-
石油应用于生活中方方面面。在石化生产区及加油站等地,由于油类物质及相关废水的排放、输送管线跑冒滴漏及防渗措施不完善等原因,往往造成地下水中石油类污染,并对当地的地下水环境造成严重威胁。人们已经意识到针对地下水中石油类污染开展治理工作的必要性和紧迫性,并将石油类污染物列为生态系统中应优先控制的潜在危险性大的毒害性污染物[1-2]。
我国针对地下水中石油类污染的模拟工作与污染运移相关问题的研究同步。20世纪80年代,周维四等[3-4]对胜坨油田一区进行了数值模拟研究。随着地下水数值模拟研究的发展,人们更加专注与某一项污染物的运移特征及预测方面研究,如郑西来等[5]针对大庆油田对地下水中石油污染物运移的耦合模型开展了相关研究。这些前期研究在摸清地下水污染物运移机制、减少模型参数中的不确定性影响、提高模型模拟的精确度等方面对地下水石油类污染治理具有积极的意义;国外则越来越多的利用GIS(地理信息系统)技术联合数值模拟技术对污染物运移进行专项研究,来系统的量化区域条件、环境影响以及健康影响[6]。
在了解该项污染修复技术手段及国内外研究现状后,以北京市丰台区某石油化工地块为例,开展了针对地下水中石油类污染物的运移模拟应用与研究。为获取真实的地块水文地质参数,先期开展了大量抽水与注水试验、弥散试验及抽出-曝气处理-回灌试验等现场工作[7-8]。在分析了地块的水文气象特征、水文地质条件等背景后,构建了地块水文地质概念模型,并利用地下水数值模拟软件对地块浅层地下水(即受污染含水层位)在修复过程中特征污染物(苯)的运移进行了数值模拟研究[9-11]。
-
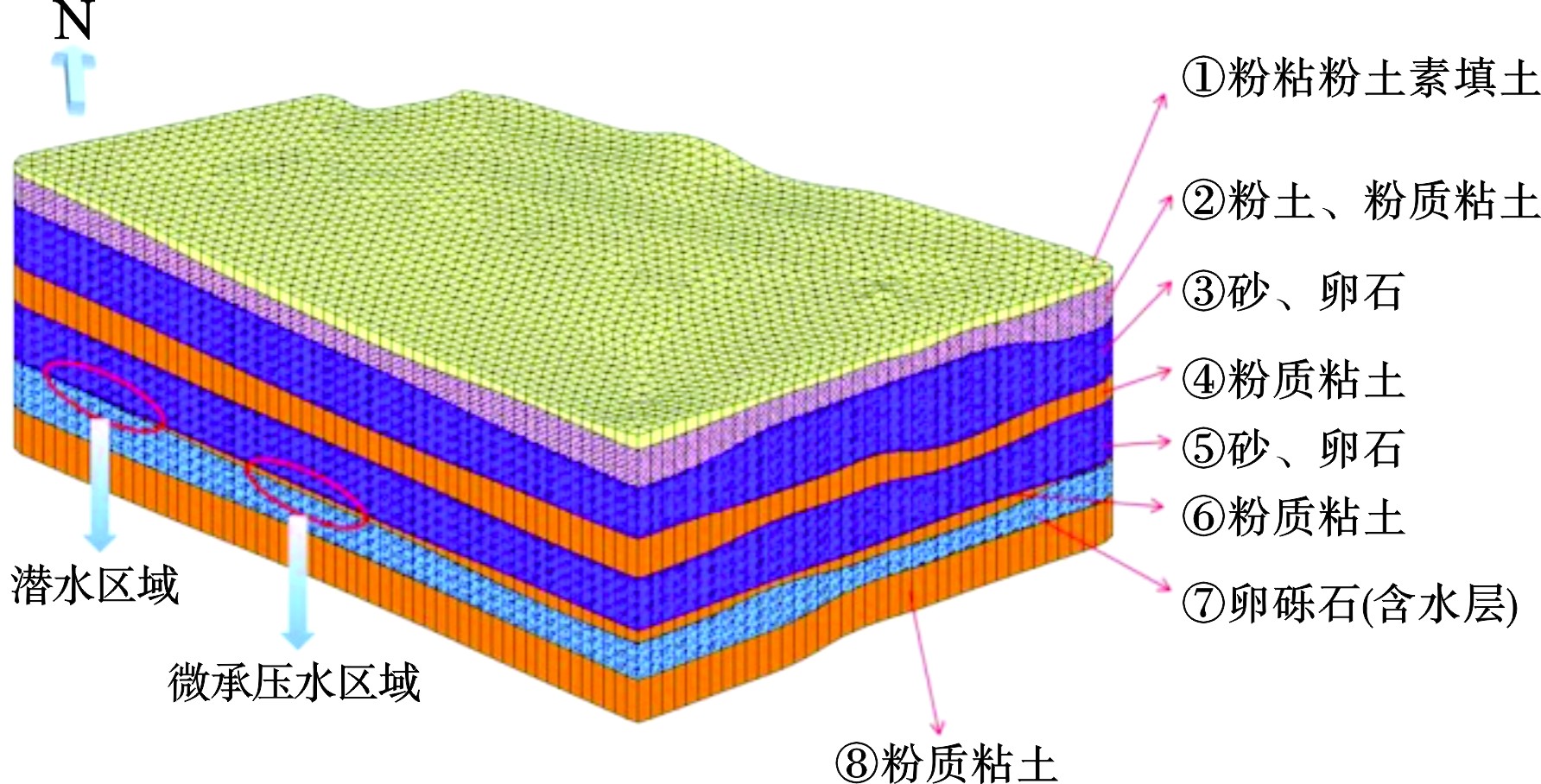
根据勘察成果,地块地面以下55 m深度范围内地层按沉积成因与年代划分为人工堆积层、新近沉积层及第四纪沉积层3大类,并按地层岩性及其赋水特性自上而下进一步划分为8个大层及其亚层。试验区三维地层结构,见图1。
试验区地形较平坦,水位埋深在24 m左右,水位年变幅较小。地下水类型为潜水,含水层介质以卵石、中砂为主。主要接受大气降水入渗和侧向径流补给,地下水径流条件较好,以侧向径流和人工开采为主要排泄方式。
-
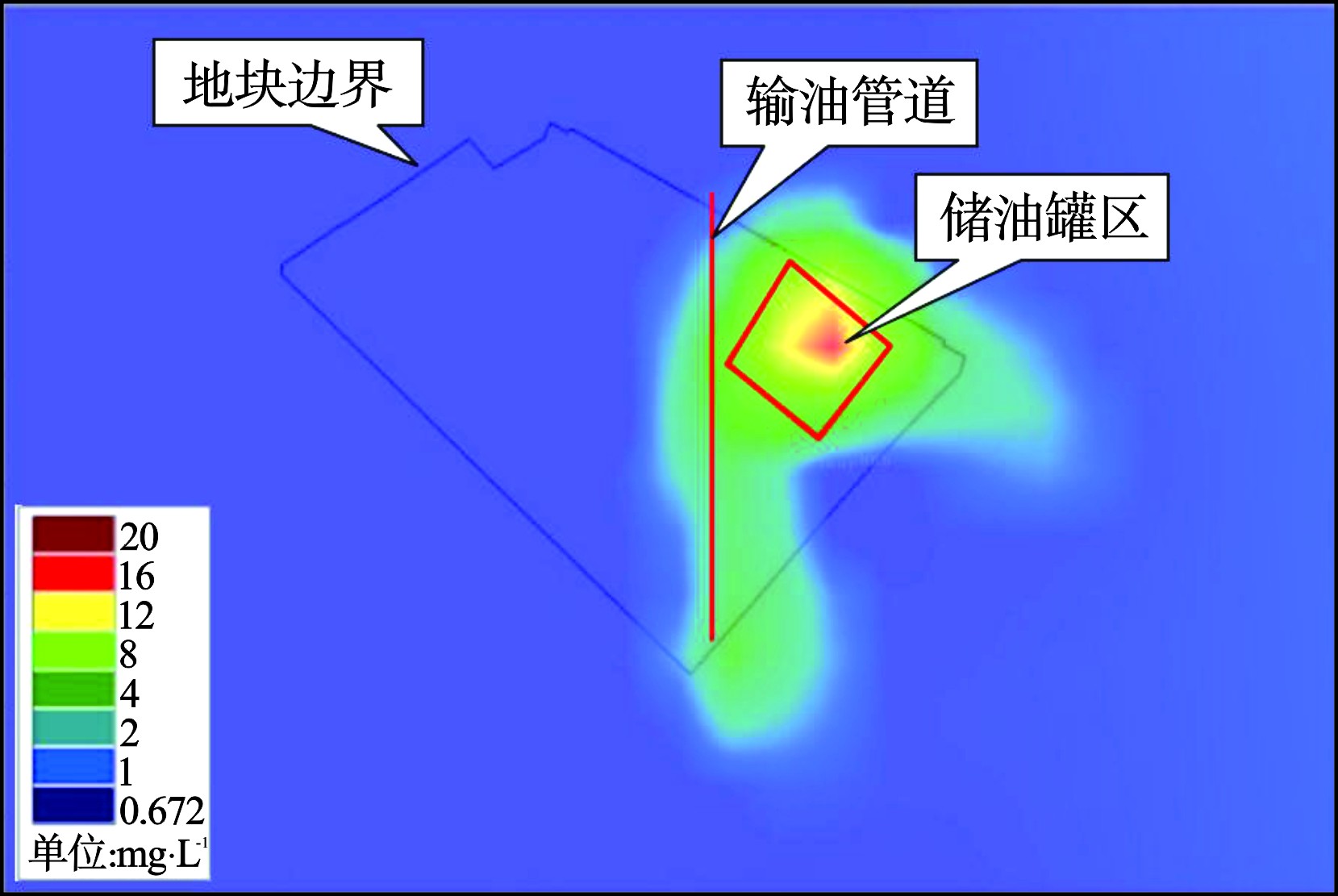
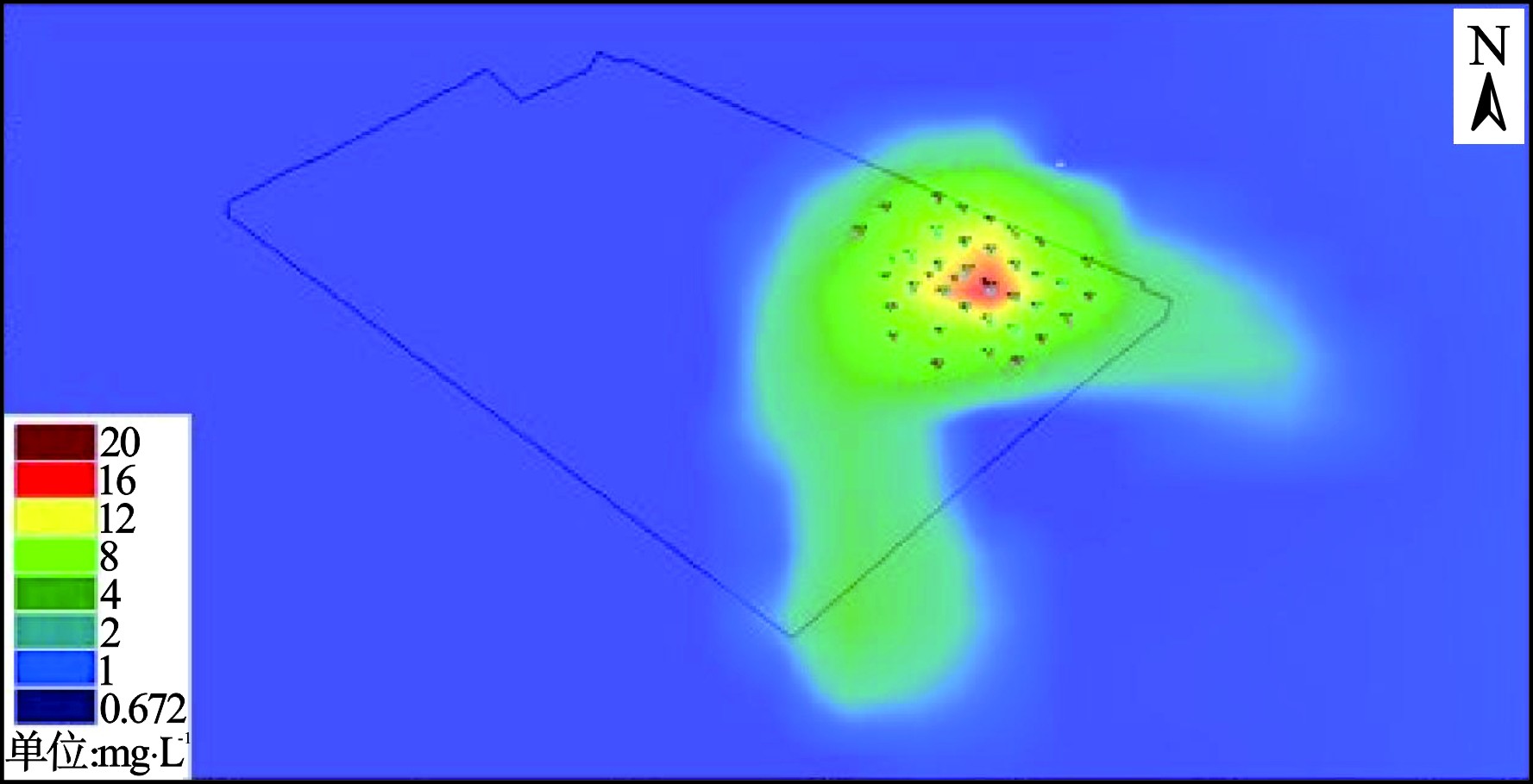
地块的污染成因主要是油料在储存、运输、生产过程中的泄漏。地块地层以高渗透性砂、卵砾石层为主,易于污染物垂向迁移,经过长期的雨水淋溶、下渗等作用形成地块内的污染现状。地块地下水样品中苯超标率最大、超标倍数最高,因此选择苯作为模拟的目标污染物。地块主要污染源及苯浓度分布,见图2。
-
数值模拟利用Visual Modflow软件开展。该软件专门用于孔隙介质中地下水流动及溶质运移数值模拟,具体包括Modflow(水流评价)、Modpath(平、剖面流线示踪)和MT3D(溶质运移)3部分。
-
与模拟区地下水系统水文地质概念模型相对应的数学模型,见式(1):
式中:Ω为渗流区域;h为含水层的水位标高,m;K为渗透系数,m·d−1;Kn为边界面法向方向的渗透系数,m·d−1;S为自由面以下含水层储水系数;μ为潜水含水层在潜水面上的重力给水度;ε为含水层的源汇项,d−1;p为潜水面的蒸发和降水等,d−1;h0为含水层的初始水位分布,m;Γ0为渗流区域的上边界,即地下水的自由表面;Γ1为渗流区域的水位边界;Γ2为渗流区域的流量边界;Γ3为混合边界;
$\vec{n}$ 为边界面法线方向;q(x,y,t) 定义为二类边界的单宽流量/m3· (d·m)−1。 -
利用上述地下水流模型建立模拟区的溶质运移模型。含有对流、弥散和源汇项、一级动力学衰减作用的溶质运移可采用以下的微分方程的定解问题表示[12],见式(2):
式中:Ω为渗流区域;c为污染组分浓度/mg·L−1;ui为3个方向下水实际流速,m·d−1;Dij为水动力弥撒张量的9个分量;R为阻滞因子,其值常>1;c0为污染组分的初始浓度/mg·L−1;Γ1为一类边界;c1为类浓度边界值,即在该边界上浓度值已知/mg·L−1;Γ2为二类边界;fi为二类边界值,即通过该边界的溶质通量已知/mg·m−2;qs为源汇项单位流量;cs为源汇项溶质浓度;λ为一级反应系数。
以上是Visual Modflow软件的理论基础。
-
为了确定合理的抽出-处理-回灌运行模式,在前期试验及抽灌井井间距、排间距确定的基础上,以地块潜水的代表性污染物苯为例,采用数值模拟技术对抽出-处理-回灌过程中苯的水平向运移进行模拟,为确定地下水抽出-处理-回灌运行模式提供技术支撑。
首先结合水文地质勘察成果,概化处理模拟区内含水层、边界及源汇项等特征条件,建立地块所在区域的水文地质特征模型,并建立水流模型及溶质运移模型[13-15],针对两种不同的地下水修复设计方案进行模拟预测。
-
考虑到模型精度的需要,水文地质概念模型的建立利用了前期地块环境调查阶段勘察资料,经过一定分析和筛选后,最终选定了地质钻孔22个(孔深在45 m深度范围内,深度以第一层含水层隔水底板以下0.5 m为准)。
模拟区地下水流从空间角度分析,地下水系统符合质量守恒定律和能量守恒定律;地块内地下水为非稳定流并符合达西定律,可概化为三维流;含水层系统具有非均质性;地下水流。故可将模拟区概化为非均质各向同性的三维非稳定地下水流系统[15-16]。
-
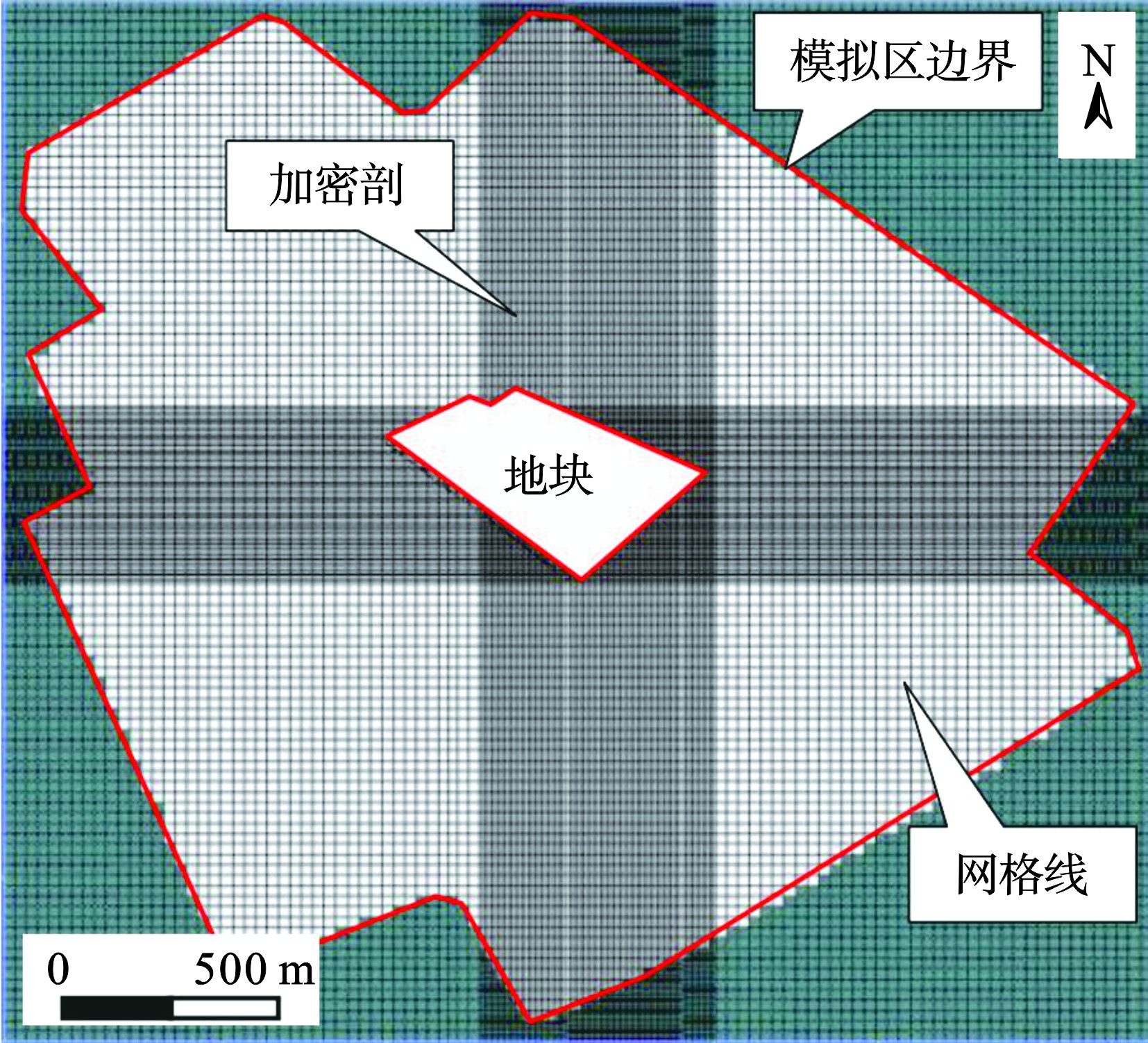
数值模型模拟范围总面积约638400 m2。根据模拟区的含水层分布、边界条件和地下水流场等,在平面上剖分成大小为2100 m×1900 m的矩形单元,共151行、162列,单元格总计24 462个。其中模拟区域分为非活动单元格和活动单元格,对污染修复地块进行网格加密处理。网格剖分,见图3。
-
结合地块钻孔记录,将区域内地层概化为7层,其中第7层为含水层,也是修复目标层。数值模拟范围中地层垂向结构概化信息,见表1。
-
模型以完整水文地质单元边界作为模型边界,模拟范围地下水水力梯度变化不大,边界设置如下:上边界为自然地面为上边界部分;下边界则取至第一层地下水隔水底板,作为隔水边界来考虑;侧向边界选取模型中西北部及东南部潜水含水层边界设置为一类定水头边界,接近项目地块所在区域实测潜水流场,模型西北-东南方向边界为零流量边界。初始浓度场按照实测区域地下水苯浓度分布确定。
-
鉴于地下水面埋藏较深,降水补给地下水量十分有限,区域内无出水量较大的工、农、生活用地下水井,且模拟期仅限于有限地抽出-回灌时段内。因此,模拟区地下水补给和排泄均为侧向径流,暂不考虑其他源汇项。
-
模型含水层水文地质参数根据地层岩性分布、现场水文地质试验(包括抽水试验、提水试验和弥散试验等)数据和不同历史时期的有关水文地质调查资料,经过一定修正后综合确定,并通过模型调整。模型的含水层主要参数取值,见表2。
-
根据潜水的水力梯度,利用达西定律计算边界取值,根据多年观测数据确定水力梯度为0.8‰。长时期内模拟区域的主要源汇项包括降水入渗补给量和地下水开采量,但是模拟区域内无长期用于生活、工业、农业的地下水开采井,且地下含水层埋深20 m以下,短期模拟暂时不考虑上述源汇项。
-
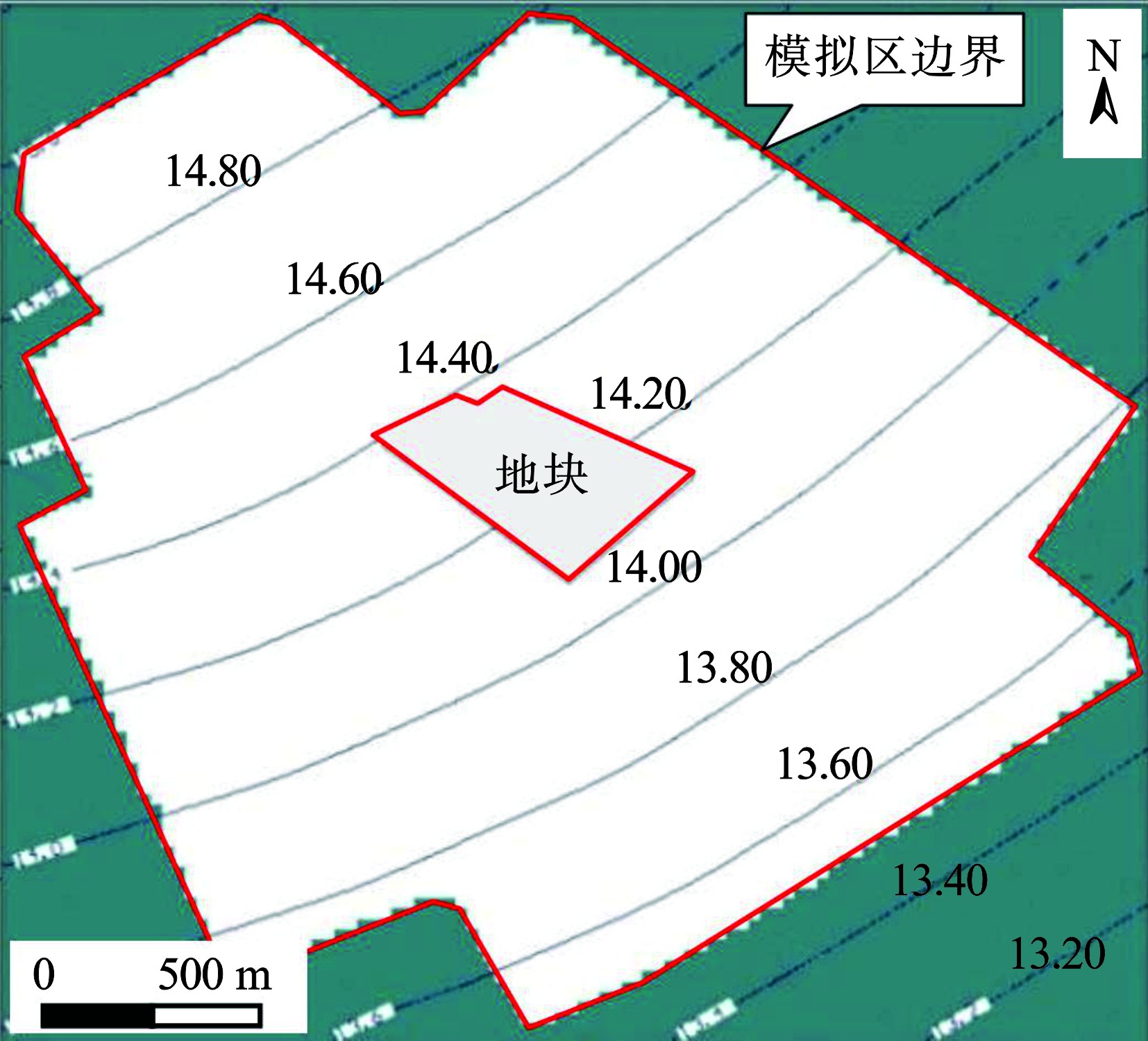
数值模拟以调查期间7月水位作为初始水位,模拟区潜水初始流场,见图4。
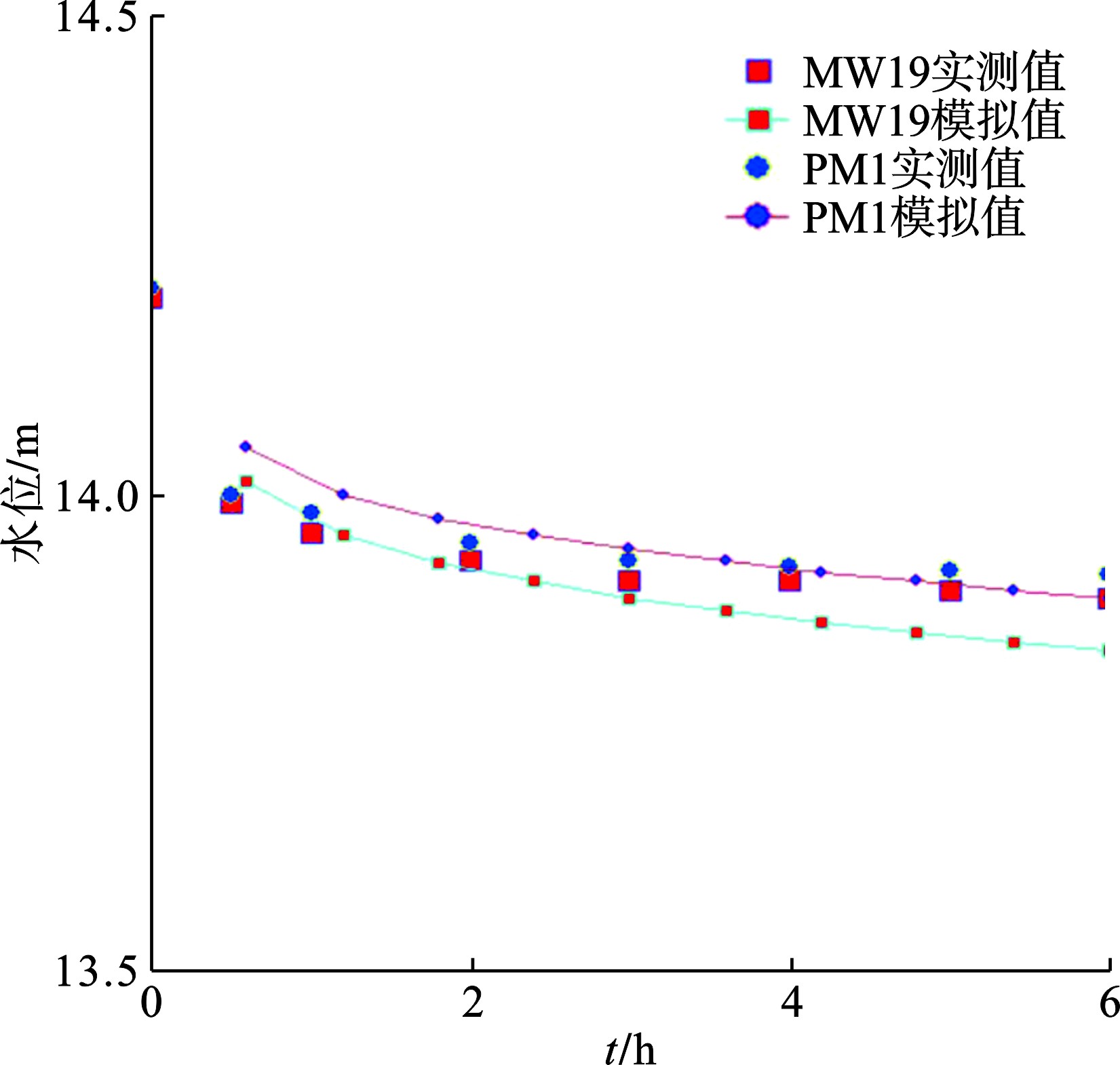
模型通过单井抽水试验完成识别过程,试验过程持续6 h,试验区地下水水位在试验2 h后基本达到稳定状态,通过对比模拟流场与实测流场进行拟合。水位监测井PM1与MW19实测值与计算值拟合,见图5。
-
模拟中弥散度及Langmuir吸附参数拟合过程是根据在污染地块内进行的 “前排抽水-后排回灌”方式的技术测试确定。
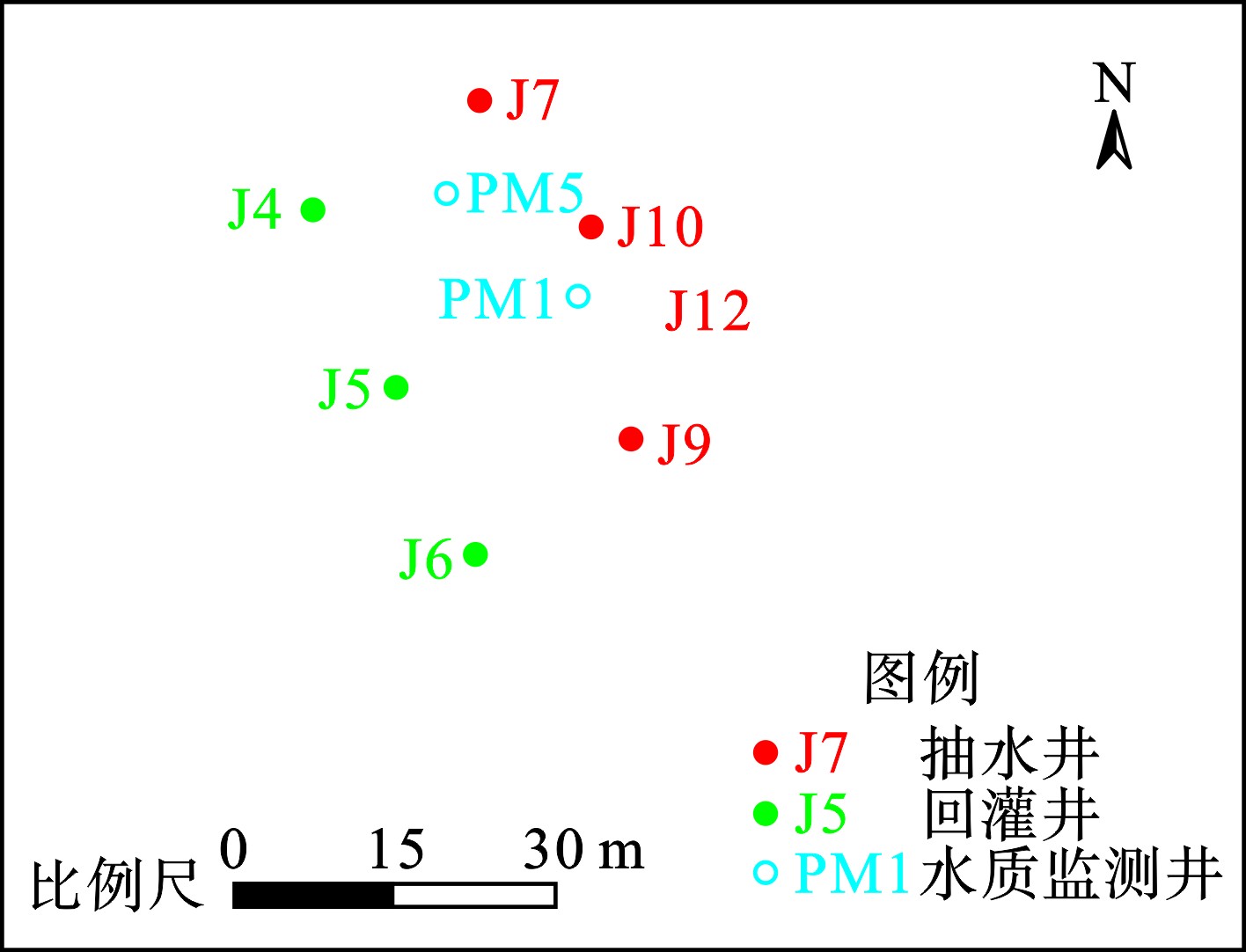
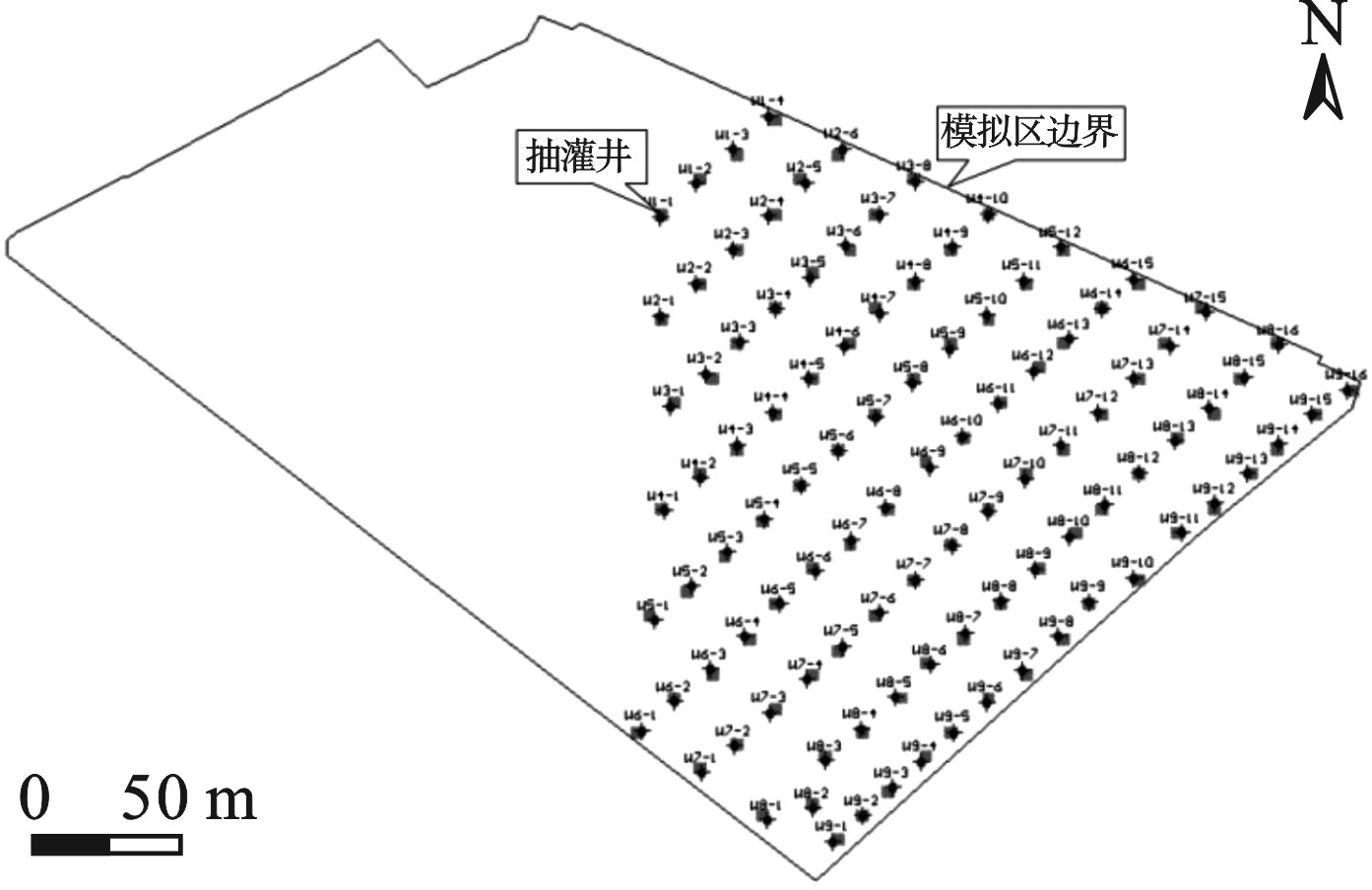
试验由4个抽水井和3个回灌井组成。在抽灌井之间布设了2个水质监测井PM1和PM5。水质监测井分布位置,见图6。
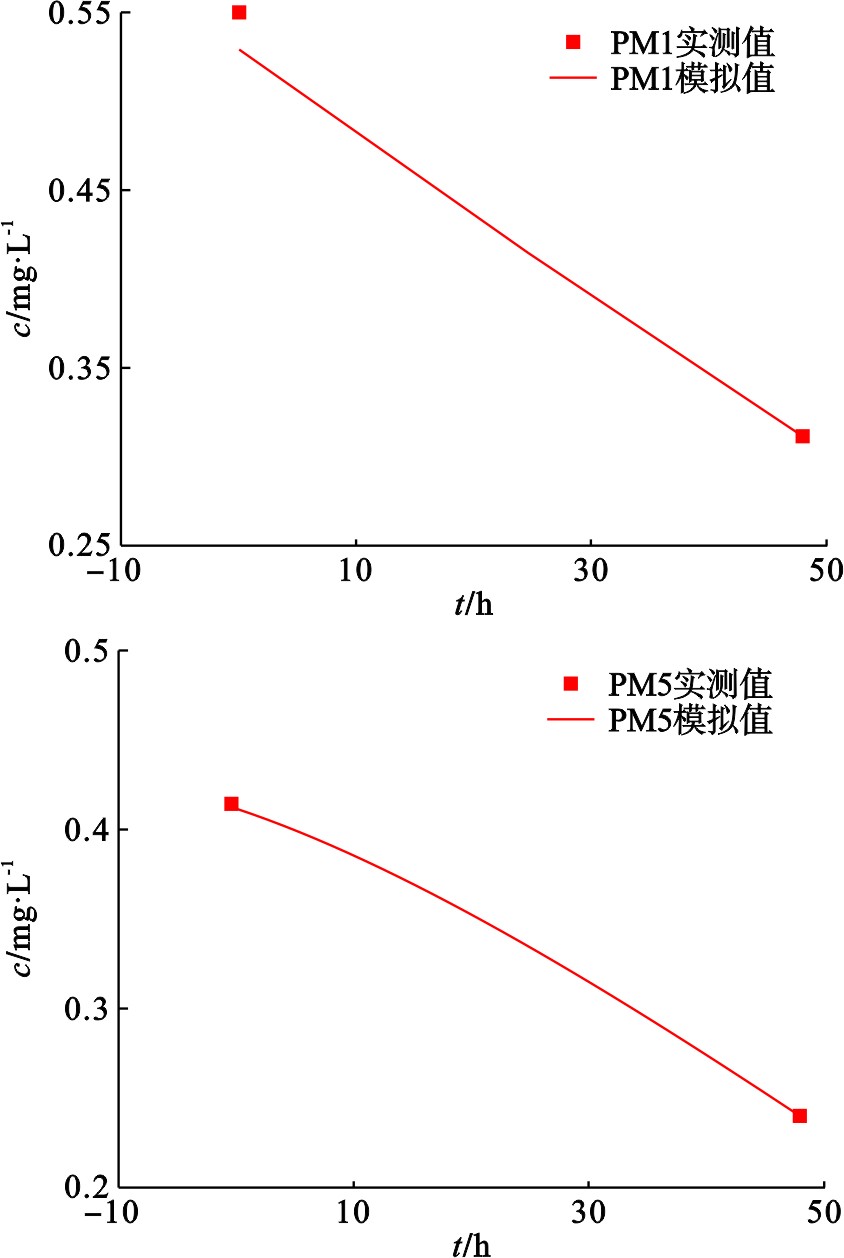
以试验前统测苯浓度作为识别过程的初始浓度场,以PM1和PM5在试验运行前及运行48 h后的统测浓度作为识别基础数据。经过不断调参后,得到两个水质监测井苯浓度的拟合结果,见图7。
从上述2个水质监测井苯浓度拟合结果,得到Langmuir吸附参数范围:Kl[1/(mg/L)]=1 E-7~3E-7,a[mg/mg]=1。
考虑最不利的苯去除效果,即吸附能力最强的情况,选择Kl[1/(mg/L)]= 3E−7作为抽出-回灌过程模拟的初始值。
-
在模型参数初步取值的基础上,通过试验阶段水位及水质动态观测数据对模型参数进一步识别和校正,得到最终模型参数,见表3。
-
在前述各项模型识别等工作的基础上,模拟预测不同抽出-回灌方案下地下水中苯的浓度变化。
根据既定的布井方案,分别从“由上游到下游逐排处理”和重污染区域“中心抽水-四周回灌”两种抽出-回灌处理思路,对抽出-回灌系统运行过程中地下水中苯浓度污染情况进行模拟预测,并根据模拟结果确定抽出-回灌运行方案的可行性。
根据调查期间7月地块内及周边地下水取样监测结果设定模型初始浓度场,模拟区地下水初始苯浓度分布情况见图2,在此浓度场基础上进行不同抽出-回灌方案的苯浓度运移模拟。
-
以苯浓度最高点为中心进行井群布设,中间位置布设17眼抽水井,井间距在15~20 m。抽水井群外围布设18眼回灌井,其中相邻回灌井井间距15~20 m,回灌井与其最近的抽水井间距15~20 m。抽水井、回灌井布设情况,见图8。
按照由浓度高到浓度低的位置分布,在抽出-回灌区域不同苯浓度区域布设水质监测井M1、M2、M3、M4(监测井所处位置苯浓度M1>M2>M3>M4),观测抽出-回灌系统对不同浓度苯污染物的去除效果。
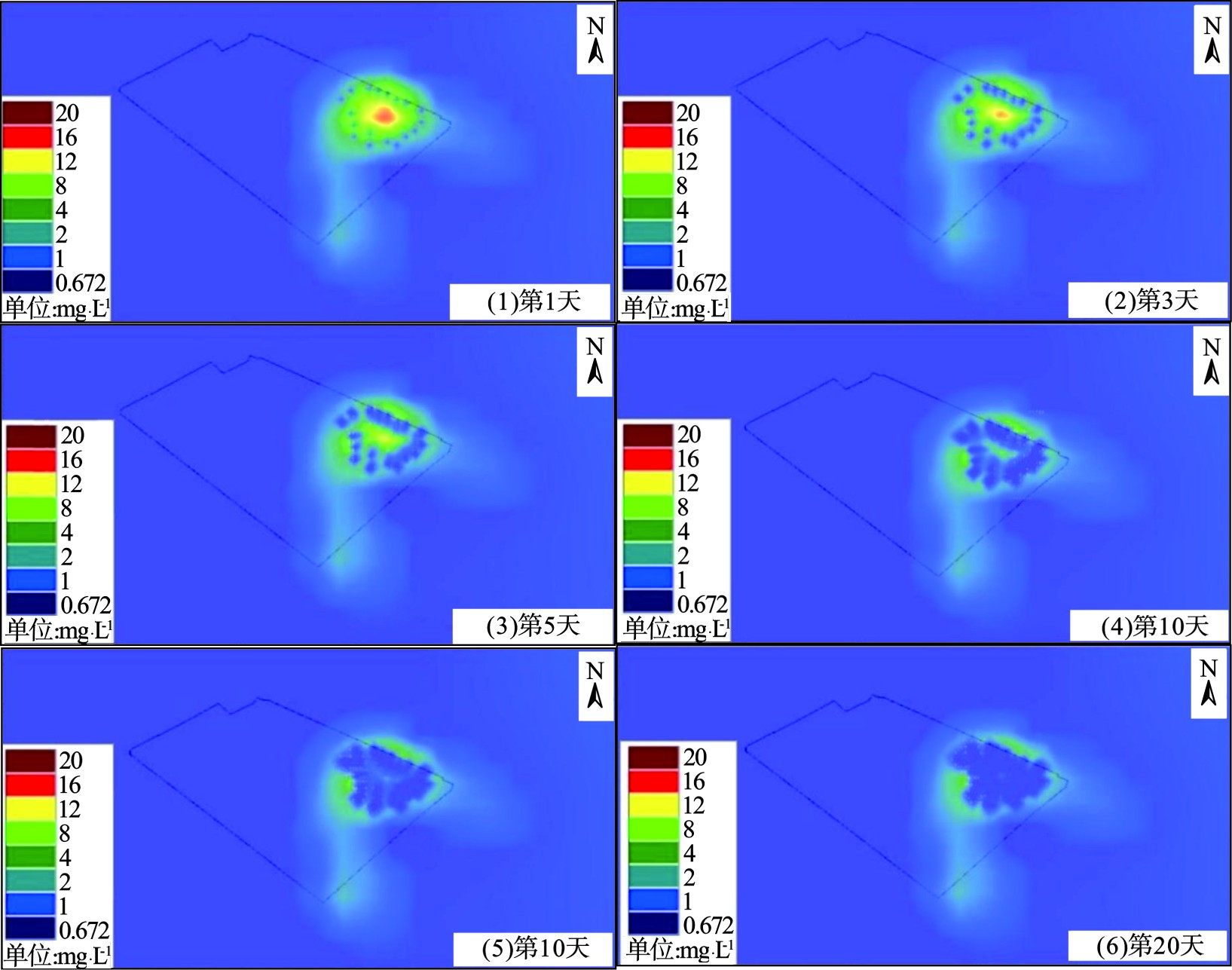
从开始运行后,回灌井进水均为地面处理后满足修复目标值的水,苯浓度均在0.672 mg/L以下,因此模型中设定回灌井浓度恒定为0.672 mg/L。模拟抽出-回灌运行时间为30 d,分别预测抽出-回灌系统运行1、3、5、10、15和20 d的苯去除效果。系统运行过程中苯浓度变化预测结果,见图9。
由上述模拟结果可知,模拟抽出-回灌1 d后,在回灌井附近5 m范围内地下水苯浓度均降至0.672 mg/L的修复目标值内;运行3 d后,回灌井附近低于修复目标值的苯浓度范围逐渐向相邻回灌井及抽水井扩展,部分可以覆盖相邻两眼回灌井;运行5 d后,中心高浓度区域由试验前的20 降至12 mg/L以下,且高浓度范围逐渐缩小,回灌井群形成苯浓度低于0.672 mg/L的闭合网络,且不断向中心重污染区域扩展。之后,中心区域苯浓度持续下降,到运行15 d时,重污染区域苯浓度基本降至3 mg/L以下,25 d之后,抽出-回灌范围内以低于符合处理目标值的区域为主,运行30 d后,重污染区域苯浓度基本降至修复目标值以下。
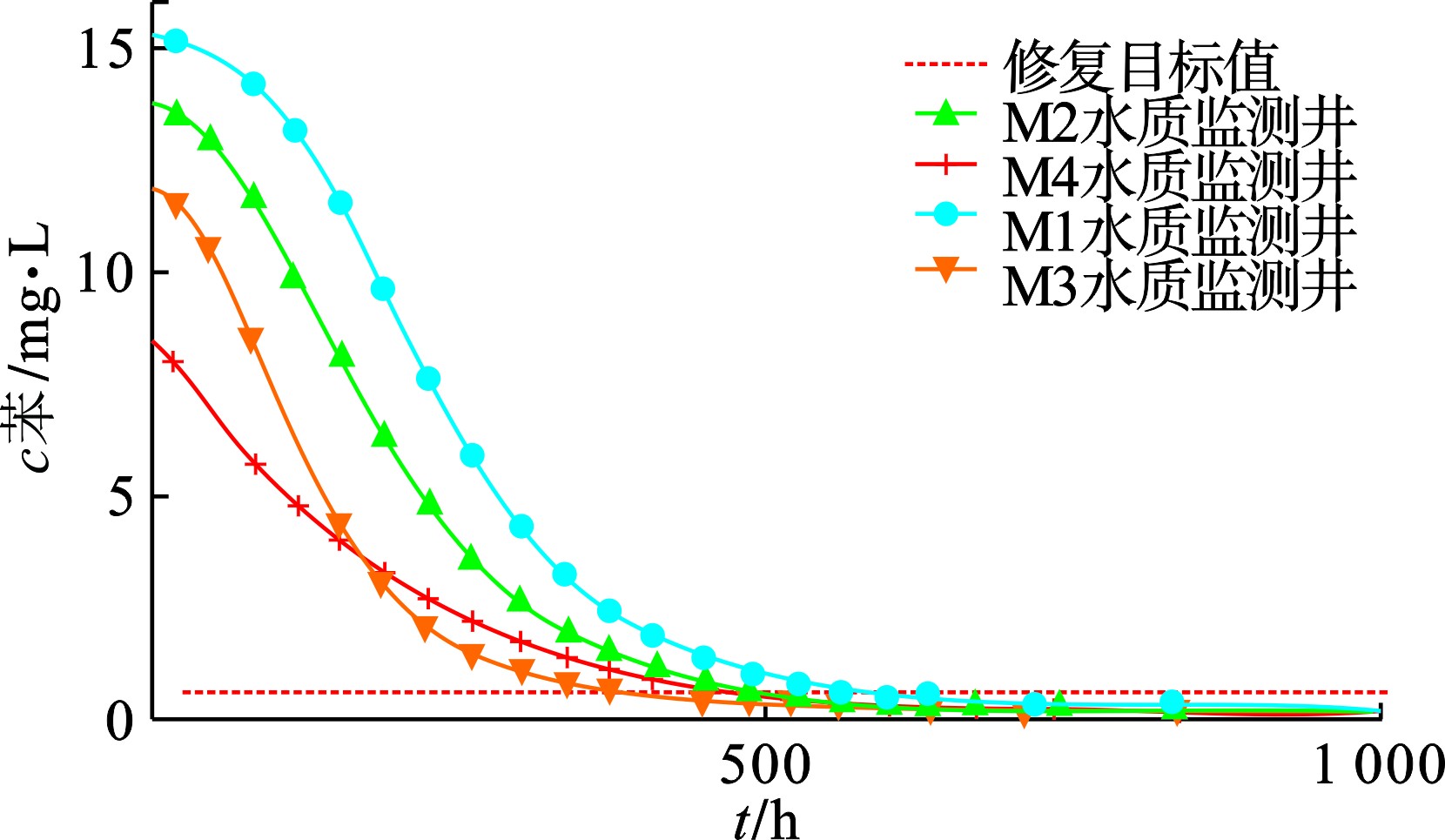
模型运行过程中,位于抽出-回灌井群内不同位置的水质监测井苯浓度随时间变化曲线,见图10。
图10可知,水质监测井苯浓度总体变化趋势呈现如下特点:在运行前300 h内下降明显,不同监测井苯浓度下降幅度在65%~90%;300 h后,苯浓度去除效率逐渐降低,500 h后污染最严重区域的苯浓度降到1 mg/L,其余水质监测井苯浓度均降至修复目标值以下,进入550 h后,抽出-回灌区域内苯浓度均降至修复目标值以下。
综上所述,针对重污染区域采用“中心抽水-四周回灌” 模式进行优先处理,可以在相对较短时间内达到降低地下水污染物浓度峰值,起到均质化地块地下水污染物的效果。因此,对重污染区域“中心抽水-四周回灌” 进行优先处理具有可行性与高效性。
-
参照“后排抽水-前排回灌”逐排处理的技术思路,本次模拟方案为地块边界内修复范围的地下水流向上游到下游(由西北向东南),以30 m的排距设计9排兼具抽水和回灌功能的井群,同一排的井间距约为20 m,共102眼。抽灌方式为逐排抽灌,从地下水流向的上游第一排井回灌和第二排井抽水为第一次抽灌模式,单次抽灌周期72 h,72 h后,第二排井回灌和第三排井抽水同时进行作为第二次抽灌,抽灌周期72 h,依次进行,直到第九排井抽水结束。抽灌井的平面布置图,见图11。
由预测结果可知,逐排运行模式中,首先在抽水井和回灌井附近苯浓度下降明显,每个相邻抽灌井之间区域处理效果明显时间段为3 d,因此在对应的3 d运行结束后,整体上是从抽灌井排向相邻井排中间位置苯浓度逐渐上升。经过一个周期运行结束后,修复地块浓度峰值由运行前的21 降至5 mg/L左右,大部分区域维持在3 mg/L以下。
根据位于第6排和第7排之间的水质监测井监测结果,苯浓度变化总体趋势呈现如下特点:第15 d时开始明显下降,到18 d临近抽出回灌结束时,不同监测井苯浓度下降幅度在45%~65%[17]。
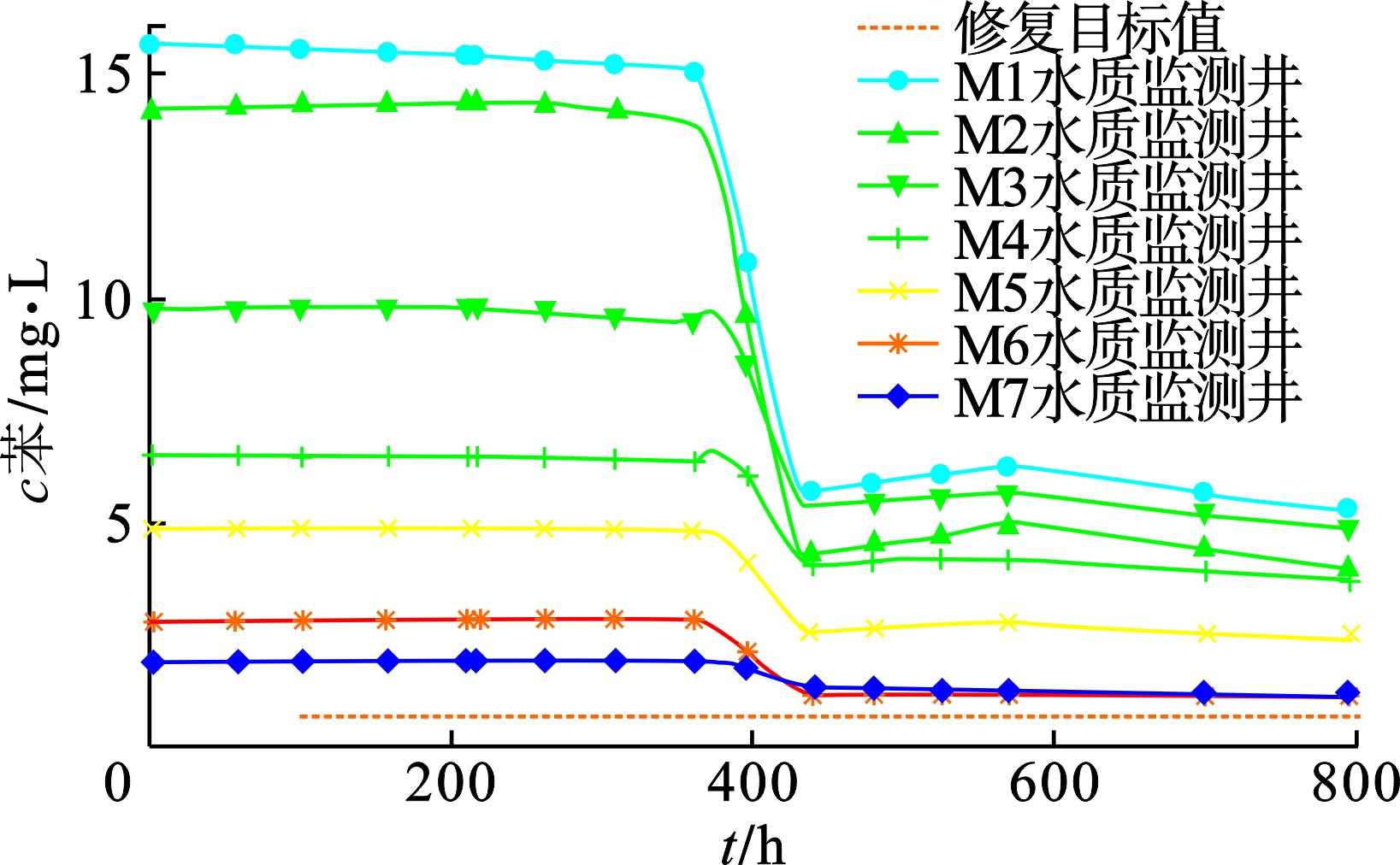
模型抽出-回灌运行时间为24 d(576 h),分别预测抽出-回灌系统运行3、6、9、12、15、18、21和24 d的苯去除效果。模型运行过程中,位于重污染区的水质监测井苯浓度随时间变化曲线,见图12。系统运行过程中苯浓度变化预测结果,见图13。
-
受模拟软件限制,回灌水苯浓度均为理想浓度0 mg/L,故本次数值模拟结果均为相对理想状态下所得。结合模拟预测结果,得到以下结论。
(1)重污染区域采用中心抽水-四周回灌优先处理时,污染物浓度基本达到修复目标值大约需要抽出-处理-回灌系统运行550 h。
(2)整个污染地块采用逐排处理时,抽出-处理-回灌系统运行一个周期(576 h)污染物浓度下降45%~65%。若按照最低处理效率(45%),将污染区域处理至目标修复值(0.672 mg/L)则需要6~7个抽出-回灌周期(每周期24 d)。
(3)重污染区域采用中心抽水-四周回灌优先处理的模式可以短期内将重污染区污染物浓度降低至地块污染平均水平及以下,有效削减高浓度峰值,缩短高浓度区域处理工期,达到地下水污染均质化作用;整个污染地块通过逐排处理的技术方案进行地下水污染修复时,对高浓度污染区域处理效果有限,且耗时较长。
重污染区域优先处理结合逐排抽出-回灌的技术方案,具备技术可行性与降低污染物浓度的高效性。
数值模拟在污染地下水抽出-处理-回灌修复技术中的应用
Application of numerical simulation in pump-treat-recharge remediation technology of polluted groundwater
-
摘要: 受污染地下水对人体健康和生态环境有较深影响,采取经济合理的地下水修复技术尤为关键。抽出-处理-回灌技术是修复污染地下水的典型代表,溶质运移数值模拟是研究地下水污染物迁移转化的重要技术支撑手段。以北京某地块石油类污染地下水为研究对象,针对重污染区域采用中心抽水-四周回灌和对整个污染区采用逐排处理两种方案,运用数值模拟分析不同模式下地下水中污染物的时空迁移规律,确定污染物去除效果。结果表明:针对重污染区优先处理时,将污染物处理达标需要约23 d;针对整个污染区采用逐排处理时,则需要6~7个处理周期(每周期24 d)。对重污染区域优先处理的模式可短期内使污染物浓度大幅降低,有效削减高浓度峰值,结合逐排抽出-回灌的修复模式,可更有效地使全区污染物浓度达到修复目标,两种模式结合使用具备技术可行性与高效性。
-
关键词:
- 地下水污染修复 /
- 抽出-处理-回灌技术 /
- 数值模拟 /
- 污染物运移预测
Abstract: Polluted groundwater had a serious impact on human health and ecological environment, so it’s critical to adopt economic and reasonable groundwater remediation technology. Pump-treat-recharge technology was a typical representative method for the remediation of contaminated groundwater, and numerical simulation of solute transport was an important technical support means to study the migration and transformation of groundwater pollutants. Taking the petroleum-contaminated groundwater of a certain site in Beijing as the research object, two schemes were adopted for the heavily polluted area, namely, central pumping and peripheral reinjection, and the whole polluted area was treated row by row. Numerical simulation was used to analyze the temporal and spatial migration of pollutants in groundwater under different modes and determined the pollutant removal effect. The results showed that 23 days were taken about for pollutants to reach the standard when priority treatment was given to the heavily polluted area, and 6~7 treatment cycles (24 days per cycle) were required when adopting row-by-row treatment in the whole pollution area. The priority treatment mode for heavily polluted areas could significantly reduce the pollutant concentration in a short period. It could reduce the peak value of high concentration, and in combination with the row-by-row repair mode, the pollutant concentration can effectively reach the remediation goal. The combination of the two modes showed technical feasibility and efficiency. -

-
表 1 模拟区地层分布
Table 1. List of stratum distribution in simulation area
成因年代 地层岩性 模型层位 人工堆积层 黏质粉土填土 1 新近沉积层 粉质黏土 2 细砂、卵石 3 第四纪沉积层 粉质黏土 4 细砂 5 粉质黏土 6 卵石 7 注:卵石为潜水赋存层位。 表 2 模型含水层水文地质参数
Table 2. List of hydrogeological parameters of model aquifer
参数 取值 渗透系数K/m·d−1 120 给水度 0.30~0.4 孔隙度 0.30 纵向弥散系数/m2·d−1 0.65 横向/纵向弥散系数比例 0.10 Langmuir
吸附参数吸附平衡常数K/1·(mg/L)−1 1E-7 最大吸附量a/mg·mg−1 1 注:数值模拟中扩散系数、弥散系数参数均由现场试验及经验值综合考虑后确定,Langmuir吸附参数参考相关经验值。 表 3 校正后含水层水文地质参数一览表
Table 3. Corrected aquifer hydrogeological parameters
参数 取值 渗透系数K/m·d−1 150 给水度 0.35 孔隙度n 0.30 纵向弥散系数/m2·d−1 0.65 横向/纵向弥散系数比例 0.10 Langmuir
吸附参数Langmuir吸附平衡常数Kl/1·(mg/L)−1 3E-7 最大吸附量a/mg·mg−1 1 -
[1] 万鹏, 张旭, 李广贺, 等. 基于模拟-优化模型的某场地污染地下水抽水方案设计[J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(11): 1608 − 1616. [2] 王战强, 张英, 姜斌, 等. 地下水有机污染的原位修复技术[J]. 环境保护科学, 2004, 30(5): 10 − 12. [3] 周维四. 垂直管中多相流动的统计研究[J]. 石油学报, 1984(03): 67 − 76. [4] 杨耀忠, 韩子臣, 周维四, 等. 多层二维二相油藏数值模拟并行技术[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2001(06): 52 − 54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2001.06.015 [5] 郑西来, 刘孝义, 杨喜成. 地下水中石油污染物运移的耦合模型及其应用研究[J]. 工程勘察, 1999(2): 39 − 43. [6] 张艳, 白相东, 张莹. 地下水污染抽出处理技术中抽水井最优布局方案研究[J]. 防灾科技学院学报, 2013, 15(2): 26 − 29. [7] 杜川, 陈素云, 牛耕. 判定地下水水动力弥散系数的综合分析法[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2017(12): 90 − 94. [8] 杜川, 陈素云, 牛耕. SVE技术中抽提真空度及相关参数的应用分析[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(12): 189 − 193. [9] 蒲敏. 污染场地地下水抽出处理技术研究[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(4): 6 − 10. [10] 宫志强, 刘明柱, 刘伟江, 等. 单井捕获地下水污染羽的优化方法[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(10): 2468 − 2474. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201812028 [11] 宫志强, 田西昭, 刘伟江, 等. 抽出-处理技术抽出污染地下水——抽出效率及抽出终点[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学), 2020, 50(4): 1139 − 1150. [12] 徐绍辉, 朱学愚. 地下水石油污染治理的水力截获技术及数值模拟[J]. 水利学报, 1999(1): 71 − 76. [13] 朱学愚, 谢春红. 地下水运移模型[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1990. [14] 孙讷正. 地下水污染——数学模型和数值方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989. [15] 赵勇胜. 地下水污染场地的控制与修复[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. [16] 王大纯, 张人权, 史毅虹, 等. 水文地质学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995. [17] 林威, 牛耕, 付全凯, 等. 使用ISCO和P&T联用技术修复某有机污染地块[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(增2): 142 − 149. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.S2.022 -



 下载:
下载: