-
随着抗生素的广泛使用,大量抗生素被排放到环境中。Zhang等研究表明,2013年中国所有抗生素的总产量估计为248000吨,其中53800吨进入环境中,抗生素的大量使用导致环境中细菌耐药性不断增加[1]。如何有效处理抗生素废水成为目前亟待解决的重要环境问题。
针对抗生素废水的处理方法包括物理法、生物法、化学法等,在诸多方法中,高级氧化法以羟基自由基作为主要氧化剂,能有效将抗生素转化为无毒无害的CO2和H2O,因而受到广泛关注。在诸多高级氧化法中,电催化氧化法由于具有操作简单、工艺条件温和、无二次污染和催化活性高等优点广受重视[2-3]。
在电催化氧化法中,电极材料是决定氧化效率的关键。在诸多电极材料中,PbO2电极因具有较高的析氧电位,较强的耐腐蚀性和高催化活性而受到广泛关注[4]。为了进一步提高PbO2电极的使用寿命和催化性能,研究者通过在Ti基底与β-PbO2活性催化层之间增加SnO2镀层和α-PbO2中间层等方法来降低Ti基底与β-PbO2活性催化层之间的内应力,减少镀层缝隙,抑制钛的钝化,延长电极使用寿命。
有研究表明,在β-PbO2活性层中添加活性粒子可以提高电催化活性[5-7],掺杂的物质主要包括金属离子(Bi3+、Fe3+、Co2+)、非金属离子(F−)、金属氧化物颗粒(如CeO2)及表面活性物质(如PTFE)等。稀土元素相比其他掺杂物质在催化改性方面具有优异性能,究其原因,是稀土元素具有特殊的4f轨道结构,导致其具有特殊的物理、化学特征,沈宏[8]分别制备了4种稀土元素(La、Gd、Nd、Ce)掺杂的PbO2电极,结果显示,不同的稀土元素对电极具有不同的性能提升效果。
在诸多稀土元素中,Er元素研究较少。本实验利用稀土元素Er对PbO2进行了掺杂改性,探究了该元素最优的掺杂比例,运用SEM、EDS和XRD等手段对制备的电极进行表征分析;同时利用制备的Er-PbO2电极对磺胺甲基嘧啶(Sulfamerazine,SMR)进行了电化学氧化降解,分析电流密度、pH值对降解效果的影响,探究了电氧化过程中SMR的降解路径。
全文HTML
-
实验中所有化学试剂均为分析纯,丙酮、氧化铅、氢氧化钠、硝酸铅、重铬酸钾、硫酸银、硫酸汞来自于国药集团化学试剂有限公司,氟化铵、氢氟酸、硝酸、磷酸、浓盐酸、正丁醇来自于北京化工厂,三氯化锑来自天津大茂化学试剂,五水四氯化锡、氟化钠来自天津福晨化学试剂厂,乙二醇来自于天津市致远化学试剂有限公司,硝酸饵来自于陕西瑞科新材料股份有限公司,聚四氟乙烯来自于东莞市展阳高分子材料有限公司,磺胺甲基嘧啶来自于北京索莱宝科技有限公司。
-
在制备Ti基底电极过程中,将2 cm×1.5 cm×1.5 mm的Ti板依次用240目、320目、600目的砂纸打磨,用超纯水、丙酮、超纯水各超声15 min,吹干备用。然后将钛板放置在HF∶H2O∶HNO3配比为1∶5∶4的溶液中进行化学刻蚀,待气泡从钛板表面析出1 min后取出,置于超纯水中超声15 min,吹干备用。以刻蚀好的Ti板为阳极,铂片为阴极,电极间距为1.5 cm,在30 V恒压条件下,置于质量分数0.3%NH4F、2%H2O的乙二醇溶液中电解30 min。再将电极置于含质量分数5%H3PO4的乙二醇溶液中电解1 h。电解之后的Ti板放置于管式炉中,以5 ℃·min−1的速度升至450 ℃烧结,得到表面生长有钛纳米管的Ti基底电极。
在制备SnO2-Sb中间层过程中,分别称量3.2 g的SbCl3,15 g的SnCl4·5H2O置于50 mL烧杯中,加入5 mL浓盐酸,30 mL正丁醇,混匀溶解得到锡锑氧化物溶液,用刷子将氧化物溶液均匀涂覆在Ti板表面,置于145 ℃烘箱中烘干20 min,重复涂烘6次,最后将电极置于500 ℃的管式炉热分解2 h。重复上述所有操作1次,待冷却后就得到Ti/SnO2-Sb电极。
以Ti/SnO2-Sb电极为阳极,Pb板为阴极,在含7.1427 g的PbO和51.2 g的NaOH的电镀液320 mL中电解1 h,50 ℃下水浴加热,电解电流为0.015 A,得到Ti/SnO2-Sb/α-PbO2电极。以制备好的α-PbO2活性层的电极为阳极,铅板为阴极,在体积为320 mL,含52.9936 g的Pb(NO3)2、11.5218 mL的HNO3、0.6718 g的NaF和1.8 mL的PTFE的电解液中电解1.5 h,制备β-PbO2活性层,65 ℃下水浴加热,电流控制为0.15 A。
本实验选取稀土元素Er对PbO2电极进行掺杂改性,研究不同掺杂比例对电化学性能的影响,因此在β-PbO2活性层的制备时在电镀液中分别加入0 、0.3547 、0.7094 、1.4187 、2.8374 g的Er(NO3)3·5H2O,来制备掺杂比例为0%、0.5%、1%、2%和4%的PbO2电极。
-
采用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electronic microscopy,SEM)来观察电极的表面形貌和微观结构,型号为日本日立Hitachi s4800,加速电压为20 kV,用扫描电子显微镜配带的X射线能谱仪(energy dispersive spectroscope, EDS)分析电极的元素组成,用X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction, XRD)分析晶相组成,并计算晶粒尺寸,型号为日本岛津XD-DI。测试条件:X射线衍射源为CuKα,管电压为36 kV,管电流为30 mA,扫描速度为4°·min−1,2θ=20°-80°。
-
采用线性极化曲线测定电极的电化学性能,仪器为上海辰华仪器有限公司的CHI 630E型电化学工作站。实验采用三电极体系,工作电极为制备的Er-PbO2电极(20 mm×15 mm),对电极为Pt电极(10 mm×10 mm),参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),采用恒流极化法,在室温下(25 ℃),电解液为0.5 mol·L−1 H2SO4的水溶液,扫描速度为10 mV·s−1。
-
以制备好的Er-PbO2电极为阳极,不锈钢电极为阴极,电极间距1.5 cm,在含有30 mg·L−1 SMR和0.2 mol·L−1的Na2SO4作为支持电解质的电解液中进行电化学氧化降解,控制恒流条件,室温(25 ℃)下电解6 h,每隔1 h取样分析。
-
利用高效液相色谱仪(high performance liquid chromatograpHy,HPLC)对SMR浓度进行分析,HPLC型号为日本岛津公司LC-20A型,色谱柱为安捷伦SB-C18 (4.6 mm×250 mm×5 μm),甲醇∶水=6∶4,柱温25 ℃,进样量为25 μL,流速为1 mL·min−1,检测波长为265 nm。COD浓度利用国标法进行测试(GB11914—1989)。
-
SMR降解中间产物由高效液相色谱串联质谱联用仪LC-MS测定。高效液相色谱仪为日本岛津公司LC-20ADXR型,质谱仪为美国Applied biosystems公司API3200 Qtrap型,色谱柱为Waters BEH-C18液相色谱柱(3.5 μm×3.0 mm×150 mm)。流动相:A相为高纯水(含0.01%的甲酸);B相为甲醇。流速为0.4 mL·min−1,采用针泵进样方式,柱温为40 ℃。
1.1. 试剂
1.2. 电极制备
1.3. 电极形貌、结构及性能分析
1.3.1. 电极形貌与晶体结构
1.3.2. 电化学性能测试
1.4. SMR降解分析
1.4.1. 污染物浓度和COD浓度的测定
1.4.2. SMR降解中间产物的测定
-
从表1可以看到Ti/Sb-SnO2/PbO2、TiO2-NCs/Sb-SnO2/PbO2的加速寿命时间分别为10 h、35 h,使用寿命时间分别为2.85 a和9.99 a,后者相比前者使用寿命提升了约2.5倍。这说明将Ti基氧化为TiO2-NCs可有效延长电极的寿命。
-
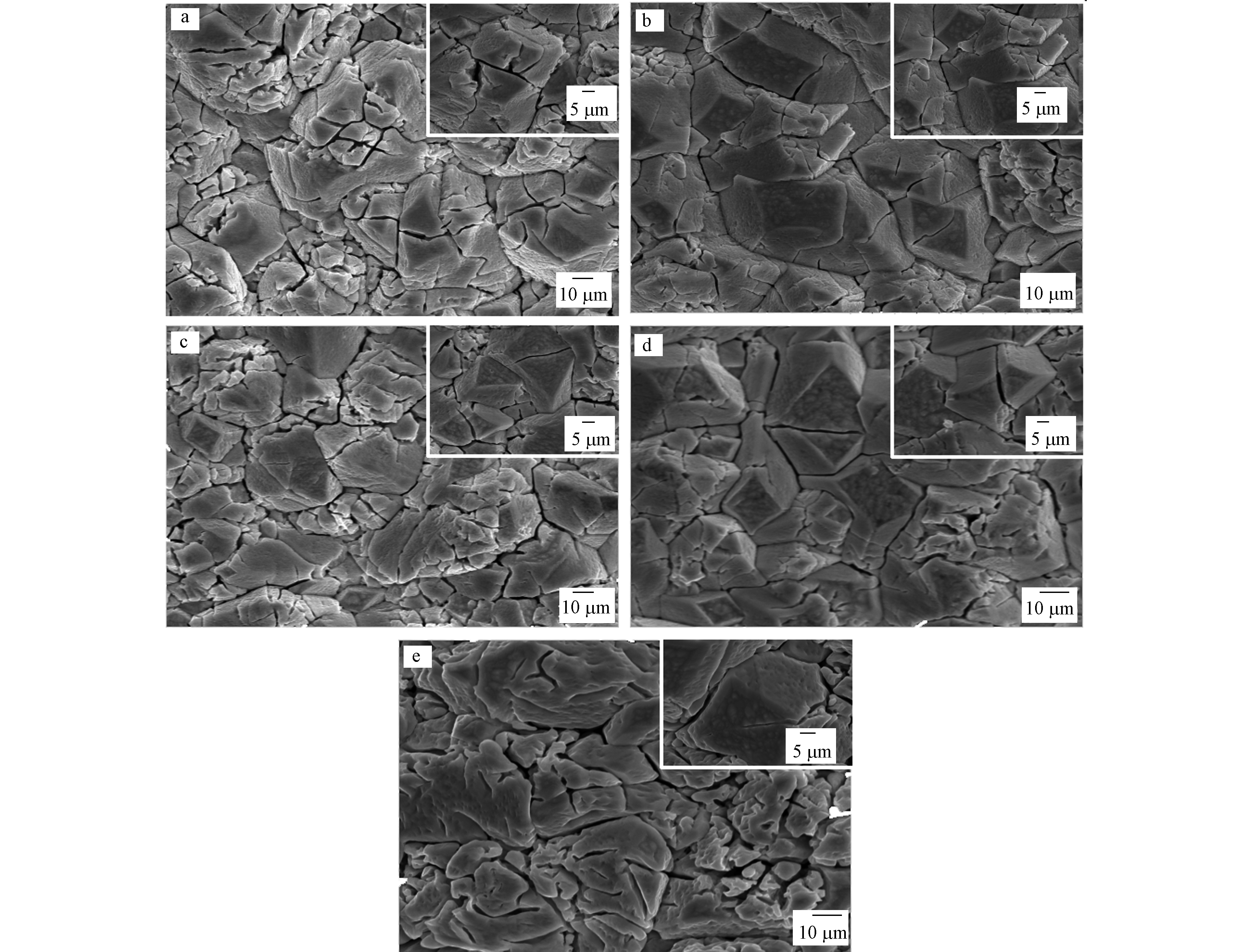
对掺杂了不同剂量的稀土元素Er的二氧化铅电极进行SEM分析,图1为掺杂剂量为0%、0.5%、1.0%、2.0%和4.0%的Er-PbO2。从图1可以明显看出,没有掺杂Er的电极表面有大量裂缝,比较粗糙,这样的表面容易造成电氧化过程中活性氧渗入钛基体,使基体钝化,增加电极内部的内应力,造成表面活性层脱落,降低电极的电催化性能,还有可能使电极失活[9],一定剂量的Er可使电极表面光滑致密,如2.0%的Er-PbO2,裂缝明显减少,可以有效阻止活性氧的扩散,但是过多的Er元素反而会起到反作用,如4.0%的Er-PbO2,表面缝隙比没有掺杂Er的更大,颗粒尺寸变大导致比表面积变小,这不利于活性位点与污染物的接触,降低电催化活性。
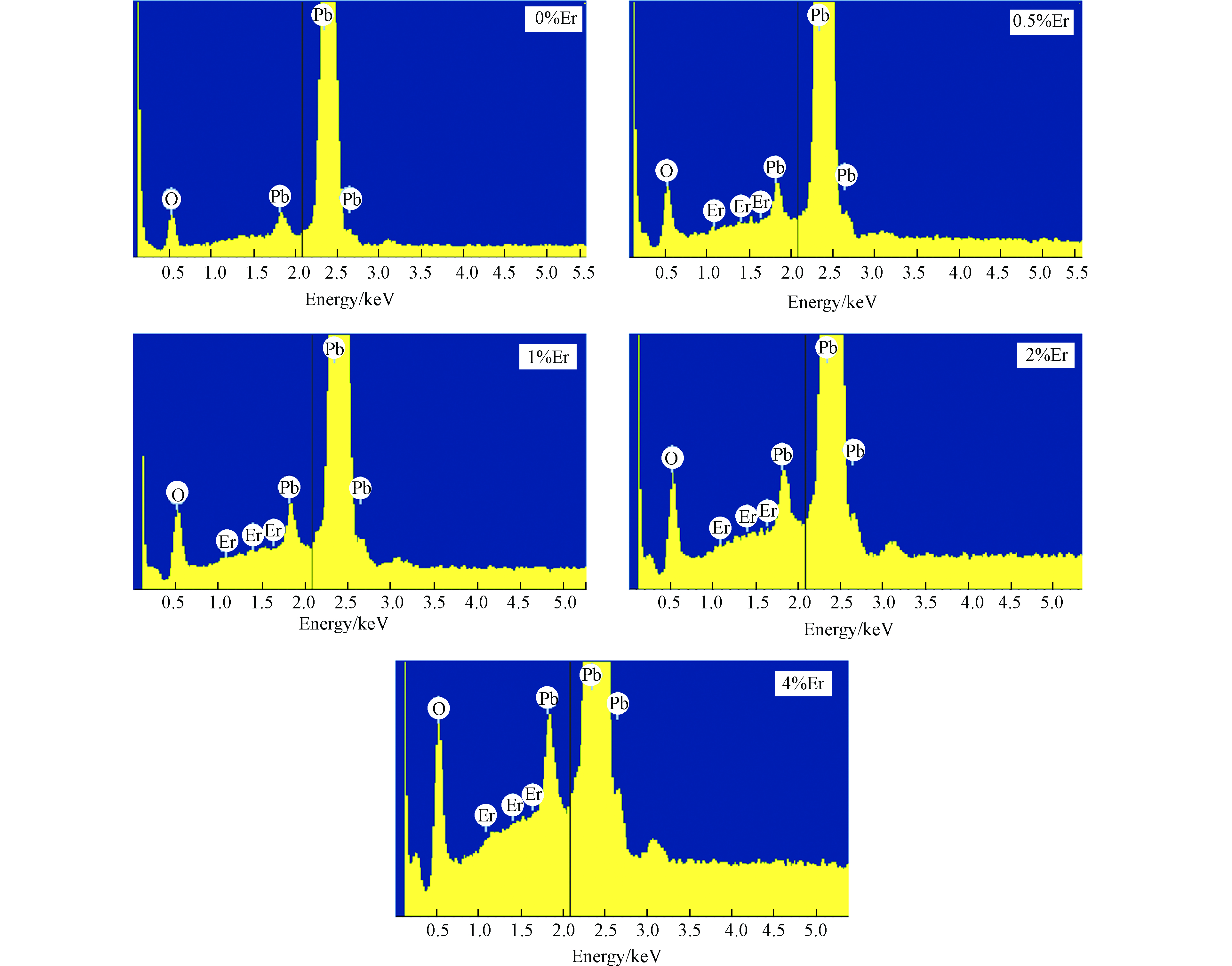
为了验证Er元素是否成功掺杂,对电极做了EDS分析,结果如图2所示,可以看出电极表面的元素主要是O、Pb,Er元素含量虽较低,但也证明了Er的成功掺杂。
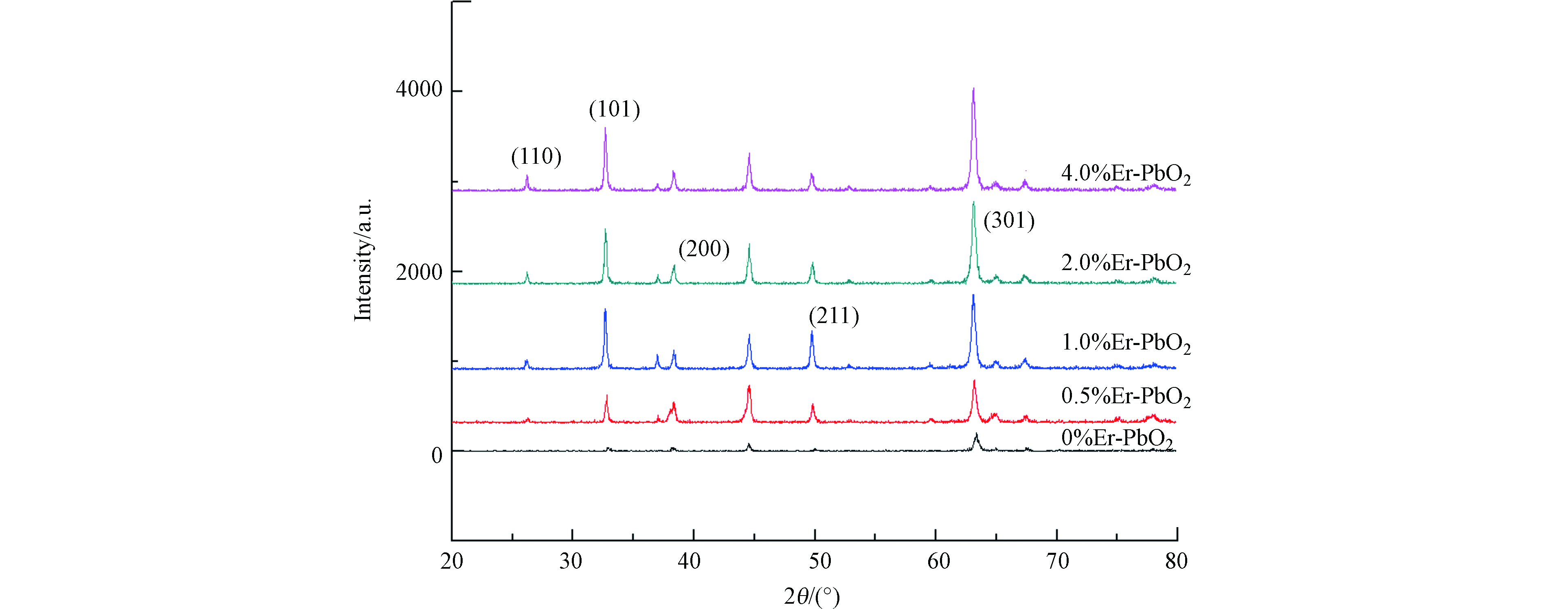
用XRD对电极的晶相组成进行分析,结果见图3。从图3可以看到,PbO2电极晶型主要是β-PbO2。与α-PbO2相比,β-PbO2具有高的电导率和电催化活性[10],图谱中2θ=25.3°、31.8°、36.1°、49.0°、62.4°处的衍射峰分别对应着β-PbO2的(110)、(101)、(200)、(211)、(220)、(301)晶面,其中(301)晶面的衍射峰强度最大,说明电极表面生长的β-PbO2以(301)晶面为主,然而,在掺杂不同剂量的稀土元素Er后,均未出现与稀土元素Er相对应的衍射峰,其可能原因是稀土元素Er以固溶形式掺入PbO2中,并取代了晶格中Pb4+的位置,因此未单独形成,故检测不到[11],虽然稀土元素未在XRD中显示,但通过晶体粒径的计算,可以看出掺杂了Er的电极晶体粒径比未掺杂的明显减小(表2)。这可能是因为Er的掺杂为PbO2晶体的生长引入了一个新的成核中心,增加了晶核的数量,而降低了在晶化过程中颗粒的生长速率,从而抑制了PbO2晶体的进一步变大[11]。其中,掺杂比例为2.0%的粒径最小,为39.96 nm,而未掺杂的PbO2粒径高达43.43 nm。更小的粒径可以提供更大的比表面积,使活性位点增加,从而加快反应速率。
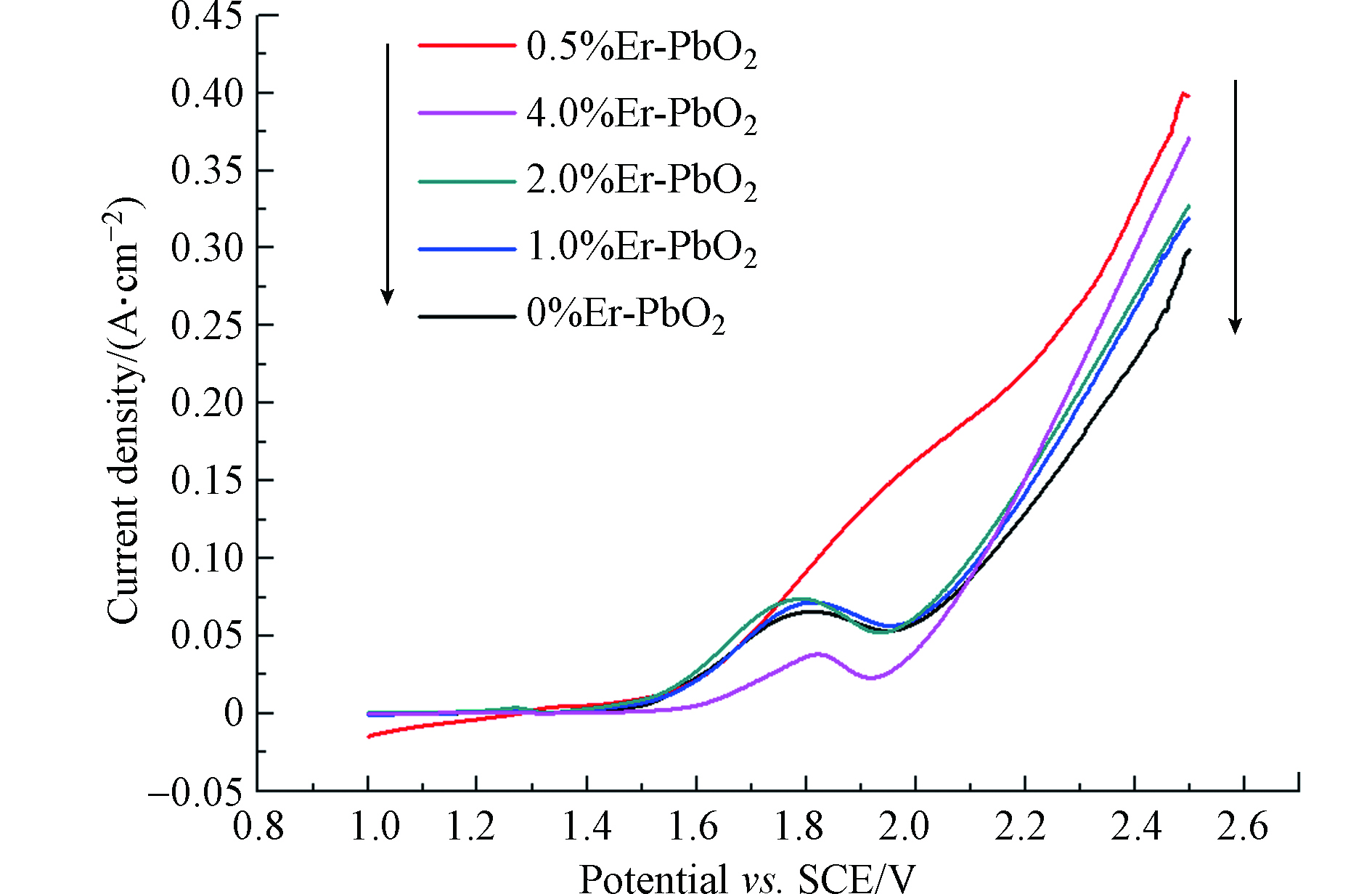
析氧反应是阳极电化学降解过程中主要的副反应,会降低电流效率,所以,选择好的电极材料,析氧电位是一个重要因素,析氧电位高,在电解反应前就不会发生析氧反应,从而使所有电流用于电解反应,提高了电流效率。本文利用线性扫描法测定不同电极的析氧电位,扫描曲线如图4所示。从图4可以看出,Er的掺杂有利于提高二氧化铅电极的析氧电位,不同电极的析氧电位不同,结果是2.0%Er-PbO2(1.82 V) >0.5%Er-PbO2(1.8 V)>4.0%Er-PbO2(1.78 V)>1.0%Er-PbO2(1.74 V)>PbO2(1.7 V),进一步证明Er元素的掺杂能够减少析氧副反应的发生、提高电流效率,最终提高电极的电催化性能。
-
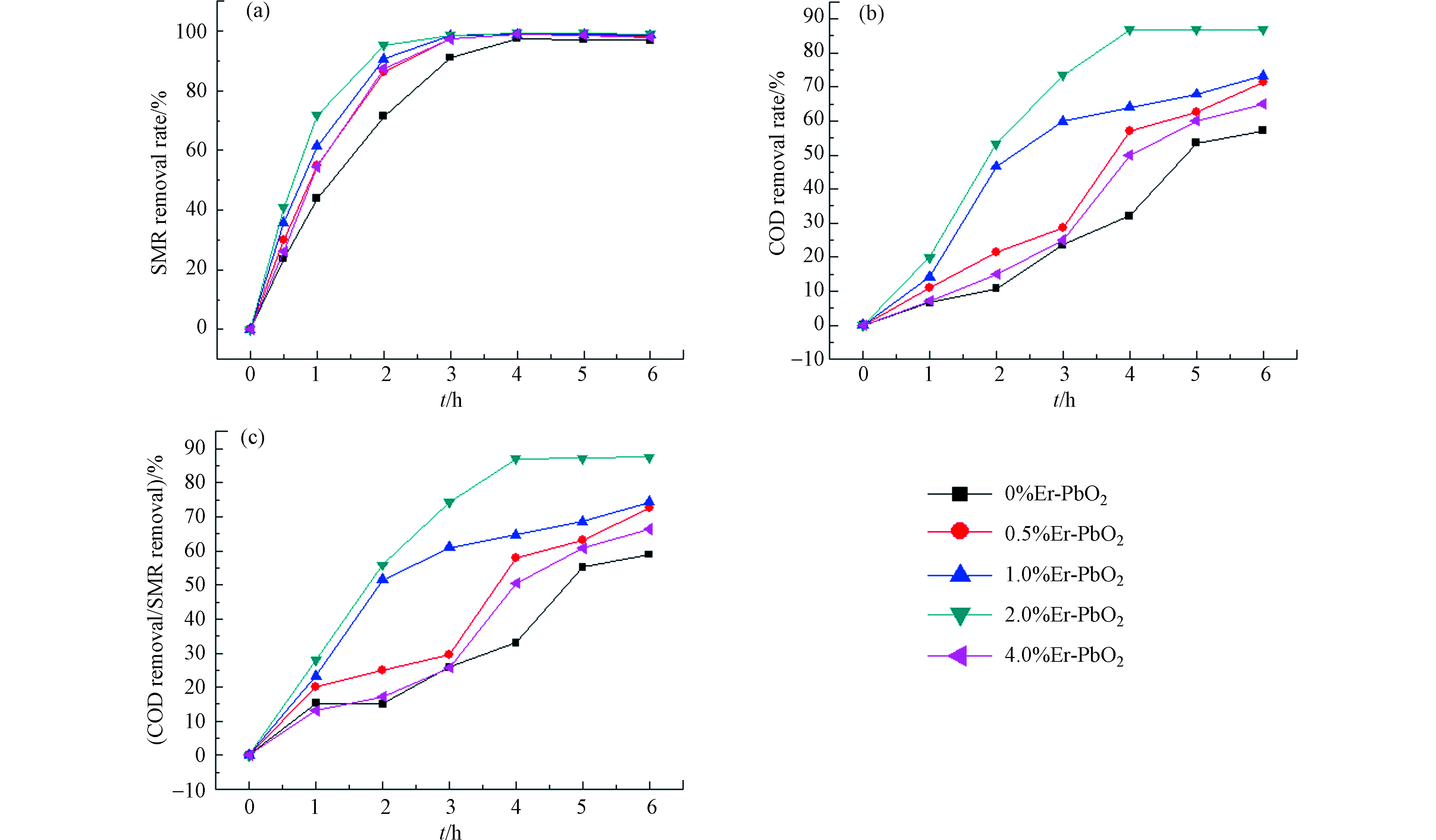
利用掺杂不同剂量Er元素的PbO2电极,对SMR进行电化学氧化降解,对比不同电极的氧化降解能力。以30 mg·L−1的SMR和0.2 mol·L-1 Na2SO4的水溶液为电解质溶液,电流密度30 mA·cm−2,电极板间距1.5 cm,以Er-PbO2电极为阳极,不锈钢板为阴极,电解时间为6 h。实验结果如图5(a)所示,不同掺杂剂量的Er-PbO2降解污染物的效果有差异。实验结果表明,掺杂2% Er-PbO2电极降解效果最好,SMR的去除速度最快,6 h后SMR去除率为99%。0.5%、1%、4%的Er-PbO2电极的污染物去除率分别为98.4%、98.7%、97.95%;与未掺杂的相比,Er-PbO2电极氧化效率均有所上升,说明Er的掺杂使得PbO2半导体的空穴浓度增大,电极表面活性位点增多,与污染物接触的面积增大,使得反应速率加快[12]。
对不同剂量的Er掺杂-PbO2电极进行COD测试,以此对比矿化率,结果如图5(b)所示。消解6 h后,0%Er-PbO2,0.5%Er-PbO2,1.0%Er-PbO2,2.0%Er-PbO2和4.0%Er-PbO2这5种电极电解污染物后的COD去除率分别为57%、71%、73%、86%、65%,由此可见,2.0%Er-PbO2对有机物的矿化能力最强,随着掺杂剂量的增加,矿化能力反而减弱。分析COD去除率和SMR去除率的关系,用以表征电化学降解过程中中间产物的积累情况,结果如图5(c)所示,比值越接近100%,说明矿化率越高,中间产物的积累越少。从图5可以看到,随着时间的增加,5种电极的COD去除率/SMR去除率一直增加,2.0%增加的最快,6 h后为87%,说明2.0%Er-PbO2的矿化能力最高。
-
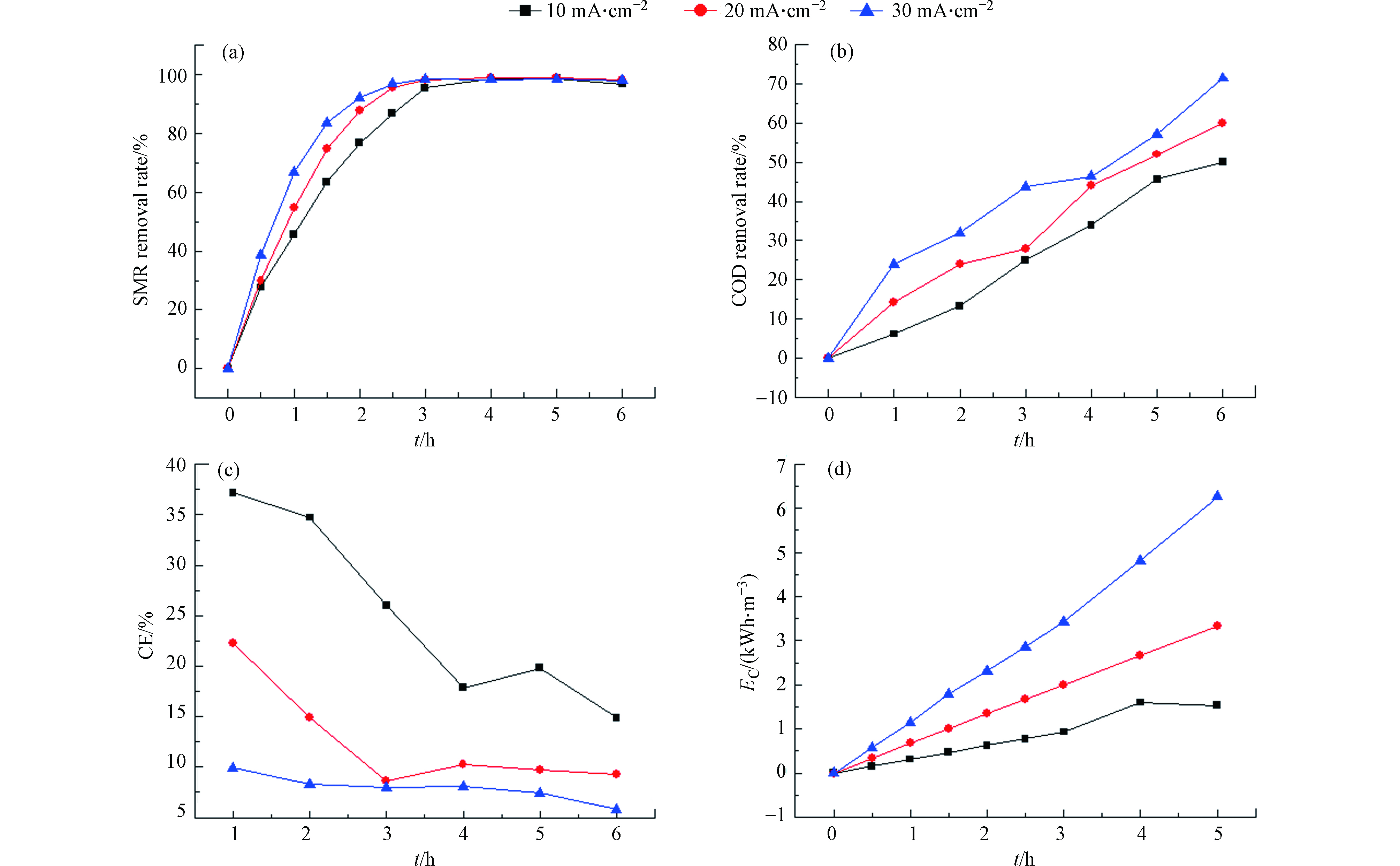
在电化学反应里,电流密度是一个关键的工艺参数,它决定着污染物的降解速率,本实验以SMR为污染物,研究了不同电流密度对降解效果的影响,图6为不同电流密度下SMR和COD在降解过程中的去除率变化曲线。同时研究了不同电流密度下,电化学降解过程中的能量消耗和电流效率,如图6所示。由图6(a)和6(b)可知,在3种电流下,SMR和COD的去除率都随着时间的增加而增加,但明显可以看出,30 mA·cm−2条件下增长速度最快,在6 h后,10、20、30 mA·cm−2这3种条件下,对SMR的去除率分别为96.61%、97.88%、98.11%,对COD的去除率分别为50%、60%、71.43%。分析这种结果的原因可能是,电流密度影响着体系中电子的产量,进而影响污染物的降解效果[13]。
由图6(c)和6(d)可以看出,电化学降解SMR的过程中,电流效率随着电流密度的增加而减小,能耗与电流密度的关系呈相反的趋势,在30 mA·cm−2的条件下能耗最大。
污染物在电极上的电催化氧化包括两个同时进行的电化学过程,一是在外加电势下污染物在电极表面直接被氧化,二是利用电催化氧化过程中产生的强氧化性基团(如·OH等)间接氧化污染物及其中间产物。PbO2为非活性电极,因此,间接氧化过程被认为是电催化降解污染物的主要方式。电化学降解过程中产生的具有强氧化性的·OH是由水在电极上放电所生成的。当·OH与污染物结合时,可以发生氧化反应,将有机物彻底氧化为CO2和H2O,但当·OH过多时,其未与有机物发生氧化反应,而是会发生析氧反应,此反应被认为是电催化氧化过程中的副反应,会降低电流效率。在低电流密度的条件下,析氧副反应不明显,电催化氧化过程产生的·OH大部分用于降解SMR及中间产物,随着电流密度的增大,形成的过多·OH并未与污染物发生氧化反应而是自身消耗发生析氧反应形成O2致使副反应所占电流比例增加,而用于降解污染物的电流减少,这是导致高电流密度条件下电流效率降低、能耗升高的根本原因[14-15]。
-
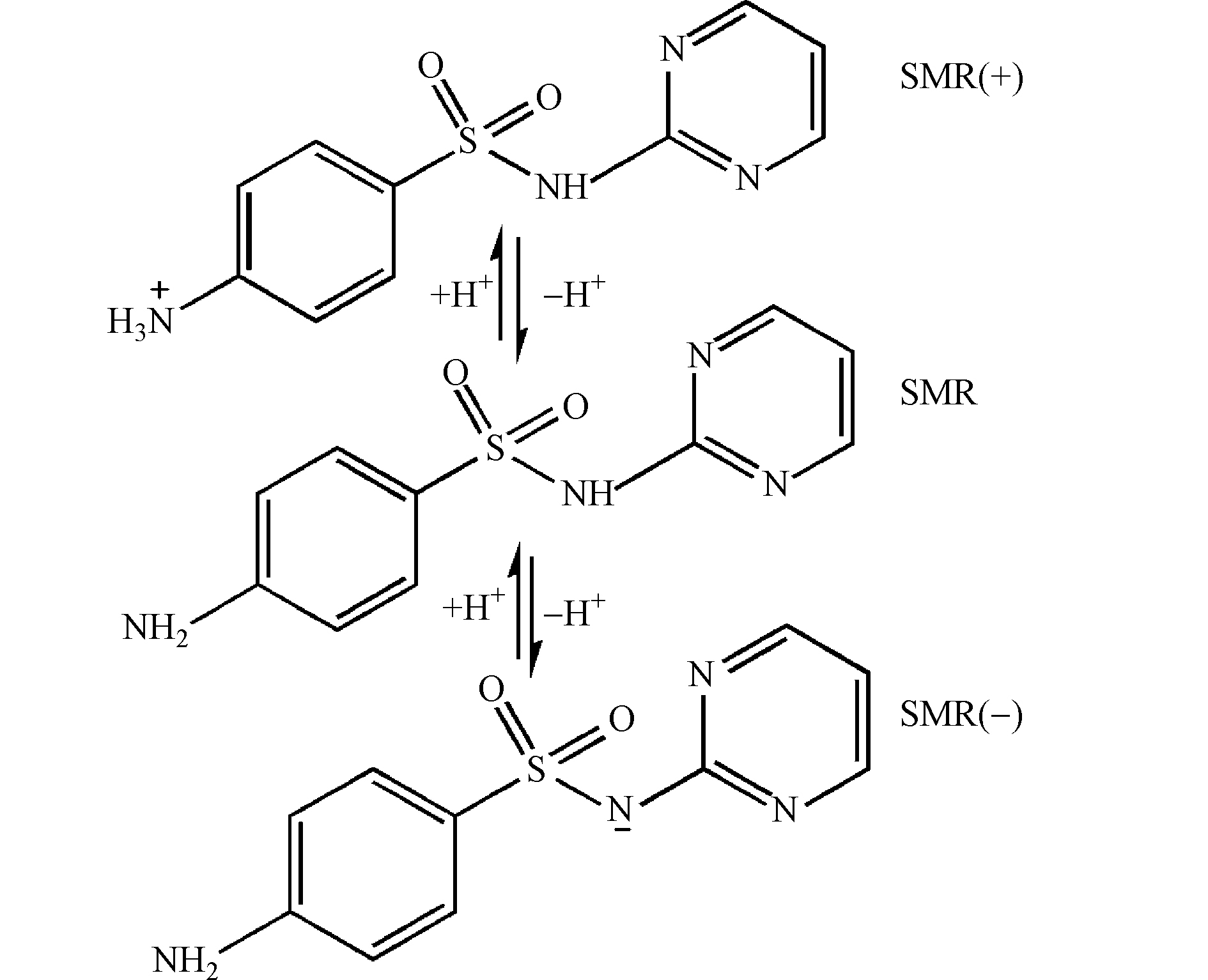
溶液的pH也是电化学反应里重要的一个因素,其影响着体系中·OH的产量。本实验以SMR为污染物,研究了不同pH对降解效果的影响,图7为不同pH下SMR和COD在降解过程中的去除率变化曲线。从图7可知,pH值由3-11,SMR和COD去除率都在下降,在6 h后,pH=3.0、pH=7.0、pH=11.0的3种条件下,对SMR的去除率分别为98.12%、97.54%、96.84%,对COD的去除率分别为95.45%、84%、63.52%,由此可知,SMR更适宜在酸性溶液中被降解。这种原因是复杂的,一方面与不同pH条件下电极表面生成·OH的产量不同有关[16-17],另一方面,SMR含有苯胺及杂环碱等基本官能团,如图8所示,在不同pH下形态会发生不同变化,导致降解效果呈现差异性[18]。
-
对电化学降解过程进行一级动力学拟合,拟合公式为
式中,C0为电解时间为0(h)时的污染物浓度(mg·L−1);C为电解时间为t(h)时的污染物浓度(mg·L−1);k为反应速率常数。
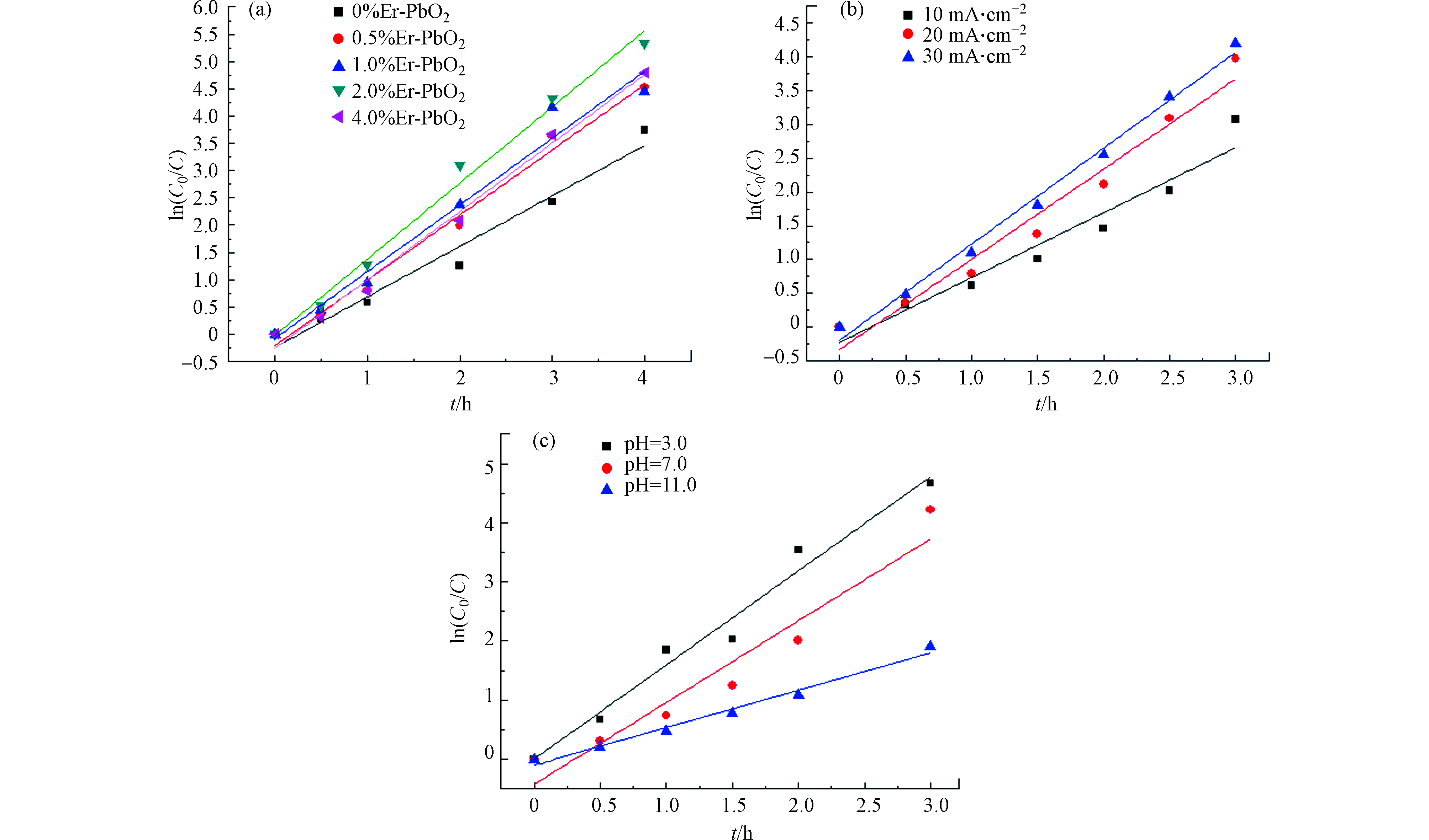
拟合之后,得到ln(C0 / C)与时间t的关系图,如图9所示。所有电极的电化学降解过程符合一级动力学方程,不同电流密度、不同pH下电极的电化学降解过程也符合一级动力学方程,其反应速率常数和判定系数如表3所示,其中掺杂比例为2.0%、电流密度为30 mA·cm−2、pH=3.0的k值最大,与前面的结论相符。
-
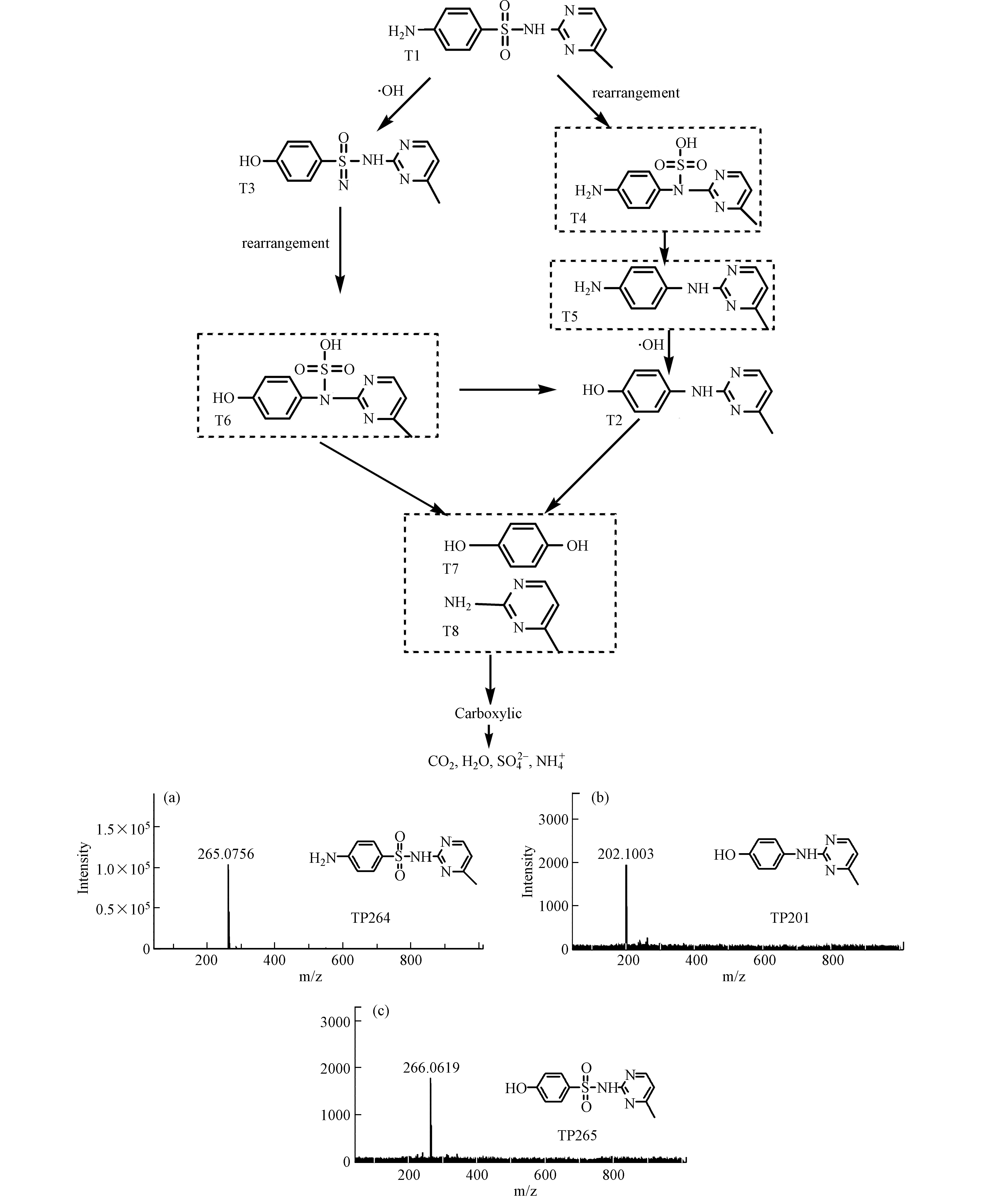
通过LC-MS测得SMR在降解过程的中间产物,如表4所示。在电氧化过程中,磺胺甲基嘧啶的降解是由于·OH的氧化作用将其分解成小分子物质,从检测到的几种中间产物可以推断SMR降解过程主要有苯环羟基化、SMILEs重排、S—N键断裂等系列反应。SMILEs重排是由于苯胺阳离子的α-C带有很强的正电荷,会吸引氮的亲核攻击,从而发生重排,SO2会被挤压最终从分子上脱除,S—N键断裂是由于羟基自由基对磺酰胺键攻击的作用,苯环上羟基化主要是芳香环上H被羟基自由基取代的作用[19]。图10是电催化氧化SMR的降解途径,SMR由于分子的SMILEs重排,生成T4,然后脱去SO2生成T5,接着T5通过苯环羟基化生成T2,T3是由T1直接发生苯环羟基化作用生成,然后发生重排脱硫也会生成T2,最终T6、T2由于C—N键的断裂并发生苯环羟基化作用,生成苯胺的羟基衍生物T7、T8,但无论哪种途径,最终这些芳香中间体都会被氧化为羧酸,最终矿化为CO2、H2O、SO42-、NH4+。
2.1. 钛纳米管与钛板的寿命比较
2.2. 电极形貌、结构及性能分析
2.3. 电化学降解SMR
2.4. 探究不同工艺参数对降解效果的影响
2.4.1. 电流密度的影响
2.4.2. pH的影响
2.5. 电化学降解的动力学分析
2.6. SMR降解过程的中间产物
-
本研究制备了以掺杂剂量分别为0%、0.5%、1.0%、2.0%、4.0%的稀土元素Er改性的PbO2电极,通过各种表征手段和电化学性能测试方法分析对比了5种电极的结构和电催化性能,从SEM和EDS的表征来看,掺杂了2.0%Er-PbO2电极表面比未掺杂的更为致密,缝隙较少。EDS结果表明Er元素成功的掺杂进入电极晶格中。XRD结果表明,制备的二氧化铅电极晶型均为β-PbO2,且掺杂了稀土元素Er,可以减小晶体粒径,从而提高电化学性能。极化曲线表明,Er元素的掺杂能够提高二氧化铅电极的析氧电位,从而提高电流效率。利用Er-PbO2电极氧化降解SMR,结果表明掺杂后的电极氧化能力均有提升,其降解能力为:2.0%Er-PbO2>1.0%Er-PbO2>0.5%Er-PbO2>4.0%Er-PbO2>0%Er-PbO2。综合来看,本实验探究的稀土元素Er的最优掺杂剂量是2.0%,本实验还探究了不同电流密度和不同pH对SMR的去除效果,探究了SMR的降解路径,结果是随着电流密度的增加,去除率在增加,而随着pH的增加,去除率在下降,SMR的降解过程主要有苯环羟基化、SMILEs重排、S—N键断裂等一系列反应。通过制备不同剂量的Er-PbO2并探究其优异的电化学性能,证明了掺杂稀土元素Er能够提升PbO2的电催化性能,可以作为一种有效的改性方式被广泛采用,同时本文也提供了最优的掺杂剂量,可以为此领域的研究提供借鉴,同时制备的Er-PbO2电极对磺胺甲基嘧啶的降解效果良好,矿化率最大可达到99%,对磺胺类抗生素的降解研究提供了新的方法。



 下载:
下载: