-
工业排放的大量挥发性有机物(VOCs)是臭氧和二次有机气溶胶的重要前驱物[1-4]。且VOCs中的绝大多数物质对人体新陈代谢和生理机能有不同的毒害作用,对呼吸系统、中枢神经系统等都会造成不同程度的损伤[5-7]。鉴于VOCs对大气环境和人体健康的诸多危害,急须对其进行有效的治理。现阶段,末端治理技术仍然是VOCs治理的一种有效手段,然而目前的研究大多集中在净化技术方面,如吸附、低温等离子体、热催化氧化和吸收等技术[8-11]。但是,VOCs的有效控制不仅取决于废气净化效率,废气收集效率对VOCs排放控制也具有重要影响。现阶段,大多数VOCs排放企业虽然配有废气净化系统,但存在废气收集效率低的问题[12]。其主要原因在于,VOCs废气收集系统阻力平衡性差导致收集系统各支路及其集气罩收集风量难以达到设计要求[13],无法实现对VOCs废气的有效收集。同时,VOCs排放企业一般有多条生产线,但共用一套废气收集系统。而实际工作中各条生产线并非同时生产,为避免废气收集系统一直保持全负荷状态而导致的电量消耗大、运行成本高等问题,须根据生产线不同的工作模式对收集系统收集风量进行同步调整。因此,研究VOCs废气收集系统实现不同工作模式下的切换,并同时保证不同模式下的系统收集效率具有重要意义。
本研究以现有的平版印刷车间废气收集系统为研究对象,提出不同工作模式下的废气收集系统风量控制方法。针对不同的工作模式,采用支路管道上增设调节阀和集气罩罩口增设三角板的联合措施,并通过数值模拟的方法对废气收集系统进行阻力平衡优化,使得各支路和集气罩罩口风量达到设计风量;保证不同工作模式下收集系统的收集效率,降低收集系统能耗,从而为VOCs废气收集系统的设计与运行提供参考。
全文HTML
-
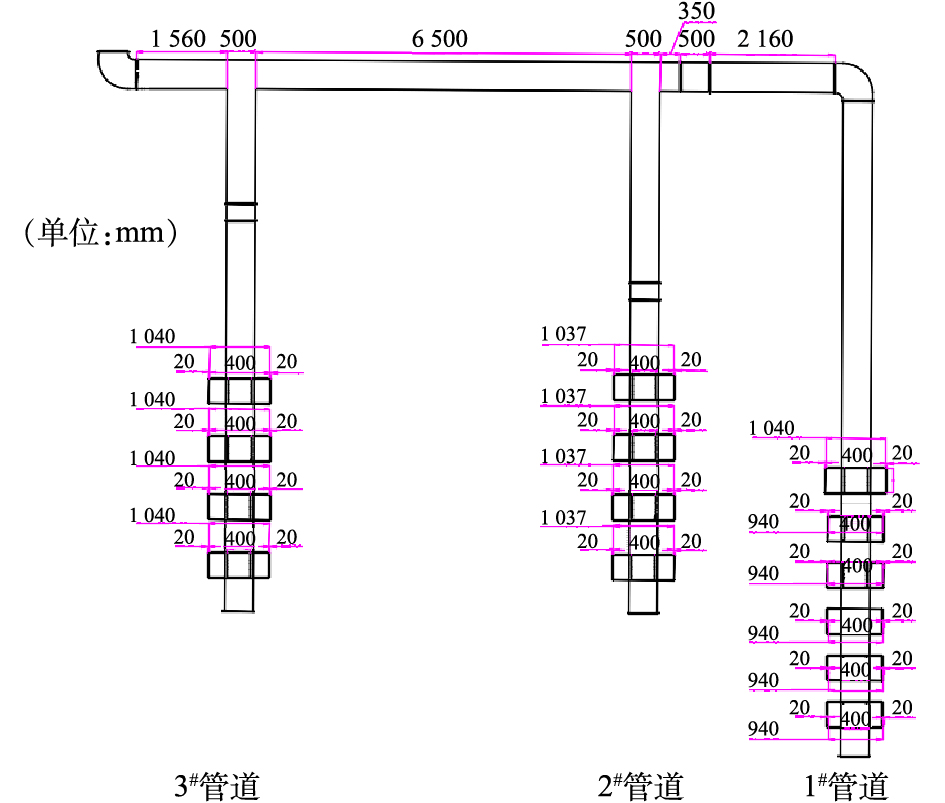
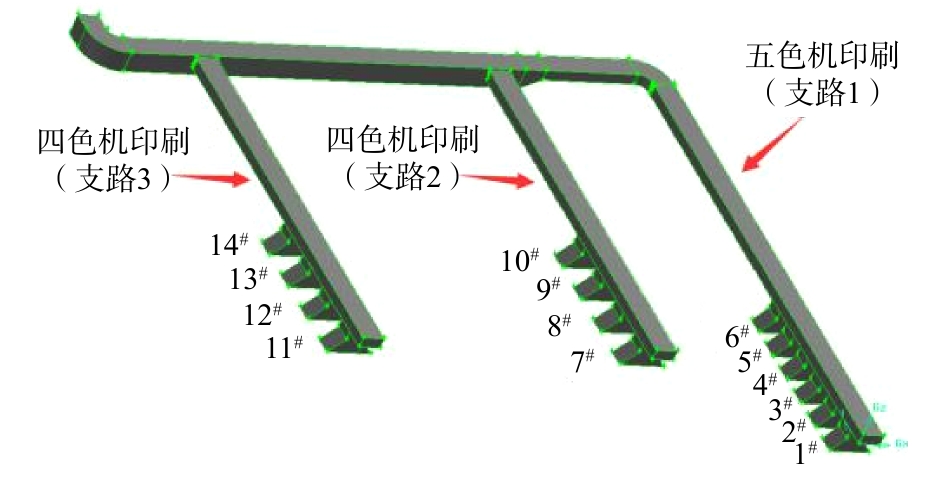
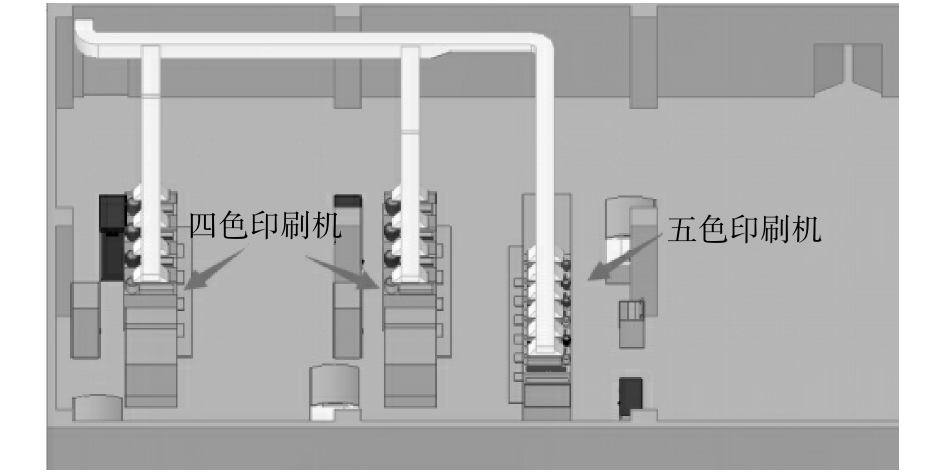
印刷车间共有2条四色印刷机生产线,1条五色印刷机生产线,14个印刷滚轴面。根据相关地方排放标准中所规定的要求[14],需要在印刷机工作时主要污染物控制面增设废气收集装置。由于印刷过程中工人需要沿着印刷线随时进行油墨的添加和设备的调控,无法及时移动集气罩,难以采用密闭罩或半密闭罩集气形式,故采用上部接收罩。现有收集系统已按照相关设计手册[14]的要求,确定了集气罩尺寸和罩口风速参数。全负荷运行下废气收集系统总风量为18 000 m3·h−1,具体的集气罩罩口风速参数和设计参数如表1所示。印刷车间每条生产线独立工作,互不影响,如图1所示。在实际工作过程中,废气收集系统共有7种不同的工作模式。不同工作模式下各支路工作状态模式如表2所示,风量控制参数如表3所示。
-
废气收集系统由3条支路和14个集气罩组成,印刷车间废气收集系统施工图如图2所示。按照废气收集系统实际结构尺寸建立1∶1的几何物理模型,同时利用前处理软件对物理模型的计算区域进行网格划分[15],模拟区域划分的总体网格数为403 289个。废气收集系统三维渲染图见图3。
本研究主要利用数值模拟仿真软件,采用标准κ-ε湍流模型模拟收集系统管道内空气的流动,从而计算出收集系统各支路的风量和阻力损失。收集系统湍流流场计算采用稳态压力求解器,压力与速度耦合采用SIMPLE算法,对流项差分模式采用二阶迎风离散模式,收集系统中的集气罩进口采用压力入口边界条件,总管出口采用压力出口边界条件[16]。
-
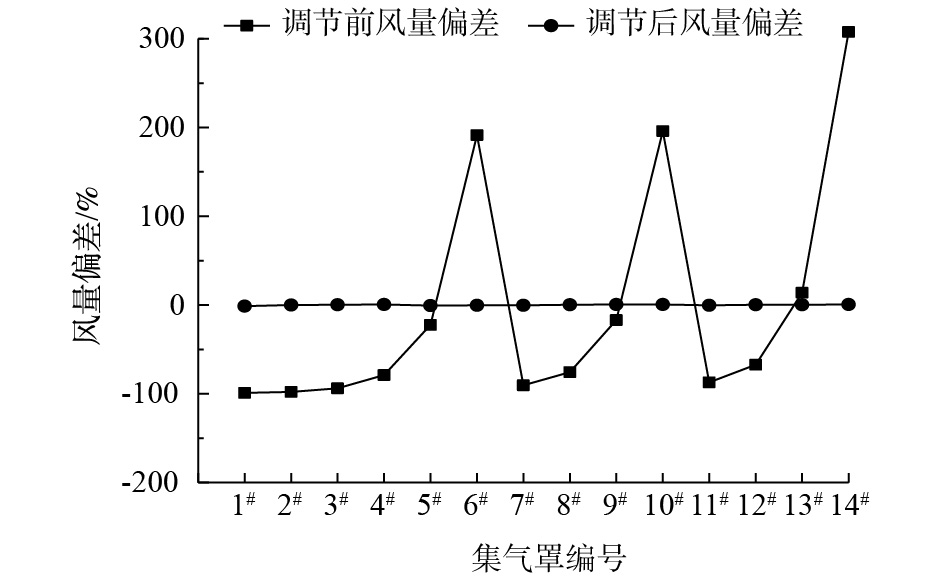
优化前全负荷模式下废气收集系统风量的模拟风量结果表明,支路3的阻力最小,模拟风量大于设计风量,风量偏差为41.81%;支路1的阻力最大,风量偏差为−33.42%;各支路管道的阻力不平衡率最大为23.77%。原设计废气收集系统不能满足管道系统阻力不平衡率不宜超过15%的设计要求[14],须调节各支路的阻力。各支路阻力模拟结果显示,支路3的管道阻力较小,可以采用增加阻力系数的方法,从而减小支路3的风量。
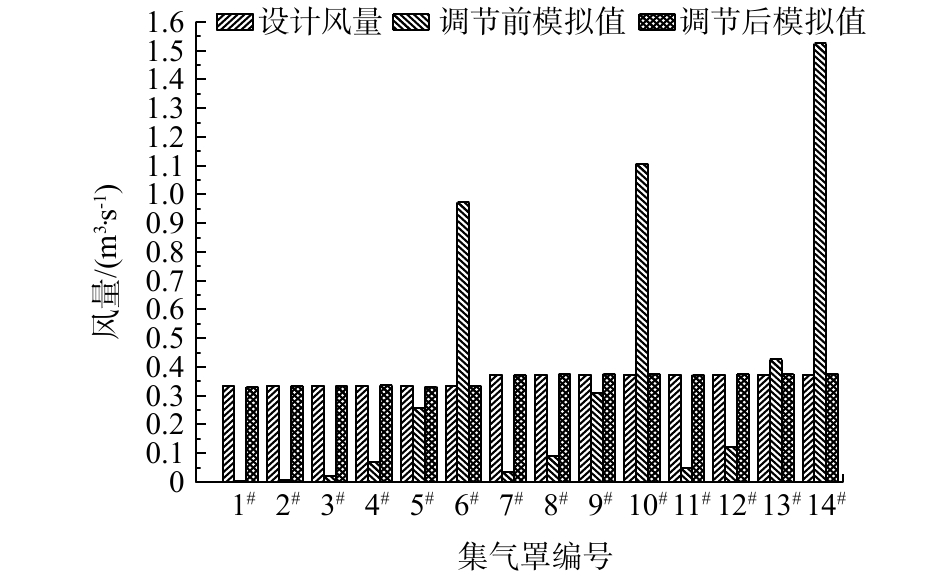
为了验证数值模拟方法的可靠性,对各集气罩进行了现场测试。测试结果表明,各集气罩的风量实测数据与模拟值具有较高的吻合性。此结果直接验证了数值模拟方法的可靠性。系统管道风量的模拟结果见表4,原设计收集系统各集气罩实测风量对比结果如图4所示。
-
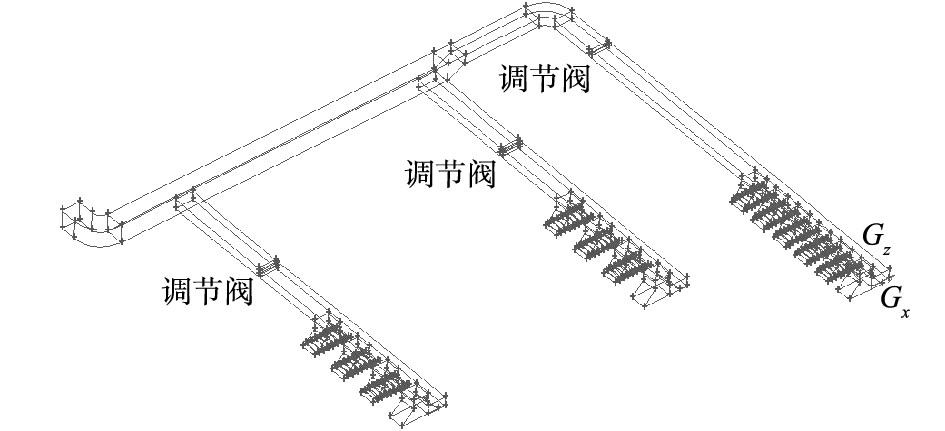
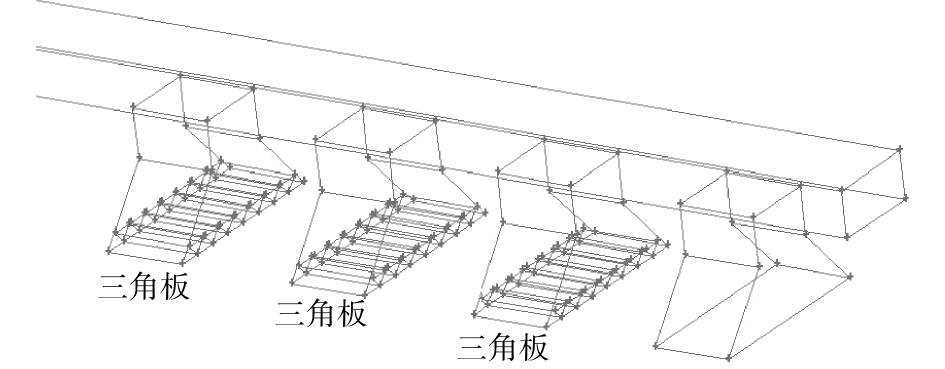
为降低支路风量较大的管道风量,在管道上增设矩形平行式多叶阀,从而增加支路的局部阻力,进而可以改变调节阀开度,使得支路3满足设计风量的要求。同时在支路3集气罩罩口增设三角板,增加集气罩的局部阻力,以达到调节集气罩风量的目的。同理,在支路2和支路1采取相似的措施,使得收集系统风量达到设计风量。经过实验后,全系统调节阀布置图和集气罩优化布置图如图5和图6所示。
支路1集气罩技术优化调节后,收集系统各支路管道风量结果和收集系统管道阻力结果如表5和表6所示。由于增加了支路1的集气罩的局部阻力,支路2和支路3的管道风量存在些许波动,风量波动处于可控范围之内。由表5和表6可知,优化前设计VOCs废气收集系统支路风量偏差最大为41.81%,支路最大阻力不平衡率为23.77%;优化后收集系统支路风量偏差最大为0.26%,支路最大阻力不平衡率为0.43%。由图7和图8可知,各个集气罩基本达到设计风量,全系统已基本达到全平衡负压状态[17]。
2.1. 研究方法
2.2. 原设计全负荷模式下收集系统管道风量的模拟验证
2.3. 全负荷模式下收集系统阻力平衡调整措施及模拟结果分析
-
在全负荷运行时VOCs的废气收集系统阻力平衡优化措施基础上,通过数值模拟的方法模拟各工作模式下收集系统的VOCs废气流动状态。保持负压工作模式下各支路调节阀的位置和各集气罩优化布置参数不变,只须通过调节各个支路管道上调节阀件开度[18],从而控制各支路的运行状态和调节各工作支路阻力的不平衡率,使得系统达到原设计参数要求,实现各工作模式收集系统全平衡负压。
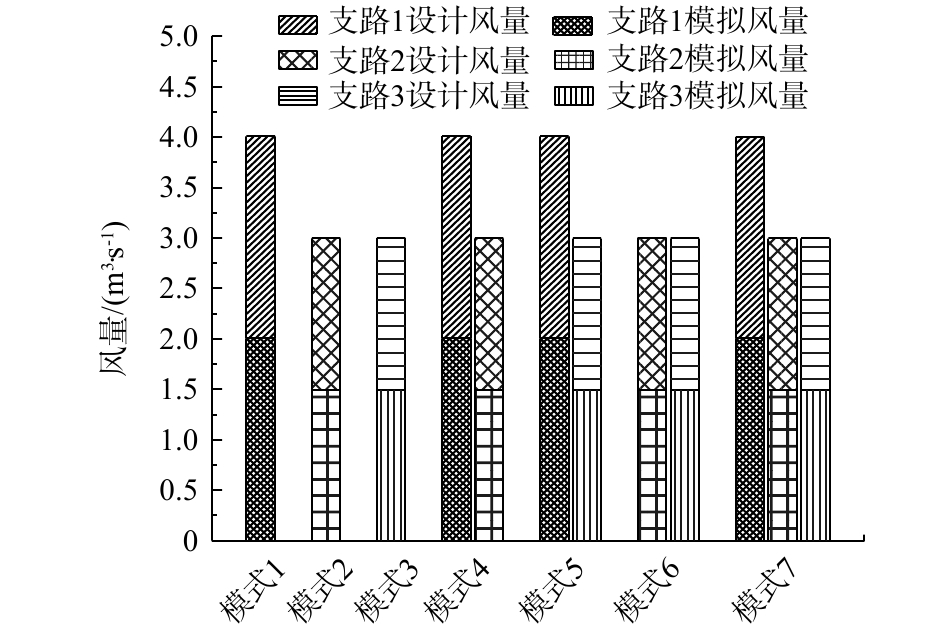
在不同工作模式下,在每条支路布置一个调节阀,通过控制调节阀开度即可实现收集系统多工作模式的切换和调节各工作支路风量的目标。对于工作模式1、2和3而言,系统只有1条支路工作。系统工作支路阀门开度为90°;其余2条支路不工作,其阀门开度均为0°。工作模式1、2和3只须改变收集系统总风量和保持各集气罩优化布置参数不变即可,使收集系统达到设计风量的要求。
而对于工作模式4、5和6而言,系统有2条支路工作。在2条支路阀门全开的状态下,若某条工作支路模拟风量小于设计风量,即说明此支路的阻力较大,则此工作支路无须进行任何阀门开度的调整,其调节阀开度保持为90°。为实现2条工作支路的阻力平衡,只须调整另外1条工作支路的阀门开度,即可让2条支路模拟风量满足设计要求。优化后,各个工作模式收集系统各支路阀门参数如表7所示,收集系统各工作模式阻力参数如表8所示。
-
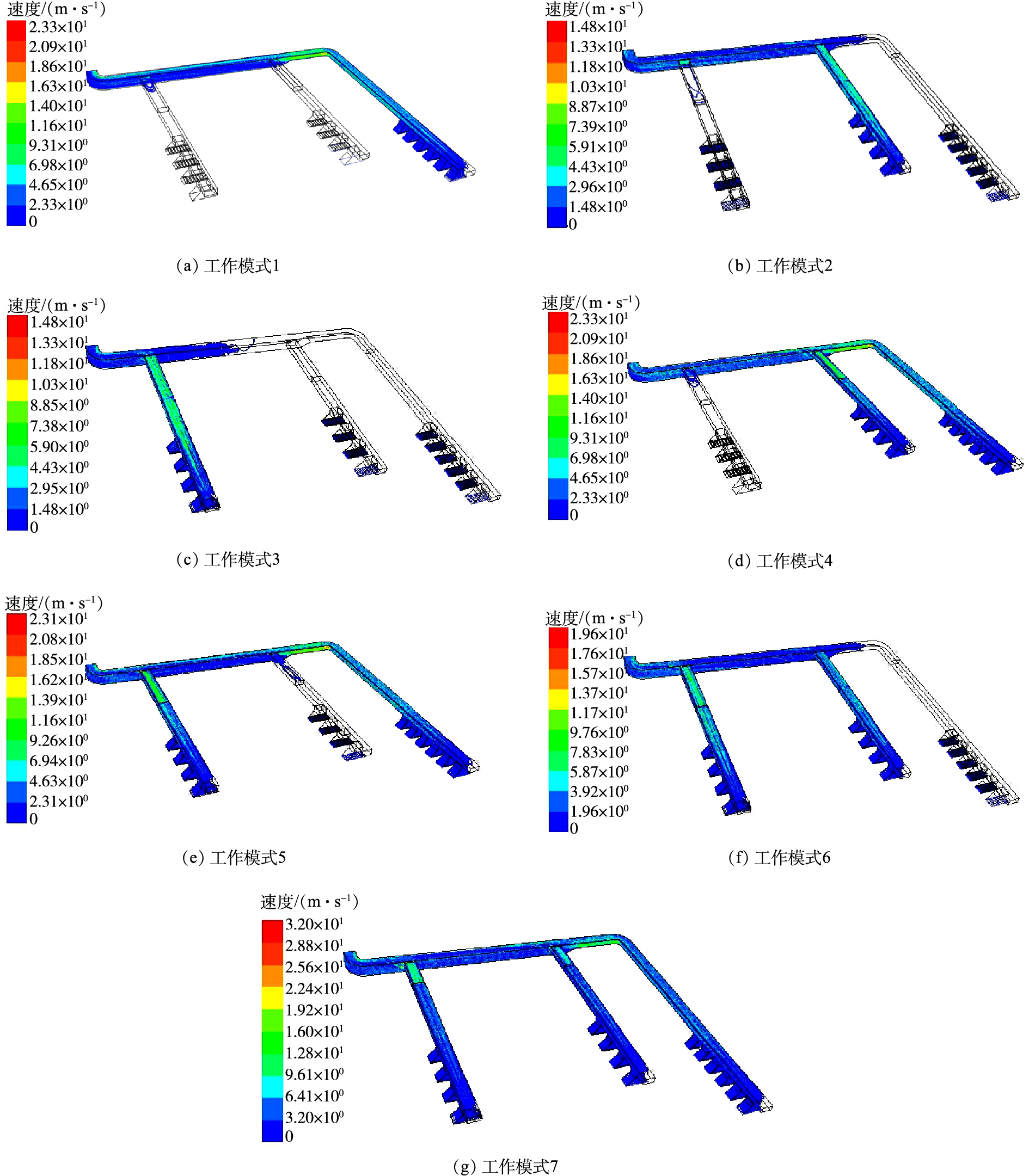
由图9(a)可知,当VOCs废气收集系统只有支路1工作时,支路2和支路3与主管的交接位置气流有稍许的扰动作用,其对支路1的风量有稍许影响。气流扰动作用对工作支路的风量影响较小,但对工作支路的集气罩的风量影响波动较大,工作支路流线如图9(b)和图9(c)所示。相关研究结果显示,风量调节阀的支管处的集气罩风量随压力的波动很大,阀前后压差改变越大,集气罩风量影响越明显[19]。相关研究结果与数值模拟结果相一致。由图9(e)~图9(g)可知,对于工作模式4、5,由于收集系统存在2条工作支路,工作支路与主管接口位置气流扰动较小。但对于工作模式6,因为支路2与主管交接口位置是一个矩形渐变管,所以气流会直接撞击主管管壁,从而造成气流漩涡。其会对2条工作支路的风量造成影响,尤其会对工作支路靠近交接口位置的集气罩风量有较大影响。
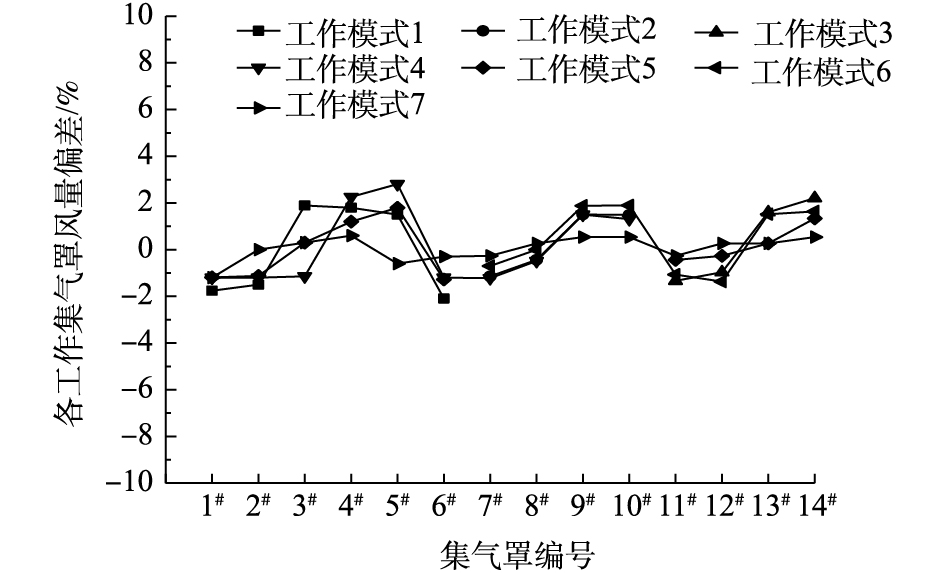
如图10所示,各个工作模式收集系统工作支路的阻力已达到平衡,风量已经达到设计风量的要求,工作支路风量最大偏差为0.261%。由图11可知,在矩形管道支路与主管交接位置处的气流扰动作用对靠近其位置的集气罩风量影响较大,工作模式1的6#集气罩风量偏差为3%,工作模式3的14#集气罩风量偏差为2%左右。随着工作支路数量的增加,各工作支路的集气罩风量偏差趋于平缓,各集气罩风量越接近于设计风量,尤其在工作模式7下,3条支路全部运行时,各集气罩风量偏差为0左右。
3.1. 阻力平衡调节控制
3.2. 模拟结果分析
-
1)系统各个支路和集气罩的实测风量跟数值模拟结果呈现相同的趋势,各支路的风量实测数据与模拟值具有较高的吻合性,从而验证了数值模拟方法的可靠性。
2)在系统支路管道增设调节阀可以有效调整压力的不平衡性。调整后,全负荷模式下收集系统支路风量最大偏差由41.81%降低至0.261%,支路最大阻力不平衡率由23.77%降低至0.43%。在集气罩罩口增设三角板能够有效调节集气罩风量,各个集气罩风量偏差为−0.2%~0.3%,收集系统能够达到全负压平衡状态。
3)采用数值模拟的方法确定各工作模式下各支路达到设计风量时的阀门开度,同时通过调节电机频率,实现了对不同工作模式的切换和各工作支路阻力平衡的调节。此方法能够保证不同工作模式下收集系统各支路阻力平衡,提高系统收集效率,降低系统的能耗,对实现VOCs废气收集系统全自动智能化管控具有重要意义。



 下载:
下载: