-
海底沉积物是记录海洋环境长期变迁、演化历史的档案馆。通过对海底沉积物中放射性同位素的探究,可以了解放射性核素在地球化学行为中扮演的角色。比如:通过放射性核素在沉积物岩心中的含量分布、深度变化,可以了解洋流活动规律、沉积物的沉积速率和年代变迁[1]。同时以海底沉积物中的放射性同位素作为天然示踪剂,也可研究海洋环境的化学演化过程和沉积物形成过程(如物质的来源与迁移等)[2]。南沙海域地形特点为递次升高的3级阶梯,由北向南走向依次可划分为深海盘、大陆坡、大陆架。通过分析一些天然放射性核素在该海域沉积物中的变化规律,可以对该海域的环境、地质、化学和生物等多方面的情况进行广泛而深入的探讨。然而,早期工作者对南沙海域的研究主要是围绕表层沉积物展开[3-6],对沉积物岩心的研究数据较为匮乏,这导致了该海域的历史演化数据很难被系统描述。
226Ra与210Pb都属于238U衰变系列核素,可以把226Ra与210Pb看成一对母子体。假定226Ra与210Pb没有其他的输入和输出,在两核素衰变达到了平衡后,通过226Ra与210Pb随深度的变化探知整个岩心在沉积过程中这2个核素是否存在额外的来源或者流失,由此可以判断过去几十年来该海域发生的一些海洋环境变化事件。沉积物岩心中的210Pb主要来源于两方面:一个是沉积物自身含有的226Ra衰变产生的210Pb,该部分210Pb经过一段时间后与沉积物中的226Ra能够达到平衡;二是沉积物自身之外的外部来源,包括降水、尘埃沉降、海水中210Pb的清除等方式进入到沉积物中,这部分210Pb称为过剩210Pb(210Pbex)[7-10]。同时,沉积物在沉降过程中,部分226Ra会通过沉积物间隙水进入水溶液中[11]。因此通过226Ra与210Pb随岩心深度的变化,可以探知这2个核素在整个岩心的沉积过程中是否存在额外的来源或者流失,从而反映海洋环境的变迁和演化。
本实验用HPGeγ谱方法分别测定6个沉积物岩心不同层段中226Ra和210Pb的含量,阐明它们随深度变化的特征,通过分析深度变化、210Pbex的沉积速率,探讨岩心在沉积过程中的所在海域环境发生的变迁,对南沙海域环境的变迁有着重要的指示意义。
全文HTML
-
本次实验在南沙海域取样6个岩心,表1给出了每个取样岩心的详细信息。该海区沉积物主要表现为钙质泥,但在深海区沉积物和半深海区沉积物中,岩心分别表现为灰色软泥与粉砂质泥。本实验岩心长度在21—29 cm之间,按间隔 4—6 cm对每个样品进行切分,用塑料袋封装。
-
采集的样品用塑料袋封装,在实验室晾干后磨细、混均、80目过筛,然后用Φ75 mm×50 mm的聚乙烯塑料样品盒密封封装,并称重。样品密封20 d后放在HPGeγ谱仪探测器端帽上方测量,收集谱数据。观察感兴趣γ射线峰面积,测量时间根据相对误差小于5%的要求而定。由于226Ra发出的射线186.2 keV(分支比3.2%)比较低,且一般的γ谱仪不能将其与235U发出的γ射线185.7 keV(分支比54%)分开,所以利用226Ra子体214Pb和214Bi发出的γ射线。其中,214Pb的γ射线峰包括241.9 keV(分支比7.5%)、295.2 keV(分支比19.1%)、351.9 keV(分支比37.1%);214Bi的γ射线峰包括609.3 keV(分支比46.1%)、1120.3 keV(分支比15.0%)、1764.5 keV(分支比15.9%)[1];而210Pb利用其自身发出的46.5 keV(分支比4.0%)的γ射线来测定。本实验刻度源的制作方法同文献[12]。
1.1. 研究海域与岩心
1.2. 样品测量方法
-
6个岩心不同层位的样品中226Ra的含量如表2所示,变化范围为(8.81±0.96)—(38.51±0.73)Bq·kg−1。从采样点的地理位置分布来看,沉积物中226Ra含量随着经纬度的变化没有明显的变化规律,但随着采样点的水深变化而变化,较深的海域含量较高,较浅的海域含量较低。并沿着水流方向(即BKAS80→BKAS64→BKAS35→ BKAS12)含量逐渐升高(水流示意图如图1[13]所示)。比较4个水深较浅的采样点(BKAS30,BKAS64,BKAS79和BKAS80)时发现:BKAS64和BKAS79比BKAS30和BKAS80要略高,说明BKAS64和BKAS79采集点可能会有其他的226Ra来源,且沿着洋流的方向对BKAS64和BKAS79采集点的226Ra含量造成一定的影响,而BKAS30和BKAS80可能没有来自大陆方向的额外输入来源,或者相比之下没有像BKAS64和BKAS79站位的那种相对稍大的大陆额外输入来源,同时水流方向对BKAS64和BKAS79的贡献相比BKAS30和BKAS80可能更大。另外,由于沉积物中230Th的衰变是226Ra的主要来源,且海水中226Ra很大部分是以溶解态存在,在BKAS30、BKAS64、BKAS79、BKAS80采样点,水越浅,导致沉积物中溶解态的226Ra迁移到上层水越多[14],更深层次的原因可能还需要分析沉积物组成、底层生物扰动及水动力变化过程等方面才能进一步得到结论。
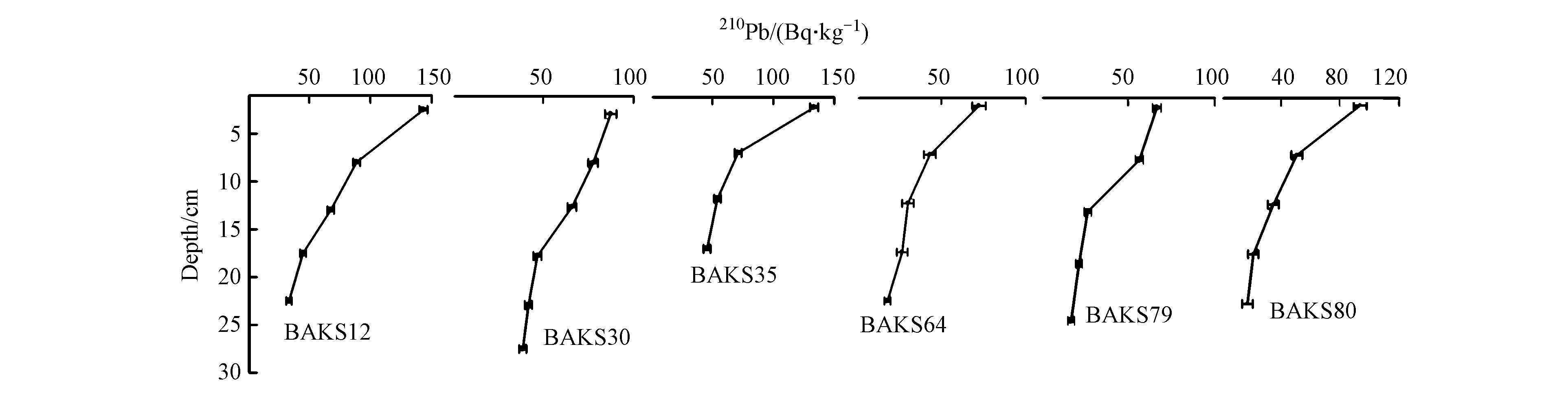
在岩心中随深度变化特征如图2所示,在BKAS12,BKAS64两个站位,226Ra含量随着岩心深度的增加先是有一个微弱的增加趋势,但是在中间深度层段有一个减小的转折点,随后含量逐渐减小;在BKAS30,BKAS35,BKAS79,BKAS80站位,226Ra核素含量随着深度的增加基本上呈现出不断减小的趋势。微弱的增加趋势反映出BKAS12,BKAS64两个站位的沉积物在不同深度处,陆源碎屑和生物碎屑所占份额存在有差别,在沉积的某些层段,有部分的生物碎屑可能流失,导致了对陆源碎屑输入的226Ra与210Pb的稀释作用变弱,从而出现这两种核素的比活度有着些许的增加。而逐渐减小的趋势除核素自身衰变外,还需要进一步探讨水文学过程的影响,在水动力过程较为活跃及生物扰动较强期间,沉积物中的226Ra与210Pb核素向上覆水体扩散的速率加快,损失较多,也会是沉积物中核素含量逐渐减小的原因[15]。
-
6个不同站位的210Pb含量及随岩心深度的变化如表2和图3,其活度变化范围(17.20±1.87) —(143.28±3.31) Bq·kg-1。比较6个岩心210Pb含量变化范围发现,BKAS12与BKAS35变化范围比较大,BKAS30、BKAS64、BKAS79、BKAS80变化范围相对较小。从含量平均值来看,BKAS12,BKAS35的210Pb含量平均值较高,比BKAS64,BKAS79的210Pb含量平均值高出一倍左右。由图3可知,同一站位不同层位210Pb的活度随着岩心深度的增加,呈现明显减小的梯度变化。由于从大气中沉降的210Pbex伴随着降水与干湿沉降,附着在悬浮颗粒中,并随着悬浮颗粒逐渐沉积在水底,本身已形成一个相对的封闭体系,而非过剩的210Pb(补偿210Pb)也会与其母体226Ra到达平衡[16]。且沉降的210Pb与黏土矿物有着非常好的亲和力,不会大量集中在有机物,因此有机物中的分子扩散效应也不会引起210Pb的大量迁移[17],所以210Pb含量随着岩心深度增加而减少整体上是由于210Pbex的衰变导致。同时,也要考虑到210Pb的化学迁移因素,比如沉积物岩心中的非碳酸盐相Pb可能会转移到可溶性碳酸盐中,再由空隙水产生了扩散迁移。而且,沉积物中的铁锰氧化物由于氧化还原反应而形成游离态,导致依附在铁锰氧化物的210Pbex也会随着向上覆水体扩散[18],从而使得210Pb含量随岩心深度而减少。210Pb的深度分布曲线表现为不稳定的沉积曲线,这表明沉积物在沉积过程中,该海域附近的沉积动力环境也发生了改变。
-
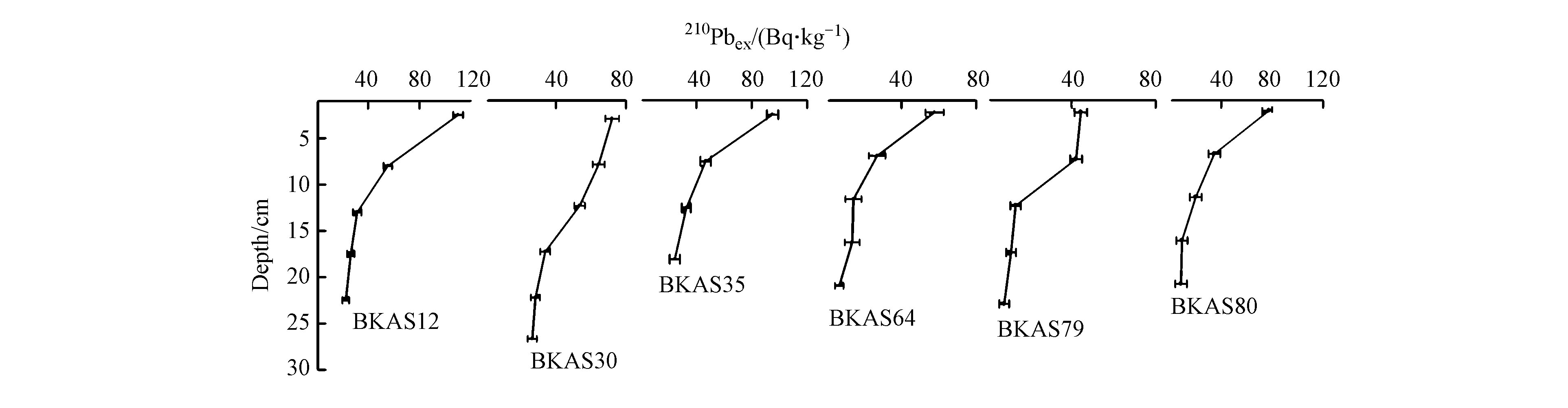
除沉积物自身含有的226Ra衰变产生的210Pb外,大气沉降到水体中的210Pb,以及水体中226Ra衰变产生的210Pb,与水体中的悬浮颗粒物质结合并随着颗粒物质沉积等额外来源,共同构成了沉积物中过剩的210Pb(210Pbex)。比较6个岩心中210Pbex的含量发现(图4),较深水域下,BKAS12,BKAS35两个岩心中210Pbex平均值较大;较浅水域下,BKAS64,BKAS79,BKAS80岩心210Pbex平均值相对较小。但在较浅水域下的BKAS30站位,210Pbex平均值却远高于接近深度下的BKAS64,BKAS79,BKAS80站位,这与该站位靠近加里曼丹岛沿岸,水深较浅,收到陆源输送的沉积物较多,导致了210Pbex的含量增加有关[19]。同时,210Pbex随站位的变化与210Pb随站位的变化基本一致,因此可以大致判断210Pbex含量随站位变化的主要影响因素是水流方向[13]和站位的水深等。从同一岩心不同层位的变化来看,这6个站位的210Pbex含量随深度变化都是逐渐减小的,趋势非常明显,这和210Pb含量随深度的变化趋势基本一致,表明210Pbex主要是受到210Pb含量的影响而不是226Ra含量的影响。由于210Pb在沉积过程中,受到人类活动的干扰、底栖生物扰动和水动力学过程等很多因素的影响,沉积过程变得十分复杂,本实验通过沉积物在埋藏过程中压实作用的定量计算(压实校正),并利用多次迭代的方法[20],计算出这6个岩心中的平均沉积速率(cm·a−1)分别为0.385、0.652、0.357、0.306、0.326、0.270。比较这6个站位发现,BKAS30的沉积速率大于其他5个采样点,原因主要是该站位靠近加里曼丹岛,水深越浅,离岸越近,210Pb经由河流、大气沉降最终进入到近岸沉积物的陆源输送越大,提高了沉积速率[19]。同时,我们利用CIC(恒定初始浓度模式),即假定210Pbex的比活度随着岩心深度的增加呈指数衰减模式,计算了6个岩心的沉积年代,得到如下结果:岩心BKAS12、BKAS30、BKAS35、BKAS64、BKAS79、BKAS80的沉积时间分别为62、44、59、82、80、93年。以本研究样品采集时间2014年作为时标,初步得到这6个岩心的沉积年代分别为1952年、1970年、1955年、1932年、1934年、1921年。
-
210Pb与226Ra都是来自于同一放射系(铀系)的核素,可以把210Pb与226Ra看成一对子母体,在整个铀系衰变链中,226Ra的半衰期(T½=1.6×103 a)远远大于210Pb的半衰期(T½=22.26 a)。由表2和图5中可知,本研究中210Pb/226Ra的比活度比值的范围1.59—5.87之间,平均值为3.1。表明在实验误差允许范围内,210Pb的含量远远高于226Ra,即所测的样品中,有着较高含量的210Pbex存在。样品中的一些层段出现210Pb/226Ra的比活度的比值偏离平均值较大的情况,这与这两个核素化学性质的差异有关,同时,沉积物中210Pb与226Ra受到不同的物理过程、生物地球化学过程、生物扰动的影响,而且不同来源的210Pb/226Ra活度比值本身也存在一定差别,因此210Pb/226Ra活度比值可用于沉积物的物质来源判别和过程的示踪[11, 21-22]。例如:生源沉积物和礁外陆源沉积物之间的差异,可用于指示人类活动引起的陆源物质输入增加(比如,河流输入、岛礁或者近岸的工程建设)对近岸珊瑚礁生态系统的影响[23]。
-
表3中列出了本研究海域226Ra与210Pb的活度,并与其他海域进行了对比。发现本研究中,226Ra活度平均值接近于南海东北部[25]、胶州湾表层[27]、孟买港[33]等海域,低于南沙海域表层[24]、北部湾白龙半岛邻近海域[29]、黄茅海广海湾[28]、阳江核电站海域[26],高于红海海岸[30]。而210Pb活度平均值接近于南沙海区[24]、胶州湾表层[27],低于南海东北部[25]、阳江核电站[26]、黄茅海广海湾海域[29]等,高于孟买港[33]、红海海岸[30]等海域。
2.1. 226Ra活度分布
2.2. 210Pb活度分布
2.3. 210Pbex活度分布及沉积速率
2.4. 210Pb/226Ra的比活度的比值
2.5. 226Ra与210Pb的活度与其他海域的比较
-
(1)用HPGeγ谱方法测定了6个来自南沙海域沉积物岩心的226Ra与210Pb,并得到如下的结果:226Ra的活度变化范围为(8.81±0.96) Bq·kg−1至(38.5±0.73) Bq·kg−1,平均值的变化范围为(13.2±0.64)—(26.4±0.79) Bq·kg−1;210Pb的活度变化范围为(17.2±1.87)—(143±3.31) Bq·kg−1,平均值的变化范围为(37.7±2.11)—(76.1±2.94) Bq·kg−1。通过210Pb/226Ra活度的比值发现,所测样品中226Ra与210Pb没有达到放射性平衡,有着明显的过剩210Pb(210Pbex)。
(2) 6个岩心不同层位的210Pb与226Ra活度随着岩心深度的增加而减小。其中,放射性核素衰变是主要原因,此外,由孔隙水产生的扩散转移、底层生物扰动以及水动力变化等也有影响。需结合沉积物的来源和组成、沉积物沉积及再悬浮过程和水流方向及流速大小等诸多因素来做进一步的探讨。
(3)利用210Pbex活度随着深度的下降趋势,在压实校正的过程中使用多次迭代的方法,并结合CIC(恒定初始浓度模式),由此计算出6个岩心的平均沉积速率和沉积年代,1952—2014年间,BKAS12平均沉积速率为0.385 cm·a−1;1970—2014年间,BKAS30平均沉积速率为0.652 cm·a−1;1955—2014年间,BKAS35平均沉积速率为0.357 cm·a−1;1932—2014年间,BKAS64平均沉积速率0.306 cm·a−1;1934—2014年间,BKAS79平均沉积速率为0.326 cm·a−1;1921—2014年间,BKAS80平均沉积速率为0.27 cm·a−1。




 下载:
下载: