-
厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonia oxidation,ANAMMOX)是一种利用厌氧氨氧化菌(anaerobic ammonia oxidation bacteria,AnAOB)在厌氧/缺氧条件下以NO2−-N为电子受体,将NH4+-N转化为N2和少量NO3−-N的新型生物脱氮技术[1]。ANAMMOX工艺被公认是替代完全硝化-反硝化工艺的废水脱氮技术[2]。相比于完全硝化-反硝化工艺,ANAMMOX具有曝气能耗低、无需投加有机碳源和污泥产量少等特点,在处理高氨氮或低C/N废水时优势显著,是水处理领域的热点技术[3-4],可广泛应用于印染废水[5]、铁路粪便污水[6]、垃圾渗滤液[7-8]、污泥消化液[9]等高氨氮废水处理领域。垃圾渗滤液是一类典型的含有高浓度NH4+-N和有机物的难处理废水。部分亚硝化/厌氧氨氧化(partial nitritation/ANAMMOX,PN/A)作为一种先进的自养脱氮技术特别适用于垃圾渗滤液处理。由于垃圾渗滤液中有机物浓度过高,不利于AnAOB生长,长期运行ANAMMOX甚至可能被反硝化所取代[10]。而且,PN/A工艺的脱氮效率理论上最高只有89%[11]。为了提高脱氮效率,研究者对基于ANAMMOX的各种组合工艺开展了广泛研究。比如REN等[12]基于一体式固定膜活性污泥的单级PN/A工艺,建立了连续推流式多级缺氧/好氧系统处理垃圾渗滤液,总无机氮去除率(total inorganic nitrogen removal efficiency,TINRE)达到98.1%,ZHANG等[13]构建的两级序批式PN/A-PD/A垃圾渗滤液处理系统,TINRE高达到98.8%。
在工程项目中,某些突发状况可能会导致废水处理系统无法正常运行。由于AnAOB对氮素基质、温度、pH和DO等环境条件的变化较为敏感[14-16],ANAMMOX工艺长期停止运行必然会导致AnAOB活性降低[2]和增殖速度变慢[17]。因此,在工程化废水处理系统无法正常运行时维持AnAOB活性,以及系统运行恢复后快速恢复工艺性能,对ANAMMOX工艺的工程应用发展具有极为重要的意义。
王莹等[18]总结了温度、底物基质、反应器类型和外加条件(重金属等)对AnAOB保藏后活性恢复的影响。李冬等[19]研究发现,在4 ℃无基质条件下保藏的ANAMMOX颗粒污泥,投加适量葡萄糖可以提高胞外聚合物(EPS)的含量,丰富ANAMMOX反应途径,使菌种活性更快恢复。XING等[20]评估了高活性的ANAMMOX颗粒污泥在4 ℃条件下饥饿50 d后的再活化特征,发现恢复运行4 d后即可恢复污泥脱氮性能,8 d后可完全恢复活性。YE等[21]对ANAMMOX污泥进行了重复短期饥饿后再活化实验,发现在低底物浓度条件下ANAMMOX脱氮能力迅速恢复。马冰冰等[22]探究了ANAMMOX生物滤柱和膜生物反应器长期饥饿后的恢复特征,结果表明长期断流后生物滤柱具有较高的稳定性,性能更易恢复,经过39 d总氮去除率恢复87.0%;膜生物反应器则在进水基质浓度较高的条件下恢复效果更好。李祥等[23]在实验室室温条件下验证了定期投加基质缓解ANAMMOX污泥活性衰减的可行性;另一研究结果表明微生物在低负荷条件下会分泌更多的EPS,有助于系统应对氮负荷的变化[24]。这为通过此类方法保持ANAMMOX污泥活性提供了理论依据。
但是,在实验室小试和模拟废水条件下对菌种活性保藏和恢复的研究与工程应用中面临的情况存在较大差距,对指导工程项目实施的可参考性存在一定的疑问。为此,本研究以处理典型老龄垃圾渗滤液的中试规模前置反硝化部分亚硝化耦合PN/A脱氮系统为研究对象,探讨了在系统无法正常运行时通过维持PN/A单元低负荷运行保持AnAOB活性的策略,并考察了系统性能恢复特征和微生物种群结构的变化特征,以期为ANAMMOX工艺在老龄垃圾渗滤液处理工程中的应用提供技术指导。
-
中试项目位于某生活垃圾填埋场,老龄垃圾渗滤液经调节池收集沉淀后直接进入中试装置进行处理。实验期间原水水质特征如下:(2 085.3~3 707.1 mg·L−1) NH4+-N,渗滤液原水中检测不到NO2−-N,(24.1~32.6 mg·L−1) NO3−-N,pH=7.74~8.13,(2 189.5~4 296.5 mg·L−1) COD, C/N比为COD值与TIN(总无机氮)质量浓度之比(0.83~1.24),属于典型的老龄化低C/N垃圾渗滤液。
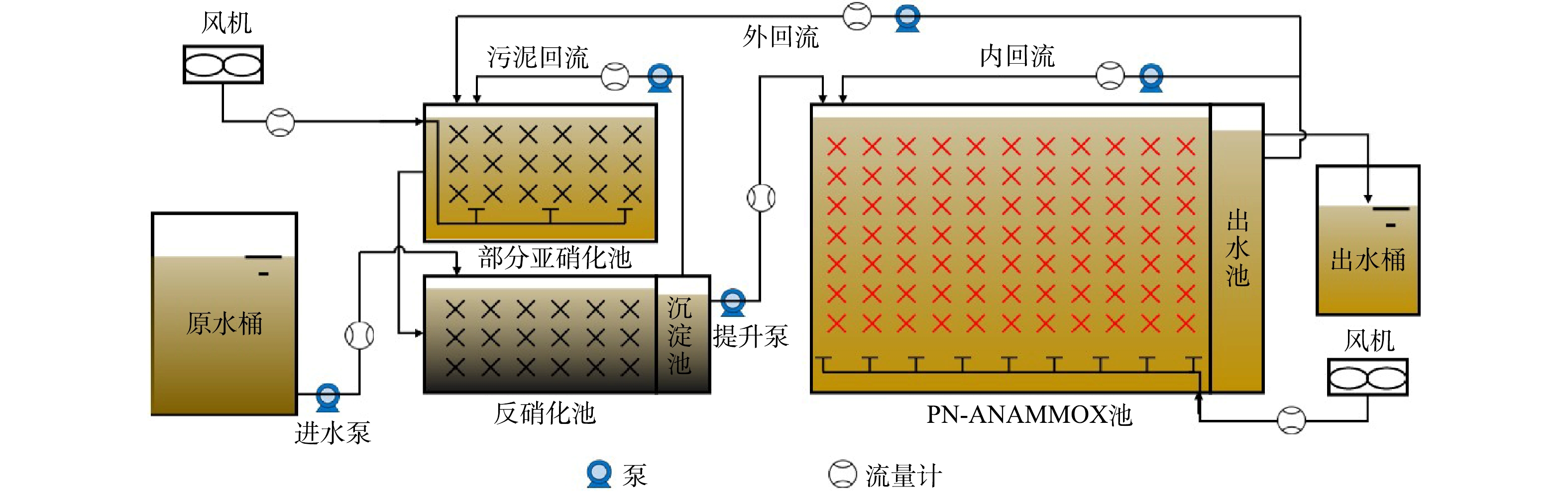
图1为中试规模前置反硝化部分亚硝化耦合PN/A组合工艺(下称“组合工艺”)实验装置示意图。原水桶体积5 m3,通过进水泵连续进水至反硝化池底部。反硝化池体积5 m3,部分亚硝化池体积8 m3,部分亚硝化池出水通过管道溢流至反硝化池,部分亚硝化池和反硝化池安装球形组合填料,填充率5%。沉淀池体积3 m3,上清液通过提升泵输送至PN/A池顶部。PN/A池体积30 m3,池内安装纤维填料,填充率20%,出水池体积3 m3,通过溢流出水至出水桶。污泥回流从沉淀池回流至部分亚硝化池;外回流从出水池回流至部分亚硝化池,用于稀释污泥回流液;PN/A单元内回流从出水池回流至PN/A单元前部用于稀释PN/A单元的进水。在部分亚硝化池和PN/A池底部安装曝气盘,通过风机连续曝气。其中PN/A单元和出水池集成为一个标准化集装箱,除进水池外其他所有单元和控制设备集成在另一个标准化集装箱中,标准化集装箱的尺寸为6 m×2.4 m×3 m,采用钢结构防腐设计。
-
渗滤液原水与部分亚硝化池出水混合进入反硝化池,反硝化菌利用渗滤液中的可生化COD作为反硝化碳源,主要利用部分亚硝化池提供的NO2−-N作为氮源,实现部分有机物和氮素的去除,避免过量有机物影响后续的ANAMMOX工艺。反硝化池出水分2个部分,一部分进入部分亚硝化池,为氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria,AOB)提供NH4+-N;另一部分作为PN/A单元进水,废水中约55%的NH4+-N在AOB作用下转化为NO2−-N,剩余NH4+-N与产生的NO2−-N在AnAOB作用下转化为N2和少量NO3−-N。系统在环境温度下运行,反硝化、部分亚硝化和PN/A单元的水温在(35±5) ℃。此组合工艺中部分亚硝化池的优点在于不必严格控制NO2−-N的产量,部分亚硝化池产生的NO2−-N主要为反硝化池提供基质,反硝化池出水中的NO2−-N也可作为后续PN/A池ANAMMOX的反应基质。此中试项目工程设计要求组合工艺出水NH4+-N低于300 mg·L−1,TIN低于450 mg·L−1,pH在6~9,以便进行下一阶段处理。
系统在不同阶段的具体运行操作步骤如下。正常运行阶段:连续进水,部分亚硝化池和PN/A池的曝气量分别为40 m3·h−1和 85 m3·h−1,DO分别控制在3.5 mg·L−1和3.0 mg·L−1左右,外回流0.3~0.4 m3·h−1,污泥回流约0.3 m3·h−1,PN/A单元内回流8~9 m3·h−1。PN/A单元低负荷运行阶段:停止进水,投加NH4Cl和NaHCO3作为氮源和碱度。PN/A单元内回流维持运行,曝气量降低至15 m3·h−1,DO维持在1 mg·L−1。关闭进水泵、提升泵、外回流泵和污泥回流泵,停止部分亚硝化池曝气,部分亚硝化池和反硝化池停止运行。PN/A单元恢复阶段:连续进水,部分亚硝化池曝气量恢复至40 m3·h−1,PN/A池曝气量根据稳定运行阶段负荷和曝气量的比例关系(负荷为0.5 kg·(m3·d)−1时,所需的曝气量约80 m3·h−1),在提高负荷的同时逐步提高曝气量,使PN/A池DO维持在 3.0 mg·L−1左右,外回流0.3~0.4 m3·h−1,污泥回流约0.3 m3·h−1,PN/A单元内回流8~9 m3·h−1。
-
实验过程中各项水质指标的监测方法参照《水和废水监测分析方法》[25]:NH4+-N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定,NO2−-N采用N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺分光光度法测定,NO3−-N采用紫外分光光度法测定,COD采用重铬酸钾法测定。TIN计为NH4+-N、NO2−-N和NO3−-N质量浓度之和。pH测定采用梅特勒-托利多SG23型多参数测试仪,温度和DO的测定采用雷磁JPB-607A便携式溶解氧测定仪。三维荧光光谱分析:水样用0.45 µm滤膜过滤,使用超纯水稀释150倍,将待测溶液TOC调节至10 mg·L−1左右,用超纯水做空白。三维荧光光谱仪参数如下:发射波长(Em) 220~550 nm,激发波长(Ex)为200~400 nm,扫描速度1 200 nm·min−1。
高通量测序:在系统正常运行最后1 d,PN/A单元低负荷运行最后1天和恢复运行第9天取PN/A单元的污泥,样品分别记为S1、S2和S3。采用高通量基因测序技术分析微生物群落结构变化特征,样品测序由上海派森诺生物科技公司完成。方法如下:取适量污泥样品,采用PowersoilDNA试剂盒提取样品DNA,使用特异性引物319F-806R对细菌的16S rRNA V3V4区进行PCR扩增反应[26],在Novaseq-PE250测序平台进行测序。
参考文献[27]中方法计算氨氮去除率(ARE)、总无机氮去除率、进水氨氮负荷(ALR)和总无机氮去除负荷(TINRR)。参考LI等[28]的方法,将PN/A单元每日去除氮的总量占整个组合工艺每日去除氮的总量的百分比作为PN/A单元的脱氮贡献率。
-
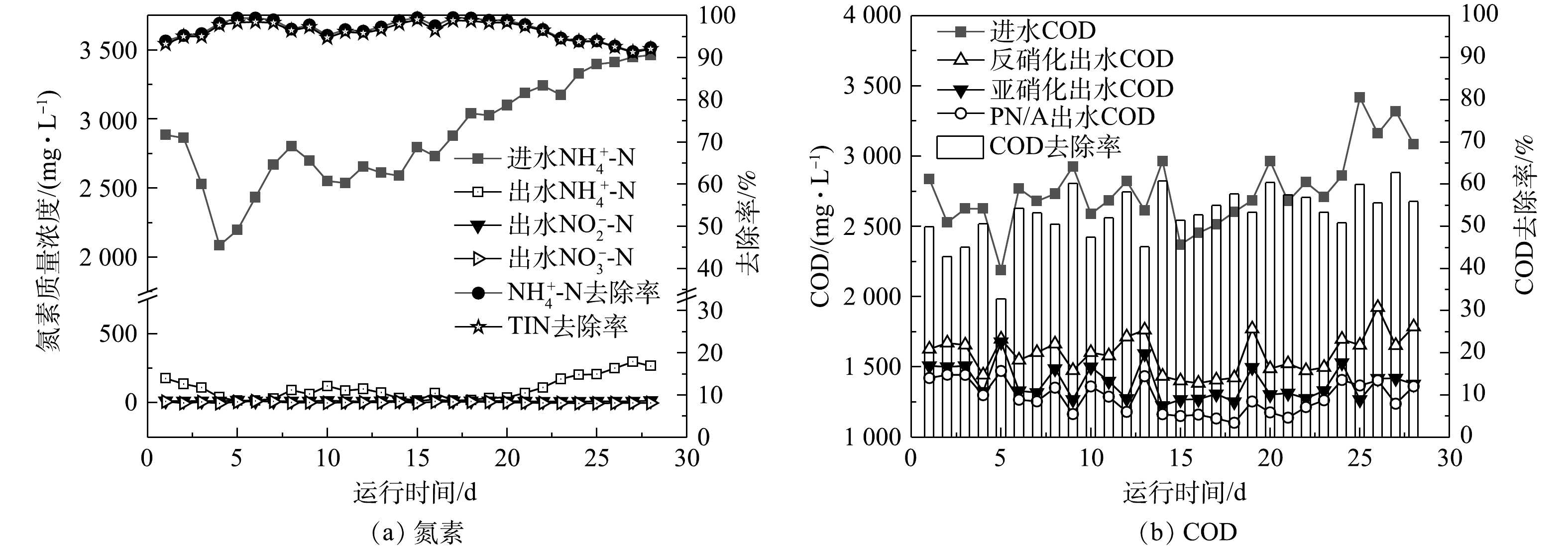
图2(a)为稳定运行阶段组合工艺进水、出水氮素浓度变化和去除率。由于进水NH4+-N质量浓度(2 085.3~3 462.7 mg·L−1)受降雨影响变化较大,稳定运行阶段根据进水NH4+-N质量浓度调节进水量。平均出水NH4+-N、NO2−-N和NO3−-N质量浓度分别为102.0、12.3和2.0 mg·L−1,平均ARE和TINRE分别达到96.6%和96.1%以上,最高ARE和TINRE分别达到99.5%和99.0%,组合工艺表现出优异的脱氮性能。其中出水中NO3−-N质量浓度低于理论值,这可能是来自反硝化池的反硝化菌与PN/A单元的AOB和AnAOB共存,通过反硝化作用将ANAMMOX产生的NO3−-N转化为NO2−-N或N2[29]。
稳定运行阶段各处理单元的COD变化和组合工艺的COD去除率见图2(b)。进水COD(2 189.5~3 416.0 mg·L−1)受降雨影响波动较大,但平均出水COD稳定在1 282.4 mg·L−1,说明处理系统对进水水质变化所导致的负荷冲击有很大的耐受性。王凡等[30]采用反硝化-短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺处理老龄垃圾渗滤液,COD去除率为36.7%。本组合工艺对垃圾渗滤液的COD去除率更高,平均可达53.1%。组合工艺处理前后渗滤液中有机物的三维荧光特性分析结果表明,出水中的COD主要是难降解的类腐殖酸类有机物[31]。
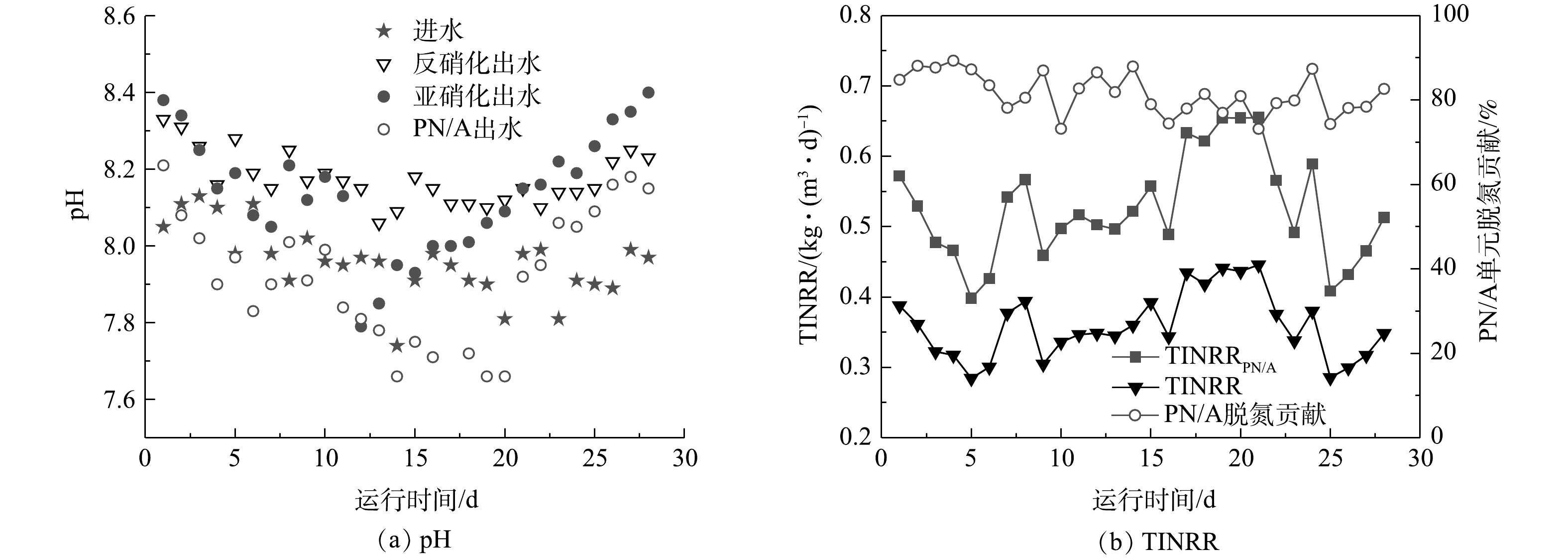
图3(a)反映了组合工艺稳定运行阶段各处理单元出水pH变化情况。其中,进水pH在7.74~8.13;因为反硝化反应会产生碱度,而亚硝化反应消耗碱度,同时由于存在污泥回流和外回流的混合稀释作用,各个反应单元的pH在7.6~8.4。AOB菌群的最适宜pH约8.0,亚硝酸盐氧化菌(nitrite oxidizing bacteria,NOB)的最适宜pH约7.0[32-33]。因此,组合工艺正常运行时无需调节pH,部分亚硝化池和PN/A池也更有利于AOB生长。
汇总各单元水质数据进行分析,正常运行阶段组合工艺的TINRR变化和PN/A单元的脱氮贡献率如图3(b)所示。结果表明,组合工艺平均TINRR为0.359 kg·(m3·d)−1,PN/A单元的平均TINRRPN/A为0.525 kg·(m3·d)−1,最高可达0.655 kg·(m3·d)−1,PN/A单元的平均脱氮贡献率达到81.5%。由上述结果可知,组合工艺的PN/A单元展示出极稳定的脱氮性能,能大幅削减老龄垃圾渗滤液的TIN。
-
上述中试项目由于垃圾渗滤液输送管道改造,渗滤液临时无法供应给中试系统。因为AnAOB对环境条件的变化极为敏感,考虑通过维持PN/A单元低负荷运行维持AnAOB活性。低负荷运行期间停止进水,投加NH4Cl作为氮源,使PN/A池内NH4+-N质量浓度维持在100~250 mg·L−1。按NaHCO3:NH4+-N质量比为10:1投加NaHCO3,质量比参照实际垃圾渗滤液的碱度与NH4+-N质量浓度确定。关于NO2−-N对AnAOB的抑制浓度,从50~350 mg·L−1众说纷纭[34],本实验过程中PN/A单元NO2−-N质量浓度维持在10 mg·L−1左右,避免对AnAOB产生抑制作用。PN/A单元低负荷运行期间平均TINRRPN/A为0.024 kg·(m3·d)−1,远低于正常运行阶段的0.525 kg·(m3·d)−1。低负荷运行10 d后管道改造施工完成,此时观察填料上的污泥呈暗红色,与正常运行阶段相比无明显变化。在第11 天系统调整回正常运行状态,恢复连续进水和曝气,部分亚硝化池和PN/A池曝气量与正常运行阶段一致(这一天作为系统恢复阶段第1天)。第11天系统出水NH4+-N和TIN质量浓度分别为340.4 mg·L−1和344.4 mg·L−1,ARE和TINRE均达到89.5%以上。TINRRPN/A为0.227 kg·(m3·d)−1,达到稳定运行阶段的43.3%,与低负荷运行阶段的TINRRPN/A=0.024 kg·(m3·d)−1相比提高9.5倍,表明AnAOB活性保持在较高水平。与李祥等人[23]在实验室室温条件下定期投加基质将ANAMMOX污泥保存15 d后的活性恢复实验结果基本一致。
因此,在整个系统无法正常运行时,通过低负荷运行维持ANAMMOX活性的策略适用于较大规模ANAMMOX废水处理项目,可以经济便利地维持AnAOB活性,有助于应对各种突发状况而导致的系统停运问题。
-
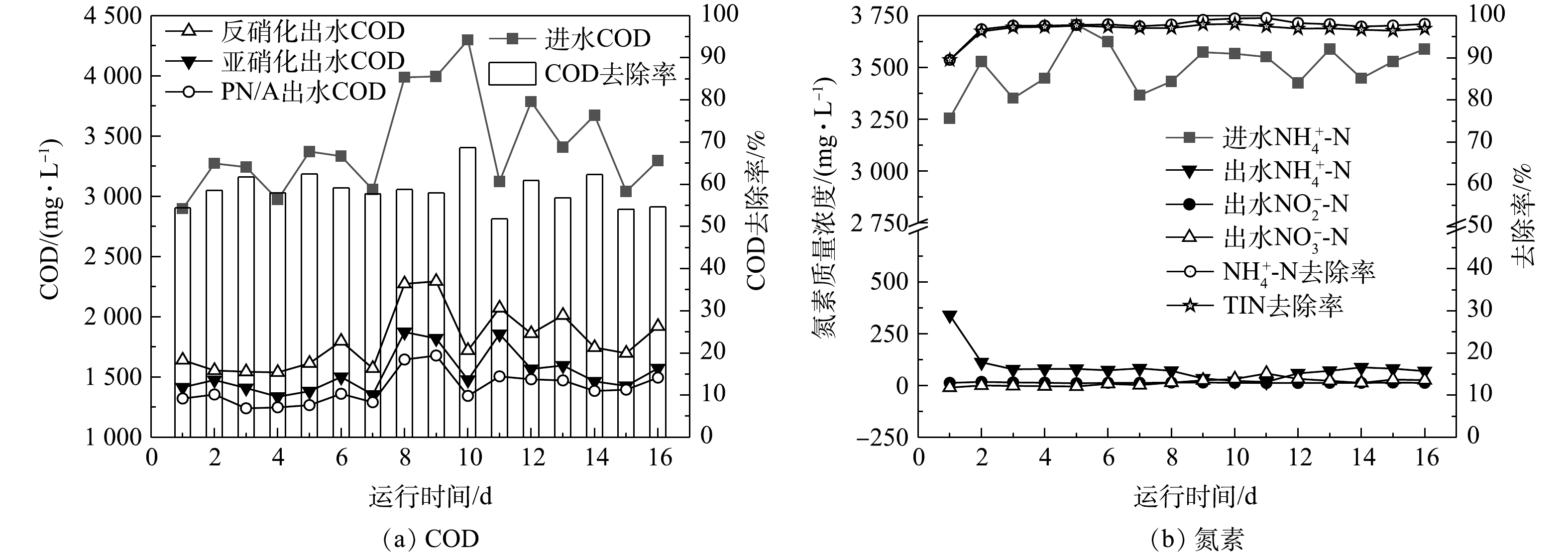
图4(a)反映了系统恢复阶段各处理单元COD的变化和去除率。平均进水和出水COD分别在3 421.7 mg·L−1和1 405.7 mg·L−1,进水COD存在较大波动,而出水COD较为稳定,平均COD去除率达到58.6%,甚至超过稳定运行阶段的53.1%,表明系统的COD去除能力可以迅速恢复。这与以前的研究结果一致, 将活性污泥饥饿处理后恢复正常运行4~5 d,污泥的硝化、反硝化和COD去除性能即可恢复或超过饥饿前的正常水平[35-37]。
关于系统脱氮性能的恢复,采用逐步提高ALR,并相应的提高PN/A池曝气量,维持DO与正常运行阶段基本一致的方法。图4(b)为恢复过程中组合工艺的氮素浓度变化和去除率,由于恢复运行第1 天ALR超过了系统的脱氮能力,出水NH4+-N质量浓度达到340.4 mg·L−1,超过了中试项目设计的出水要求。为快速降低PN/A池的NH4+-N,在第2天关闭进水泵、提升泵和外回流泵,并根据PN/A池负荷与曝气量的比例关系降低曝气量,闷曝1 d后PN/A池NH4+-N降至112.9 mg·L−1,然后根据系统能力恢复进水。由图4(b)分析可知,在系统脱氮性能恢复过程中平均进水NH4+-N质量浓度为3 499.3 mg·L−1,平均出水NH4+-N、NO2−-N和NO3−-N质量浓度分别在85.6、13.9和15.8 mg·L−1,平均ARE和 TINRE分别超过97.5%和96.7%。因此,采用逐步提高ALR的恢复策略,在恢复阶段系统出水也能满足工艺设计要求。
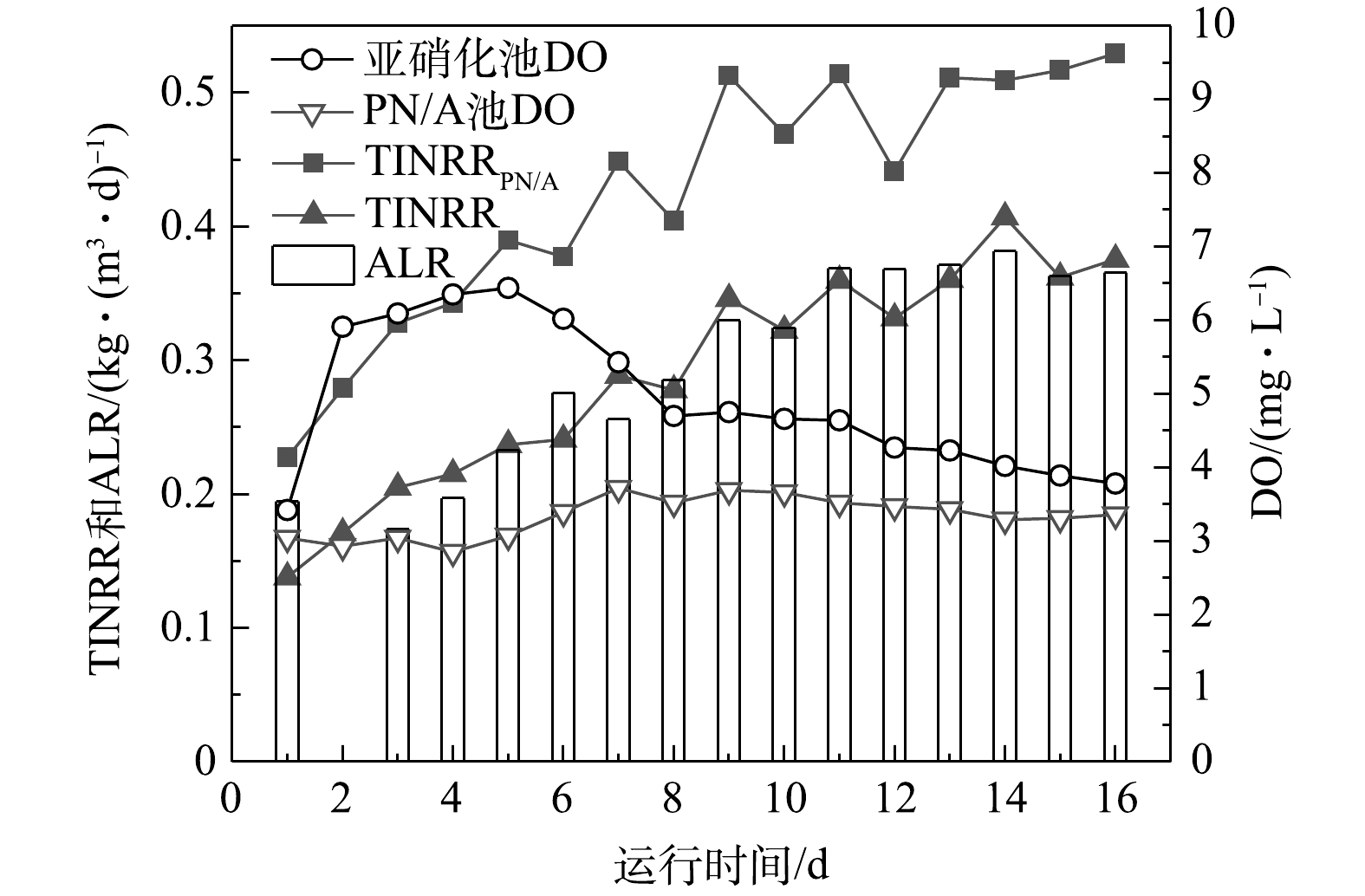
图5为组合工艺恢复阶段ALR和TINRR的变化。在系统性能恢复阶段,PN/A单元和组合工艺的TINRR逐渐升高,在恢复运行第9天,TINRRPN/A已经达到0.513 kg·(m3·d)−1,恢复到稳定运行阶段的97.7%;整个组合工艺的TINRR也恢复到0.346 kg·(m3·d)−1,达到稳定运行阶段的96.4%。结果表明,组合工艺的脱氮性能经过9 d得到完全恢复。
通常,当ANAMMOX系统处于完全饥饿状态时,菌体会进行内源呼吸进而导致AnAOB活性降低,甚至大量死亡分解[19]。由于AnAOB生长周期较长,倍增速度缓慢,因此,系统性能的恢复需要较长时间[22,38]。马冰冰等[22]将ANAMMOX生物滤柱通过长期饥饿后,经过39 d后NRE恢复到87.0%;ANAMMOX膜生物反应器的恢复则需要更长时间,经过76 d 后NRE恢复到87.6%。LI等[39]直接使用渗滤液原水恢复长期休眠的DN-PN-ANAMMOX工艺时,由于原水NH4+-N质量浓度很高以及耦合工艺微生物活性难以同时恢复,容易导致NH4+-N和NO2−-N积累,抑制微生物活性,通过延长HRT,恢复31 d后NRE才达到70.9%。本研究发现,采用简单投加基质维持PN/A单元低负荷运行,可以实现将AnAOB活性维持在较高水平,这种简单的活性维持策略适用于较大规模的ANAMMOX工艺废水处理项目。在系统脱氮性能恢复过程中直接使用渗滤液原水,通过逐步提高进水负荷结合控制DO的恢复策略可以实现工艺性能快速恢复。
-
以Goods coverage(覆盖度)指数表征微生物测序样品覆盖度,本实验中样品覆盖度均大于0.99。以Shannon指数表征微生物群落的多样性,Shannon指数越大表明微生物群落多样性越高[40]。结果表明,S1和S2的 Shannon指数分别为7.512和7.909,这说明PN/A单元低负荷运行期间会导致优势菌群比例降低,微生物群落的生物多样性升高。恢复运行第9天Shannon指数下降到7.524(S3),此时组合工艺的脱氮性能已得到完全恢复,说明原本占优势的菌种相对丰度得到恢复,导致微生物群落的生物多样性降低。
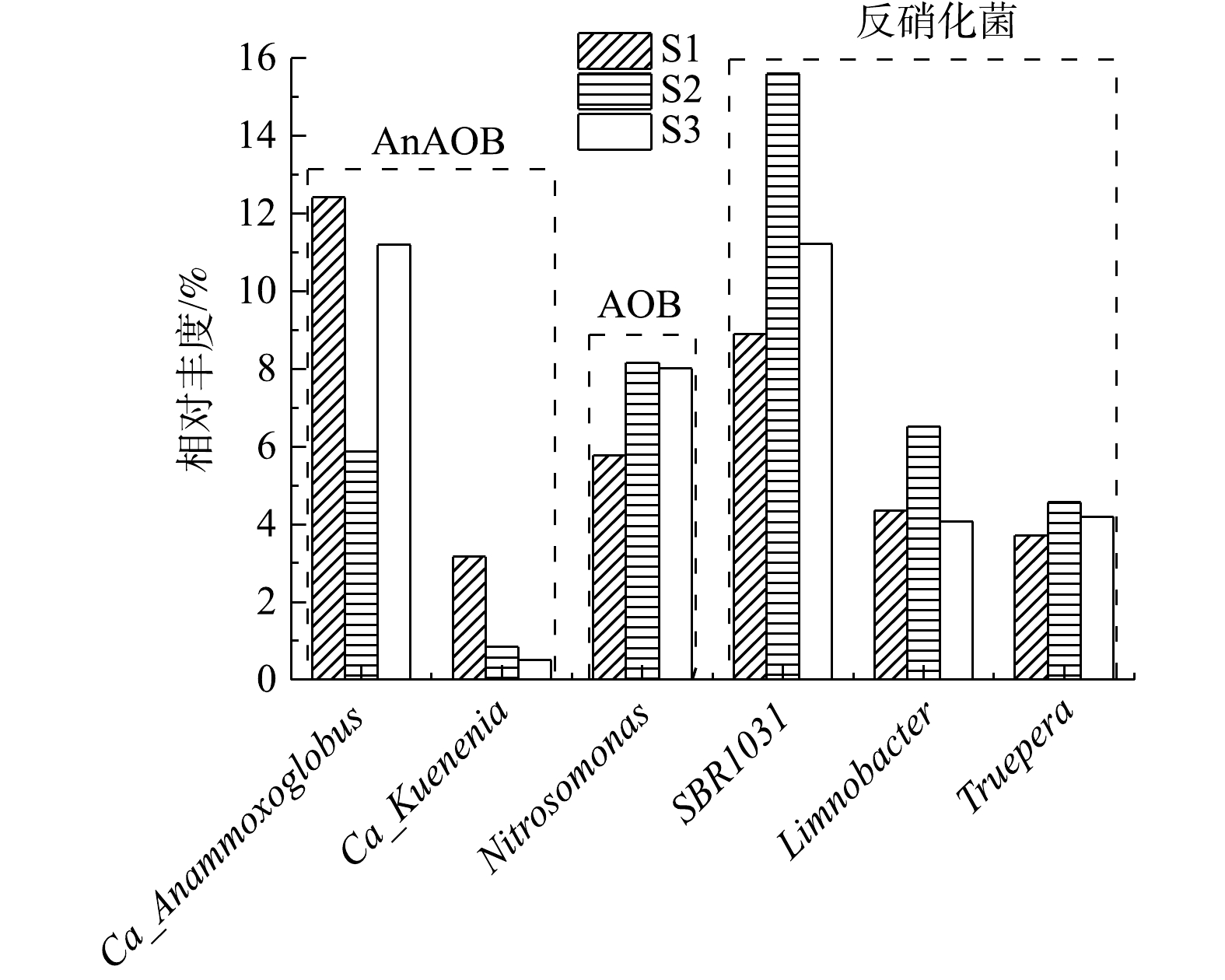
图6为脱氮相关功能微生物在属水平上的分布情况。AnAOB属于浮霉菌属的一个分支,目前共有7个菌属被鉴定为属于AnAOB[41],Ca_Anammoxoglobus和Ca_Kuenenia两个ANAMMOX菌属在3个污泥样品中均被检出。稳定运行阶段2个菌属的相对丰度分别为12.41%和3.17%(S1),低负荷运行10 d后相对丰度均有所降低,分别为5.88%和0.85%(S2),系统恢复后的相对丰度分别为11.19%和0.51%(S3)。说明 Ca_Anammoxoglobus更能适应老龄垃圾渗滤液水质,是PN/A单元的AnAOB优势菌属。恢复运行第9天,Ca_Anammoxoglobus菌属的相对丰度已基本恢复到系统稳定运行时的正常水平,这与整个系统的脱氮能力恢复情况相吻合。而S3中Ca_Kuenenia菌属的相对丰度相比于S2进一步降低,CAO等[42]研究发现Ca_Kuenenia菌属的生长速率较低,因此在系统恢复过程中Ca_Kuenenia菌属的增殖速度较慢,导致其相对丰度进一步降低。
由图6可知,在S1中AOB菌属Nitrosomonas的相对丰度为5.78%,低负荷运行10 d后,由于原本占优势的AnAOB相对丰度下降,Nitrosomonas的相对丰度上升到8.16%(S2),系统完全恢复后Nitrosomonas的相对丰度下降到8.01%(S3)。NOB在PN/A单元未检出,这是因为游离氨(FA)质量浓度处于2.33~58.80 mg·L−1,高于其对NOB的抑制范围(0.1~1 mg·L−1),实现对NOB菌群的选择性抑制[43]。在PN/A单元低负荷运行期间,DO质量浓度维持在1 mg·L−1,低于NOB的氧饱和系数(1.2~1.5 mg·L−1),同样可以选择性抑制NOB[44]。由图6可知,在PN/A单元占优势的反硝化菌属有3种,分别为SBR1031、Limnobacter和Truepera,其中SBR1031是常见的与AnAOB共存的短程反硝化菌属[45],有研究表明,Limnobacter可以保护AnAOB 免受高浓度有机物和高DO的影响[46],上述3种反硝化菌属相对丰度的变化与AOB菌属相同。这些具有反硝化脱氮功能的微生物在PN/A单元可通过与AnAOB合作互补的形式参与脱氮,使PN/A出水中的NO3−-N浓度低于理论值[45]。
-
1)中试实验结果表明,在脱氮系统无法正常运行时,维持组合工艺的PN/A单元低负荷运行可以有效保持AnAOB活性。
2)通过逐步提高进水负荷结合控制DO的恢复策略,仅需9 d即可快速恢复组合工艺的脱氮性能,TINRRPN/A达到稳定运行阶段的97.7%,整个组合工艺的TINRR达到稳定运行阶段的96.4%。
3)高通量测序结果表明,Ca_Anammoxoglobus菌属更能适应老龄垃圾渗滤液水质,是PN/A单元的AnAOB优势菌属,其在稳定运行阶段最后1 d和恢复运行第9天的相对丰度分别为12.41%和11.19%,其相对丰度的变化与系统脱氮能力的恢复情况相吻合。
低负荷运行对中试ANAMMOX活性维持的影响和工艺性能恢复特征
Impacts of low-load operation on ANAMMOX activity maintenance at pilot scale and the recovery characteristics of the process performance
-
摘要: 基于前置反硝化部分亚硝化耦合部分亚硝化(PN)/厌氧氨氧化(A)垃圾渗滤液中试处理系统,研究了系统无法正常运行时维持PN/A单元低负荷运行保持ANAMMOX微生物活性的可行性,并探究了系统性能恢复特征。结果表明,低负荷运行10 d后PN/A单元总无机氮去除负荷(TINRRPN/A)仍有0.227 kg·(m3·d)−1,达到稳定运行阶段的43.3%,氨氮和总无机氮去除率都达到89.5%以上,说明低负荷运行可以有效缓解ANAMMOX污泥活性的衰减。采用逐步提高进水氨氮负荷结合控制DO的恢复策略,经过9 d系统性能得到完全恢复。TINRRPN/A恢复到0.513 kg·(m3·d)−1,达到稳定运行阶段的97.7%。高通量测序结果表明,Ca_Anammoxoglobus菌属更能适应老龄垃圾渗滤液水质,其稳定运行阶段和恢复后的相对丰度分别为12.41%和11.19%。以上研究结果有望为厌氧氨氧化工艺的工程应用提供有益的技术指导。Abstract: Based on the combined process of pre-denitrification, partial nitritation and partial nitritation(PN)/ANAMMOX(A) for landfill leachate treatment at the pilot-scale, the feasibility of activity maintenance of anammox bacteria by low-load operation and the recovery characteristics of the process performance under the abnormal operation conditions were studied. The results showed that the total inorganic nitrogen removal rate of PN/A process (TINRRPN/A) remained at 0.227 kg·(m3·d)−1 after 10 days of low-load operation of the PN/A reactor, and it reached 43.3% of the value at the stable operation stage, and the removal rates of ammonia nitrogen and total inorganic nitrogen were both above 89.5%. This indicated that the attenuation of the activity of ANAMMOX sludge could be effectively alleviated by low-load operation. Based on a recovery strategy combining stepwise increase of ammonia loading rate and DO control, the system performance could be completely restored after 9 days. The TINRRPN/A restored to 0.513 kg·(m3·d)−1 and reached 97.7% of the value at the stable operation stage. The results of high-throughput sequencing showed that Ca_Anammoxoglobus was more suitable to mature landfill leachate, its relative abundances at the stable operation stage and after recovery of the PN/A were 12.41% and 11.19%, respectively. This study provides a useful technical guidance for the engineering application of the ANAMMOX process.
-
Key words:
- anaerobic ammonia oxidation /
- activity maintenance /
- rapid recovery /
- pilot-scale
-

-
-
[1] KARTAL B, KUENEN J G, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M. Sewage treatment with anammox[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5979): 702-703. doi: 10.1126/science.1185941 [2] ALI M, OKABE S. Anammox-based technologies for nitrogen removal: advances in process start-up and remaining issues[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 141: 144-153. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.094 [3] QIAO S, KANDA R, NISHIYAMA T, et al. Partial nitrification treatment for high ammonium wastewater from magnesium ammonium phosphate process of methane fermentation digester liquor[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2010, 109(2): 124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.07.014 [4] GUO J H, WANG S Y, HUANG H J, et al. Efficient and integrated start-up strategy for partial nitrification to nitrite treating low C/N domestic wastewater[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 60(12): 3243-3251. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.619 [5] 陈佼, 李晓媛, 任燕玲, 等. 组合CRI工艺对印染二级生化出水的深度脱氮效果[J]. 工业水处理, 2022, 42(1): 71-76. [6] 张文兵. 铁路高浓度粪便污水处理的工艺设计[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2019, 63(5): 153-156. [7] WU L N, YAN Z B, HUANG S, et al. Rapid start-up and stable maintenance of partial nitrification–anaerobic ammonium oxidation treatment of landfill leachate at low temperatures[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 191: 110131. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110131 [8] 陈小珍, 汪晓军, CHAYANGKUN K, 等. 反硝化-高效部分亚硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺处理老龄垃圾渗滤液[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 345-352. [9] WU L N, SHEN M Y, LI J, et al. Cooperation between partial-nitrification, complete ammonia oxidation (comammox), and anaerobic ammonia oxidation (anammox) in sludge digestion liquid for nitrogen removal[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 112965. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112965 [10] LI J L, ZHANG L, PENG Y Z, et al. Effect of low COD/N ratios on stability of single-stage partial nitritation/anammox (SPN/A) process in a long-term operation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 244: 192-197. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.127 [11] WANG Z, ZHANG L, ZHANG F Z, et al. A continuous-flow combined process based on partial nitrification-Anammox and partial denitrification-Anammox (PN/A+PD/A) for enhanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 297: 122483. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122483 [12] REN S, WANG Z, JIANG H, et al. Efficient nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate in a step feed continuous plug-flow system based on one-stage anammox process[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 347: 126676. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126676 [13] ZHANG F Z, PENG Y Z, LIU Y W, et al. Improving stability of mainstream Anammox in an innovative two-stage process for advanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 340: 125617. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125617 [14] 陈方敏, 高佳琦, 黄勇, 等. 基质暴露水平对ANAMMOX微生物活性及生物量的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 5066-5072. [15] TAO W D, HE Y L, WANG Z Y, et al. Effects of pH and temperature on coupling nitritation and anammox in biofilters treating dairy wastewater[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 47: 76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.06.035 [16] YIN Z X, DOS SANTOS C E D, VILAPLANA J G, et al. Importance of the combined effects of dissolved oxygen and pH on optimization of nitrogen removal in anammox-enriched granular sludge[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2016, 51(9): 1274-1282. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2016.05.025 [17] STROUS M, HEIJNEN J, KUENEN J G, et al. The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1998, 50(5): 589-596. doi: 10.1007/s002530051340 [18] 王莹, 杨开亮, 王博, 等. 厌氧氨氧化菌的保藏与活性恢复研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2019, 45(7): 6-12. [19] 李冬, 刘名扬, 张杰, 等. 厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的长期保藏及快速活性恢复[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(6): 2957-2965. [20] XING B S, GUO Q, JIANG X Y, et al. Long-term starvation and subsequent reactivation of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) granules[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 287: 575-584. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.11.090 [21] YE L H, LI D, ZHANG J, et al. Resuscitation of starved anaerobic ammonium oxidation sludge system: Impacts of repeated short-term starvation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 263: 458-466. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.126 [22] 马冰冰, 张肖静, 张涵, 等. 长期饥饿后厌氧氨氧化工艺的运行及恢复性能研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(6): 2611-2618. [23] 李祥, 朱莉, 黄勇, 等. 常温下基质与时间对ANAMMOX污泥活性保藏影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(9): 3333-3338. [24] 彭永臻, 王锦程, 李翔晨, 等. 氮负荷对短程反硝化耦合厌氧氨氧化生物膜系统脱氮性能的影响[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(12): 1367-1376. [25] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [26] CHEN Z G, ZHENG X W, CHEN Y X, et al. Nitrite accumulation stability evaluation for low-strength ammonium wastewater by adsorption and biological desorption of zeolite under different operational temperature[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 704: 135260. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135260 [27] CHEN X Z, WANG X J, CHEN X K, et al. Salt inhibition on partial nitritation performance of ammonium-rich saline wastewater in the zeolite biological aerated filter[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 280: 287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.048 [28] LI J, QIANG Z M, YU D S, et al. Performance and microbial community of simultaneous anammox and denitrification (SAD) process in a sequencing batch reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 218: 1064-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.081 [29] 严子春, 唐瑞祥, 吴大冰. 有机物对厌氧氨氧化生物膜反应器脱氮效能及微生物群落的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(4): 1303-1308. [30] 王凡, 陆明羽, 殷记强, 等. 反硝化-短程硝化-厌氧氨氧化工艺处理晚期垃圾渗滤液的脱氮除碳性能[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3782-3788. [31] LI X, LU M Y, QIU Q C, et al. The effect of different denitrification and partial nitrification-Anammox coupling forms on nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate at the pilot-scale[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 297: 122430. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122430 [32] 傅金祥, 张羽, 杨洪旭, 等. 短程硝化反硝化影响因素研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2010, 30(12): 38-41. [33] RASZKA A, SURMACZ‐GÓRSKA J, ŻABCZYŃSKI S, et al. The population dynamics of nitrifiers in ammonium‐rich systems[J]. Water Environment Research, 2011, 83(12): 2159-2169. doi: 10.2175/106143011X12989211841331 [34] 侯晓帮, 操家顺, 周可为. 厌氧氨氧化抑制试验及复活策略研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(23): 55-60. [35] YILMAZ G, LEMAIRE R, KELLER J, et al. Effectiveness of an alternating aerobic, anoxic/anaerobic strategy for maintaining biomass activity of BNR sludge during long-term starvation[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(12): 2590-2598. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.011 [36] 杜兴治, 吴志超, 周振, 等. A2/O工艺重新启动试验的污泥活性恢复研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2009, 31(1): 69-73. [37] PIJUAN M, WERNER U, YUAN Z G. Effect of long term anaerobic and intermittent anaerobic/aerobic starvation on aerobic granules[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(14): 3622-3632. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.05.007 [38] ZHANG X J, CHEN T, ZHANG J, et al. Performance of the nitrogen removal, bioactivity and microbial community responded to elevated norfloxacin antibiotic in an Anammox biofilm system[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 210: 1185-1192. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.100 [39] LI X, TAO R J, TIAN M J, et al. Recovery and dormancy of nitrogen removal characteristics in the pilot-scale denitrification-partial nitrification-Anammox process for landfill leachate treatment[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 300: 113711. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113711 [40] 赵晴, 刘梦莹, 吕慧, 等. 耦合短程硝化反硝化的垃圾渗滤液厌氧氨氧化处理系统构建及微生物群落分析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4195-4201. [41] 王众. 厌氧氨氧化处理晚期垃圾渗滤液的工艺技术与机理[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. [42] CAO S B, DU R, LI B K, et al. High-throughput profiling of microbial community structures in an ANAMMOX-UASB reactor treating high-strength wastewater[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(14): 6457-6467. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7427-6 [43] ANTHONISEN A C, LOEHR R C, PRAKASAM T B S, et al. Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid[J]. Journal (Water Pollution Control Federation), 1976, 48(5): 835-852. [44] PICIOREANU C, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M, HEIJNEN J J. Modelling the effect of oxygen concentration on nitrite accumulation in a biofilm airlift suspension reactor[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1997, 36(1): 147-156. doi: 10.2166/wst.1997.0034 [45] CHEN Z G, WANG X J, ZHOU S W, et al. Large-scale (500 kg N/day) two-stage partial nitritation/anammox (PN/A) process for liquid-ammonia mercerization wastewater treatment: Rapid start-up and long-term operational performance[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 326: 116404. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116404 [46] WANG C, LIU S T, XU X C, et al. Achieving mainstream nitrogen removal through simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification process in an integrated fixed film activated sludge reactor[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 203: 457-466. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.016 -



 下载:
下载: