-
石油的勘探、储存、运输以及提炼过程中会导致一系列土壤石油污染问题。石油烃进入土壤后,会破坏土壤的颗粒结构,影响其通气性[1],影响土壤中微生物及农作物的生长[2];而且,石油烃进入食物链后会对人体产生不可逆性的致癌、致畸、致突变的三致作用[3]。2014年《全国土壤污染调查公报》[4]表明,13个采油区的494个土壤点位中,石油烃及多环芳烃超标率高达23.6%,治理石油烃污染土壤刻不容缓。
石油烃主要由饱和烃(如正构烷烃,异构烷烃和环烷烃等),以及不饱和烃(如多环芳烃)和少量的含硫氮氧的杂原子化合物等组成[5-7]。国际上将总石油烃(TPHs)分为挥发性石油烃(VPHs)(含碳原子数为C6~C9);以及可萃取性石油烃(EPHs)(含碳原子数为C10~C40[8-9])。我国在2018年发布的《土壤环境质量 建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 36600-2018)[10]中,首次新增了石油烃类(C10~C40)污染物项目,但该标准以及相应的检测方法只能表征土壤石油烃总量,而对石油烃的类别、来源及毒性当量的管控存在很大的空白,从而导致土壤修复标准研究落后于修复技术[11]。因此,在修复过程中,对石油烃中不同来源的组分进行更细致的分段研究是十分必要的。
基于处理污染物范围广、适用性强、修复周期短、去除效率高等优点,热脱附法目前已经受到了土壤修复从业者的密切关注[12-13]。热脱附技术是在通入载气的情况下,通过在特定的设备中进行直接或间接的热交换,将土壤固相中有机污染物加热至足够高的温度,使其从土壤介质转移到气相进行分离,温度通常高于100 ℃低于600 ℃[14]。目前,欧美国家已实现土壤热脱附技术的大规模商业化和工程化;而我国则处于起步阶段,并且目前大部分研究主要集中于多环芳烃(PAHs)、多氯联苯(PCBs)、有机氯农药(OCPs)等污染物[15-17],关于石油污染土壤热脱附的研究较少。
本研究以石油烃为目标污染物,根据含碳量的不同,将可萃取性石油烃分为5个组分进行了分段研究;探讨了热脱附过程中,污染物浓度以及载气含氧量对热脱附效果的影响,为热脱附技术用于修复石油污染场地的实际应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
正构烷烃标液(C10~C40混标,31组分,1 000 mg·L−1溶于正己烷,美国o2si试剂公司);正己烷、丙酮、二氯甲烷和无水硫酸钠均为分析纯(国药集团化学试剂公司);原油从扬州的江苏油田附近获得;活性炭,用于尾气捕获(上海Heatton实验室)。
供试土壤采自河南新乡城郊农田土壤表层(0~20 cm),土壤类型为棕壤,pH为8.34,含水率为3.36%,有机质含量为25.03 g·kg−1,比表面积为17.27 m2·g−1,总孔体积为1.03 cm3·g−1,平均孔径为94.08 nm,其中黏粒(<0.002 mm)占比为8.98%,粉砂(0.02~0.002 mm)占比为35.57%,砂粒(0.02~2 mm)占比为55.45%。土壤采集后,去除碎石及植物残体等杂物,自然风干后,过20目筛(0.85 mm)备用。
将备用土壤用正己烷和二氯甲烷的混合溶液进行萃取,以去除潜在的有机污染物。为获得均匀的石油烃污染土壤,首先配制原油与正己烷体积比为2∶5的原油污染溶液,再将污染溶液引入到装有200 g土壤的1 000 mL圆底烧瓶中,通过加入不同体积的污染溶液,获得不同污染浓度范围的石油烃污染土壤。然后使用定轨摇床振荡器振荡24 h,接下来使用旋转蒸发仪旋蒸2 h去除正己烷溶液。将污染土壤样品储存于密闭容器中,在4 ℃的条件下平衡,2周后进行实验。
-
异位热脱附实验系统如图1所示,主要由载气输送部分、水平管式炉(博蕴通TL1200,最大功率为3.5 kW,最高温度为1 200 ℃,刚玉管内径为73 mm)以及尾气处理部分3部分组成。
首先将平铺在石英舟的污染土壤样品(5 g)放入管式炉的冷却段,然后用氮气流吹扫30 min。以10 ℃·min−1的速率升温达到特定温度,将土壤样品推入等温区域进行不同时长的热脱附,在热脱附期间同时通入300 mL·min−1的载气气流。热脱附处理后,将石英舟推入冷却段中,进行1 h的吹扫冷却后,从管式炉中取出存放于4 ℃的暗室中待分析,实验进行3组平行。
石油烃初始浓度影响实验在热脱附温度300 ℃,载气为氮气,停留时间为20 min,初始浓度为5 000、10 000、20 000、30 000、40 000 mg·kg−1下进行。在载气含氧量影响实验中,氧气体积分数由氧气和氮气进行控制,总流速保持为300 mL·min−1,通过质量流量计控制2种气体的流速,从而控制热脱附载气中的含氧量,载气含氧量为0、6%、9%、12%、15%、18%和21%。
-
称取2.00 g土壤,用滤纸包裹放入50 mL离心管中,加入20 mL二氯甲烷与丙酮的混合溶剂进行超声固液萃取,然后将萃取后样品夹入索式提取器中,离心管提取液倒入烧瓶,继续进行54 ℃水浴萃取16 h。过5~8 cm厚无水硫酸钠层进行固液分离,将过滤后有机溶剂旋转蒸发浓缩至干,定容至1 mL,然后转移至2 mL样品瓶中,供气相色谱(Agilent 7890A)进行EPHs的浓度测定,仪器设置条件参照《土壤和沉积物 石油烃(C10~C40)的测定 气相色谱法》(HJ 1021-2019)[18]。
采用文献中的方法[19],对EPHs浓度进行分段积分的定量检测。将EPHs的柴油段(DRO,C10~C28)分为3段,分别命名为DRO1(C10~C16)、DRO2(C16~C22)、DRO3(C22~C28);将重油段(ORO,C28~C40)分为2段,分别命名为ORO1(C28~C34)和ORO2(C34~C40)。
EPHs各段的浓度计算方法:将总碳原子为i的正构烷烃用nCi表示,将nCi的保留时间用rt(i)表示,并将样品中的石油烃含量间隔[rt(i),rt(i+1)]表示为QTPH(i)。因此,
${Q_{{\rm{EPH(}}{C_{m \sim n}})}} $ 定义为nCm(包括nCm)和nCn(一般不包括nCn;当n=40时,包括nC40)之间的石油烃含量,计算方法见式(1)和式(2)。采用外标法峰面积进行分析,采用校正曲线法进行分析,该方法的回收率为95%~110%。对土壤中石油烃含量进行3组平行测试,所获数据用Q值检验法(置信度95%)剔除异值后,取其平均值。
式中:Re为污染物去除率;C0为污染物初始浓度,mg·kg−1;C为处理后污染物浓度,mg·kg−1。
1.1. 实验原料
1.2. 实验装置及方法
1.3. 分析方法
-
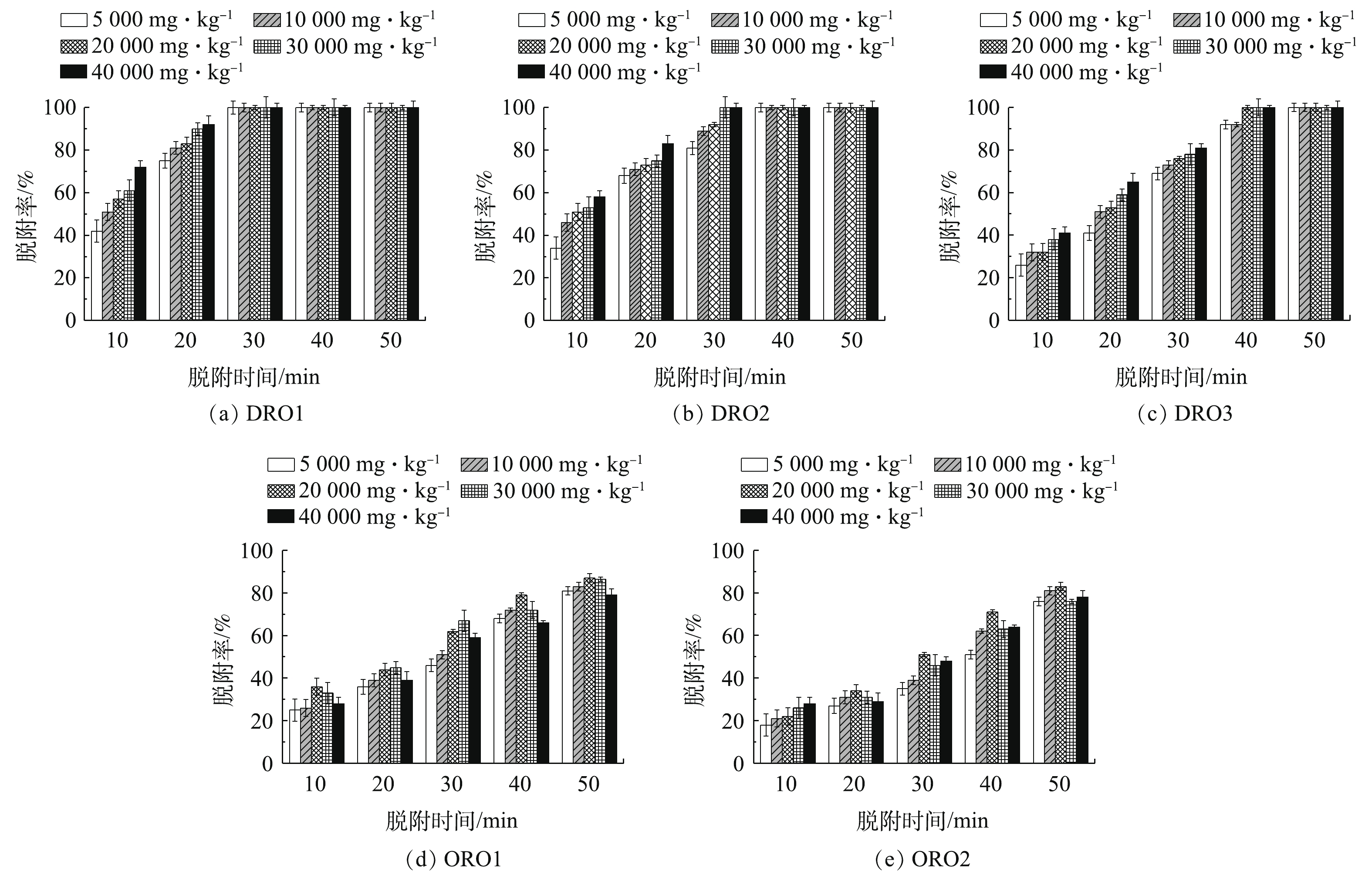
不同污染水平下,土壤中EPHs总去除率的动态变化如图2所示。由图2可知,随着初始浓度的增加,可萃取石油烃脱附效率呈现明显增加的趋势。在初始浓度为5 000~20 000 mg·kg−1时,在20 min内的脱附率均不超过50%;而当初始浓度增加到30 000和40 000 mg·kg−1时,脱附时间为20 min时脱附率可以分别达到58.7%和68.2%。这表明,在热脱附的初期阶段增大污染物浓度可以使得热脱附效率获得很大的提升。但是,随着热脱附时间的增长以及脱附率的不断增加,当热脱附时间为40 min时,不同污染浓度下的热脱附率差别并不明显,效率几乎接近80%左右。这可能与土壤与石油烃的吸附行为以及脱除顺序有密切联系,脱附初期主要去除的是吸附在土壤表面的表层石油烃,脱除焓约等于蒸发焓,并且大多数表面污染物与土壤进行的是物理吸附[20],所以比较容易脱除。并且随着污染物浓度的增大,土壤吸附的石油烃越容易达到饱和,裸露在表层的石油烃也就越多,这也导致了脱附效率的增高。而随着脱附时间增加,大部分表层石油烃脱附完全,土壤中剩余的石油烃分子都被土壤颗粒包裹和吸附[21],较难脱附,所以在脱附后期,增大初始浓度效果并不明显。
不同污染水平下土壤中EPHs剩余含量的动态变化如图3所示。由图3可知,当热脱附时间为10 min时,虽然40 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤脱附率较高,可以达到35.6%,但5 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤脱附率仅为8.36%。但由图3可知,40 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤在经过10 min热脱附处理后的残余浓度却仍然可达26 120.6 mg·kg−1,为5 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤相同处理后剩余浓度的6倍。随着脱附时间的增加,高浓度污染土壤在相同处理条件下石油烃剩余浓度与低浓度污染土壤的剩余浓度相差逐渐减小。在处理时间为30 min时,40 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤与5 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤的残余浓度只相差约3 400 mg·kg−1;当处理时间为40 min和50 min时,40 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤的残余浓度分别为3 261.6 mg·kg−1和407.1 mg·kg−1,分别低于《土壤环境质量 建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 36600-2018)[22]中总石油烃(C10~C40)第一类用地的管制值和筛选值。这表明,异位热脱附技术不仅对石油烃污染浓度较大的土壤有较高的去除效率,而且也可以使修复后的高污染浓度土壤残余浓度达到修复目标值。所以异位热脱附技术处理范围较广,并且在处理高石油烃污染浓度土壤是非常具有潜力的。目前,许多欧美国家已针对高浓度污染土壤进行了异位热脱附技术的应用[23]。
-
不同污染水平下土壤中EPHs不同组分去除率的动态变化如图4所示。由图4(a)~图4(c)可知,DRO组分在50 min内均可达到完全脱附。其中,DRO1组分在30 min即可达到完全脱附,而DRO2和DRO3达到完全脱附的时间较长,分别在40 min和50 min时达到完全脱附。由图4(d)和图4(e)可见,ORO组分在50 min之内不能完全脱附,ORO1的最高效率也只能达到83%左右。可以看出,脱附效率与石油烃组分的含碳量成反比,这是因为含碳量越高的组分,其相对沸点就越高则越难脱附。由图4可知,在30 min前,DOR组分相同时间的脱附率随污染浓度的升高而升高,而ORO组分的脱附率在相同时间下,随着污染物浓度的上升,会出现先增大后减小的趋势。结合图3中脱附率在30 min后随污染物浓度的增大而效率提升不明显的现象,可以发现,这主要是由于30 min后,石油烃中柴油段DRO组分完全脱附,而重油段ORO组分随污染物浓度的增高会降低脱附效率所引起的,其可能的原因是由于ORO组分包含大量的高碳化合物,如沥青质等。这些物质包含许多高环的多环芳烃[24],随着污染浓度的增加,这些高碳链分子也增加。所以当高碳链分子增加到一定限度时,会发生与土壤的吸附作用。其原因可能是以分子间力为主导的物理吸附转变为有化学键主导的化学吸附[25],需要更大的能量进行脱附反应,从而导致脱附率逐渐降低。
-
不同组分的EPHs在250 ℃和400 ℃条件下,在不同氧含量段的去除率如图5所示。如图5(a)所示,在250 ℃时,DRO中3个组分的去除率均随着气氛含氧量的增加而呈现明显的增长趋势。这可能是由于DRO的沸点比ORO低,在有氧情况下会优于ORO蒸发并进行燃烧[25],而当氧气量增加时,DRO的燃烧现象会更剧烈,从而促进热脱附效率的上升。其中,DRO1的去除率增长较为迅速,从含氧量0(N2载气)时的76.2%提升到了含氧量为21%时的95.4%。DRO2和DRO3的增长效率也很明显,去除率分别提升了16.5%和18.9%。相比于DRO组分,ORO组分的去除率变化相对稳定,含氧量对ORO两个组分的提升效率均只有5%左右。同时也可以看出,在低温段(250 ℃)时,通过含氧量的调节均可使DRO组分去除率保持在50%以上,对DRO组分有很好的去除效果,而对于沸点较高的ORO组分去除效率则均低于25%,并且很难通过含氧量的增加来大幅度提高去除率。而如图5(b)所示,在高温段(400 ℃)下,ORO组分的脱附效率相比于250 ℃时显著增加,均高于50%;并且,随着含氧量的增加,脱附效率也有明显的增加,ORO1组分的脱附效率增加了12.4%并且在含氧量为12%时达到最高值,而ORO2在含氧量为15%时达到最高值,相比于0时的脱附效率增加了16.2%。DOR组分在高温热脱附下效率都能达到88%以上,与ORO不相同的是,含氧量对DRO组分的影响不大,脱附效率变化均在2%左右。载气种类的影响主要体现在改变了载气与土壤之间的传质,载气种类的不同改变了传质的扩散系数[26],进而影响脱附效率。可以发现,含氧量只有在一定温度下对特定组分有明显的促进效率,对于在某一温度下脱附效率过高或过低的组分,含氧量的提升均不能产生明显的效率增强作用。
-
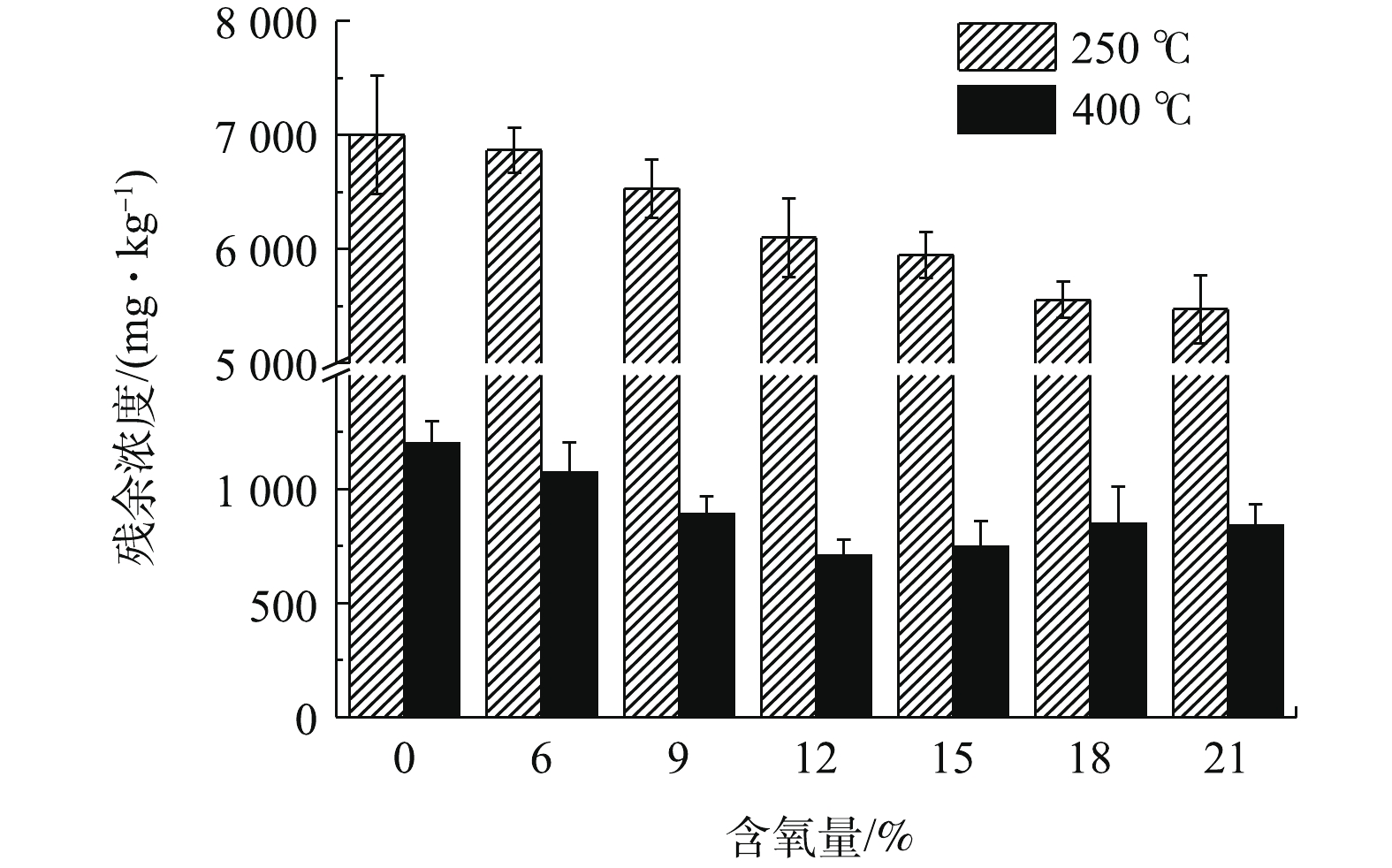
EPHs总量随含氧量增加的变化趋势见图6。如图6所示,相同含氧量条件下,EPHs残留浓度随温度的升高而迅速下降。在相同含氧量的条件下,250 ℃处理下,土壤残余EPHs浓度约为400 ℃条件下的6~8倍;而在相同温度下,250 ℃条件下残余浓度仅降低1 528.8 mg·kg−1,下降比例不到1/5。这也说明在温度和含氧量变化的条件下,温度对残余浓度可以起到决定性作用。同时也可以看出,在低温段,随着含氧量的升高,浓度一直持续降低,而高温段会出现先降低后升高的现象,并且在含氧量为12%时达到最低值。结合图5各个组分脱附效率的变化情况,高低温段脱附效率随含氧量变化不一致的原因可能是,低温段主要受到了DRO脱附行为的影响,而高温段则被ORO脱附行为主导。
土壤中DRO组分与ORO组分分别占EPHs总量的比例如图7所示。如图7(a)所示,在低温段下,ORO组分占比随着气氛含氧量的增加而增加,占比约为60%。DRO3和DRO2组分的占比变化不大,而DRO1组分占比随着气氛含氧量的增加而明显减少。如图7(b)所示,ORO组分占比相比于低温段显著提高,约为80%左右,而随着含氧量的增加,ORO组分占比会先增加后减少。这种现象可能的原因是,在载气氧含量低时,ORO会发生微量热解反应和不完全燃烧反应,随着含氧量的增高,反应程度逐渐加剧。而当载气含氧量过量时,热解所产生的小分子石油烃并不能被及时转移到气相中,从而使得小分子烃重吸附于土壤固相中,造成了DRO占比组分的增高和ORO组分占比的相对减少。
2.1. 不同污染水平中EPHs的脱附情况
2.2. 不同污染水平中EPHs的脱附情况
2.3. 不同含氧量条件下EPHs中不同组分的脱附效率
2.4. 不同含氧量气氛下残余EPHs及其成分分析
-
1)在异位热脱附初期20 min之前,土壤中EPHs去除率随着污染浓度的增加,呈现明显升高的趋势;但在热脱附后期40 min后,不同污染浓度下的热脱附效率差别并不明显。
2)异位热脱附技术对石油烃高污染浓度土壤同样有较高的去除效果,40 000 mg·kg−1污染土壤经过50 min的300 ℃热脱附处理后,残余浓度为407.1 mg·kg−1,低于《土壤环境质量 建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准》(GB 36600-2018)中总石油烃(C10~C40)第一类用地的筛选值。
3)异位热脱附处理下DRO组分几乎可以达到完全脱附,且DOR组分在相同处理下的脱附率随污染浓度的升高而升高;而ORO组分相对于DRO组分脱附率较低且不能达到完全脱附,ORO组分的脱附效率在相同处理下,随着污染物浓度的上升会出现先增大后减小的趋势。
4)在低温段(250 ℃)处理下,由于蒸发燃烧现象,DRO去除率均随着气氛含氧量的增加而呈现明显的增长趋势,而ORO组分去除率较低且受含氧量变化的影响较小;在高温段(400 ℃)处理下,DRO去除率高于88%,但含氧量对DRO组分脱附率几乎没有影响,而ORO去除率上升到50%以上,且ORO1和ORO2分别在12%和15%的含氧量下达到去除率最大值。
5)在低温段处理下,EPHs的总量随着含氧量的升高,浓度一直持续降低且土壤中残留的ORO组分占比随着气氛含氧量的增加而增加;在高温段处理下,EPHs的总量出现先降低后升高的现象,随着含氧量的增加,ORO组分占比会先增加后减少。




 下载:
下载: