-
电芬顿法是芬顿法的分支,基于O2在阴极的二电子还原产生H2O2,并与溶液中添加的Fe2+发生芬顿反应产生强氧化性的羟基自由基·OH,从而氧化降解有机污染物。由于可方便地控制H2O2的连续生成,同时芬顿反应的产物Fe3+在阴极被还原为Fe2+,使Fe2+得以再生利用。相对于普通的芬顿法和其他的电化学方法,该方法所需Fe2+浓度小,高效、低能耗,且易于实现自动化控制[1-2]。
电芬顿法的技术瓶颈在于对氧的二电子还原需要具有高催化活性的阴极材料。碳材料因其化学稳定性高、价格低廉、易于表面修饰等优点而受到青睐。与传统的三维碳材料石墨等相比,由石墨剥离得到的二维材料石墨烯具有超高电导率、超大的比表面积、优异的导热和导电性等优点[3-4],是理想的电极基体材料。另一类纳米碳分支——碳量子点(CQDs),是一种主要由sp2/sp3杂化碳构成的零维碳纳米材料[5],直径通常小于10 nm,在其表面有丰富的官能团和边缘缺陷[6-7]。已有文献将CQDs结合于碳基电极表面用于电化学分析目的,显著提升了电极的电化学响应,显示CQDs具有明显的电化学催化活性[8-10]。另外,CQDs和掺氮碳量子点N-CQDs修饰的rGO复合电极也被用于电池、超级电容器等电能存储与转换材料以及光催化中[11-13]。CQDs零维的小尺寸、丰富的表面以及边缘缺陷等结构特性可能是其催化性能的来源[14]。但目前为止,尚未见到将CQDs修饰电极用于电化学催化降解污染物的报道。
基于零维CQDs和二维石墨烯材料的特性,本研究将合成的零维CQDs与制备的二维材料rGO结合,并载于石墨片(graphite flake,GF)表面制备了CQDs-rGO/GF复合电极,将该复合电极用在电芬顿法中做阴极材料,考察了由溶解氧二电子还原生成过氧化氢的情况。对硝基苯酚(PNP)是有毒性和生物蓄积性的苯酚衍生物[15],是制造药物、染料和农药等的原料,也是常用的皮革防腐剂,其结构稳定,不易生物降解。以PNP为目标污染物,考察了所制备的复合电极电芬顿体系对PNP的降解性能。
全文HTML
-
分别以325目石墨粉(CP,河南义祥新材料有限公司)和葡萄糖(AR,天津科密欧化学试剂有限公司)为原料制备氧化石墨烯以及碳量子点,以石墨片(10 cm×2 cm,青岛宝丰石墨制品有限公司)为基体电极,以对硝基苯酚(AR,上海山浦化工有限公司)为目标污染物,以Nafion PFSA Polymer(质量分数为5.0%,美国杜邦公司)为制备电极的粘合剂,降解过程通入氧气(99.99%,腾龙化工有限公司,西安)。其余所用试剂均为分析纯。使用紫外可见分光光度计(Nicolet Evolution 300,美国尼高力仪器公司,美国)测量体系中过氧化氢和PNP的吸光度;使用荧光分光光度计(F97PRO,上海凌光技术有限公司)测定生成羟基自由基的相对含量,并对合成的电极材料进行表征;通过傅里叶红外光谱仪(IR-21,日本岛津公司)表征电极材料的官能团结构,TEM(JEM-F200,日本电子株式会社)表征材料的形貌结构;双显恒电位仪(DJS-292,上海雷兹新泾仪器有限公司)为电芬顿体系提供电源。
-
氧化石墨烯由改进的Hummer’s法[16]制备。将325目石墨粉分散于浓硫酸中,于冰水浴中缓慢加入高锰酸钾并不断搅拌。加入超纯水和30% H2O2溶液终止反应。过滤洗涤后取沉淀于去离子水中超声,将所得悬浮液离心,收集棕黄色上清液并烘干,得到GO。将GO于去离子水超声至分散均匀后,加入85% N2H4·H2O,水浴24 h,用45 μm滤膜过滤洗涤,将滤渣烘干得黑色部分还原石墨烯rGO。
以葡萄糖为原料用水热法制备碳量子点[17],将葡萄糖水溶液装入反应釜,180 ℃下保温24 h。取出后冷却得浅黄色溶液,用45 μm滤膜过滤后,旋转蒸发得到凝胶状固体CQDs。取一定量CQDs凝胶状固体进行红外光谱和TEM检测。将一定量CQDs溶于水后测定紫外-可见吸收光谱和荧光光谱。
称取一定量的rGO和不同量的CQDs于烧杯中,加入N, N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)和5% Nafion试剂,搅拌并超声至均匀,制成一系列不同CQDs/rGO比例的均匀液体。将均匀液体涂抹在石墨片表面上(涂敷面积5.5 cm×2 cm,双面),于电热恒温干燥箱中160 ℃烘干30 min,即得到rGO/GF或CQDs-rGO/GF电极。
-
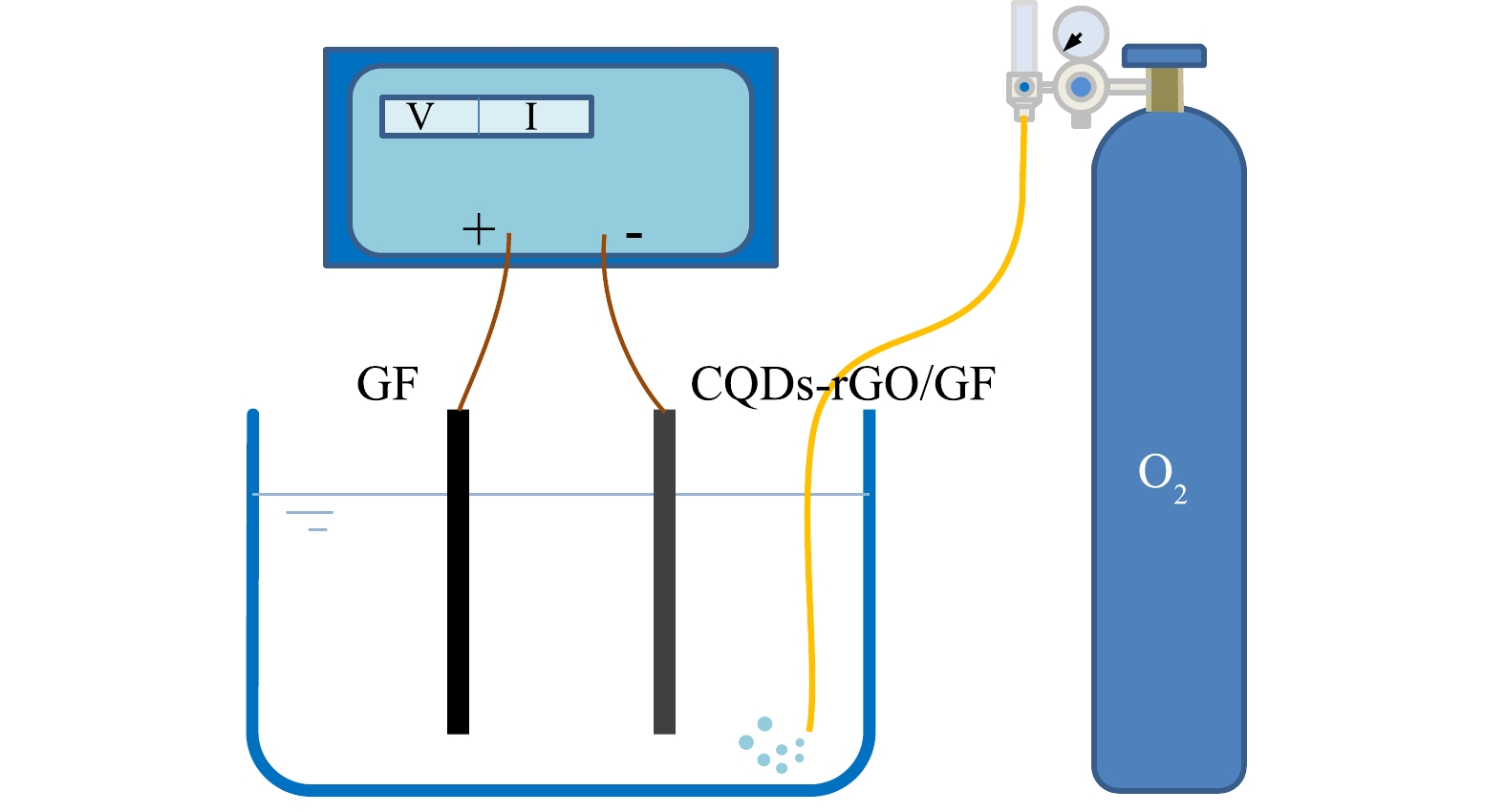
实验装置如图1所示,以双显恒电位仪为控制电源,以制备的电极为阴极,石墨片(100 mm×20 mm×2 mm)为阳极,在200 mL 0.050 mol·L−1的Na2SO4电解质溶液中,用稀H2SO4或NaOH调节pH,持续通入氧气,以恒电流电解方式使溶解氧还原生成过氧化氢。电解过程中每间隔15 min取样,用碘试剂法[18]测定生成的过氧化氢。
在电芬顿体系中加入初始溶度为240 mg·L−1的PNP,通氧条件下进行恒电流电解,每间隔15 min取样,以紫外-可见分光光度法检测PNP的浓度,以重铬酸钾法测定COD,计算其去除率,以邻二氮菲分光光度法测定溶液中Fe2+的浓度。所取样品中用盐酸羟胺还原Fe3+为Fe2+后测定二者的总浓度,并取二者差值为Fe3+浓度。
1.1. 试剂与仪器
1.2. 复合阴极的制备
1.3. 电芬顿体系的建立和降解实验
-
用TEM对CQDs固体的形貌和结构进行了表征。由图2可见,CQDs为直径不大于6 nm的零维点。HRTEM的表征结果表明,CQDs的晶面间距0.21 nm,对应于石墨相的(100)晶面[19-20]。
CQDs水溶液的紫外吸收光谱和荧光光谱如图3所示。其中,紫外吸收光谱显示CQDs在225 nm和280 nm处有强的吸收。由于葡萄糖分子本身没有紫外光吸收,该处吸收应该是石墨相CQDs的共轭C=C跃迁产生的。当激发波长为360 nm时,CQDs在480 nm发射较强的荧光,这是CQDs的显著特征,与文献报道的结果[21-22]一致。
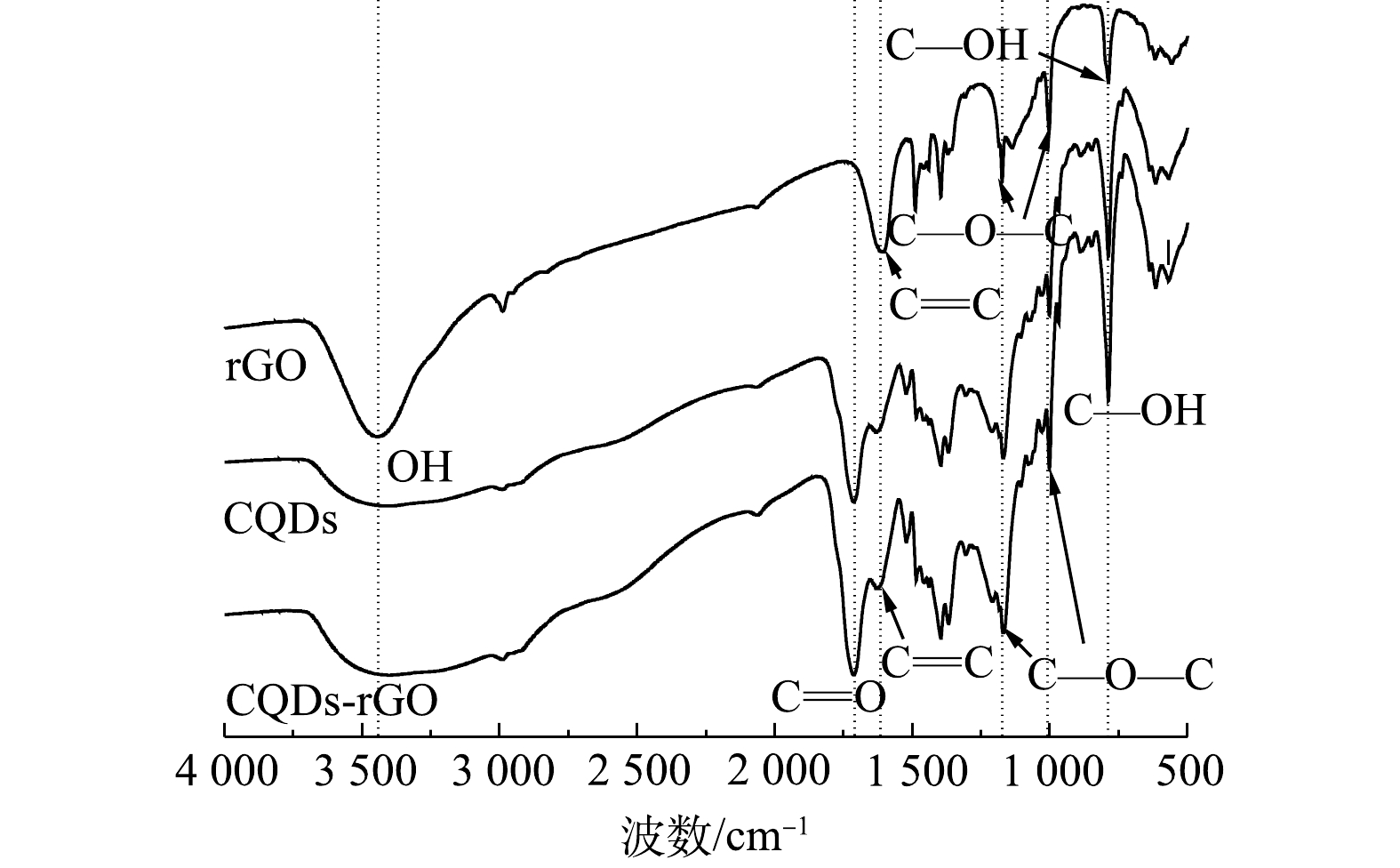
制备的CQDs的红外光谱如图4所示。CQDs在3 454、1 110、1 045 cm−1处的吸收峰分别对应于含氧基团O—H和C—OH的伸缩振动峰[23-24],在1 710 cm−1处有明显的C=O的伸缩振动峰[25],在1 653 cm−1处为C=C的伸缩振动吸收峰[26],在2 900 cm−1处的饱和C—H伸缩振动峰[27],这表明碳量子点结构中含有不饱和C=C、C=O和饱和CH等基团。这与已有研究结果一致,即在水热反应过程中,葡萄糖分子经过脱水、聚合、碳化和钝化过程,最终生成以石墨相C=C为内核,并有亲水的羟基和羰基等基团分布的零维量子点结构[28-29]。由图4还可知,rGO与CQDs有基本一致的红外光谱吸收谱图,只是在rGO中无C=O吸收峰,其他含氧官能团的强度也相对较弱。这表明制备的rGO以剥离的石墨为主要结构,但所制备的为微还原氧化石墨烯,仍然有一定量的含氧官能团[30],这部分含氧官能团有可能为结合CQDs提供位点,有利于CQDs在其表面的结合。复合材料rGO-CQDs的红外光谱显示,其C=O和C—OH吸收峰强度比CQDs明显有所降低,而C=C和C—O—C峰强度则变化不大,表明复合材料中CQDs与rGO可能以羧基和羟基等含氧官能团相结合。
由图5可见,由石墨剥离得到的GO和rGO均呈现卷曲的片状结构,但rGO的卷曲状态有所减弱,这可能是由于rGO的表面含氧官能团减少,其层间作用力减弱的缘故。当存在CQDs时,rGO的片状结构没有受到影响。
-
将制备的CQDs-rGO/GF电极用于电芬顿体系中做阴极,考察体系中电生过氧化氢的性能。分别考察了CQDs和rGO使用量、电解电流和溶液pH对过氧化氢生成量的影响,结果如图6所示。由图6(a)可见,相比于石墨片GF阴极,rGO/GF阴极体系中H2O2的生成量增大,当GF电极上rGO负载量达到3 mg 以上时,其对H2O2生成量的影响已不明显。因此,后续实验均取每片石墨片电极上5 mg rGO的负载量。随着CQDs的加入,CQDs-rGO/GF阴极体系中过氧化氢的生成量相比rGO/GF阴极显著增大。当CQDs的负载量由0 mg增大至50 mg时,过氧化氢的生成量由26.0 mg·L−1升高至48.2 mg·L−1;但当CQDs的负载量进一步增大至70 mg时,过氧化氢的生成量反而降低。这可能是由于过高的负载量会导致CQDs的聚集[11],影响电极的导电性,阻碍电极表面电子传递的结果。因此,CQDs-rGO/GF复合电极的最佳负载条件是50 mg CQDs和5 mg rGO。可见CQDs的存在显著改善了rGO/GF电极的性能,对氧的二电子还原生成过氧化氢的反应有明显的催化效果。
电解电流对过氧化氢生成量的影响结果如图6(b)所示。当控制电流密度分别由0.45 mA·cm−2升至0.91 mA·cm−2的过程中,H2O2生成量先增大后减小,在0.82 mA·cm−2时达到最大。适当提高电解电流会使更多的溶解氧在阴极还原生成过氧化氢,但过高的电解电流会使生成的过氧化氢在电极表面进一步还原,消耗生成的过氧化氢。溶液pH也是影响过氧化氢生成量的重要因素,不同pH下CQDs/rGO/GF阴极体系中过氧化氢的生成量的结果如图6(c)所示。当溶液pH为3.0时,体系中H2O2的产生量最大。随着pH由3.0升高至9.0,体系中H2O2的产生量则由48.2 mg·L−1降低至 31.53 mg·L−1。这是因为O2电化学还原生成H2O2的过程中有氢离子的参与,酸性条件对氧的电化学还原有利。综上所述,生成过氧化氢的最佳条件是:CQDs和rGO的负载量分别为50 mg和5 mg,电流密度为0.82 mA·cm−2,溶液pH为3.0。
-
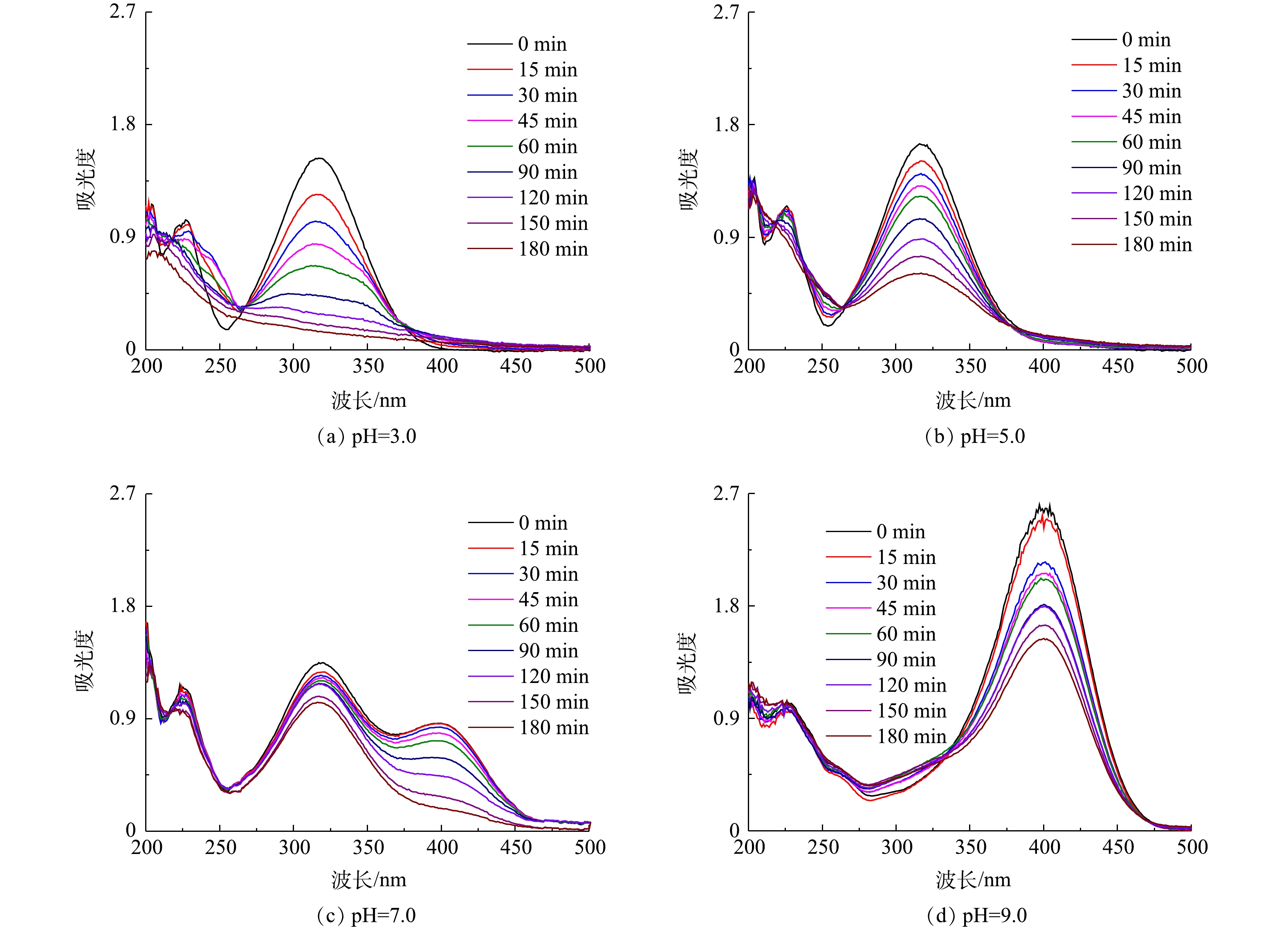
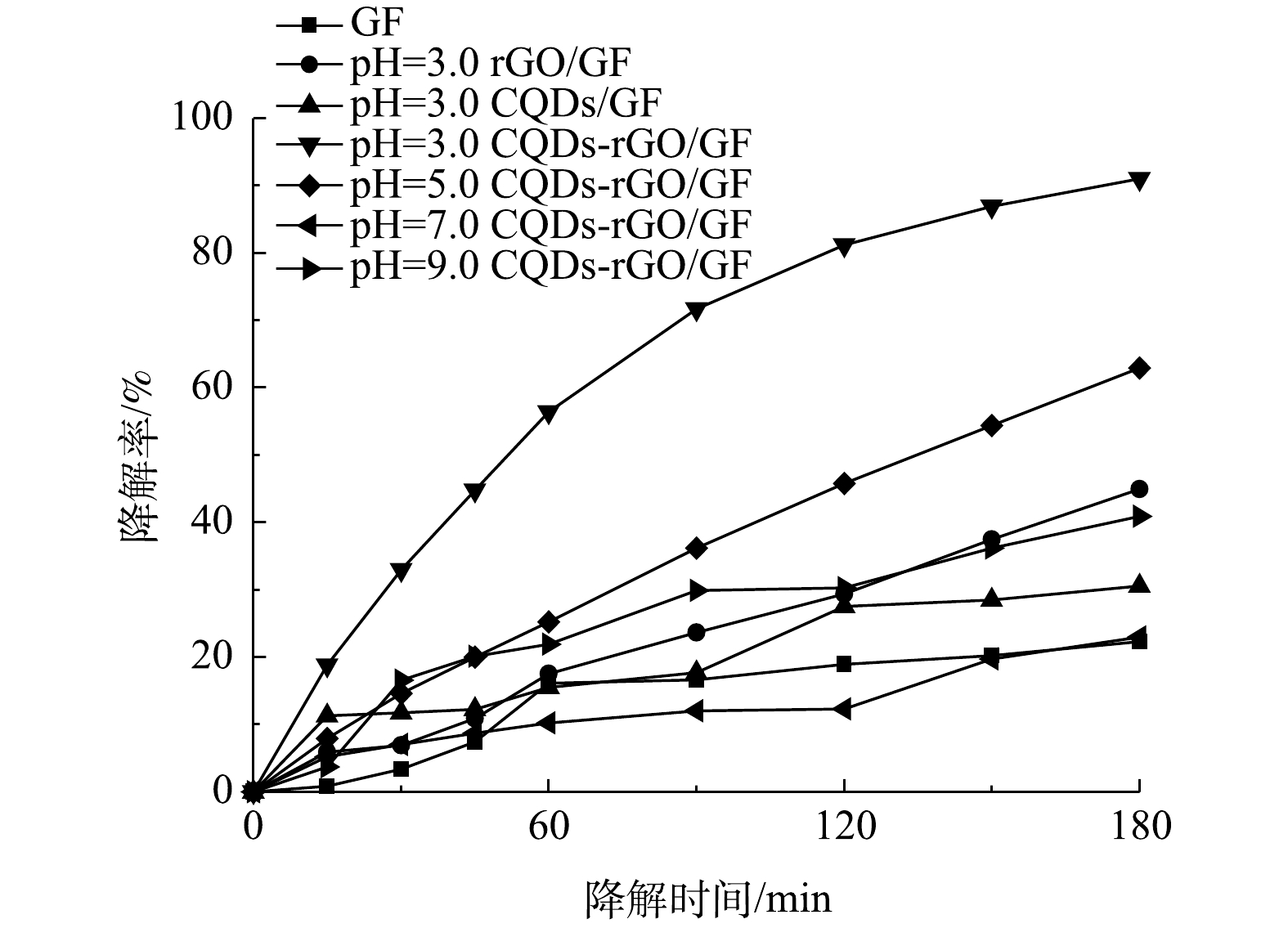
在电解液中加入Fe2+,与生成的H2O2构成芬顿体系,用以降解污染物PNP。首先考察了pH对PNP降解效果的影响。PNP为有机弱酸,pKa为7.14。在pH为7.0附近,其酸式体和碱式体将发生转化,这一结构变化清楚地体现在其紫外可见吸收光谱中。如图7(a)~(d)所示:在pH为3.0~5.0时,PNP以酸式的形式存在,其在226 nm和318 nm处的2个紫外吸收峰,分别对应于其结构中苯环的π-π*跃迁和苯环与助色团(—OH和—NO2)的n→π*跃迁[31-32];当pH增大至9.0时,其酚羟基质子解离,PNP以碱式体形式存在,氧负离子增大了硝基苯的电子密度,使吸收峰红移至401 nm处;在pH为7.0~9.0时,PNP以酸式体和碱式体共存。在降解过程中,通过PNP的紫外可见吸收光谱变化可清楚地看出PNP的降解过程。当pH为3.0时,随着电解时间的延长,PNP在226 nm和318 nm处的特征峰强度均明显降低;在pH为7.0和pH为9.0时,其226 nm处的吸收峰强度降低不明显,仅318 nm和401 nm处的吸收峰强度有所降低。为便于比较,在pH分别为3.0、5.0、7.0时以318 nm处的吸收峰强度为基准,计算电解180 min时PNP的降解率(图8),分别为91.0%、62.9%、23.1%。当pH为9.0时,以401 nm处的吸收峰为基准,计算PNP的降解率为40.9%。此外,比较了没有CQDs负载的rGO/GF电极和没有rGO的CQDs/GF电极在pH为3.0时对PNP的降解率。结果表明,rGO/GF和CQDs/GF电极对PNP的降解率均低于CQDs-rGO/GF电极,分别为45%和31%,表明CQDs的负载促进了PNP在rGO/GF电极上的降解,但CQDs对GF电极本身的作用不明显,CQDs与rGO可能存在协同作用。
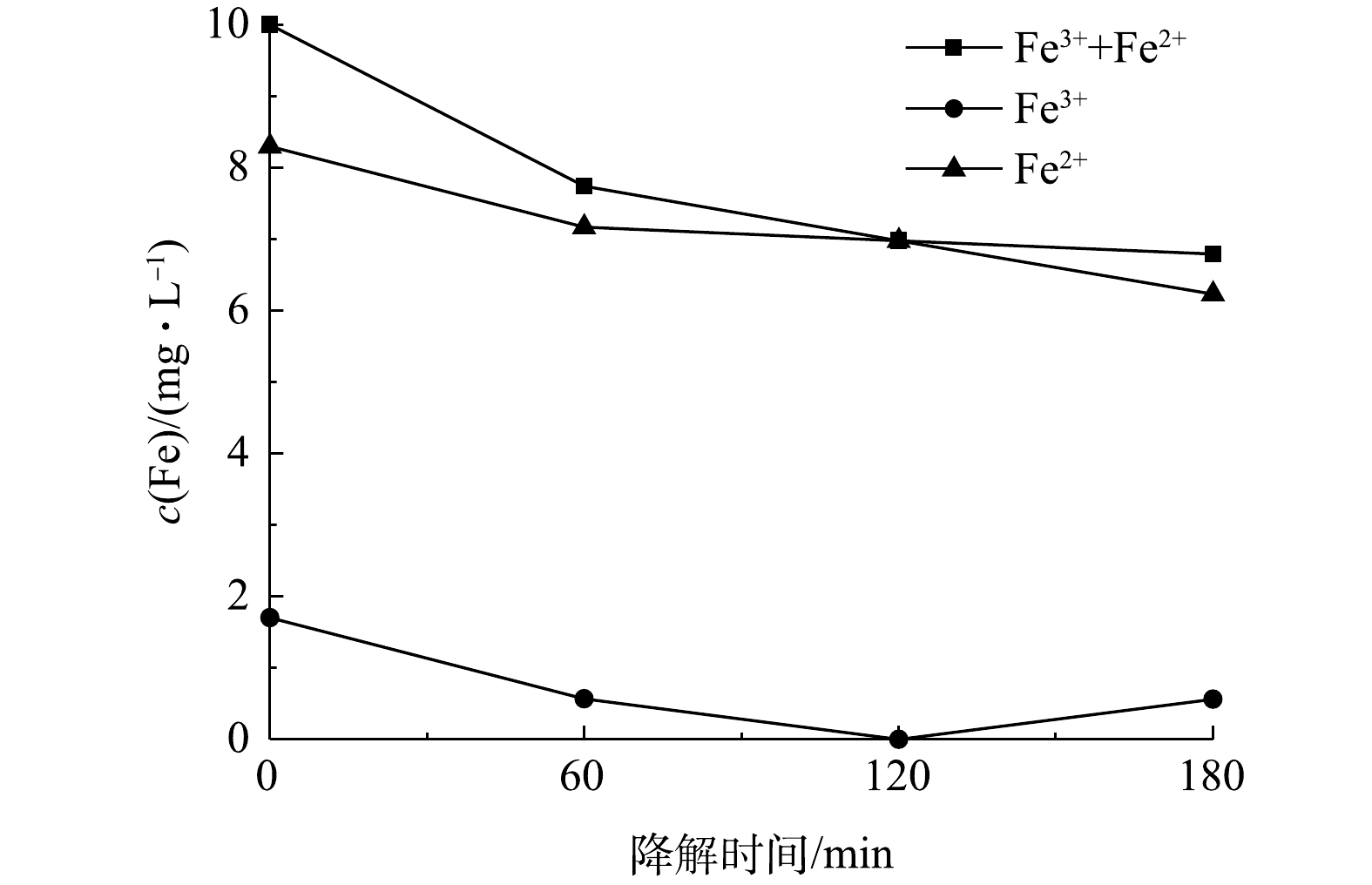
考察了Fe2+浓度对PNP降解效果的影响,结果如图9(a)所示。随着Fe2+浓度从2.5 mg·L−1增大至10 mg·L−1,PNP的降解率由64.2%升高至81.9%;继续增大Fe2+浓度至12.5 mg·L−1时,PNP的降解率反而减小。这是由于过高的Fe2+会与消耗芬顿反应产生的·OH的缘故。因此,后续实验采用的Fe2+浓度均为10 mg·L−1。此外,考察了电解电流对PNP降解率的影响,结果如图9(b)所示。随着电流密度由0.82 mA·cm−2增大至1.36 mA·cm−2,PNP的降解率逐渐提高至91.0%;继续提高电流,降解率反而降低。与生成H2O2的最佳电流密度0.82 mA·cm−2相比,电芬顿体系中PNP降解的最佳电流密度高很多。在电芬顿体系中,加入的Fe2+不断与生成的H2O2反应生成Fe3+,Fe3+会在阴极还原使Fe2+再生,形成Fe3+-Fe2+循环,保证了在较低的Fe2+浓度条件下的芬顿反应。同时,Fe3+的电化学还原也使电解回路中的电流增大,造成电芬顿体系中PNP降解的最佳电流密度高于没有Fe2+存在时过氧化氢生成的最佳电流。这一点可以从降解过程中溶液Fe2+和Fe3+浓度的变化(图10)得到证实。由图10可见,在整个降解过程中,Fe3+浓度维持在低于2 mg·L−1的水平,铁盐主要以Fe2+的形式存在,表明芬顿反应消耗的Fe2+可通过Fe3+在阴极的还原得到及时补充。由图10还可看到,随着电解时间的延长,溶液中的总铁浓度在120 min内稍有降低,之后则保持不变,这应该是少量铁盐吸附在电极表面的结果。但该浓度变化较小,对整个体系的性能影响不大。
为进一步验证该体系中·OH对降解PNP的作用,在溶液中加入·OH清除剂异丙醇,考察了异丙醇存在时PNP的降解情况。由于异丙醇与·OH的反应速率很快,二者的反应会造成以·OH为主要活性物种的电芬顿体系中污染物降解率的降低。如图9(c)所示,加入异丙醇后,PNP的降解明显受到抑制,180 min降解率由91.0% 降低至56.0%,这间接证实了·OH是该体系降解PNP的主要活性物种。
-
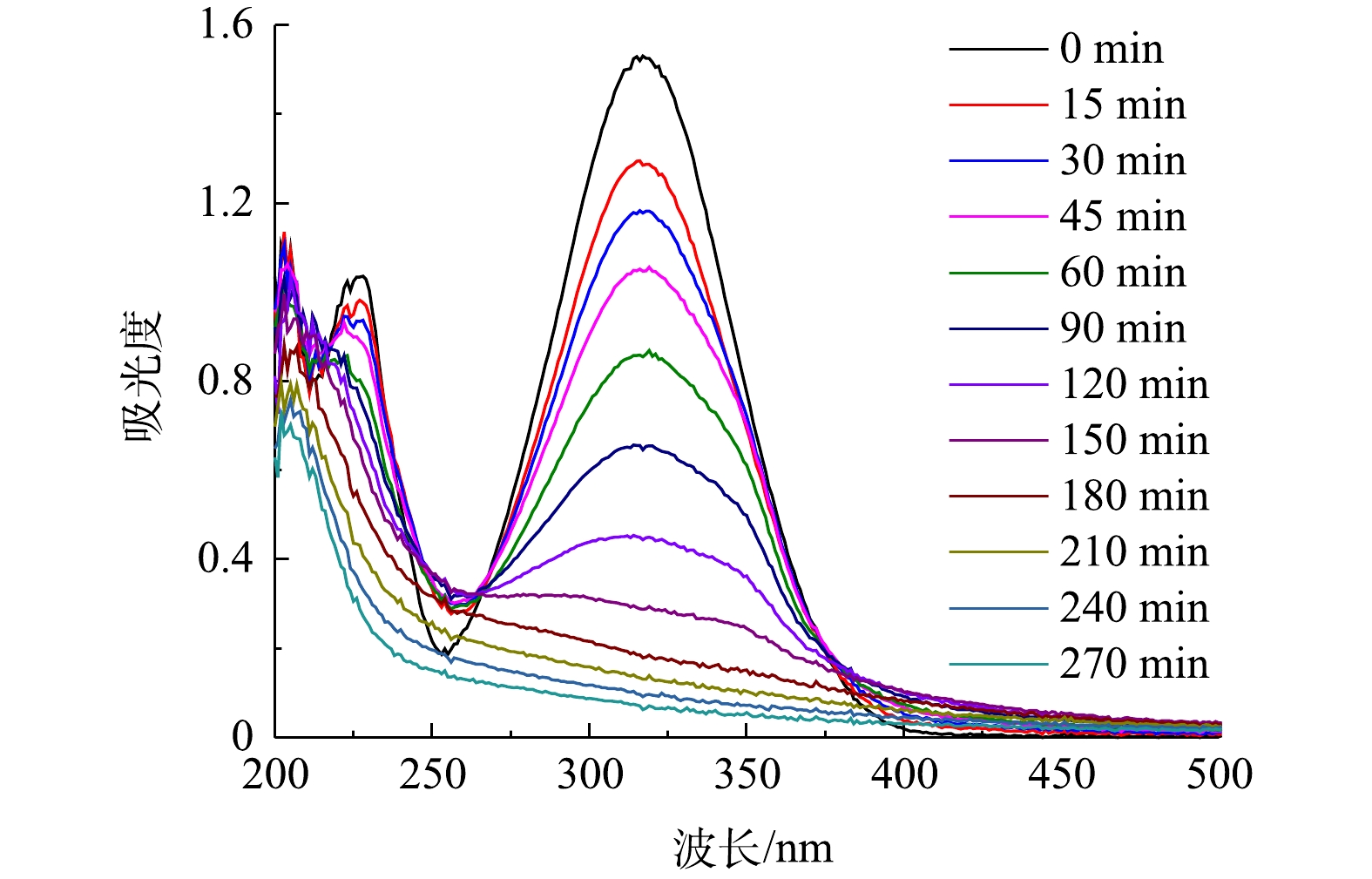
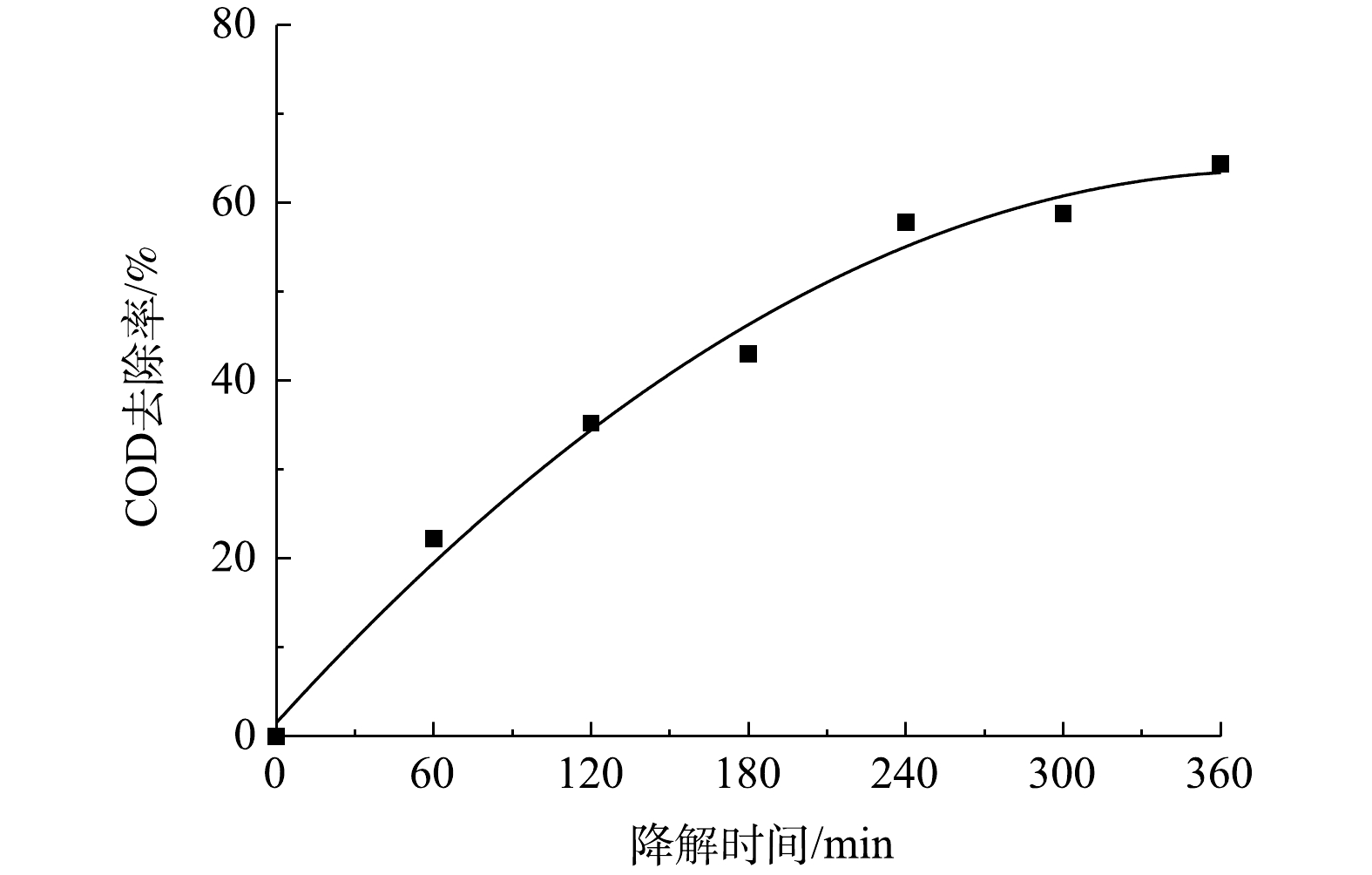
由以上实验结果和讨论可见,在CQDs-rGO/GF阴极电芬顿体系中,CQDs通过促进氧电化学还原生成过氧化氢而强化了羟基自由基的生成,该体系对PNP的降解是羟基自由基作用的结果。PNP的降解过程可由其紫外可见吸收光谱的变化清晰地体现。在最佳降解条件下,PNP的紫外可见吸收光谱变化如图11所示。降解过程中PNP的π→π*和n→π*跃迁吸收峰强度均降低直至消失,表明其共轭大π结构被破坏。但是,245~260 nm内的吸光度在电解150 min内逐渐增加,150 min至360 min时又降低至接近零。PNP本身在400~500 nm的可见光波长范围内没有吸收峰,表现为PNP溶液为无色。随着降解的进行,该范围内的吸光度值发生先增大后减小的变化,相应地观察到溶液颜色的改变。在0~150 min时,随着400~500 nm处吸光度的增大,溶液的颜色也由无色逐渐变为浅黄色,再进一步加深变为红棕色。在150~270 min时,这个波长范围内的吸光度开始减小直至为零,表现为溶液的红棕色逐渐变浅,最后转化为无色。这些现象表明,PNP在降解过程中有中间产物的生成。测定了PNP降解过程中COD的变化,如图12所示,结果显示COD去除率随降解时间的延长而逐渐增大,爱降解360 min时PNP溶液中的COD去除率达到64.3%,表明大部分的PNP被矿化分解,其余则被降解为非共轭的小分子有机物,在紫外谱图中表现为200~300 nm波长内尚有较弱的吸收。黄卫红等[33]利用GC/MS技术对PNP降解的中间产物进行了分析,认为主要中间产物有4-硝基儿茶酚、对苯二酚、对苯醌、丁二醇、丁酸和草酸。其中·OH攻击苯环上电子密度较大的碳原子,使PNP分子羟基化,生成4-硝基儿茶酚,进一步在羟基自由基的攻击下硝基脱离苯环,转化成对苯二酚,呈现棕黄色溶液。对苯二酚进而生成对苯醌的红棕色溶液。在羟基自由基作用下对苯醌开环生成丁二醇、丁酸、草酸等小分子有机酸,部分有机酸进一步降解为CO2和H2O,实现了PNP的矿化。这与PNP降解过程中其紫外可见光谱所呈现的变化结果是一致的,可见,在本文的电芬顿体系中,在电生·OH的作用下,PNP也经历了类似的降解过程,该降解过程可简单地用紫外可见吸收光谱进行表征。
2.1. CQDs和rGO的表征
2.2. CQDs-rGO/GF阴极电生过氧化氢的性能
2.3. CQDs/rGO/GF阴极电芬顿体系对PNP的降解
2.4. PNP可能的降解机理
-
1)将制备的粒径约5 nm的石墨相结构的CQDs,与二维材料石墨烯rGO结合得到了CQDs-rGO/GF复合电极,CQDs明显增强了电极的催化性能,该电极做阴极时O2的电化学还原产物H2O2的生成量是rGO/GF阴极的1.9倍,是空白GF阴极的2.4倍。
2)在Fe2+存在时的电芬顿体系对PNP有较好的降解效果,在pH为3.0、电流密度为1.36 mA·cm−2、Fe2+浓度为10 mg·L−1降解180 min时PNP的降解率达到91.0%,且羟基自由基是PNP降解过程中的主要活性物种。
3)在该电芬顿体系中360 min时PNP的COD去除率为64.3%。电解过程中PNP紫外可见吸收光谱的变化清晰地呈现了PNP的降解过程:PNP的共轭结构首先被破坏,生成中间产物,最终大部分中间产物被进一步降解为小分子有机物,进而实现了对大部分PNP的矿化和去除。





 下载:
下载: