新型溴系阻燃剂环境污染现状研究进展
Current research progress on environmental pollution of novel brominated flame retardant
-
摘要: 新型溴系阻燃剂(NBFRs,novel brominated flame retardants)作为传统溴系阻燃剂的替代品已广泛应用于电子产品、纺织品、家具等商品中,随着这些商品的生产、使用和处置,NBFRs不可避免地释放到环境中,给环境和人体带来潜在的危害.部分NBFRs可通过摄食和呼吸作用进入人体对人体产生一定危害,已被证明具有潜在的生物毒性.而NBFRs的环境污染现状研究对控制NBFRs的污染具有重要意义.近年来有不少研究者对不同环境基质中的NBFRs进行了定量测定.基于这些研究成果,本文综述了近年来环境中NBFRs的研究现状、进展,重点介绍了水体、沉积物和大气中NBFRs的含量分布.多种类型水体中NBFRs的浓度水平在ng·L-1至μg·L-1之间,浓度受地区工业生产和季节等因素影响,且不同污水处理系统对水体中NBFRs的去除效率具有一定差异;NBFRs倾向于分布在富含有机碳的介质中,沉积物中NBFRs的含量在ng·g-1至μg·g-1级别,浓度与地区工业生产、化合物性质以及总有机碳含量等因素有关;大气中的NBFRs倾向吸附于颗粒相中,在两相中的含量分别为pg·m-3和ng·g-1级别,其含量受环境因素影响较为复杂.Abstract: Novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs), as substitutes for traditional brominated flame retardants, have been widely used in electronic products, textiles, and furniture. The emission of NBFRs into environment by the production, use and dispose of these products is inevitable, which may have adverse effects to the environment and human body. Several NBFRs have been proved to have potentially ecotoxicity and can cause adverse effect to human through ingestion and inhalation. The studies of environmental pollution caused by NBFRs have great significance in providing references for pollution control. The review attempted to summarize current research progress on environmental pollution of NBFRs. The occurrence of NBFRs in water, air, dust, soil, sediment and sludge were documented. Concentrations of NBFRs in water ranges from ng·L-1 to μg·L-1, which were influenced by regional industrial manufacture, season and other factors. Moreover, different wastewater treatment processes had different removal efficiency for NBFRs in wastewater. NBFRs tended to partition to medium with higher content of organic carbon and were detected in the range from ng·g-1 to μg·g-1 in sediment, dust and sewage sludge. The concentration was related to regional industrial manufacture, chemical properties of NBFRs and total organic carbon. NBFRs tended to be adsorbed in atmospheric particulate, and the concentrations in air and dust are pg·m-3 and ng·g-1, respectively, and the concentration levels were influenced by various factors.
-
微生物燃料电池(microbial fuel cell, MFC)是一种能同步处理废水与产电的绿色技术,其阳极微生物能够通过氧化废水中的有机物以产生电子和质子氢。电子通过直接/间接的方式传递至阳极表面并进一步通过外电路传输至阴极,质子氢通过质子交换膜传递到阴极,从而形成回路产生电流[1-2]。阳极材料在MFC运行中起到关键作用,主要影响微生物的生长与附着及电子传递[3]。
理想的阳极材料应具有良好的生物相容性、高比表面积、高电子转移速率、强稳定性、高孔隙率、低成本、易制备等特点[3-4]。传统的MFC阳极材料多以碳材料为基底,虽然碳材料具有良好的生物相容性,但其导电性差、电子转移速率低、强度低、易变形和价格昂贵等缺点限制了其产电性能和实际应用[5]。与传统碳材料(碳布、碳纸)相比,不锈钢纤维毡(stainless steel fiber felt, SSFF)具有高导电性、三维多孔固体结构、良好的耐腐蚀性和价格低廉等优势,是理想的基底材料[6-7]。GUO等[6]将热处理后的SSFF作生物电化学系统的阳极材料获得的电流密度是未热处理的7倍;HOU等[7-8]通过浸渍法、电聚合等方法分别制备了羧基石墨烯/SSFF、碳纳米管/SSFF、聚苯胺/SSFF和活性炭/SSFF阳极并应用在MFC阳极中,分别获得了650、620、580和451 mV的稳定输出电压。这表明SSFF具有作为MFC基材的潜力,但SSFF较差的生物相容性和高过电位限制了其在生物电化学系统中作为阳极的应用[9],因此需要对SSFF进行表面修饰以提高生物相容性和电子转移速率。
石墨烯作为一种新型碳纳米材料,具有高比表面积、高电导率和良好的生物相容性等特点,一直是材料改性研究的一大热点[10-11]。侯俊先[4]通过先浸渍后电化学还原的方法将还原氧化石墨烯(reduced graphene oxide, RGO)负载在SSFF上作为MFC阳极,获得了4.45 A·m−2的最大电流密度,是SSFF阳极-MFC的1.6倍。原诗瑶[12]通过水热反应法制备了RGO/MnO2/泡沫镍阳极并应用在MFC中,获得了643.9 mW·m−2的最大功率密度,是泡沫镍阳极-MFC的2.6倍。这表明SSFF和泡沫镍经RGO修饰后均能改善MFC的产电性能。二氧化钛(TiO2)作为一种半导体金属氧化物,由于良好的生物相容性、亲水性和无毒性,在锂电池和生物传感器等领域中得到广泛应用[13-14]。JIA等[13]制备了纳米TiO2/碳纸作为MFC阳极,获得了392 mW·m−2的最大功率密度,比未修饰的碳纸高50%。因此,对SSFF进行RGO和纳米TiO2修饰,有望在保留SSFF高导电性和耐腐蚀性的同时改善SSFF的生物相容性,将改性材料应用于MFC阳极中有望同步处理废水与高效产电。
本研究以SSFF为基底,以GO和纳米TiO2为原料制备改性材料RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF,以SSFF为对照,通过电化学测试和物理表征分析材料的电化学特性、物理结构和表观形貌,将SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF分别作为构建的MFC的阳极,对其产电性能和COD去除速率进行探究,旨在为后续MFC阳极改性研究提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 药品和材料
本实验所采用的主要药品和材料包括P25二氧化钛(AR,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司)、氧化石墨烯(AR,苏州碳丰科技有限公司)、抗坏血酸(AR,西陇科学股份有限公司)、无水乙醇(AR,西陇科学股份有限公司)和不锈钢纤维毡(316L,过滤精度≥100 μm,厚0.6 mm,迈鹏辰电子科技有限公司)。
1.2 材料的制备
1) 材料预处理。将SSFF裁剪为长3 cm、宽1.5 cm的方形片,先在丙酮中超声20 min,RO水冲洗;再放入无水乙醇中超声20 min,RO水冲洗;再放入1 mol·L−1的H2SO4 中浸泡 2 h,RO水冲洗;最后在RO水中超声20 min取出,60 °C烘箱中烘12 h,获得SSFF(对照组)。
2) RGO/SSFF的制备。分别配制3 g·L−1的氧化石墨烯(graphene oxide, GO)溶液和抗坏血酸(LAA)溶液,GO溶液超声至分散后,将LAA溶液倒入,将混合溶液超声20 min。再将SSFF放入混合溶液中,超声5 min。然后将SSFF转移到反应釜中,用移液枪吸取100 μL的混合溶液,均匀滴在SSFF表面,反应釜在100 °C烘箱反应2 h;待反应釜冷却至室温后,取出材料,RO水冲洗,60 °C烘箱中烘12 h,获得RGO/SSFF。
3) TiO2/RGO/SSFF的制备。称取0.05 g的纳米TiO2粉末,加入10 mL的无水乙醇,超声20 min,得到稳定的纳米TiO2-无水乙醇悬浊液。将制备好的RGO/SSFF标记为A、B两面,将A面朝上放入悬浊液,浸渍12 h后,80 °C 烘箱内干燥2 h。烘干后,在B面重复以上操作,最后将负载完成的材料放入350 °C马弗炉中,负载固定化2 h,自然冷却后取出,获得 TiO2/RGO/SSFF。
1.3 材料的电化学性能测试
利用电化学工作站(CHI660e,上海辰华仪器有限公司)的三电极体系(工作电极(SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF)、对电极(铂片电极)和参比电极(R232饱和甘汞电极)),对SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF进行循环伏安(CV)曲线、塔菲尔(Tafel)曲线和电化学阻抗谱(EIS)测试。测试时使用250 mL密封电解槽,电解液为5 mmol·L−1铁氰化钾溶液,CV 测试扫描范围为0.7~1.1 V,扫描速度为 25 mV·s−1。EIS测试频率为 0.1~1 000 kHz。Tafel 测试的扫描电压为0.72~1.65 V,扫描速度为10 mV·s−1。电容(Q)和交换电流(i0) 的计算方法参见本课题组已有的研究[15]。
1.4 材料的物理表征
采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,捷克TESCAN MIRA LMS)、全自动比表面及孔隙度分析仪(BET,美国Micromeritics ASAP)、原位红外分析仪(FTIR,美国Frontier)、X射线衍射仪(XRD,日本Rigaku SmartLab SE)、X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,美国Thermo Scientific K-Alpha)分别对材料的形貌、比表面积、官能团、晶体结构、分子结构和元素价态等方面进行表征。由于块状样品在FT-IR、XRD测试中不易出峰,因此使用刀片刮取样品表面粉末后再进行测试。
1.5 微生物燃料电池(MFC)的应用
本实验采用双室MFC,由2个四方形有机玻璃及2个挡板组成,中间用质子交换膜(杜邦N117,苏州晟尔科技有限公司)隔开。单室内部均为直径5.5 cm、深5 cm的圆柱形室,有效容积约为118 mL。阴极材料(长4 cm,宽2 cm,厚0.5 cm)采用碳毡。以SSFF、RGO/SSFF、TiO2/RGO/SSFF作为阳极材料(长1.5 cm,宽1 cm,厚0.12 cm)的MFC装置分别命名为MFC-CK、MFC-RG和MFC-TRG。用钛丝连接阴阳电极和外电路,外电路接1 000 Ω的电阻。阳极室厌氧污泥采自桂林市秀峰区漓泉啤酒厂厌氧池。每个反应器阳极添加20 mL的厌氧污泥和90 mL的营养液,阴极添加90 mL 50 mmol·L−1 磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS),阴极曝气。3组MFC同时运行,每2 d更换一次阳极液。1 L阳极营养液的基本成分为2.56 g乙酸钠、50 mmol·L−1 PBS和1 mL微量营养液。微量营养液的配制参见LIU等研究中的方法[16]。
1.6 出水COD的测定及电压数据采集
每周期结束时,在取样口取5 mL水样 (取3次)用于测定出水COD,测定方法为重铬酸钾微波消解法。
用电脑连通 LabQuest mini 主机并连接电压传感器 DVP-BTA(威尼尔软件与技术公司,美国),每5 min记录一次外接电阻两端的电压。在第4周期结束后,断开外接电阻,监测开路电压。当开路电压达到最大值时,接入可调节电阻箱(23023型简式电阻箱,中秦教学设备有限公司,中国),采用万用表(VC990C+,深圳胜利仪器仪表有限公司,中国)由高到低测定不同外电阻(200~9 999 Ω)下的阴、阳极电势及输出电压,电压稳定时间为30 min。根据输出电压和阳极表面积(1.5 cm2)计算功率密度并绘制功率密度曲线[15]。
2. 结果和讨论
2.1 材料的电化学性能表征
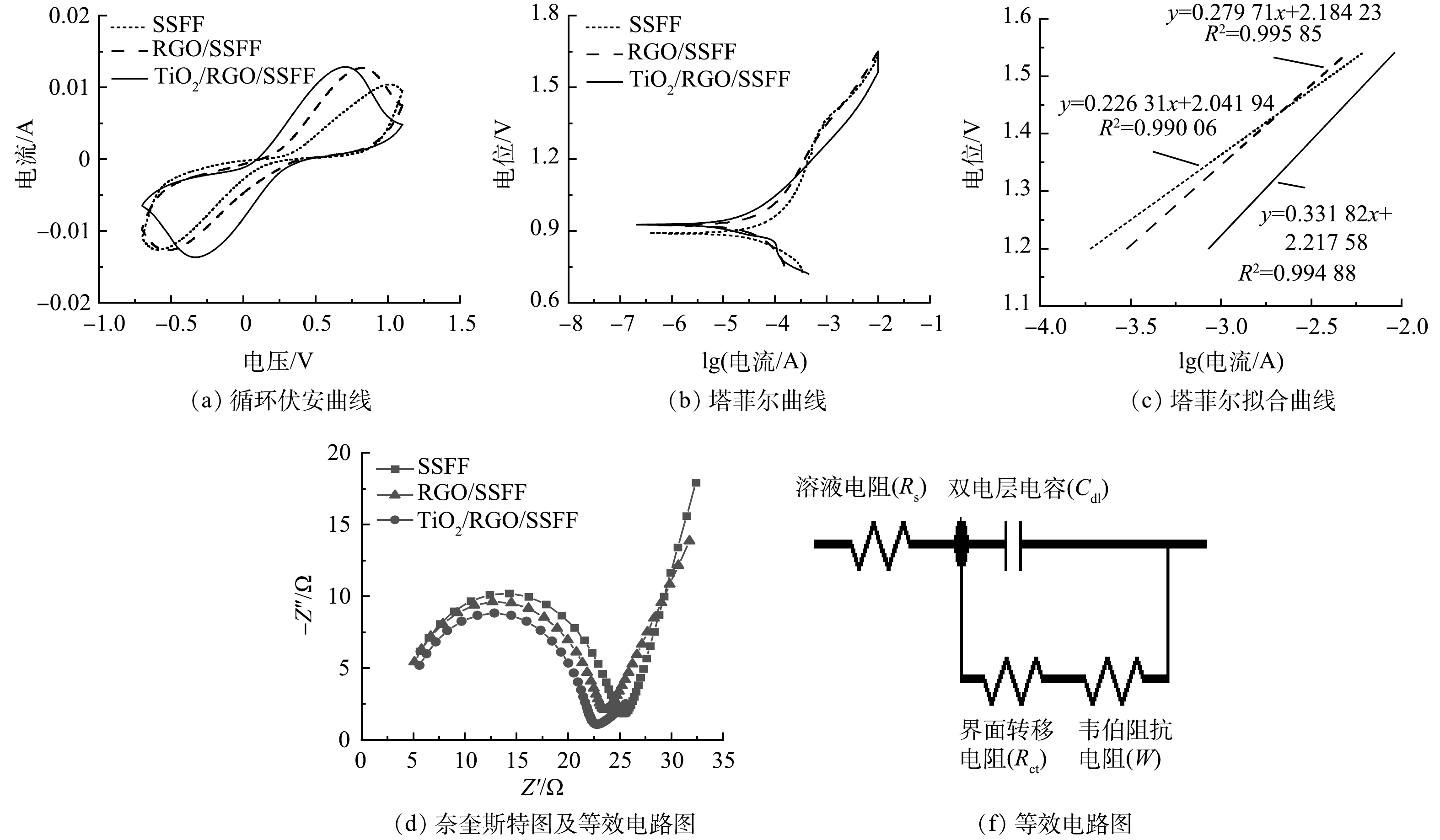
通过电化学测试探究材料改性前后的电化学性能。由循环伏安曲线(图1(a))可计算出SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的电容,分别为326.8、413.9和446.9 mF,由此可以看出,SSFF经修饰后电容增大[17]。此外,3种材料的循环伏安曲线都出现了明显的氧化和还原峰,SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的氧化峰电流分别为10.42、12.72和12.85 mA,其氧化电流/还原电流之比(x)分别为1.21、1.004和1.06。x越趋近于1,电极反应的可逆性就越高[15]。3种材料氧化峰和还原峰的峰电位差(ΔE)分别为1.597 V(SSFF)、1.342 V(RGO/SSFF) 和1.038 V(TiO2/RGO/SSFF)。ΔE越小,材料转移的电子数量越多[18],表明RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF具有更强的电子转移能力。这可能得益于RGO良好的导电性和纳米TiO2优异的电催化性能[10, 13]。
3种材料的塔菲尔曲线及线性拟合曲线(拟合区间为1.2~1.55 V)如图1(b)和图1(c)所示。根据拟合曲线公式计算出TiO2/RGO/SSFF和RGO/SSFF的交换电流(i0),分别是SSFF(i0=9.49×10−7 mA)的218.4倍和16.4倍,表明TiO2/RGO/SSFF和RGO/SSFF具有更快的氧化还原速率。该结果进一步证实了修饰在SSFF上的RGO和纳米TiO2均可提高SSFF的电子转移速率[19]。
图1(d)和图1(f)为3种材料经Zview2软件拟合得到的奈奎斯特图及拟合所用等效电路图。等效电路图由溶液电阻(Rs)、界面转移电阻(Rct)、双电层电容(Cdl)和韦伯阻抗电阻(W)构成[20]。SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的Rct分别为21.45、19.65和18.16 Ω。界面转移电阻越小,材料电子转移能力越强,表明GO和纳米TiO2 对SSFF的修饰使其电子转移能力得到增强 [10, 14]。RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的W分别为3.116 和4.746 Ω,均小于SSFF(W=6.01 Ω)。W越小越有利于电子传递,离子向电极界面的扩散能力越强 [15]。此外,SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的Cdl分别为2.31×10−5、2.67×10−5和2.78×10−5 mF。SSFF经修饰后双电层电容增大,表明RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF上电荷储存和释放过程比SSFF更易进行,这可归因于RGO的负载[21]。
2.2 材料的物理表征
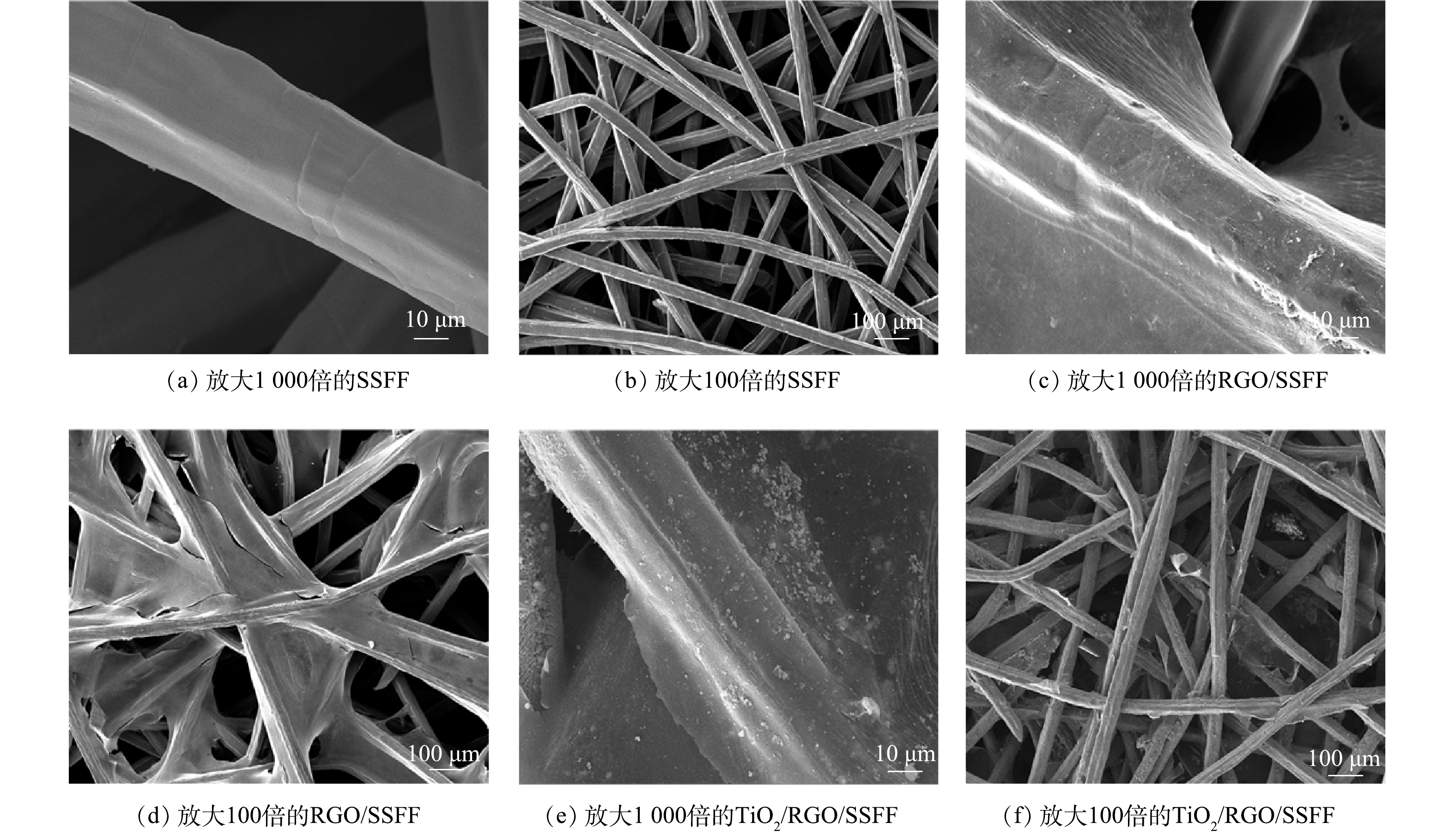
SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的SEM图如图2所示。可以看出:SSFF表面光滑,具有立体的三维结构(图2 (a)和图2 (b));RGO薄膜成功包覆在SSFF的骨架上形成RGO/SSFF(图2 (c)和图2 (d)) ;纳米TiO2成功负载在RGO/SSFF上,形成TiO2/RGO/SSFF(图2 (e)和图2 (f))。
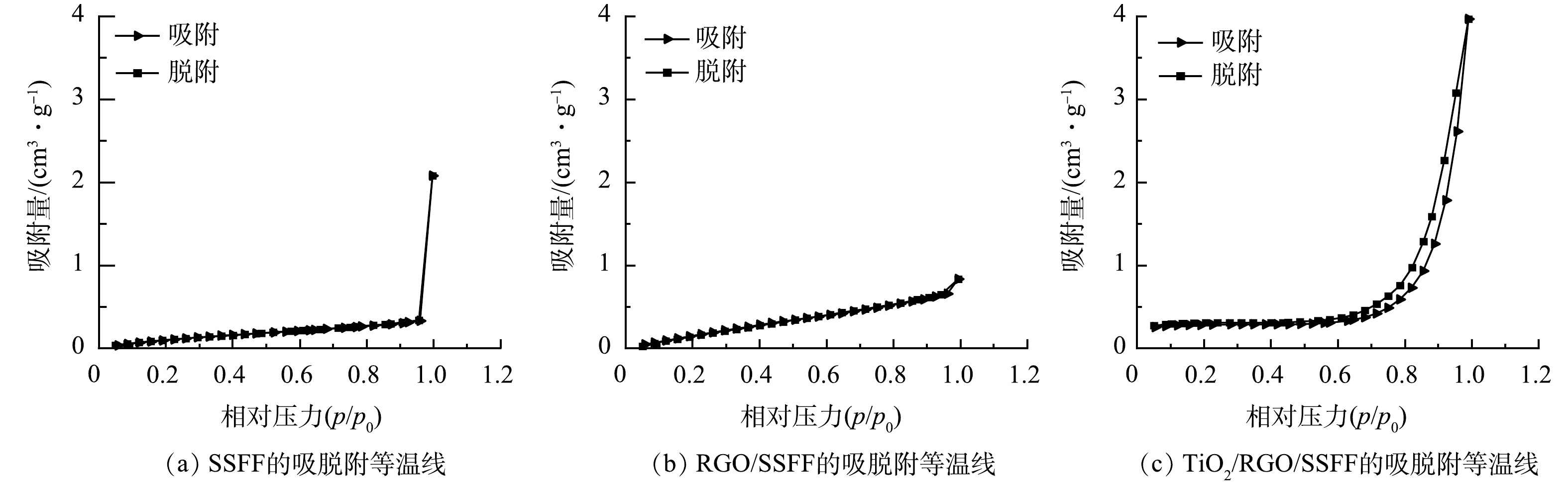
SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的等温吸脱附曲线和BET测试结果见图3和表1。SSFF的等温线类型确定为Type-Ⅲ型(图3(a)),是典型的固体材料吸脱附曲线[22]。RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的等温线类型均为Type-Ⅳ型(图3(b)和图3 (c))。TiO2/RGO/SSFF的等温线在0.5~1.0相对压力区间内,有更明显的H3型回滞环,为介孔结构,这一现象可归因于纳米TiO2的负载[23]。 RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的比表面积分别是SSFF(0.57 m²·g−1)的2倍和1.58倍,吸附平均孔径分别是SSFF(5.63 nm)的 1.39倍和4.19倍。
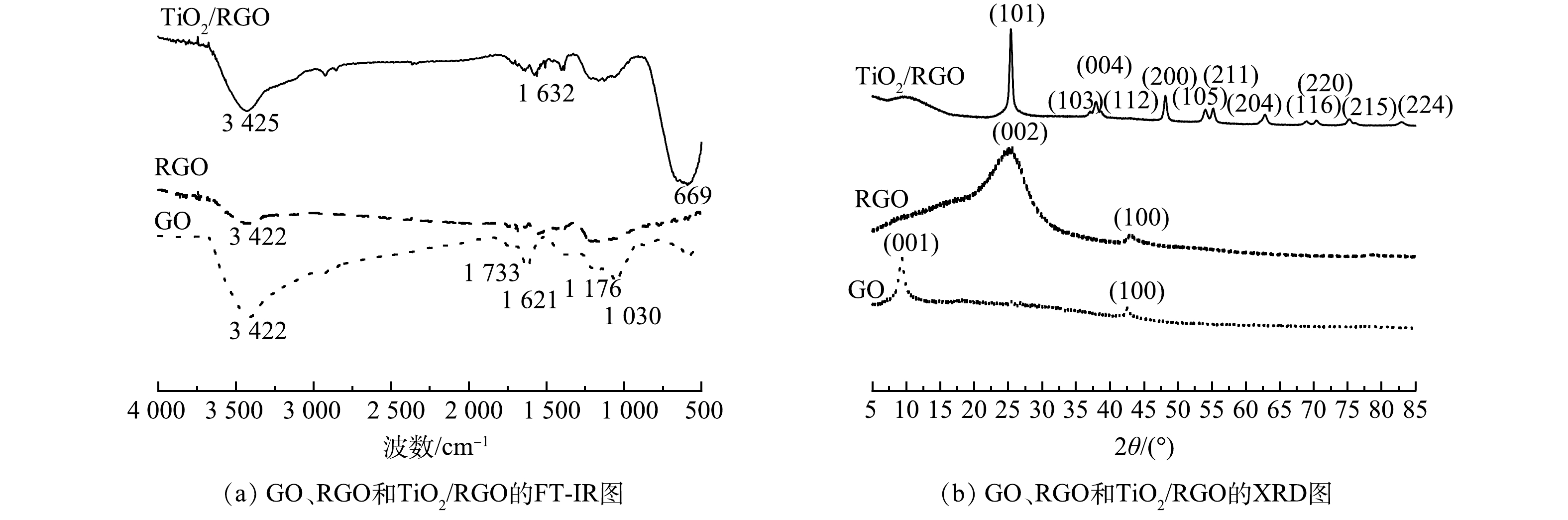
表 1 SSFF、RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的BET测试结果Table 1. BET measurement results of SSFF, RGO/SSFF and TiO2/RGO/SSFF材料 BET比表面积/ (m²·g−1) BJH吸附平均孔径/nm SSFF 0.57 5.63 RGO/SSFF 1.14 7.82 TiO2/RGO/SSFF 0.90 23.58 图4(a)为GO、RGO和TiO2/RGO的红外光谱图。在GO的图谱中,在3 422 cm−1处出现了O—H的伸缩振动峰,这可归因于GO中的结合水[24-25];在1 621 cm−1处为C=C的骨架振动峰,1 733 cm−1处为C=O的伸缩振动峰,1 176 cm−1和1 030 cm−1处分别为C—O的弯曲振动峰和伸缩振动峰[23, 26]。与GO相比,在RGO图谱中,3 422、1 621、1 176和1 030 cm−1处出现的含氧官能团的峰,强度都大幅度减小甚至消失,表明GO成功被还原并负载在SSFF上[23-24]。在TiO2/RGO图谱中,在1 632 cm−1处出现了C=C的骨架振动峰,在669 cm−1 处出现了TiO2的特征峰,表明TiO2和RGO在SSFF上成功负载[27],这与SEM结果一致。
图4(b)为GO、RGO和TiO2/RGO的XRD图。在GO的图谱中,2θ为9.38°和42.82°处分别出现一强一弱的衍射峰,分别对应GO的(001)和(100)晶面[28]。这主要是因为GO中含有大量的含氧基团 [26, 28]。在RGO的图谱中,2θ为25.34°和42.82°时出现的特征峰分别对应RGO的(002)和(100)晶面[29]。与GO图谱相比,2θ为9.38°的强衍射峰消失,在25.34 °出现了一个新的较宽的衍射峰,表明GO成功被还原,由于石墨烯片层较小且形状无规则,所以形成较宽的衍射峰[19, 30];在TiO2/RGO的图谱中,TiO2(锐钛矿)晶面所对应的2θ角分别为25.4°(101)、37.06°(103)、37.9°(004)、38.7°(112)、48.18°(200)、54.06°(105)、55.22°(211)、62.86°(204)、68.96°(116)、70.34°(220)、75.3°(215)和82.74°(224),表明纳米TiO2成功负载在材料上。然而,RGO的衍射峰未在TiO2/RGO中显现,这是因为TiO2的负载使RGO的衍射峰峰趋于平缓,这与CAO等[31]的测试结果相一致。
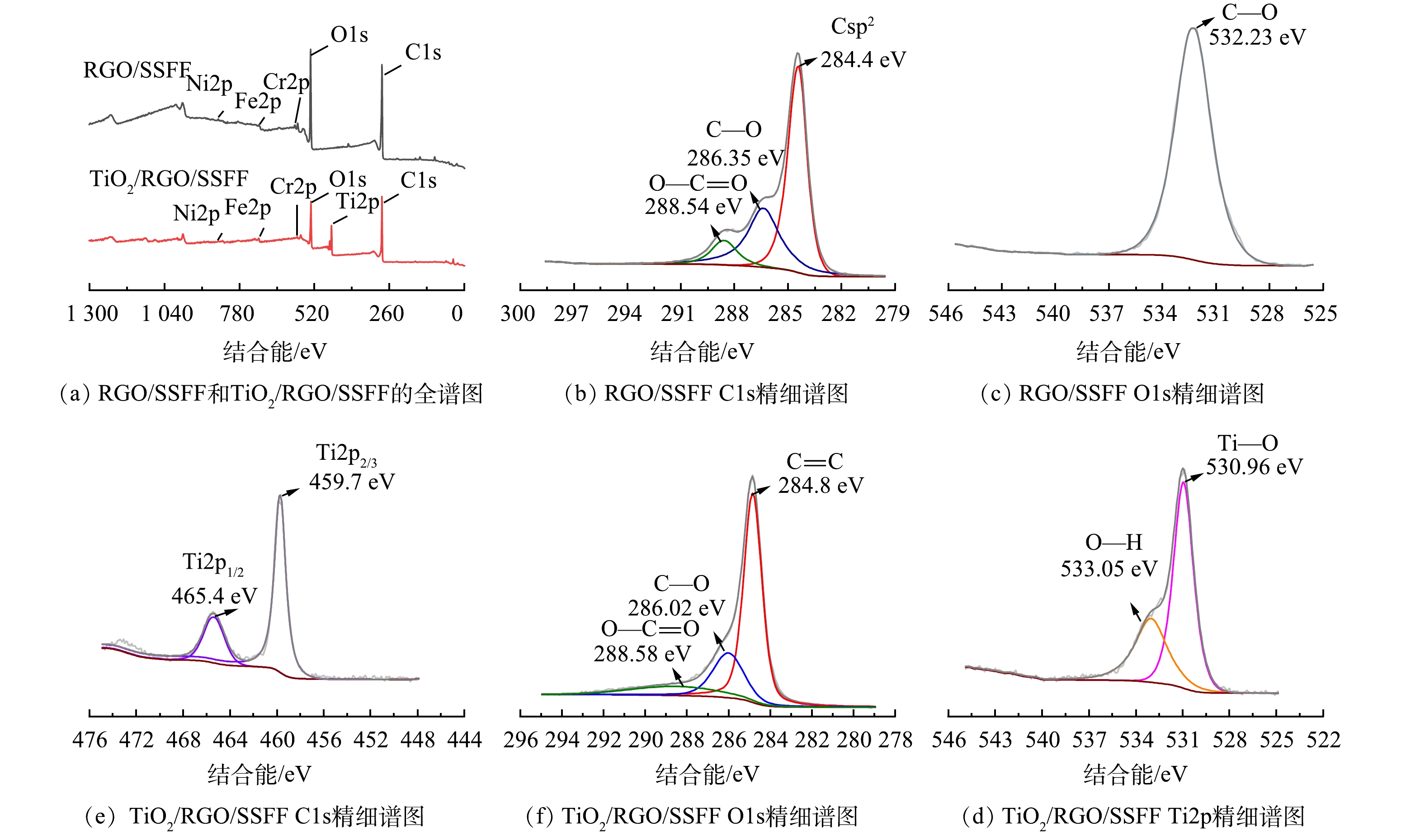
RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的XPS结果如图5所示。由图5(a)可以看出,RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF主要由C、O、Fe、Cr、Ni、Ti 6种元素组成,Fe、Cr、Ni是基底SSFF所具有的金属元素[32]。图5(b)中284.4、286.35和288.54 eV处出现的峰分别对应RGO的Csp2、C—O和O—C=O键[33];图5(c)中532.23 eV处出现的峰对应C—O键,与C1s峰测量结果相对应[22],表明RGO成功负载至SSFF上;图5(e)中284.8、286.02和288.58 eV处出现的峰分别对应RGO的C—C、C—O和O—C=O键[34];图5(f)中530.96 eV和533.05 eV处出现的峰分别对应Ti—O键和O—H键[24];图5(d)中465.4 eV和459.7 eV处出现的峰分别对应Ti2p1/2和Ti2p3/2,表明Ti4+的存在[35-36]。这些结果表明RGO和纳米TiO2均成功负载至SSFF。
2.3 不同阳极MFC的COD去除速率及产电性能分析
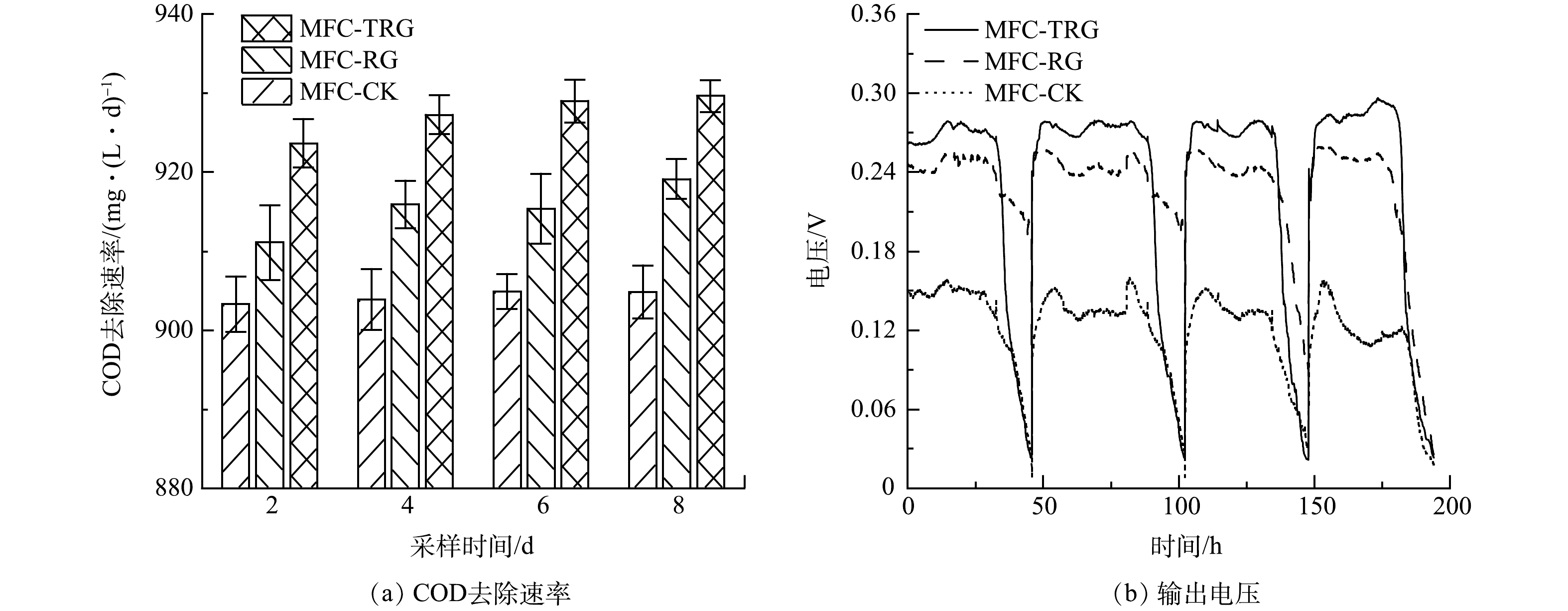
不同阳极MFC的COD去速效率和稳定输出电压如图6(a)和图6(b)所示。MFC-TRG、MFC-RG和MFC-CK的 COD去除速率分别为929.62、919.12和904.80 mg·(L·d)−1,COD去除率均在90%以上。周期初始时阳极营养物质充足,电压快速稳定,直到底物耗尽,电压快速下降(图6(b))。这一运行规律与其他研究[21, 37] 一致。与其他研究(表2)相比,本研究具有更高的COD去除速率。MFC-TRG的稳定输出电压为280 mV,分别比MFC-RG(245 mV)和MFC-CK(130 mV)高14.3%和115.4%。这可能是因为修饰的RGO 改善了SSFF的生物相容性,从而促使微生物更好地附着生长[38-39],同时纳米TiO2进一步促进了微生物/电极界面的电子转移[30]。
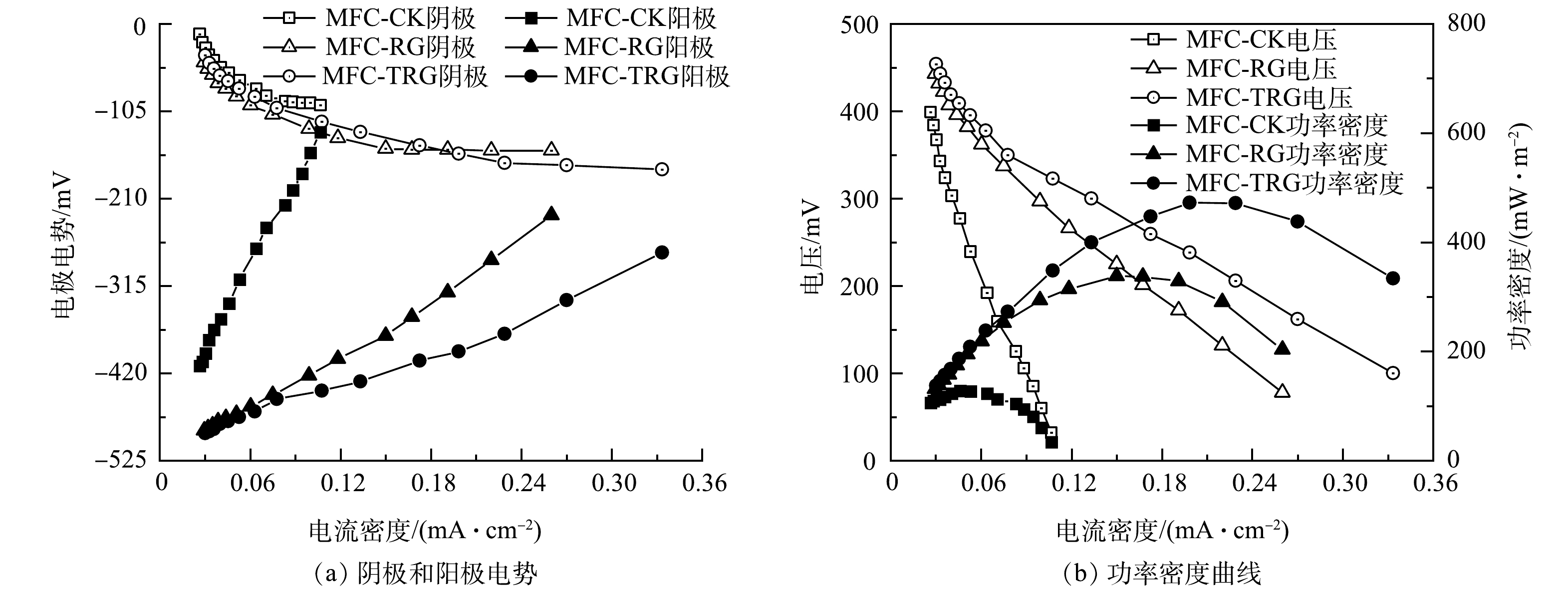
表 2 与其他已报道 MFCs 在COD去除速率及产电性能上的比较Table 2. Comparison of COD removal rate and electricity generation performance with other reported MFCs阳极材料 碳源基质 质量浓度/(g·L−1) COD去除速率/(g·(L·d)−1) 输出电压/mV 最大功率密度/(mW·m−2) 来源 TiO2/RGO/SSFF 乙酸钠 2 0.93 280 472 本研究 RGO/SSFF 乙酸钠 2 0.91 245 337.5 本研究 SSFF 乙酸钠 2 0.9 130 127.9 本研究 RGO/碳纸 葡萄糖 1 ≤0.53 580 368 [41] RGO/碳布 葡萄糖 5 0.363 — 52.5 [42] RGO/石墨块 乳酸钠 0.43 ≤0.29 150 102 [43] GO/沸石/碳毡 乙酸钠 3 ≤1 560 280.56 [44] 聚苯胺/SSFF 乙酸钠 0.78 ≤0.39 451 360 [7] TiO2/碳纸 碳酸氢钠 2.5 ≤1.47 — 392 [13] GO气凝胶/不锈钢刷 乳酸钠 0.67 ≤0.22 500 490 [37] RGO气凝胶/钛网 乙酸钠 0.78 ≤0.39 490 583 [45] 碳纳米管/SSFF 乙酸钠 0.78 ≤0.26 620 1280 [4] RGO/SSFF 乙酸钠 0.64 ≤0.32 — 2393 [4] MFC的阴阳极电势和功率密度曲线如图7(a)和图7(b)所示。可以看出,当电流密度从0 mA·cm−2增大到0.1 mA·cm−2时,MFC-CK、MFC-RG和MFC-TRG的阳极电势分别提高了62.23%、13.50%和10.36%。MFC-TRG的阳极电势变化幅度更小,表明其具有更好的阳极性能和更稳定的生物膜[37]。在相同电流密度范围内,MFC-TRG的电压降幅明显小于MFC-RG和MFC-CK(图7(b)),电压的降低主要受欧姆极化和传质损耗影响。欧姆损耗主要受阳极的内阻影响,传质损耗主要归因于还原化合物向电极供应氧化化合物有限或有限放电能力[15, 40]。该结果表明MFC-TRG具有更小的内阻。MFC-TRG最大功率密度为472.03 mW·cm−2 ,是MFC-RG和MFC-CK的1.4倍和3.7倍。本研究所获得的最大功率密度优于表2中的部分研究[7, 13, 41-44]。与GUO等[41]报道的RGO/碳纸阳极-MFC相比,本研究中MFC-TRG获得的功率密度是其功率密度(368 mW·cm−2)的1.28倍。同时,本研究与侯俊先[4]报道的恒电位法制备的RGO/SSFF阳极-MFC(2393 mW·m−2)相比,尚存一定的差距。这可能是其阳极接种微生物经过1 a的驯化或采用铁氰化钾作为阴极液导致的。
3. 结论
1) 电化学性能测试结果表明,与SSFF相比,修饰后的RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF具有更大的电容、更强的电子转移能力、更低的界面转移电阻和更高的交换电流密度。
2) SEM、FT-IR、XRD和XPS分析结果证实了RGO和纳米TiO2成功负载于SSFF基底材料上。RGO/SSFF和TiO2/RGO/SSFF的BET比表面积分别是SSFF的2倍和1.58倍。
3) 与MFC-RG和MFC-CK相比,MFC-TRG具有更高的 COD去除速率(929.62 mg·(L·d)−1)和输出电压(280 mV)。MFC-TRG和MFC-RG的输出功率密度分别为472.03 mW·m−2和337.50 mW·m−2,均高于MFC-CK。
-
[1] TOMS L M L,HEARN L, KENNEDY K, et al. Concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in matched samples of human milk, dust and indoor air[J]. Environment International, 2009, 35(6):864-869. [2] LAM J C W, LAM P K S. Occurrence and ecological risk of halogenated flame retardants (HFRs) in coastal zones[J]. Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 67:389-409. [3] 苏冠勇. 多溴联苯醚及其衍生物的环境调查、致毒机制及其基于芳烃受体活性的健康风险评估研究[D]. 南京:南京大学, 2013. SU G Y. Environmental investigation and toxicological mechanism of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and their derivatives and health risk assessment based on aromatic receptor activity[D]. Nangjing:Nanjing University, 2013(in Chinese). [4] UNEP. SC-4/14:Listing of hexabromodiphenyl ether and heptabromodiphenyl ether[R]. Stockholm Convention Organic on Persistent Pollutants:Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee Fourth meeting, 2009. [5] UNEP. SC-4/18:Listing of tetrabromodiphenyl ether and pentabromodiphenyl ether[R]. Stockholm Convention Organic on Persistent Pollutants:Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee Fourth meeting, 2009. [6] UNEP. SC-8/10:Listing of decabromodiphenyl ether (commercial mixture, c-decaBDE)[R]. Stockholm Convention Organic on Persistent Pollutants:Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee Eighth meeting, 2017. [7] UNEP. SC-6/13:Listing of hexabromocyclododecane[R]. Stockholm Convention Organic on Persistent Pollutants:Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee Sixth meeting, 2013. [8] COVACI A, HARRAD S, ABDALLAH A E, et al. Novel brominated flame retardants:A review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour[J]. Environment International, 2011, 37(2):532-556. [9] MCGRATH T J, MORRISON P D, BALL A S, et al. Detection of novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) in the urban soils of Melbourne, Australia[J]. Emerging Contaminants, 2017, 3(1):23-31. [10] YU G, BU Q, CAO Z, et al. Brominated flame retardants (BFRs):A review on environmental contamination in China[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 150:479-490. [11] 李英明, 王亚群, 江桂斌. 新型持久性有机污染物PBDEs概述[J]. 实验与分析, 2008(1):38-39. LI Y M, WANG Y Q, JIANG G B. Overview of new persistent organic pollutant PBDEs[J]. Experiment and Analysis, 2008 (1):38-39(in Chinese).
[12] 陈田, 余旸帆, 白易, 等. 十溴二苯乙烷污染水平及毒性研究进展[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2018, 52(8):855-861. CHEN T, YU Y F, BAI Y, et al. Decabromodiphenyl ethane:A review of its pollution levels and toxicity[J]. China Jounal Prevent Method, 2018, 52(8):855-861(in Chinese).
[13] CANADA GAZETTE. Order adding toxic substances to schedule 1 to the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999[EB/OL].[2019-6-29]. http://www.gazette.gc.ca/rp-pr/p1/2019/2019-06-29/html/reg2-eng.html#reg [14] ZHANG X, LI J, CHEN M J, et al. Toxicity of the brominated flame retardant tris-(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate in zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(15):1548-1555. [15] EZECHIÁŠ M, SVOBODOVÁ K, CAJTHAML T. Hormonal activities of new brominated flame retardants[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 87(7):820-824. [16] XIONG P, YAN X T, ZHU Q Q, et al. A review of environmental occurrence, fate, and toxicity of novel brominated flame retardants[J]. Environment Science & Technology, 2019, 53(23):13551-13569. [17] POLO M, LLOMPART M, GARCIA-JARES C, et al. Development of a solid-phase microextraction method for the analysis of phenolic flame retardants in water samples[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2006, 1124(1/2):11-21. [18] NIU D, QIU Y, DU X, et al. Novel brominated flame retardants in house dust from Shanghai, China:Levels, temporal variation, and human exposure[J]. Environmental Sciences Europe, 2019, 31(1):6. [19] PRADHAN A, ASNAKE S, KHARLYNGDOH J B, et al. In silico and biological analysis of anti-androgen activity of the brominated flame retardants ATE, BATE and DPTE in zebrafish[J]. Chemico Biological Interactions, 2015, 233:35-45. [20] KHALAF H, LARSSON A, BERG H, et al. Diastereomers of the brominated flame retardant 1,2-dibromo-4-(1,2 dibromoethyl)cyclohexane induce androgen receptor activation in the HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line and the LNCaP prostate cancer cell line[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2009, 117(12):1853-1859. [21] LARSSON A, ERIKSSON L A, ANDERSSON P L, et al. Identification of the brominated flame retardant 1,2-dibromo-4-(1,2-dibromoethyl)cyclohexane as an androgen agonist[J]. J Med Chem, 2006, 49(25):7366-7372. [22] GANCI A P, VANE C H, ABDALLAH A E, et al. Legacy PBDEs and NBFRs in sediments of the tidal River Thames using liquid chromatography coupled to a high resolution accurate mass Orbitrap mass spectrometer[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658:1355-1366. [23] PAPACHLIMITZOU A, BARBER J L, LOSADA S, et al. A review of the analysis of novel brominated flame retardants[J]. J. Chromatogr A, 2012, 1219:15-28. [24] LÓPEZ P, BRANDSMA S A, LEONARDS P E G, et al. Methods for the determination of phenolic brominated flame retardants, and by-products, formulation intermediates and decomposition products of brominated flame retardants in water[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2009, 1216(3):334-345. [25] ZHOU S N, REINER E J, MARVIN C, et al. Development of liquid chromatography atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of halogenated flame retardants in wastewater[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2010, 396(3):1311-1320. [26] LAW K, HALLDORSON T, DANELL R, et al. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of some brominated flame retardants in a Lake Winnipeg (Canada) food web[J]. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 2006, 25(8):2177-2186. [27] XIE Z, MÖLLER A, AHRENS L, et al. Brominated flame retardants and Dechlorane Plus in air and sea water of the Atlantic Ocean and the Antarctic[C]//Proceedings of the BFR2010 Conference, Kyoto, Japan, 2010. [28] HE M J, LUO X J, CHEN M Y, et al. Bioaccumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and decabromodiphenyl ethane in fish from a river system in a highly industrialized area, South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012,419:109-115. [29] WANG Y, WU X, ZHAO H, et al. Characterization of PBDEs and novel brominated flame retardants in seawater near a coastal mariculture area of the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 580:1446-1452. [30] HOU L, JIANG J, GAN Z, et al. Spatial distribution of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in surface water, sediment, groundwater, and wild Fish in Chengdu, China[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 2019, 77(2):279-290 [31] MÖLLER A, XIE Z,BUSCH J,et al. Non-PBDE brominated flame retardants and Dechlorane Plus in air and seawater of the Arctic[C]//Proceedings of the BFR2010 Conference, Kyoto, Japan, 2010. [32] RUAN T, WANG Y W, WANG C, et al. Identification and evaluation of a eovel heterocyclic brominated flame retardant tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) isocyanurate in environmental matrices near a manufacturing plant in southern China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(9):3080-3086. [33] KHAN M U, LI J, ZHANG G, et al. First insight into the levels and distribution of flame retardants in potable water in Pakistan:An underestimated problem with an associated health risk diagnosis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 565:346-359. [34] LI B, WANG K L, MA X, et al. Deca-BDE and alternative halogenated flame retardants in a wastewater treatment plant in Harbin (2009-2016):Occurrence, temporal trends, seasonal variation, and fate[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 625:1156-1163. [35] RUAN Y, ZHANG K, LAM J C W, et al. Stereoisomer-specific occurrence, distribution, and fate of chiral brominated flame retardants in different wastewater treatment systems in Hong Kong[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 374:211-218. [36] FENG H, RUAN Y, WU R, et al. Occurrence of disinfection by-products in sewage treatment plants and the marine environment in Hong Kong[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 181:404-411. [37] KIM M, GUERRA P, ALAEE M, et al. Occurrence and fate of four novel brominated flame retardants in wastewater treatment plants[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2014, 21(23):13394-13404. [38] MAN Y B, CHOW K L, MAN M, et al. Profiles and removal efficiency of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by two different types of sewage treatment work in Hong Kong[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 505:261-268. [39] SHANMUGANATHAN M, ZHANG Z, SVERKO E, et al. Analysis of halogenated flame retardants in Canadian wastewater treatment plants using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS)[J]. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 2018, 53(4):167-180. [40] QIU X, MARVIN C H, HITES R A. Dechlorane plus and other flame retardants in a sediment core from lake Ontario[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(17):6014-6019. [41] HOH E, ZHU L, HITES R A. Novel flame retardants, 1,2-bis(2,4,6-tribromophenoxy)ethane and 2,3,4,5,6-pentabromoethylbenzene, in United States' environmental samples[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(8):2472-2477. [42] SHI T, CHEN S J, LUO X J, et al. Occurrence of brominated flame retardants other than polybrominated diphenyl ethers in environmental and biota samples from southern China[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 74(7):910-916. [43] KÖPPEN R, BECKER R, JUNG C, et al. Investigation of extraction procedures and HPLC-DAD/MS for the determination of the brominated flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol A bis(2,3-dibromopropylether) in environmental samples[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2006, 384(7/8):1485-1492. [44] KIERKEGAARD A, BJÖRKLUND J, FRIDÉN U. Identification of the flame retardant decabromodiphenyl ethane in the environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(12):3247-3253. [45] SUTTON R, CHEN D, SUN J, et al. Characterization of brominated, chlorinated, and phosphate flame retardants in San Francisco Bay, an urban estuary.[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 652:212-223. [46] ZHANG X L, LUO X J, CHEN S J, et al. Spatial distribution and vertical profile of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, tetrabromobisphenol A, and decabromodiphenylethane in river sediment from an industrialized region of South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(6):1917-1923. [47] ILYAS M, SUDARYANTO A, SETIAWAN I E, et al. Characterization of polychlorinated biphenyls and brominated flame retardants in surface soils from Surabaya, Indonesia[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 83(6):783-791. [48] MCGRATH T J, BALL A S, CLARKE B O. Critical review of soil contamination by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs); concentrations, sources and congener profiles[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 230:741-757. [49] WANG S, WANG Y, SONG M, et al. Distributions and compositions of old and emerging flame retardants in the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil in an e-waste contaminated area of South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 208:619-625. [50] RICKLUND N, KIERKEGAARD A, MCLACHLAN M S, et al. Mass balance of decabromodiphenyl ethane and decabromodiphenyl ether in a WWTP[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 74(3):389-394. [51] GORGA M, MARTINEZ E, GINEBREDA A, et al. Determination of PBDEs, HBB, PBEB, DBDPE, HBCD, TBBPA and related compounds in sewage sludge from Catalonia (Spain)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 444:51-59. [52] MATTSSON P E, NORSTRÖM Å, RAPPE C. Identification of the flame retardant pentabromotoluene in sewage sludge.[J]. J Chromatogr, 1975, 111:209-213. [53] WEISSER M. Investigations on the contamination of municipal sewage sludges with organic pollutants[C]//Universität Karlsruhe (Schriftenreihe ISWW, 63); 1992. [54] KLOSTERHAUS S, KONSTANTINOV A, STAPLETON H. Characterization of the brominated chemicals in a PentaBDE replacement mixture and their detection in biosolids collected from two San Francisco Bay area wastewater treatment plants[R]. Northern California Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. [55] OBERG K, WARMAN K, OBERG T. Distribution and levels of brominated flame retardants in sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2002, 48(8):805-809. [56] 张宏莉,仇雁翎, 葛元新, 等. 中国大气环境中溴代阻燃剂污染特征研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(3):192-199. ZHANG H L, QIU Y L, GE Y X, el a1. Study progress on pollution characteristics of brominated flame retardants BFRs in China atmospheric environment[J]. Environmental Science &Technology, 2016, 39(3):192-199(in Chinese).
[57] SJÖDIN A, CARLSSON H, THURESSON K, et al. Flame retardants in indoor air at an electronics recycling plant and at other work environments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(3):448-454. [58] STAPLETON H M, ALLEN J G, KELLY S M, et al. Alternate and new brominated flame retardants detected in U.S. house dust[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2008, 42(18):6910-6916. [59] ZHU J, HOU Y, FENG Y L, et al. Identification and determination of hexachlorocyclopentadienyl- dibromocyclooctane (HCDBCO) in residential indoor air and dust:A previously unreported halogenated flame retardant in the environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(2):386-391. [60] SUN J, XU Y, ZHOU H, et al. Levels, occurrence and human exposure to novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) and dechlorane plus (DP) in dust from different indoor environments in Hangzhou, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 631/632:1212-1220. [61] SAITO I, ONUKI A, SETO H. Indoor organophosphate and polybrominated flame retardants in Tokyo[J]. Indoor Air, 2007, 17(1):28-36. [62] JULANDER A, WESTBERG H, ENGWALL M, et al. Distribution of brominated flame retardants in different dust fractions in air from an electronics recycling facility[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2005, 350(1/3):151-160. [63] AL-OMRAN L S, HARRAD S. Distribution pattern of legacy and "novel" brominated flame retardants in different particle size fractions of indoor dust in Birmingham, United Kingdom[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 157:124-131. [64] VENIER M, HITES R A. Flame retardants in the atmosphere near the Great Lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(13):4745-4751. [65] ZHANG W, WANG P, ZHU Y, et al. Brominated flame retardants in atmospheric fine particles in the Beijing- Tianjin-Hebei region, China:Spatial and temporal distribution and human exposure assessment[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171:181-189. [66] ZHAO J, WANG P, WANG C, et al. Novel brominated flame retardants in West Antarctic atmosphere (2011-2018):Temporal trends, sources and chiral signature[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 720:137557. [67] YU Y, HUNG H, ALEXANDROU N, et al. Multiyear measurements of flame retardants and organochlorine pesticides in air in Canada's western Sub-Arctic[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(14):8623-8630. [68] MA W L, LI W L, ZHANG Z F, et al. Occurrence and source apportionment of atmospheric halogenated flame retardants in Lhasa City in the Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 607/608:1109-1116. [69] MCGRATH T J, MORRISON P D, BALL A S, et al. Concentrations of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in indoor dust in Melbourne, Australia:An assessment of human exposure[J]. Environment International, 2018, 113:191-201. [70] LEE H K, KANG H, LEE S, et al. Human exposure to legacy and emerging flame retardants in indoor dust:A multiple-exposure assessment of PBDEs[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719:137386. [71] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, TAN F, et al. Characteristics of halogenated flame retardants in the atmosphere of Dalian, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2020, 223:117219. [72] YADAV I C, DEVI N L, KUMAR A, et al. Airborne brominated, chlorinated and organophosphate ester flame retardants inside the buildings of the Indian state of Bihar:Exploration of source and human exposure[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020,191:110212. [73] TORRE A DELA, NAVARRO I, SANZ P, et al. Organophosphate compounds, polybrominated diphenyl ethers and novel brominated flame retardants in European indoor house dust:Use, evidence for replacements and assessment of human exposure[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 382:121009. [74] ANH H Q, WATANABE I, TUE N M, et al. Polyurethane foam-based passive air sampling for simultaneous determination of POP- and PAH-related compounds:A case study in informal waste processing and urban areas, northern Vietnam[J]. Chemosphere, 2020,247:125991. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 石勇,何万远,欧阳二明. 微生物燃料电池在废水处理中的研究概况. 现代化工. 2024(04): 61-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 徐勇杰,祁家冉,米文贤,李语涵,刘小红,司友斌. rGO/Ag复合修饰电极的微生物燃料电池对五氟磺草胺的降解效果. 农业工程学报. 2023(21): 213-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 7119
- HTML全文浏览数: 7119
- PDF下载数: 303
- 施引文献: 6




 下载:
下载: