-
随着纺织和造纸工艺等规模的逐渐扩大,芳香族化合物染料废水的排放已经成为水污染的主要问题之一。当前的污水处理方法[1-2](吸附、混凝、沉淀等)存在去除成本高,操作复杂,难以同时除去多种污染物且易产生二次有毒产物等缺点,因此迫切需要找到一种更有效的污水净化工艺。具有高效降解能力的光催化技术是近年来的研究热点之一[3-5],光催化技术是利用光催化剂(纳米氧化锌等)将有机污染物降解成无毒的CO2和H2O等小分子物质[6-8]。但是由于纳米氧化锌(ZnO)等光催化剂回收难度大,易造成二次污染等缺陷,限制了其大范围的应用。因此如何制备一种柔性载体负载光催化剂在高效催化的同时克服其二次污染的问题是当前的研究热点之一,采用静电纺丝制备的ZnO复合纳米纤维膜具有易于回收、表面积大、吸附容量大等优点,扩大了ZnO在光催化领域的范围应用。
聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)是一种多功能玻璃态生物相容性良好的聚合物,对可见光具有优异的透过性、良好的加工能力,通过静电纺丝制备的PMMA纳米纤维膜耐磨性、力学性能和亲水性能较差,很难单独应用于污水处理等领域[9-10]。聚氨酯(PU)与染料的亲和性好、挠曲性好等优点,常被用于增强静电纺丝中纳米纤维膜的拉伸强度、弹性等力学性能[11-12]。
等离子体处理是通过电场的加速,使获得能量的分子被激发或者发生电离形成活性基团,同时空气中的水分和氧气在高能电子的作用下也可产生大量的新生态氢、羟基等活性基团,以此改变高分子材料的结构,达到对材料表面进行亲水性改性或纤维表面清洁的方法[13-16]。
本文通过静电纺丝制备了纤维形态良好,易于回收的PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜,并通过等离子技术增强其亲水性能。对制备的复合纳米纤维膜进行拉伸强度、静态接触角、吸附性能和光催化性能等测试,并探究其对亚甲基蓝、罗丹明B和活性红染料废水的降解能力及重复使用性能。
全文HTML
-
聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)、聚氨酯(PU)、罗丹明B(RhB)均为分析纯,购于阿拉丁试剂有限公司。活性红、亚甲基蓝(MB)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)、纳米氧化锌(ZnO)均为分析纯,购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
SH05-03磁力搅拌器(上海梅颖浦仪器仪表制造有限公司)、FS-1200超声波处理器(上海生析超声仪器有限公司)、FA2004分析天平(上海恒平科学仪器有限公司)、静电纺丝装置(自制)、SCE100 TS Series Barrel Plasma Etcher(Anatech USA)。
-
(1)PMMA/PU静电纺丝液的制备
称量适量的聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯和聚氨酯(PMMA、PU)溶于N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)中,采用磁力搅拌器于30 ℃搅拌2 h直至完全溶解,制备质量分数为30%的PMMA/PU(PMMA∶PU质量配比分别为为8∶2、7∶3、6∶4)混合纺丝液。
(2)PMMA/PU/ZnO静电纺丝液的制备
称取一定质量的ZnO分散于静电纺丝液中(ZnO的质量占PMMA/PU总质量的2.0%、4.0%、6.0%、8.0%),采用磁力搅拌器及超声处理促进ZnO纳米粒子在纺丝液中均匀分布。
(3)复合纳米纤维膜的制备
将纺丝液移至注射器内,调节纺丝液流速为0.3 mL·h−1,电压为19 kV,接受距离为15 cm,于室温下进行静电纺丝,经干燥后分别得到PMMA/PU、PMMA/PU/ ZnO复合纳米纤维膜。
-
对待测的各种样品进行喷金处理后,进行SEM表观纤维形态测试,并借助能谱仪对添加ZnO前后的复合纳米纤维膜进行元素分析。
-
采用等离子处理仪对PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜进行亲水性处理,考察时间为1 min,供应气体为空气时不同处理功率(5、10、15 W)对复合纳米纤维膜亲水性能的影响,利用SDC-100S接触角测量仪测量复合纳米纤维膜的静态接触角。选取处理前与处理后PMMA/PU复合纳米纤维膜为测试对象,每种样品分别测试5次,测量结果取平均值,分析等离子改性条件对复合纳米纤维膜性能的影响。
-
将PMMA/PU复合纳米纤维膜试样裁剪成宽10 mm的条形,在YG141D型织物厚度仪上测量纤维膜的厚度,每个试样的厚度测量10次,得出复合纳米纤维膜的平均厚度,计算纤维膜的截面积。利用YG020型电子单纱强力机进行力学性能测试,夹持试样部分长度为20 mm。每个试样测5次得到复合纳米纤维膜的断裂强度(cN·mm−2)。
-
取40 mg复合纳米纤维膜,等离子处理后复合纳米纤维膜(处理时间为1 min,功率为15 W)在50 mL的亚甲基蓝、活性红和罗丹明B溶液中进行吸附实验,每隔30 min移取少量反应溶液进行吸光度测试,直到吸光度保持不变,每组测试重复3次。
-
称取40 mg PMMA/PU和PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜,放于50 mL浓度分别为5.0 mg·L−1亚甲基蓝溶液、10.0 mg·L−1罗丹明B和50.0 mg·L−1活性红溶液中,于XPA光化学反应仪中进行光催化实验。首先对复合纳米纤维膜进行避光吸附,然后在300 W汞灯照射下,每隔30 min取空白对照组和试验组,利用UV-5500型紫外可见分光光度计测定溶液的吸光度。反应底物的降解率(Q)计算如公式(1)所示:
式中,A0,At分别为反应前与t min后反应底物的最大吸收波长处吸光度数值。
-
重复使用率是衡量优良催化剂性能的指标之一。对40 mg PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜重复使用3次,测量复合纳米纤维重复降解次数对其降解性能的影响。
1.1. 实验材料及仪器
1.2. 复合纳米纤维膜的制备
1.3. 复合纳米纤维膜的表征
1.4. PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜处理前后亲水性能测试
1.5. PMMA/PU复合纳米纤维膜的力学性能测试
1.6. 复合纳米纤维膜吸附性能测试
1.7. PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜光催化性能测试
1.8. PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜重复使用性能测试
-
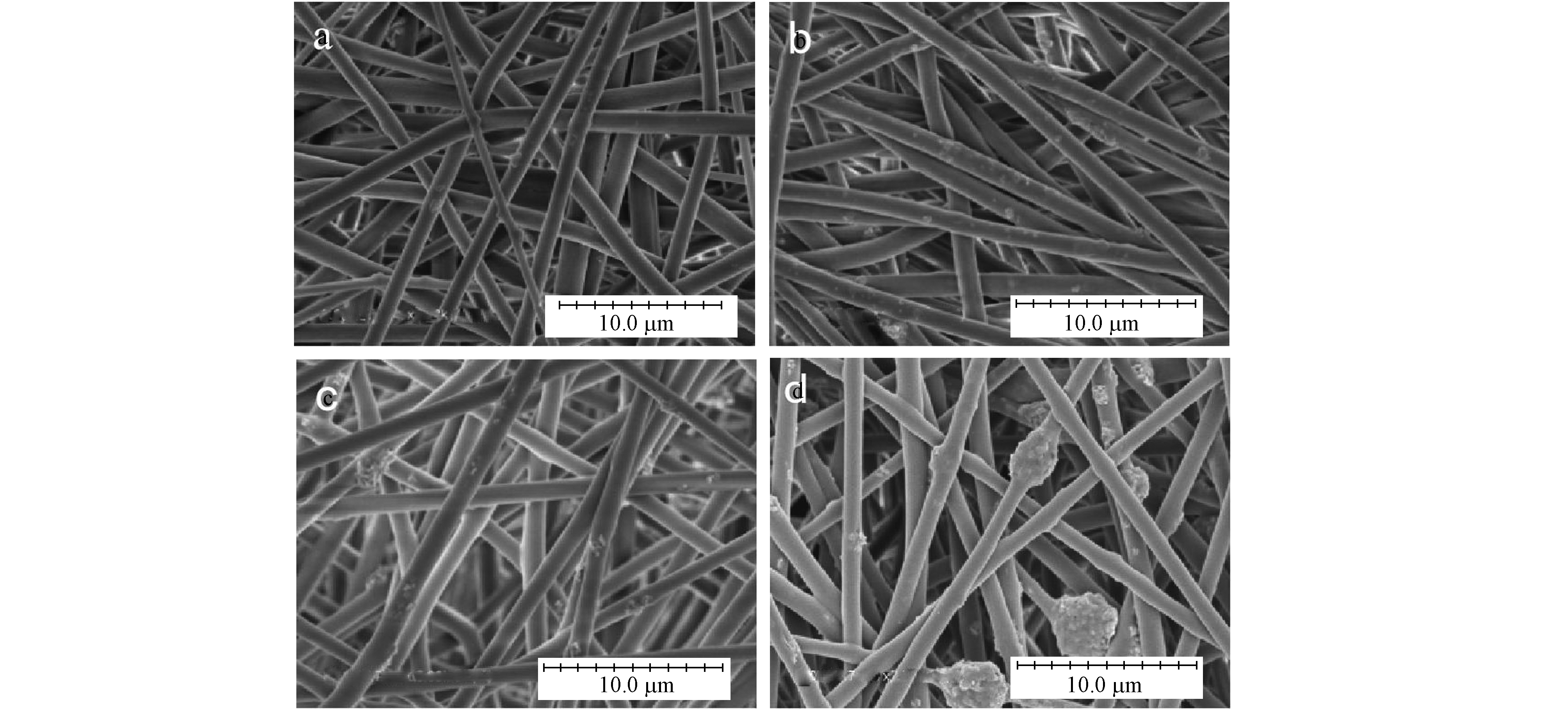
采用日本日立S-4800扫描电子显微镜,对按不同比例(PMMA∶PU配比为6∶4、7∶3、8∶2)混纺的复合纳米纤维膜进行形貌观察,结果如图1所示。
由图1可以看出,静电纺制备的PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜形态良好,当PMMA的质量配比较小时,纤维的直径均匀程度较低,随着PMMA的成分逐渐增加,复合纳米纤维膜直径分布较为均匀,但纤维直径逐渐增大。当PMMA/PU配比为7:3时,纤维具有良好的均匀性和较小的纤维直径,适合应用于光催化剂ZnO的载体。
采用日本日立S-4800扫描电子显微镜,对添加不同质量分数的ZnO的PMMA/PU(PMMA∶PU为7∶3)复合纳米纤维膜进行形貌观察,结果如图2所示。
由图2可知,添加适量的ZnO粉体对复合纳米纤维膜形态无明显影响,随着ZnO质量分数的增加,复合纳米纤维膜的纤维上ZnO含量越多,当ZnO质量分数添加到达8%时,ZnO的团聚现象较为严重。当ZnO质量分数增加到10%时,ZnO大量团聚导致难以形成均匀的静电纺丝溶液,无法进行静电纺丝。
-
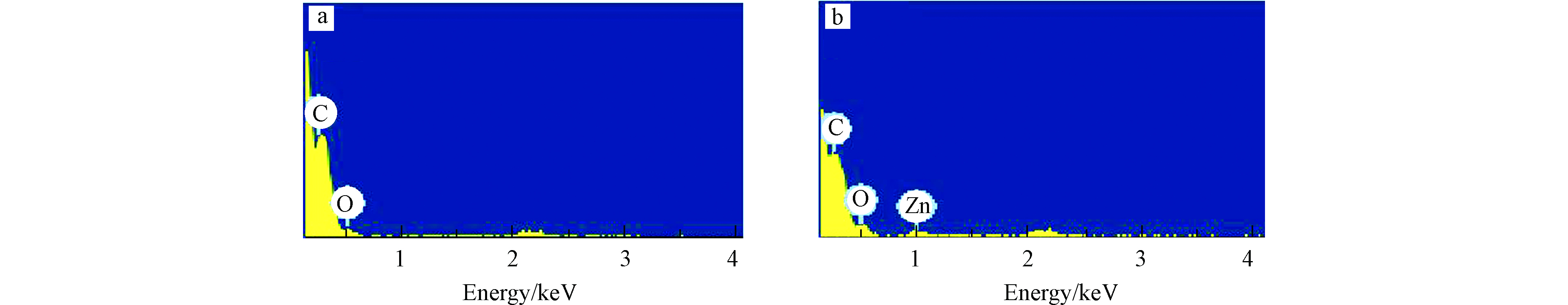
采用日本日立S-4800型扫描电子能谱仪对PMMA/PU复合纳米纤维膜和PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜进行能谱分析,结果如图3所示。如图3所示,PMMA/PU复合纳米纤维膜主要含有C、O元素,PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜存在C、O、Zn 3种元素,结果说明ZnO成功的负载在复合纳米纤维膜上。
-
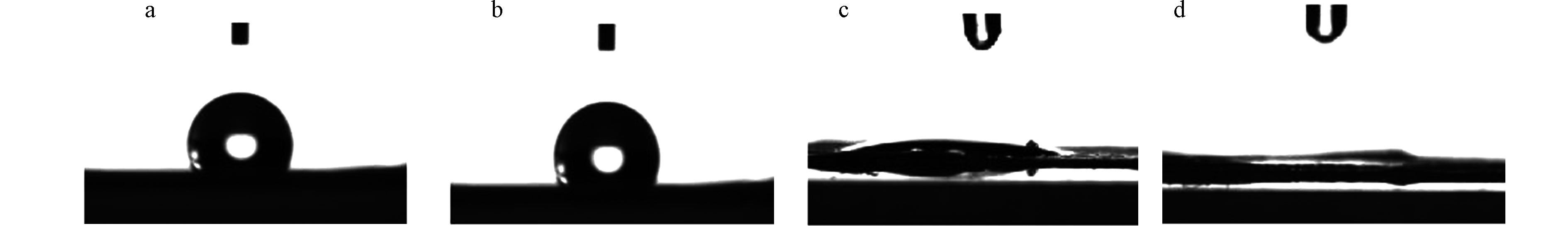
利用SDC-100S接触角测定仪测量等离子处理前后PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜的亲水性能,结果如图4所示。由图4分析可知,未经等离子仪处理的复合纳米纤维膜接触角为127.0°,表现为疏水性能。等离子处理功率为5 W和10 W时,复合纳米纤维膜的静态接触角分别为103.7°和10.2°,复合纳米纤维膜的静态接触角的变化表明随着处理功率的增加,复合纳米纤维膜由疏水性向亲水性转变。当处理功率为15 W时,液滴下降后能迅速的渗入复合纳米纤维膜,其静态接触角接近0°,表明经等离子仪处理后复合纳米纤维膜具备良好的亲水性能。
-
利用YG020型电子单纱强力机对复合纳米纤维膜,等离子处理后复合纳米纤维膜(处理时间为1 min,功率为15 W)的力学性能及其断裂伸长率进行测试,测试结果如表1所示。
由表1分析可知,PMMA纳米纤维膜的断裂伸长率仅为17.83%,通过与PU的混合纺丝,其断裂伸长率增加至81.42%,其弹性变形能力得到增加。通过等离子处理PMMA/PU复合纳米纤维膜后,其断裂强度与伸长率下降程度较小,原因是等离子处理与使用强氧化性化学试剂处理改善材料的亲水性能方式不同,只存在对纤维表面进行较弱的刻蚀[17-18],因此对复合纳米纤维膜损伤较小,充分地体现出等离子处理的优势。
-
取40 mg复合纳米纤维膜,等离子处理后复合纳米纤维膜(处理时间为1 min,功率为15 W)在50 mL的亚甲基蓝、活性红和罗丹明B溶液中进行吸附实验,通过式(1)得出吸附率,实验结果见图5。
由图5可知,PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜经过等离子处理后,对3种染料溶液的吸附性能均有一定的提升,原因是经过等离子处理后复合纳米纤维膜上含有大量亲水基团,能够增加对染料分子的吸附能力,使其与纤维膜上的ZnO颗粒进行充分接触,有助于后续光催化反应的进行,当吸附一定时间后,其对3种染料的吸附不再增加,因此表现为吸附性能而不是降解性能,对后续光催化降解染料性能不会产生影响。
-
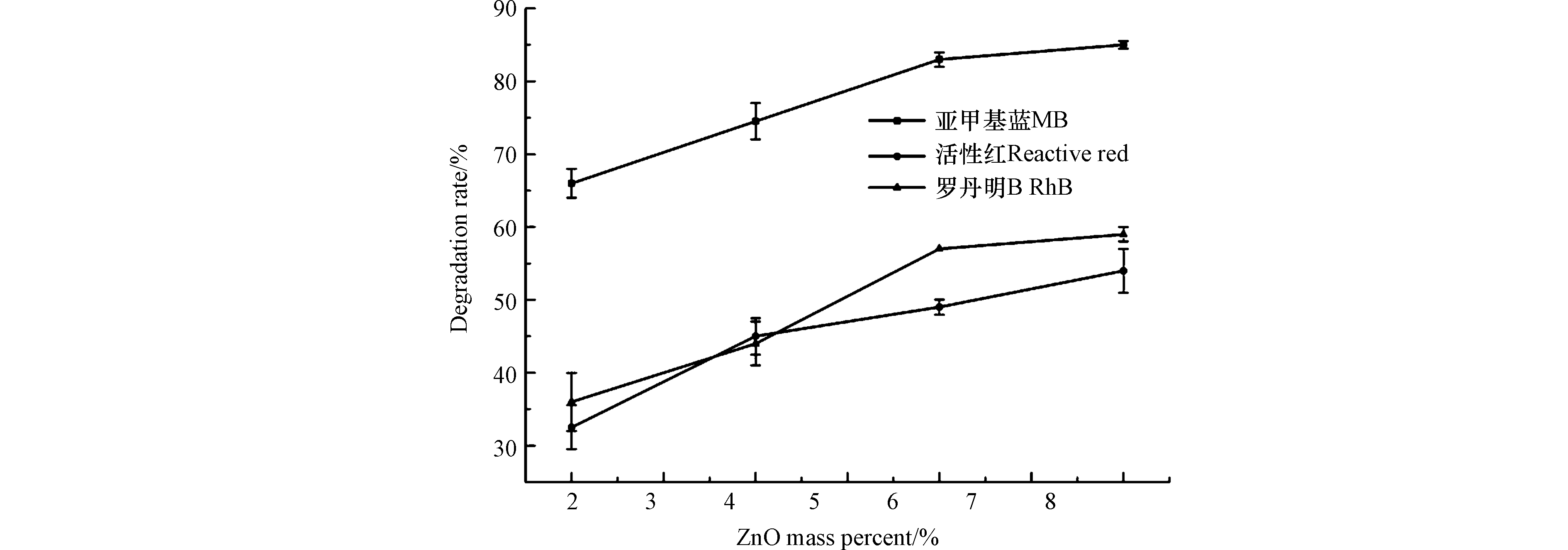
取40 mg等离子处理后复合纳米纤维膜(处理时间为1 min,功率为15 W)于50 mL的亚甲基蓝、活性红和罗丹明B溶液中,达到吸附平衡后,在300 W汞灯下进行光催化实验,并通过式(1)计算出其降解率,结果如图6所示。
由图6分析可得,随着ZnO质量分数的增加,PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜对3种染料溶液的降解率不断地增加,当反应时间达到120 min,ZnO质量分数分别为6%和8%时,其对亚甲基蓝和罗丹明B的降解率趋于平稳,降解率分别达到85 %和54 %,随着 ZnO添加量继续增加,无明显上升的趋势。当 ZnO质量分数达到8%时其对活性红的降解率为59 %且未趋向平稳,由于ZnO质量分数增加,静电纺丝难度增加和纤维膜性能的恶化,无法探究更高 ZnO质量分数的复合纳米纤维膜对活性红的降解性能。
-
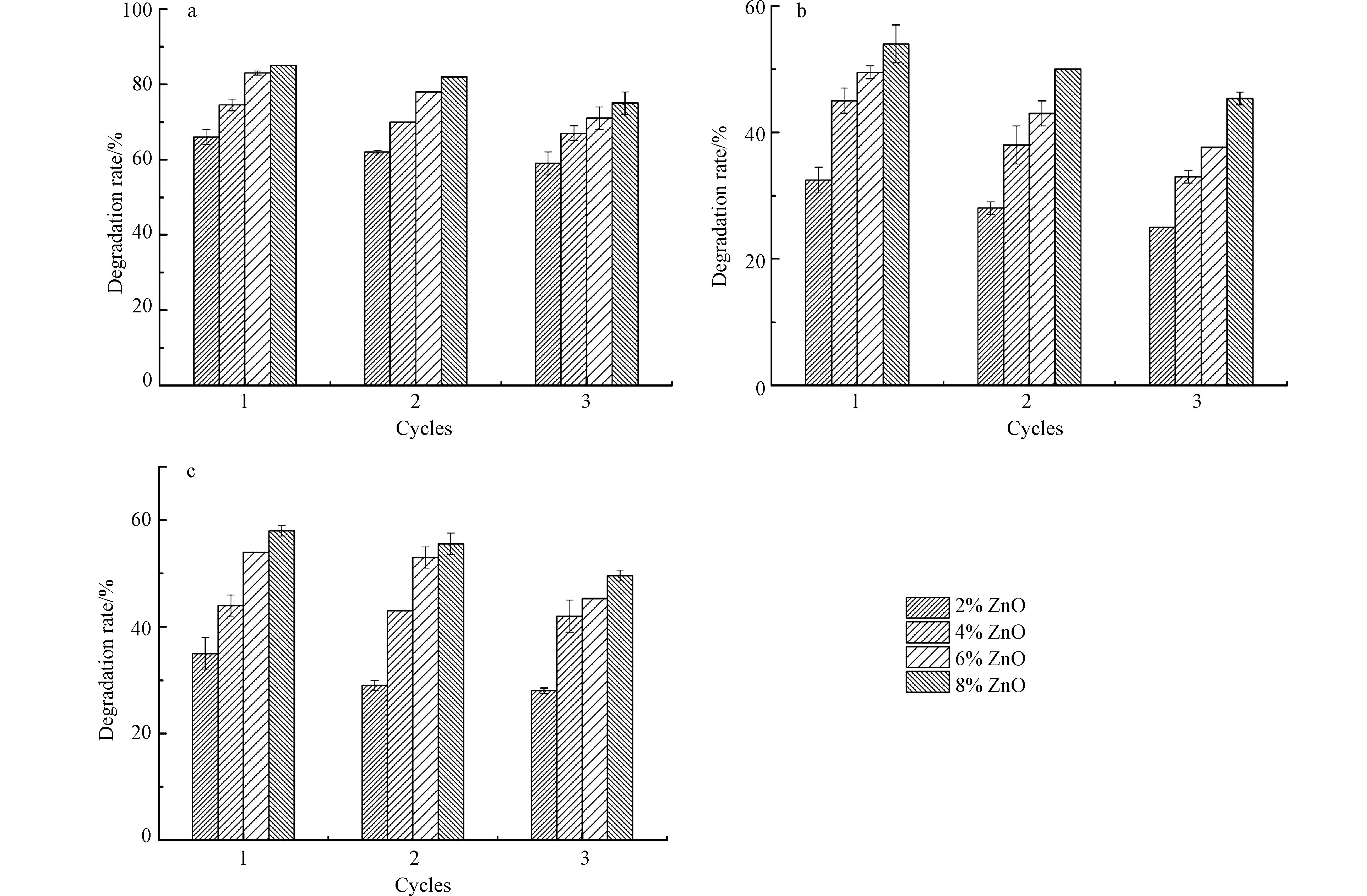
将40 mg 等离子处理后的PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜重复使用3次,并结合公式(1)计算出每次的降解率,结果如图7所示。由图7可知,PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜重复使用3次后对亚甲基蓝、活性红和罗丹明B的仍具备良好的催化性能,仍能达到初次对染料降解效果的82.3%、83.3%和79.7%。主要是因为复合纳米纤维膜在重复使用过程中不会发生纤维的溶胀甚至溶解作用,只存在少量的ZnO从复合纳米纤维膜中脱落,使其能够保持良好的降解性能。
2.1. 复合纳米纤维膜的纤维形态表征
2.1.1. 扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察
2.1.2. 能谱(EDX)分析
2.2. 复合纳米纤维膜亲水性能测试
2.3. 复合纳米纤维膜力学性能测试
2.4. 复合纳米纤维膜吸附性能测试
2.5. 复合纳米纤维膜光催化性能测试
2.6. PMMA/PU/ZnO 复合纳米纤维膜重复性实验
-
利用静电纺丝技术成功制备了形态较好,纤维直径均匀的PMMA/PU/ZnO复合纳米纤维膜,经等离子处理后,对复合纳米纤维膜进行光催化测试发现:ZnO质量分数为8%的复合纳米纤维膜,2 h内对亚甲基蓝、罗丹明B和活性红的降解率可达到85%、59%和54%,重复使用3次后的PMMA/PU/ ZnO复合纳米纤维膜对亚甲基蓝、罗丹明B和活性红的光催化活性与第一次之比仍可达到82.3%、79.7%和83.3%以上,表明复合纳米纤维膜具备良好的光催化性能及其重复使用性能。




 下载:
下载: