-
硝酸盐是地下水常量组分。近年来,硝酸盐污染成为全球最普遍、污染面积最大的地下水污染。农业化肥过量使用及城市、工矿企业污水无序排放是地下水硝酸盐污染的主要原因[1]。我国现为氮肥施用最多的国家,约占世界施用总量的30%[2]。在无合理农业管理措施情况下,作物对氮肥的利用率仅为30%—40%[3]。过量的氮肥最终以硝酸盐的形式在淋滤下进入水体。我国华北平原氮污染较为广泛,12.2%的地下水受到不同程度的“三氮”污染[4],且呈增加趋势。茹淑华等[5]通过对河北省11个地区连续7年的地下水硝酸盐含量监测,发现河北省地下水硝酸盐平均含量呈逐年明显增加的趋势,超标频率明显增加,由2006年的6.96%增加到了2012年的10.60%。武海英[6]通过对张家口地区8年地下水监测数据的分析,指出张家口地区地下水“三氮”污染总体情况不乐观,在所分析的监测井中有近一半“三氮”超标,坝上地区和市区“三氮”污染情况较坝下严重。硝酸盐可能通过地下水的饮用进入人体。高浓度的硝酸盐可导致高铁血红蛋白症,对婴幼儿的危害尤为显著;此外硝酸盐在人体中可能被还原为亚硝酸盐,与仲胺类作用形成致癌的亚硝胺类,严重危害人体健康[7-8]。预防、控制和治理地下水硝酸盐污染成为了重要环境问题。
安固里淖内陆河流域位于河北省西北部坝上环京津地区,半干旱气候,降雨稀少而蒸发强烈,地表水资源极为有限,地下水几乎是当地唯一的供水水源。区内农业、畜牧业活动范围广、强度大,地下水已受到硝酸盐的污染。同时,流域含水层多为岩浆岩,强非均质性,裂隙、孔洞发育,地表覆盖第四系土层大多较薄,导致硝酸盐更易进入地下水系统,且易扩散,而运移路径复杂,污染状况难以模拟。地下水对研究区生态系统、居民生产生活以及社会的稳定发展均有重要影响。而多年来对该区域的研究多集中于资源型缺水问题,硝酸盐的广泛分布和积累问题急需得到重视。
本文以水化学方法结合土地利用类型揭示流域内地下水硝酸盐污染分布特征及成因,为安固里淖内陆河流域的硝酸盐污染提供防治依据,提出指导当地生产生活的理论依据,为有限地下水资源的水质提供保障。
-
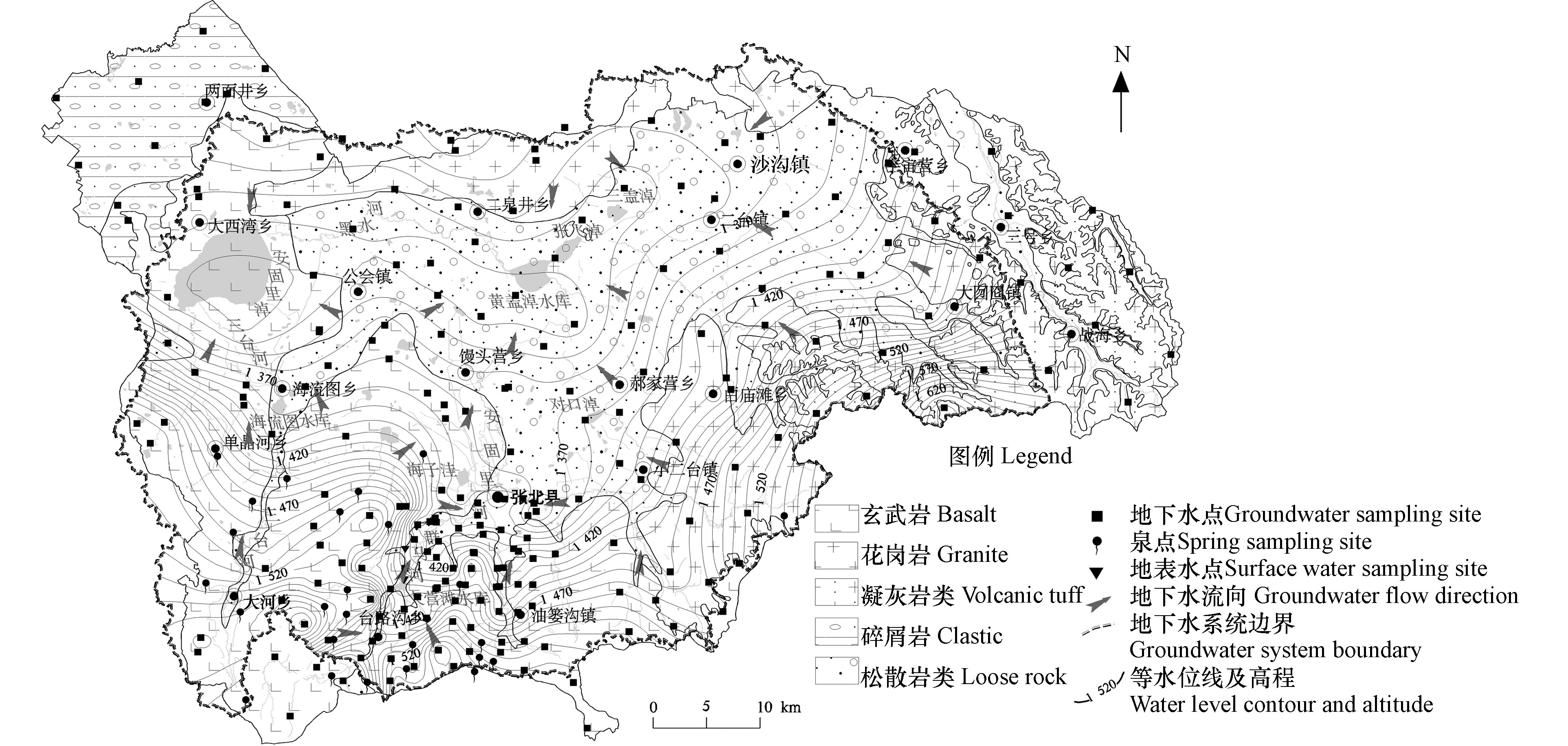
安固里淖内陆河流域位于河北省张家口市张北县,属于内蒙高原南缘,流域面积约3635 km2。地势总体南高北低,南部坝头一带为剥蚀熔岩台地,北部为波状平原,半干旱大陆性气候,据张北气象台观测资料,多年平均降水量383.8 mm(1981—2011年),多年平均蒸发量1655.1 mm(2000—2009年),河系水量稀少,补给来源为大气降水。目前流域内的主要河流为西南部三台河和中部安固里河,多至中游已下渗并消亡,安固里淖于2005年干涸,至今已干涸多年。
研究区属内流区,区域四周为地下水补给区:西—西南部分布有玄武岩孔洞裂隙含水岩组,厚度约50—300 m,玄武岩厚度向东逐渐变薄,东部玄武岩下伏泥岩,无供水价值;东南部和北部为受构造抬升的侵入岩,供水岩组为花岗岩裂隙水;东部为凝灰岩裂隙水,厚度小于100 m。地下水以侧向径流的方式补给区域中部第四系松散岩类孔隙水,第四系厚度30—100 m,由补给区向排泄区逐渐变厚,小部分第四系下部为碎屑岩类裂隙水,具有双层结构,因中间无稳定隔水层,可视为一个含水岩组。区域内地表水、地下水的流向与地形一致,由流域四周海拔高处向流域北部最低处的安固里淖和黄盖淖径流,于此蒸发排泄(图1)。作为内流区,地下水组分随水流向下游径流并在排泄区积累,研究区地下水的补给来源为大气降水、地表水、灌溉回归水,排泄以开采、蒸发为主。
研究区农业和畜牧业活动分布广泛,城镇附近蔬菜种植更为集中,用水量及施肥量均较高,且城镇居民生活、工业废水排放量大;流域内村庄星罗棋布,部分农户在院子中养殖牲畜,人畜生活污水在院子中累积,而自用机井无防护,地下水污染风险高。
-
根据张北县多年平均气象资料,7—9月是主要降水月份,降水量占全年的60.1%。为掌握一个水文年典型时段水质情况,在雨季前后即2018年7月初和9月末开展采样工作,两期分别采样163、95组,共计采集水样258组,其中地下水230组,地表水2组,泉水26组,采样点布置如图1所示。采样点包含研究区所有含水层类型,其中玄武岩裂隙孔洞水含水层采样109组,取样深度3—170 m;松散岩类孔隙水含水层102组,取样深度3—100 m;花岗岩及凝灰岩裂隙水采样点19组,取样深度为25—60 m。现场检测水样的水温、电导率、pH值、DO、Eh值等指标;现场滴定碱度;水样采样容器为250 mL聚乙烯瓶,每个采样点采集两瓶,经0.45 μm滤膜过滤,硝酸盐及常见阴阳离子指标采样容器密封保存于4 ℃环境;重金属指标水样过滤后加入浓硝酸硝化至pH<2,密封保存于4 ℃环境。
实验室内,电感耦合等离子体-质谱仪(NexlON350X)测定重金属及微量离子,火焰原子吸收光谱仪(contrAA300)测定钾钠离子,钙镁使用滴定法测定,离子色谱仪(万通883)测定常规阴离子,亚硝酸盐、铵离子使用紫外可见分光光度计(普析TU-1901)测定。地下水中硝酸盐、亚硝酸盐和氨氮的检出限分别为0.04、0.004、0.04 mg·L−1。
-
对研究区内所采集水样的水化学参数进行分析,结果如表1所示。区内水样pH均值在7以上,最高为8.59,流域水体呈弱碱性。泉分布于流域西南部补给区,受地下水补给,在地形切割较深处出露成泉,其补给范围和出露地点均位于流域上游,径流距离较短,泉水样各组分含量较低,TDS平均293.34 mg·L−1;结合采样点位置,发现流域下游地下水水质整体较差,TDS最高达4398.57 mg·L−1;两期共102组地下水样中硝酸盐含量超地下水Ⅲ类标准,超标率达44.3%,部分地点超标严重,硝酸盐浓度最高达786.45 mg·L−1;地表水发源于南部山区,受大气降水补给,径流同时补给地下水,至下游多已消亡,地表水组分含量较低,仅氨氮的含量高于地下水和泉水。
按含水层类型分析,玄武岩裂隙孔洞水TDS平均618.57 mg·L−1,HCO3-Ca·Mg为主要水化学类型,近县城地区受人类影响出现HCO3·Cl-Ca·Mg (Na)型;花岗岩或凝灰岩裂隙水TDS平均732.57 mg·L−1,水化学类型以HCO3-Ca·Mg为主;第四系孔隙水TDS平均757.94 mg·L−1,水化学类型较复杂,阴阳离子类型出现了Cl型和Na型。研究区玄武岩裂隙孔洞含水层的连通性优于侵入岩裂隙含水层,径流条件较好,地下水流速较快,溶解组分整体较低,而第四系孔隙水主要存在于流域下游,地下水运移路程远时间长,水中溶解组分较多,水化学类型复杂。
对流域内地下水进行质量评价及地下水类型划分(图2)。HCO3-Ca型地下水广泛分布于山前地带,水流交替作用强烈,溶解性总固体范围在100—500 mg·L−1之间。由山前向流域下游过渡,水流交替作用减弱,地下水径流路径增长,溶滤更加充分,且内流流域地下水无法向外排泄,溶解性总固体逐渐升高,阴离子类型由HCO3型向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl、Cl·HCO3、Cl型过渡,水化学类型环带状展布,流域地势最低区域内地下水水质等级普遍低于Ⅲ级。
-
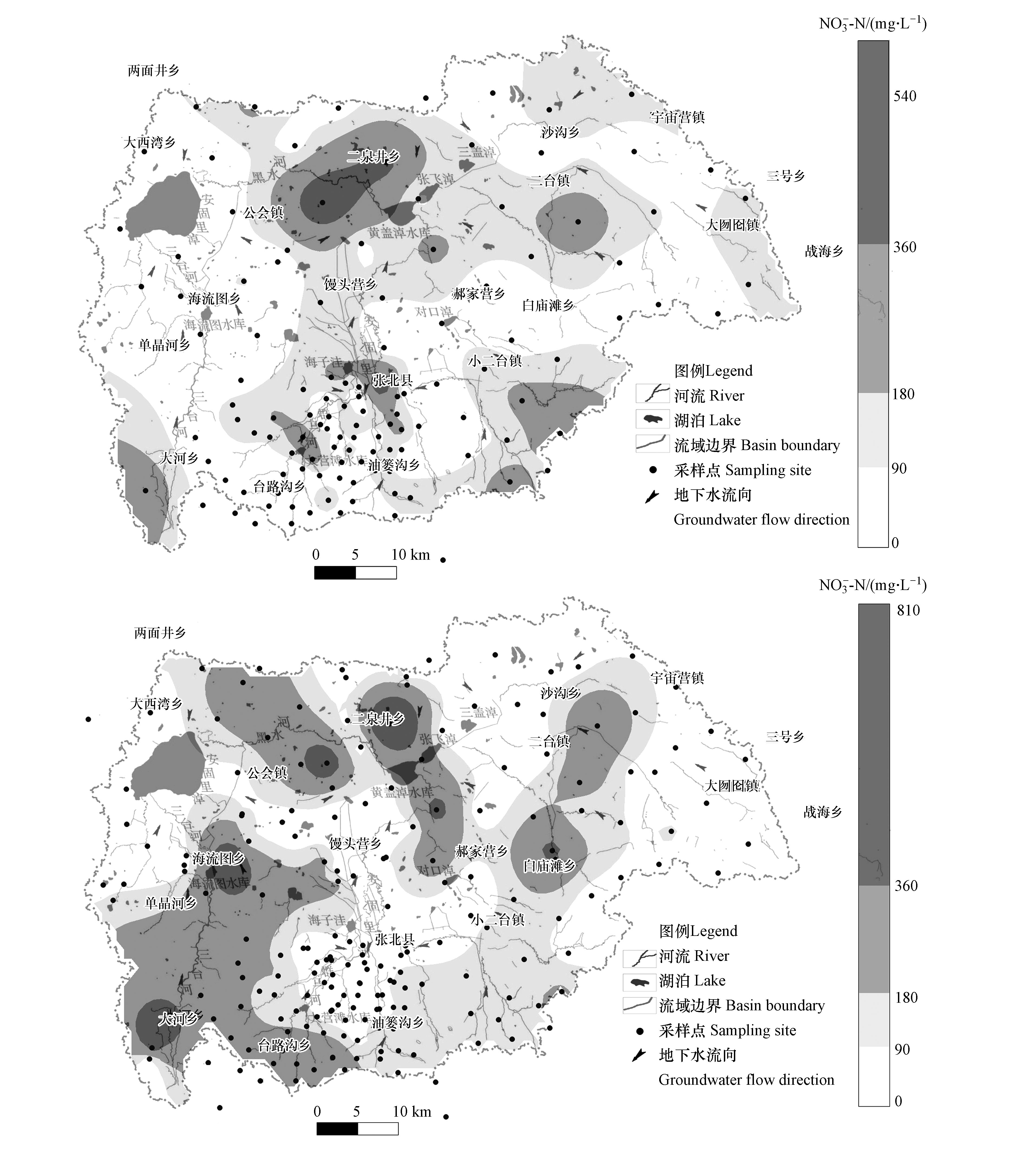
根据两期水样数据绘制NO3−浓度分布图。雨季前NO3−浓度超标区点状分布于流域四周的补给区,片状分布于流域北部排泄区;降雨期过后,受污染的地下水向下游径流,补给区点状分布的NO3−浓度超标区减少,但径流区浓度增加,超标范围随流向呈条带状分布,排泄区浓度升高。由补给区至径流、排泄区,硝酸盐含量呈增加趋势。
由图3(a),7月初NO3−浓度超标区域主要点状分布于流域南部补给区,浓度为294.99—313.76 mg·L−1,补给区为剥蚀熔岩台地,地势高,含水层为玄武岩或花岗岩裂隙孔洞,上覆第四系厚度很小,地下水易受到污染,但村庄较下游平原稀少,仅有小面积耕作和少量散养牲畜养殖,因此超标点分散且数量较少;张北县城、县城西南位于流域中南部径流区,县城工农业发达且生活污水排量大,县城西南为蔬菜集中种植区,施肥密集,在径流区形成了小片集中超标区,NO3−最高值点位于张北县城西,达587.36 mg·L−1,推测与大量施肥有关;北部属流域排泄区,为波状平原,村庄及农牧活动较多,同时地下水受到整个流域的补给,化学组分在此区域累积,NO3−浓度超标区域片状分布,公会镇东至二泉井乡NO3−浓度较高,浓度范围为418.90—557.86 mg·L−1。
由图3(b),9月末流域补给区由于地下水向下游径流强烈,NO3−浓度减小,流域东南补给区下降较为明显,但径流区超标面积增大,尤其流域西南部的大河乡至海流图乡一线,且大河乡NO3−浓度升高,高于7月初,现为464.34 mg·L−1。三台河位于山间宽缓沟谷,受到沿途两岸地表径流的补给,易受到农业和生活废水的污染,且该河流量相对较大,断流段较少,河水向南径流的同时下渗补给地下水,因此地下水沿三台河方向向北径流形成污染带,至海流图乡一带的流域排泄区,径流变缓,NO3−浓度上升至593.25 mg·L−1,浓度明显高于上游。张北县和县西的超标区域消失,但其下游的郝家营乡西出现超标情况,沿径流方向呈条带状分布,推测为农田施肥期已过且硝酸盐随地下水径流向下游运移所致。此外,下游排泄区公会镇东至二泉井乡一带NO3−浓度增高,为575.40—786.45 mg·L−1。
-
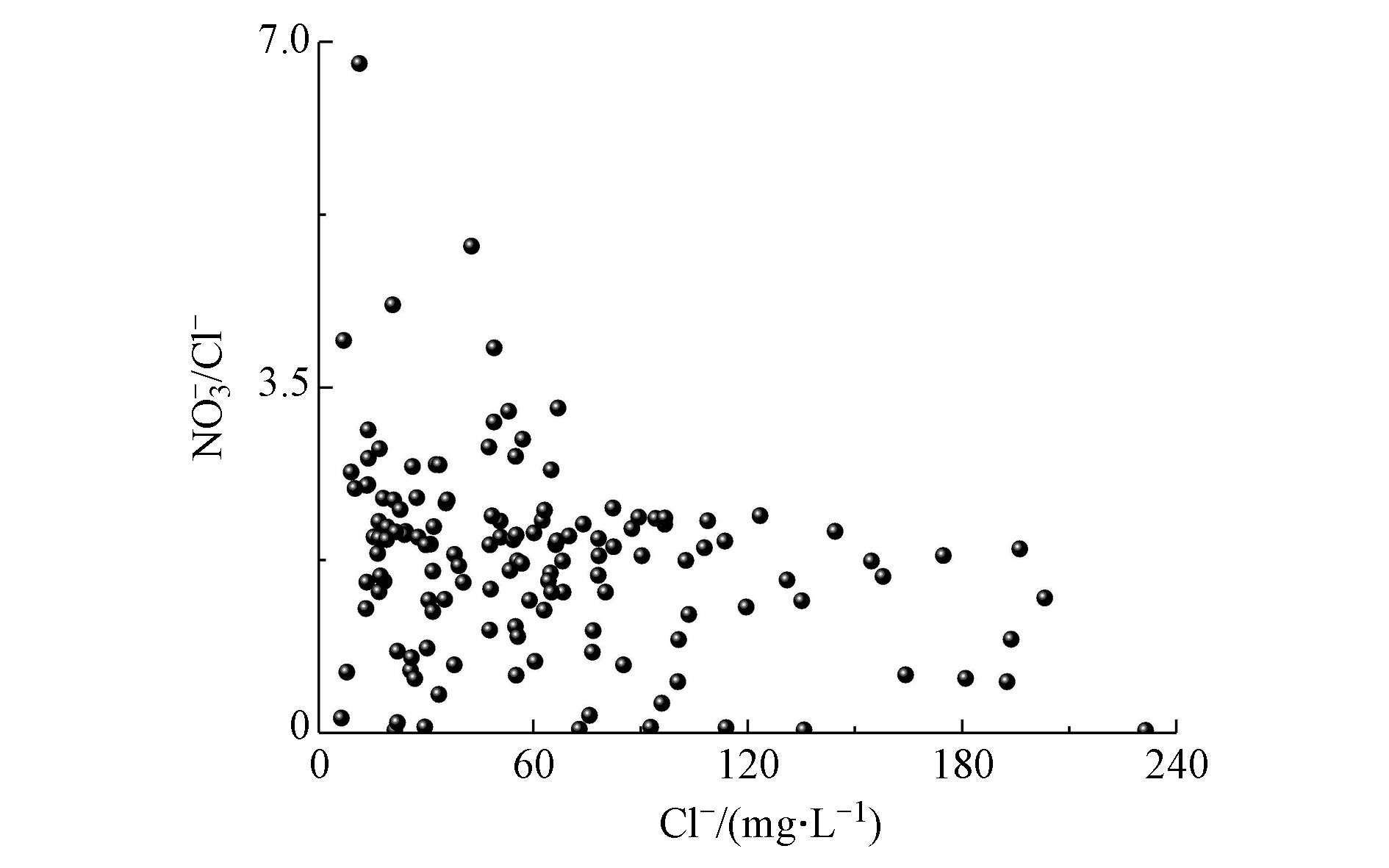
Cl−在水中较为稳定,不易受到物理吸附、化学反应和微生物的影响,是水体污染源的良好指标[9-10],NO3−/ Cl−比值可为氮的来源提供研究依据[11-12],化肥中若含Cl−,则其通常随NO3−增加,而人畜生活污水则具有高Cl−低NO3−的特点。根据水质数据,NO3−/Cl−浓度比例与Cl−浓度见图4。点的分布较为分散,说明NO3−和Cl−的来源不同[13]。右下角的点Cl−浓度很高而NO3−/Cl−比值较低,表明NO3−主要来自生活和人畜排泄废水,与部分水井旁有牲畜散养,卫生较差有关;左上角的点Cl−浓度较低而NO3−/Cl−比值较高,表明地下水受农业化肥输入影响大[14-15],与张北农业以低耗水作物甜菜产业为重点领域[16-17],但对肥力要求较高[18],施肥量较大相一致。
地下水中的SO42−通常由石膏溶解而来,浓度有限[12]。研究区内SO42−和Cl−有很强的线性关系(R2=0.86),说明SO42−有其他重要来源,且氨氮化肥的主要成分就是(NH4)2SO4和NH4Cl,这与图4得出的化肥对地下水NO3−浓度有贡献的推论相一致。
研究区地下水组分相关系数(表2)表明NO3−与SO42−、Cl−浓度呈显著正相关,说明安固里淖内陆河流域地下水中硝酸盐主要来源为化肥和人畜排泄废水,与上文推断相符。同时NO3−与TDS呈显著正相关,而与井深、埋深、第四系厚度相关性很弱,推测原因为流域内包气带隔污性差透水性好,污染物易下渗,地下水运移过程中组分的积累是NO3−浓度高的主要原因。
-
安固里淖内陆河流域内包气带以砂土和岩浆岩风化壳为主,隔污性差,含水层透水性好,因此地下水硝酸盐浓度影响因素主要从人类活动、自然因素和氧化还原条件方面考虑。
(1)土地利用类型
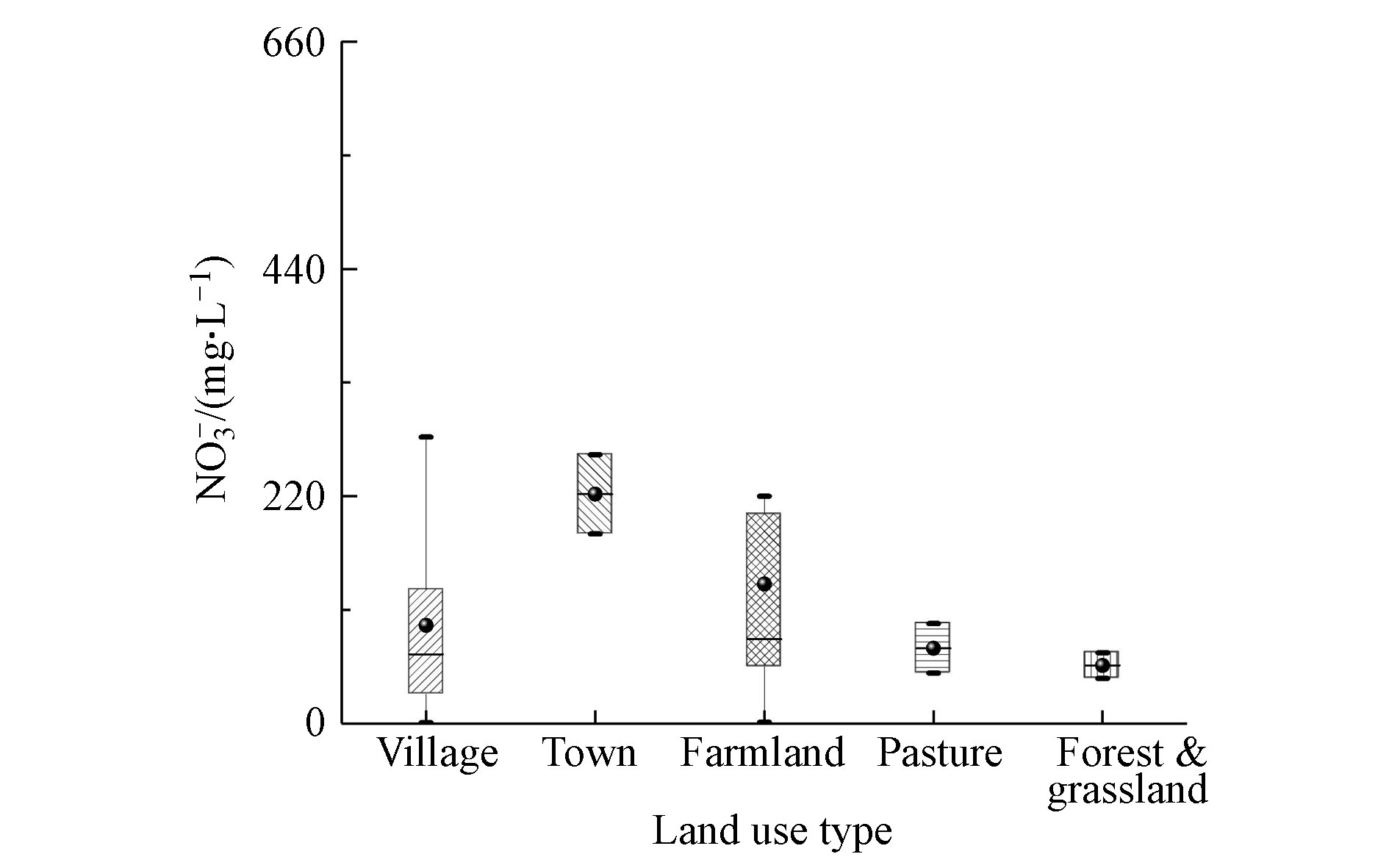
本文将安固里淖内陆河流域内土地利用类型分为城镇、村庄、农田、牧场和林草地等5种,不同土地利用类型地下水中NO3−浓度对比见图5。城镇污染源较多,NO3−浓度最高,平均值221.96 mg·L−1;农田因化肥使用,NO3−平均浓度为134.98 mg·L−1;村庄地下水受人畜影响,NO3−浓度平均值为94.99 mg·L−1;牧场NO3−浓度较低为72.85 mg·L−1;林草地地下水中NO3−浓度最低,均值为56.15 mg·L−1。地下水中NO3−浓度受土地利用类型影响显著。
(2)降雨
由于流域包气带厚度小(3—25 m),隔污性差透水性好,硝酸盐易渗入地下水,雨季前后其浓度有明显变化。根据气象资料,研究区7月初处于流域内雨季初期,9月末雨季结束。2018年度的两次采样中,选取了流域内20个相同点位,检测雨季前后NO3−浓度差异,结果雨季后有12个点位NO3−浓度明显上升,平均上升20.97 mg·L−1,最高达82.99 mg·L−1;其余点位NO3−浓度与雨季前基本持平或略有减少,其中6个点位NO3浓度减少量小于5 mg·L−1。这与鲁垠涛等[19]在某小流域得出地下水硝酸盐污染雨季浓度升高的研究结果一致。可见9月末绝大部分采样点的NO3−浓度均高于7月初,且首次采样NO3−浓度平均值为178.96 mg·L−1,第二次采样中升至222.71 mg·L−1,证明了流域内地下水在雨季后NO3−的积累显著。
(3)氧化还原条件
含水层氧化还原条件对氮的存在形态起决定性作用[20]。流域地下水Eh均值319.92 mV,pH均值7.81,为适宜硝化细菌生长的弱碱性氧化环境[21-23],利于硝化反应进行,流域中的氮最终转化为NO3−。流域地下水DO值平均7.07 mg·L−1,根据孔洞开合大小和连通性由小至大,花岗岩和凝灰岩裂隙水的DO最小,平均6.11 mg·L−1,玄武岩裂隙孔洞水增至6.77 mg·L−1,第四系孔隙水DO均值最高,为7.58 mg·L−1,不利于反硝化作用的进行[24-26],NO3−的浓度也依此序增加(表3),同时地下水中NO2−和NH4+浓度非常低,平均仅0.14 mg·L−1和0.07 mg·L−1,NH4+基本无检出,NO2−作为中间产物在极低浓度下呈现随DO值增加的趋势,也证明流域内硝化作用强烈,导致NO3−的浓度升高,污染面积大。
-
(1)安固里淖内流河流域内地下水呈弱碱性,HCO3-Ca类型地下水主要分布在山前地带,由山前向流域下游过渡,阴离子类型由HCO3型向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl、Cl·HCO3、Cl型过渡,水化学类型环带状展布。水质整体较差,TDS普遍较高,部分地点
NO−3 超标严重,最高达786.45 mg·L−1,超标率达44.3%。(2)
NO−3 主要来源于农业施肥和人畜生活污水排放,且9月末集中降雨结束后,相同井位的水样较7月初的NO−3 浓度有增加。污染羽7月初片状分布,随时间向下游迁移,9月末污染范围扩大,在流域径流区沿地下水流向条带状分布。(3)安固里淖内陆河流域地下水资源短缺,农业等人类活动剧烈,含水层非均质性且处于氧化条件,研究区地下水环境问题日益严重,尤其
NO−3 污染面积大,程度重。研究NO−3 在流域地下水中的时空分布特征及成因对流域农业污染防控和治理具有指导意义。
安固里淖内陆河流域地下水硝酸盐污染时空分布特征及成因分析
Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and origin analysis of nitrate pollution in groundwater in Angulinao inland river basin
-
摘要: 安固里淖内陆河流域为严重缺水区,多年来,此区域的地下水研究集中水资源量及其开发方向,含水层遭受的污染受到了忽视,其中硝酸盐污染是安固里淖内陆河流域最突出的水质问题。本研究采集流域雨季前和雨季后地下水样品共258组进行全分析检测,分析流域硝酸盐分布及成因。结果表明,流域补给区水化学类型以HCO3-Ca为主,阴离子类型沿流向向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl、Cl·HCO3、Cl型过渡;部分地点硝酸盐超标严重,超标率达44.3%;降雨期结束后流域硝酸盐浓度升高,且污染羽沿地下水流向扩大呈条带状分布;流域地下水处于弱碱性氧化条件,适宜硝酸盐的积累。硝酸盐主要受土地利用类型影响,来源主要为农业化肥和人畜生活用水排放。Abstract: Angulinao inland river basin was a severe water shortage area, and the issues about the amount and use of groundwater resources in this area were paid much attention. However, the groundwater contamination including nitrate contamination has been neglected in this area. The present study investigated the distribution of groundwater nitrate and its factors in the Angulinao inland river basin, and 258 groundwater samples were collected for analysis. The results showed that HCO3-Ca was the main hydrochemical type in the recharge area of the basin, and the anionic type was evolved with HCO3·SO4, HCO3·Cl, Cl·HCO3, Cl type along the groundwater flow. Nitrate concentrations in 44.3% groundwater samples in this area exceeded the standard for groundwater quality in China. The concentration of groundwater nitrate in this area increased after the rainfall period, and the pollution plume expanded along the flow direction of groundwater. The groundwater in this area characterized by weak alkaline and oxidation conditions was in favor of the enrichment of nitrate. Groundwater nitrate in this area originated mainly from agricultural fertilizer and discharge of domestic water, and the distribution of nitrate in groundwater was mainly affected by land use type.
-
Key words:
- Angulinao /
- inland river basin /
- groundwater /
- nitrate /
- distribution /
- origin
-
硝酸盐是地下水常量组分。近年来,硝酸盐污染成为全球最普遍、污染面积最大的地下水污染。农业化肥过量使用及城市、工矿企业污水无序排放是地下水硝酸盐污染的主要原因[1]。我国现为氮肥施用最多的国家,约占世界施用总量的30%[2]。在无合理农业管理措施情况下,作物对氮肥的利用率仅为30%—40%[3]。过量的氮肥最终以硝酸盐的形式在淋滤下进入水体。我国华北平原氮污染较为广泛,12.2%的地下水受到不同程度的“三氮”污染[4],且呈增加趋势。茹淑华等[5]通过对河北省11个地区连续7年的地下水硝酸盐含量监测,发现河北省地下水硝酸盐平均含量呈逐年明显增加的趋势,超标频率明显增加,由2006年的6.96%增加到了2012年的10.60%。武海英[6]通过对张家口地区8年地下水监测数据的分析,指出张家口地区地下水“三氮”污染总体情况不乐观,在所分析的监测井中有近一半“三氮”超标,坝上地区和市区“三氮”污染情况较坝下严重。硝酸盐可能通过地下水的饮用进入人体。高浓度的硝酸盐可导致高铁血红蛋白症,对婴幼儿的危害尤为显著;此外硝酸盐在人体中可能被还原为亚硝酸盐,与仲胺类作用形成致癌的亚硝胺类,严重危害人体健康[7-8]。预防、控制和治理地下水硝酸盐污染成为了重要环境问题。
安固里淖内陆河流域位于河北省西北部坝上环京津地区,半干旱气候,降雨稀少而蒸发强烈,地表水资源极为有限,地下水几乎是当地唯一的供水水源。区内农业、畜牧业活动范围广、强度大,地下水已受到硝酸盐的污染。同时,流域含水层多为岩浆岩,强非均质性,裂隙、孔洞发育,地表覆盖第四系土层大多较薄,导致硝酸盐更易进入地下水系统,且易扩散,而运移路径复杂,污染状况难以模拟。地下水对研究区生态系统、居民生产生活以及社会的稳定发展均有重要影响。而多年来对该区域的研究多集中于资源型缺水问题,硝酸盐的广泛分布和积累问题急需得到重视。
本文以水化学方法结合土地利用类型揭示流域内地下水硝酸盐污染分布特征及成因,为安固里淖内陆河流域的硝酸盐污染提供防治依据,提出指导当地生产生活的理论依据,为有限地下水资源的水质提供保障。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区概况
安固里淖内陆河流域位于河北省张家口市张北县,属于内蒙高原南缘,流域面积约3635 km2。地势总体南高北低,南部坝头一带为剥蚀熔岩台地,北部为波状平原,半干旱大陆性气候,据张北气象台观测资料,多年平均降水量383.8 mm(1981—2011年),多年平均蒸发量1655.1 mm(2000—2009年),河系水量稀少,补给来源为大气降水。目前流域内的主要河流为西南部三台河和中部安固里河,多至中游已下渗并消亡,安固里淖于2005年干涸,至今已干涸多年。
研究区属内流区,区域四周为地下水补给区:西—西南部分布有玄武岩孔洞裂隙含水岩组,厚度约50—300 m,玄武岩厚度向东逐渐变薄,东部玄武岩下伏泥岩,无供水价值;东南部和北部为受构造抬升的侵入岩,供水岩组为花岗岩裂隙水;东部为凝灰岩裂隙水,厚度小于100 m。地下水以侧向径流的方式补给区域中部第四系松散岩类孔隙水,第四系厚度30—100 m,由补给区向排泄区逐渐变厚,小部分第四系下部为碎屑岩类裂隙水,具有双层结构,因中间无稳定隔水层,可视为一个含水岩组。区域内地表水、地下水的流向与地形一致,由流域四周海拔高处向流域北部最低处的安固里淖和黄盖淖径流,于此蒸发排泄(图1)。作为内流区,地下水组分随水流向下游径流并在排泄区积累,研究区地下水的补给来源为大气降水、地表水、灌溉回归水,排泄以开采、蒸发为主。
研究区农业和畜牧业活动分布广泛,城镇附近蔬菜种植更为集中,用水量及施肥量均较高,且城镇居民生活、工业废水排放量大;流域内村庄星罗棋布,部分农户在院子中养殖牲畜,人畜生活污水在院子中累积,而自用机井无防护,地下水污染风险高。
1.2 样品采集与分析方法
根据张北县多年平均气象资料,7—9月是主要降水月份,降水量占全年的60.1%。为掌握一个水文年典型时段水质情况,在雨季前后即2018年7月初和9月末开展采样工作,两期分别采样163、95组,共计采集水样258组,其中地下水230组,地表水2组,泉水26组,采样点布置如图1所示。采样点包含研究区所有含水层类型,其中玄武岩裂隙孔洞水含水层采样109组,取样深度3—170 m;松散岩类孔隙水含水层102组,取样深度3—100 m;花岗岩及凝灰岩裂隙水采样点19组,取样深度为25—60 m。现场检测水样的水温、电导率、pH值、DO、Eh值等指标;现场滴定碱度;水样采样容器为250 mL聚乙烯瓶,每个采样点采集两瓶,经0.45 μm滤膜过滤,硝酸盐及常见阴阳离子指标采样容器密封保存于4 ℃环境;重金属指标水样过滤后加入浓硝酸硝化至pH<2,密封保存于4 ℃环境。
实验室内,电感耦合等离子体-质谱仪(NexlON350X)测定重金属及微量离子,火焰原子吸收光谱仪(contrAA300)测定钾钠离子,钙镁使用滴定法测定,离子色谱仪(万通883)测定常规阴离子,亚硝酸盐、铵离子使用紫外可见分光光度计(普析TU-1901)测定。地下水中硝酸盐、亚硝酸盐和氨氮的检出限分别为0.04、0.004、0.04 mg·L−1。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 水化学特征
对研究区内所采集水样的水化学参数进行分析,结果如表1所示。区内水样pH均值在7以上,最高为8.59,流域水体呈弱碱性。泉分布于流域西南部补给区,受地下水补给,在地形切割较深处出露成泉,其补给范围和出露地点均位于流域上游,径流距离较短,泉水样各组分含量较低,TDS平均293.34 mg·L−1;结合采样点位置,发现流域下游地下水水质整体较差,TDS最高达4398.57 mg·L−1;两期共102组地下水样中硝酸盐含量超地下水Ⅲ类标准,超标率达44.3%,部分地点超标严重,硝酸盐浓度最高达786.45 mg·L−1;地表水发源于南部山区,受大气降水补给,径流同时补给地下水,至下游多已消亡,地表水组分含量较低,仅氨氮的含量高于地下水和泉水。
表 1 研究区地下水、泉水及地表水水化学参数统计(mg·L−1)Table 1. Statistics of chemical parameters of groundwater, spring and surface water in the study area(mg·L−1)pH Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ SO42− Cl− NO3− NO2− NH4+ TDS DO 地下水 最大值 8.59 1176.73 368.7 377.83 892.84 1367.56 786.45 11.53 6.00 4398.57 9.9 平均值 7.85 107.50 97.73 47.10 107.05 153.87 111.03 0.14 0.07 797.15 7.07 最小值 6.40 6.80 10.46 4.90 1.50 6.28 0.56 0 0 130.80 1.3 泉水 最大值 8.42 29.65 99.80 31.36 76.51 56.31 107.11 0.62 0.04 500.67 12.6 平均值 7.87 16.37 56.86 14.36 31.82 18.99 31.23 0.04 0 293.34 8.43 最小值 7.44 7.14 23.09 5.79 13.72 4.02 3.20 0 0 127.00 4.7 地表水 最大值 7.80 27.57 81.12 28.64 31.16 23.85 0.92 0.09 20.86 433.30 17.00 平均值 7.68 25.82 59.56 24.70 28.75 22.75 0.90 0.04 10.43 357.98 10.01 最小值 7.55 24.06 38.00 20.76 26.34 21.65 0.89 0 0 282.65 3.02 按含水层类型分析,玄武岩裂隙孔洞水TDS平均618.57 mg·L−1,HCO3-Ca·Mg为主要水化学类型,近县城地区受人类影响出现HCO3·Cl-Ca·Mg (Na)型;花岗岩或凝灰岩裂隙水TDS平均732.57 mg·L−1,水化学类型以HCO3-Ca·Mg为主;第四系孔隙水TDS平均757.94 mg·L−1,水化学类型较复杂,阴阳离子类型出现了Cl型和Na型。研究区玄武岩裂隙孔洞含水层的连通性优于侵入岩裂隙含水层,径流条件较好,地下水流速较快,溶解组分整体较低,而第四系孔隙水主要存在于流域下游,地下水运移路程远时间长,水中溶解组分较多,水化学类型复杂。
对流域内地下水进行质量评价及地下水类型划分(图2)。HCO3-Ca型地下水广泛分布于山前地带,水流交替作用强烈,溶解性总固体范围在100—500 mg·L−1之间。由山前向流域下游过渡,水流交替作用减弱,地下水径流路径增长,溶滤更加充分,且内流流域地下水无法向外排泄,溶解性总固体逐渐升高,阴离子类型由HCO3型向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl、Cl·HCO3、Cl型过渡,水化学类型环带状展布,流域地势最低区域内地下水水质等级普遍低于Ⅲ级。
2.2 地下水硝酸盐时空分布特征
根据两期水样数据绘制NO3−浓度分布图。雨季前NO3−浓度超标区点状分布于流域四周的补给区,片状分布于流域北部排泄区;降雨期过后,受污染的地下水向下游径流,补给区点状分布的NO3−浓度超标区减少,但径流区浓度增加,超标范围随流向呈条带状分布,排泄区浓度升高。由补给区至径流、排泄区,硝酸盐含量呈增加趋势。
由图3(a),7月初NO3−浓度超标区域主要点状分布于流域南部补给区,浓度为294.99—313.76 mg·L−1,补给区为剥蚀熔岩台地,地势高,含水层为玄武岩或花岗岩裂隙孔洞,上覆第四系厚度很小,地下水易受到污染,但村庄较下游平原稀少,仅有小面积耕作和少量散养牲畜养殖,因此超标点分散且数量较少;张北县城、县城西南位于流域中南部径流区,县城工农业发达且生活污水排量大,县城西南为蔬菜集中种植区,施肥密集,在径流区形成了小片集中超标区,NO3−最高值点位于张北县城西,达587.36 mg·L−1,推测与大量施肥有关;北部属流域排泄区,为波状平原,村庄及农牧活动较多,同时地下水受到整个流域的补给,化学组分在此区域累积,NO3−浓度超标区域片状分布,公会镇东至二泉井乡NO3−浓度较高,浓度范围为418.90—557.86 mg·L−1。
由图3(b),9月末流域补给区由于地下水向下游径流强烈,NO3−浓度减小,流域东南补给区下降较为明显,但径流区超标面积增大,尤其流域西南部的大河乡至海流图乡一线,且大河乡NO3−浓度升高,高于7月初,现为464.34 mg·L−1。三台河位于山间宽缓沟谷,受到沿途两岸地表径流的补给,易受到农业和生活废水的污染,且该河流量相对较大,断流段较少,河水向南径流的同时下渗补给地下水,因此地下水沿三台河方向向北径流形成污染带,至海流图乡一带的流域排泄区,径流变缓,NO3−浓度上升至593.25 mg·L−1,浓度明显高于上游。张北县和县西的超标区域消失,但其下游的郝家营乡西出现超标情况,沿径流方向呈条带状分布,推测为农田施肥期已过且硝酸盐随地下水径流向下游运移所致。此外,下游排泄区公会镇东至二泉井乡一带NO3−浓度增高,为575.40—786.45 mg·L−1。
2.3 地下水硝酸盐来源分析
Cl−在水中较为稳定,不易受到物理吸附、化学反应和微生物的影响,是水体污染源的良好指标[9-10],NO3−/ Cl−比值可为氮的来源提供研究依据[11-12],化肥中若含Cl−,则其通常随NO3−增加,而人畜生活污水则具有高Cl−低NO3−的特点。根据水质数据,NO3−/Cl−浓度比例与Cl−浓度见图4。点的分布较为分散,说明NO3−和Cl−的来源不同[13]。右下角的点Cl−浓度很高而NO3−/Cl−比值较低,表明NO3−主要来自生活和人畜排泄废水,与部分水井旁有牲畜散养,卫生较差有关;左上角的点Cl−浓度较低而NO3−/Cl−比值较高,表明地下水受农业化肥输入影响大[14-15],与张北农业以低耗水作物甜菜产业为重点领域[16-17],但对肥力要求较高[18],施肥量较大相一致。
地下水中的SO42−通常由石膏溶解而来,浓度有限[12]。研究区内SO42−和Cl−有很强的线性关系(R2=0.86),说明SO42−有其他重要来源,且氨氮化肥的主要成分就是(NH4)2SO4和NH4Cl,这与图4得出的化肥对地下水NO3−浓度有贡献的推论相一致。
研究区地下水组分相关系数(表2)表明NO3−与SO42−、Cl−浓度呈显著正相关,说明安固里淖内陆河流域地下水中硝酸盐主要来源为化肥和人畜排泄废水,与上文推断相符。同时NO3−与TDS呈显著正相关,而与井深、埋深、第四系厚度相关性很弱,推测原因为流域内包气带隔污性差透水性好,污染物易下渗,地下水运移过程中组分的积累是NO3−浓度高的主要原因。
表 2 研究区地下水组分相关系数统计表Table 2. Statistical table of correlation coefficient of groundwater components in the study area井深Well depth 埋深Groundwater depth 第四系厚度Quaternary thickness 硝酸盐NO3− 氯化物Cl− 硫酸盐SO42− 溶解性总固体TDS 井深 1.000 埋深 0.468** 1.000 第四系厚度 0.465** 0.252** 1.000 硝酸盐 −0.259** −0.197* −0.170* 1.000 氯化物 −0.071 −0.068 −0.045 0.597** 1.000 硫酸盐 −0.180* −0.310** −0.129 0.514** 0.817** 1.000 溶解性总固体 −0.151 −0.173* −0.093 0.674** 0.953** 0.867** 1.000 注:**:在置信度(双测)为0.01时,相关性显著;*:在置信度(双测)为0.05时,相关性显著. Note:**: 0.01 level(bilateral) significantly correlated; *: 0.05 level(bilateral) significantly correlated. 2.4 地下水硝酸盐浓度影响因素
安固里淖内陆河流域内包气带以砂土和岩浆岩风化壳为主,隔污性差,含水层透水性好,因此地下水硝酸盐浓度影响因素主要从人类活动、自然因素和氧化还原条件方面考虑。
(1)土地利用类型
本文将安固里淖内陆河流域内土地利用类型分为城镇、村庄、农田、牧场和林草地等5种,不同土地利用类型地下水中NO3−浓度对比见图5。城镇污染源较多,NO3−浓度最高,平均值221.96 mg·L−1;农田因化肥使用,NO3−平均浓度为134.98 mg·L−1;村庄地下水受人畜影响,NO3−浓度平均值为94.99 mg·L−1;牧场NO3−浓度较低为72.85 mg·L−1;林草地地下水中NO3−浓度最低,均值为56.15 mg·L−1。地下水中NO3−浓度受土地利用类型影响显著。
(2)降雨
由于流域包气带厚度小(3—25 m),隔污性差透水性好,硝酸盐易渗入地下水,雨季前后其浓度有明显变化。根据气象资料,研究区7月初处于流域内雨季初期,9月末雨季结束。2018年度的两次采样中,选取了流域内20个相同点位,检测雨季前后NO3−浓度差异,结果雨季后有12个点位NO3−浓度明显上升,平均上升20.97 mg·L−1,最高达82.99 mg·L−1;其余点位NO3−浓度与雨季前基本持平或略有减少,其中6个点位NO3浓度减少量小于5 mg·L−1。这与鲁垠涛等[19]在某小流域得出地下水硝酸盐污染雨季浓度升高的研究结果一致。可见9月末绝大部分采样点的NO3−浓度均高于7月初,且首次采样NO3−浓度平均值为178.96 mg·L−1,第二次采样中升至222.71 mg·L−1,证明了流域内地下水在雨季后NO3−的积累显著。
(3)氧化还原条件
含水层氧化还原条件对氮的存在形态起决定性作用[20]。流域地下水Eh均值319.92 mV,pH均值7.81,为适宜硝化细菌生长的弱碱性氧化环境[21-23],利于硝化反应进行,流域中的氮最终转化为NO3−。流域地下水DO值平均7.07 mg·L−1,根据孔洞开合大小和连通性由小至大,花岗岩和凝灰岩裂隙水的DO最小,平均6.11 mg·L−1,玄武岩裂隙孔洞水增至6.77 mg·L−1,第四系孔隙水DO均值最高,为7.58 mg·L−1,不利于反硝化作用的进行[24-26],NO3−的浓度也依此序增加(表3),同时地下水中NO2−和NH4+浓度非常低,平均仅0.14 mg·L−1和0.07 mg·L−1,NH4+基本无检出,NO2−作为中间产物在极低浓度下呈现随DO值增加的趋势,也证明流域内硝化作用强烈,导致NO3−的浓度升高,污染面积大。
表 3 不同含水层氧化还原条件与不同形态氮含量关系(mg·L−1)Table 3. Relationship between redox conditions and nitrogen content in different aquifersDO NO−3 NO−2 NH+4 花岗岩和凝灰岩裂隙水 6.11 82.07 0.10 0 玄武岩裂隙孔洞水 6.77 107.8. 0.11 0.01 第四系孔隙水 7.58 115.25 0.32 0.19 3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)安固里淖内流河流域内地下水呈弱碱性,HCO3-Ca类型地下水主要分布在山前地带,由山前向流域下游过渡,阴离子类型由HCO3型向HCO3·SO4、HCO3·Cl、Cl·HCO3、Cl型过渡,水化学类型环带状展布。水质整体较差,TDS普遍较高,部分地点
NO−3 (2)
NO−3 NO−3 (3)安固里淖内陆河流域地下水资源短缺,农业等人类活动剧烈,含水层非均质性且处于氧化条件,研究区地下水环境问题日益严重,尤其
NO−3 NO−3 -
表 1 研究区地下水、泉水及地表水水化学参数统计(mg·L−1)
Table 1. Statistics of chemical parameters of groundwater, spring and surface water in the study area(mg·L−1)
pH Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ SO42− Cl− NO3− NO2− NH4+ TDS DO 地下水 最大值 8.59 1176.73 368.7 377.83 892.84 1367.56 786.45 11.53 6.00 4398.57 9.9 平均值 7.85 107.50 97.73 47.10 107.05 153.87 111.03 0.14 0.07 797.15 7.07 最小值 6.40 6.80 10.46 4.90 1.50 6.28 0.56 0 0 130.80 1.3 泉水 最大值 8.42 29.65 99.80 31.36 76.51 56.31 107.11 0.62 0.04 500.67 12.6 平均值 7.87 16.37 56.86 14.36 31.82 18.99 31.23 0.04 0 293.34 8.43 最小值 7.44 7.14 23.09 5.79 13.72 4.02 3.20 0 0 127.00 4.7 地表水 最大值 7.80 27.57 81.12 28.64 31.16 23.85 0.92 0.09 20.86 433.30 17.00 平均值 7.68 25.82 59.56 24.70 28.75 22.75 0.90 0.04 10.43 357.98 10.01 最小值 7.55 24.06 38.00 20.76 26.34 21.65 0.89 0 0 282.65 3.02 表 2 研究区地下水组分相关系数统计表
Table 2. Statistical table of correlation coefficient of groundwater components in the study area
井深Well depth 埋深Groundwater depth 第四系厚度Quaternary thickness 硝酸盐NO3− 氯化物Cl− 硫酸盐SO42− 溶解性总固体TDS 井深 1.000 埋深 0.468** 1.000 第四系厚度 0.465** 0.252** 1.000 硝酸盐 −0.259** −0.197* −0.170* 1.000 氯化物 −0.071 −0.068 −0.045 0.597** 1.000 硫酸盐 −0.180* −0.310** −0.129 0.514** 0.817** 1.000 溶解性总固体 −0.151 −0.173* −0.093 0.674** 0.953** 0.867** 1.000 注:**:在置信度(双测)为0.01时,相关性显著;*:在置信度(双测)为0.05时,相关性显著. Note:**: 0.01 level(bilateral) significantly correlated; *: 0.05 level(bilateral) significantly correlated. 表 3 不同含水层氧化还原条件与不同形态氮含量关系(mg·L−1)
Table 3. Relationship between redox conditions and nitrogen content in different aquifers
DO NO−3 NO−2 NH+4 花岗岩和凝灰岩裂隙水 6.11 82.07 0.10 0 玄武岩裂隙孔洞水 6.77 107.8. 0.11 0.01 第四系孔隙水 7.58 115.25 0.32 0.19 -
[1] 张兆吉, 费宇红, 郭春艳, 等. 华北平原区域地下水污染评价 [J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(5): 1456-1461. ZHANG Z J, FEI Y H, GUO C Y, et al. Regional groundwater contamination assessment in the North China Plain [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(5): 1456-1461(in Chinese).
[2] 张庆忠, 陈欣, 沈善敏. 农田土壤硝酸盐积累与淋失研究进展 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(2): 233-238. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.02.026 ZHANG Q Z, CHEN X, SHEN S M. Advances in studies on accumulation and leaching of nitrate in farming soil [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(2): 233-238(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.02.026
[3] JU X T, XING G X, CHEN X, et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(9): 3041-3046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813417106 [4] 蓝梅, 董萌, 吴宏举. 地下水硝酸盐氮污染原位修复研究进展 [J]. 工业水处理, 2015, 35(8): 15-17. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2015.35(8).015 LAN M, DONG M, WU H J. Research progress in-situ remediation technology of groundwater nitrate nitrogen pollution [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2015, 35(8): 15-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2015.35(8).015
[5] 茹淑华, 张国印, 孙世友, 等. 河北省地下水硝酸盐污染总体状况及时空变异规律 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2013, 30(5): 48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.05.011 RU S H, ZHANG G Y, SUN S Y, et al. Status of the contamination and spatial-temporal variations of nitrate in groundwater of Hebei Province, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2013, 30(5): 48-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.05.011
[6] 武海英. 张家口地区地下水氮污染分析及防治对策研究 [J]. 河北建筑工程学院学报, 2017, 35(2): 94-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4185.2017.02.022 WU H Y. Analysis of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Zhangjiakou area and its controlling counter measures [J]. Journal of Hebei Institute of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2017, 35(2): 94-97(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4185.2017.02.022
[7] 龚荧, 马雷, 杨章贤, 等. 不同固态碳源去除地下水硝酸盐的试验研究 [J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(6): 124-130. GONG Y, MA L, YANG Z X, et al. Experimental study on groundwater nitrate removal using different solid carbon sources [J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology, 2018, 41(6): 124-130(in Chinese).
[8] 吴海燕, 傅世锋, 蔡晓琼, 等. 东山岛地下水"三氮"空间分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(9): 3203-3211. WU H Y, FU S F, CAI X Q, et al. Spatial variation of ammonia-N, nitrate-N and nitrite-N in groundwater of Dongshan Island [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(9): 3203-3211(in Chinese).
[9] XING M, LIU W, WANG Z, et al. Relationship of nitrate isotopic character to population density in the Loess Plateau of Northwest China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013, 35: 110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.04.002 [10] LU L, CHENG H, PU X, et al. Nitrate behaviors and source apportionment in an aquatic system from a watershed with intensive agricultural activities [J]. Environmental Science: Processes Impacts, 2015, 17(1): 131-144. doi: 10.1039/C4EM00502C [11] CHEN F, CHEN J J. Nitrate Sources and watershed denitrification inferred from nitrate dual isotopes in the Beijiang River, South China [J]. Biogeochemistry, 2009, 94(2): 163-174. doi: 10.1007/s10533-009-9316-x [12] WEI Y N, FAN W, WANG W, et al. Identification of nitrate pollution sources of groundwater and analysis of potential pollution paths in loess regions: a case study in Tongchuan region, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(12): 423.1-423.13. [13] 李耕, 韩志伟, 申春华, 等. 典型岩溶小流域水体中硝酸盐分布特征及成因: 以普定后寨河流域为例 [J]. 地球科学, 2019(9): 2899-2908. LI G, HAN Z W, SHEN C H, et al. Distribution characteristics and causes of nitrate in waters of typical small Karst catchment: A case of the Houzhai River catchment [J]. Earth Science, 2019(9): 2899-2908(in Chinese).
[14] 申春华, 韩志伟, 郭永丽, 等. 典型岩溶地下河系统不同水体中硝酸盐时空分布规律及其影响因素分析 [J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(8): 1255-1264. SHEN C H, HAN Z W, GUO Y L, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and factors influencing nitrate level in waters of a typical karst underground river system [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(8): 1255-1264(in Chinese).
[15] LIU C Q, LI S L, LANG Y C, et al. Using δ15N and δ18O values to identify nitrate sources in Karst ground water, Guiyang, southwest China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(22): 6928-6933. [16] 张楠楠. 河北省环京津地区现代农业发展研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2018. ZHANG N N. Research on the development of modern agriculture in Hebei area around Beijing and Tianjin[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University (in Chinese).
[17] 林惠凤, 刘某承, 焦雯珺, 等. 转换灌溉方式对农户种植决策和经济的影响——以河北省张北县为例 [J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(8): 1293-1300. LIN H F, LIU M C, JIAO W J, et al. Effect of irrigation method on farmers’ planting decision and the economy: A case in Zhangbei County, Hebei Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(8): 1293-1300(in Chinese).
[18] 王强. 基于GIS的张家口坝上地区农业分区研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2008. WANG Q. Agricultural zoning study on Bashang areas in Zhangjiakou based on GIS[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University, 2008 (in Chinese).
[19] 鲁垠涛, 刘芳, 姚宏, 等. 北京密云水库小流域地下水硝酸盐污染来源示踪 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(1): 180-188. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.01.2015052501 LU Y T, LIU F, YAO H, et al. Source analysis of nitrate pollution source in groundwater in a small watershed of Miyun Reservoir in Beijing [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(1): 180-188(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.01.2015052501
[20] 梁秀娟, 肖长来, 盛洪勋, 等. 吉林市地下水中“三氮”迁移转化规律 [J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007, 37(2): 335-345. LIANG X J, XIAO C L, SHENG H X, et al. Migration and transformation of ammonia-nitrite-nitrates in groundwater in the city of Jilin [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2007, 37(2): 335-345(in Chinese).
[21] 於嘉闻, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 新疆喀什地区东部地下水“三氮”空间分布特征及影响因素 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(11): 2402-2410. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016040804 YU J W, ZHOU J L, ZENG Y Y, et al. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of “Three-Nitrogen” in groundwater of the eastern area of Kashgar, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(11): 2402-2410(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016040804
[22] 王贺, 谷洪彪, 迟宝明, 等. 柳江盆地浅层地下水硝酸盐分布特征及影响因素分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(5): 109-116. WANG H, GU H B, CHI B M, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of nitrate pollution in shallow groundwater of Liujiang Basin [J]. Environment Science, 2016, 37(5): 109-116(in Chinese).
[23] 吕晓立, 刘景涛, 朱亮, 等. 兰州市地下水中“三氮”污染特征及成因 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(1): 97-102. LV X L, LIU J T, ZHU L, et al. Distribution and source of nitrogen pollution in groundwater of Lanzhou city [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(1): 97-102(in Chinese).
[24] GILLHAM R W, CHERRY J A. Field evidence of denitrification in shallow groundwater flow systems [J]. Water Quality Research Journal, 1978, 13(1): 53-72. doi: 10.2166/wqrj.1978.006 [25] TRUDELL M R, GILLHAM R W, CHERRY J A. An in-situ study of the occurrence and rate of denitrification in a shallow unconfined sand aquifer [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1986, 83(3-4): 251-268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(86)90155-1 [26] 陈法锦, 李学辉, 贾国东. 氮氧同位素在河流硝酸盐研究中的应用 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2007, 22(12): 1251-1257. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.12.005 CHEN F J, LI X H, JIA G D. The application of nitrogen and oxygen isotopes in the study of nitrate in rivers [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(12): 1251-1257(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.12.005
-






 下载:
下载: