-
混凝是一种常见的水处理工艺,混凝剂可使水中胶体粒子和微小悬浮物发生聚集,从而通过沉淀作用将其分离,进而达到净化水的目的[1]。铝盐混凝剂是一种高效无机混凝剂,不同类别铝盐在水解时形态差异较大,按照与Ferron试剂的反应速度不同,其可分为Ala、Alb和Alc[2],3种形态的铝分子质量和稳定性都逐步增强[3]。一般来讲,Ala形态只具有压缩双电层性能;Alb形态具有最强的电中和性能;而Alc形态由于其颗粒粒度已达到一定的尺寸,从而具有较高的吸附架桥性能[4-5]。
虽然铝系混凝剂对于水中污染物具有显著的去除作用,但水体中的残余铝对人体健康和输水过程具有显著影响。有研究表明,铝的毒性不仅与总铝浓度有关,还与铝的存在形态密切相关[6]。溶解态铝对人体造成的危害较大,其会通过饮食摄入的方式进入人体并积累残留,从而产生一定慢性中毒,如引发学习记忆障碍、骨软化、抑制免疫功能、睾丸毒性病理改变以及胚胎发育致畸形等[7-9]。溶解态余铝的产生是由于铝盐混凝剂在净化水过程时容易以溶解态的单体或小聚合体的形式与溶解性有机物中的羧基、酚基类活性基团络合,形成溶于水的有机络合态铝而残留在水中[10-12]。总体而言,目前对出水残余铝的研究主要集中在分子质量小于1 000、1 000~3 000和3 000~10 000 Da的溶解态铝、颗粒态铝以及总铝5个方面,溶解态铝由于其尺寸在超滤范围内[13],因此,又被称为超滤膜分级余铝。
本文主要对出水中超滤膜分级余铝和混凝过程进行了研究,以黄河上游水源水作为实验样本,研究了Al13和AlCl3 2种不同铝形态的混凝剂在不同投加量下的混凝过程,结合出水中的溶解态余铝含量、UV254、pH、浊度和絮体特性的变化趋势,探究了铝形态对出水残余铝及混凝过程的影响机制,以期为实际工程生产中余铝的控制及絮体调控提供参考。
-
1)实验原水。本实验选用黄河上游水源水作为原水进行实验,对其进行水质分析,其表征结果为UV254为 0.045 cm−1,pH为7.94,浊度为2.13 NTU,水中总有机碳的质量浓度(以TOC计)为2.143 mg·L−1。
2)混凝剂。氯化铝(AlCl3·6H2O)分析纯,购自上海升德医药科技有限公司。利用慢速滴碱法制备出 OH+与Al3+物质的量的比为2.2:1的PACl溶液,然后加硫酸钠形成硫酸铝十三沉淀,利用氯化钡溶液置换出Alb含量大于 90%,Al含量为0.1 mol·L−1的Al13溶液[14]。利用Ferron络合比色法[15]测定Al13和AlCl3 2种混凝剂中Al的形态,实验结果列于表1。结果表明,AlCl3中主要的铝形态为Ala,而Al13中主要铝形态为Alb,选择此2种混凝剂可有效探究铝形态对混凝过程及出水余铝的影响。
3)实验设备。搅拌采用HJ-6A型六联电动搅拌仪(上海汗诺),药品称量采用FA2204C型电子天平(上海天美),测试余铝含量采用EXPEC 7000型ICP-MS(北京吉天仪器),UV254的测定765型紫外可见分光光度计(上海仪电),pH的测定采用pHs-3C型pH仪(上海理达仪器厂),浊度测试采用2100P型的浊度仪(美国Hach公司),粒度的测定采用Mastersizer 2000型的激光粒度仪(Malvern,UK)。
-
1)混凝实验。首先取1 L实验原水倒入烧杯中,以250 r·min−1搅拌30 s,再加入一定量混凝剂,以200 r·min−1搅拌90 s,之后以40 r·min−1搅拌10 min,最后静置沉淀30 min。混凝剂投加量为0.01~0.08 mmol·L−1(以Al原子量计算),浓度梯度为0.01 mmol·L−1。
2)分级实验。在混凝结束后,利用膜分离技术进行过滤分级实验[13]。利用从大到小多种孔径的滤膜,逐步分离出溶解态铝、3 000~10 000、1 000~3 000 和小于1 000 Da的溶解态铝。首先,将含有颗粒态和溶解态铝的混凝后出水利用0.45 μm的膜进行过滤,颗粒态铝被截留;利用截留分子质量为10 000 Da的膜对第1次渗出液进行过滤,分子质量大于10 000 Da的铝被截留;再利用截留分子质量为3 000 Da的膜对第2次渗出液进行过滤,在3 000~10 000 Da的铝被截留;利用截留分子质量为1 000 Da的膜对第3次渗出液进行过滤,1 000~3 000 Da的铝被截留,小于1 000 Da的铝存在于最终渗出液中。
-
使用ICP-MS测定出水中的余铝含量,使用紫外分光光度计分析出水中的UV254,使用pH计测试出水pH,使用浊度仪分析出水浊度,使用马尔文激光粒度仪测试絮体粒度,强度因子,恢复因子以及分形维数。
-
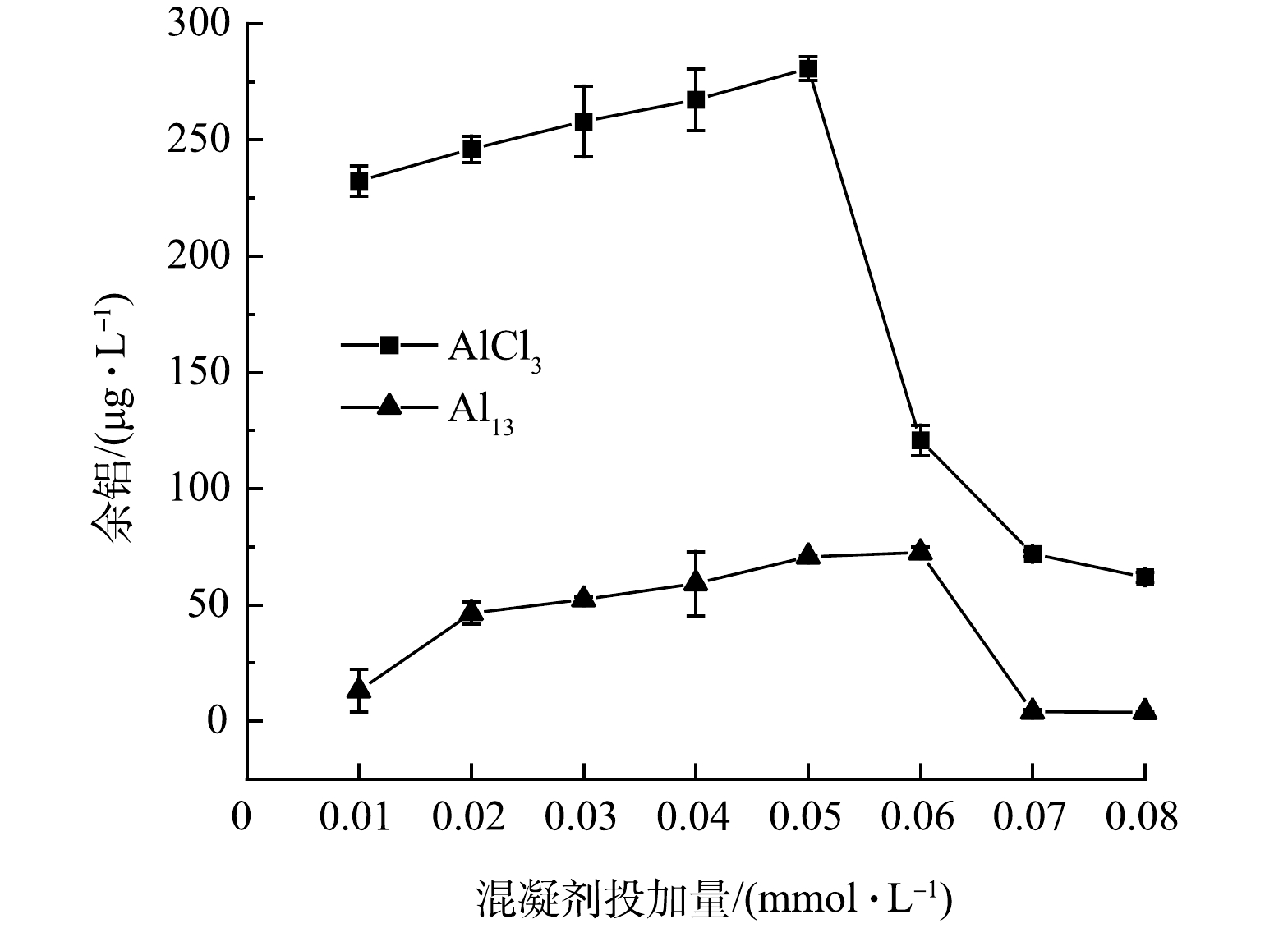
1)溶解态余铝。图1反映了2种混凝剂在不同投加量下出水中溶解态铝浓度变化的趋势。结果表明,随着混凝剂投加量的增加,残余铝质量浓度均呈现出先增后减的趋势。当使用0.05 mmol·L−1 AlCl3作为混凝剂时,余铝质量浓度最大值为280.59 μg·L−1,之后开始迅速下降;而当0.06 mmol·L−1 Al13作为混凝剂时,余铝质量浓度最大值为72.43 μg·L−1。这是因为在混凝剂投加量较低时,铝以络合体形式存在于出水中,导致余铝浓度上升,而随着投加量的增加至一定限值,水中开始形成絮体,余铝浓度出现下降[2]。总体来看,在投加量范围内,Al13作为混凝剂时,出水中余铝质量浓度均低于0.2 mg·L−1,且受混凝剂投加量影响较小。
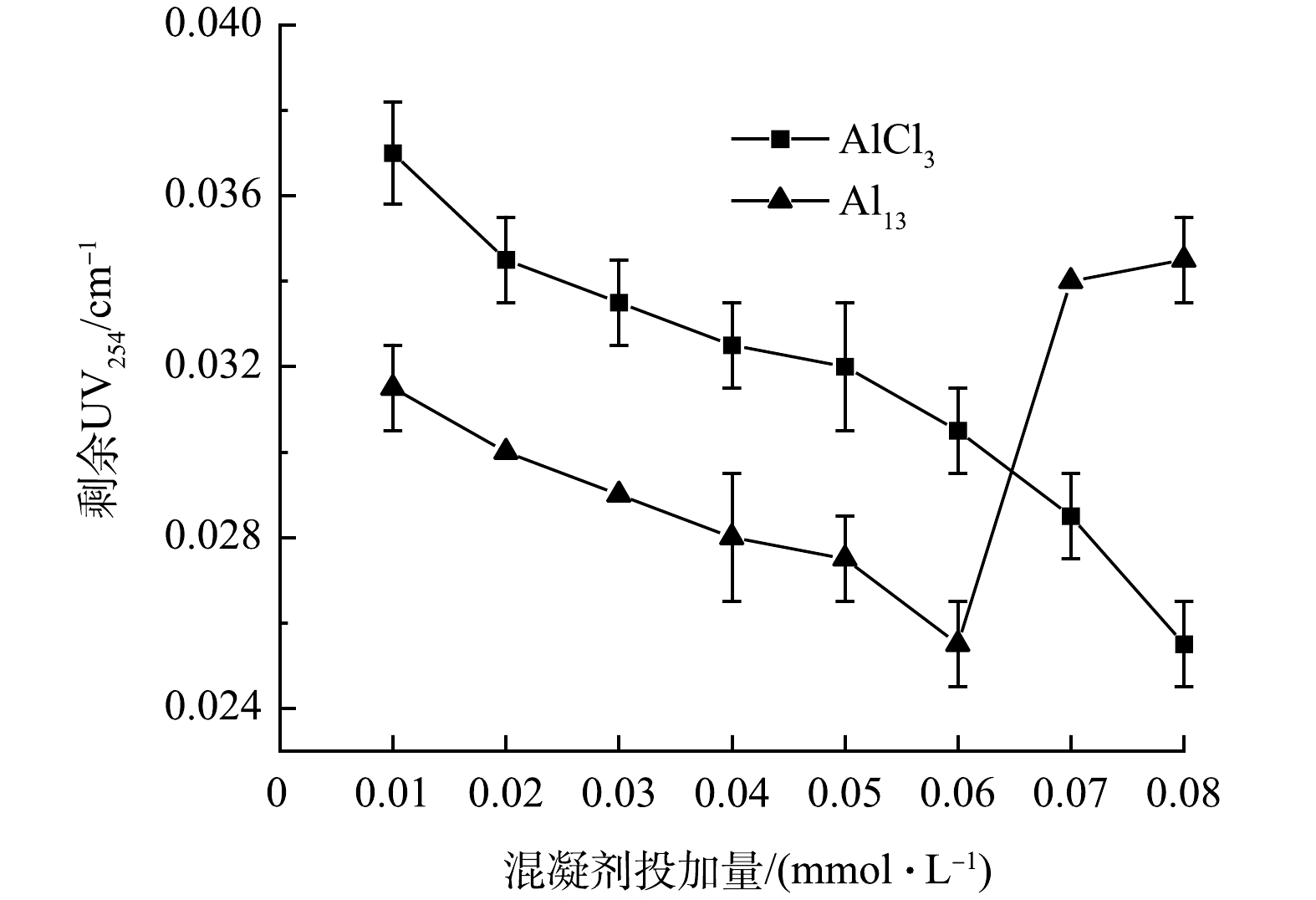
2) UV254变化。图2反映了2种混凝剂在不同投加量下出水中UV254变化的趋势。在投加量范围内,2种混凝剂出水中UV254均随着投加量的增加出现下降趋势,对有机物均有一定去除效果。在投加量较低时,Al13有更强的电中和能力,其表现出比AlCl3更高的芳香类物质去除率;但当投加量超过0.06 mmol·L−1时,Al13出水中UV254从0.026 cm−1急剧上升至0.034 cm−1,这是因为Al13浓度过高导致的电荷逆转,Al13的正电荷较高使颗粒和胶体带有较高的同号正电荷,相对排斥而复稳,而AlCl3通过吸附架桥和网捕卷扫作用仍对UV254有较好的去除效果[16]。
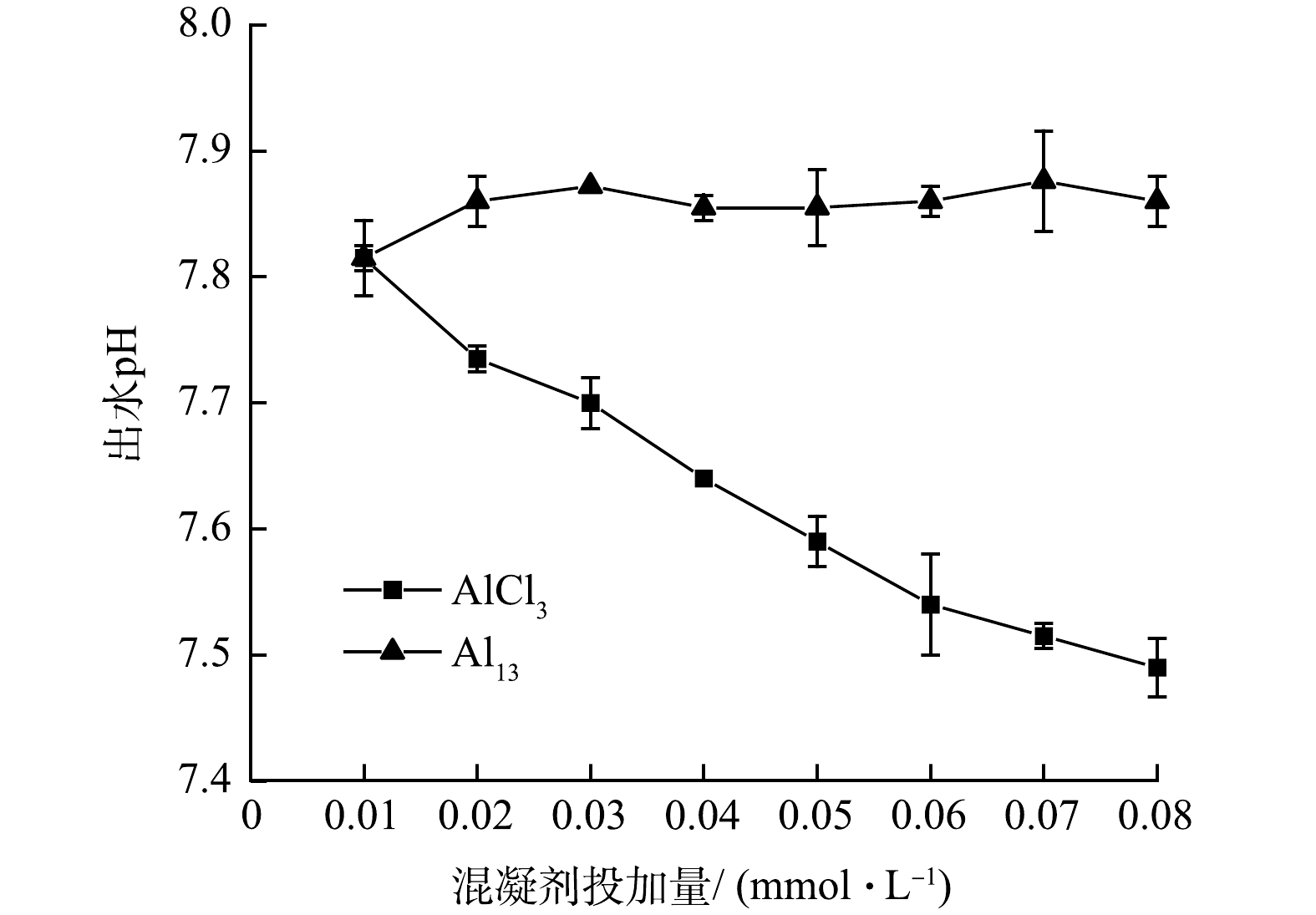
3) pH的变化。图3反映了2种混凝剂在不同投加量下出水pH的变化趋势。可见,在不同投加量下,Al13作为混凝剂时对出水pH影响较小。分析原因在于Al13具有更好的形态稳定性,对于出水水质的影响较小。当AlCl3作为混凝剂时,随着投加量的增加,AlCl3水解反应导致出水pH逐渐降低。
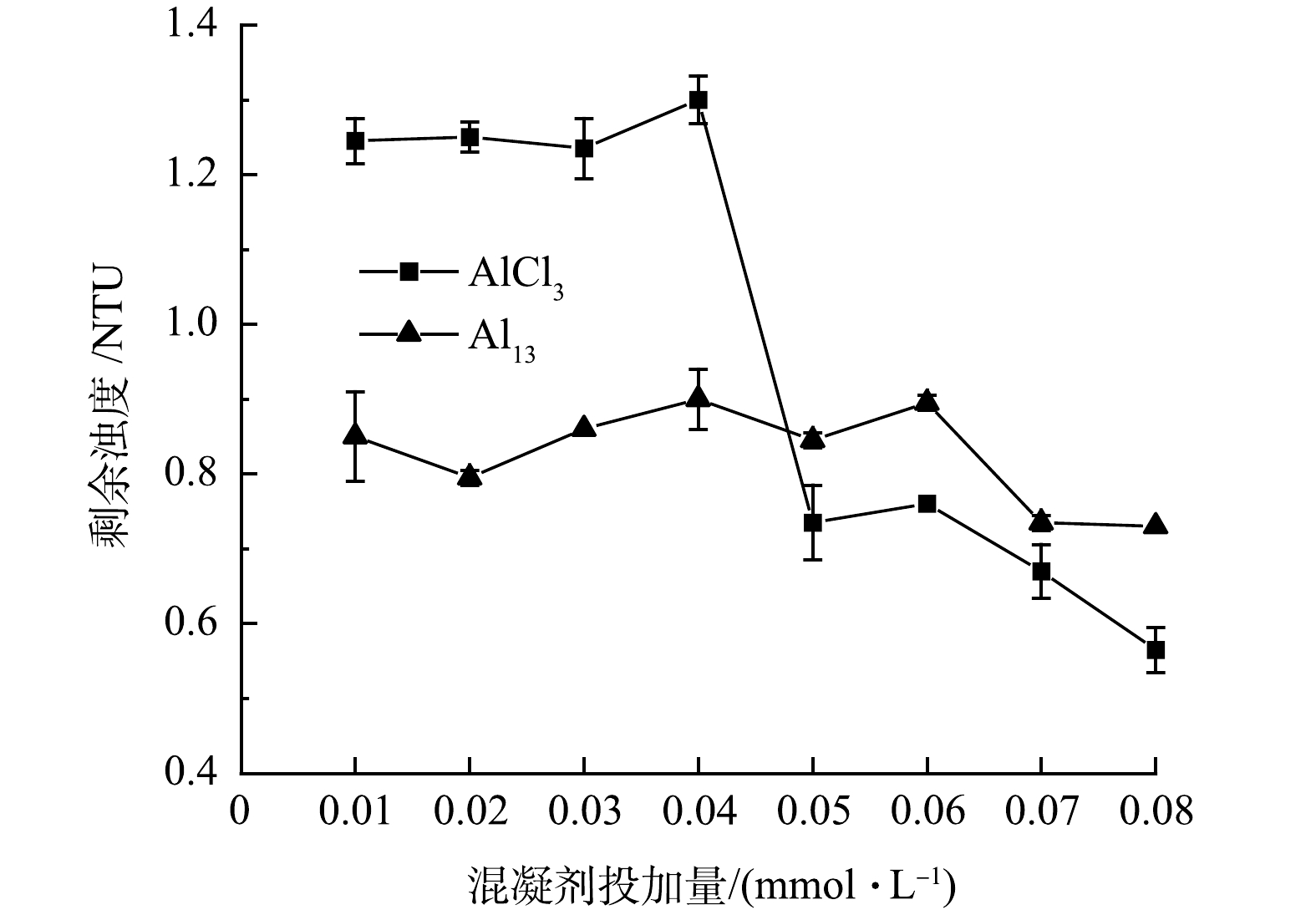
4)浊度的变化。图4反映了2种混凝剂在不同投加量下出水浊度变化的趋势。对比图1溶解态余铝浓度的变化可以看出,余铝和余浊存在一定的相关性[17]。随着AlCl3投加量的增加,出水浊度变化较大,在投加量较低时,出水浊度较高,在投加量从0.04 mmol·L−1增加到0.05 mmol·L−1时,出水浊度从1.3 NTU降至0.735 NTU,进一步增加投加量,出水浊度仍表现出下降趋势。而当Al13作为混凝剂时,出水浊度相对较低且稳定,均在0.73~0.895 NTU。分析原因在于Al13具有较高的正电荷,在低投加量时可以通过吸附电中和作用中和悬浮和胶体颗粒之间的静电排斥力[14],而且其水解后的Alb形态能通过表面络合等模式与腐殖酸形成沉淀物,然后通过网捕卷扫作用去除体系中存在的颗粒,从而达到较好的除浊效果[2]。
-
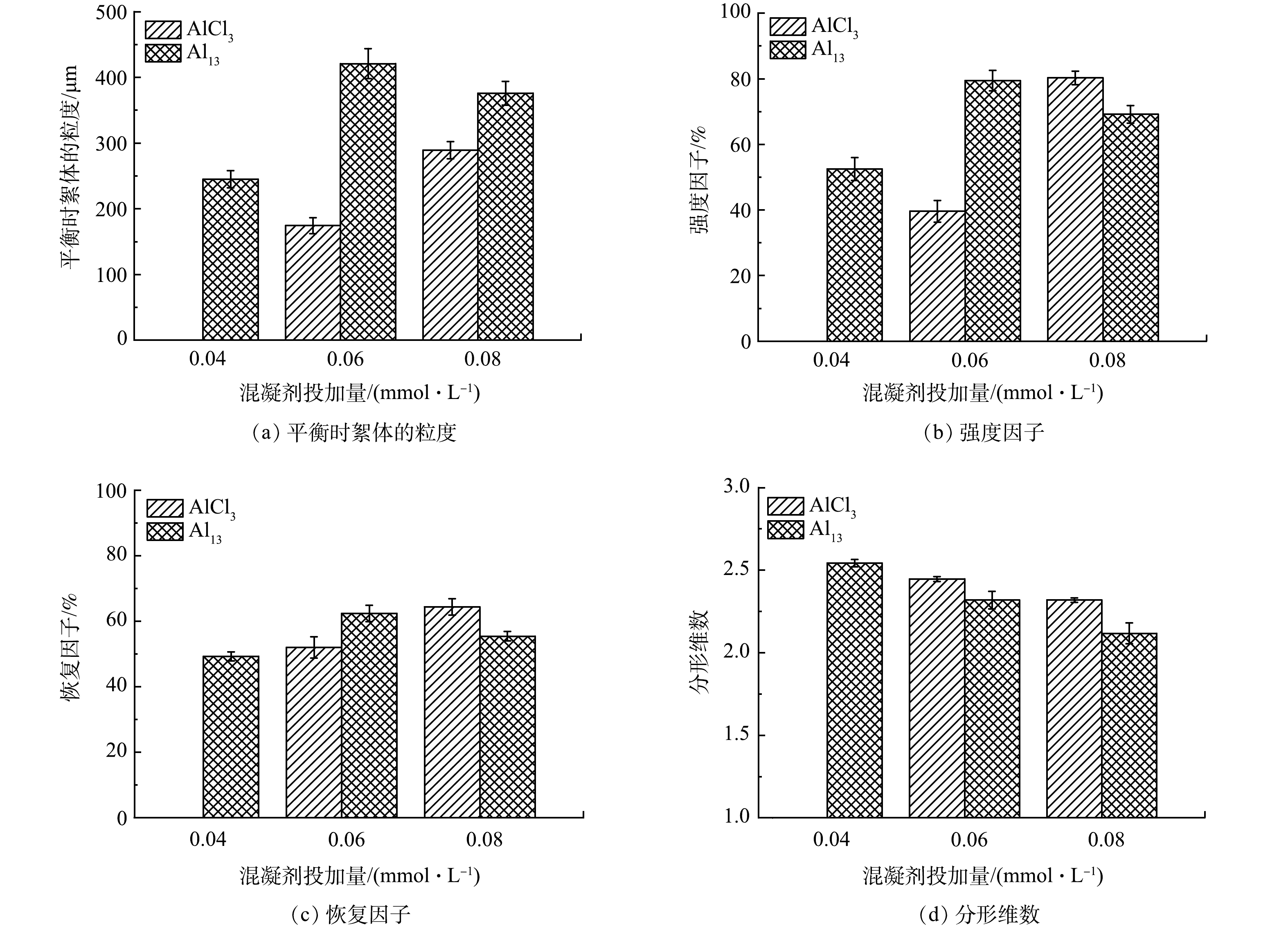
图5反映了2种混凝剂在不同投加量下絮体特征的变化(当AlCl3作为混凝剂时,在浓度为0.04 mmol·L−1时未出现絮体)。图5(a)为平衡时絮体的粒度变化。当Al13作为混凝剂时,絮体粒度均较大,且当Al13浓度为0.06 mmol·L−1时粒度达到最大;当AlCl3作为混凝剂时,絮体粒度表现为随投加量的增加而变大。图5(b)为平衡时絮体的强度因子变化。絮体强度因子越高,代表其抗剪切能力越强,当Al13作为混凝剂时絮体强度因子较稳定,而当AlCl3作为混凝剂时,絮体强度为随投加量的增加而迅速增加,且在AlCl3为0.08 mmol·L−1时超过Al13。这说明低投加量下Al13形成的污泥絮体抗剪切能力更强,而高投加量下则AlCl3的更强。图5(c)为平衡时絮体的恢复因子变化,絮体恢复因子越高,代表絮体被破坏后越容易重新团聚成絮体,2种混凝剂均表现出较稳定的性能,在低浓度时,Al13作为混凝剂的恢复因子较大,絮体受到破坏后更容易恢复;而在高浓度时,AlCl3作为混凝剂形成的絮体受到破坏后更容易恢复[18]。图5(d)中的分形维数代表平衡时絮体的分形体不规则的量度[19],分形维数越高,意味着絮体越紧实[20],2种混凝剂均表现出随投加量增加而下降的趋势,且不同投加量下AlCl3紧实度均高于Al13。
-
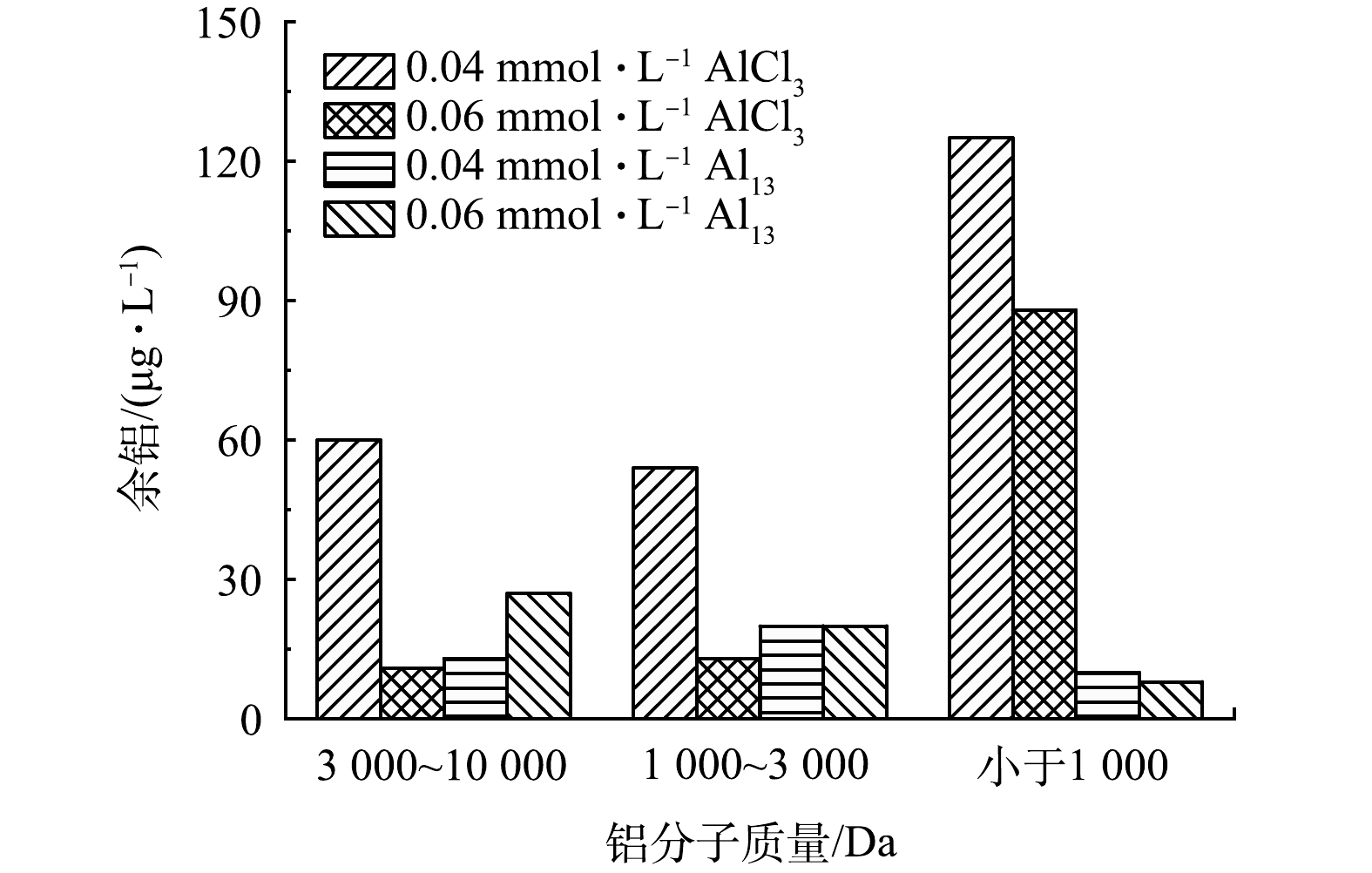
图6反映了2种混凝剂在不同投加量下出水中总溶解铝及各分子质量铝的质量浓度变化。可见,不同浓度下AlCl3做混凝剂时出水总溶解铝均高于Al13体系,值得注意的是,随着混凝剂投加量从0.04 mmol·L−1增加至0.06 mmol·L−1,投加Al13的出水中总溶解铝质量浓度从52 μg·L−1略微增长至67 μg·L−1,但投加AlCl3的则从267 μg·L−1急剧下降123 μg·L−1,质量浓度急剧的下降是由于水中的浊度变化导致总溶解铝的质量浓度出现变化[10],图4中的浊度变化也证明了这一点。
从各分级铝的质量浓度来看,AlCl3在不同投加量下出水中均为小于1000 Da的铝占比最大(分子质量较低的余铝不容易在滤池中被去除,造成出水中余铝质量浓度升高),而Al13在投加量为0.04 mmol·L−1时1 000~3 000 Da的铝占比最高,在投加量为0.06 mmol·L−1时,3 000~10 000 Da的铝占比最高,这与图6(a)中相应不同投加量下的絮体粒度变化趋势一致。
-
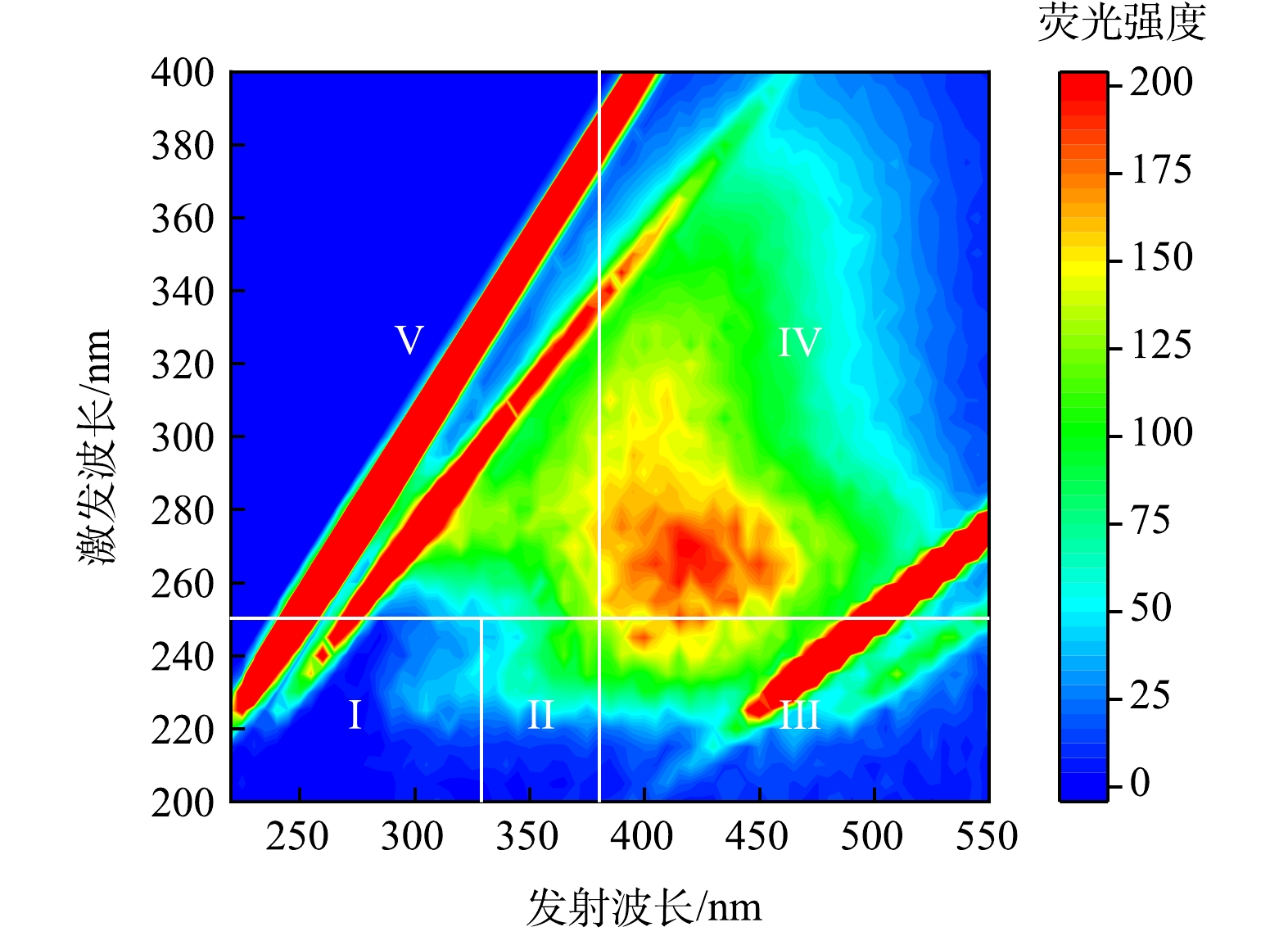
图7为原水的三维荧光图[14],其中区域I为蛋白质1,区域II为蛋白质2,区域III为富里酸,区域IV为微生物代谢产物,区域V为腐殖酸。根据计算,原水中的有机物主要为腐殖酸及微生物代谢产物,总计含量超过65%,而亲水性的蛋白质含量较低(约为23%)。
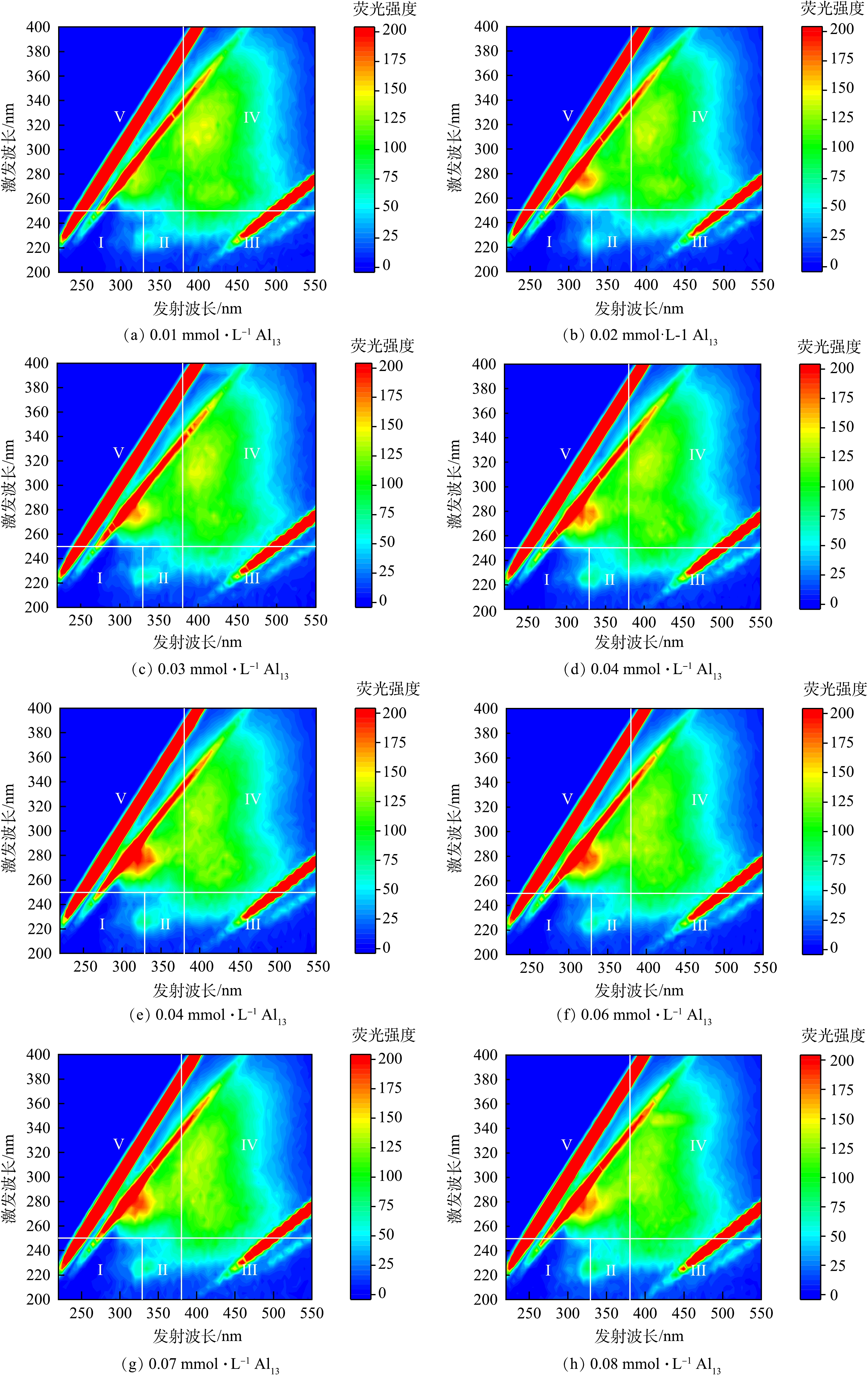
图8为在不同Al13投加量下出水的三维荧光光谱。可见,在不同Al13投加量下,荧光图中各区域的响应强度无明显变化。对比图7中的原水三维荧光图可发现,富里酸和腐殖酸区域的响应强度明显下降。这是因为Al13有很强的电中和能力,在低投加量下就可达到芳香类物质较高的去除率[14]。
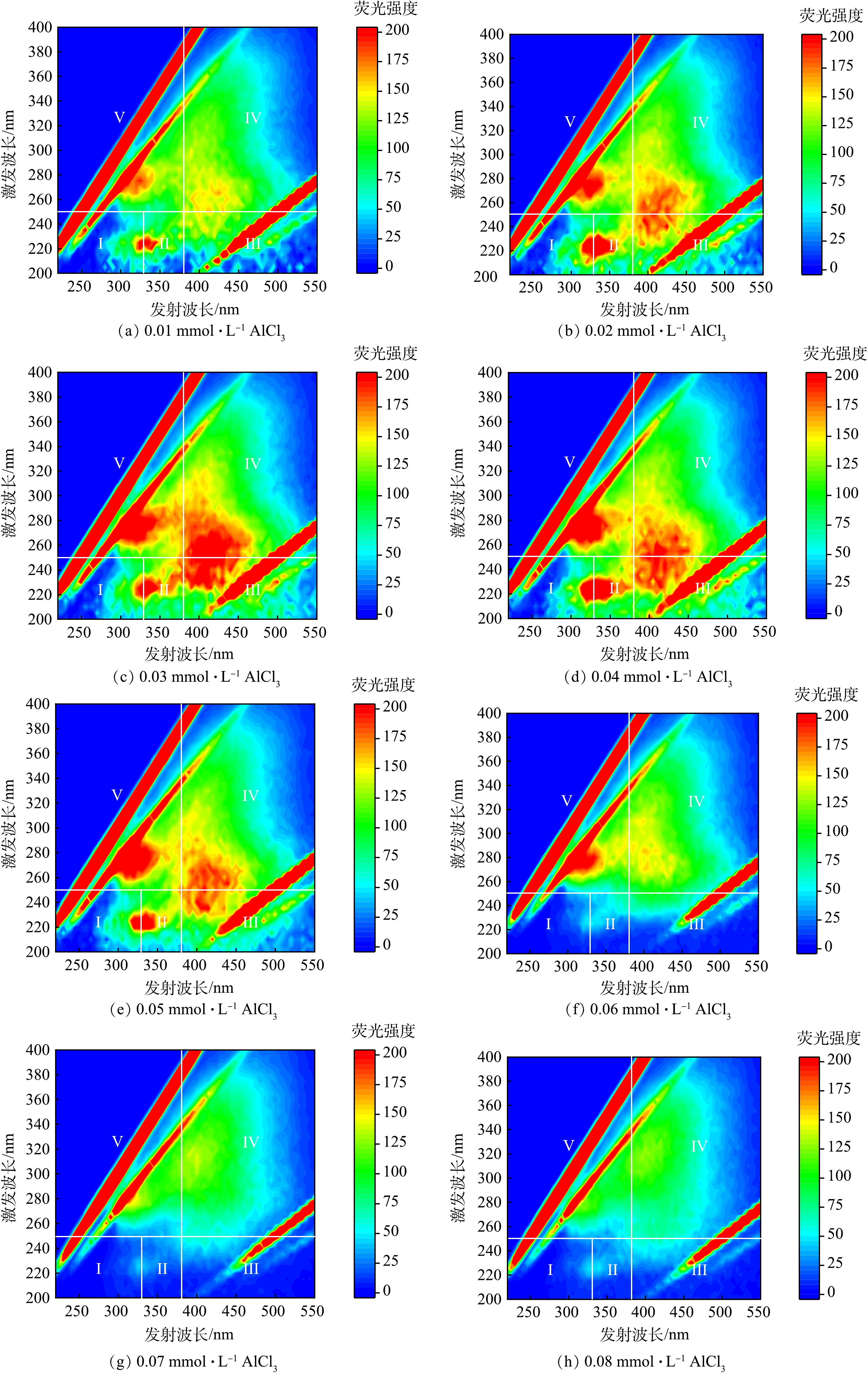
图9反映了AlCl3在不同投加量下出水的三维荧光光谱。AlCl3投加量对荧光光谱中各区域的响应强度影响较大。对比图1中的原水三维荧光光谱可见,当投加量小于0.04 mmol·L−1时,富里酸、腐殖酸、蛋白质和微生物代谢产物区域的响应强度有所增加;而AlCl3超过0.04 mmol·L−1后,以上4个区域的响应强度均出现明显下降,这说明在AlCl3高投加量下对几种有机物均有一定的去除能力。
对比图8和图9可以发现,Al13对富里酸和腐殖酸的去除效果要优于AlCl3,且在较低投加量下就表现出较好的去除效果,但其对蛋白质和微生物代谢产物的去除效果较弱;而AlCl3对4种有机物均能去除,但由于其工作原理是通过吸附架桥和网捕卷扫作用,因此需要在较高质量浓度时才有效果[14]。
-
1)混凝剂的投加量限值为0.01~0.08 mmol·L−1,投加量过高会造成混凝剂的浪费,但投加量过低则会导致水中残余铝浓度较高。2种混凝剂的最优投加量均为0.06 mmol·L−1。
2)对比2种混凝剂可以发现,Al13具有更优的混凝性能,在0.06 mmol·L−1的最佳Al13投加量时,残余铝质量浓度为72.43 μg·L−1,UV254为0.034 cm−1,pH为7.86,浊度为0.895 NTU,而且在投加量为0.01 mmol·L−1时对芳香类物质有较高的去除率。
混凝剂中的铝形态对黄河水源水中出水余铝的影响
Effects of Aluminum form in coagulant on residual Aluminum in effluent of the source water of Yellow River
-
摘要: 铝系混凝剂是应用最广泛的无机混凝剂,改善混凝剂中的铝形态可有效提高混凝效果,但其在净水过程中产生的余铝对人体健康及输水过程具有显著的影响。本文研究了氯化铝(AlCl3)和高聚十三铝(Al13) 2种混凝剂在处理黄河上游水源水时的混凝过程,结合出水中的溶解态及不同分子质量余铝含量、有机物紫外吸光度(UV254)、pH、浊度、有机物种类及含量和絮体特性的变化趋势,探究混凝剂中的铝形态对混凝过程的影响。结果表明,在实验投加量范围内,当Al13做混凝剂时,出水余铝质量浓度均低于0.2 mg·L−1。Al13具有较高的形态稳定性,在混凝过程中对出水pH影响较小。絮体粒度随混凝剂投加量的增加而增加,Al13投加量达到0.08 mmol·L−1时絮体粒度下降(强度因子由于静电排斥作用而下降)。在不同投加量下,使用AlCl3做混凝剂时出水余铝均高于Al13体系,且在不同投加量下AlCl3体系出水余铝中小于1 000 Da的余铝占比最大。Al13对富里酸和腐殖酸的去除效果优于AlCl3,且AlCl3在较高投加量下才能实现水中有机物的有效去除。Abstract: Al-based coagulants are the most widely used inorganic coagulants, and the optimized Al species can improve the coagulation performances, but the residual aluminum produced in the treatment process has significant impacts on human health and water transport process. In this study, Al13 and AlCl3 were used as coagulants to treat the source water of Yellow River, and the coagulation process was investigated. Combined with variations of the concentration of dissolved residual aluminum and residual aluminum with different molecular weights, UV254, pH, turbidity, concentration or species of organic matter and flocs characteristics, effects of aluminum species on residual aluminum and coagulation performances were investigated. The results showed that when Al13 was used as coagulant, the mass concentration of residual aluminum was lower than 0.2 mg·L−1, and the concentration was less affected by the dosage. Due to its high stability of species, Al13 had less effects on pH of effluent during coagulation process. The particle size of flocs increased with the increase of coagulant dosage, but it decreased when the dosage of Al13 reached 0.08 mmol·L-1 (the strength factors decreased due to electrostatic repulsion). The residual aluminum using AlCl3 as coagulant was higher than that in Al13 system at different dosages, and the proportion of residual aluminum with molecular weight lower than 1000 Da in AlCl3 was the largest in AlCl3 system. The removal efficiency of fulvic acid and humic acid using Al13 was better than using AlCl3, the latter could achieve high effective removal of organics in water at high dosages.
-
Key words:
- coagulation /
- Al13 /
- AlCl3 /
- residual aluminum /
- flocs
-

-
表 1 混凝剂的Al形态分布
Table 1. Al species for coagulants used in this study
Al形态 Ala/% Alb/% Alc/% AlCl3 95.21 3.28 1.51 Al13 2.93 96.27 0.80 -
[1] 郝二成, 左利峰. 浅谈水处理中混凝工艺发展[J]. 山东煤炭科技, 2008, 4: 97-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2008.05.062 [2] 王趁义, 张彩华, 毕树平, 等. Al-Ferron逐时络合比色光度法测定聚合铝溶液中Ala, Alb和Alc三种铝形态的时间界限研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2005, 25(2): 252-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2005.02.026 [3] 赵华章, 杨宏伟, 蒋展鹏, 等. 混凝沉淀过程中铝系混凝剂的形态转化规律[J]. 中国环境科学, 2005, 25(2): 183-187. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2005.02.013 [4] WANG W Y, YUE Q Y, GAO B Y, et al. Floc proprieties and ultrafiltration characteristics by chitosan compound aluminum species coagulant under different pH conditions[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2016, 68: 224-231. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2016.08.041 [5] 王东升, 汤鸿霄, GREGORY J. IPF-PACl混凝动力学研究形态组成的重要性[J]. 环境科学学报, 2001, 21: 17-22. [6] BERTHON G. Aluminium speciation in relation to aluminium bioavailability, metabolism and toxicity[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2002, 228: 319-341. doi: 10.1016/S0010-8545(02)00021-8 [7] 赵鑫荣, 刘佳琪, 洪帆, 等. 铝神经毒性对学习记忆功能的影响[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2018, 41(5): 590-592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1633.2018.05.020 [8] 庞洁. 铝对人体的毒性及相关食品安全问题研究进展[J]. 内科, 2011, 6(5): 470-473. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7768.2011.05.038 [9] 杨忠莲, 高宝玉. 水体中残余铝的含量、组分、危害及控制研究进展[J]. 精细化工, 2013, 30(4): 412-419. doi: 10.13550/j.jxhg.2013.04.021 [10] 李勐卓, 程继夏, 顾军农, 等. 铁-铝盐混凝剂混合投加工艺控制溶解性残余铝的机理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(2): 580-587. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202005084 [11] YAN M Q, HAN X Z, ZHANG C Y. Investigating the features in differential absorbance spectra of NOM associated with metal ion binding: A comparison of experimental data and TD-DFT calculations for model compounds[J]. Water Research, 2017, 124: 496-503. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.004 [12] 杨晓莉, 赵建明, 于永军, 等. 铝元素在农村饮用水中的含量及风险分析[J]. 源研究与管理, 2019, 01: 52-54. [13] WU J H, XIA M J, LI Z W, et al. Facile preparation of polyvinylidene fluoride substrate supported thin film composite polyamide nanofiltration: Effect of substrate pore size[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 638: 119699. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119699 [14] 童庆, 徐慧, 樊华, 等. Al13改性羟基磷灰石的除氟性能研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(7): 2748-2757. [15] CAO B D, ZHANG W J, WANG Q D, et al. Wastewater sludge dewaterability enhancement using hydroxyl aluminum conditioning: Role of aluminum speciation[J]. Water Research, 2016, 105: 615-624. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.016 [16] 王志红, 崔福义, 郑学书, 等. 混凝沉淀中影响除铝效率的因素[J]. 中国给水排水, 2001, 17(10): 5-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2001.10.002 [17] 徐伟颖. 纳米Al13的混凝行为、絮体特性及对膜污染的影响研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2012. [18] JARVIS P, JEFFERSON B, PARSONS S A. Breakage, regrowth, and fractal nature of natural organic matter flocs[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39: 2307-2314. [19] 任鹏飞. 基于颗粒形态变化的变速沉淀过程稳定性控制机制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016. [20] TANG P, GREENWOOD J, RAPER J A. A model to describe the settling behavior of fractal aggregates[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 247(1): 210-219. doi: 10.1006/jcis.2001.8028 -



 下载:
下载: