-
含酚废水主要来源于煤制气、制药和焦化过程,是目前极具代表性的高毒性难降解废水[1]。酚类物质是一种毒性很强的原型质毒物,对大部分生物都有影响,轻则腐蚀皮肤,重则使中枢神经受到抑制甚至引发癌症[2]。另外,酚类物质产量较大,据统计,每年全球产生的酚类物质大约有5×104 t[3]。鉴于其毒性大、产量大、分布广泛等特点,酚类污染物不仅是我国环境优先控制污染物之一,而且也是美国环保署列出的65种有毒污染物以及129种优先控制污染物之一[4]。
目前,含酚废水常见的处理方法主要有生化法和物化法,物化法以Fenton法和O3催化氧化法等高级氧化技术为主。生物法碍于较高的毒性降解效率低,制约了该方法在该类废水处理中的应用[5]。近年来,高级氧化技术因其高效、经济、无二次污染等特点备受研究者们的青睐。刘金泉等[6]发现多种O3耦合工艺降解有机物相较于单一O3均有更好的效果;姚宏嘉等[7]制备了生物炭负载γ-MnO2复合纳米材料来活化过一硫酸盐 (PMS) 降解对氯苯酚,反应40 min后降解率可达100%;马海涛[8]发现等离子体协同铁碳填料活化过硫酸盐 (PS) 对污水中苯酚去除率较高;朱彤等[9]发现UV/O3/TiO2耦合体系可以解决O3利用率低的问题,高效降解2,4,6-三氯苯酚。然而,高级氧化技术在应用过程中也存在一些问题,Fenton反应过程产生大量铁泥,造成后续处理负担大;臭氧均相或非均相催化氧化技术臭氧利用率低是导致运行成本高的主要原因。因此,针对难降解、高毒性有机物的去除,探索一种高效、清洁的水处理技术势在必行。
本研究选用苯酚作为目标污染物,利用UV催化O3和PS对含酚废水进行处理。对UV/O3、UV/PS、UV/O3/PS等工艺对苯酚的去除效果与矿化率进行比较;并对pH、O3投加量及PS投加量等影响因素进行研究;同时,对反应动力学、自由基产生规律进行分析,探索反应机理,为UV/O3/PS耦合工艺对含酚废水的降解提供可靠的理论基础。
-
1) 试剂。苯酚 (C6H7O) 、过硫酸钠 (Na2S2O8) 、氢氧化钠 (NaOH) 、铁氰化钾 (K3[Fe(CN)6]) 、4-氨基安替比林 (C11H13N3O) 、碳酸氢钠 (NaHCO3) 、叔丁醇 (C4H10O) 、氯化铵 (NH4Cl) ,均为分析纯;氨水 (NH3∙H2O,25%~28%) ;硫酸 (H2SO4,98%) ;无水乙醇 (C2H6O,99.5%) ;不含酚的去离子水。
2) 仪器。臭氧发生器 (ICT-10,美国Mellifiq有限公司) ;臭氧浓度仪 (IDEAL-2000,北京海富达科技有限公司) ;氧气流量检测仪 (D08-1F型,北京七星华创电子股份有限公司) ;紫外分光光度计 (DR6000,美国哈希水质分析仪器有限公司) ,用于苯酚浓度的定量分析;蠕动泵 (BT100-1L,保定兰格恒流泵有限公司) ;紫外灯 (NLC-050,40 W,工作波长253.7 nm,福建新大陆环保科技有限公司) ;总有机碳分析仪 (TOC-Lcph,日本岛津有限公司) ,用于TOC的定量分析;pH计 (S400-B,上海梅特勒托利多科技有限公司) ,用于检测反应前后的pH值;ESR分析仪 (JEOL FA-200,日本电子有限公司) 。
-
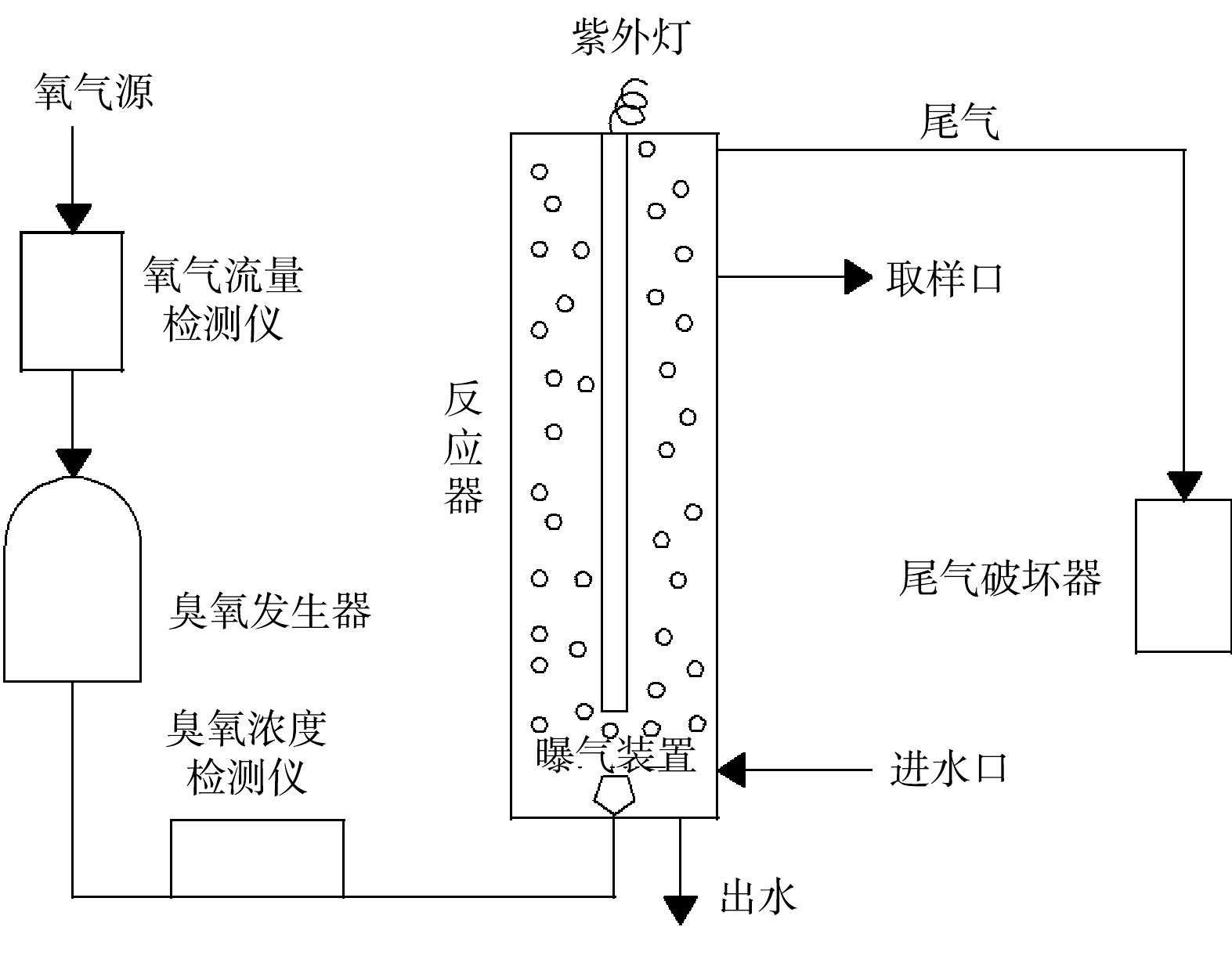
实验装置如图1所示。反应器为立式圆柱体,外壳材质为不锈钢,内径5 cm,高为1.1 m,有效容积为1 L,反应器内嵌紫外灯,由石英玻璃管 (直径为28 mm,高度为90 mm) 作保护套管,反应器底部装有O3布气器;设备配置O3发生器,以纯氧为气源,氧气流量检测仪控制氧气流量,并利用O3浓度测试仪实时监测反应器O3浓度;反应后尾气进入O3破坏装置净化后外排;Na2S2O8在水样进入反应器前添加到水样中。
-
1) 苯酚降解实验。配制一定浓度的苯酚模拟废水,将一定量的Na2S2O8提前加入水样中,用蠕动泵将水从反应器底部进水口抽入反应器中;待反应器充满后,打开氧气管道阀门,当氧气流量监控仪示数稳定后,通过操作面板上的按键控制O3发生器与紫外灯的开启。通过调整O3发生器的功率,观察O3浓度检测仪的示数可以调整氧气被高压电场放电转化的效率,从而调整固定时间内O3的总投加量[10],O3总投加量为氧气流量监控仪、O3浓度测试仪和反应时间的乘积。
2) 协同因子计算。UV/O3/PS耦合工艺的协同效应可以用协同因子[11]来表示,计算方法见式(1)~式(4)。协同因子大于1时,表示该反应体系具有良好的协同效应。
式中:f1为UV/O3/PS 体系与UV/O3、PS体系的协同因子;f2为UV/O3/PS 体系与UV/PS、O3体系的协同因子;f3为UV/O3/PS 体系与O3/PS、UV体系的协同因子;f4为UV/O3/PS 体系与UV、O3、PS体系的协同因子; r (UV/O3/PS) 、r (UV/O3) 、r (UV/ PS) 、r (O3/ PS) 、r (UV) 、r (O3) 、r (PS) 分别为UV/O3/PS、UV/O3、UV/ PS、UV、O3、PS反应体系中苯酚的去除率。
3) 反应动力学模型。为了进一步对3种降解效果明显的工艺进行比较,对其降解过程进行了动力学拟合。苯酚与溶解O3和自由基的反应可视为二级平行反应,因此,动力学方程[12]见式(5)。
式中:C为苯酚的质量浓度,mg·L−1;
${{k}}_{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ 和${{k}}_{\text{ROS}}$ 为O3反应和自由基反应的反应速率;${{C}}_{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ 和${{C}}_{\text{ROS}}$ 为水溶液中O3和自由基的质量浓度,mg·L−1;t为时间,min。式(5)变形后可得式(6)。
式中:k为反应动力学常数,min−1;
${{k}\text{=}{k}}_{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{C}}_{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{+}{{k}}_{\text{ROS}}{{C}}_{\text{ROS}}$ ;其他符号说明见式(5)。将式(6)进行积分,可得式(7)。
式中:C为任意时刻苯酚的质量浓度,mg·L−1;C0为初始时刻苯酚质量浓度,mg·L−1;k为拟一级反应动力学常数,min−1;t为时间,min。
-
O3质量浓度采用O3浓度仪检测;pH值采用pH计测定;总有机碳测定采用TOC分析仪;苯酚质量浓度采用HJ503-2009的4-氨基安替比林分光光度法[13]测定;自由基采用电子自旋共振波谱仪 (ESR) 检测,使用5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯烷-N-氧化物 (DMPO) 对UV/O3/PS反应体系中产生的自由基进行捕获,检测UV/O3/PS体系中产生的活性物质与DMPO形成的加合物,中心磁场强度为3.5×107 T、扫描宽度为1×106 T、频率为9.5 GHz、功率为2.25 mW。
-
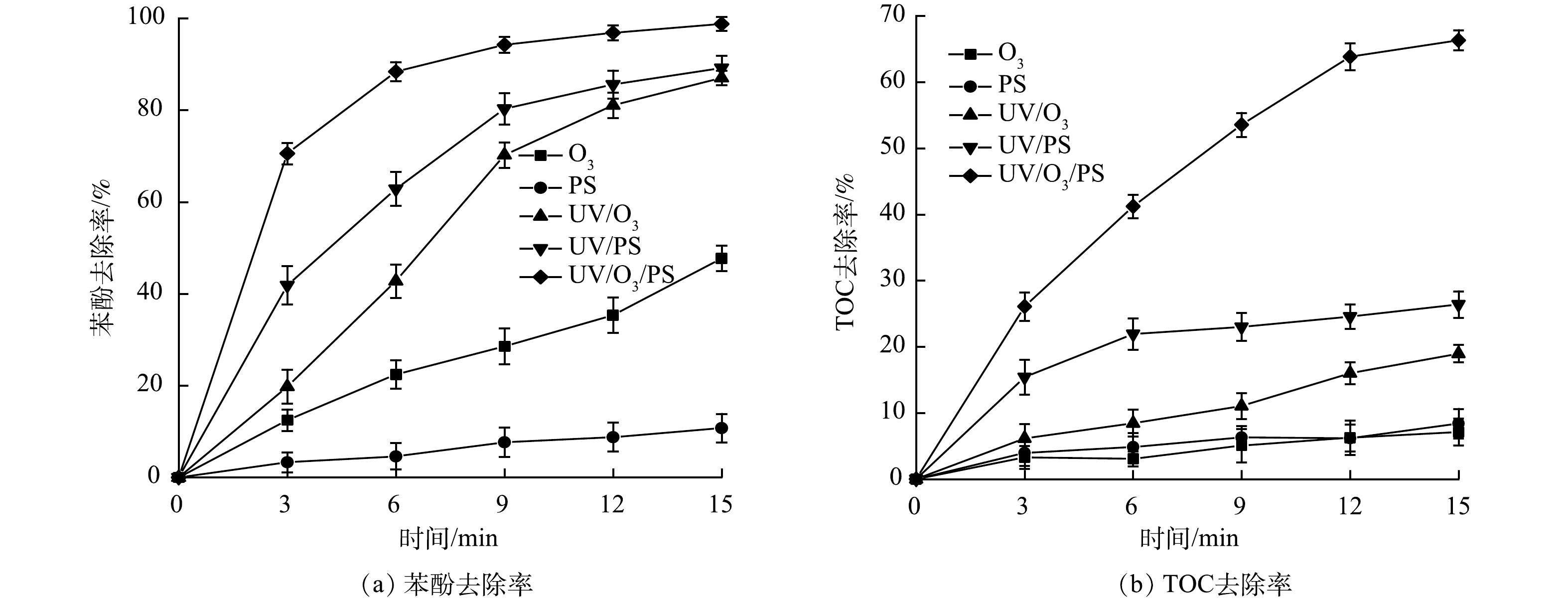
不同工艺的降解效果对比见图2。实验中配制25 mg·L−1的苯酚模拟废水,原水pH=6;Na2S2O8投加量均为1 mmol·L−1;O3质量浓度为50 mg·L−1、氧气流量为200 mL·min−1,据计算,O3投加量为10 mg·min−1;原水TOC为18.56 mg·L−1。图2(a)为不同工艺体系对苯酚的去除效果。可以看出UV/O3/PS体系相比其他体系对苯酚的降解效果更好。单一的O3或单一的PS对苯酚的降解能力较弱。反应3 min时,UV/O3/PS体系对苯酚的去除率达70.56%,UV/O3与UV/PS体系对苯酚的去除率分别为19.78%和41.85%。随着反应时间的延长,各反应体系对苯酚的去除效率均有所提高。当反应达到15 min时,UV/O3/PS体系对苯酚的去除率已经达到98.78%,而UV/O3体系和UV/PS体系只达到87.04%和89.19%。
图2(b)体现了反应过程中不同反应体系对苯酚的矿化效果。可以看出,反应进行15 min后,UV/O3/PS体系对苯酚有很好的矿化作用,矿化率可达66.33%,而UV/O3与UV/ PS体系对苯酚的矿化率分别为18.97%和26.4%。由以上结果可知,UV/O3/PS耦合工艺对苯酚降解和矿化作用均优于UV/O3和UV/PS体系,特别是对苯酚的矿化作用优势尤为明显。原因可能是:O3是一种强氧化剂,但其自身具有选择性,单独使用降解效率不高。PS与O3类似,氧化还原电位为2.01 V,常温下较为稳定,通常反应速率较为有限[14];相较于单一的O3或PS体系,在UV的催化下,O3会通过链式反应产生氧化还原电位较高 (1.8~2.7 V) 且不具有选择性的羟基自由基 (·OH) ,从而大幅提高降解能力。而UV/O3/PS体系相比起UV/O3体系,PS在受到UV催化后会产生·OH和硫酸根自由基 (·SO4−) ,其中,·SO4−同样拥有高氧化还原电位 (2.5~3.1 V) 且不具备选择性,并且·SO4−还拥有比·OH更长的半衰期及更广的pH适用范围[15],因此,在UV/O3体系中引入PS对促进强氧化性物质产生有显著作用,是UV/O3/PS体系相较于其他体系具有更强的降解、矿化能力的主要原因。
-
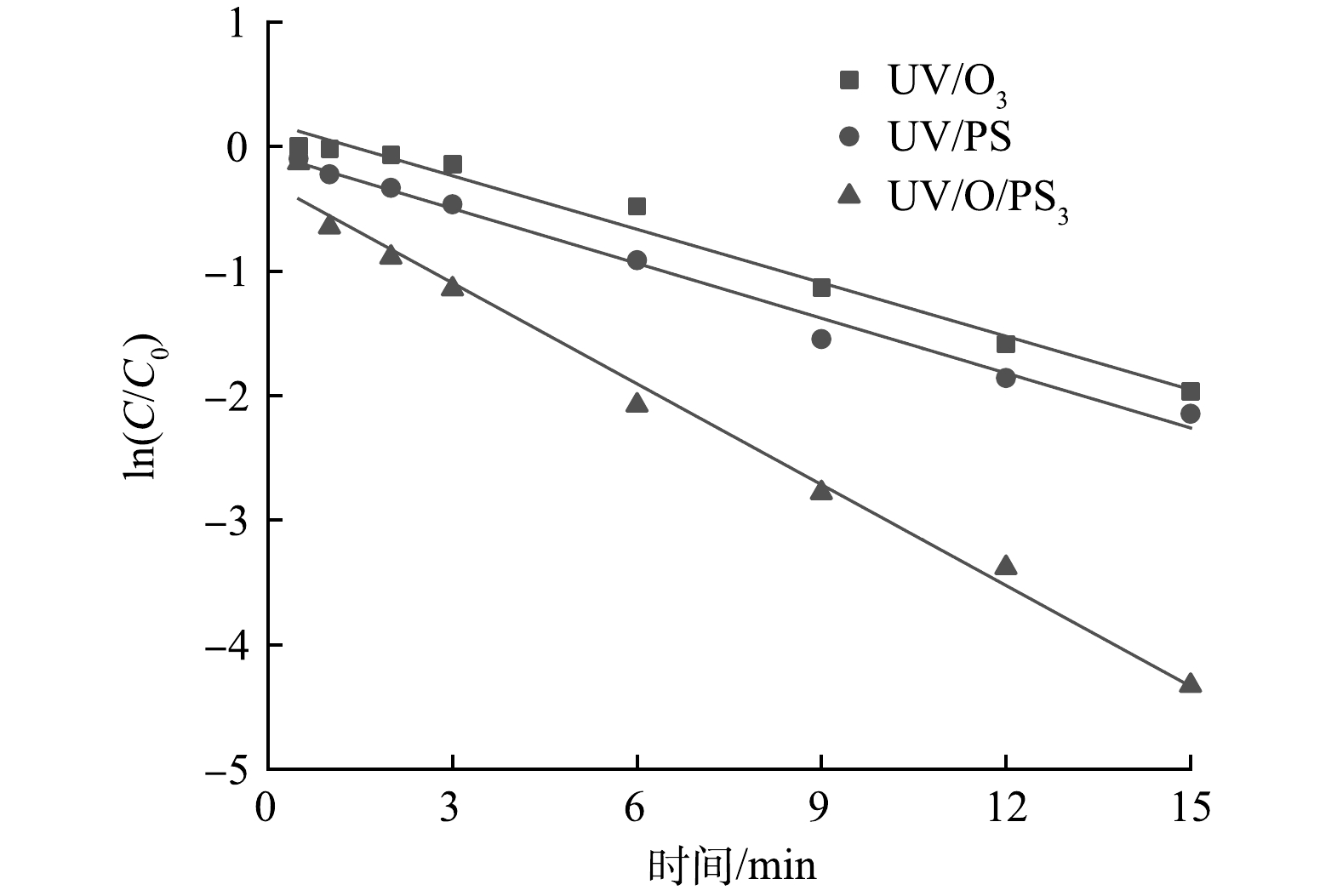
反应动力学分析结果如图3所示。可以看出:UV/O3、UV/PS、UV/O3/PS工艺对苯酚的降解均符合准一级反应动力学模型,反应动力学方程如表1所示。UV/O3/PS工艺的反应速率常数为0.269 9 min−1,高于UV/O3工艺的0.143 1 min−1和UV/PS工艺的0.146 8 min−1,说明UV/O3/PS耦合工艺的反应速率更快,对苯酚的降解更高效。同时,经过计算可知:反应6 min时,协同因子f1、f2、f3、f4分别为1.87、1.40、3.38和3.83;反应15 min后,协同因子f1、f2、f3、f4分别为1.01、1.01、1.55和1.85。由此可见,UV/O3/PS工艺也具有良好的协同效应。
-
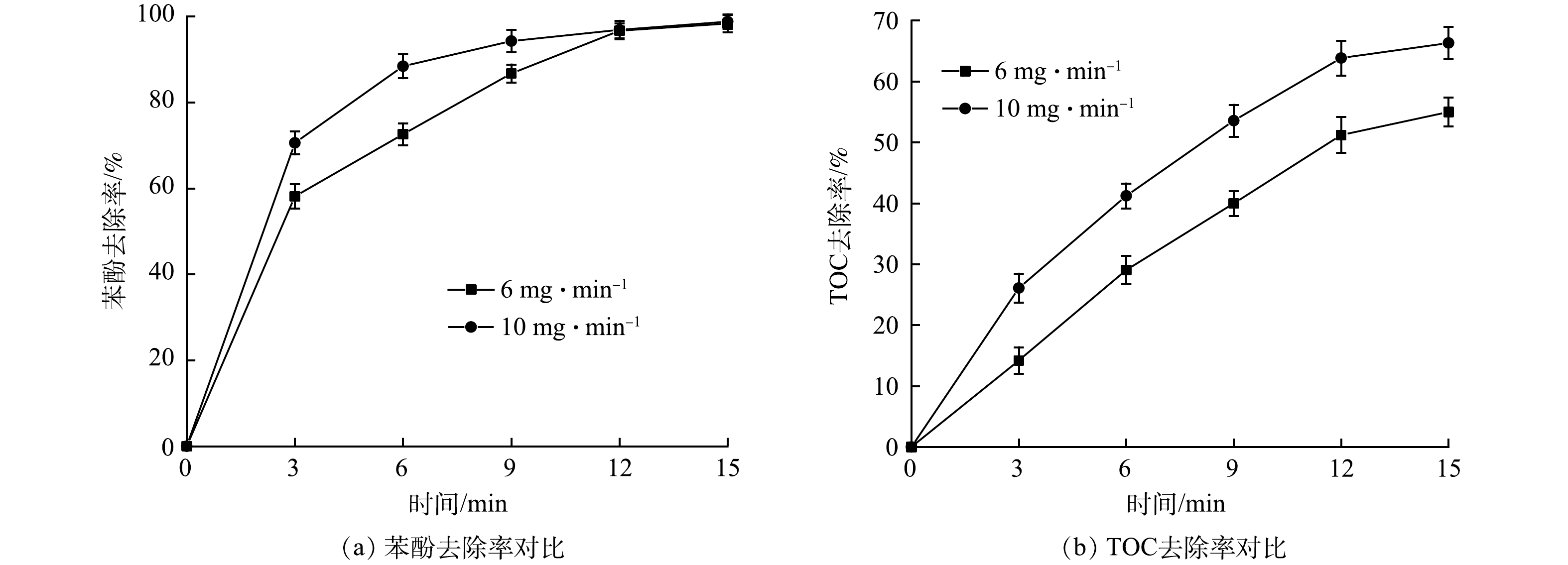
1) O3投加量的影响。不同O3投加量对苯酚降解的影响如图4所示,反应条件除O3投加量外与2.1节中的条件相同。可以看出,随着O3投加量的增加,苯酚的降解效率和矿化效率均有所提高,这可能是由于O3在水中受到254 nm紫外光激发会初步生成·OH和·HO2,·OH 会与水中的有机物反应进一步产生·O2−;随后,·O2−与O3会快速反应产生·O3−,进一步形成大量·OH,反应式[16-17]见式(8)~式(10)。当O3浓度降低时,·OH的产量随之降低,进而导致降解效率降低。另外,也有研究[18]表明,当水中O3投加量过高时,一些没有及时分解的O3同样会消耗·OH干扰链式反应,反应式见式(11)。因此,O3的投加量需要控制在适当的范围内,过高或过低都会降低系统的矿化效率。
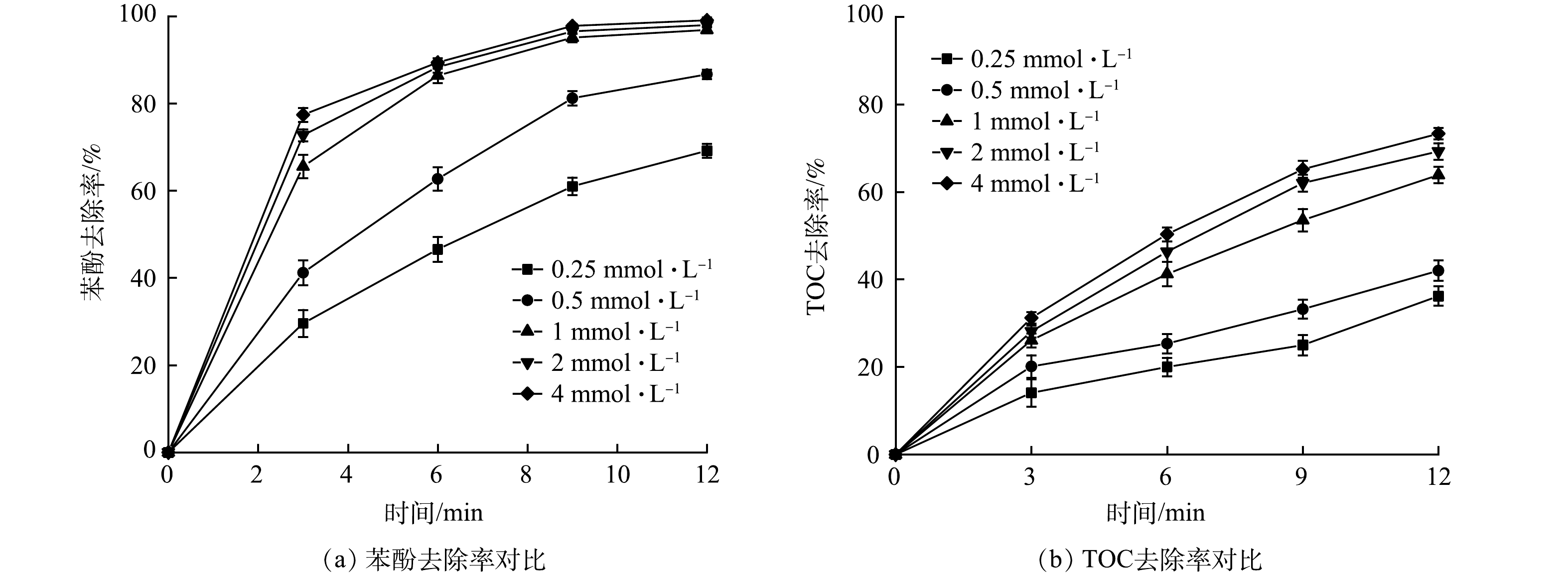
2) PS投加量的影响。由图5可知,随着PS投加量的增加,UV/O3/PS体系对苯酚的降解效果也随之增强 (反应条件除PS投加量外同2.1节) 。在反应时间为3 min时,投加0.25 mmol·L−1 PS对苯酚的降解率为29.59%,随着PS投加量的增加对苯酚的降解效率也随之增加,当投加量为4 mmol·L−1时达到77.41%,矿化效率同样随着PS投加量的增加而提高。主要原因是:在其他影响因素不变的情况下,随着反应体系内PS浓度的增加,UV催化后产生的·OH和·SO4−的浓度也随之增加,进而提高苯酚去除率。实验结果表明,在PS投加量为1 mmol·L−1,反应时间为6 min的情况下,苯酚的去除率已经达到86.41%,与此同时投加2 mmol·L−1和4 mmol·L−1的体系中苯酚的去除率为88.33%和89.41%。可以看出,尽管PS投加量和降解效率成正相关,但大量投加相比于适量投加提升率有限;有研究[19]表明,PS含量过多的污水排放到土壤中,受热可能将铵盐转化为硝基副产物造成污染。因此,在实际应用中应当适量投加Na2S2O8。
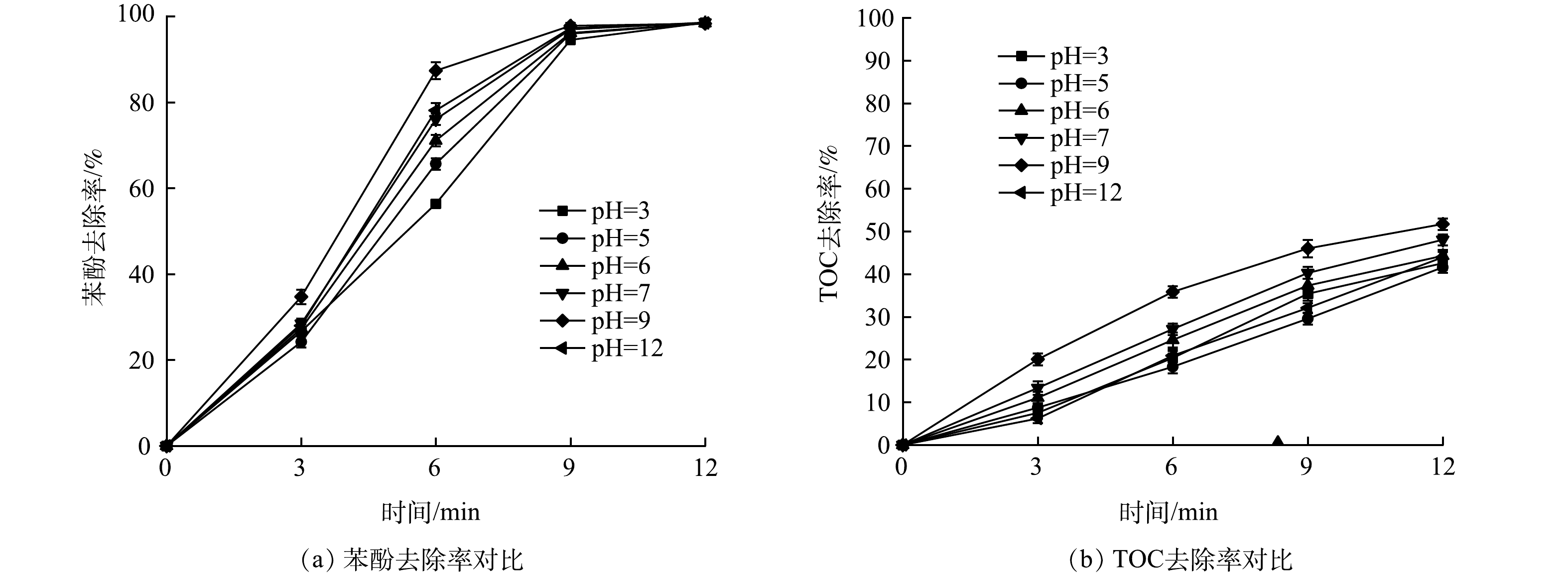
3) pH的影响。pH是影响高级氧化效果的重要因素之一。实验前测定配置苯酚质量浓度为25 mg·L−1时溶液的pH为6.8,其他反应条件同2.1节。反应前,用1 mol·L−1的H2SO4和NaOH溶液调节反应体系的pH至约3、5、7、9、11,考查偏酸、偏碱性条件下苯酚的降解效果和矿化效果。由图6可以看出,随着pH逐渐升高,苯酚的去除率呈先升高后降低的趋势,当pH大于9时,去除率降低,但总体差距并不大,说明UV/O3/PS体系对苯酚的降解矿化受pH的影响较小,适用范围较广。其原因[20]是:首先,pH越高,不仅可以促进O3链式反应中·OH的产生,还可以促进·SO4−的产生,因此碱性条件下苯酚的降解速率高于酸性环境;其次,当pH过高时,反而会使链式反应向产生·O2−的一边偏移,产生·OH的量减少,进而降低苯酚的去除率[21],因而使得pH=11的体系降解效率和矿化率低于pH=9的体系;此外,酸性条件下无法促进·OH的产生,·SO4−也会与酸反应生成一些氧化能力一般的中间体,反应式见式(12)。因此,理论上酸性条件下苯酚的降解效率低于中性与碱性条件。但另一方面,通过酸活化S2O82−的不对称—O—O—键,可以产生额外的·SO4−,反应见式(13) [22],且反应过程中pH并未有升高的情况,故苯酚的降解与矿化相较于中性条件下并未有较大差距,说明UV/O3/PS体系对酸碱度的适应范围较广。
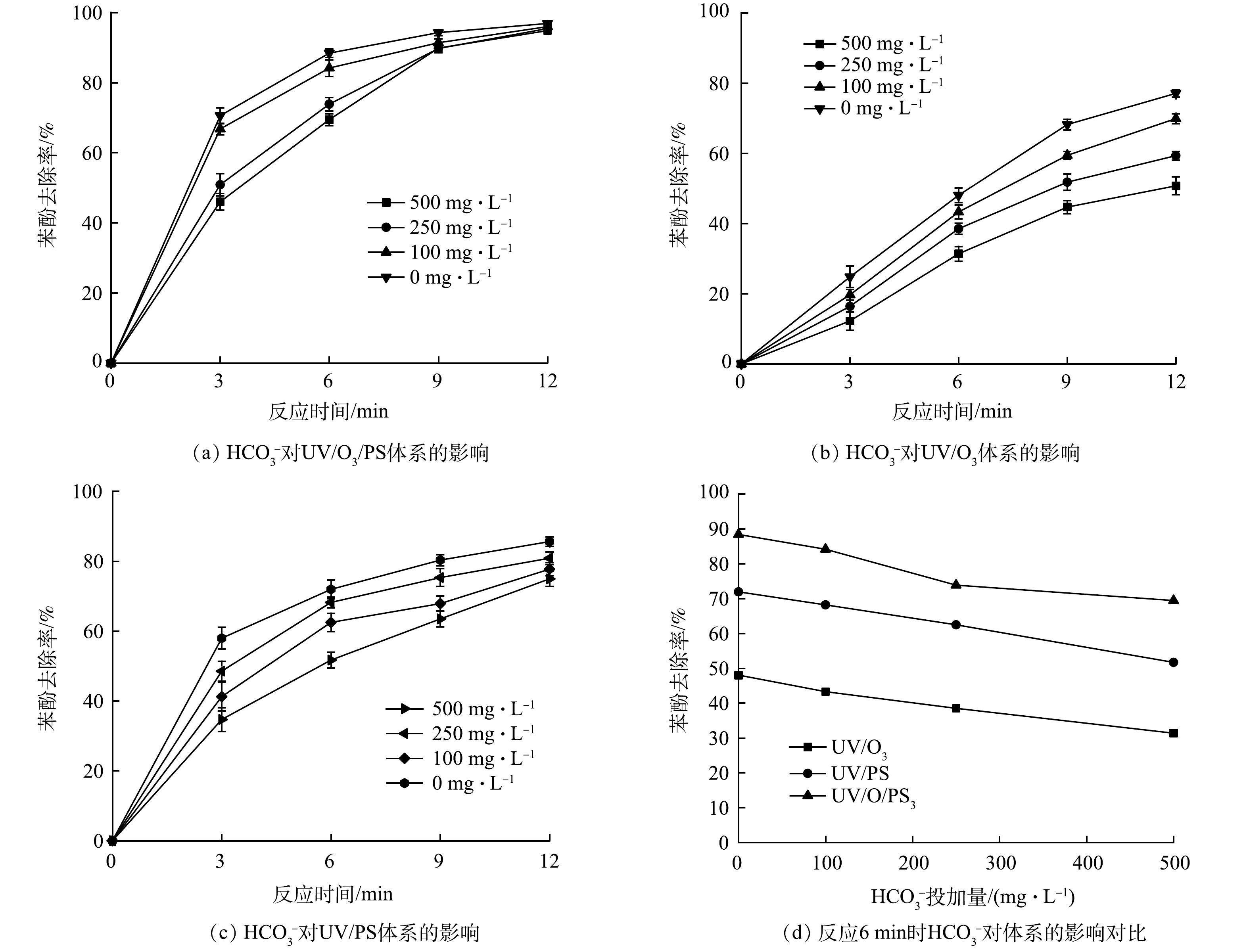
4) 碳酸氢根的影响。碳酸根和碳酸氢根是水体中最常见的自由基捕获剂,有研究[23]表明,水体中的无机碳主要以HCO3−的形式存在,质量浓度为50~250 mg·L−1左右。HCO3−会与水中的·OH反应生成CO2和H2O,使原本参与降解苯酚的·OH的量减少,从而影响苯酚的降解。实验前,用NaHCO3配制含HCO3−质量浓度为100、250、500 mg·L−1的模拟废水,加入UV/O3和UV/O3/PS 2种反应体系中,考查HCO3−对苯酚降解的抑制作用,比较2种反应体系对HCO3−干扰的适应能力 (其他反应条件与2.1节相同) ,实验结果如图7所示。可以看出,在未加入HCO3−时,反应3 min,苯酚去除率达到了70.56%,而投加500 mg·L−1的HCO3−后去除率只有46.00%,降低了24.56%。原因是:UV催化O3与PS产生的·OH和·SO4−被HCO3−及其水解产物抢先反应,导致降解苯酚的自由基数量减少,反应式[24]如式(14)~式(18)所示。已有研究[25]表明,苯酚与·OH反应速率常数k约为2.63×106 mol·(L·s)−1,HCO3−和CO32−与·OH反应速率常数k分别为8.5×106 mol·(L·s)−1和3.9×108 mol·(L·s)−1,苯酚的降解易受到HCO3−和CO32−的干扰,因而降解效果变差。
而在UV/O3体系中,反应3 min、投加500 mg∙L−1 HCO3−时,由图7可以看出,UV/O3体系中苯酚的降解率仅有12.26%,与未添加相比去除率降低了12.55%;当反应时间达到9 min时,苯酚的去除率相比起UV/O3/PS体系仍较低;在UV/PS体系中,尽管降解效果同样受到了HCO3−和CO32−的影响而降低,但在反应进行到12 min时,投加500 mg∙L−1 HCO3−的去除率仅降低了10.66%。这是因为,HCO3−及CO32−与·OH的反应速率相比·SO4−较高,HCO3−和CO32−与·SO4−反应速率常数k分别为2.8×106 mol·(L·s)−1和6.1×106 mol·(L·s)−1,故对UV/O3体系的影响也就越大[24]。
-
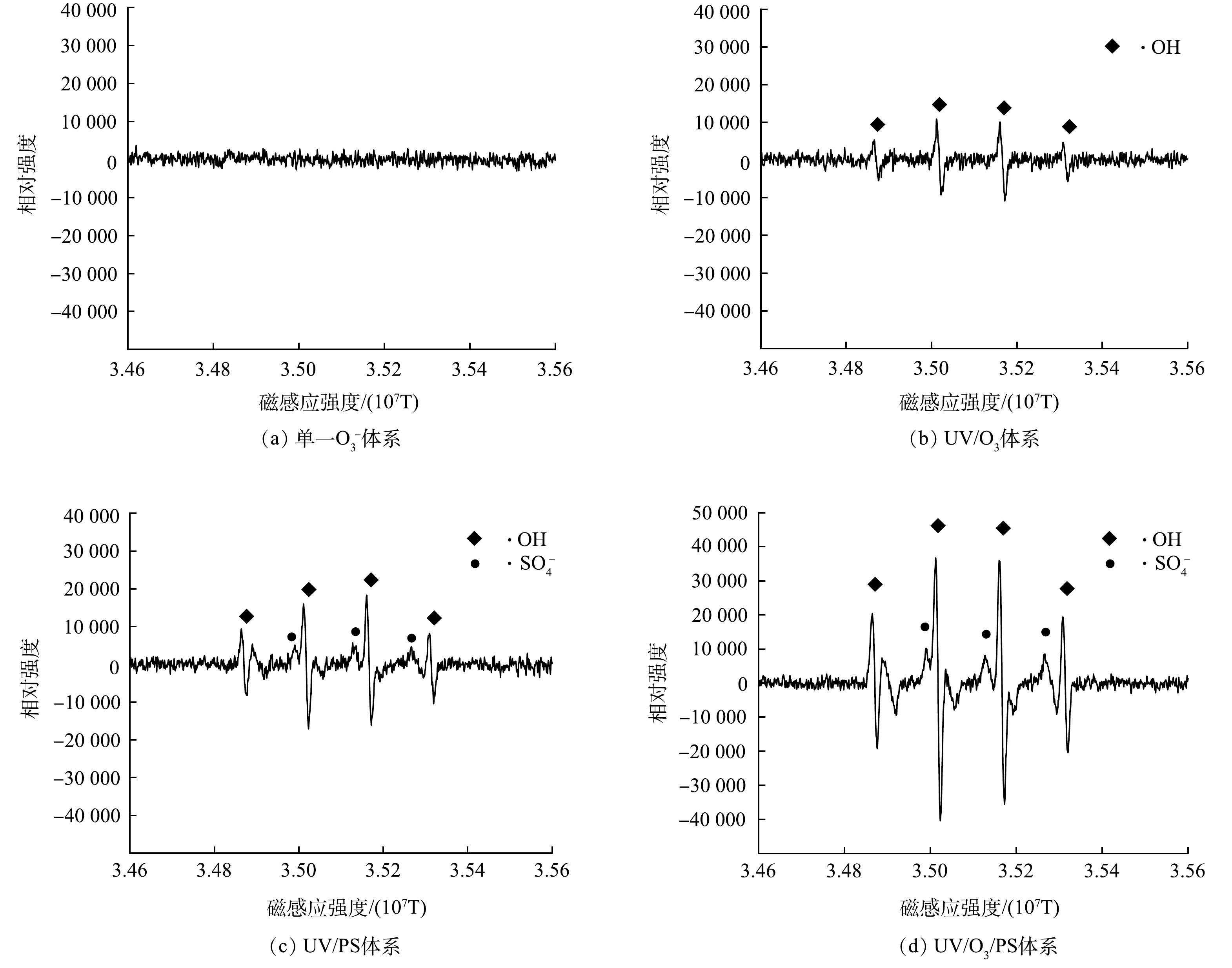
强氧化性活性物质的产生量是影响反应体系降解有机物效率的关键因素,在本研究中,采用ESR对单一O3、UV/O3、UV/PS、UV/O3/PS 4种体系分别进行自由基检测,结果如图8所示。可以看出,实验检测到1:2:2:1的四重峰和1:1:1的三重峰,这是典型的DMPO捕获·OH和·SO4−的形成的DMPO-·OH加合物和DMPO-·SO4−加合物特征峰。在单独O3反应体系中未能检测出明显的DMPO-·OH加合物和DMPO-·SO4−加合物特征峰,说明在该反应体系中,O3直接氧化反应占主导地位;在UV/O3、UV/PS和UV/O3/PS体系中,检测到了明显的DMPO-·OH加合物特征峰,说明在此3个反应体系中产生了具有强氧化性质的·OH,并且从图(8)中可以看出3个反应体系产生的·OH的量从大到小排序为UV/O3/PS>UV/PS>UV/O3。UV/PS体系中还检测到DMPO-·SO4−加合物特征峰,说明在UV的催化下,PS分解产生了·OH和·SO4−,并且DMPO-·OH加合物的特征峰强度略高于UV/O3体系;在UV/O3/PS体系中,同样同时检测到了DMPO-·OH加合物和DMPO-·SO4−加合物特征峰,并且这2种特征峰强度均高于UV/O3或UV/PS体系。这表明耦合体系对自由基的产生具有促进作用,强氧化性物质的产量增加,进而强化了对污染物的去除效果。
-
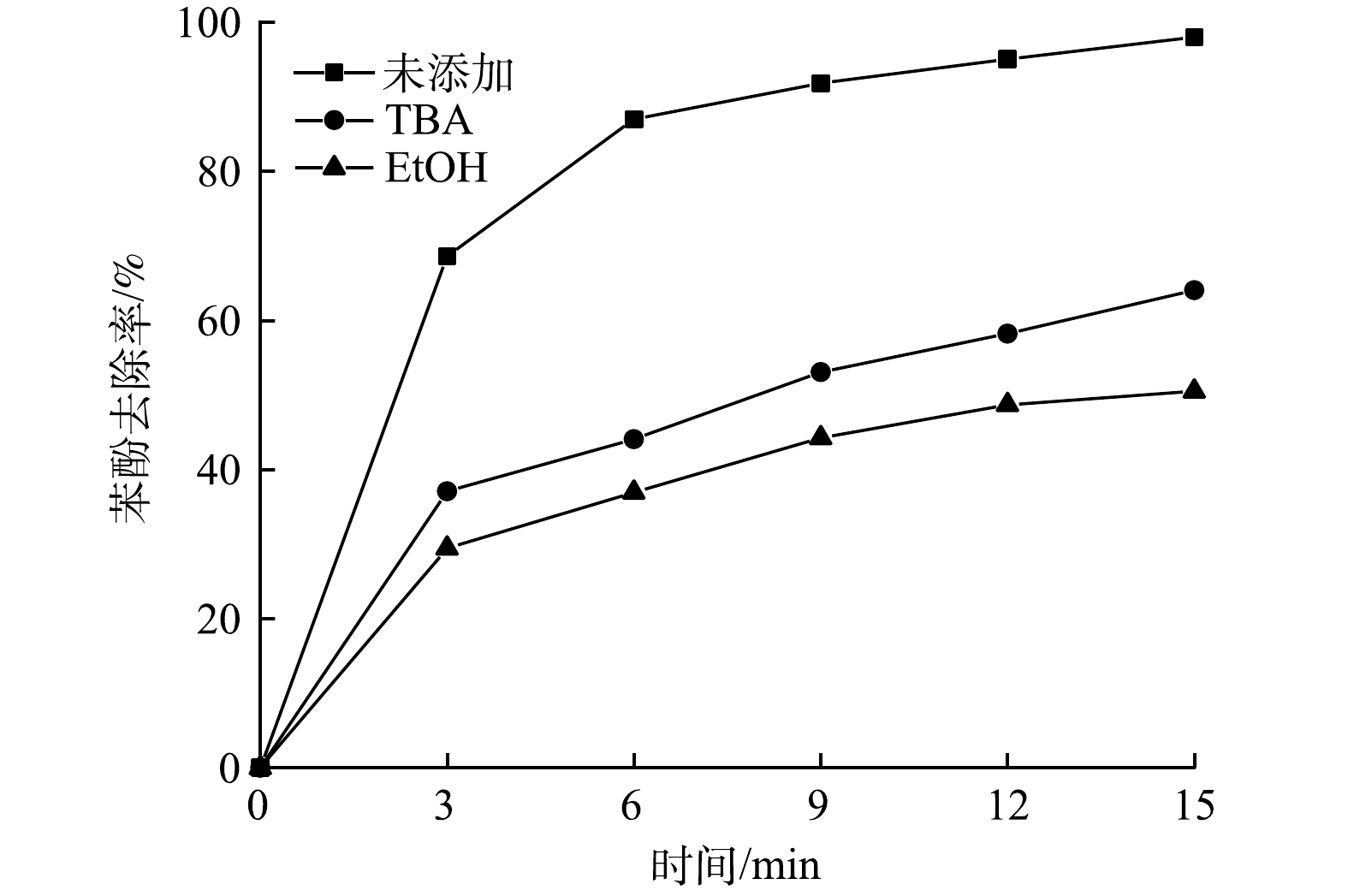
采用淬灭实验来验证活性物质对降解有机物的作用。·OH和·SO4−是UV/O3/PS体系中的主要自由基,而叔丁醇 (TBA) 和乙醇 (EtOH) 是这2种自由基常见的淬灭剂,EtOH与·OH和·SO4−的反应速率分别为0.8×109~1.0×109 mol·(L·s)−1和 0.9×107~1.3×107 mol·(L·s)−1,TBA与·OH和·SO4−的反应速率分别为3.8×108~7.6×108 mol·(L·s)−1和4.0×105~9.1×105 mol·(L·s)−1[25-26],因此,EtOH可以与·OH和·SO4−快速反应产生中间惰性物质,使自由基难以参与对苯酚的降解,而TBA则近似看作仅与·OH快速反应产生惰性物质。过量的淬灭剂可使·OH和·SO4−完全淬灭,本实验将适量的EtOH与TBA添加到废水中,投加量均为50 mmol∙L−1。其他反应条件同2.1节,分别进行2次实验,实验结果如图9所示。可以看出,当废水中含有EtOH时,苯酚的降解率从不含自由基捕获剂的98.78%降到了50.48%,而当废水中含有TBA时,苯酚降解率降到了64.04%,略高于含有EtOH的体系。其原因是TBA淬灭了·OH的活性,但是·SO4−仍具有较强的氧化性,对苯酚的降解作用依然存在。
-
1) 由实验结果对比可知:单一的O3或PS对苯酚的降解效果不佳,UV/O3、UV/PS、UV/O3/PS工艺对苯酚均有降解效果,而UV/O3/PS对苯酚的降解速率和矿化率则明显优于其他工艺;并且从反应动力学和协同因子上来看,UV/O3/PS体系也拥有最高的反应速率常数和最好的协同效果。
2) UV/O3/PS体系中,随着O3或PS投加量的增加,苯酚的去除效率也随之增加,但考虑到经济及污染等方面,对于25 mg·L−1的苯酚质量浓度,投加100 mg·L−1的O3及1 mmol·L−1的Na2S2O8较为合适。
3) UV/O3/PS体系中,去除有机物的主要活性物质为·OH和·SO4−,而非 O3或PS对苯酚的直接氧化;UV/O3/PS耦合体系对自由基的产生具有促进作用,活性物质产量较高,且对pH和HCO3−的适应范围较广。
UV/O3/PS耦合工艺在含酚废水处理中的应用
Application of UV/O3/PS coupling process in the treatment of phenol wastewater
-
摘要: 针对目前高级氧化技术处理含酚废水存在O3利用率低等缺点,为提高反应体系强氧化性物质的含量,强化水体中酚类物质的降解与矿化,提出了UV/O3/PS耦合体系;在探究多种不同耦合体系的苯酚降解率和TOC去除率、反应影响因素和活性物质的基础上,进一步发掘该体系降解含酚废水的潜力与优势。结果表明:UV/O3/PS体系在15 min内可将苯酚完全降解;相较于单一的UV/O3法或UV/PS法,水中酚类的矿化率分别提高了47.36%和39.93%;通过对多种影响因素进行分析,确定了UV/O3/PS体系中合适的O3与PS投加量,并发现UV/O3/PS体系对pH和HCO3− 适应范围较广,在难降解废水处理中具有广泛的应用价值;通过ESR分析发现耦合体系在UV的催化下产生的·OH和·SO4−比单一体系更多,具有促进作用。由此可知,UV/O3/PS耦合工艺能在较广的适应范围内较好的降解酚类物质。该研究结果可为UV/O3/PS耦合工艺对含酚废水的降解提供理论参考。Abstract: In view of the low utilization rate of O3 in the treatment of phenol containing wastewater by the advanced oxidation technology at current, UV/O3/PS coupling system is proposed to improve the content of strong oxidizing substances in the reaction system and strengthen the degradation and mineralization of phenol substances in the wastewater; On the basis of exploring the phenol degradation rate, TOC removal rate, reaction influencing factors and active substances of various coupling systems, the potential and advantages of this system in degrading phenolic wastewater were further studied. The results showed that the UV/O3/PS system could completely degrade phenol within 15 minutes. Compared with the single UV/O3 method or UV/PS method, the mineralization rate of phenols in water increased by 47.36% and 39.93%, respectively. Through analysis of various influencing factors, the appropriate dosages of O3 and PS in the UV/O3/PS system were determined. It was found that the UV/O3/PS system had a wide range of adaptability to pH and HCO3−, which implied that this system had an extensive application value in the treatment of refractory wastewater. In addition, ESR analysis showed that the coupling system produced more ·OH and ·SO4− under the catalysis of UV than the single system, which had a promoting effect. Thus, the UV/O3/PS coupling process had a better performance on phenols degradation in a wide range of applications. The research results can provide a theoretical reference for the degradation of phenolic wastewater by UV/O3/PS coupling process.
-
Key words:
- UV/O3/PS /
- free radical /
- phenolic wastewater /
- advanced oxidation /
- synergistic effect
-

-
表 1 不同工艺的准一级动力学参数
Table 1. Quasi first order kinetic parameters of different processes
工艺名称 速率常数k/ min−1 R2 动力学方程 UV/O3/PS 0.269 9 0.988 3 ln(C/C0)=−0.269 9t−0.287 1 UV/O3 0.143 1 0.981 5 ln(C/C0)=−0.143 1t+0.192 9 UV/PS 0.146 8 0.988 0 ln(C/C0)=−0.146 8t-0.058 8 -
[1] 王勇, 杜明辉, 张宁, 等. α-Fe2O3催化臭氧氧化处理苯酚废水效果及机理[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(8): 1-14. [2] KALAICHELVAN S, SUNDARAGANESAN N, DERELIO, et al. Experimental, theoretical calculations of the vi-brational spectra and conformational analysis of 2, 4- di-tert-butylphenol[J]. Spectrochimica Acta:Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2012, 85(1): 198-209. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2011.09.061 [3] BACH C, DAUCHY X, SEVERIN I, et al. Effect of temperature on the release of intentionally and non-intentionally added substances from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles into water: Chemical analysis and potential toxicity[J]. Food Chemistry, 2013, 139(1/2/3/4): 672-680. [4] MACRAENA R, JOSEMANUEL M M, INMACULADA J D, et al. Screening of hormone-like activities in bottled waters available in Southern Spain using receptor-specific bioassays[J]. Environment International, 2015, 74(5): 125-135. [5] 强喆林, 王玲, 吴迪, 等. 含酚废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 当代化工, 2021, 50(9): 2206-2210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2021.09.042 [6] 刘金泉, 李天增, 王发珍, 等. O3、H2O2/O3及UV/O3在焦化废水深度处理中的应用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(3): 501-505. [7] 姚宏嘉, 陈星, 张玉, 等. 生物炭负载γ-MnO2纳米复合材料活化过一硫酸盐降解对氯苯酚的性能及机理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(6): 1833-1844. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202201078 [8] 马海涛. 等离子体协同铁碳微电解活化过硫酸盐降解苯酚的研究[D]. 内蒙古: 内蒙古科技大学, 2021. [9] 朱彤, 杨世鹏, 谭伟强, 等. UV/O3/TiO2耦合工艺降解2, 4, 6-三氯苯酚[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(3): 7-13. [10] 黄会静, 许钊. 净水厂常用进口臭氧发生器设备选型对比[J]. 科学技术创新, 2021(2): 160-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2021.02.068 [11] SUN C, CHEN T, HUANG Q X, et al. Activation of persulfate by CO2-activated biochar for improved phenolic pollutant degradation: Performance and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 380: 122519. [12] 陆一新, 何悦, 张建强, 等. UV/PS降解阿特拉津机理及动力学分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(3): 635-642. [13] 大连市环境监测中心. 水质 挥发酚的测定 4-氨基安替比林分光光度法: HJ 503-2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. [14] 杨世迎, 陈友媛, 胥慧真, 等. 过硫酸盐活化高级氧化新技术[J]. 化学进展, 2008, 20(9): 1433-1438. [15] LIU B, QU F S, CHEN W, et al. Microcystis aeruginosa- laden water treatment using enhanced coagulation by persulfate/Fe(II), ozone and permanganate: Comparison of the simultaneous and successive oxidant dosing strategy[J]. Water Research, 2017, 125: 72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.035 [16] ACERO, JUAN L, VON G T, et al. Characterization of oxidation processes: Ozonation and the AOP O3/H2O2[J]. Journal American Water Works Association, 2001, 93(10): 90-100. doi: 10.1002/j.1551-8833.2001.tb09311.x [17] STAEHELIN J, HOIGNE J. Decomposition of ozone in water in the presence of organic solutes acting as promoters and inhibitors of radical chain reactions.[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1985, 19(12): 1206-1213. [18] 邵青, 王颖, 李晶, 等. 紫外/臭氧工艺在水处理中的技术原理及研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2019, 35(14): 16-23. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.14.003 [19] 杨培增, 岳泓伸, 季跃飞, 等. 土壤铵氮在热活化过硫酸盐氧化过程中的转化[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(1): 267-275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.01.029 [20] QIN W L, LIN Z, SUN L, et al. A preliminary study on the integrated UV/ozone/persulfate process for efficient abatement of atrazine[J]. Ozone Science and Engineering, 2020, 42: 558-564. doi: 10.1080/01919512.2020.1746631 [21] 陈傲蕾, 常风民, 汪翠萍, 等. O3/UV降解含氮杂环化合物喹啉[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(10): 3884-3890. [22] YANG, Y, GUO, H G, ZHANG, Y L, et al. Degradation of bisphenol a using ozone/persulfate process: Kinetics and mechanism[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2016, 227(2): 53. doi: 10.1007/s11270-016-2746-x [23] 李海翔, 林华, 陆兰晶. 硝基苯类化合物高级氧化与生物还原处理技术研究[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2014. [24] TAN C Q, GAO N Y, DENG Y, et al. Degradation of antipyrine by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/PS[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 260(C): 1008-1016. [25] YANG W W, WU T T. Investigation of matrix effects in laboratory studies of catalytic ozonation processes[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(8): 3468-3477. [26] 林艺佳. 过氧化钙强化Fenton氧化处理苯酚废水的性能及机制研究[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2021. -



 下载:
下载: