雨次降雨前40~50 min的雨水定义为初期雨水。由监测结果可见,3场屋面初期雨水COD、NH3-N、TN径流时间浓度均值(EMC)均远远高于《地表水环境质量标准》V类标准,其中2016年8月2日降雨前30 min、40 min的屋面径流,重金属Cr、Pb径流时间浓度均值(EMC)也均超出《地表水环境质量标准》V类标准。且3场典型屋面径流中整场径流的污染物平均浓度(EMC)均小于初期雨水中的污染物径流时间浓度均值(EMC),其中暴雨初期雨水中的污染物径流时间浓度均值(EMC)是整场径流平均浓度(EMC)的1.7倍,这均表明屋面初期雨水水质相对较差。根据监测结果,屋面初期雨水SS、COD、浊度、TP、NH3-N、TN浓度分别是54.29~209.68 mg·L−1、79.89~351.085 mg·L−1、34.38~132.76 NTU、0.045~0.255 mg·L−1、17.64~20.12 mg·L−1、21.61~24.5 mg·L−1,重金属Cr、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni、Cd浓度分别是30.57~621.2、44.36~133.12、163.25~935.44、25.98~126.76、14.89~106.25和1.12~4.69 μg·L−1。
-
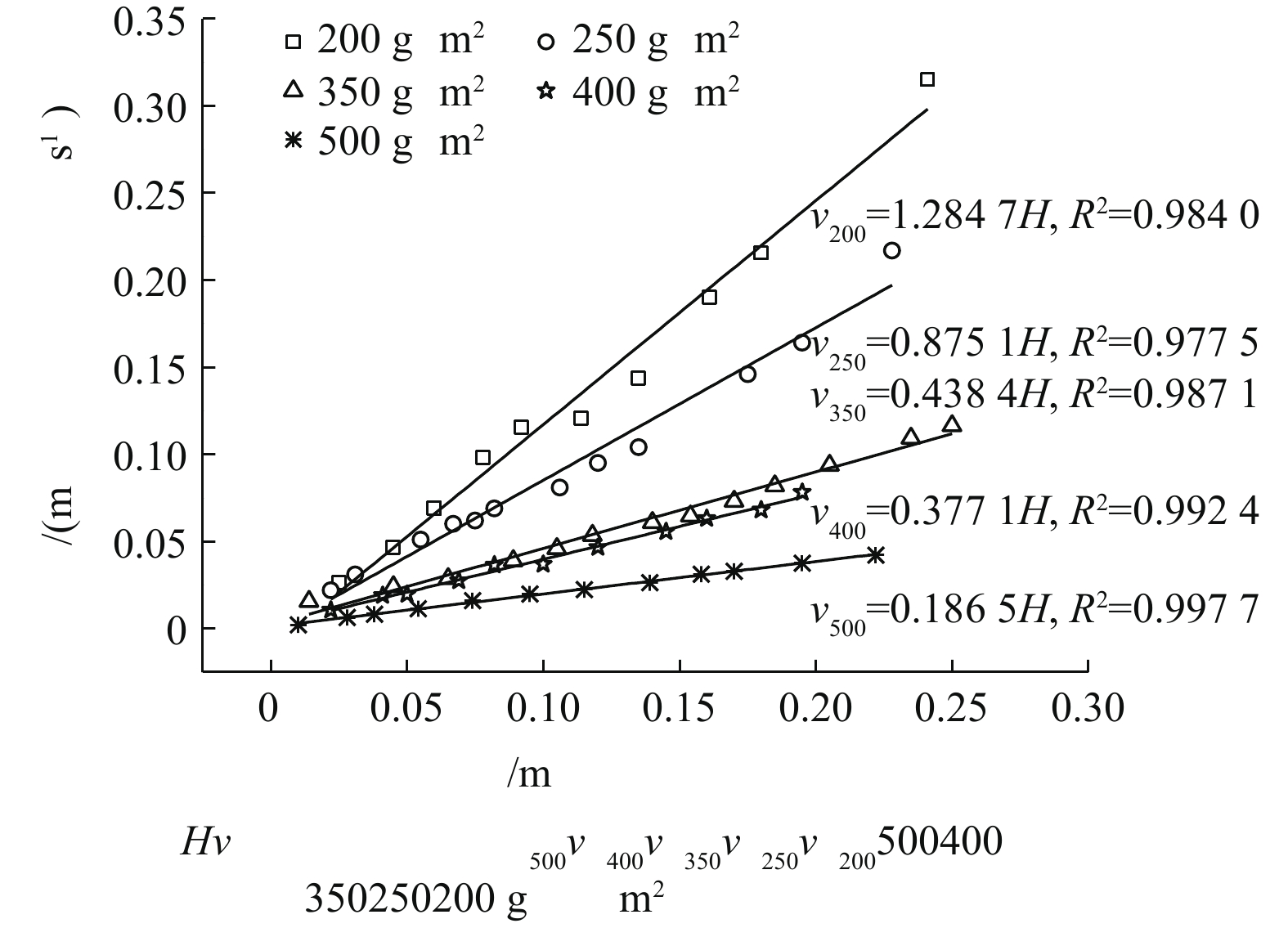
如图5所示,5种不同规格土工布的过滤速度与过滤水头之间均呈线性关系。5种不同规格土工布的过滤速度与过滤水头之间拟合的线性关系见图5。单位面积质量越大的土工布,其透水能力越差,在相同过滤压力下,单位面积质量越大的土工布,其过滤速度越小。
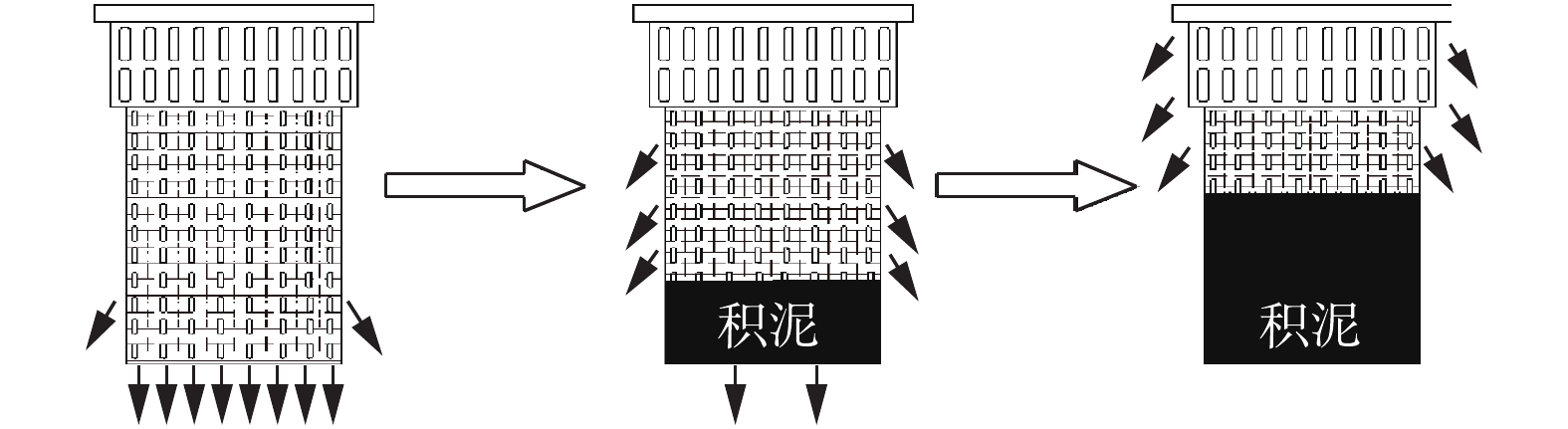
本实验以单位面积质量350 g·m−2土工布为例研究截污装置在不同的截污量下过滤压力与过滤速度之间的关系,从而明确截污装置的工作状态,实验结果见图6。由图6可知,在截污装置工作中,有一定截污量的土工布所需的过滤压力大于清洁土工布的过滤压力。截污量越大,土工布过滤时所需压力越大,但在某一截污量下,土工布过滤速度和过滤压力之间仍基本呈线性关系。截污装置工作状态见图7。在截污装置运行初始,径流主要经过装置底部过滤出水,随着使用时间的延长,底部土工布孔隙逐渐被堵塞,装置内出现一定厚度的淤积层,网袋内积水,其过滤压力增大,径流经装置底面和侧面土工布过滤,出水流入铸铁管中。随着截污装置拦截的污染物越来越多,底部土工布孔隙最终被完全堵塞,其透水能力也完全丧失,装置内淤积层上部的径流经侧面土工布过滤出水。当装置内淤积层达到某一高度,在某一降雨强度下,淤积层上部雨水径流的高度超过截污网袋过滤的高度时,这部分雨水径流则通过溢流孔流入铸铁管中,此时表明截污装置已无截污效果,须清理或更换截污网袋。
-
由图8可知,200、250、350、400、500 g·m−2的土工布制成的截污装置均有一定的截污效果,SS的平均去除率分别为59.22%、67.07%、86.63%、88.90%、94.48%;浊度的平均去除率分别为39.88%、46.32%、68.12%、71.79%、82.83%;TN的平均去除率分别为6.91%、13.64%、19.70%、23.15%、24.19%;NH3-N的平均去除率分别为0.66%、1.37%、3.89%、8.61%、12.13%;TP的平均去除率分别为37.12%、44.65%、79.77%、82.37%、89.62%;COD的平均去除率分别为42.29%、50.36%、60.84%、76.80%、91.53%。由此可见,土工布单位面积质量越大,过滤出水中SS、浊度、TN、NH3-N、TP、COD去除率越高,水质越好。经500 g·m−2土工布过滤出水的浊度满足《生活杂用水水质标准》(GB/T 18920-2002)用于厕所便器冲洗、城市绿化、消防、道路清扫等要求。经350、400和500 g·m−2土工布过滤出水的SS满足《城市污水再生利用景观用水水质》(GB/T 18921-2002)中观赏性景观环境用水的水质标准。所以最终选定350、400和500 g·m−2这3种土工布作为截污过滤材料。由图8可见,5种不同规格的土工布截污装置出水水质均具有波动性,这是因为实验进水采用蠕动泵控制,而水中颗粒物易于沉降,尽管进水箱配置了机械搅拌装置,但仍很难保证进水浓度一直均匀,且实际雨水径流中的颗粒物也易于沉降,这与实际情况相符。
-
1)截污装置溢流区开口率计算。根据《建筑给水排水设计规范》(GB 50015-2010),一般性建筑屋面设计重现期为2~5 a。本研究根据雨水斗设计重现期5 a,GB 50015-2010规定单斗集流面积上限为600 m2;西安市暴雨强度的计算方法[22]见式(1),小流域汇水区径流量的计算方法[29]见式(2),通过计算可知87型铸铁雨水斗单斗5 a一遇的暴雨径流量为15.07 L·s−1。
式中:q为设计暴雨强度,L·(s·hm2)−1;P为设计重现期,a;t为建筑屋面集流时间,min,通常取5 min;Q为设计径流量,L·s−1;
$\psi$ 为径流系数,根据《建筑给水排水设计规范》(GB 50015-2010),屋面$\psi$ 取0.90~1.00,本研究$\psi$ 取1,研究最大径流量时截污装置的设计参数;A为集流面积,hm2。该截污装置溢流部分的开孔率计算方法[22, 30]见式(3)。
式中:Q为孔口出流量,m3·s−1;μ为孔口流量系数,取值0.7;ω为孔口面积,m2;g为重力加速度,9.8 m·s−2;h为大孔口形心上方水深,m,本研究截污装置上部设计高度为0.2 m,开孔形心设计拟定于装置上部中心0.1 m处。
根据截污装置设计参数,计算其上部总面积为0.113 04 m2,由式(2)和式(3)在降雨重现期5 a的条件下计算可知,截污装置溢流区孔口面积为0.015 4 m2,则装置上部应确保开孔率不少于13.7%。为规避下部截污网袋堵塞致使屋面积水,上部截污装置溢流区开孔率越大,溢流效果越好。
2)截污装置过滤高度计算。截污装置工作初始,截污网袋清洁,其透水能力为底面和侧面网袋透水能力之和,如式(5)所示。
式中:Q底、Q侧分别为截污网袋底部和侧面的流量,m3·s−1;b为截污网袋底面直径,m;v为某种规格土工布截污网袋的过滤速度,m·s−1;H为某种规格土工布截污网袋的过滤水头,m。
随着截污装置长时间的工作,其底部网袋堵塞,主要通过侧面网袋过滤出水,即式(4)的积分项。在仅考虑截污装置侧面出水、不产生溢流的情况下,根据式(4)计算各种规格的截污网袋在不同降雨重现期所需要的过滤高度,结果见表3。由表3可知,在降雨重现期为2、3、4和5 a 且不发生溢流的情况下,500 g·m−2土工布截污网袋须至少保证的有效过滤高度分别为479、520、547和568 mm。可通过定期清理或必要时更换截污网袋的方式确保截污装置的有效过滤高度。
2.1. 初期雨水污染水平分析
2.2. 截污装置透水性能
2.3. 截污装置截污效果
2.4. 截污装置开孔率、过滤高度设计
-
1)对西安市3场降雨屋面径流水质随径流时间的变化过程进行分析,可将暴雨次降雨前30~40 min、大雨和小雨次降雨前40~50 min的雨水称为初期雨水。
2)在不发生溢流的情况下,由200、250、350、400和500 g·m−2的土工布制成的截污装置均有一定的截污效果,截污装置可有效减轻屋面初期径流污染负荷,改善径流水质。
3)根据西安市的降雨特征和87型雨水斗使用情况,要使截污装置在5 a一遇的暴雨下避免屋面积水,则截污装置溢流部分开孔面积至少应为0.015 4 m2,即开孔率应不小于13.7%。
4) 500 g·m−2土工布截污网袋在2、3、4和5 a的降雨重现期下有效截污,截污网袋须至少保证的有效过滤区高度分别为479、520、547和568 mm。




 下载:
下载: