-
施氏矿物(Schwertmannite)是一种次生铁(Fe)-羟基硫酸盐矿物,其结晶度弱、比表面积大,目前在环境污染治理中得到广泛关注[1]。其产生源包括酸性矿山排水[2]、酸性硫酸盐土壤[3]、煤矿[4],以及铜堆渗滤液溶液等特定废液/固体废物[5]。
作为一种新型环境友好的铁基材料,施氏矿物独特的孔道结构和离子交换性能使其对水相中的无机污染物具有良好的吸附能力,例如砷[6]、六价铬[7]、镉和铅[8]等。同时,施氏矿物可以通过光催化、活化过硫酸盐降解溶液中磺胺甲恶唑[9]、土霉素[10]、甲基橙[11]等有机污染物。目前有关施氏矿物的研究论文逐渐增多,亟需对其研究现状和存在的问题进行系统的分析,以期推动施氏矿物在污染治理领域的研究和利用。
文献计量法经常被用于研究和衡量研究人员、政府、研究机构、大学、科学出版商和期刊在特定科学学科中的研究进展和趋势[12]。通过概述特定科学领域的最新发展,可以确定其主要趋势和存在问题,从而使研究方向更能聚焦于解决特定领域科学技术进步的障碍。近年来,文献计量研究在多个科学领域得到广泛应用,包括全球可持续和可持续发展[13]、土壤生态系统服务[14]、二氧化碳封存[15]、过硫酸盐氧化技术[16]、绿色纳米材料合成[17]等,这进一步证实了该方法对现有文献深度整理的重要性。
为了更好地跟踪施氏矿物在全球范围内的研究趋势,本研究提取了1990—2021年期间Web of Science (WoS)核心合集数据库和中国知网(CNKI)数据库收录的施氏矿物相关研究论文,分析了文献数量、发表刊物、研究团队(国家、机构和作者)以及文献被引频次等信息,结合关键词共现网络图和关键词突现图等梳理和回顾了施氏矿物的研究热点与发展趋势。通过系统归纳30年来施氏矿物的结构-性质关系及其在环境污染治理领域的研究成果,探讨了关于该功能材料研究面临的挑战,以期为今后的相关研究提供有益参考。
-
为提高数据代表性和可获取性,本研究数据来源于WoS核心合集数据库和CNKI数据库,检索及下载时间为2021年11月1日。其中,英文和中文文献分别以“Schwertmannite”和“施氏矿物”为检索主题,数据采集时间段为1990—2021年。通过查阅已检索文献标题和摘要,进一步筛选出符合要求的英文和中文文献分别为872和88篇。
-
本研究主要采用了两款常见可视化软件进行文献统计分析[18-19],即VOSviewer(1.6.17版本)和CiteSpace(5.8.R3版本)。其中,VOSviewer用于绘制作者合作、机构合作和关键词共现图,CiteSpace软件用于绘制关键词突现图。
-
从WoS核心合集数据库获得的数据,以txt格式导出全纪录供CiteSpace进行分析,以制表符分隔文件格式导出全记录供VOSviewer进行分析;从CNKI数据库获得的数据,以Refworks格式导出,供CiteSpace和VOSviewer进行分析。同时借助了Office统计软件Excel 2016和文献管理软件EndNote 2020对数据做了一些处理和分析。
-
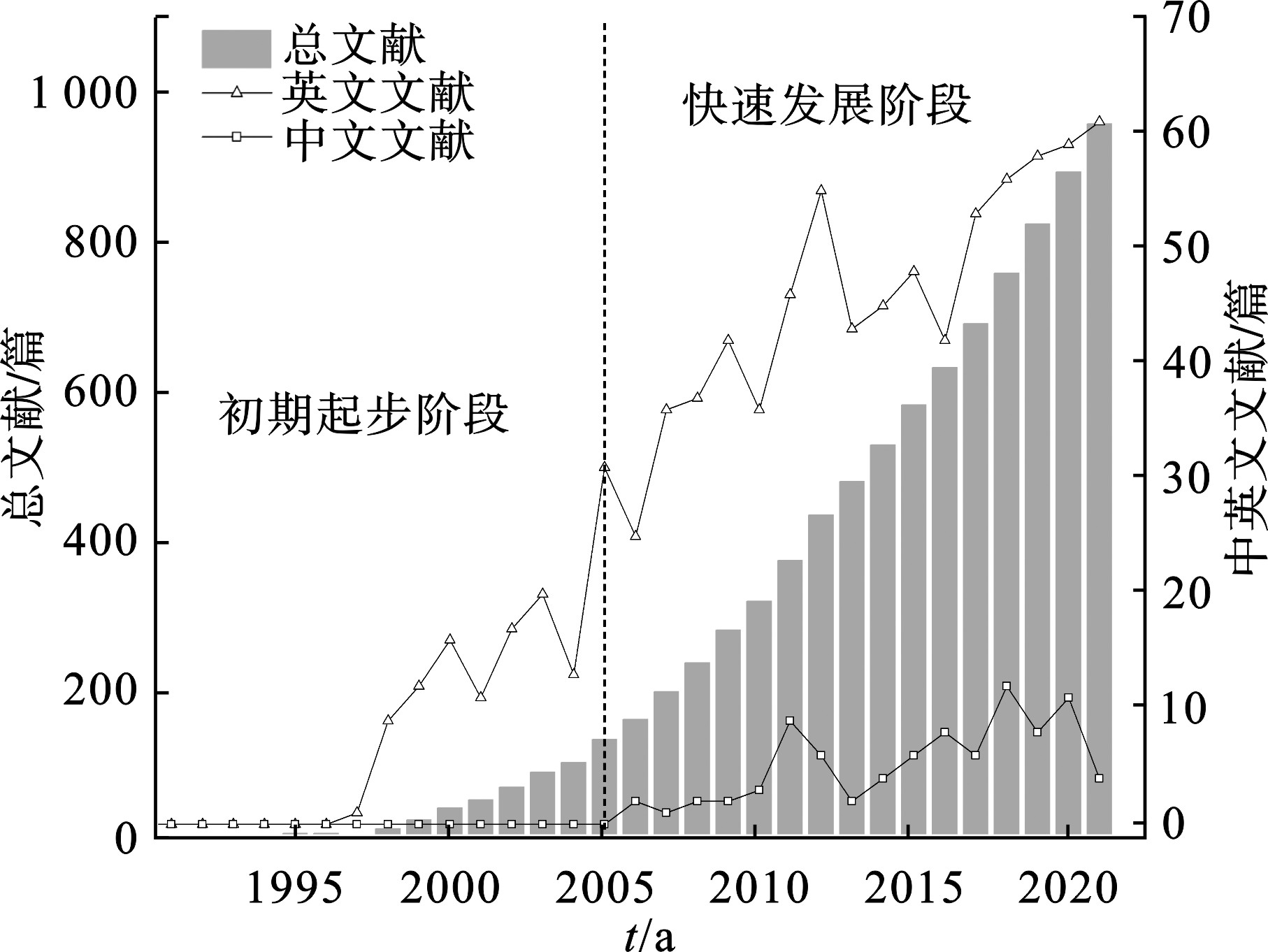
施氏矿物相关研究发文量时间序列变化,见图1。
图1可知,1990—2021年WoS核心合集数据库和CKNI数据库共收录与施氏矿物相关的研究论文共960篇。其中,英文文献占比90.83%,中文文献占比9.17%。从中英文总发文量态势来看,施氏矿物研究可大致分为2个阶段:初期起步阶段和快速发展阶段。初期起步阶段(1993—2005年)发文量逐年慢速增长,文献基本为英文且年均发文量不足10篇。自2006年起,施氏矿物的研究进入快速发展阶段,中英文总年均发文量达60篇以上。随着全球对矿山酸性排水环境污染治理以及天然绿色铁基材料开发的重视[20],预计未来施氏矿物的研究文献量会持续增加。
-
基于WoS数据库发文量排名前10的作者统计,见表1。
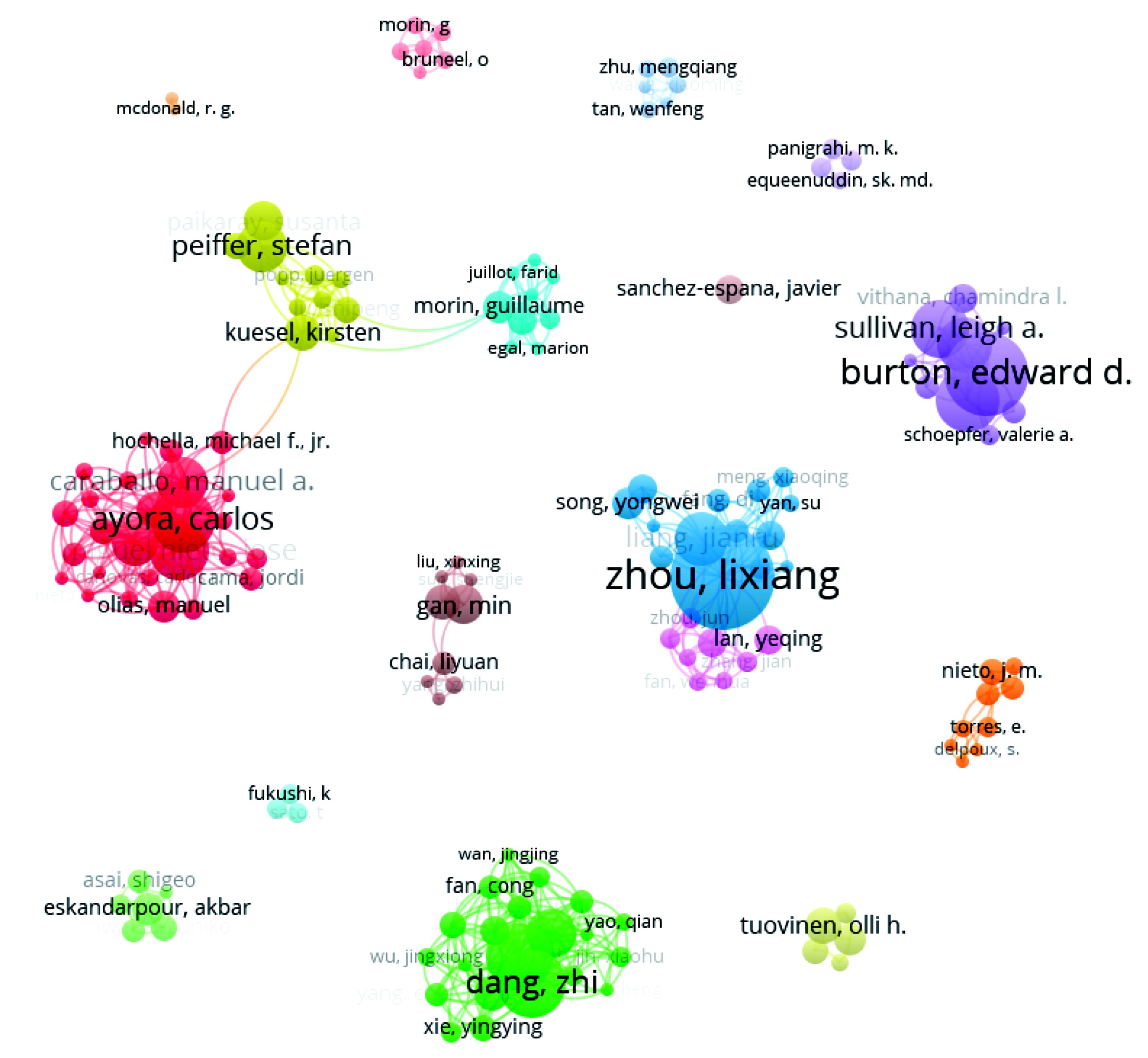
中国、西班牙和澳大利亚的研究人员发表文章数量较多,研究活跃,施氏矿物的研究有较为成型的研究群体。然而,仅部分教授团队进行了一定合作,其余各研究群体间合作较少。发文作者关系,见图2。
-
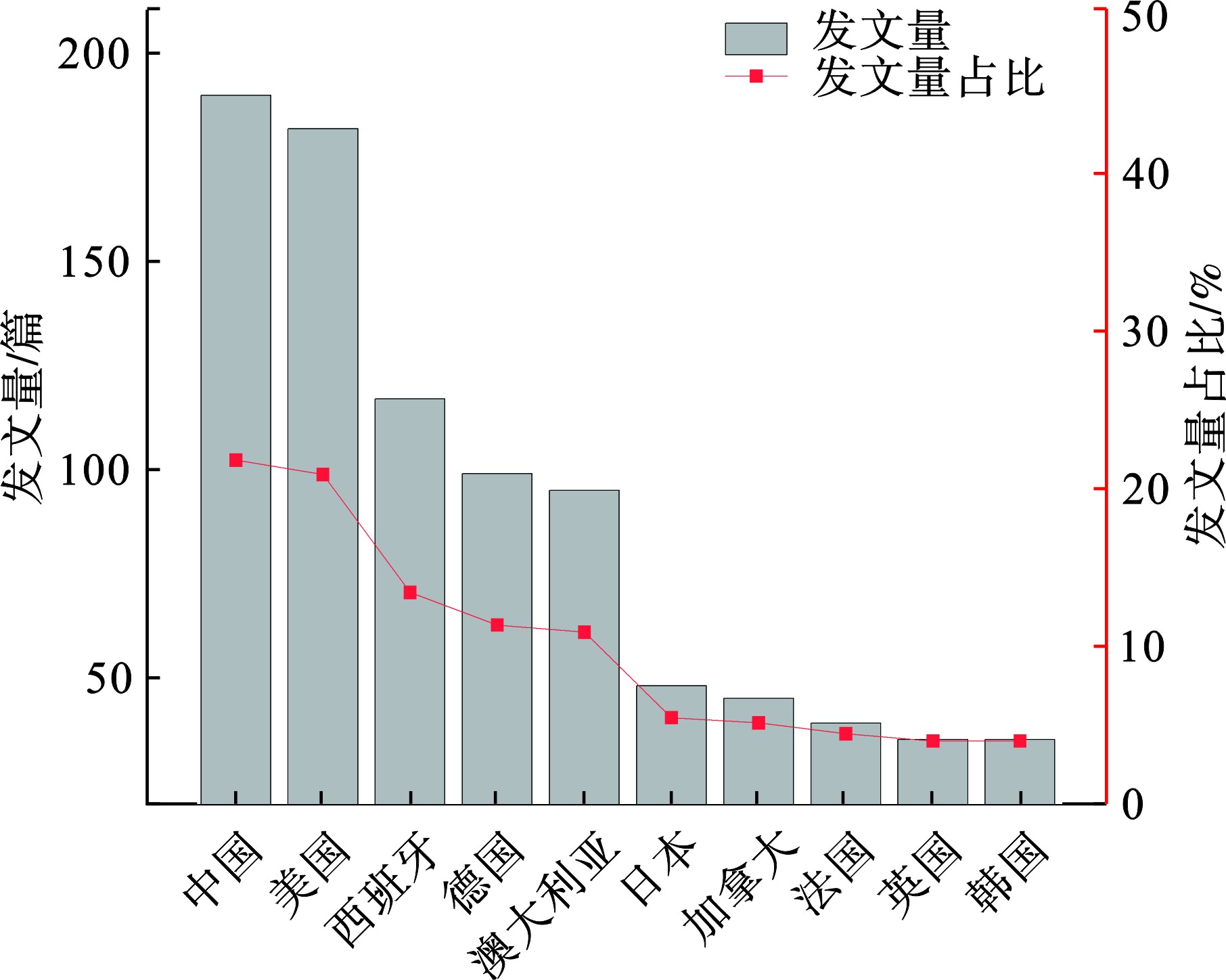
全球共50多个国家参与了施氏矿物的研究。研究最多的10个国家,见图3。其中,中国发文量最多(191篇),其次是美国(183篇)、西班牙(118篇)、德国(100篇)、澳大利亚(96篇)等。中美两国学者在施氏矿物研究领域发文量相近,都远高于其他国家,各占总发文量的21.9%和21.0%,说明中美两国学者对该材料的研究较为活跃。
全球范围内共有780多个研究机构参与了施氏矿物相关研究。在前10的研究机构中,西班牙4所,美国2所,中国、澳大利亚、法国和德国各1所,见表2。西班牙对施氏矿物的研究机构较多可能与其境内存在的矿山污染问题有关。位于西班牙西南部的伊比利亚黄铁矿带至今已有5 000年的开采历史,上游酸性排水对廷托河和奥迪尔河水质造成了严重影响(pH接近1),是全球典型的酸性矿山排水研究区域[21]。
-
施氏矿物研究文献共发表在240个国际期刊上,前10名高发文期刊施氏矿物主题累计发文量370篇,占总文献的42.4%。影响因子较低的APPLIED GEOCHEMISTRY发文量最多,达76篇,见表3。从来源出版物来看,施氏矿物的研究成果主要发表在与“地球化学”“环境科学”以及“矿物”等主题相关的期刊中。
被引频次最高的10篇文献,见表4。1996年发表的文章“Schwertmannite and the chemical modeling of iron in acid sulfate waters”被引用次数最高,达831次。文章分析采自28个矿山排水点的赭色沉积物和水溶液,发现在pH在2.8~4.5内的水体环境下的沉积物主要为施氏矿物,同时含有少量针铁矿。结合矿物学、水环境化学分析和模型模拟,发现实验室合成的施氏矿物在543 d后完全转化为针铁矿。对施氏矿物在自然环境下的生成条件和稳定性进行了较为全面的分析,为后续不同地区施氏矿物的发现和性质研究奠定基础,在施氏矿物的研究中做出开创性的工作。
-
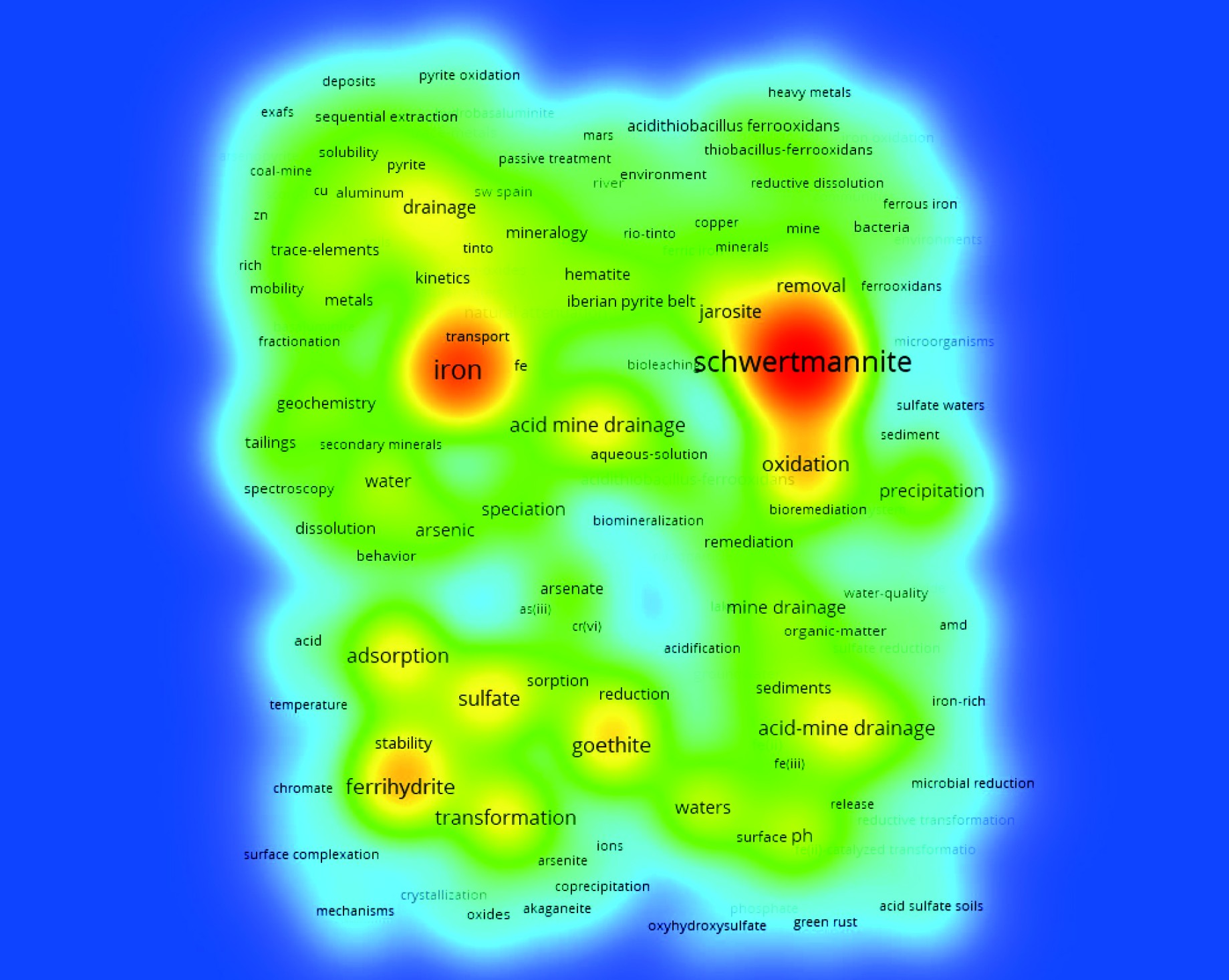
关键词分析被认为是在特定领域表征科学领域的重要工具[22]。它可以反映文章的主题,作者聚焦的核心内容,是研究主题的高度概括。经分析,WoS核心数据库中关于施氏矿物的关键词总数为3 003个。关键词出现频率>10次的共有152个。常见的关键词包括铁、酸性矿山废水、针铁矿、赤铁矿、硫酸盐、吸附、稳定性、转化、氧化等,可为分析施氏矿物的研究方向提供参考,见图4。
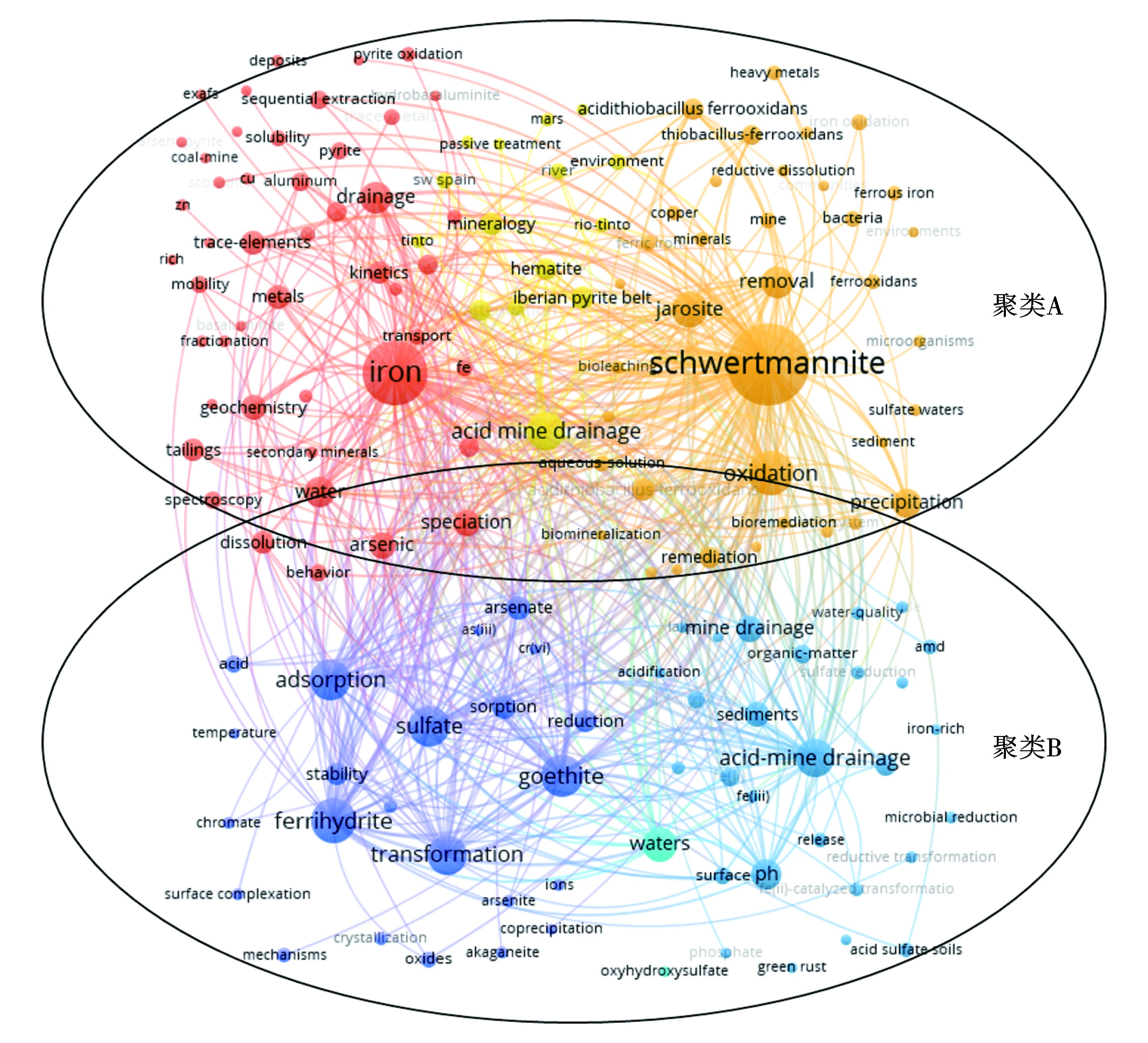
152个关键词大致可分为2个聚类。聚类A的主要关注点在于铁、硫、溶解、转化、沉淀、次生矿物、微生物等。这部分相关研究致力于探究施氏矿物在环境中的形成过程、地球环境行为以及结构-性质关系等。聚类B的主要关注点在于水铁矿、针铁矿、吸附、去除、稳定性、砷、六价铬、催化等。这部分侧重于施氏矿物的应用,如作为重金属吸附材料和光催化材料等,见图5。与聚类A关键词相比,聚类比关键词节点较小且分散,说明对于实施矿物的应用研究有待进一步发掘。
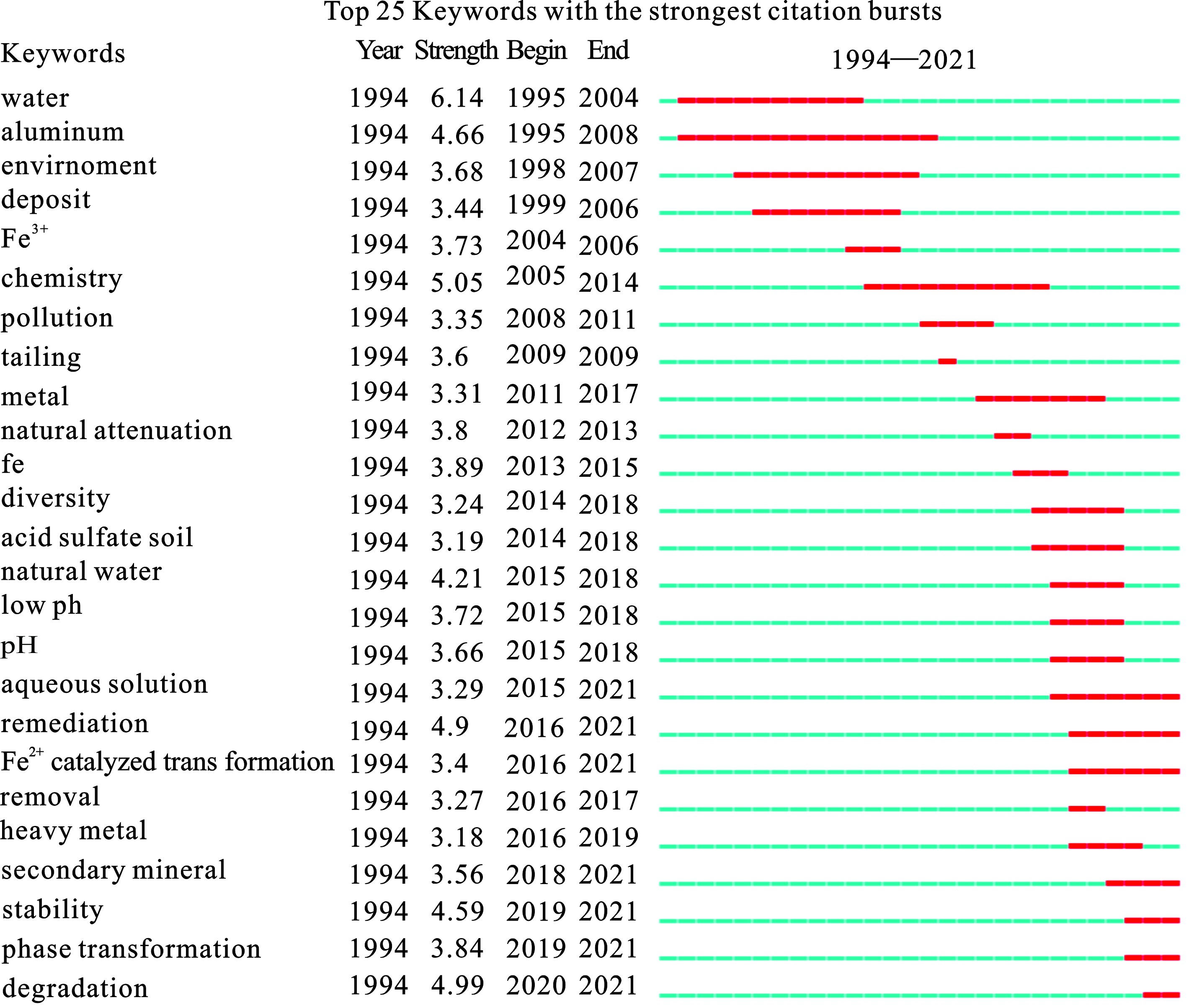
CiteSpace软件的Burstness突现图可以形象地展示研究对象随时间变化的演进过程,以便直观了解研究实时热点及研究前沿的变化,并对此进行分析预测[23]。早期研究论文中,水、化学、沉积关键词突现强度最高,2010年左右,污染控制、自然衰减等关键词开始出现。而2015年以后,修复、催化、转化、稳定性等关键词开始出现。这说明关于施氏矿物的研究从早期的性质-结构分析,逐渐进入应用探索,特别关注环境修复、光催化,以及应用过程中矿物结构的稳定性等,见图6。
-
(1)关于施氏矿物结构-性质的文献分析。自20世纪90年代初BIGHAM et al[24]首次报道从俄亥俄州东部煤田的酸性矿井排水系统的沉积物样品中发现了该矿物以来,学者对施氏矿物的结构、物相、形貌、化学式等开展了一系列研究。普遍认为,施氏矿物的理论通式可以表示为Fe8O8(OH)8−2x(SO4)x(1≤x≤1.75)。其中,Fe/S摩尔比在4.6~8.0之间,
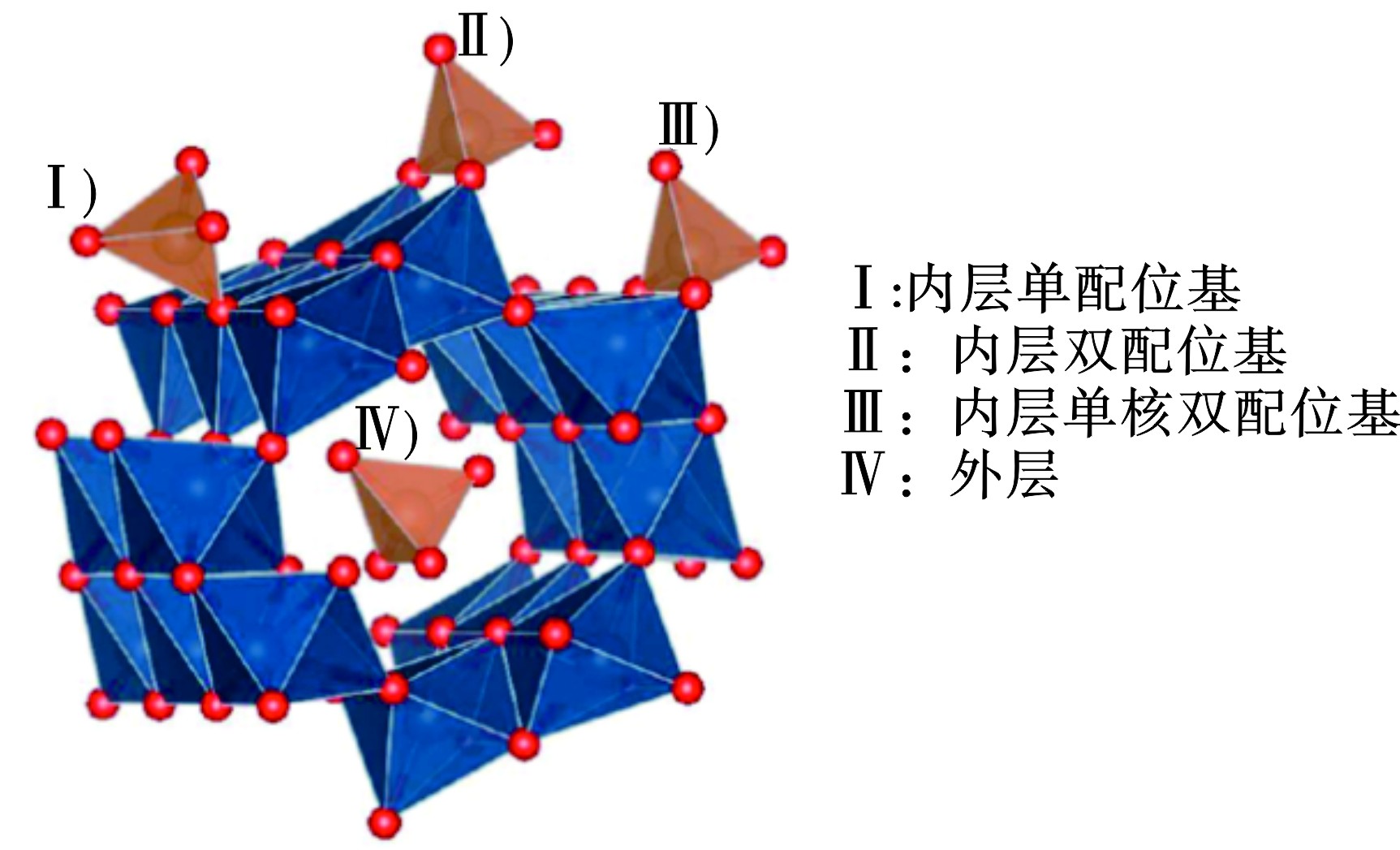
${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 的质量百分比在5.3%到32%之间(不考虑结晶水)[2, 25]。施氏矿物颗粒大小从纳米级到微米级不等,比表面积范围为2~330 m2 /g[1]。X射线衍射(XRD)表征表明,施氏矿物由8-线衍射组成,剖面在0.486和0.146 nm之间(主要在约26.3°、35.2°、55.3°和61.3°)[26],其结晶特性比黄钾铁矾和针铁矿差,但与水铁矿非常相似[27]。施氏矿物具有有序通道的多重三维结构,见图6。通道孔中的${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 离子可以容易地被具有类似半径的其他离子取代,例如${\rm{PO}}_4^{3-} $ 、(SeO4)2−、${\rm{CrO}}_4^{2-} $ 或${\rm{AsO}}_4^{3-} $ [28]。天然施氏矿物的形成过程包括2个主要步骤,即Fe2+的氧化和Fe3+的水解沉淀。基于此,目前研发了多种人工合成方法,如Fe2+的化学氧化、生物氧化,以及Fe3+的快速水解)等,见表5。化学氧化法是最早的施氏矿物生产方法,但成本较高。快速水解和生物方法是施氏矿物较大规模生产的首选。不同的合成策略及其可调参数对施氏矿物的结构/形貌有较大影响。FRENCH et al[29]发现温度影响施氏矿物表面针状体的密度,在高温下(75 ℃)针状体呈树状,而在室温下针状体排列更紧密。ZHANG et al[30]发现,与生物氧化产物相比,Fe3+快速水解及透析纯化后的施氏矿物颜色较浅且比表面积较大。在研究施氏矿物结构、反应性和污染物去除能力时,应从不同的角度探讨合成策略或方法与材料性能的关系,通过热稳定性改性、酸性改性、有机改性、均匀造粒等优化调节施氏矿物的性质,以期对实际应用中的可控优化问题有更清晰的认识。
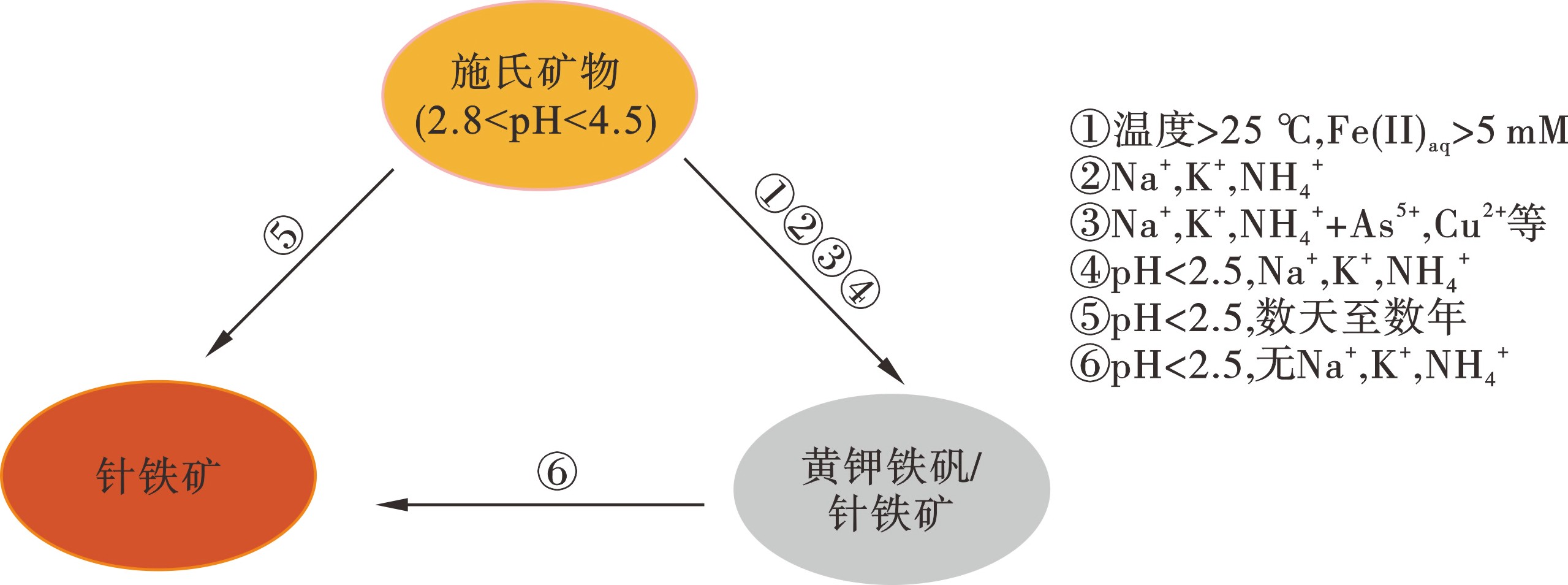
(2)关于施氏矿物稳定性文献分析。根据文献计量分析,共有约150篇论文研究了施氏矿物的环境稳定性。结果发现,作为一种低结晶度矿物,施氏矿物在合成、储存及使用过程中,其结构和性质处于亚稳定状态,可以通过脱水和重结晶过程转化为其他矿物,影响因素包括pH、Fe3+浓度、热处理、有机物以及共存离子等[37-39],见图7。
当pH为2.5~4.5时,施氏矿物将转变黄钾铁矾,或在强酸环境下(pH≤2.5)转变为针铁矿。当pH>7.5,针铁矿是常见的稳定产物[1]。BURTON et al[40]发现在缺氧还原的沉积环境中,施氏矿物可以迅速转化为针铁矿。在pH为2~7,随着pH升高,合成的施氏矿物转化成针铁矿的速率进一步加快[2],见图8。此外,KUBICKI et al[41]指出有机物中的—COOH和—NH2等基团可以与Fe3+等形成配位体,进而促进施氏矿物的溶解。VITHANA et al[38]也证实了在pH为4.5和6.5的条件下富里酸可以促进含砷施氏矿物中砷的再次释放。可以看出,施氏矿物对污染物去除的长期有效性,及其在不同环境条件下的转化过程和污染物固定、再次释放过程是实现施氏矿物应用前需解决的问题。
(3)关于施氏矿物实际应用的文献分析。近年来,施氏矿物的实际应用主要集中在环境污染治理领域,如水体重金属物吸附、有机物光催化降解和土壤重金属钝化等。在水环境治理方面,施氏矿物可以去除
${\rm{AsO}}_4^{3-} $ 、${\rm{CrO}}_4^{2-} $ 、${\rm{SbO}}_4^{3-} $ 、Cd2+、Cu2+,以及F−等污染物,文献超过百篇。BURTON et al[31]发现${\rm{AsO}}_4^{3-} $ 在低pH条件下的吸附量最大,而提高pH则有利促进于${\rm{AsO}}_3^{3-} $ 的吸附。进一步分析发现,${\rm{AsO}}_4^{3-} $ 吸附动力学遵循伪二级速率方程,存在两阶段的粒子内扩散过程。扩散速率参数的大小顺序为不规则颗粒>圆柱形颗粒>球形颗粒,主要与不规则颗粒具有最大的孔体积和孔隙率有关[42]。施氏矿物对${\rm{CrO}}_4^{2-} $ 的吸附机理与${\rm{AsO}}_4^{3-} $ 类似,均为污染物与铁羟基基团形成内层配合物[43]。而${\rm{SbO}}_4^{3-} $ 则是通过与施氏矿物表面形成外层配合体去除[35]。除氧阴离子外,施氏矿物对F−也展现了良好的吸附能力,吸附量达97.7 mg/g(30 ℃)[34]。这与F−很容易进入通道孔形成稳定的络合物,以及施氏矿物表面存在的—OH和$ {\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ 基团与F−进行离子交换有关。此外,施氏矿物对Cd2+、Cu2+和稀土元素等阳离子污染物也有较好的吸附效果[44-45]。施氏矿物多孔道结构以表面存在的阴离子基团有利于实现对水体中各种污染物去除。虽然施氏矿物在水体重金属污染修复领域已开展大量研究,但多数仍处于实验室阶段,需要进一步开展放大实验研究。关于研究施氏矿物去除有机污染物方面的论文始于2016年,至今共约15篇论文,涉及的有机物包括苯酚、磺胺、亚甲基蓝、硝基苯等[46-50]。WANG et al[36]发现施氏矿物作为催化剂,在苯酚氧化过程中表现出较高的耐盐性和良好的重复使用性。YANG et al[51]开发了一种原位修复技术,将施氏矿物/H2O2体系与电动力技术联用去除河流沉积物中的邻苯二甲酸盐和对乙酰氨基酚,发现其修复性能优于间歇降解法试验。LI et al[52]通过超声强化施氏矿物/H2O2体系,显著提高了双酚A的降解效率。较传统的铁基材料,施氏矿物由于兼具吸附和光催化能力,可以在较宽pH范围内实现污染物降解[53]。考虑到施氏矿物可以替代传统催化工艺中的其他类型铁基催化剂[54],预计未来该物质在有机物光催化降解方面会发挥更重要的作用。
施氏矿物在土壤修复方面应用的研究论文首次出现在2016年,目前发文量仅数篇。CHAI et al[55]采用生物合成的施氏矿物处理As污染土壤,发现经酸碱活化后,施氏矿物可以在较低用量条件下显著降低土壤中的水溶性As含量。YANG et al[56]发现As(Ⅲ)氧化菌和施氏矿物联合比单一采用As(Ⅲ)氧化菌处理高砷污染土壤显示了更好的As固定化效果,为高砷污染土壤绿色可持续修复开发了新的解决方案。然而,施氏矿物在土壤中的应用仍处于起步阶段且污染物种类单一,对于施氏矿物处理后土壤中施氏矿物的长期稳定性和重金属的再释放风险是未来重点研究方向。
随着研究的不断深入,施氏矿物在水体和土壤中重金属修复、光催化降解有机物等领域的潜能逐渐被发掘。基于施氏矿物在环境污染治理领域的应用探索正在进行并向绿色、经济、可持续的方向不断发展。但是到目前为止,大量研究主要集中在重金属污染水体修复方面。相对而言,对于该功能材料在光催化降解有机物以及土壤等复杂环境体系中的重金属修复等方向的应用挑战不容小觑,未来应给予更多关注。
-
(1)根据30年来施氏矿物研究发文量整体呈增长态势得出,研究初期发文量较少且趋势较为波动。2006年起,施氏矿物研究的发文量逐年递增,现可达60篇以上。随着全球对酸性矿山污染治理的不断重视,中国学者也对施氏矿物展开大量研究。
(2)发文量前三的国家为中国、美国、西班牙。从研究团体和研究机构来看,施氏矿物的研究有较为成型的作者合作群体,研究团队和研究机构之间合作交流较少。
(3)根据关键词分析,目前研究热点是吸附、修复、催化、转化和稳定性等。目前,对天然、合成及As/Cr掺杂施氏矿物在不同pH、温度、共存离子和有机物条件下的稳定性进行了研究。然而,在土壤和水体修复过程中,弱结晶的施氏矿物易转化为其他矿物(如针铁矿等)。对于相变发生过程,污染物再次释放过程和持续时间等问题,仍然缺乏系统的模拟和跟踪研究。
(4)根据施氏矿物在环境污染领域发文量及研究内容分析发现,施氏矿物对污染水体中阴阳离子的去除研究较多。作为一种新型环境功能材料,施氏矿物可替代传统铁基材料通过类芬顿反应等实现多种有机污染物(如苯酚和双酚A等)的降解。然而,其在反应过程中的循环利用能力和化学稳定性仍需进一步深入研究。
基于文献计量的环境功能材料施氏矿物的研究趋势分析
Research trend of the environmental functional material Schwertmannite based on bibliometrics analysis
-
摘要: 基于文献计量学分析方法,利用Web of Science核心合集数据库和中国知网(CKNI)数据库对1990—2021年期间有关施氏矿物的文献进行梳理和总结。通过分析发文量、国家、作者、研究机构、关键词等数据,绘制了关键词频次密度图和关键词突现图等,以回顾施氏矿物的研究历史,发掘其研究热点和研究趋势。结果表明:自20世纪90年代初施氏矿物首次报道以来,其相关发文量稳步上升,现超过60篇/年。关于施氏矿物的初期研究热点为其结构性质解析等,现阶段研究热点为其在重金属污染水体和土壤修复,以及光催化降解有机污染物等领域的应用探索。建议深入研究复杂环境体系中施氏矿物的稳定性及相变过程,以促进该环境友好功能材料在生态修复领域的进一步发展。Abstract: Based on the bibliometrics analysis method, the literatures on Schwertmannite from 1990 to 2021 were reviewed and summarized using the Web of Science core collection database and the China National Knowledge Network (CKNI) database. By analyzing databases such as publication volume, countries, authors, research institutions, and keywords, the keywords frequency density map and the emergent map were drawn to review the research history of Schwertmannite and identify research hotspots and trends. The results showed that publication volume related to Schwertmannite had steadily increased since their initial report in the early 1990s with more than 60 publications per year currently. In the early stage, the focus of the research on Schwertmannite was on the analysis of its structure and properties, while the current research hotpots included their application in the fields of heavy metal adsorption, soil remediation, and photocatalysis. It is suggested to study the environmental stability and the phase transformation process of Schwertmannite in complex environmental systems to promote the further development of these environmentally friendly functional materials in the field of the ecological restoration.
-
Key words:
- Schwertmannite /
- environmental remediation /
- research trends /
- bibliometrics analysis
-

-
表 1 施氏矿物研究发文量最多的学者(前10)
Table 1. The research scholar with the largest number of published papers on Schwertmannite (top 10)
序号 学者 国家 机构 文献数/
量篇总被引/
数次篇均被引
数次h指数 1 ZHOU L X(周立祥) 中国 南京农业大学 55 1060 20.78 20 2 NIETO J 西班牙 韦尔瓦大学 37 1564 42.27 21 3 BUTTON E 澳大利亚 南十字星大学 37 1579 42.68 20 4 AYORA C 西班牙 哈乌梅-阿尔梅拉
地球科学研究所28 1274 45.50 19 5 DANG Z(党志) 中国 华南理工大学 26 386 14.85 10 6 LU G N(卢桂宁) 中国 华南理工大学 25 384 17.45 10 7 SULLIVAN L 澳大利亚 堪培拉大学 25 1311 52.44 15 8 BUSH R 澳大利亚 南十字星大学 24 1371 57.13 16 9 JOHNSTON S 澳大利亚 南十字星大学 23 980 42.61 15 10 PEIFFER S 德国 拜罗伊特大学 23 928 40.35 10 表 2 施氏矿物研究机构(前10)
Table 2. The research institution with the largest number of publications on Schwertmannite (top 10)
排名 所属机构 国家 发文量/篇 总被引/
次篇均被
引/次1 UNIVERSIDAD DE HUELVA(韦尔瓦大学) 西班牙 53 1 933 36.47 2 CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS CSIC
(西班牙高等科研理事会)西班牙 52 2 043 38.55 3 NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY(南京农业大学) 中国 51 1 087 20.90 4 CSIC CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION Y DESARROLLO PASCUAL VILA CID CSIC(西班牙高等科研理事会研究与开发中心) 西班牙 46 1 935 42.07 5 CSIC INSTITUTO DE DIAGNOSTICO AMBIENTAL Y ESTUDIOS DEL AGUA IDAEA(环境诊断研究所和思想研究中心) 西班牙 36 1 243 34.53 6 SOUTHERN CROSS UNIVERSITY(南十字星大学) 澳大利亚 35 1 526 43.60 7 CENTRE NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE CNRS
(法国国家科学研究中心)法国 33 1 458 44.18 8 UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR(美国内政部) 美国 28 1 613 57.61 9 UNITED STATES GEOLOGICAL SURVEY(美国地质调查所) 美国 28 1 613 57.61 10 UNIVERSITY OF BAYREUTH(拜罗伊特大学) 德国 27 939 34.78 表 3 收录施氏矿物研究论文最多的期刊(前10)
Table 3. The journal with the largest collection of Schwertmannite research papers (top 10)
排名 期刊名称 发文量/篇 引用数/次 大类JCR分区 影响因子(2020 a) 1 APPLIED GEOCHEMISTRY 76 4 589 Q2 3.524 2 GEOCHIMICA ET COSMOCHIMICA ACTA 53 4 206 Q1 5.010 3 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY 49 3 059 Q1 9.028 4 CHEMICAL GEOLOGY 44 1 651 Q1 4.015 5 JOURNAL OF HAZARDOUS MATERIALS 31 1 119 Q1 10.588 6 SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT 28 801 Q1 7.963 7 CHEMOSPHERE 28 560 Q1 7.086 8 JOURNAL OF GEOCHEMICAL EXPLORATION 22 1260 Q1 3.746 9 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND POLLUTION RESEARCH 20 274 Q2 4.223 10 MINERALS 19 256 Q1 2.644 表 4 被引频次最高的施氏矿物研究文献(前10)
Table 4. The most frequently cited research papers on Schwertmannite (top 10)
排名 论文标题 发表年份 通讯作者 作者机构 国家 所属期刊 被引数/次 1 Schwertmannite and the chemical modeling of iron in acid sulfate waters 1996 BIGHAM J 俄亥俄
州立
大学美国 GEOCHIMICA ET COSMOCHIMICA ACTA 831 2 Nanoparticulate iron oxide minerals in soils and sediments: unique properties and contaminant scavenging mechanisms 2005 WAYCHUNAS G 劳伦斯伯
克利国家
实验室美国 JOURNAL OF NANOPARTICLE RESEARCH 466 3 An in situ ATR-FTIR investigation of sulfate bonding mechanisms on goethite 1999 PEAK D 特拉华大学 美国 JOURNAL OF COLLOID AND INTERFACE SCIENCE 394 4 Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Odiel river watershed, Huelva, SW Spain): Geochemistry, mineralogy and environmental implications 2005 ESPANA J 西班牙地
质和采矿
研究所西班牙 APPLIED GEOCHEMISTRY 387 5 Scavenging of As from acid mine drainage by schwertmannite and ferrihydrite: A comparison with synthetic analogues 2002 BIGHAM J 俄亥俄州
立大学美国 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY 328 6 Schwertmannite, a new iron oxyhydroxysulphate from Pyhasalmi, Finland, and other localities 1994 BIGHAM J 俄亥俄州
立大学美国 MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE 317 7 Formation and stability of schwertmannite in acidic mining lakes 2004 REGENSPURG S 科罗拉多
矿业学院美国 GEOCHIMICA ET COSMOCHIMICA ACTA 312 8 Use and limitations of second-derivative diffuse reflectance spectroscopy in the visible to near-infrared range to identify and quantify Fe oxide minerals in soils 1998 SCHEINOST A 特拉华大学 美国 CLAYS AND CLAY MINERALS 304 9 Removal of trace metals by coprecipitation with Fe, Al and Mn from natural waters contaminated with acid mine drainage in the Ducktown Mining District, Tennessee 2002 BIGHAM J 俄亥俄州
立大学美国 APPLIED GEOCHEMISTRY 300 10 Trace metal adsorption onto an acid mine drainage iron(III) oxy hydroxy sulfate 1998 WEBSTER J 环境科学与
研究机构新西兰 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY 288 -
[1] SCHOEPFER V A, BURTON E D. Schwertmannite: A review of its occurrence, formation, structure, stability and interactions with oxyanions[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021: 221:103811. [2] REGENSPURG S, BRAND A, PEIFFER S. Formation and stability of Schwertmannite in acidic mining lakes[J]. Geochimica etCosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(6): 1185 − 1197. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.07.015 [3] MOSLEY L M, DANG T, MCLAUGHLIN M J, et al. Extreme biogeochemical effects following simulation of recurrent drought in acid sulfate soils[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2022, 136:105146. [4] RIBEIRO J, TAFFAREL S R, SAMPAIO C H, et al. Mineral speciation and fate of some hazardous contaminants in coal waste pile from anthracite mining in Portugal[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2013, 109-110: 15 − 23. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.01.007 [5] HOUNGALOUNE S, KAWAAI T, HIROYOSHI N, et al. Study on Schwertmannite production from copper heap leach solutions and its efficiency in arsenic removal from acidic sulfate solutions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 147-148: 30 − 40. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.04.001 [6] YING H, HUANG K, FENG X, et al. As(Ⅲ) adsorption–oxidation behavior and mechanisms on Cr(VI)-incorporated Schwertmannite[J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2021, 8(6): 1593 − 1602. doi: 10.1039/D1EN00104C [7] LI X, GUO C, JIN X, et al. Mechanisms of Cr(VI) adsorption on Schwertmannite under environmental disturbance: Changes in surface complex structures[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 125781. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125781 [8] 何楚城, 李晓飞, 祝紫莹, 等. 柠檬酸-施氏矿物复合体对Cd和Pb的吸附研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(12): 4793 − 4802. [9] YAN S, ZHAN L, MENG X, et al. Role of Schwertmannite or jarosite in photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole in ultraviolet/peroxydisulfate system[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 274:118991. [10] 王妍燕, 师欣茹, 毕文龙, 等. 施氏矿物协同Cu(II)活化过硫酸盐去除水中土霉素的效果[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 42(2): 108 − 116. [11] 周佳兴, 董燕, 刘奋武, 等. NaBH4对施氏矿物-黄铁矾生物化学合成的影响及矿物在催化降解甲基橙中的应用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(4): 1242 − 1251. [12] XIYANG H. A visual analysis of the research on the use of mobile phones by college students based on VOSviewer[J]. International Journal of Education and Management Engineering, 2020, 10(6): 10 − 16. [13] OLAWUMI T O, CHAN D W M. A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 183: 231 − 250. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.162 [14] 陈甜倩, 高阳, 冯喆, 等. 基于CiteSpace的土壤生态系统服务研究热点与趋势[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2021, 26(7): 204 − 219. [15] DAVARAZAR M, JAHANIANFARD D, SHEIKHNEJAD Y, et al. Underground carbon dioxide sequestration for climate change mitigation – A scientometric study[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2019, 33: 179 − 188. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2019.05.022 [16] 蒲生彦, 吕雪, 张颖. 基于文献计量的全球活化过硫酸盐氧化技术研究趋势分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(10): 2895 − 2908. [17] KHALAJ M, KAMALI M, COSTA M E V, et al. Green synthesis of nanomaterials - A scientometric assessment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 267:122036. [18] WANG X, ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Progress in urban metabolism research and hotspot analysis based on CiteSpace analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 281:125224. [19] KASAVAN S, YUSOFF S, RAHMAT FAKRI M F, et al. Plastic pollution in water ecosystems: A bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2020[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 313:127946. [20] ACHARYA B S, KHAREL G. Acid mine drainage from coal mining in the United States – An overview[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 588:125061. [21] CANOVAS C R, OLIAS M, NIETO J M, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the Tinto and Odiel Rivers (SW Spain). Factors controlling metal contents[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2007, 373(1): 363 − 382. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.11.022 [22] SHRIVASTAVA R, MAHAJAN P. Artificial Intelligence Research in India: A Scientometric Analysis[J]. Science & Technology Libraries, 2016, 35(2): 136 − 151. [23] ZHANG J, JIANG L, LIU Z, et al. A bibliometric and visual analysis of indoor occupation environmental health risks: Development, hotspots and trend directions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 300:126824. [24] BLGHAM J M, SCHWERTMANN U, CARLSON L, et al. A poorly crystallized oxyhydroxysulfate of iron formed by bacterial oxidation of Fe(II) in acid mine waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(10): 2743 − 2758. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90009-A [25] SáNCHEZ-ESPAñA J, YUSTA I, DIEZ-ERCILLA M. Schwertmannite and hydrobasaluminite: A re-evaluation of their solubility and control on the iron and aluminium concentration in acidic pit lakes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(9-10): 1752 − 1774. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.020 [26] JöNSSON J, PERSSON P, SJöBERG S, et al. Schwertmannite precipitated from acid mine drainage: phase transformation, sulphate release and surface properties[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(1): 179 − 191. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.04.008 [27] REGENSPURG S, PEIFFER S. Arsenate and chromate incorporation in Schwertmannite[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(6): 1226 − 1239. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.12.002 [28] WANG X, YING H, ZHAO W, et al. Molecular-scale understanding of sulfate exchange from Schwertmannite by chromate versus arsenate[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(9): 5857 − 5867. [29] FRENCH R A, MONSEGUE N, MURAYAMA M, et al. The structure and transformation of the nanomineral Schwertmannite: a synthetic analog representative of field samples[J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2013, 41(4): 237 − 246. [30] ZHANG C, ZHANG Z, CHEN M, et al. The influence of fractal nature on Schwertmannite adsorption properties[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(45): 27895 − 27899. doi: 10.1039/C7RA04114D [31] BURTON E D, BUSH R T, JOHNSTON S G, et al. Sorption of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) to Schwertmannite[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(24): 9202 − 9207. [32] 李浙英, 梁剑茹, 柏双友, 等. 生物成因与化学成因施氏矿物的合成、表征及其对As(III)的吸附[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(3): 460 − 467. [33] MORI J F, LU S, HANDEL M, et al. Schwertmannite formation at cell junctions by a new filament-forming Fe(II)-oxidizing isolate affiliated with the novel genus Acidithrix[J]. Microbiology (Reading), 2016, 162(1): 62 − 71. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000205 [34] ESKANDARPOUR A, ONYANGO M S, OCHIENG A, et al. Removal of fluoride ions from aqueous solution at low pH using Schwertmannite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 152(2): 571 − 579. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.020 [35] LI Y, MOHAN D, PITTMAN C U, et al. Removal of antimonate and antimonite from water by Schwertmannite granules[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2016, 57(53): 25639 − 25652. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2016.1155176 [36] WANG W M, SONG J, HAN X. Schwertmannite as a new Fenton-like catalyst in the oxidation of phenol by H2O2[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 262: 412 − 419. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.076 [37] PAIKARAY S. Environmental Stability of Schwertmannite: A Review[J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2020, 40(3): 570 − 586. [38] VITHANA C L, SULLIVAN L A, BURTON E D, et al. Liberation of acidity and arsenic from Schwertmannite: Effect of fulvic acid[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 372: 1 − 11. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.02.012 [39] CARABALLO M A, RIMSTIDT J D, MACíAS F, et al. Metastability, nanocrystallinity and pseudo-solid solution effects on the understanding of Schwertmannite solubility[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 360-361: 22 − 31. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.09.023 [40] BURTON E D, JOHNSTON S G, KRAAL P, et al. Sulfate availability drives divergent evolution of arsenic speciation during microbially mediated reductive transformation of Schwertmannite[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(5): 2221 − 2229. [41] KUBICKI J D, TUNEGA D, KRAEMER S. A density functional theory investigation of oxalate and Fe(II) adsorption onto the (010) goethite surface with implications for ligand- and reduction-promoted dissolution[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 464: 14 − 22. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.08.010 [42] DOU X, MOHAN D, PITTMAN C U, JR. Arsenate adsorption on three types of granular Schwertmannite[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(9): 2938 − 2948. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.01.035 [43] ANTELO J, FIOL S, GONDAR D, et al. Comparison of arsenate, chromate and molybdate binding on Schwertmannite: surface adsorption vs anion-exchange[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2012, 386(1): 338 − 343. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2012.07.008 [44] GAN M, SUN S, ZHENG Z, et al. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) by AlPO4 modified biosynthetic Schwertmannite[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 356: 986 − 997. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.200 [45] HERMASSI M, GRANADOS M, VALDERRAMA C, et al. Recovery of rare earth elements from acidic mine waters: An unknown secondary resource[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 810: 152258. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152258 [46] MA S, JING J, LIU P, et al. High selectivity and effectiveness for removal of tetracycline and its related drug resistance in food wastewater through Schwertmannite/graphene oxide catalyzed photo-Fenton-like oxidation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 392: 122437. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122437 [47] LI T, WANG Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Organic carbon modified Fe3O4/Schwertmannite for heterogeneous Fenton reaction featuring synergistic in-situ H2O2 generation and activation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 276. [48] LIU L D, WANG W M, LIU L, et al. Catalytic activities of dissolved and Sch-immobilized Mo in H2O2 decomposition: Implications for phenol oxidation under acidic conditions[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 185: 371 − 377. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.12.010 [49] ZHU Y, ZENG C, ZHU R, et al. TiO2/Schwertmannite nanocomposites as superior co-catalysts in heterogeneous photo-Fenton process[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2019, 80: 208 − 217. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.12.014 [50] DUAN H, LIU Y, YIN X, et al. Degradation of nitrobenzene by Fenton-like reaction in a H2O2/schwertmannite system[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 283: 873 − 879. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.033 [51] YANG G C C, HUANG S C, WANG C L, et al. Degradation of phthalate esters and acetaminophen in river sediments using the electrokinetic process integrated with a novel Fenton-like process catalyzed by nanoscale Schwertmannite[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 159: 282 − 292. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.119 [52] LI X, ZHANG Y, XIE Y, et al. Ultrasonic-enhanced Fenton-like degradation of bisphenol A using a bio-synthesized Schwertmannite catalyst[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 344: 689 − 697. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.019 [53] 王鹤茹, 宋永伟, 徐峙辉, 等. 化学合成施氏矿物与 H2O2共存体系下光化学处理垃圾渗滤液的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(4): 1407 − 1413. [54] LI T, ZHU P, WANG D, et al. Efficient utilization of the electron energy of antibiotics to accelerate Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle in heterogeneous Fenton reaction induced by bamboo biochar/Schwertmannite[J]. Environmental research, 2022, 209: 112830. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112830 [55] CHAI L, TANG J, LIAO Y, et al. Biosynthesis of Schwertmannite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its application in arsenic immobilization in the contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2016, 16(10): 2430 − 2438. doi: 10.1007/s11368-016-1449-7 [56] YANG Z, WU Z, LIAO Y, et al. Combination of microbial oxidation and biogenic Schwertmannite immobilization: A potential remediation for highly arsenic-contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 181: 1 − 8. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.041 -



 下载:
下载: