-
近年来,氨选择性催化还原法 (NH3-SCR) 是对低温烟道气中氮氧化物 (NOx) 的有效控制办法。该方法的关键是开发低温高稳定性脱硝催化剂。这类催化剂有低温Mn基催化剂[1]、中温的V-Mo(W)-O/TiO2[2]、中温Cu基催化剂[3]和Ce基催化剂等[4]。Mn基催化剂低温活性好,但抗硫稳定性差。LIU等[5]通过Eu改性Mn/TiO2催化剂,提高了表面Mn4+含量,并有效地降低了TiO2的结晶度,使催化剂抗硫性较Mn/TiO2有很大提升,能有效抗硫的同时NO转化率从20%提升到80%。ZHANG等[6]通过Sb改性了Mn/PG (凹凸棒石催化剂) ,提高了活性组分的分散度,且SbOx会优先与SO2反应,保护了活性组分,减少了MnSO4的生成,使催化剂抗硫抗水脱硝活性得到显著提升,但脱硝效率呈下降趋势。本课题组在提高Mn基催化剂的抗硫性方面开展了大量研究[7-10],制得了低温活性和抗硫性较好的Mn基催化剂。对抗硫后的催化剂进行表征发现,催化剂表面仍有一定量的硫存在,且载体晶型也会发生细微改变。改性后的Mn基催化剂抗硫性虽得到一定提升,但其工业应用中的稳定性仍有待验证。降低Cu基催化剂和Ce基催化剂的活性温度也是研究热点。但Cu基催化剂[11-12]和Ce基催化剂[13-14]的活性温度通常都在250 ℃以上,故不能满足低温脱硝要求。
V-Mo(W)-O/TiO2为传统商用催化剂,在温度高于300 ℃时具有较高的活性和抗硫性。但低于该温度时,则存在脱硝效率低、易发生硫中毒等现象。为提高钒基催化剂的低温活性和抗硫性,从载体改性、助剂添加、优化制备方法等方面对钒基催化剂进行了改性处理。通过调节载体表面酸性和孔结构、调节催化剂的活性组分价态、晶型、活性组分分散度和添加其他低温活性组分等办法可提高其低温活性和抗硫性[15-16]。MARBERGER等 [17]通过酸性SiO2对载体表面进行修饰以增加V2O5-WO3/TiO2表面酸性,阻止了TiO2载体的烧结,从而使催化剂的活性和稳定性明显提升。LI等[18]通过Nb掺杂增加了CeVO催化剂的氧空位和表面酸性,增加了Ce3+和V5+的表面物种含量,使催化剂在210~420 ℃时的NOx维持在90%以上,并且拥有很好的抗硫性。CHEN等[19]通过采用N2和H2非热等离子体处理法制备了V-Ce-Ni/TiO2催化剂,提高了活性组分的分散度,增加了催化剂表面酸性,从而提升了催化剂的低温活性,使得催化剂在230 ℃~350 ℃的NO转化率接近100%。这表明通过改性钒基催化剂可降低其活性温度,且提升其抗硫性。然而,在220 ℃以下,低温钒基催化剂的SCR活性仍然很差。因此,在脱硝过程中,降低催化剂活性温度,且拥有较好抗硫稳定性,仍是低温脱硝催化剂研究热点。
基于V-Mo(W)-O/TiO2较好的抗硫稳定性[20-21]和本课题组前期制备的Ge改性低温钒基催化剂[22],采用Ge稳定TiO2晶型,增加其表面的酸性位,调变TiO2与V、Mo之间的电子作用,使催化剂表现出低温高活性和高抗硫稳定性,但仍不能满足低温烟道气脱硝要求。本研究通过进一步掺杂Mn改善催化剂低温活性,优化载体对V-Mo活性组分的电子效应,制备出具有低温高脱硝活性和高稳定性的V-Mo-O/(Ge-Mn-TiO2)催化剂,并其进行活性和结构性能表征,从而探究其低温高活性和高稳定性的机理,以期为低温烟气中氮氧化物的控制技术提供参考。
-
1) Ge-Mn共改性TiO2载体 (Ge-Mn-TiO2) 的制备。采用共沉淀法制备载体,将10.015 8 g硫酸氧钛溶于去离子水中,并在60 ℃下水浴加热搅拌0.5 h;将0.026 3 g氧化锗溶解于21%的碳酸氢铵中得到氧化锗溶液;将0.614 0 g乙酸锰溶于10 mL去离子水中,得到乙酸锰溶液;将氧化锗和乙酸锰溶液同时缓慢滴入含有硫酸氧钛溶液的烧瓶中,然后缓慢滴加氨水 (25%) 至pH为9,并不断搅拌2 h;经抽滤、洗涤,得到锗锰钛复合沉淀物,于烘箱中110 ℃干燥12 h,后于空气气氛管式炉中500 ℃恒温焙烧4 h,制得Ge-xMn-TiO2 (x为Mn和Ti原子摩尔比,分别为0.02:1、0.04:1、0.1:1、0.4:1) 载体。根据文献[22],确定Ge/Ti原子比为0.004。
2) 前驱体制备。采用浸渍法负载活性组分,将与载体的质量分数为3% (以V2O5计) 的偏钒酸铵、6% (以MoO3计) 的钼酸铵作为V、Mo的前驱体,制得的催化剂记为V-Mo-O/Ge-xMn-TiO2和V-Mo-O/Ge-TiO2。催化剂经过研磨、压片、粉碎并过筛40~60目后,用于催化剂脱硝性能评估和表征。
-
SCR脱硝催化剂活性评价装置如图1所示。模拟烟气由NO (体积分数0.1%) ,NH3 (体积分数0.1%) 、O2 (体积分数7%) 和N2 (平衡气) 组成。采用42i -HL高浓度NO-NO2-NOx分析仪检测反应器进出口气体中的NO体积分数。活性测试的温度区间为120~260 °C。抗硫稳定性测试在200 ℃、SO2体积分数为0.01%的模拟烟气条件下进行,持续时间为40 h。
NO转化率和N2选择性采用式 (1)~(2) 计算。
式中:
$ {\eta }_{\mathrm{N}\mathrm{O}} $ 代表NO转化率;$ {S}_{{\mathrm{N}}_{2}} $ 代表N2选择性。 -
采用北京贝士德比表面及孔径分析仪 (3H-2000PMI) 来测定催化剂的比表面积及孔径。采用德国布鲁克DA ADVANCE A25 X射线衍射仪对样品粉末进行XRD测试,得到晶体结构。扫描是2θ为10°~90°内,扫描速度10o·min−1,步长为0.02。采用美国康塔ChemBETPulsarTPD/TPR全自动化学吸附分析仪对样品进行NH3-TPD和H2-TPR分析。将粒径为0.25~0.38 mm的样品 (50 mg) 置于反应管中。具体操作详见文献[23]。采用Thermo Scientific K-Alpha (美国Thermo公司) X-射线光电子能谱仪对催化剂进行表面元素分析。以Al-Kα射线 (1486.6eV) 为X射线激发源,样品表面的荷电用C 1s (284.8 eV) 进行校正。
-
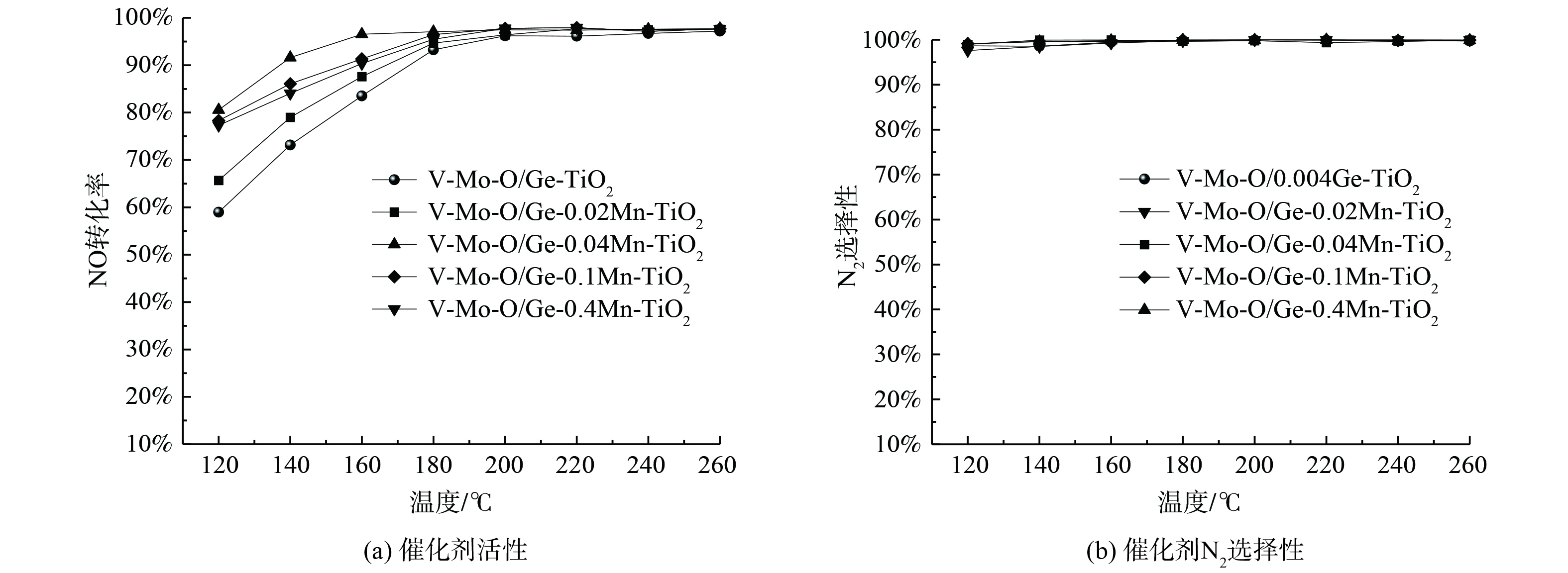
对Ge-Mn共改性TiO2负载催化剂V-Mo-O/Ge-xMn-TiO2催化剂的低温活性进行考察,并与无Mn掺杂的V-Mo-O/Ge- TiO2催化剂进行比较。由于烟道气中的NOx 95%以上都是NO,故主要考察NO的转化率,结果如图2所示。在低于180 ℃的温度区间,Mn掺杂后催化剂活性明显提高。当Mn/TiO2=0.04时,催化剂表现出最高的低温活性,在140 ℃时脱硝效率达到92%。这表明Ge-Mn共掺杂改性可显著提高V-Mo-O/TiO2催化剂的低温活性。然而,Mn含量进一步增加时,活性逐渐下降,这是由于Mn增加会阻碍TiO2与V、Mo之间的相互作用,从而导致催化剂活性降低。图2 (b) 为催化剂N2选择性测试结果,Ge-Mn共掺杂改性对整个测试温度区间内催化剂的N2选择性基本没有影响。
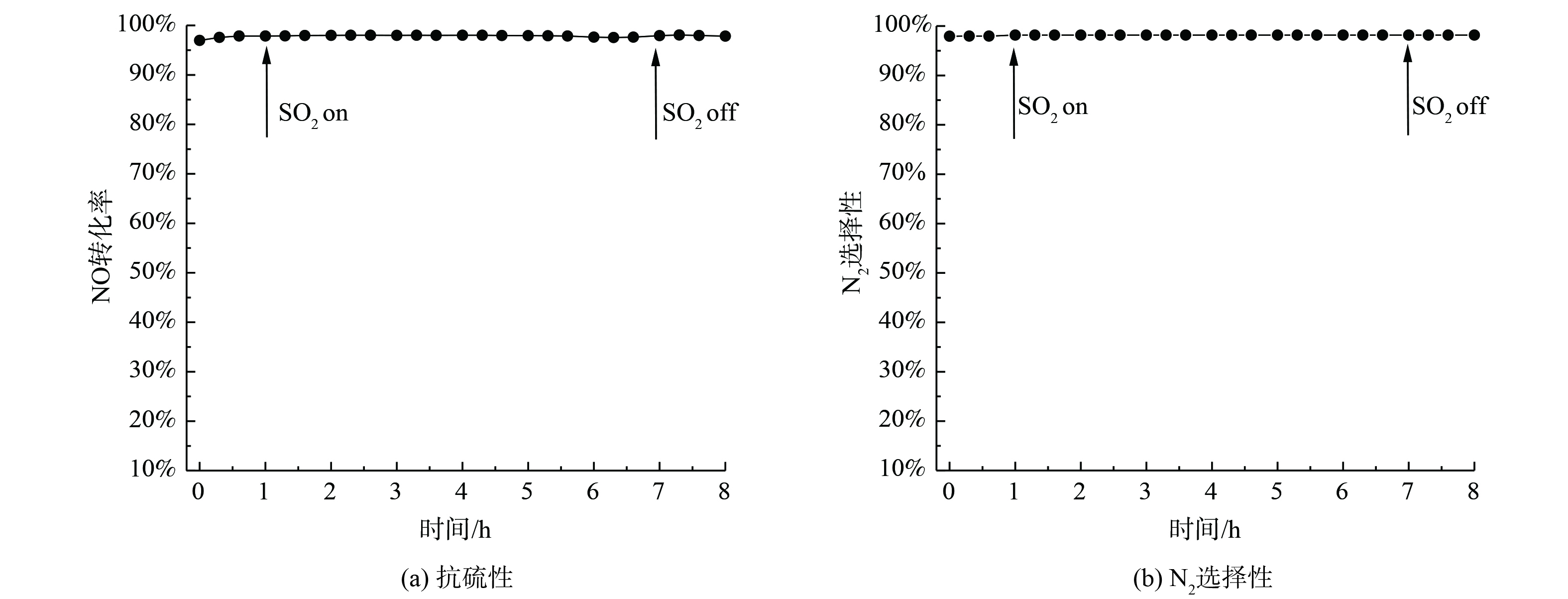
为考察改性剂对催化剂抗硫稳定性的影响,对V-Mo-O/Ge-0.04Mn-TiO2进行200 ℃时、体积分数0.01%SO2的抗硫稳定性测试,结果如图3(a)所示。SO2的加入对催化剂活性并没有影响,持续40 h脱硝活性始终保持在98%以上。图3(b)表明,在抗硫稳定性测试中,催化剂的N2选择性始终保持在98%以上,这说明Ge-Mn共掺杂改性后的催化剂具有低温高抗硫稳定性。
-
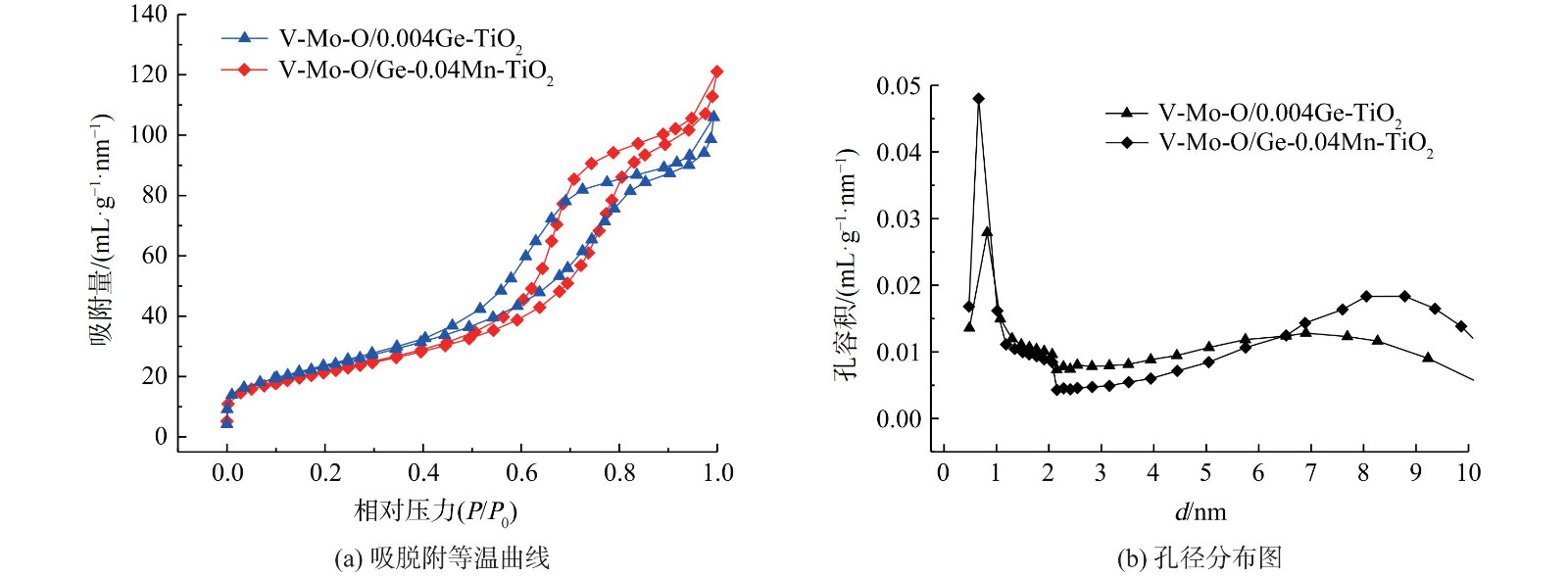
为考察Ge-Mn共掺杂对催化剂的孔结构及比表面积的影响,并对催化剂进行N2吸附-脱附测试,与Ge掺杂改性催化剂做对比,结果如图4所示。
Ge-Mn共改性后,催化剂的介孔略有变化。采用多点法计算催化剂的BET比表面积发现,V-Mo-O/0.004Ge-TiO2 的SBET为85.68 m2·g−1,而V-Mo-O/Ge-0.04Mn-TiO2的SBET为80.45 m2·g−1,表面积降低了5.23 m2·g−1。通过孔径分布图发现,大于6.5 nm的孔容积增加了48.98%。活性数据表明,Ge-Mn共改性后催化剂的低温活性明显提高。这说明低温较大的孔更有助于反应物料的进出,可通过降低传质阻力来增大低温脱硝反应速率。
-
为考察改性组分对催化剂表面活性组分存在晶型的影响,对Ge-Mn共掺杂改性TiO2负载催化剂进行XRD分析,结果如图5所示。Ge-Mn共掺杂改性后,主要呈现2θ为 25.3°、37.9°和48.1°处的TiO2锐钛矿特征衍射峰 (ICDD PDF#21-1272) ,以及在2θ 为33.0°、55.2°处的Mn2O3特征衍射峰 (ICDD PDF#41-1442) 。且Mn掺杂后,TiO2衍射峰强度降低且衍射峰位置略有偏移。根据离子半径分析,Ge4+的离子半径为53 pm,Mn3+的离子半径为64.5 pm,Ge离子半径远小于Ti4+ (60.5 pm) 的离子半径,对TiO2晶格畸变影响较小。而和Ti4+的离子半径相近的Mn3+离子则会挤入晶格,从而导致TiO2结晶度降低且发生一定畸变。图中并未观察到活性组分V、Mo的特征衍射峰。这说明活性组分在载体表面分布均匀,呈不定形状态存在或存在晶粒低于检测限,故高分散的活性组分和非晶态及锐钛矿晶型TiO2有利于催化剂表现出低温高活性[24]。
-
在NH3-SCR反应中,催化剂表面的酸性位含量和种类对N2的选择性和低温活性具有重要的影响,故对催化剂样品进行NH3-TPD表征来分析Ge-Mn共掺杂改性对催化剂表面酸量和酸强度的影响[25],结果如图6所示。Ge-Mn共改性后氨脱附峰面积明显提高,尤其是中高温脱附峰面积有较大提高,且各脱附峰的温度均降低了约40 ℃。这说明Mn的加入增加了催化剂表面的总酸位数量,尤其是增加了中强酸位数量,同时使酸强度略有降低。酸性位的增加和酸强度的降低有利于NH3的吸附,并抑制SO2的吸附和深度氧化,而中强酸性位的增加则更有利于NH3的吸附活化[26],从而使催化剂表现出低温高活性和抗硫稳定性。
-
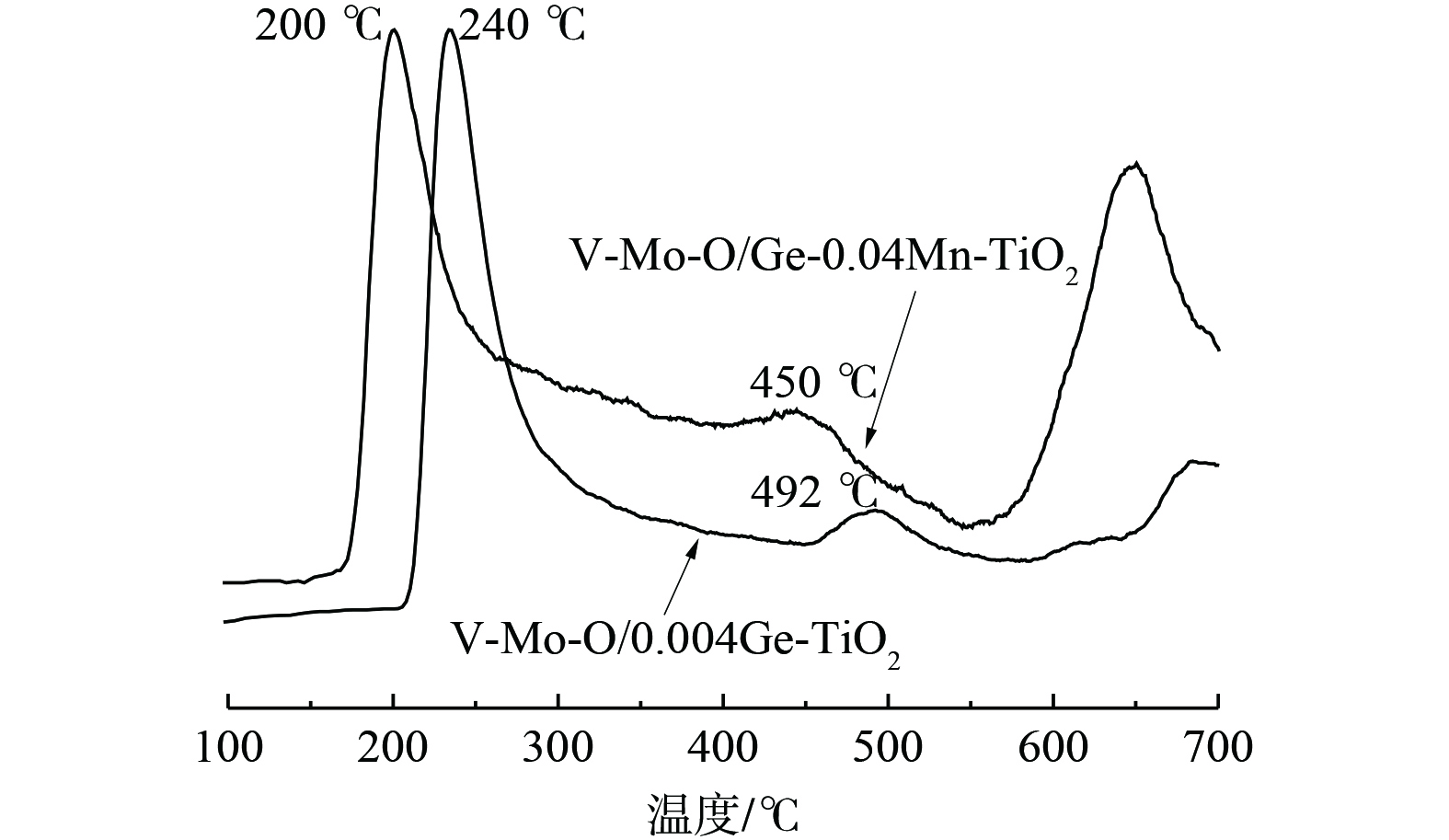
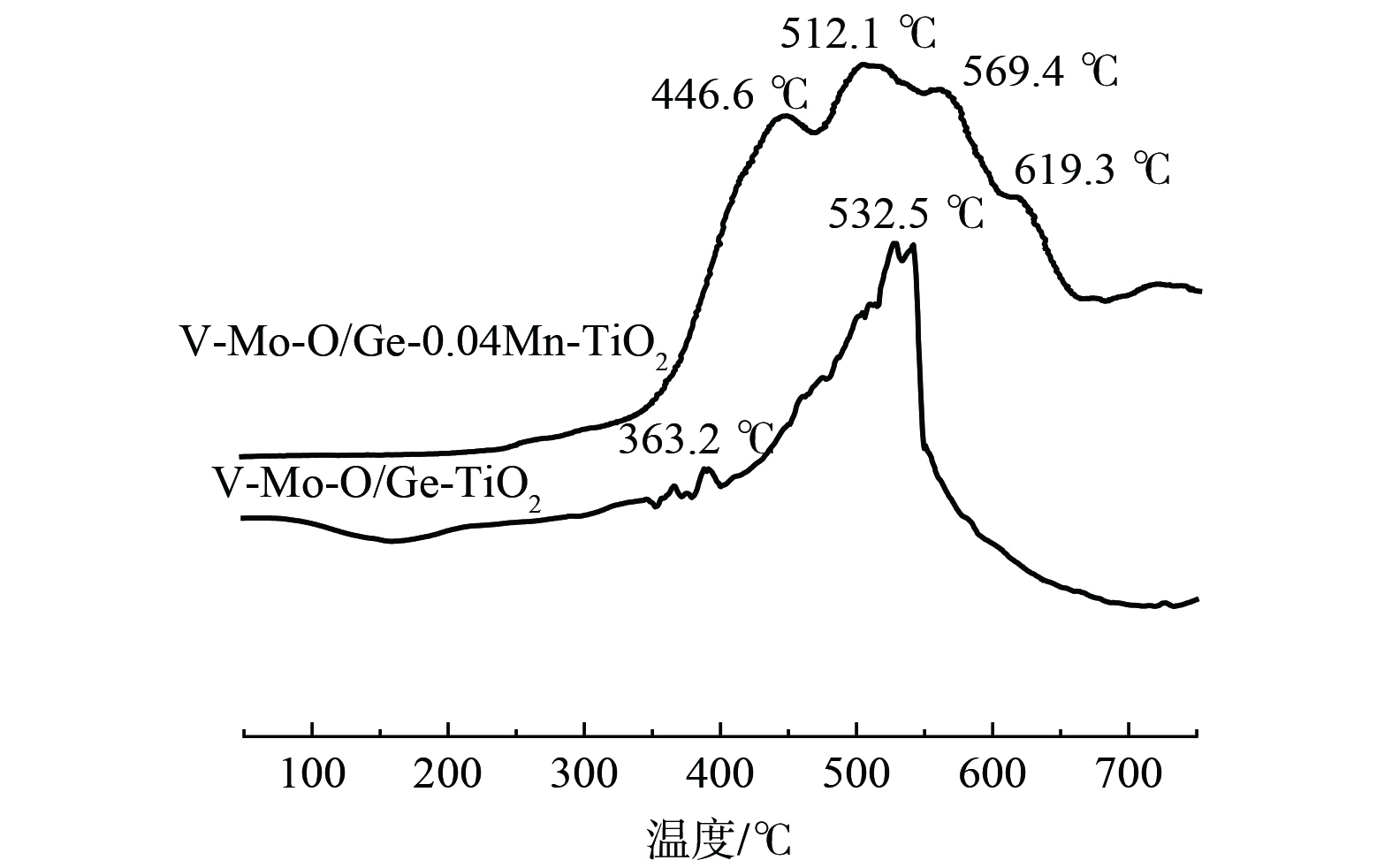
对Ge-Mn共掺杂改性负载催化剂进行了H2-TPR分析以考察催化剂表面的氧化还原性,结果如图7所示。V-Mo-O/Ge-0.04Mn-TiO2在350 ℃到650 ℃出现较宽的还原峰。446.6 ℃的还原峰归为MnO2还原为Mn2O3的还原峰[27],512.1 ℃为分散的V2O5的还原峰[28],569.4 ℃为Mn2O3还原为Mn3O4和MoO3还原为Mo2O5的还原峰[29],619.3 ℃为GeO2的还原峰[30],而V-Mo-O/Ge-TiO2还原峰仅出现在363.2 ℃和532.5 ℃,分别归为高度分散的V2O5 (V5+) 物种的还原和分散的V2O5的还原峰,以及八配位的Mo6+—Mo5+—Mo4+的还原峰[31]。活性数据表明,将Ge-Mn共改性后,催化剂的还原温度总体降低,且呈现很宽的还原峰。这说明改性后的催化剂在低温下更易于发生氧化还原反应,且容易形成各元素的氧化还原反应的接力,使催化剂表面始终具有带活性的Mo6+和V5+组分,并通过有氧条件下的氧化还原循环使催化剂呈现低温高活性。
-
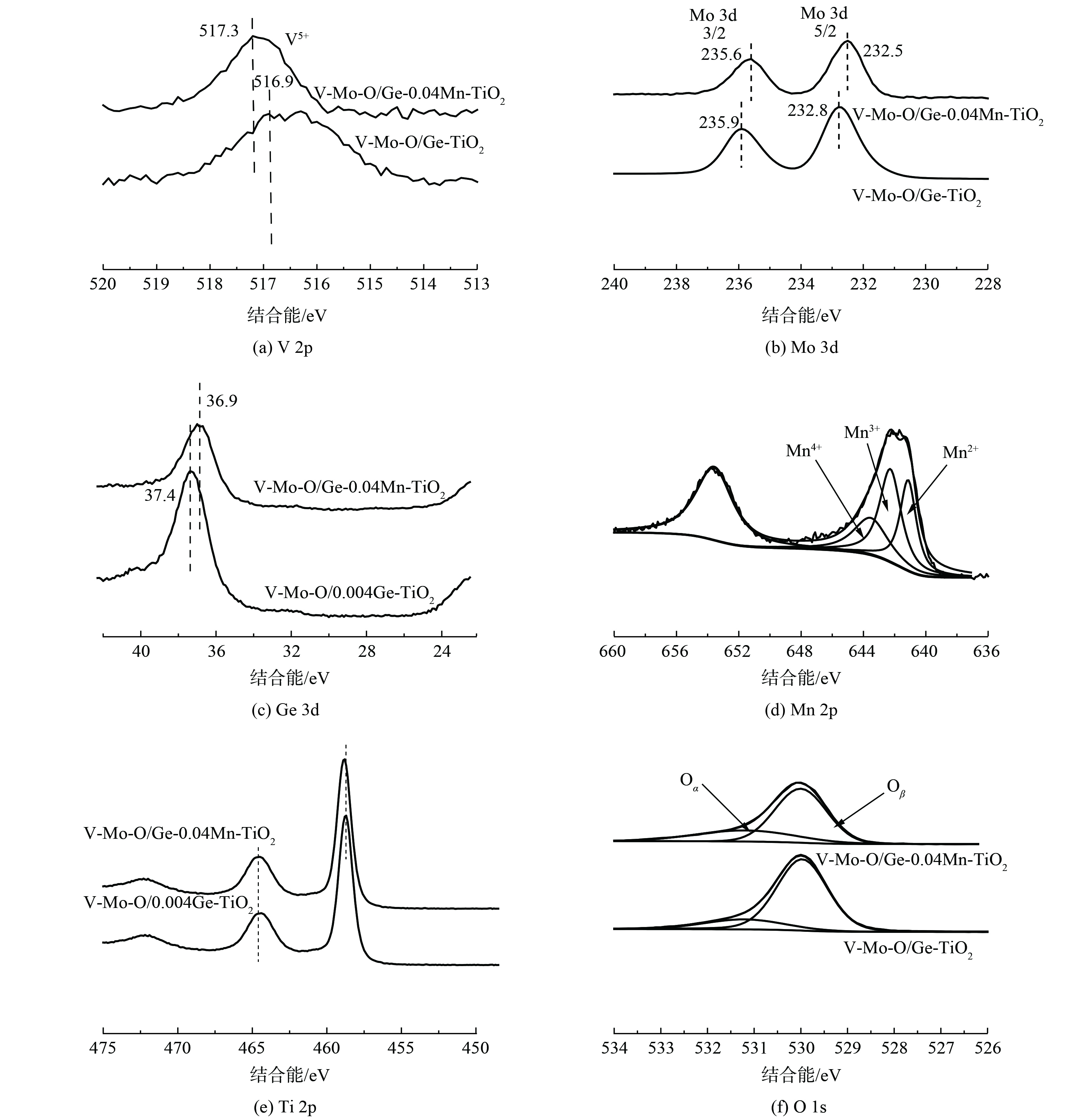
为考察催化剂改性前后表面各元素价态变化对催化活性的影响,对改性催化剂进行了XPS分析,得到V2p、Mo3d、Ge3d、Mn2p、Ti2p和O1s的结合能谱图,结果如图8所示。图8 (a) V2p XPS结合能峰表明,加入Mn后V2p的结合能明显增加,且峰宽变窄。这说明V主要以V5+形式存在。图8 (b) 为Mo的3d XPS谱图,图中236.0 eV和232.8 eV2个峰分别属于Mo3d3/2和Mo3d5/2。加入Mn后,催化剂的Mo3d结合能降低了0.3 eV,这表明低价态的Mo5+含量增加。图8 (c) 中Ge 3d的结合能降低了0.5 eV,这说明加入Mn后,催化剂表面Ge的价态降低,Ge2+含量增加。对Mn2p的XPS曲线进行分峰拟合,Mn2p3/2分峰的结合能分别为641.1 eV、642.3 eV和643.5 eV,对应Mn2+、Mn3+和Mn4+,这说明Mn主要以这3种价态存在。在Ti2p XPS谱图中,459.7 eV和464.4 eV的峰值归因于Ti2p3/2和Ti2p1/2,为Ti4+的特征峰。而Mn改性后,催化剂的Ti2p结合能向高结合能移动,这说明Mn掺杂后Ti的电负性增加,吸收电子的能力增加有利于中高温酸性位点的增加,与NH3-TPD分析结果相对应[32]。
结合H2-TPR分析可知,加入Mn可使催化剂表面元素周围的电子云发生变化,使V5+、Mo5+、Ge2+含量增加。基于文献[33-34]和课题组前期研究,这些表面元素在NH3-SCR反应过程中发生V5+—V4+、Mo5+—Mo6+、Ge2+—Ge4+和Mn4+—Mn3+之间的转化,而Mn3+很容易被O2氧化为Mn4+,而Mn与其余3个组分间的电子转移,又可使具有活性的V5+在参与催化反应后快速完成自身还原,从而达到低温快速氧化还原的催化循环。
对抗硫前后催化剂进行XPS分析发现:催化剂各元素结合能基本没有发生变化,且催化剂表面S含量基本没有变化;新鲜催化剂表面硫含量为0.34% (原子含量,采用硫酸氧钛为Ti源制备残余的硫) ,抗硫后催化剂表面硫含量为0.36%,可认为催化剂表面没有硫酸铵盐生成。同时,不同元素间的相互作用也会导致催化剂表面O的结合能发生变化,对O1s进行分峰拟合,将催化剂表面氧分为晶格氧 (Oβ) 和化学吸附氧 (Oα) 。Oβ结合能为529.7 eV,Oα结合能为531.5 eV。将拟合结果列于表1中,Mn催化剂改性后的化学吸附氧 (Oα/Oα+Oβ) 的比例由22.36%升至27.95%,而化学吸附氧的增加也增强了催化剂表面对NH3的络合吸附活化。
-
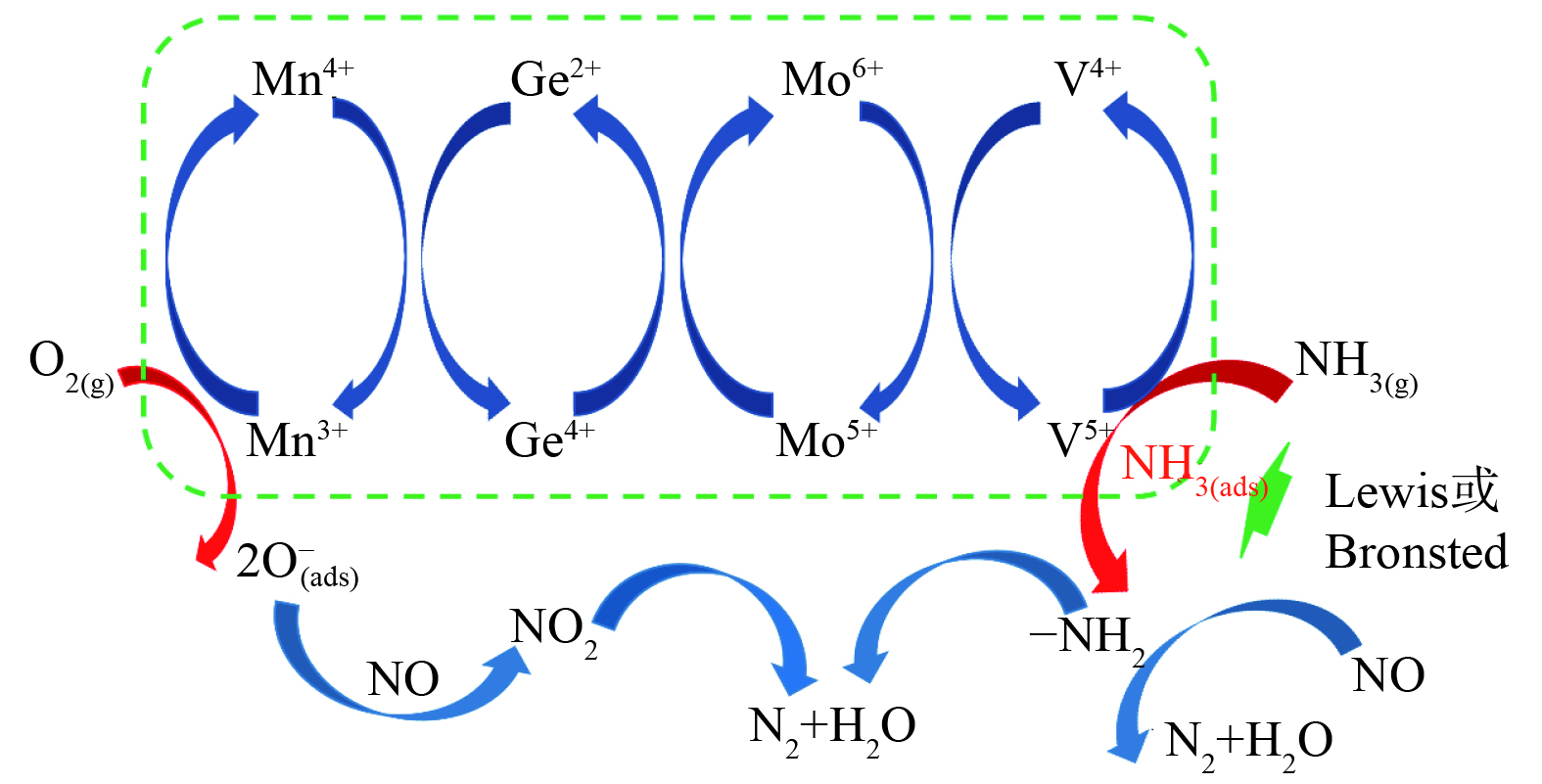
通过对催化剂的表征分析发现,具有合适孔径、丰富的表面酸性位和中强酸位、高含量的V5+使催化剂表现出较好的低温活性和抗硫稳定性。V-Ti催化剂中高V4+/V5+和高Mo6+含量能表现出较好的低温脱硝活性[35],与本研究得出的高V5+含量和低Mo5+催化剂有高低温活性相矛盾。分析其原因,本催化剂体系多了一个Mn离子掺杂,而Mn的加入,不仅降低了活性组分的还原温度,且形成了一个较宽温度范围的还原峰。这表明活性组分和掺杂离子的还原不是单一过程,而是存在还原相互影响的作用。由于Mn离子容易被O2氧化,基于H2-TPR和XPS分析结果可知:Mn主要以+3和+4状态存在,Mn3+很容易被O2氧化成Mn4+;由于Mn4+可将Mo5+氧化成Mo6+,而Mo6+又容易将V4+氧化成V5+;V5+表现很强的吸附活化NH3的催化作用,从而提高了催化剂的脱硝活性。而所形成的活性组分的氧化还原循环的存在,也抑制了NH3的深度氧化,表面丰富的酸性位也抑制了SO2的吸附和深度氧化,从而使催化剂表现出较高的低温活性、高选择性和高抗硫性。结合V基催化剂的NH3-SCR脱硝反应机理[36],梳理催化剂的脱硝反应机理如图9所示。
-
1) Ge-Mn共改性TiO2载体负载V、Mo活性组分后,催化剂的低温活性显著增加, 140 ℃时脱硝活性即达到92%,且在SO2存在下,40 h保持活性不降低,具有高耐硫稳定性。
2) Ge-Mn共改性TiO2后,使所制备催化剂表面总酸性位和中高强度酸性位得到显著增加,同时Mn与V、Mo、Ge活性组分发生了相互作用,使V5+含量增加,且形成了低温易发生的活性组分氧化还原循环,从而提高了催化剂的低温活性和高抗硫稳定性。
3) Ge-Mn共改性V-Mo-O/Ge-Mn-TiO2催化剂不仅具有商用V-Mo-O/TiO2催化剂的高抗硫性,而且表现出较好的低温活性,可为低温烟道气中NOx的脱除提供参考。
Ge-Mn共掺杂对V-Mo-O/TiO2催化剂低温脱硝活性的影响
Effect of Ge-Mn co-doping on low-temperature denitrification activity of V-Mo-O/TiO2 catalyst
-
摘要: 采用共沉淀法制备Ge-Mn共改性TiO2载体,考察了V-Mo-O/Ge-xMn-TiO2催化剂的低温氨选择性催化还原 (NH3-SCR) 活性和抗硫稳定性。Ge-Mn的加入可显著提高催化剂在低温窗口下的脱硝活性,且具有较高的N2选择性和抗硫稳定性。当Ge:Mn:Ti的原子摩尔比为0.004:0.04:1,在140 ℃时脱硝活性为92%。催化剂的N2吸附-脱附、NH3-TPD、H2-TPR、XRD和XPS分析结果表明:Mn加入使催化剂的介孔增加,表面总酸性位和中高强度酸性位量显著增加,从而增加了催化剂对NH3的吸附活化和对SO2吸附的抑制;Mn与V、Mo、Ge活性组分发生了强电子相互作用,使V5+含量增加,且使低温活性组分的氧化还原循环易于进行,进而增加了催化剂的低温脱硝活性。这说明增加的表面总酸性位和中高强度酸性位量、增加的V5+和由此形成的低温条件促进了活性组分氧化还原循环,最终提高了催化剂的低温活性和高抗硫稳定性。本研究可为低温脱硝催化剂的研发及应用提供参考。Abstract: Ge-Mn co-modified TiO2 support was prepared by co-precipitation method, and the activity and sulfur resistance of low-temperature ammonia selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR) and sulfur resistance of V-Mo-O/Ge-xMn-TiO2 catalysts were investigated. Compared with traditional V-Mo-O/TiO2 catalysts, the addition of Ge-Mn significantly improved the denitrification activity of the catalyst at low temperature window, and at the same time had high N2 selectivity and stable sulfur resistance. When the Ge:Mn:Ti atomic molar ratio was 0.004:0.04:1, the denitrification activity could reach 92% at 140 °C. The N2 adsorption-desorption, NH3-TPD, H2-TPR, XRD and XPS analysis results of the catalyst showed that the addition of Mn increased the mesoporosity of the catalyst, meanwhile the total surface acid sites and the amount of medium and high strength acid sites increased significantly, which increased the catalyst's adsorption activation of NH3 and inhibition of SO2 adsorption. Mn interacted with the active components of V, Mo, and Ge, which increased the content of V5+ and facilitated the redox cycle of the active components at low temperature, thus the low-temperature denitration activity of the catalyst was increased. Therefore, the increase of total surface acid sites, medium-strength acid sites, high-strength acid sites, and V5+ content and the formation of a low-temperature facile redox cycle of active components improved the catalyst's low-temperature activity and high sulfur resistance stability.
-
Key words:
- Co-modification /
- low temperature /
- SCR /
- carrier /
- catalyst
-

-
表 1 催化剂表面O1s分峰拟合结果
Table 1. Fitting results of O1s peaks on catalyst surface
样品名称 Oα Oβ Oα/Oα+Oβ V-Mo-O/0.004Ge-TiO2 294,912 84,937 22.36% V-Mo-O/Ge-0.04Mn-TiO2 231,062 64,141 27.95% -
[1] ZHU H T, SONG L Y, LI K, et al. Low-temperature SCR catalyst development and industrial applications in China[J]. Catalysts, 2022, 12(3): 341. doi: 10.3390/catal12030341 [2] ISABELLA NOVA, ENRICO TRONCONI, Kinetic study of the NO/NO2-NH3 SCR reactions over a V2O5–WO3/TiO2 commercial catalyst for the after treatment of Diesel engines exhausts[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2009, 42(26): 183-190. [3] ZHANG S T, PANG L, CHEN Z, et al. Cu/SSZ-13 and Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts for deNOx in diesel exhaust: Current status, challebges, and future perspectives[J]. Applied Catalysts A:General, 2020, 607: 117855. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117855 [4] LIU W J, LONG Y F, LIU S N, et al. Promotional effect of Ce in NH3-SCO and NH3-SCR reactions over Cu-Ce/SCR catalysts[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2022, 107: 197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2021.11.045 [5] LIU J, GUO R T, LI M Y, et al. Enhancement of the SO2 resistance of Mn/TiO2 SCR catalyst by Eu modification: A mechanism study[J]. Fuel, 2018, 223: 385-393. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.062 [6] ZHANG X L, LV S S, ZHANG X C, et al. Improvement of the activity and SO2 tolerance of Sb-modified Mn/PG catalysts for NH3-SCR at a low temperature[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 101: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.07.027 [7] 魏永林, 陈红萍, 侯欣辛等, Fe-Mn/TiO2低温NH3-SCR脱硝催化剂的SO2中毒机理[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(4): 4132-4139. [8] 魏永林, 陈红萍, 侯欣辛, 等, 低温脱硝催化剂抗硫性能研究[J]. 河北冶金, 2021(2): 1-6. [9] 杨旭, 陈红萍, 齐雪. 脱硝催化剂的硫中毒机理研究[J]. 现代化工, 2018, 38(2): 20-24. [10] HOU X X, CHEN H P, LIANG Y H, et al. La modified Fe–Mn/TiO2 catalysts to improve SO2 resistance for NH3-SCR at low-temperature[J]. Catalysis Surveys from Asia, 2020, 24: 291-299. doi: 10.1007/s10563-020-09309-1 [11] CHEN C M, GAO Y, LIU S T et al. Review on the latest developments in modified vanadium-titanium-based SCR catalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 39(8): 1347-1365. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(18)63090-6 [12] LIU T K, WEI L Q, YAO Y Y, et al. La promoted CuO-MnOx catalysts for optimizing SCR performance of NO with CO[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 546: 148971. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.148971 [13] WANG Y, LI G G, ZHANG S Q, et al. Promoting effect of Ce and Mn addition on Cu-SSZ-39 zeolites for NH3-SCR reaction: Activity, hydrothermal stability, and mechanism study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 393: 124782. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124782 [14] ZHANG K, WANG J J, GUAN P F, et al. Low-temperature NH3-SCR catalytic characteristic of Ce-Fe solid solutions based on rare earth concentrate[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2020, 128: 110871. [15] WU Z B, JIN R B, LIU Y, et al. Ceria modified MnOx/TiO2 as a superior catalyst for NO reduction with NH3 at low-temperature[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2008, 9(13): 2217-2220. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2008.05.001 [16] NIU Y Q, SHANG T, HUI S E, et al. Synergistic removal of NO and N2O in low-temperature SCR process with MnOx/Ti based catalyst doped with Ce and V[J]. Fuel, 2016, 185: 316-322. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.07.122 [17] MARBERGER A, FERRI D, RENTSCH D, et al. Effect of SiO2 on co-impregnated V2O5/WO3/TiO2 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 320: 123-132. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.11.037 [18] LI Y, ZHANG Z, ZHAO X, et al. Effects of Nb-modified CeVO4 to form surface Ce-O-Nb bonds on improving low-temperature NH3-SCR deNO activity and resistance to SO2 & H2O[J]. Fuel, 2023, 331: 125799. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125799 [19] CHEN G, XU J, YU H, et al. Effect of the non-thermal plasma treatment on the structure and SCR activity of vanadium-based catalysts[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122286. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122286 [20] SALAZAR M, CRUZ A, CADENA A A, et al. Effect of the electronic state of Ti on M-doped TiO2 nanoparticles (M=Zn, Ga or Ge) with high photocatalytic activities: A experimental and DFT molecular study[J]. Material Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2017, 58: 8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2016.10.050 [21] ZHANG W G, LV D. Preparation and characterization of Ge/TiO2 one-dimensional photonic crystal with low infrared-emissivity in the 8~14 μm band[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2020, 124: 110747. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110747 [22] 李泽清. 低温抗硫抗碱钒基脱硝催化剂的研究[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2022. [23] 侯欣辛. 助剂对Fe-Mn催化剂低温抗硫脱硝活性的影响[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2020. [24] MUHAMMAD S A, NASRUDIN A R, PANDEY A K, et al. Improved electron transfer of TiO2 based dye sensitized solar cells using Ge as sintering aid[J]. Optik, 2018, 157: 134-140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.11.073 [25] FRANCOIS G, CHRISTOPHE G, NOLVEN G, et al. Individual amounts of Lewis and Brønsted acid sites on metal oxides from NH3 adsorption equilibrium: Case of TiO2 based solids[J]. Catalysis Today, 2020, 168: 259-268. [26] INHAK S, HWANGHO L, SE W J, et al. Understanding the dynamic behavior of acid sites on TiO2-supported vanadia catalysts via operando DRIFTS under SCR-relevant conditions[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 382: 269-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2019.12.041 [27] GAO Y, WU X D, RAN R, et al. Effects of MoOx on dispersion of vanadia and low-temperature NH3-SCR activity of titania supported catalysts: Liquid acidity and steric hindrance[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 585: 152710-152719. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152710 [28] ZHANG D J, MA Z R, WANG B D, et al. Effect of manganese and/or ceria loading on V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 NH3 selective catalytic reduction catalyst[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 379(23): 305-312. [29] CHEN L, LI J H, GE M F, et al. The poisoning effect of alkali metals doping over nano V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 170(26): 531-539. [30] MUHAMMAD S M, PULLUR A K, HEON P H. Novel sulfation effect on low-temperature activity enhancement of CeO2-added Sb-V2O5/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2014, 152(26): 28-37. [31] MITRAN G, NEATU F, PAVEL O D, et al. Behavior of molybdenum-vanadium mixed oxides in selective oxidation and disproportionation of toluene[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(5): 748-756. doi: 10.3390/ma12050748 [32] GONG P J, XIE J L, CHENG X K, et al. Elucidate the promotional effects of Sn on Ce-Ti catalysts for NH3-SCR activity[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2020, 93(3): 1053-1063. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2019.09.006 [33] LIU X S, SUI Z M, CEHN H F, et al. Structures and catalytic performances of Me/SAPO-34 (Me=Mn, Ni, Co) catalysts for low-tem perature SCR of NOx by ammonia[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 104: 137-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.11.018 [34] LI C, SRIRIM V, LIU Z Y, et al. Sequentially prepared Mo-V-Based SCR catalyst for simultaneous HgO oxidation and NO reduction[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2021, 614: 12. [35] DONG W K, KWANG H P, HEON P H, et al. The role of molybdenum on the enhanced performance and SO2 resistance of V/Mo-Ti catalysts for NH3-SCR[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 481: 1167-1177. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.118 [36] HU W S, ZHANG S, QI X, et al. Mechanistic investigation of NH3 oxidation over V-0.5Ce(SO4)2/Ti NH3-SCR catalyst[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2018, 112: 1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.04.010 -




 下载:
下载: